Graphene Formation through Spontaneous Exfoliation of Graphite by Chlorosulfonic Acid: A DFT Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
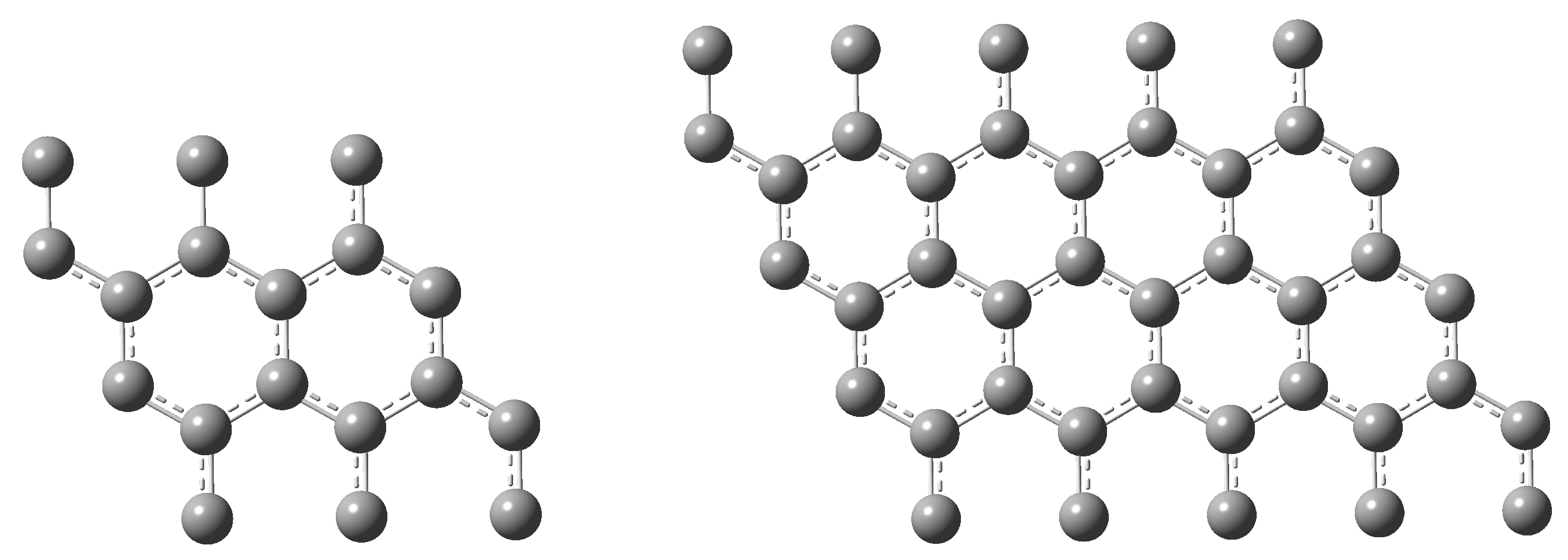
3.1. The HSOCl Molecule and Its Geometrical Matching with Carbon Rings
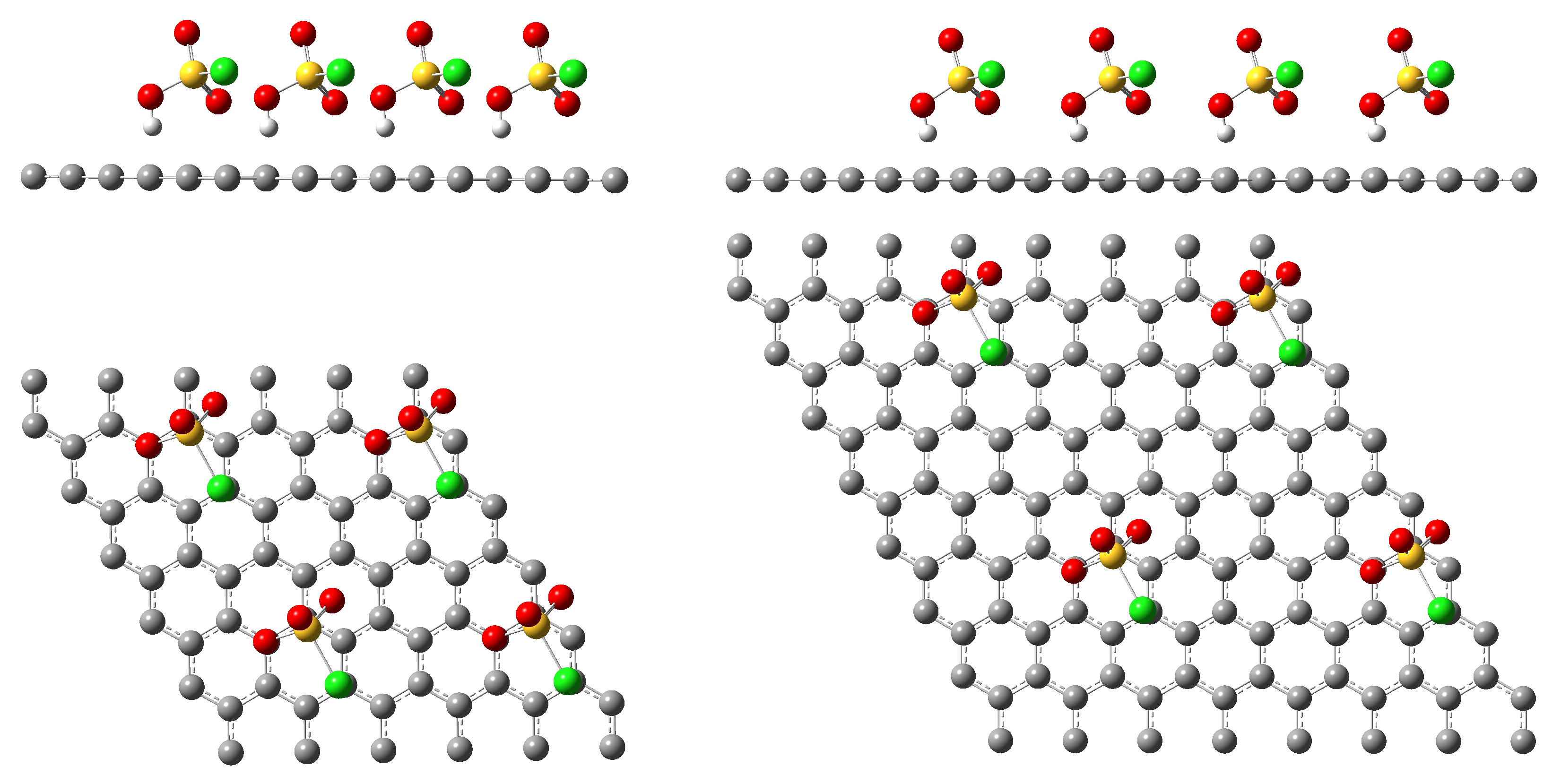
3.2. Interaction Energies and Charge Transfer to MLG
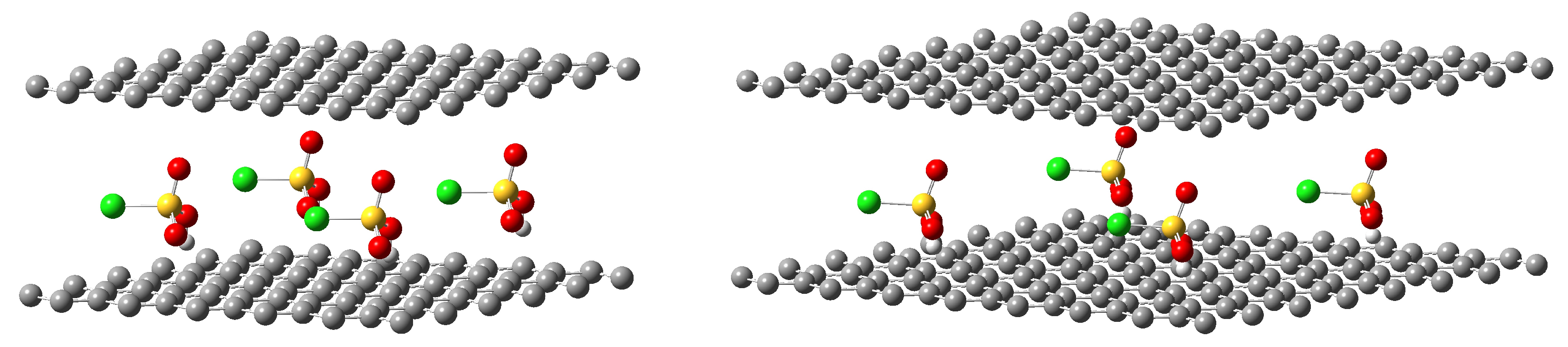
3.3. Interaction Energies and Charge Transfer to BLG
3.4. The Efficiency of Chlorosulfonic Acid to Prevent Reaggregation
3.5. Electronic Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BLG | Bilayer graphene |
| CSA | Chlorosulfonic acid |
| CTAB | Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide |
| DOS | Density of states |
| DFT | Density Functional Theory |
| GGA | Generalized Gradient Approximation |
| HOPG | Highly oriented pyrolytic graphite |
| LDA | Local Density Approximation |
| MLG | Monolayer graphene |
| NPE | Nonylphenolethoxylate |
| SDBS | Sodium dodecyl benzenesulfonate |
| SDS | Sodium dodecylsulfate |
| SNLS | Sodium N-lauroylsarcosinate hydrate |
References
- Novoselov, K.S.; Geim, A.K.; Morozov, S.V.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Dubonos, S.V.; Grigorieva, I.V.; Firsov, A.A. Electric Field Effect in Atomically Thin Carbon Films. Science 2004, 306, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, J.N. Liquid Exfoliation of Defect-Free Graphene. Accounts Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blake, P.; Brimicombe, P.D.; Nair, R.R.; Booth, T.J.; Jiang, D.; Schedin, F.; Ponomarenko, L.A.; Morozov, S.V.; Gleeson, H.F.; Hill, E.W.; et al. Graphene-Based Liquid Crystal Device. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 1704–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, Y.; Nicolosi, V.; Lotya, M.; Blighe, F.M.; Sun, Z.; De, S.; McGovern, I.T.; Holland, B.; Byrne, M.; Gun’ko, Y.K.; et al. High-yield production of graphene by liquid-phase exfoliation of graphite. Nat. Nanotech. 2008, 3, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, U.; O’Neill, A.; Lotya, M.; De, S.; Coleman, J.N. High-Concentration Solvent Exfoliation of Graphene. Small 2010, 6, 864–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bepete, G.; Anglaret, E.; Ortolani, L.; Morandi, V.; Huang, K.; Pénicaud, A.; Drummond, C. Surfactant-free single-layer graphene in water. Nat. Chem. 2017, 9, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salavagione, H.J.; Sherwood, J.; De bruyn, M.; Budarin, V.L.; Ellis, G.J.; Clark, J.H.; Shuttleworth, P.S. Identification of high performance solvents for the sustainable processing of graphene. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 2550–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, B.; Ranjbar, Z.; Hashjin, R.R.; Rezvani Moghaddam, A.; Momen, G.; Ranjbar, B. Dispersing graphene in aqueous media: Investigating the effect of different surfactants. