Tuning of the Viscosity Maximum and the Temperature Effect on Wormlike Micelle Solutions Using Hydrotropic and Inorganic Salts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Rheometry
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Rheological Properties of EHAC/NaSal Solutions at Room Temperature
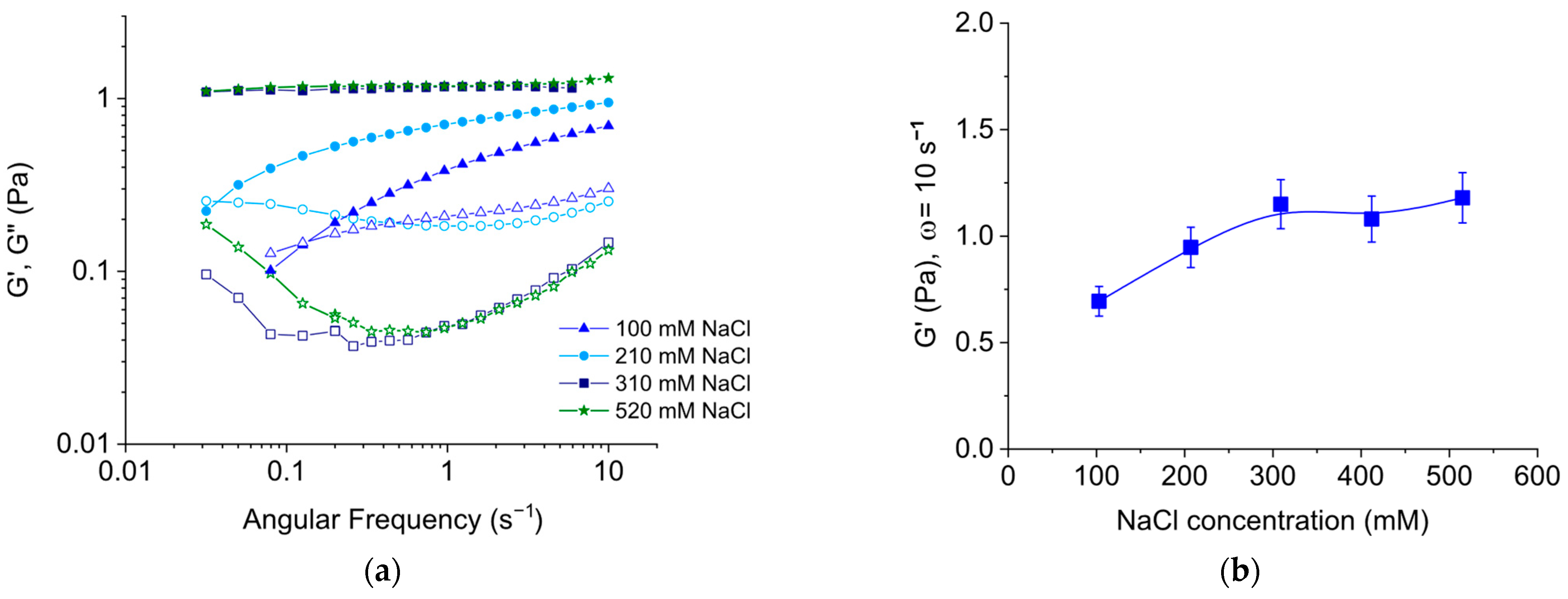
3.1.1. Effect of Salt Concentration
3.1.2. Effect of Surfactant Concentration
3.2. Comparison of Rheological Properties of EHAC/NaSal and EHAC/NaCl Solutions at Room Temperature
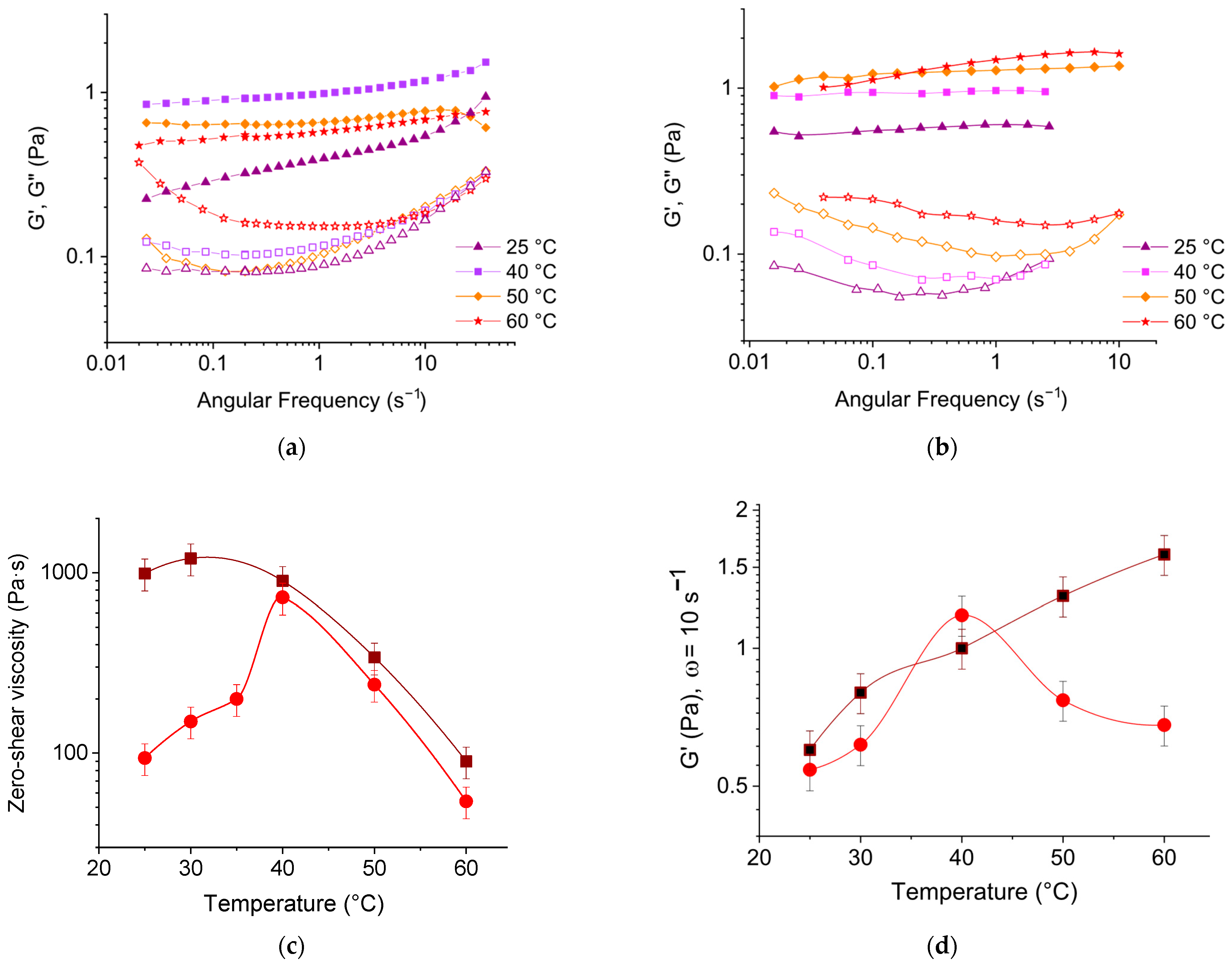
3.3. Effect of Temperature on Rheological Properties of EHAC/NaSal Solutions
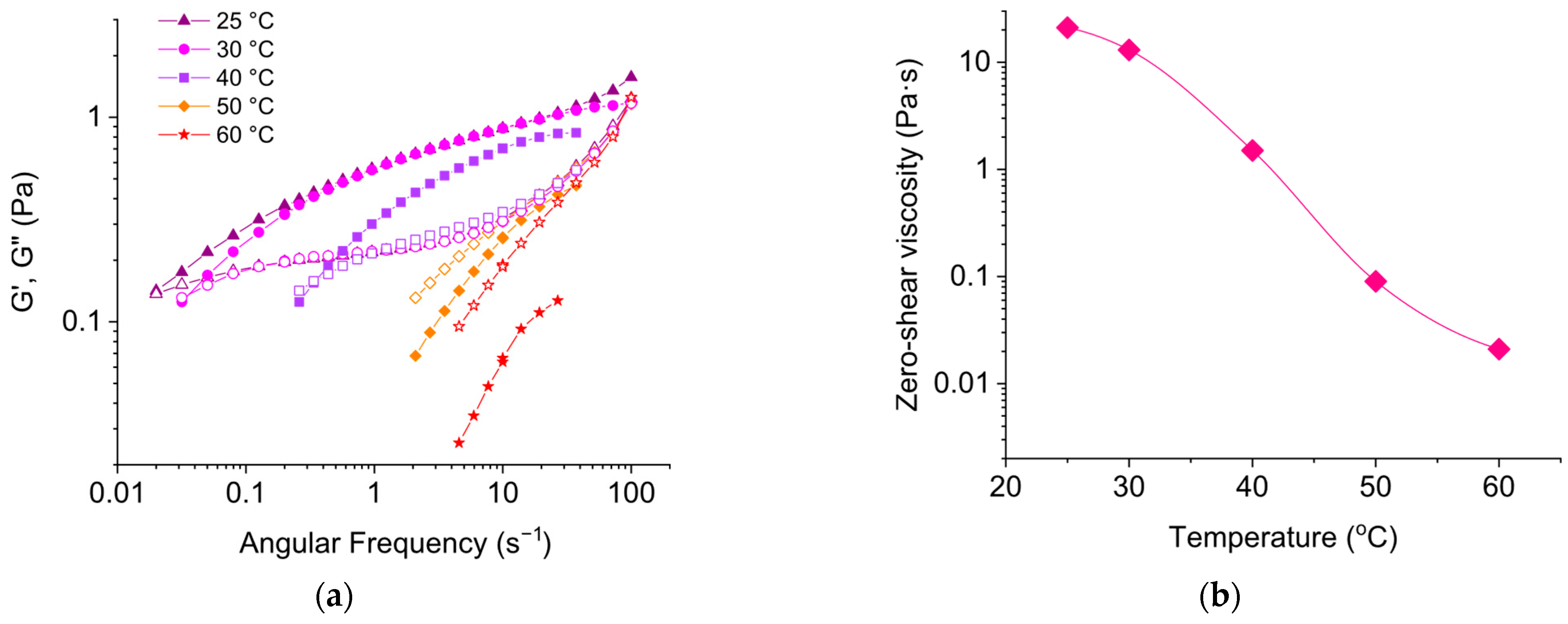
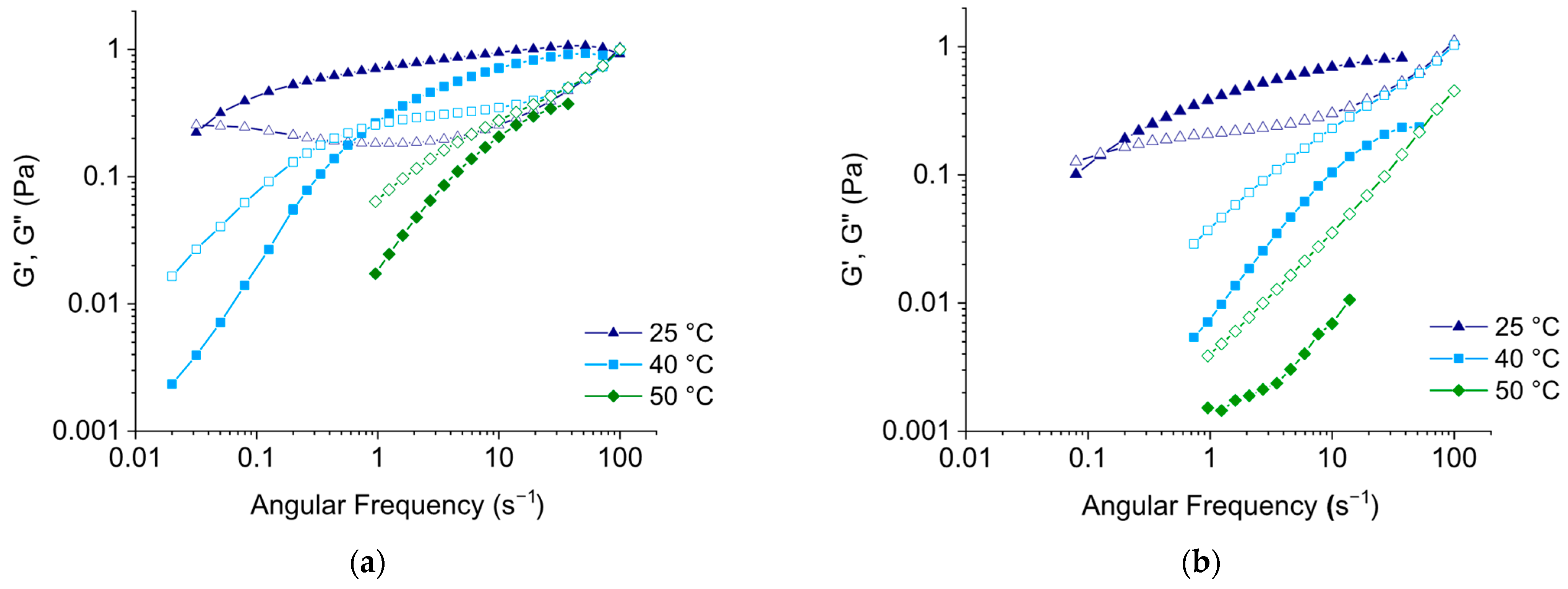
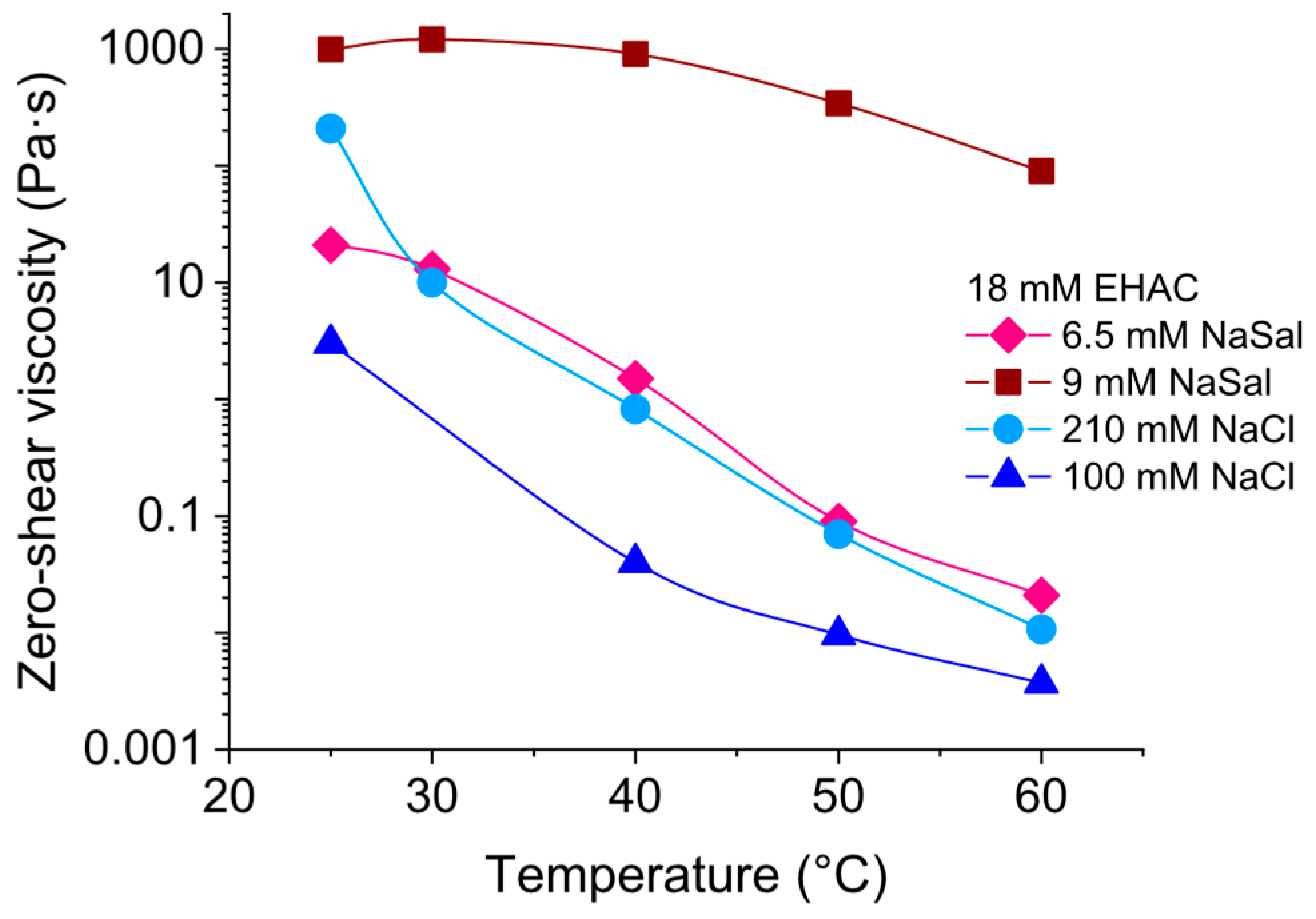
3.4. Comparison of Rheological Properties of EHAC/NaSal and EHAC/NaCl Solutions at Elevated Temperatures
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| WLM | Wormlike micelle |
| EHAC | Erucyl bis(hydroxyethyl)methylammonium chloride |
| NaSal | Sodium salicylate |
| DCTAC | Docosyl(trimethyl)azanium chloride |
| SHNC | 3-hydroxy naphthalene-2-carboxylate |
Appendix A
| Quantity | Symbol | Unit (SI) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zero-shear viscosity | η0 | Pa·s | Viscosity plateau measured at low shear rate. |
| Storage modulus | G′ | Pa | Elastic part of the sample response from dynamic rheological measurements. |
| Loss modulus | G′′ | Pa | Inelastic part of the sample response from dynamic rheological measurements. |
| Shear rate | - | s−1 | Rate of shear applied during rheology tests. |
| Salt concentration | - | mol/L | Concentration of salt in solution. |
| Surfactant concentration | - | mol/L | Concentration of surfactant in solution. |
| Salt-to-surfactant molar ratio | - | - | Molar ratio of salt to surfactant. |
| Frequency | ω | s−1 | Frequency of oscillatory rheological measurement. |
| Relaxation time | τrel | s | Characteristic time for network relaxation. |
| Activation energy | Ea | kJ/mol | Energy barrier for temperature-related processes. |
