Abstract
Quick and reliable identification of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 in the population is required to manage the COVID-19 pandemic. This is a prospective observational study of diagnostic accuracy. Paired swab samples from 317 asymptomatic individuals referring to a drive-in testing facility were tested in parallel by means of the rapid antigen test developed by Jiangsu Bioperfectus Technologies and routine nucleic acid detection. Overall specificity was 100% and sensitivity was 49% but reached 87% at higher viral loads (Ct < 25). In this study, the antigen detection test showed high specificity and good sensitivity in asymptomatic individuals carrying higher viral loads. The assay performance worsened with lower viral loads, making it useful when a rapidly deployable test is essential and to assess a potential risk of immediate transmission in the community, but not recommended for testing asymptomatic individuals.
1. Introduction
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2), the causal agent of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), is having a profound impact on global health with long-lasting effects on the economy worldwide. Global control of the pandemic will require a pervasive rollout of effective vaccines. However, an efficient contact-tracing protocol and mass community testing will remain essential until full coverage is obtained. Therefore, there is an urgent need for accurate and rapid test methods to quickly identify large numbers of infected individuals and asymptomatic carriers to prevent virus transmission and assure timely isolation procedures.
A large proportion of SARS-CoV-2-infected individuals with high viral loads might be asymptomatic [1,2]. Nucleic acid amplification tests (NAAT) such as the reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) technology are the routine for virus detection. RT-PCR is highly sensitive and specific [3,4]. However, RT-PCR has disadvantages, including the necessity of professional laboratory expertise, costly reagents, and centralized equipment. Therefore, alternatives have been developed, including antigen tests that detect viral proteins in respiratory samples [5]. Antigen tests are more cost-effective and generally optimized for point-of-care (POC) use. The advantages of antigen tests, such as relatively low cost and short turnaround time, can contribute to prompt identification of contagious individuals with high viral loads. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), RT-PCR testing should be considered after negative antigen test results in symptomatic individuals and after positive antigen test results in asymptomatic individuals [6]. Although antigen tests might not be as accurate as RT-PCR testing, they are more accessible in terms of availability and ease of use and can be used to scale-up testing in the community [7,8].
Rapid antigen diagnostic tests (Ag-RDT), also called antigen point-of-care tests (Ag-POCT) or lateral flow devices (LFD), are a viable alternative to NAAT for detecting infected individuals in the population [9]. There is a large number of Ag-RDTs available on the market, with different sensitivities [10,11,12,13,14]. Hence, independent assessment is key to informed decisions on their proper use for mass testing.
The main objective of this study was to evaluate the performance of the Bioperfectus Technologies Novel Corona Virus (SARS-CoV-2) Ag Rapid Test Kit produced by Jiangsu Bioperfectus Technologies for the direct detection of SARS-CoV-2 antigens in comparison to the gold-standard RT-PCR method. Paired specimens were nasopharyngeal swabs prospectively collected from asymptomatic or pauci-symptomatic individuals in an area of intense virus circulation. The results show an overall sensitivity of 49%, with specificity of 100% and increased sensitivity of 87% below 25 Ct.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
This was an observational and cross-sectional study on swab samples collected prospectively from 317 individuals who referred for a SARS-CoV-2 molecular assay at a drive-in testing center in Trieste, Italy, between February and May 2021. Two deep nasopharyngeal swab specimens were collected from the same individual for RT-PCR and Ag-RDT. One swab was analyzed by RT-PCR and, once the specimen was confirmed positive, the other swab from the same donor was tested with the antigen test within 24 h from collection, with specimens preserved at 4 °C. The swabs for RT-PCR were maintained in virus transport media (VTM), while the swabs for AG-RDT were not resuspended in a medium during storage and were resuspended in a lysis buffer for RDT at the time of testing (<24 h from collection). Study design required at least 200 PCR specimens and 100 negative PCR specimens to be evaluated: 70% of the specimens were selected to have cycle threshold (Ct) values < 30, and 30% of the specimens had Ct values ≥ 30 on the comparator PCR assay according to the WHO recommendations for emergency use listing (EUL) [15].
