The Individual and the Organizational Model of Quantum Decision-Making and Learning: An Introduction and the Application of the Quadruple Loop Learning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Decision-Making (DM)
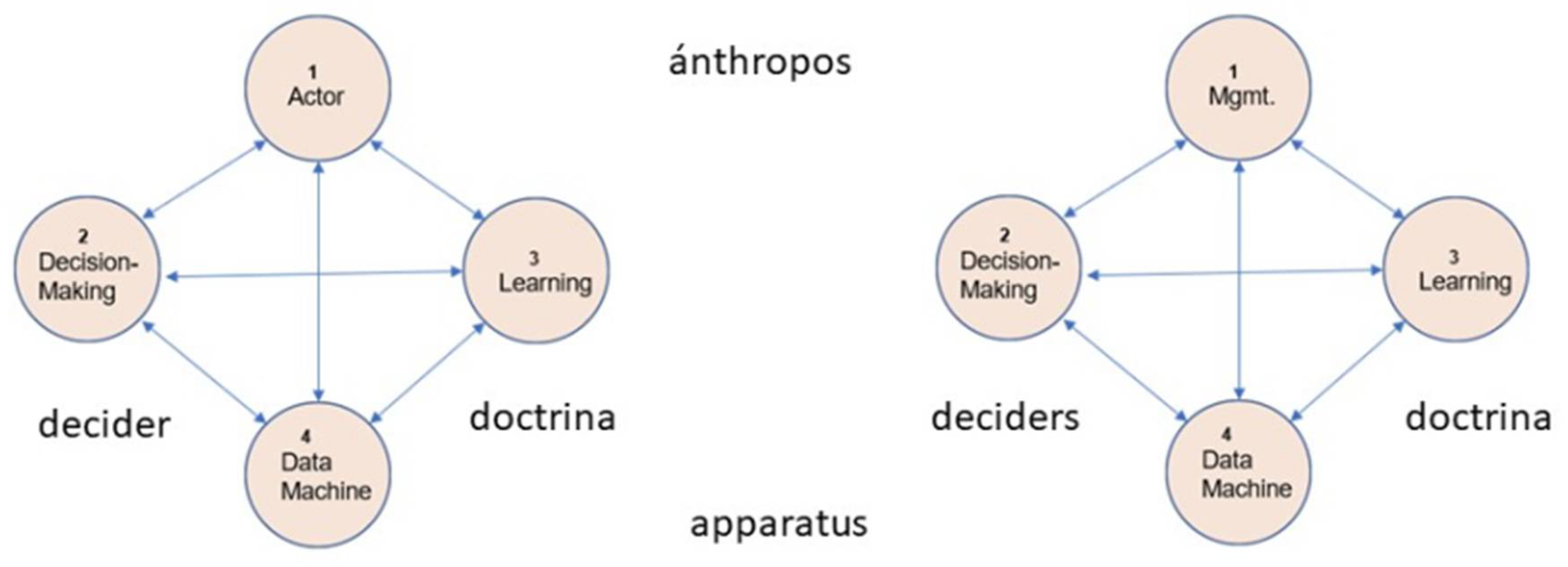
3. The AADD (Ánthrōpos, Apparatus, Decider, Doctrina) Diamond Model
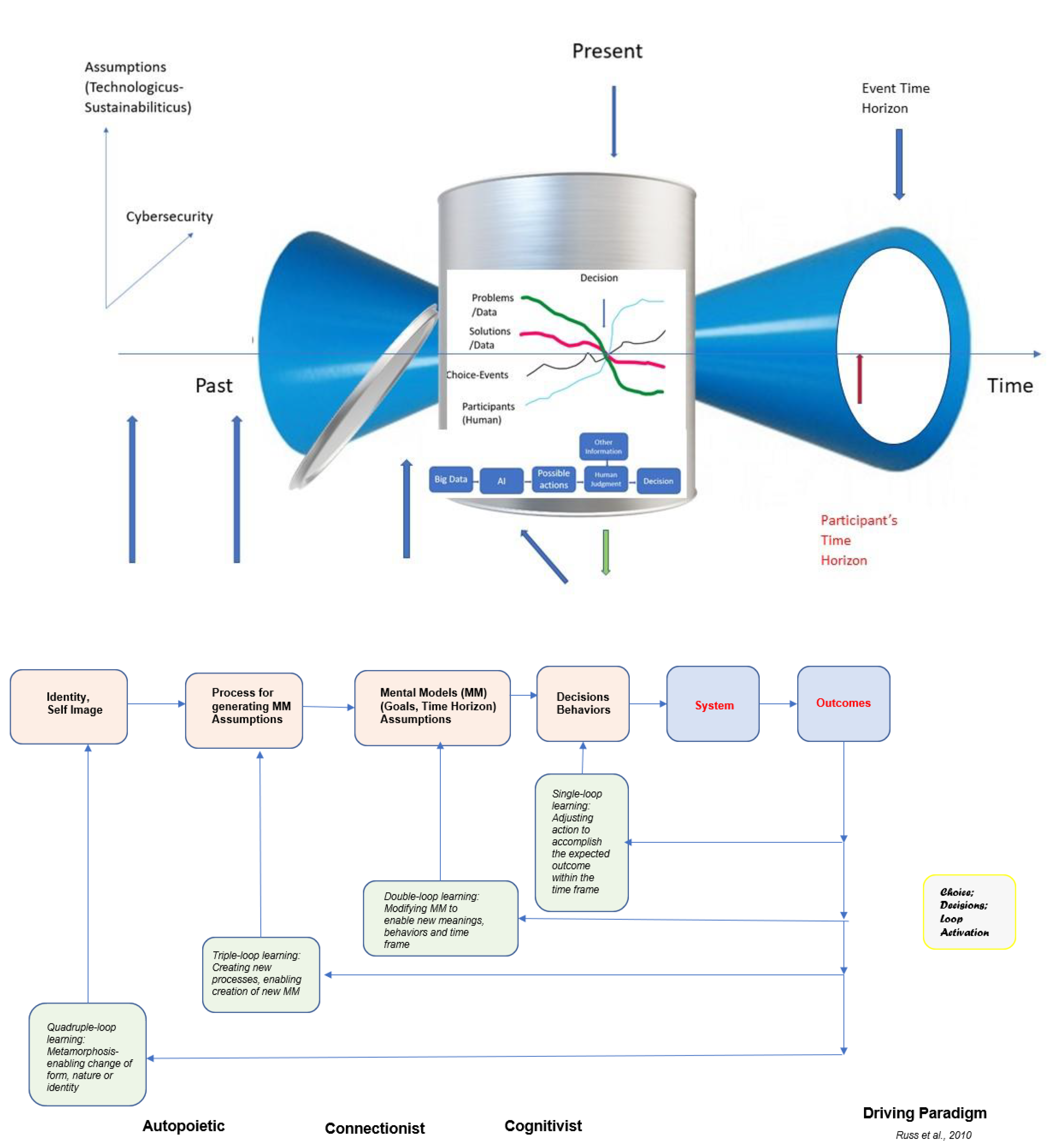
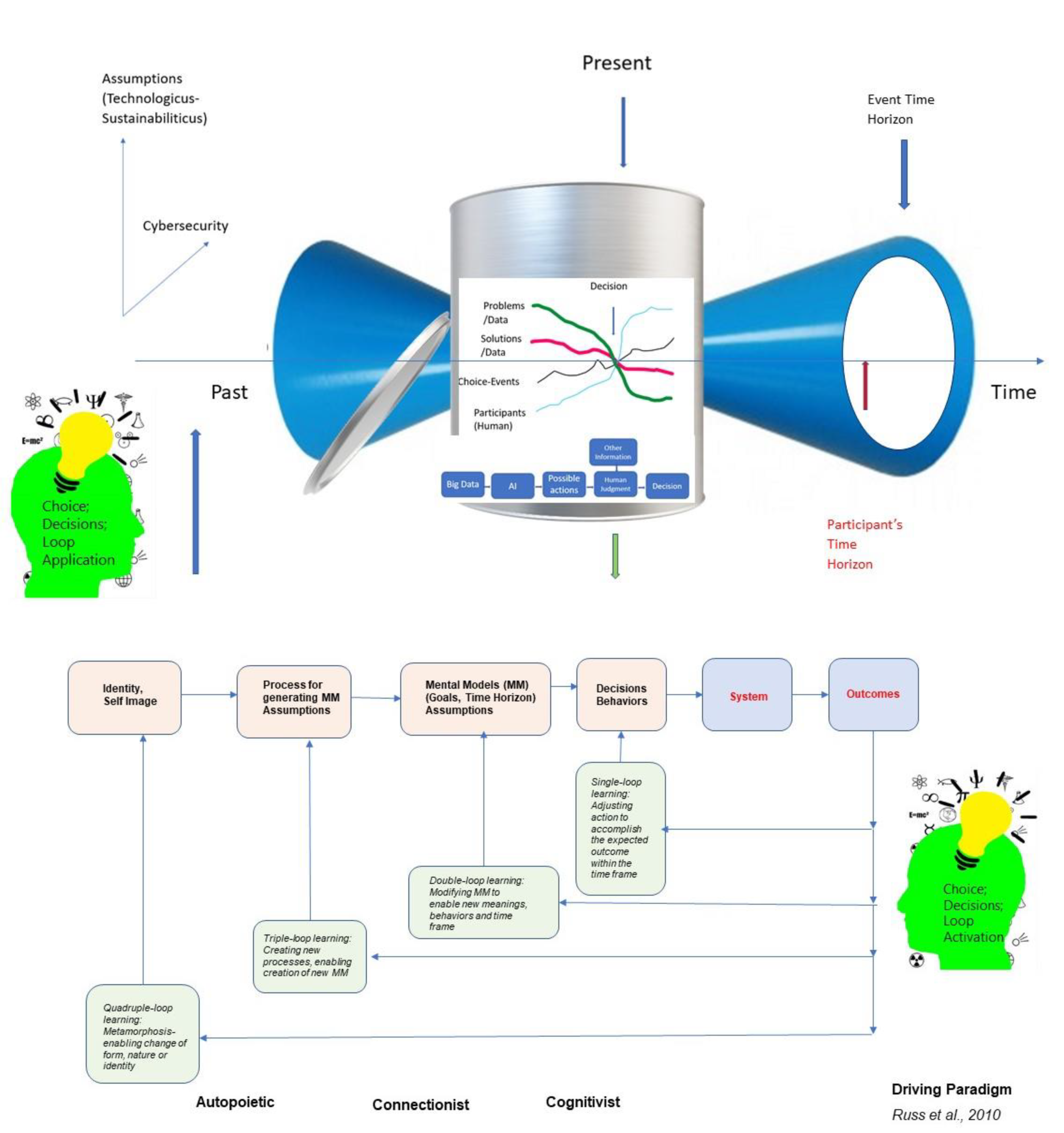
4. The Quantum Metaphor and Maybe More
5. The Learning Feedback Loops—The Quadruple Loop Learning Model
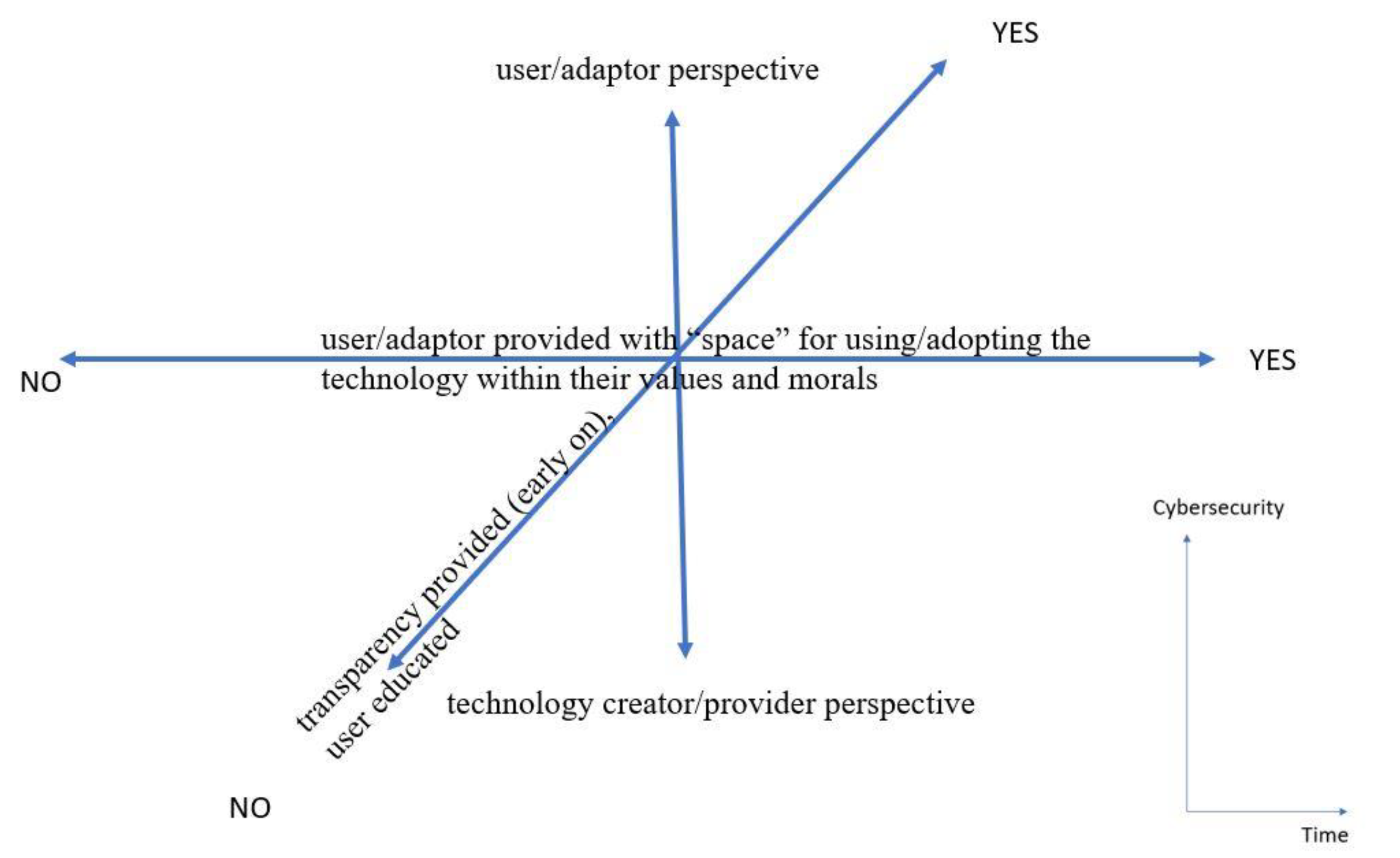
6. Ethics and Cybersecurity
“Homo-Technologicus—“a symbiotic creature in which biology and technology intimately interact”, so that what results is “not simply ‘homo sapiens plus technology’, but rather homo sapiens transformed by ‘technology’ into ‘a new evolutionary unit, undergoing a new kind of evolution in a new