| End-cap energy | Ec | kJ/mol | Energy required to create two end-caps from a semi-infinite cylinder for neutral micelles. |
| Electrostatic energy | Ee | kJ/mol | Energy related to the degree of charge of the micelle and the concentration of free ions in the solution. |
| Temperature | T | K or °C | Temperature of the system during experiments. |
| Contour length of micelles | L | nm | Length of micelle chain. |
| Persistence length | lp | nm | Persistence length describing micelle stiffness. |
| Entanglement length | le | nm | Contour length between entanglements in the micelle network. |
References
- Philippova, O. Wormlike Micelles: Advances in Systems, Characterisation and Applications; Dreiss, C., Ed.; Soft Matter Series; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2017; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg, K.; Jönsson, B.; Kronberg, B.; Lindman, B. Surfactants and Polymers in Aqueous Solution; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Richtering, W. The Colloidal Domain—Where Physics, Chemistry, Biology and Technology Meet. Appl. Rheol. 2019, 11, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatory, A.; Kern, F.; Lequeux, F.; Appell, J.; Porte, G.; Morie, N.; Ott, A.; Urbach, W. Entangled versus Multiconnected Network of Wormlike Micelles. Langmuir 1993, 9, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, F.; Lequeux, F.; Zana, R.; Candau, S.J. Dynamical Properties of Salt-Free Viscoelastic Micellar Solutions. Langmuir 1994, 10, 1714–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.X.; Zhou, H.; Wei, Y.Q.; Mei, Y.J.; Wang, H. Effect of TBAB/KCl on Constructing Anionic Wormlike Micelles. Wuli Huaxue Xuebao/Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 2015, 31, 2124–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatory, A.; Lequeux, F.; Kern, F.; Candau, S.J. Linear and Nonlinear Viscoelasticity of Semidilute Solutions of Wormlike Micelles at High Salt Content. Langmuir 1993, 9, 1456–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molchanov, V.S.; Philippova, O.E. Effects of Concentration and Temperature on Viscoelastic