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 582, 123870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotya, M.; Hernandez, Y.; King, P.J.; Smith, R.J.; Nicolosi, V.; Karlsson, L.S.; Blighe, F.M.; De, S.; Wang, Z.; McGovern, I.T.; et al. Liquid Phase Production of Graphene by Exfoliation of Graphite in Surfactant/Water Solutions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 3611–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotya, M.; King, P.J.; Khan, U.; De, S.; Coleman, J.N. High-Concentration, Surfactant-Stabilized Graphene Dispersions. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 3155–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Wang, N.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xie, Z.; Li, Z.; Pambou, E.; Li, R.; Chen, C.; et al. Direct exfoliation of graphite into graphene in aqueous solutions of amphiphilic peptides. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Englert, J.M.; Röhrl, J.; Schmidt, C.D.; Graupner, R.; Hundhausen, M.; Hauke, F.; Hirsch, A. Soluble Graphene: Generation of Aqueous Graphene Solutions Aided by a Perylenebisimide-Based Bolaamphiphile. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 4265–4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardyani, T.; Mohamed, A.; Abu Bakar, S.; Sagisaka, M.; Hafiz Mamat, M.; Khairul Ahmad, M.; Ibrahim, S.; Abdul Khalil, H.; King, S.M.; Rogers, S.E.; et al. A guide to designing graphene-philic surfactants. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 620, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akter, N.; Mawardi Ayob, M.T.; Radiman, S.; Khandaker, M.U.; Osman, H.; Alamri, S. Bio-Surfactant Assisted Aqueous Exfoliation of High-Quality Few-Layered Graphene. Crystals 2021, 11, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethurajaperumal, A.; Varrla, E. High-Quality and Efficient Liquid-Phase Exfoliation of Few-Layered Graphene by Natural Surfactant. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 14746–14760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Huang, X.; Liu, F.; Yang, X.; Rosler, C.; Fischer, R.A.; Muhler, M.; Schuhmann, W. Amine-based solvents for exfoliating graphite to graphene outperform the dispersing capacity of N-methyl-pyrrolidone and surfactants. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 10382–10385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, R.V.; Maraschin, T.G.; Koppe, G.C.; Dias, L.W.; Balzaretti, N.M.; Galland, G.B.; Regina de Souza Basso, N. Cardanol surfactant/ultrasound-assisted exfoliation of graphite in a water/ethanol solution. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 290, 126578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Q.; Zhong, B.; Tan, H.; Navik, R.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Y. Improved Dispersibility of Graphene in an Aqueous Solution by Reduced Graphene Oxide Surfactant: Experimental Verification and Density Functional Theory Calculation. Langmuir 2022, 38, 8222–8231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambe, P.; Sharma, A.; Kulkarni, H.; Panda, B. Surfactant assisted dispersion of graphene in aqueous solution using mixed surfactants. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 56, 1217–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.B.; Wang, Z.H.; Suo, W.H.; Wang, Y.; Wen, J.C.; Li, Y.F.; Suo, H.L.; Liu, M.; Ma, L. Performance of graphene dispersion by using mixed surfactants. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 095009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbourne, A.; McLean, B.; Voïtchovsky, K.; Warr, G.G.; Atkin, R. Molecular Resolution in situ Imaging of Spontaneous Graphene Exfoliation. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 3118–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.S.; Dutta, N.K.; Choudhury, N.R. Poly(ionic liquid)-Stabilized Graphene Nanoinks for Scalable 3D Printing of Graphene Aerogels. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 11608–11619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, R.; Tamas, G.; Irin, F.; Aquino, A.J.; Green, M.J.; Quitevis, E.L. Direct exfoliation of graphene in ionic liquids with aromatic groups. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 463, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, S.; Sundqvist, B.; Talyzin, A.V. Enormous Lattice Expansion of Hummers Graphite Oxide in Alcohols at Low Temperatures. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 1395–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khannanov, A.; Kiiamov, A.; Galyaltdinov, S.; Tayurskii, D.A.; Dimiev, A.M. Pristine graphite oxide retains its C-axis registry in methanol. The way to alternative purification method. Carbon 2021, 173, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Advincula, P.A.; Luong, D.X.; Chen, W.; Raghuraman, S.; Shahsavari, R.; Tour, J.M. Flash graphene from rubber waste. Carbon 2021, 178, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behabtu, N.; Lomeda, J.R.; Green, M.J.; Higginbotham, A.L.; Sinitskii, A.; Kosynkin, D.V.; Tsentalovich, D.; Parra-Vasquez, A.N.G.; Schmidt, J.; Kesselman, E.; et al. Spontaneous high-concentration dispersions and liquid crystals of graphene. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudarzi, M.M.; Asaad, M.; Mao, B.; Pinter, G.; Guo, J.; Smith, M.; Zhong, X.; Georgiou, T.; Gorbachev, R.; Haigh, S.J.; et al. Chlorosulfuric acid-assisted production of functional 2D materials. NPJ 2D Mater. Appl. 2021, 5, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlay, I.; Tudoran, L.B. Chlorosulfonic Acid-based Room Temperature Chemical Expansion Route for the Bulk Production of Graphite Nanoplatelets. Fullerenes Nanotub. Carbon Nanostruct. 2013, 21, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagona, G.; Bittencourt, C.; Arenal, R.; Tagmatarchis, N. Exfoliated semiconducting pure 2H-MoS2 and 2H-WS2 assisted by chlorosulfonic acid. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 12950–12953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Jiang, X.; Zhu, L. From graphite to graphene: Direct liquid-phase exfoliation of graphite to produce single- and few-layered pristine graphene. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 10592–10606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, J.D. The Structure of Graphite. Proc. R. Soc. London Ser. A 1924, 106, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero, N.A.; Alonso, J.A. The interaction of sulfuric acid with graphene and formation of adsorbed crystals. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 485705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, I.G.; Cordero, N.A.; Alonso, J.A. Surfactant effect of sulfuric acid on the exfoliation of bilayer graphene. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 84, 165424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, I.G.; Cordero, N.A. Interaction of sodium bisulfate with mono- and bi-layer graphene. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2012, 14, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, L.B. Intercalation Compounds of Graphite. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 1976, 6, 181–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuelson, L.; Batra, I.P. Electronic properties of various stages of lithium intercalated graphite. J. Phys. C Solid State Phys. 1980, 13, 5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.K.; Lee, S.C.; Ahn, J.P.; Kim, S.C.; Wilson, J.I.B.; John, P. The growth of AA graphite on (111) diamond. J. Chem. Phys. 2008, 129, 234709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horiuchi, S.; Gotou, T.; Fujiwara, M.; Sotoaka, R.; Hirata, M.; Kimoto, K.; Asaka, T.; Yokosawa, T.; Matsui, Y.; Watanabe, K.; et al. Carbon Nanofilm with a New Structure and Property. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 42, L1073–L1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Suenaga, K.; Harris, P.J.F.; Iijima, S. Open and Closed Edges of Graphene Layers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 015501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolmogorov, A.N.; Crespi, V.H. Registry-dependent interlayer potential for graphitic systems. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 71, 235415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, B.R.K.; Satpathy, S. Strain and electric field modulation of the electronic structure of bilayer graphene. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 80, 165430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakarova-Käck, S.D.; Vojvodic, A.; Kleis, J.; Hyldgaard, P.; Schröder, E. Binding of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and graphene dimers in density functional theory. New J. Phys. 2010, 12, 013017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, S.; Kobayashi, T. Electronic Properties of Graphite with Rotational Stacking Arrangement. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 48, 050207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohenberg, P.; Kohn, W. Inhomogeneous Electron Gas. Phys. Rev. 1964, 136, B864–B871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn, W.; Sham, L.J. Self-Consistent Equations Including Exchange and Correlation Effects. Phys. Rev. 1965, 140, A1133–A1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dacapo. Available online: https://wiki.fysik.dtu.dk/dacapo/Introduction (accessed on 26 November 2022).
