Association of ABO Blood Groups, D Antigen, and Comorbidities with COVID-19 Outcomes in Hospitalized Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. COVID-19 Patients Stratification and Voluntary Blood Donors
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Characteristics
3.2. Distribution of ABO Blood Groups and the D Antigen Among Blood Donors and SARS-CoV-2-Infected Participants
3.3. The Influence of Blood Groups and Comorbidities on Patient Outcomes
4. Discussion
4.1. Association of ABO Blood Groups with COVID-19 Severity
4.2. ABO Blood Groups and COVID-19 Mortality
4.3. D Antigen and COVID-19 Outcomes
4.4. ABO Blood Groups and the D Antigen Distribution in COVID-19 Patients and Blood Donors
4.5. Influence of Comorbidities on COVID-19 Outcomes
4.6. Gender Differences in COVID-19 Outcomes
4.7. Implications for Risk Stratification
4.8. Limitations of This Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus disease 2019 |
| ICU | Intensive care unit |
| SARS-CoV-2 | Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 |
| UHC | University Hospital Center |
| vWF | von Willebrand factor |
References
- World Health Organization. 2023 Data.who.int, WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard > Cases [Dashboard]. 2025. Available online: https://data.who.int/dashboards/covid19/cases?m49=191&n=c (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Treatment Guidelines; National Institutes of Health (US): Bethesda, MD, USA, 2021. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK570371/ (accessed on 11 February 2025).
- Talukder, A.; Razu, S.R.; Alif, S.M.; Rahman, M.A.; Islam, S.M.S. Association between symptoms and severity of disease in hospitalized novel coronavirus (COVID-19) patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Multidiscip. Healthc. 2022, 15, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dede, G.; Filiopoulou, E.; Paroni, D.V.; Michalakelis, C.; Kamalakis, T. Analysis and evaluation of major COVID-19 features: A pairwise comparison approach. Oper. Res. Forum 2023, 4, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justino, D.C.P.; Silva, D.F.O.; da Silva Costa, K.T.; de Morais, T.N.B.; de Andrade, F.B. Prevalence of comorbidities in deceased patients with COVID-19: A systematic review. Medicine 2022, 101, e30246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooling, L. Blood groups in infection and host susceptibility. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 801–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abegaz, S.B. Human ABO blood groups and their associations with different diseases. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 6629060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Garner, R.; Salehi, S.; La Rocca, M.; Duncan, D. Association between ABO blood types and coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), genetic associations, and underlying molecular mechanisms: A literature review of 23 studies. Ann. Hematol. 