Properties of Aqueous Potassium Oleate Solutions. Colloid J. 2009, 71, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molchanov, V.S.; Shashkina, Y.A.; Philippova, O.E.; Khokhlov, A.R. Viscoelastic Properties of Aqueous Anionic Surfactant (Potassium oleate) Solutions. Colloid J. 2005, 67, 606–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pletneva, V.A.; Molchanov, V.S.; Philippova, O.E. Effect of Polymer on Rheological Behavior of Heated Solutions of Potassium Oleate Cylindrical Micelles. Colloid J. 2010, 72, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croce, V.; Cosgrove, T.; Maitland, G.; Hughes, T.; Karlsson, G. Rheology, Cryogenic Transmission Electron Spectroscopy, and Small-Angle Neutron Scattering of Highly Viscoelastic Wormlike Micellar Solutions. Langmuir 2003, 19, 8536–8541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magid, L.J. The Surfactant-Polyelectrolyte Analogy. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 4064–4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelaere, E.; Cressely, R. Rheological Behavior of an Elongated Micellar Solution at Low and High Salt Concentrations. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1998, 276, 1050–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.; Tang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Song, S. Hofmeister Series: Insights of Ion Specificity from Amphiphilic Assembly and Interface Property. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 6229–6239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, K.; Mitra, D.; Guha, S.; Moulik, S.P. Salt Effect on Self-Aggregation of Sodium Dodecylsulfate (SDS) and Tetradecyltrimethylammonium Bromide (TTAB): Physicochemical Correlation and Assessment in the Light of Hofmeister (Lyotropic) Effect. J. Mol. Liq. 2009, 146, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachy, N.; Jagoda-Cwiklik, B.; Vácha, R.; Touraud, D.; Jungwirth, P.; Kunz, W. Hofmeister Series and Specific Interactions of Charged Headgroups with Aqueous Ions. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 146, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boström, M.; Williams, D.R.M.; Ninham, B.W. Ion Specificity of Micelles Explained by Ionic Dispersion Forces. Langmuir 2002, 18, 6010–6014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koroleva, S.V.; Korchak, P.; Victorov, A.I. Molecular Thermodynamic Modeling of the Specific Effect of Salt on the Aggregation of Nonionic Surfactants. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2020, 65, 987–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warmbier-Wytykowska, E.; Williams, A.P.; Rozanski, J.; Fischer, P.; Lutz-Bueno, V.; Handschin, S.; Baraldi, L.; Warmbier, J.; Wagner, P.; Różańska, S. How Do the Valency and Radii of Cations Affect the Rheological Properties of Aqueous Solutions of Zwitterionic and Anionic Surfactant Mixtures? Langmuir 2025, 41, 3561–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abezgauz, L.; Kuperkar, K.; Hassan, P.A.; Ramon, O.; Bahadur, P.; Danino, D. Effect of Hofmeister Anions on Micellization and Micellar Growth of the Surfactant Cetylpyridinium Chloride. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 342, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isabettini, S.; Böni, L.J.; Baumgartner, M.; Saito, K.; Kuster, S.; Fischer, P.; Lutz-Bueno, V. Higher Salt Hydrophobicity Lengthens Ionic Wormlike Micelles and Stabilizes Them upon Heating. Langmuir 2021, 37, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oelschlaeger, C.; Suwita, P.; Willenbacher, N. Effect of Counterion Binding Efficiency on Structure and Dynamics of Wormlike Micelles. Langmuir 2010, 26, 7045–7053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleines, M.; Kunz, W.; Zemb, T.; Benczédi, D.; Fieber, W. Molecular Factors Governing the Viscosity Peak of Giant Micelles in the Presence of Salt and Fragrances. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 537, 682–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhloufi, R.; Cressely, R. Temperature Dependence of the Non-Newtonian Viscosity of Elongated Micellar Solutions. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1992, 270, 1035–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candau, S.J.; Hirsch, E.; Zana, R.; Delsanti, M. Rheological Properties of Semidilute and Concentrated Aqueous Solutions of Cetyltrimethylammonium Bromide in the Presence of Potassium Bromide. Langmuir 1989, 5, 1225–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, S.R.; Edlund, H.; Kaler, E.W. Cloud-Point Phenomena in Wormlike Micellar Systems Containing Cationic Surfactant and Salt. Langmuir 2002, 18, 1056–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalur, G.C.; Frounfelker, B.D.; Cipriano, B.H.; Norman, A.I.; Raghavan, S.R. Viscosity Increase with Temperature in Cationic Surfactant Solutions Due to the Growth of Wormlike Micelles. Langmuir 2005, 21, 10998–11004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Guo, W.; Zhu, Q.; Ge, H.; Yang, H.; Ke, Y.; Shi, X.; Lu, X.; Feng, Y.; Yin, H. Supramolecular Self-Assembly of Robust, Ultra-Stable, and High-Temperature-Resistant Viscoelastic Worm-like Micelles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 649, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, S.R.; Kaler, E.W. Highly Viscoelastic Wormlike Micellar Solutions Formed by Cationic Surfactants with Long Unsaturated Tails. Langmuir 2001, 17, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashkina, J.A.; Philippova, O.E.; Zaroslov, Y.D.; Khokhlov, A.R.; Pryakhina, T.A.; Blagodatskikh, I.V. Rheology of Viscoelastic Solutions of Cationic Surfactant. Effect of Added Associating Polymer. Langmuir 2005, 21, 1524–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, P.A.; Candau, S.J.; Kern, F.; Manohar, C. Rheology of Wormlike Micelles with Varying Hydrophobicity of the Counterion. Langmuir 1998, 14, 6025–6029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehage, H.; Hoffmann, H. Rheological Properties of Viscoelastic Surfactant Systems. J. Phys. Chem. 1988, 92, 4712–4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molchanov, V.S.; Kuklin, A.I.; Orekhov, A.S.; Arkharova, N.A.; Philippova, O.E. Temporally Persistent Networks of Long-Lived Mixed Wormlike Micelles of Zwitterionic and Anionic Surfactants. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 342, 116955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molchanov, V.S.; Rostovtsev, A.V.; Shishkhanova, K.B.; Kuklin, A.I.; Philippova, O.E. Strong Viscosity Increase in Aqueous Solutions of Cationic C22-Tailed Surfactant Wormlike Micelles. Fluids 2022, 7, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cates, M.E.; Candau, S.J. Statics and Dynamics of Worm-like Surfactant Micelles. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 1990, 2, 6869–6892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safran, S.A.; Pincus, P.A.; Cates, M.E.; MacKintosh, F.C. Growth of Charged Micelles. J. Phys. Paris 1990, 51, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, P.D.; Magid, L.J.; Hayter, J.B. Structure and Flow in Surfactant Solutions; Herb, C.A., Prud’homme, R.K., Eds.; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1994; ISBN 0841230544/9780841230545. [Google Scholar]
- Kumars, R.; Kalur, G.C.; Ziserman, L.; Danino, D.; Raghavan, S.R. Wormlike Micelles of a C22-Tailed Zwitterionic Betaine Surfactant: From Viscoelastic Solutions to Elastic Gels. Langmuir 2007, 23, 12849–12856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, P.; Rehage, H.; Grüning, B. Linear Flow Properties of Dimer Acid Betaine Solutions with and without Changes Ionic Strength. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 11041–11046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molchanov, V.S.; Pletneva, V.A.; Kuklin, A.I.; Philippova, O.E. Nanocomposite Composed of Charged Wormlike Micelles and Magnetic Particles. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 848, 012013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molchanov, V.S.; Philippova, O.E.; Khokhlov, A.R.; Kovalev, Y.A.; Kuklin, A.I. Self-Assembled Networks Highly Responsive to Hydrocarbons. Langmuir 2007, 23, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cates, M.E.; Fielding, S.M. Rheology of Giant Micelles. Adv. Phys. 2006, 55, 799–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.S.; Marques, C.; Cates, M.E. Dynamics