- Girifalco, L.A.; Hodak, M. Van der Waals binding energies in graphitic structures. Phys. Rev. B 2002, 65, 125404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, M.; Nishidate, K. Semiempirical approach to the energetics of interlayer binding in graphite. Phys. Rev. B 2004, 70, 205431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birowska, M.; Milowska, K.; Majewski, J.A. Van Der Waals Density Functionals for Graphene Layers and Graphite. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2011, 120, 845–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hod, O. Graphite and hexagonal boron-nitride have the same interlayer distance. Why? J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2012, 8, 1360–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Rojas, R.M.; Contreras-Solorio, D.A.; Hernández, L.; Enciso, A. Band gap variation in bi, tri and few-layered 2D graphene/hBN heterostructures. Solid State Commun. 2022, 341, 114553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderbilt, D. Soft self-consistent pseudopotentials in a generalized eigenvalue formalism. Phys. Rev. B 1990, 41, 7892–7895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khantha, M.; Cordero, N.A.; Molina, L.M.; Alonso, J.A.; Girifalco, L.A. Interaction of lithium with graphene: An ab initio study. Phys. Rev. B 2004, 70, 125422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khantha, M.; Cordero, N.A.; Alonso, J.A.; Cawkwell, M.; Girifalco, L.A. Interaction and concerted diffusion of lithium in a (5,5) carbon nanotube. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 78, 115430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, M.; Nakada, K.; Ishii, A. DFT calculations for SO4/graphene with and without a Pd atom. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2014, 83, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monkhorst, H.J.; Pack, J.D. Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations. Phys. Rev. B 1976, 13, 5188–5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian 09. Gaussian Inc. Wallingford CT 2009. Available online: https://gaussian.com/ (accessed on 26 November 2022).