2021, 100, 1123–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Nanchal, R.; Hererra, M.; Sakhuja, A.; Patel, D.; Meersman, M.; Calton, D.; Guddati, K.A. Does ABO blood groups affect outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients? J. Hematol. 2021, 10, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, E.; Felipe, S.; de Freitas, R.; Araújo, V.; Soares, P.; Ribeiro, J.; dos Santos, L.H.; Osório Alves, J.; Canabrava, N.; van Tilburg, M. ABO blood group and link to COVID-19: A comprehensive review of the reported associations and their possible underlying mechanisms. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 169, 105658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, F. Review: ABO blood group system—ABH oligosaccharide antigens, anti-A and anti-B, A and B glycosyltransferases, and ABO genes. Immunohematology 2004, 20, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anstee, D.J. The relationship between blood groups and disease. Blood 2010, 115, 4635–4643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuawwad, M.T.; Taha, M.J.J.; Abu-Ismail, L.; Alrubasy, W.A.; Sameer, S.K.; Abuawwad, I.T.; Al-Bustanji, Y.; Nashwan, A.J. Effects of ABO blood groups and RH-factor on COVID-19 transmission, course and outcome: A review. Front. Med. 2023, 12, 1045060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamayo-Velasco, Á.; Peñarrubia-Ponce, M.J.; Álvarez, F.J.; de la Fuente, I.; Pérez-González, S.; Andaluz-Ojeda, D. ABO blood system and COVID-19 susceptibility: Anti-A and anti-B antibodies are the key points. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 882477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillon, P.; Clément, M.; Sébille, V.; Rivain, J.-G.; Chou, C.-F.; Ruvoën-Clouet, N.; Le Pendu, J. Inhibition of the interaction between the SARS-CoV spike protein and its cellular receptor by anti-histo-blood group antibodies. Glycobiology 2008, 18, 1085–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibeeb, S.; Khan, A. ABO blood group association and COVID-19. COVID-19 susceptibility and severity: A review. Hematol. Transfus. Cell Ther. 2022, 44, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gérard, C.; Maggipinto, G.; Minon, J.M. COVID-19 and ABO blood group: Another viewpoint. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 190, e93–e94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñiz-Diaz, E.; Llopis, J.; Parra, R.; Roig, I.; Ferrer, G.; Grifols, J.; Millan, A.; Ene, G.; Ramiro, L.; Maglio, L.; et al. Relationship between the ABO blood group and COVID-19 susceptibility, severity and mortality in two cohorts of patients. Blood Transfus. 2021, 19, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukhari, R.; Breiman, A.; Jazat, J.; Ruvoën-Clouet, N.; Martinez, S.; Damais-Cepitelli, A.; Le Niger, C.; Devie-Hubert, I.; Penasse, F.; Maurier, D.; et al. ABO blood group incompatibility protects against SARS-CoV-2 transmission. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 799519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, B.; Rout, B.; Rajashree, P.; Kar, S.K.; Sahoo, D.; Sahu, K.K.; Otta, S. ABO blood grouping and COVID-19: A hospital-based study in Eastern India. Egypt. J. Med. Hum. Genet. 2022, 23, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullerdiek, J.; Reisinger, E.; Rommel, B.; Dotzauer, A. ABO blood groups and the risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Protoplasma 2022, 259, 1381–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almadhi, M.A.; Abdulrahman, A.; Alawadhi, A.; Rabaan, A.A.; Atkin, S.; AlQahtani, M. The effects of ABO blood group and antibody class on the risk of COVID-19 infection and severity of clinical outcomes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flegel, W.A. Molecular genetics and clinical applications for RH. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2011, 44, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zietz, M.; Zucker, J.; Tatonetti, N.P. Associations between blood type and COVID-19 infection, intubation, and death. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franchini, M.; Capra, M.; Targher, G.; Montagnana, M.; Lippi, G. Relationship between ABO blood group and von Willebrand factor levels: From biology to clinical implications. Thromb. J. 2007, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liumbruno, G.M.; Franchini, M. Beyond immunohaematology: The role of the ABO blood group in human diseases. Blood Transfus. 2013, 11, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, S.E.; O’Sullivan, J.M.; O’Donnell, J.S. The relationship between ABO blood group, von Willebrand factor, and primary hemostasis. Blood 2020, 136, 2864–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, R.; Bloch, E.M.; Pirenne, F.; Al-Riyami, A.Z.; Crowe, E.; Dau, L.; Land, K.; Townsend, M.; Jecko, T.; Rahimi-Levene, N.; et al. ABO blood group and COVID-19: A review on behalf of the ISBT COVID-19 Working Group. Vox Sang. 2021, 116, 849–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawdat, D.; Hajeer, A.; Massadeh, S.; Aljawini, N.; Abedalthagafi, A.S.; Alaamery, M. Correlation between ABO blood group phenotype and the risk of COVID-19 infection and severity of disease in Saudi Arabian cohort. J. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2022, 12, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra Soares, D.M.; Sa Araujo, D.A.B.; de Brito de Souza, J.; Maurico, R.B.; Bezerra Soares, E.M.; de Castro Alves Neto, F.; Nogueira Pinheiro, M.S.; de Vasconcelos Gama, V.C.; Braga-Neto, P.; Nobrega, P.R.; et al. Correlation between ABO blood type, susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 disease severity: A systematic review. Hematol. Transfus. Cell Ther. 2023, 45, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerico, C.; Zalba-Marcos, S.; Quintana-Diaz, M.; Lopez-Villar, O.; Santolalla-Arnedo, I.; Abad-Motos, A.; Laso-Morales, M.J.; Sancho, E.; Subira, M.; Bassas, E.; et al. Relationsip between ABO blood group distribution and COVID-19 infection in patients admitted to the ICU: A multicenter observational Spanish study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, N.A.; Al-Bajalan, S.J.; Rahman, H.S.; Mohammed, M.S. Correlation of SARS-CoV-2 infection severity with ABO blood groups and RhD antigen: A case-control study. Int. J. Med. Res. 2022, 50, 3000605221110493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bshaena, A.M.; Almajdoub, O.H.; Alshwesh, R.A.; Omran, E.A.; Haq, S.; Ismail, F. Association between ABO blood group system and COVID-19 severity. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2022, 3, 570–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucijanić, M.; Piskač Živković, N.; Zelenika, M.; Barišić-Jaman, M.; Jurin, I.; Matijaca, A.; Zagorec, N.; Lagančić, M.; Osmani, B.; Bušić, I.; et al. Survival after hospital discharge in patients hospitalized for acute coronavirus disease 2019: Data on 2586 patients from a tertiary center registry. Croat. Med. J. 2022, 63, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jukić, T.; Hećimović, A.; Vuk, T.; Vinković, M.; Kereš, T.; Lampalo, M.; Kruhonja Galić, Z.; Jagnjić, S. Prevalence of ABO and RhD blood group phenotypes in the Croatian population and in patients with severe COVID-19 in Croatia. Blood Transfus. 2022, 20, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yang, Y.; Huang, H.; Li, D.; Gu, D.; Lu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, L.; Liu, T.; Liu, Y.; et al. Relationship between the ABO blood group and the COVID-19 susceptibility. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, 328–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Feng, Z.; Li, P.; Yu, Q. Relationship between ABO blood group distribution and clinical characteristics in patients with COVID-19. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 509, 220–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellinghaus, D.; Degenhardt, F.; Bujanda, L.; Buti, M.; Albillos, A.; Invernizzi, P.; Fernandez, J.; Prati, D.; Baselli, G.; Asselta, R.; et al. Genomewide Association Study of Severe Covid-19 with Respiratory Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1522–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latz, C.A.; DeCarlo, C.; Boitano, L.; Png, C.Y.M.; Patell, R.; Conrad, M.F.; Eagleton, M.; Dua, A. Blood type and outcomes in patients with COVID-19. Ann. Hematol. 2020, 99, 2113–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoiland, R.L.; Fergusson, N.A.; Mitra, A.R.; Griesdale, D.E.G.; Devine, D.V.; Stukas, S.; Cooper, J.; Foster, D.; Chen, L.Y.C.; Lee, A.Y.Y.; et al. The association of ABO blood group with indices of disease severity and multiorgan dysfunction in COVID-19. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 4981–4989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pairo-Castineira, E.; Clohisey, S.; Klaric, L.; Bretherich, A.D.; Rawlik, K.; Pasko, D.; Walker, S.; Parkinson, N.; Fourman, M.H.; Russell, C.D.; et al. Genetic mechanisms of critical illness in COVID-19. Nature 2021, 591, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.C.; Arthur, C.M.; Jan, H.M.; Garcia-Beltran, W.F.; Patel, K.R.; Rathgeber, M.F.; Verkerke, H.P.; Cheedarla, N.; Jajosky, R.P.; Paul, A.; et al. Blood group A enhances SARS-CoV-2 infection. Blood 2023, 142, 742–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerbage, A.; Haddad, S.F.; Nasr, L.; Riachy, A.; Mekhael, E.; Nassim, N.; Hoyek, K.; Sleilaty, G.; Nasr, F.; Riachy, M. Impact of ABO and Rhesus blood groups on COVID-19 susceptibility and severity: A case-control study. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 1162–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lilić, M.; Jaklin, G.; Gojčeta, K.; Raos, M.; Golubić-Ćepulić, B. Uncommon RHD variants and an unconventional RHCE hybrid allele with D epitope expression in blood donors from northwestern Croatia. Transfusion, 2025; early view. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebhard, C.; Regitz-Zagrosek, V.; Neuhauser, H.K.; Morgan, R.; Klein, S.L. Impact of sex and gender on COVID-19 outcomes in Europe. Biol. Sex Differ. 2020, 11, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scully, E.P.; Haverfield, J.; Ursin, R.L.; Tannenbaum, C.; Klein, S.L. Considering how biological sex impacts immune responses and COVID-19 outcomes. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 442–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
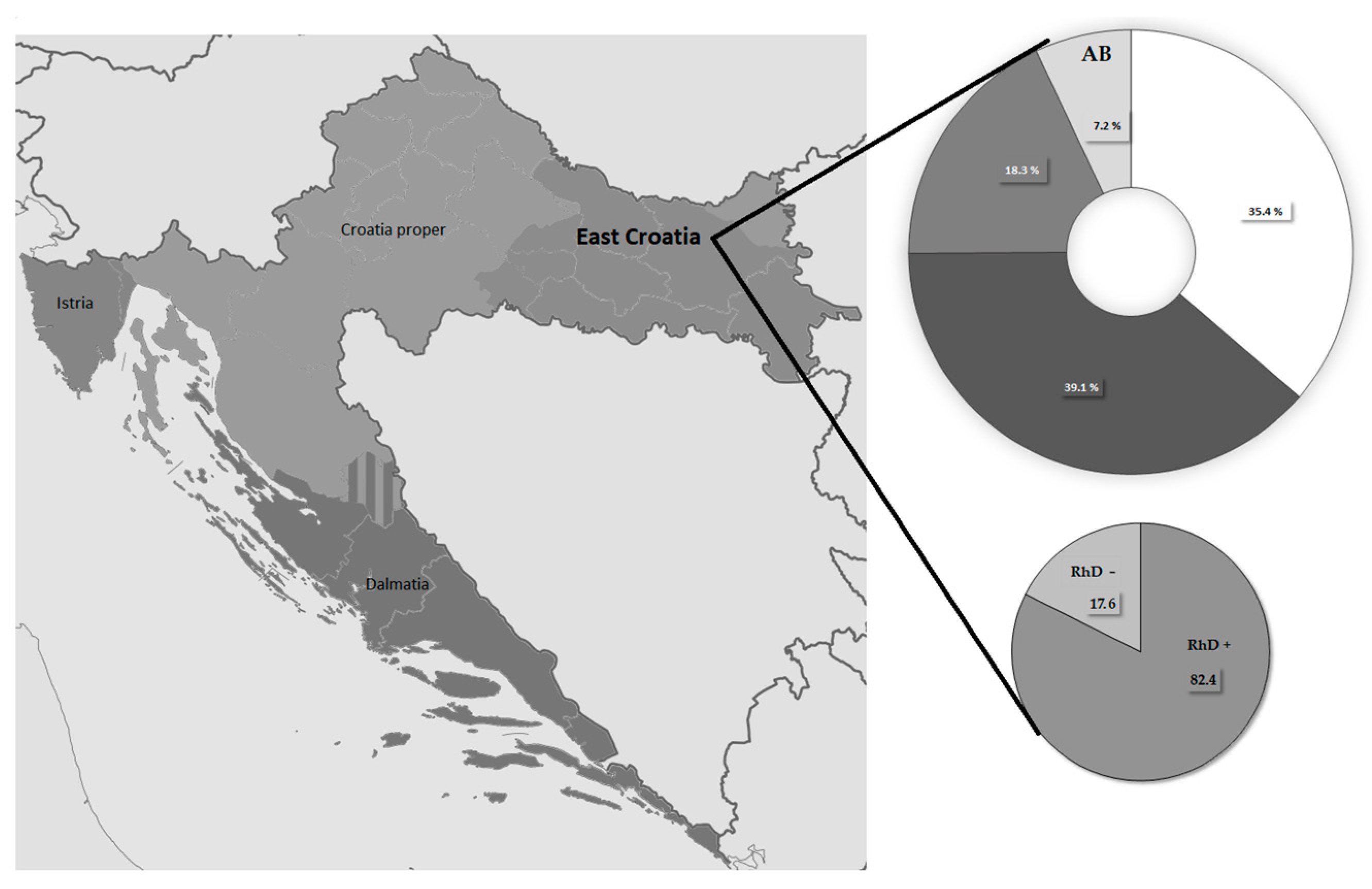

| Blood Donors (n = 7086) | COVID-19 Patients (n = 1687) | p * | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (male/female) [n (%)] | 5051 (71.3)/ 2039 (28.7) | 915 (54.2)/ 772 (45.8) | <0.001 |
| Age [median (IQR)] | 36 (28–46) | 71 (63–79) | <0.001 |
| ABO Blood Group [n (%)] | |||
| O | 2574 (36.3) | 533 (31.6) | <0.001 |
| A | 2734 (38.6) | 692 (41.0) | 0.06 |
| B | 1282 (18.1) | 318 (18.9) | 0.48 |
| AB | 496 (7.0) | 144 (8.5) | 0.03 |
| D antigen (positive/negative) [n (%)] | 5820 (82.1)/ 1266 (17.9) | 1418 (84.1)/ 269 (15.9) | 0.06 |
| COVID-19 Patient Outcomes (n = 1687) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Discharged (n = 1160) | Deceased (n = 527) | p * | |
| Age [median (IQR)] | 70.5 (61–79) | 73 (65–79) | <0.001 |
| Sex (male/female) [n (%)] | 625 (53.9)/535 (46.1) | 290 (55.0)/237 (45.0) | 0.66 |
| Hypertension [n (%)] | 583 (50.5) | 281 (53.6) | 0.24 |
| Diabetes [n (%)] | 34 (2.9) | 15 (2.9) | 0.92 |