environment’” (Ref. [79] (p. 23)), driven by cost efficiencies and instrumental effectiveness within the techno-economic, universal and ontocentric perspectives and expecting adaptation of the ‘homo sapiens’ to the technology.”
“Homo sustainabiliticus—a symbiotic being in which biology, technology and morality intimately interact driven by optimization and the balance of costs of the technology solution, while modifying it to optimize the user’s adaptation, especially regarding her abilities and the social acceptance recognizing cultural and symbolic differences and environmental responsibilities based on biocentric ethics and the socio-philosophical point of view within her cultural, social, physical, logistic and legal context and cognizant of the ethical dilemmas of adapting the technology to her needs, specifically at the design stage”.[1] (p. 19)
7. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Russ, M. Knowledge management for sustainable development in the era of continuously accelerating technological revolutions: A framework and models. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahneman, D. Thinking, Fast and Slow; Macmillan: Basingstoke, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ransbotham, S.; Khodabandeh, S.; Kiron, D.; Candelon, F.; Chu, M.; LaFountain, B. Expanding AI’s Impact with Organizational Learning; MIT Sloan Management Review and Boston Consulting Group: Boston, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Iansiti, M.; Lakhani, K.R. Competing in the Age of AI.; Harvard Business Review Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Araujo, T.; Helberger, N.; Kruikemeier, S.; de Vreese, C.H. In AI we trust? Perceptions about automated decision-making by artificial intelligence. AI Soc. 2020, 35, 611–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarrahi, M.H. Artificial intelligence and the future of work: Human-AI symbiosis in organizational decision making. Bus. Horiz. 2018, 61, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, N.; Rappon, T.; Berta, W. Applications of artificial neural networks in health care organizational decision-making: A scoping review. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshawi, R.; Sakr, S.; Talia, D.; Trunfio, P. Big data systems meet machine learning challenges: Towards big data science as a service. Big Data Res. 2018, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stobierski, T. The Advantages of Data-Driven Decision-Making. Harvard Business School Online. 26 August 2019. Available online: https://online.hbs.edu/blog/post/data-driven-decision-making (accessed on 14 March 2021).