- Kim, Y.; Hong, S.; Jung, S.; Strano, M.S.; Choi, J.; Baik, S. Dielectrophoresis of surface conductance modulated single-walled carbon nanotubes using catanionic surfactants. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 1541–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matarredona, O.; Rhoads, H.; Li, Z.R.; Harwell, J.H.; Balzano, L.; Resasco, D.E. Dispersion of single-walled carbon nanotubes in aqueous solutions of the anionic surfactant NaDDBS. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 13357–13367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, D.W.; Brown, J.M.; Anderson, D.P.; Zhao, J.; Chokalingam, K.; Tomlin, D.; Ilavsky, J. Structure and dispersion of carbon nanotubes. J. Appl. Cryst. 2003, 36, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulliken, R.S. Electronic Population Analysis on LCAO-MO Molecular Wave Functions. 1. J. Chem. Phys. 1955, 23, 1833–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskin, Y.; Meyer, L. Lattice Constants of Graphite at Low Temperatures. Phys. Rev. 1955, 100, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Dai, S.; Li, X.; Yang, J.; Srolovitz, D.J.; Zheng, Q. Measurement of the cleavage energy of graphite. Nat. Comm. 2015, 6, 8853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlier, J.C.; Gonze, X.; Michenaud, J.P. Graphite Interplanar Bonding: Electronic Delocalization and van der Waals Interaction. Europhys. Lett. 1994, 28, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, X.; Dong, J. Infrared and Raman spectra of AA-stacking bilayer graphene. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 065711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuganathan, N.; Ganeshalingam, S. Encapsulation and Adsorption of Halogens into Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Micro 2021, 1, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, M.; Amawashi, H. Dependence of band structures on stacking and field in layered graphene. Solid State Commun. 