2.2. Reagents
The index Ag-RDT was the Novel Corona Virus (SARS-CoV-2) Ag Rapid Test Kit manufactured by Jiangsu Bioperfectus Technologies Co., Ltd. (reference number SC30107W, batch number 20201101) performed according to the instructions. Briefly, the swab was resuspended vigorously in a tube with the supplied extraction buffer, closed with a dropper cap, and mixed by flicking. Then, the tube was inverted, and 2–3 drops were deposited in the reservoir of a test cassette. The assay was visually assessed after 15 min of incubation at room temperature and recorded with a photo.
The comparator RT-PCR test varied depending on the source available at the time of sampling. The following kits were used during this study: GSD NovaPrime®® SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) (Eurofins Tecna s.r.l.); NLM Leaflet ITA SARS-CoV-2 Real Time (AA1571/96S and /960S); NeoPlex™ COVID-19 (Eurospital); SARS-CoV-2 ELITe MGB®®Kit (ELITechGroup); Bosphore novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) detection kit. Each test has its own targets in the SARS-CoV-2 genome and internal controls. Positive and negative samples were assigned based on the RT-PCR results and referred to the participants. The Ct values were averaged for each sample to obtain a single value used for stratification of data.
Quantification of SARS-CoV-2 genomes was performed using synthetic viral RNA as previously described, with a procedure and reagents freely available through the ICGEB [16,17,18]. Calculated logarithmic dilutions of viral RNA from a laboratory isolate (SARS-CoV-2 ICGEB-FVG_5) were plotted against the average Ct values of the Liferiver RT-PCR method from two independent replicates in triplicate repeats to obtain a nonlinear regression standard curve to interpolate the unknown values using GraphPad Prism version 9.0.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
The confusion matrix (contingency 2 × 2 table) method for data analysis was used to derive parameters such as sensitivity, specificity, negative and positive predictive values, precision, and accuracy of the index assay compared with the reference. The Cohen’s kappa coefficient was used to measure the interrater reliability. The data were analyzed with R [19]. To compare the assay with the reference, the caret package (https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=caret - accessed on 1 September 2021) was used to compute the main confusion matrix statistics. The irr package (https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=irr - accessed on 1 September 2021) was used to compute the value of Cohen’s kappa, a parameter commonly used to measure interrater reliability [20], while the vcd package (https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vcd- accessed on 1 September 2021) was employed to obtain its 95% confidence interval. For data refining, assay sensitivity and accuracy were calculated considering only the reference positive cases in function of their RT-PCR results. The results were finally visualized using the “ggplot2 (https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=ggplot2- accessed on 1 September 2021) and gridExtra (https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=gridExtra- accessed on 1 September 2021) packages.
3. Results
Sensitivity and Specificity of Ag-RDT
A total of 317 samples were collected between February and May 2021 in a drive-in SARS-CoV-2 testing facility located in Trieste, Italy. The sample included 120 negative RT-PCR samples collected in parallel with the positive ones each week across the study. According to study design, 67% of the positive RT-PCR samples were selected with a Ct < 30, while the remaining ones had Ct ≥ 30. Individuals referring to the drive-in for testing were asymptomatic or pauci-symptomatic subjects who needed a COVID-19 test for various reasons, including travel and exit from quarantine. Circulation of SARS-CoV-2 in the area during the period of the study showed a shift towards the B.117 variant (alpha variant), typical of the third epidemic wave that hit Italy between February and April 2021 [21]. Indeed, the major variants of concern (VOC: alpha, beta, gamma, delta) and variants of interest (VOI: epsilon, zeta, theta, iota, kappa, lambda) are covered by the test and could be detected with the limits of detection (LOD) comparable with the original sequence (40 pg/mL). The rapid antigen tests should also remain unaffected based on the preliminary analysis of the nucleocapsid of the omicron VOC as well. The nucleocapsid of omicron carries mutations G204R and R203K that are already present in the previous variants, so it is unlikely to cause problems, as well as P13L and 31–33del (deletion E31, R32, S33) that are outside of the binding sites of the antibodies used in the test according to in silico simulations. However, verification of this is underway.