- Trakadas, P.; Simoens, P.; Gkonis, P.; Sarakis, L.; Angelopoulos, A.; Ramallo-González, A.P.; Skarmeta, A.; Trochoutsos, C.; Calvο, D.; Pariente, T.; et al. An artificial intelligence-based collaboration approach in industrial IoT manufacturing: Key concepts, architectural extensions and potential applications. Sensors 2020, 20, 5480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soon, C.S.; Brass, M.; Heinze, H.J.; Haynes, J.D. Unconscious determinants of free decisions in the human brain. Nat. Neurosci. 2008, 11, 543–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haggard, P. The neurocognitive bases of human volition. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2019, 70, 9–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecker, B. Clinical translation of memory reconsolidation research: Therapeutic methodology for transformational change by erasing implicit emotional learnings driving symptom production. Int. J. Neuropsychother. 2018, 6, 1–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lavilléon, G.; Lacroix, M.; Rondi-Reig, L.; Benchenane, K. Explicit memory creation during sleep demonstrates a causal role of place cells in navigation. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 493–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casadio, M.; Ranganathan, R.; Mussa-Ivaldi, F.A. The body-machine interface: A new perspective on an old theme. J. Mot. Behav. 2012, 44, 419–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wood, H. Human–machine interfaces expand the functionality of prosthetic limbs. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2014, 10, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lance, B.J.; Kerick, S.E.; Ries, A.J.; Oie, K.S.; McDowell, K. Brain–computer interface technologies in the coming decades. In Proceedings of the IEEE (Issue: Special Centennial Issue, May 13 2012); IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Volume 100, pp. 1585–1599. Available online: https://arxiv.org/ftp/arxiv/papers/1211/1211.0886.pdf (accessed on 14 March 2021). [CrossRef]
- Kapur, A.; Sarawgi, U.; Wadkins, E.; Wu, M.; Hollenstein, N.; Maes, P. Non-Invasive Silent Speech Recognition in Multiple Sclerosis with Dysphonia. Machine Learning for Health Workshop. PMLR, April 2020; pp. 25–38. Available online: http://proceedings.mlr.press/v116/kapur20a.html (accessed on 14 March 2021).
- Martins, N.R.B.; Angelica, A.; Chakravarthy, K.; Svidinenko, Y.; Boehm, F.J.; Opris, I.; Lebedev, M.A.; Swan, M.; Garan, S.A.; Rosenfeld, J.V.; et al. Human brain/cloud interface. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Stocco, A.; Losey, D.M.; Abernethy, J.A.; Prat, C.S.; Rao, R.P.N. BrainNet: A multi-person brain-to-brain interface for direct collaboration between brains. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fortunato, V.C.R.; Giraldi, J.D.M.E.; De Oliveira, J.H.C. A review of studies on neuromarketing: Practical results, techniques, contributions and limitations. J. Manag. Res. 2014, 6, 201–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nilashi, M.; Samad, S.; Ahmadi, N.; Ahani, A.; Abumalloh, R.A.; Asadi, S.; Abdullah, R.; Ibrahim, O.; Yadegaridehkordi, E. Neuromarketing: A review of research and implications for marketing. J. Soft Comput. Decis. Support Syst. 2020, 7, 23–31. [Google Scholar]
- McMichael, A.J.; Woodruff, R.E.; Hales, S. Climate change and human health: Present and future risks. Lancet 2006, 367, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Yang, F.; Yang, C.; Chen, X.; Zhang, L.; Chi, Y.; Yang, G. Identification of potential impacts of climate change and anthropogenic activities on streamflow alterations in the Tarim River Basin, China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musk, E. Making humans a multi-planetary species. New Space 2017, 5, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istvan, Z. Death Could Soon Become a Curable Disease. Metro.co.uk. 14 May 2019. Available online: https://metro.co.uk/2019/05/14/death-could-soon-become-a-curable-disease-9191393/ (accessed on 14 March 2021).