2007, 142, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Qi, L.; Huang, J.Y.; Li, J. Geometric and electronic structure of graphene bilayer edges. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 80, 165407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Chiu, C.W.; Lin, M.F. Deformation effects on electronic structures of bilayer graphenes. Physica E 2010, 42, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grüneis, A.; Attaccalite, C.; Rubio, A.; Vyalikh, D.V.; Molodtsov, S.L.; Fink, J.; Follath, R.; Eberhardt, W.; Büchner, B.; Pichler, T. Angle-resolved photoemission study of the graphite intercalation compound KC8: A key to graphene. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 80, 075431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
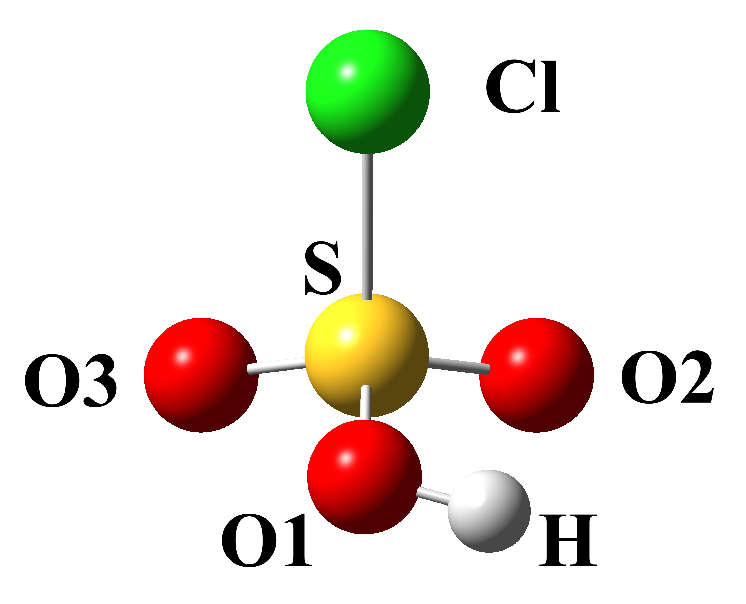
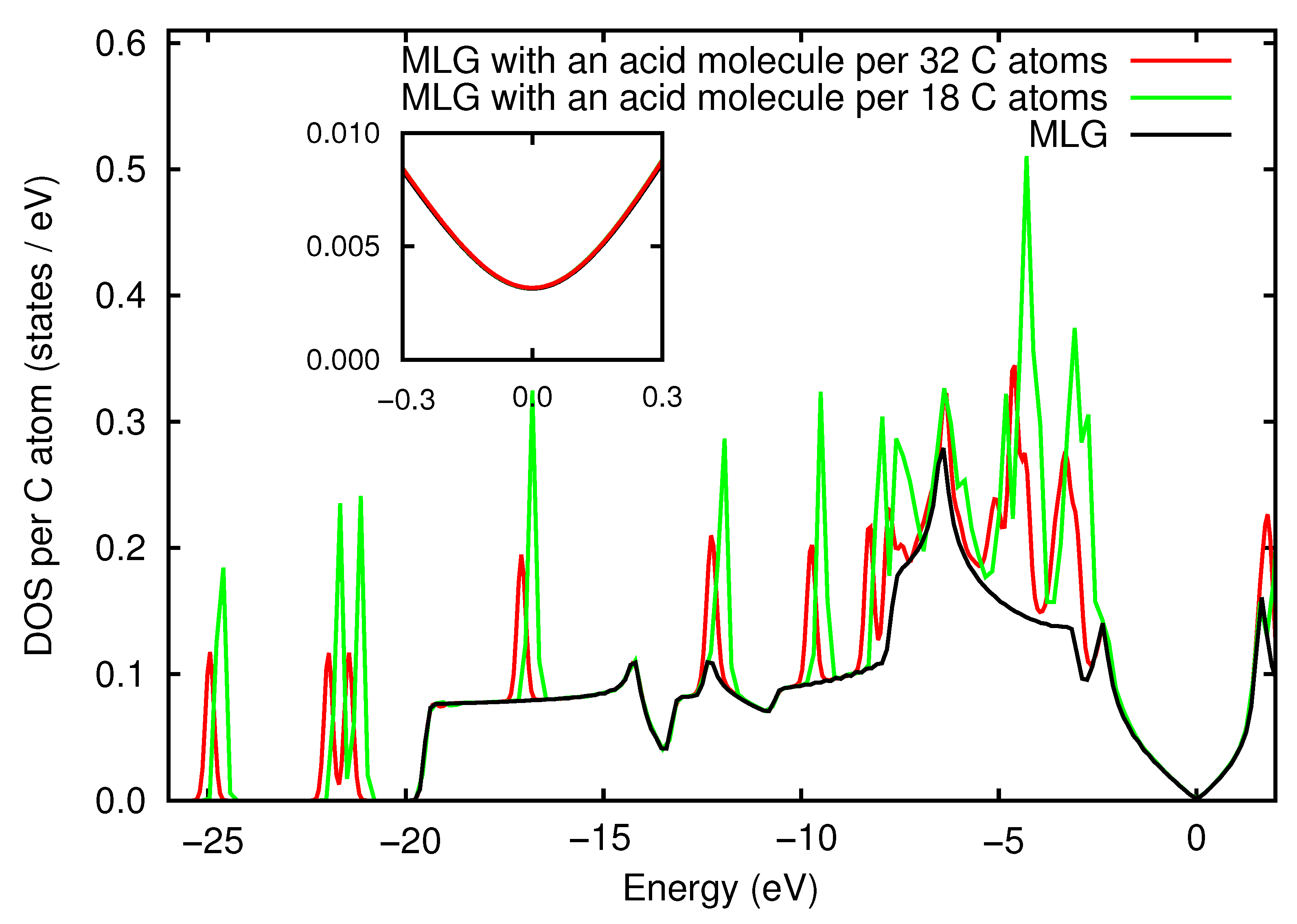
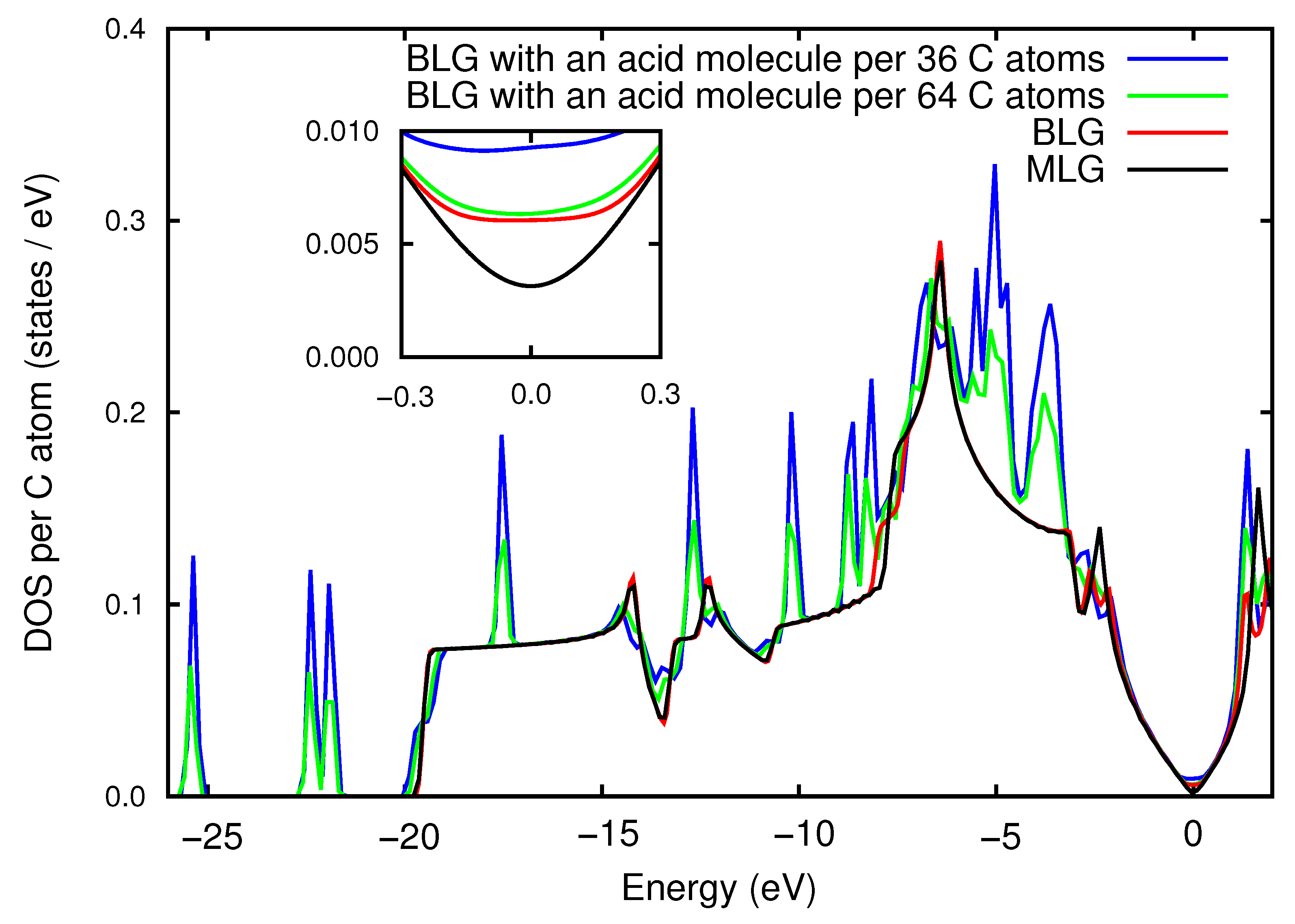
| Distances | Planar Angles | Dihedral Angles | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gaussian | Dacapo | Gaussian | Dacapo | Gaussian | Dacapo | ||||||
| LDA | MP2 | LDA | LDA | MP2 | LDA | LDA | MP2 | LDA | |||
| S-O1 | 1.61 | 1.62 | 1.60 | O1-S-Cl | 100.4 | 100.3 | 100.3 | O1-S-Cl-O2 | 111.1 | 111.0 | 110.7 |
| S-O2 | 1.44 | 1.45 | 1.43 | O2-S-Cl | 106.9 | 107.0 | 106.6 | O2-S-Cl-O3 | 135.6 | 135.9 | 135.7 |
| S-O3 | 1.45 | 1.41 | 1.41 | O3-S-Cl | 107.5 | 107.5 | 107.4 | O3-S-Cl-O1 | 113.3 | 113.1 | 113.6 |
| S-Cl | 2.05 | 2.05 | 2.07 | S-O1-H | 107.4 | 107.5 | 108.7 | ||||
| O3-H | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.98 | ||||||||
| Chlorosulfonic Acid | Sulfuric Acid [33] | Sodium Bisulfate [35] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conc. | (eV) | (e) | (eV) | (e) | (eV) | (e) | |
| MLG | Low | 0.36 | 0.44 | 0.29 | 0.30 | 0.44 | 0.11 |
| High | 0.34 | 0.36 | 0.34 | 0.26 | 0.54 | 0.04 | |
| AB-BLG | Low | 0.35 | 0.43 | ||||
| High | 0.33 | 0.36 | |||||
| AA-BLG | Low | 0.42 | 0.43 | ||||
| High | 0.49 | 0.36 | |||||