Overall clinical sensitivity of the Ag-RDT was 49%, with a specificity of 100%, positive predictive value (PPV) of 100%, and negative predictive value (NPV) of 55%. The overall accuracy of the test was 68%, with the 95% confidence interval between 35% and 50% (95% confidence interval (CI), 35–50%) and the p-value of 4.2 × 10−23 (McNemar’s test). Stratification of the Ag-RDT data on the RT-PCR Ct values showed that sensitivity spiked to 87% at Ct < 25 (N = 91, accuracy of 87% with 95% CI = 78–93%, p-value = 0.0015) while decreasing rapidly at Ct ≥ 25 (N = 106, sensitivity of 17%, accuracy of 17% with 95% CI = 10–26%, p-value = 18 × 10−20). The validity of the Ag-RDT for Ct < 25 is visually evident in Figure 1 and Table 1, which summarizes the data.
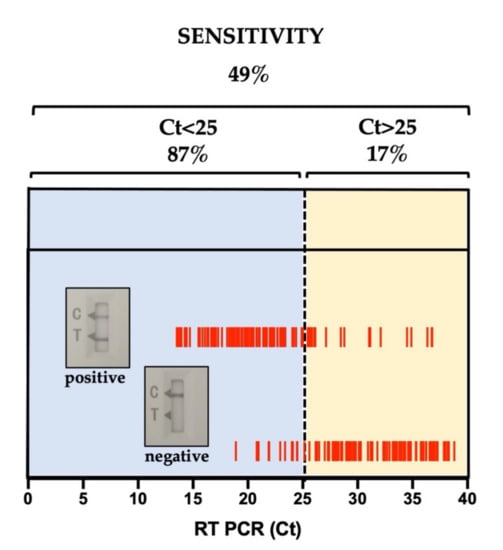
Figure 1.
Ag-RDT data analysis. Stratification of Ag-RDT sensitivities on RT-PCR Ct values. Stratification of the Bioperfectus Ag-RDT lateral flow (positive/negative) on the RT-PCR Ct values obtained in the trial. Data for sensitivity within the stratification windows are summarized in Table 1 and described in the text.

Table 1.
Stratification of data on Ct values.
According to the manufacturer’s specification, the clinical sensitivity of the Ag-RDT compared to RT-PCR was 97.06%, with a specificity of 99.15%, from studies conducted on symptomatic individuals [22]. These values meet the WHO criteria on the use of SARS-CoV-2 Ag-RDTs (≥80% sensitivity and ≥97% specificity compared to an approved NAAT [9]. These assays are to be considered for use only in the areas where NAAT is unavailable or where the health system may be overburdened, leading to prolonged NAAT turnaround times (>48−72 h). The manufacturer’s declared LOD was 100 plaque-forming units/mL, which was confirmed in an independent assessment and calculated to correspond to 1.5 × 108 genomes/mL, well above the LOD of the RT-PCR assays used in this study that ranged between 104 to 2.6 × 102 genomes/mL according to the manufacturer’s specifications. These data confirm that Ag-RDTs are most likely to perform well in patients with high viral loads, which usually appear 1–3 days before symptom onset and early symptomatic phases of the illness (first 5–7 days).
4. Discussion
The study presented here, which includes a significant proportion of low viral load samples, provides further support for the correct use of Ag-RDTs in early symptomatic individuals and in the scenarios depicted by WHO [9] that include (i) quick evaluation of suspected outbreaks in remote settings and in closed or semi-closed groups including schools, care homes, cruise ships, prisons, workplaces, etc.; (ii) monitoring of trends in disease incidence and actuation of isolation procedures where there is widespread community transmission. Ag-RDT can also be applied in the following specific situations: (i) when testing is required for large gatherings of people, such as concerts or other events; (ii) to allow to return to work in the countries adopting the requirement of a green pass (e.g., Italy [21]); (iii) for travel. In these scenarios, the validity of the Ag-RDT results should not exceed 48 h. In fact, the chances of isolating infectious SARS-CoV-2 and transmitting the virus are drastically reduced at low viral loads with Ct < 25 [23,24,25,26].