- Daft, R. Management, 11th ed.; Cengage Learning: Boston, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lau, R.R. Models of decision-making. In Oxford Handbook of Political Psychology; Sears, D.O., Huddy, L., Jervis, R., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2003; pp. 19–59. Available online: https://psycnet.apa.org/record/2003-88243-002 (accessed on 14 March 2021).
- Milner, T.; Rosenstreich, D. A review of consumer decision-making models and development of a new model for financial services. J. Financ. Serv. 2013, 18, 106–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, C.; Dowlatabadi, H. Models of decision-making and residential energy use. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2007, 32, 169–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langley, A.; Mintzberg, H.; Pitcher, P.; Posada, E.; Saint-Macary, J. Opening up decision making: The view from the black stool. Organ. Sci. 1995, 6, 260–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutt, P.C.; Wilson, D.C. (Eds.) Handbook of Decision-Making; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- Luoma, J. Model-based organizational decision making: A behavioral lens. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2016, 249, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M.D.; March, J.G.; Olsen, J.P. A garbage can model of organizational choice. Adm. Sci. Q. 1972, 17, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choo, C.W. Sensemaking, knowledge creation, and decision making. In The Strategic Management of Intellectual Capital and Organizational Knowledge; Choo, C.W., Bontis, N., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2002; pp. 79–88. [Google Scholar]
- Hashem, I.A.T.; Yaqoob, I.; Anuar, N.B.; Mokhtar, S.; Gani, A.; Khan, S.U. The rise of “big data” on cloud computing: Review and open research issues. Inf. Syst. 2015, 47, 98–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spatharou, A.; Hieronimus, S.; Jenkins, J. Transforming Healthcare with AI: The Impact on the Workforce and Organizations. McKinsey & Company, 10 March 2020. Available online: https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/healthcare-systems-and-services/our-insights/transforming-healthcare-with-ai (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- Gottieb, J.; Weinberg, A. Catch Them If You Can: How Leaders in Data and Analytics Have Pulled Ahead. McKinsey Anal. 2019, 1–8. Available online: https://www.mckinsey.com/~/media/McKinsey/Business%20Functions/McKinsey%20Analytics/Our%20Insights/Catch%20them%20if%20you%20can%20How%20leaders%20in%20data%20and%20analytics%20have%20pulled%20ahead/Catch-them-if-you-can-How-leaders-in-data-and-analytics-have-pulled-ahead.pdf (accessed on 13 March 2021).
- Akter, S.; Michael, K.; Uddin, M.R.; McCarthy, G.; Rahman, M. Transforming business using digital innovations: The application of AI, blockchain, cloud and data analytics. Ann. Oper. Res. 2020, 1–33. Available online: https://scholars.uow.edu.au/display/publication142615 (accessed on 11 June 2021). [CrossRef]
- Kahneman, D.; Sibony, O.; Sunstein, C.R. Noise: A Flaw in Human Judgment; Hachette Book Group: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Briggs, G.A.D.; Butterfield, J.N.; Zeilinger, A. The Oxford questions on the foundations of quantum physics. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2013, 469, 20130299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merali, Z. This Twist on Schrödinger’s Cat Paradox Has Major Implications for Quantum Theory. Scientific American. 17 August 2020. Available online: https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/this-twist-on-schroedingers-cat-paradox-has-major-implications-for-quantum-theory/ (accessed on 13 March 2021).