| AA Stacking | AB Stacking | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Å) | (meV/at) | (Å) | (meV/at) | |
| Exp. | 3.55 | - | 3.34 [63] | 60.5 [64] |
| This work | 3.65 | 7.0 | 3.35 | 12.6 |
| Ref. [65] | 3.66 | 9.8 | 3.30 | 19.6 |
| Ref. [66] | 3.59 | - | - | - |
| Ref. [41] | 3.57 | - | 3.34 | 48.0 |
| Chlorosulfonic Acid | Sulfuric Acid [34] | Sodium Bisulfate [35] | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conc. | Stacking | (Å) | (eV) | (eV) | (e) | (Å) | (eV) | (e) | (Å) | (eV) | (e) |
| Low | AB | 7.78 | −0.25 | 0.43 | 0.41 | ||||||
| AA | 7.87 | 0.08 | 0.42 | 0.54 | 7.6 | 0.09 | 0.48 | 7.8 | 0.22 | 0.14 | |
| High | AB | 7.85 | 0.01 | 0.49 | 0.39 | ||||||
| AA | 8.00 | 0.34 | 0.42 | 0.42 | 7.6 | 0.24 | 0.39 | 7.8 | 0.33 | 0.09 | |
| (Å) | (eV) | d(H–C) (Å) | d(O–C) (Å) | (e) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.55 | 0.04 | 1.86 | 2.71 | 0.56 |
| 7.71 | 0.06 | 1.88 | 2.81 | 0.55 |
| 7.87 | 0.08 | 1.90 | 2.93 | 0.54 |
| 8.20 | 0.07 | 1.93 | 3.20 | 0.53 |
| 8.56 | 0.04 | 1.96 | 3.49 | 0.51 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bol-Arreba, A.; Ayala, I.G.; Cordero, N.A. Graphene Formation through Spontaneous Exfoliation of Graphite by Chlorosulfonic Acid: A DFT Study. Micro 2023, 3, 143-155. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro3010011
Bol-Arreba A, Ayala IG, Cordero NA. Graphene Formation through Spontaneous Exfoliation of Graphite by Chlorosulfonic Acid: A DFT Study. Micro. 2023; 3(1):143-155. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro3010011
Chicago/Turabian StyleBol-Arreba, Alfredo, Isabel G. Ayala, and Nicolás A. Cordero. 2023. "Graphene Formation through Spontaneous Exfoliation of Graphite by Chlorosulfonic Acid: A DFT Study" Micro 3, no. 1: 143-155. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro3010011
APA StyleBol-Arreba, A., Ayala, I. G., & Cordero, N. A. (2023). Graphene Formation through Spontaneous Exfoliation of Graphite by Chlorosulfonic Acid: A DFT Study. Micro, 3(1), 143-155. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro3010011