To conclude, the results clearly show that Ag-RDT is highly specific, but sensitivity is acceptable only at Ct < 25 with higher viral loads. The test is therefore applicable in situations where POCT is essential or where a short-term evaluation of infectivity is required. Ag-RDT remains not recommended for testing individuals in a drive-in setting.
Author Contributions
A.M., F.L., W.J. and S.Z. conceived the study, designed the clinical study, and coordinated the work. A.M. wrote the manuscript and analyzed the data. G.T., B.Y., Z.L. and E.O. performed the experiments. P.M. performed the statistical calculations. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of this manuscript.
Funding
Intramural funds from the ICGEB and liberal financial contribution to A.M. from Generali SpA, SNAM SpA, and Beneficentia Stiftung in the context of the COVID-19 emergency is hereby acknowledged.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was approved by the local ethics committee—Comitato Etico Unico Regionale (reference number CEUR-2021-Os-61).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all the subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
Jiangsu Bioperfectus Technologies Co., Ltd. provided and shipped a Novel Corona Virus (SARS-CoV-2) Ag Rapid Test Kit free of charge. Jiangsu Bioperfectus Technologies Co. contributed to the design of the clinical study but did not play any role in data analysis or interpretation. Casa di cura Salus—Policlinico Triestino SpA contributed to the design of the clinical study, performed the RT-PCR analysis, and provided the samples for Ag-RDT that were used at the ICGEB.
References
- Oran, D.P.; Topol, E.J. Prevalence of Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Narrative Review. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 173, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.C.; Lu, S.C.; Bai, C.H.; Wang, P.Y.; Lee, K.Y.; Wang, Y.H. Diagnostic Accuracy of SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Tests for Community Transmission Screening: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int, J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 11451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, J.; Whiting, P.F.; Brush, J.E. Interpreting a COVID-19 test result. BMJ 2020, 369, m1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieberman, J.A.; Pepper, G.; Naccache, S.N.; Huang, M.L.; Jerome, K.R.; Greninger, A.L. Comparison of Commercially Available and Laboratory-Developed Assays for In Vitro Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in Clinical Laboratories. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e00821–e00820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toptan, T.; Eckermann, L.; Pfeiffer, A.E.; Hoehl, S.; Ciesek, S.; Drosten, C.; Corman, V.M. Evaluation of a SARS-CoV-2 rapid antigen test: Potential to help reduce community spread? J. Clin. Virol. 2021, 135, 104713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CDC. Interim Guide for Antigen Testing for SARS-CoV-2. 2021. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/lab/resources/antigen-tests-guidelines.html (accessed on 12 October 2021).
- Pray, I.W.; Ford, L.; Cole, D.; Lee, C.; Bigouette, J.P.; Abedi, G.R.; Bushman, D.; Delahoy, M.J.; Currie, D.; Cherney, B.; et al. Performance of an Antigen-Based Test for Asymptomatic and Symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Testing at Two University Campuses—Wisconsin, September-October 2020. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2021, 69, 1642–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peeling, R.W.; Olliaro, P.L.; Boeras, D.I.; Fongwen, N. Scaling up COVID-19 rapid antigen tests: Promises and challenges. Lancet Infect. Dis 2021, 21, e290–e295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Antigen-Detection in the Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 Infection using Rapid Immunoassays: Interim Guidance. 2020. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/334253 (accessed on 5 September 2021).