- Josephson, B.D. ‘Beyond quantum theory: A realist psycho-biological interpretation of reality’ revisited. Biosystems 2002, 64, 43–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paul, M. Your Memory is Like the Telephone Game: Each Time You Recall an Event, Your Brain Distorts It. Northwestern.edu. 19 September 2012. Available online: https://news.northwestern.edu/stories/2012/09/your-memory-is-like-the-telephone-game (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- Dolan, E.W. Neural Representations of Reality Are Altered by Expectations. Psypost.org. 14 March 2021. Available online: https://www.psypost.org/2021/03/neural-representations-of-reality-are-altered-by-expectations-60051 (accessed on 13 March 2021).
- Fernandez, E. Are the Past and Future Real? The Physics and Philosophy of Time. Forbes.com. 10 November 2019. Available online: https://www.forbes.com/sites/fernandezelizabeth/2019/11/10/are-the-past-and-future-real-the-physics-and-philosophy-of-time/?sh=1fa56fca4905 (accessed on 13 March 2021).
- Russ, M. Introduction and a theoretical framework for knowledge management for sustainable water systems. In Handbook of Knowledge Management for Sustainable Water Systems; Russ, M., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.M. A hierarchy of limitations in machine learning. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.05193. [Google Scholar]
- Worden, D.M.; William & Mary’s Raymond A. Mason School of Business, Williamsburg, VA, USA. Personal communication, 2021.
- Meyer, R.; Madrigal, A.C. Why the Pandemic Experts Failed: We’re Still Thinking about Pandemic Data in the Wrong Ways. The Atlantic. 15 March 2021. Available online: https://www.theatlantic.com/science/archive/2021/03/americas-coronavirus-catastrophe-began-with-data/618287/ (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- McCradden, M.D.; Joshi, S.; Mazwi, M.; Anderson, J.A. Ethical limitations of algorithmic fairness solutions in health care machine learning. Lancet Digit. Health 2020, 2, e221–e223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Valerdi, L.M.; Luz María, A.V.; Mercado-García, V.R.; Víctor Rodrigo, M.G. Enrichment of human-computer interaction in brain-computer interfaces via virtual environments. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2017, 2017, 6076913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myllykoski, J. Strategic Change Emerging in Time. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Oulu Graduate School, University of Oulu, Oulu, Finland, 2017. Available online: http://jultika.oulu.fi/files/isbn9789526215426.pdf (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- Renko, M.; Kroeck, K.G.; Bullough, A. Expectancy theory and nascent entrepreneurship. Small Bus. Econ. 2012, 39, 667–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rennekamp, K.; Rupar, K.K.; Seybert, N. Impaired judgment: The effects of asset impairment reversibility and cognitive dissonance on future investment. Acc. Rev. 2015, 90, 739–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Parthasarathi, T.; Kable, J.W. The ventral and dorsal default mode networks are dissociably modulated by the vividness and valence of imagined events. J. Neurosci. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yukalov, V.I.; Sornette, D. Quantum probability and quantum decision-making. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2016, 374, 2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russ, M.; Fineman, R.; Jones, J.K. Conceptual theory: What do you know? In Knowledge Management Strategies for Business Development; Russ, M., Ed.; Business Science Reference: Hershey, PA, USA, 2010; pp. 1–22. Available online: https://www.uwgb.edu/UWGBCMS/media/faculty-site-russm/files/chapter_1_russ__fineman_jones_2008.pdf (accessed on 30 March 2020). [CrossRef]
- Seidl, D. Luhmann’s theory of autopoietic social systems. Munich Bus. Res. 2004, 2, 1–28. Available online: https://www.zfog.bwl.uni-muenchen.de/files/mitarbeiter/paper2004_2.pdf (accessed on 13 March 2021).