| Hypertension and diabetes [n (%)] | 295 (25.6) | 161 (30.7) | 0.03 |
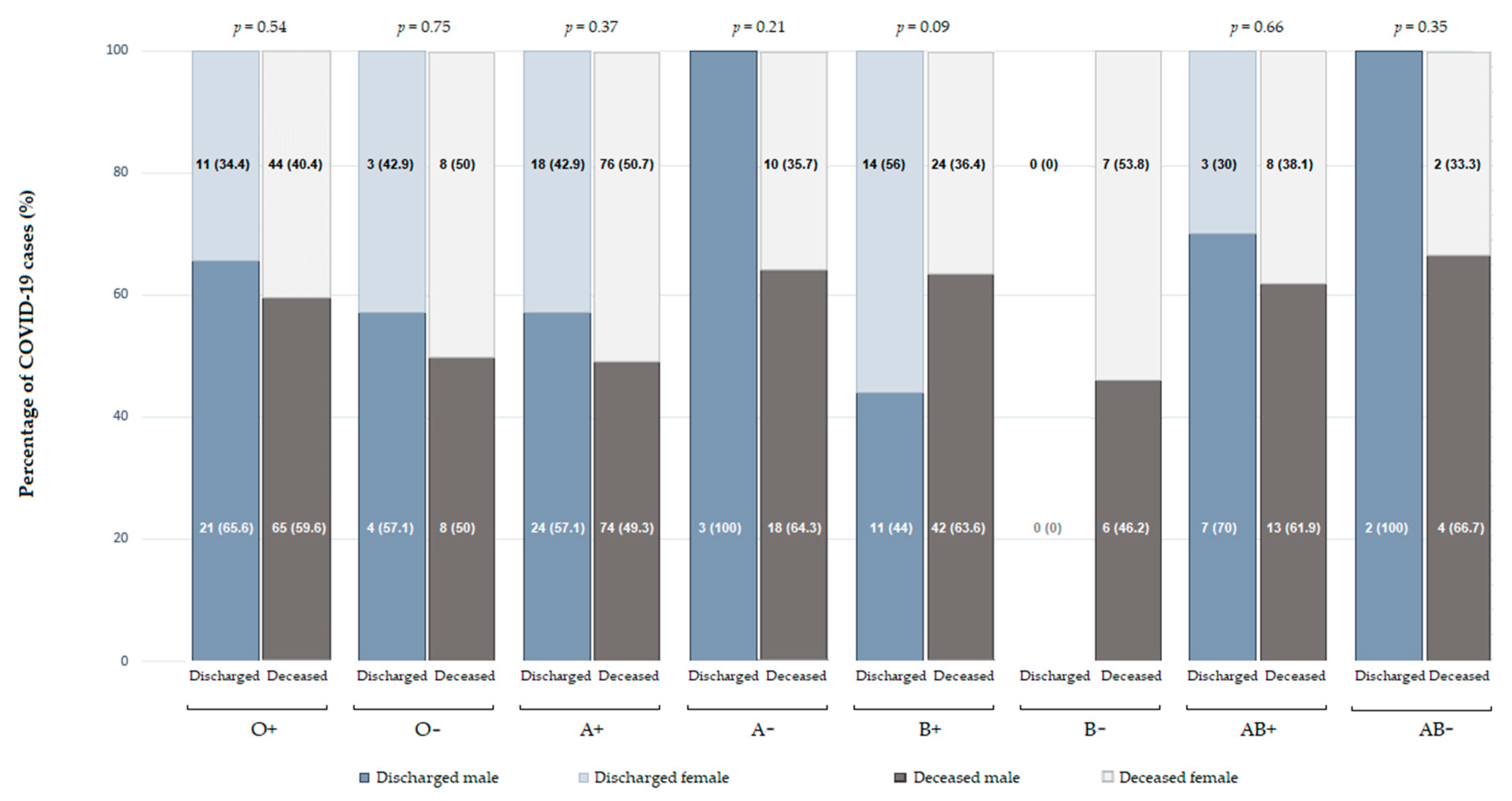
| ABO blood group [n (%)] | |||
| O | 372 (32.1) | 161 (30.6) | 0.53 |
| A | 457 (39.4) | 235 (44.6) | 0.04 |
| B | 224 (19.3) | 94 (17.8) | 0.47 |
| AB | 107 (9.2) | 37 (7.0) | 0.13 |
| D antigen (positive/negative) [n (%)] | 975 (84.1)/185 (15.9) | 443 (84.1)/84 (15.9) | 0.99 |
| Independent Variables | β | Wald | p | OR | 95% CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||||
| Age | 0.02 | 24.994 | <0.001 | 1.02 | 1.01 | 1.03 |
| Sex (male) | 0.05 | 0.193 | 0.66 | 1.05 | 0.85 | 1.29 |
| Hypertension only | 0.12 | 1.391 | 0.24 | 1.13 | 0.92 | 1.39 |
| Diabetes only | −0.03 | 0.009 | 0.92 | 0.97 | 0.52 | 1.79 |
| Hypertension and diabetes | 0.25 | 4.480 | 0.03 | 1.29 | 1.03 | 1.62 |
| Blood group O | −0.07 | 0.387 | 0.53 | 0.93 | 0.75 | 1.16 |
| Blood group A | 0.21 | 4.037 | 0.04 | 1.24 | 1.01 | 1.52 |
| Blood group B | −0.09 | 0.514 | 0.47 | 0.91 | 0.69 | 1.18 |
| Blood group AB | −0.29 | 2.240 | 0.14 | 0.74 | 0.51 | 1.09 |
| D antigen-positive | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.75 | 1.33 |
| Independent Variables | β | Wald | p | OR | 95% CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||||
| Age | 0.019 | 20.935 | <0.001 | 1.02 | 1.01 | 1.03 |
| Hypertension and diabetes | 0.205 | 3.062 | 0.08 | 1.23 | 0.98 | 1.54 |
| Blood group A | 0.188 | 3.068 | 0.08 | 1.21 | 0.98 | 1.49 |
| Constant * | −2.283 | 56.159 | <0.001 | 0.10 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suver Stević, M.; Lilić, M.; Marczi, S.; Nešković, N.; Haršanji-Drenjančević, I.; Perić, L.; Sabadi, D.; Glegj, M.; Samardžija, M. Association of ABO Blood Groups, D Antigen, and Comorbidities with COVID-19 Outcomes in Hospitalized Patients. COVID 2025, 5, 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/covid5060090
Suver Stević M, Lilić M, Marczi S, Nešković N, Haršanji-Drenjančević I, Perić L, Sabadi D, Glegj M, Samardžija M. Association of ABO Blood Groups, D Antigen, and Comorbidities with COVID-19 Outcomes in Hospitalized Patients. COVID. 2025; 5(6):90. https://doi.org/10.3390/covid5060090
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuver Stević, Mirjana, Marko Lilić, Saška Marczi, Nenad Nešković, Ivana Haršanji-Drenjančević, Ljiljana Perić, Dario Sabadi, Mirna Glegj, and Marina Samardžija. 2025. "Association of ABO Blood Groups, D Antigen, and Comorbidities with COVID-19 Outcomes in Hospitalized Patients" COVID 5, no. 6: 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/covid5060090
APA StyleSuver Stević, M., Lilić, M., Marczi, S., Nešković, N., Haršanji-Drenjančević, I., Perić, L., Sabadi, D., Glegj, M., & Samardžija, M. (2025). Association of ABO Blood Groups, D Antigen, and Comorbidities with COVID-19 Outcomes in Hospitalized Patients. COVID, 5(6), 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/covid5060090