- Wagenhauser, I.; Knies, K.; Rauschenberger, V.; Eisenmann, M.; McDonogh, M.; Petri, N.; Andres, O.; Flemming, S.; Gawlik, M.; Papsdorf, M.; et al. Clinical performance evaluation of SARS-CoV-2 rapid antigen testing in point of care usage in comparison to RT-qPCR. EBioMedicine 2021, 69, 103455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohmer, N.; Toptan, T.; Pallas, C.; Karaca, O.; Pfeiffer, A.; Westhaus, S.; Widera, M.; Berger, A.; Hoehl, S.; Kammel, M.; et al. The Comparative Clinical Performance of Four SARS-CoV-2 Rapid Antigen Tests and Their Correlation to Infectivity In Vitro. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickering, S.; Batra, R.; Merrick, B.; Snell, L.B.; Nebbia, G.; Douthwaite, S.; Reid, F.; Patel, A.; Ik, M.T.K.; Patel, B.; et al. Comparative performance of SARS-CoV-2 lateral flow antigen tests and association with detection of infectious virus in clinical specimens: A single-centre laboratory evaluation study. Lancet Microbe 2021, 2, e461–e471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stromer, A.; Rose, R.; Schafer, M.; Schon, F.; Vollersen, A.; Lorentz, T.; Fickenscher, H.; Krumbholz, A. Performance of a Point-of-Care Test for the Rapid Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Antigen. Microorganisms 2020, 9, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corman, V.M.; Haage, V.C.; Bleicker, T.; Schmidt, M.L.; Muhlemann, B.; Zuchowski, M.; Jo, W.K.; Tscheak, P.; Möncke-Buchner, E.; Müller, M.A.; et al. Comparison of seven commercial SARS-CoV-2 rapid point-of-care antigen tests: A single-centre laboratory evaluation study. Lancet Microbe 2021, 2, e311–e319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Emergency Use Listing Procedure for In Vitro Diagnostics. 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/teams/regulation-prequalification/eul (accessed on 1 September 2021).
- ICGEB. COVID-19/SARS-CoV-2 Resource Page. 2020. Available online: https://www.icgeb.org/covid19-resources/ (accessed on 1 April 2021).
- Rajasekharan, S.; Bonotto, R.M.; Alves, L.N.; Kazungu, Y.; Poggianella, M.; Martinez-Orellana, P.; Skoko, N.; Polez, S.; Marcello, A. Inhibitors of Protein Glycosylation Are Active against the Coronavirus Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. Viruses 2021, 13, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, M.M.; Bitew, M.; Fokam, J.; Lelo, E.A.; Ahidjo, A.; Asmamaw, K.; Beloumou, G.A.; Bulimo, W.D.; Buratti, E.; Chenwi, C.; et al. Diagnostic performance of a colorimetric RT-LAMP for the identification of SARS-CoV-2: A multicenter prospective clinical evaluation in sub-Saharan Africa. EClinicalMedicine 2021, 40, 101101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Team CR. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Available online: http://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 1 April 2021).
- Cohen, J. A coeffcient of agreement for nominal scales. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1960, 20, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Italy. Novel Coronavirus Portal. 2021. Available online: https://www.salute.gov.it/portale/nuovocoronavirus/homeNuovoCoronavirus.jsp?lingua=english (accessed on 5 September 2021).
- FIND. Diagnosis for All. 2021. Available online: https://www.finddx.org/product/novel-corona-virus-sars-cov-2-ag-rapid-test-kit (accessed on 5 September 2021).
- Cevik, M.; Tate, M.; Lloyd, O.; Maraolo, A.E.; Schafers, J.; Ho, A. SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV, and MERS-CoV viral load dynamics, duration of viral shedding, and infectiousness: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Microbe 2021, 2, e13–e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singanayagam, A.; Patel, M.; Charlett, A.; Lopez Bernal, J.; Saliba, V.; Ellis, J.; Ladhani, S.; Zambon, M.; Gopal, R. Duration of infectiousness and correlation with RT-PCR cycle threshold values in cases of COVID-19, England, January to May 2020. Euro Surveill 2020, 25, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Scola, B.; Le Bideau, M.; Andreani, J.; Hoang, V.T.; Grimaldier, C.; Colson, P.; Gautret, P.; Raoult, D. Viral RNA load as determined by cell culture as a management tool for discharge of SARS-CoV-2 patients from infectious disease wards. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 39, 1059–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullard, J.; Dust, K.; Funk, D.; Strong, J.E.; Alexander, D.; Garnett, L.; Boodman, C.; Bello, A.; Hedley, A.; Schiffman, Z.; et al. Predicting Infectious Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 From Diagnostic Samples. Clin. Infect. Dis 2020, 71, 2663–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).