- Kross, E. Chatter: The Voice in Our Head, Why It Matters, and How to Harness It; Crown Publishing Group: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Scharmer, C.O. Theory U: Learning from the Future Asiit Emerges; Berrett-Koehler Publishers: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, H.K.; Nofsinger, J.R. Psychological biases of investors. Financ. Serv. Rev. 2002, 11, 97–116. [Google Scholar]
- Chira, I.; Adams, M.; Thornton, B. Behavioral bias within the decision-making process. J. Bus. Econ. Res. 2008, 6, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colson, E. What AI-Driven Decision-Making Looks Like. HBR.org. 2019. Available online: https://hbr.org/2019/07/what-ai-driven-decision-making-looks-like (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- Senge, P. The Fifth Discipline: The Art &Practice of the Learning Organization; Doubleday: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, R.S.; Norton, D.P. Using the balanced score card as a strategic management system. Harv. Bus. Rev. 1996, 74, 75–85. [Google Scholar]
- Crossan, M.M.; Lane, H.W.; White, R.E. An organizational learning framework: From intuition to institution. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1999, 24, 522–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Argyris, C. Double loop learning in organizations. Harv. Bus. Rev. 1977, 55, 115–125. [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood, J. The role of reflection in single and double loop learning. J. Adv. Nurs. 1998, 27, 1048–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leifer, L.J.; Steinert, M. Dancing with ambiguity: Causality behavior, design thinking, and triple-loop-learning. Inf. Knowl. Syst. Manag. 2011, 10, 151–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McClory, S.; Read, M.; Labib, A. Conceptualising the lessons-learned process in project management: Towards a triple-loop learning framework. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2017, 35, 1322–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peschl, M.F. Triple-loop learning as foundation for profound change, individual cultivation, and radical innovation: Construction processes beyond scientific and rational knowledge. Constr. Found. 2007, 2, 136–145. [Google Scholar]
- Yuthas, K.; Dillard, J.F.; Rogers, R.K. Beyond agency and structure: Triple-loop learning. J. Bus. Ethics 2004, 51, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, C. Starbucks: The third place. In Strategic Management; Palgrave: London, UK, 2004; pp. 766–772. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M. Alphabet: The Becoming of Google; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, M.; Robbie, K.; Ennew, C. Serial entrepreneurs. Br. J. Manag. 1997, 8, 251–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, C. Innovation Secrets of Steve Jobs: Insanely Different Principles for Breakthrough Success; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Hwang, C.; Moon, M.J. Policy learning and crisis policy-making: Quadruple-loop learning and COVID-19 responses in South Korea. Policy Soc. 2020, 39, 363–381. Available online: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/14494035.2020.1785195 (accessed on 15 March 2021). [CrossRef]
- Longo, G.O. Body and technology: Continuity or discontinuity. In Mediating the Human Body: Communication, Technology and Fashion; Fortunati, L., Katz, J.E., Riccini, R., Eds.; Lawrence Erlbaum: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 2002; pp. 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Rieger, C.; Majchrzak, T.A. Towards the Definitive Evaluation Framework for Cross-Platform App Development Approaches. J. Syst. Softw. 2019, 153, 175–199. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0164121219300743 (accessed on 11 June 2021). [CrossRef]
- Greene, D.; Hoffmann, A.L.; Stark, L. Better, nicer, clearer, fairer: A critical assessment of the movement for ethical artificial intelligence and machine learning. In Proceedings of the 52nd Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Maui, HI, USA, 8–11 January 2019; pp. 2122–2131. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, B. Lifelong machine learning. Synth. Lect. Artif. Intell. Mach. Learn. 2018, 12, 1–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Russ, M. The Individual and the Organizational Model of Quantum Decision-Making and Learning: An Introduction and the Application of the Quadruple Loop Learning. Merits 2021, 1, 34-46. https://doi.org/10.3390/merits1010005
Russ M. The Individual and the Organizational Model of Quantum Decision-Making and Learning: An Introduction and the Application of the Quadruple Loop Learning. Merits. 2021; 1(1):34-46. https://doi.org/10.3390/merits1010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuss, Meir. 2021. "The Individual and the Organizational Model of Quantum Decision-Making and Learning: An Introduction and the Application of the Quadruple Loop Learning" Merits 1, no. 1: 34-46. https://doi.org/10.3390/merits1010005
APA StyleRuss, M. (2021). The Individual and the Organizational Model of Quantum Decision-Making and Learning: An Introduction and the Application of the Quadruple Loop Learning. Merits, 1(1), 34-46. https://doi.org/10.3390/merits1010005