of Wormlike Micelles: The “Bond-Interchange” Reaction Scheme. Langmuir 1993, 9, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehlcr, R.D.; Raghavan, S.R.; Kaier, E.W. Microstructure and Dynamics of Wormlike Micellar Solutions Formed by Mixing Cationic and Anionic Surfactants. J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 11035–11044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, P.; Rehage, H. Rheological Master Curves of Viscoelastic Surfactant Solutions by Varying the Solvent Viscosity and Temperature. Langmuir 1997, 13, 7012–7020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.S.; Cates, M.E. Linear Viscoelasticity of Living Polymers: A Quantitative Probe of Chemical Relaxation Times. Langmuir 1991, 7, 1590–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granek, R.; Cates, M.E. Stress Relaxation in Living Polymers: Results from a Poisson Renewal Model. J. Chem. Phys. 1992, 96, 4758–4767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Pei, S.; Wang, M.; Yan, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhang, J. Study on the Transformation from Linear to Branched Wormlike Micelles: An Insight from Molecular Dynamics Simulation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 494, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Gennes, P.G.; Witten, T.A. Scaling Concepts in Polymer Physics. Phys. Today 1980, 33, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerke, G.; Pedersen, J.S.; Egelhaaf, S.U.; Schurtenberger, P. Flexibility of Charged and Uncharged Polymer-like Micelles. Langmuir 1998, 14, 6013–6024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponton, A.; Schott, C.; Quemada, D. Rheological Behavior of Flexible Elongated Micelles: Temperature Effect in an Isotropic Phase. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1998, 145, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmiento-Gomez, E.; Lopez-Diaz, D.; Castillo, R. Microrheology and Characteristic Lengths in Wormlike Micelles Made of a Zwitterionic Surfactant and SDS in Brine. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 12193–12202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rózańska, S. Rheology of Wormlike Micelles in Mixed Solutions of Cocoamidopropyl Betaine and Sodium Dodecylbenzenesulfonate. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 482, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuryashov, D.A.; Philippova, O.E.; Molchanov, V.S.; Bashkirtseva, N.Y.; Diyarov, I.N. Temperature Effect on the Viscoelastic Properties of Solutions of Cylindrical Mixed Micelles of Zwitterionic and Anionic Surfactants. Colloid J. 2010, 72, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carver, M.; Smith, T.L.; Gee, J.C.; Delichere, A.; Caponetti, E.; Magid, L.J. Tuning of Micellar Structure and Dynamics in Aqueous Salt-Free Solutions of Cetyltrimethylammonium Mono- and Dichlorobenzoates. Langmuir 1996, 12, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, F.; Zana, R.; Candau, S.J. Rheological Properties of Semidilute and Concentrated Aqueous Solutions of Cetyltrimethylammonium Chloride in the Presence of Sodium Salicylate and Sodium Chloride. Langmuir 1991, 7, 1344–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oelschlaeger, C.; Schopferer, M.; Scheffold, F.; Willenbacher, N. Linear-to-Branched Micelles Transition: A Rheometry and Diffusing Wave Spectroscopy (DWS) Study. Langmuir 2009, 25, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, S.H.; Huang, Y.E.; Raghavan, S.R. Contrasting Effects of Temperature on the Rheology of Normal and Reverse Wormlike Micelles. Langmuir 2007, 23, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, R.; Narayanan, J.; Hassan, P.A.; Manohar, C.; Salkar, R.A.; Kern, F.; Candau, S.J. Effect of the Lipophilicity of the Counterion on the Viscoelasticity of Micellar Solutions of Cationic Surfactants. Langmuir 1998, 14, 4364–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, R.G.; Shrestha, L.K.; Aramaki, K. Wormlike Micelles in Mixed Amino Acid-Based Anionic/Nonionic Surfactant Systems. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 322, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
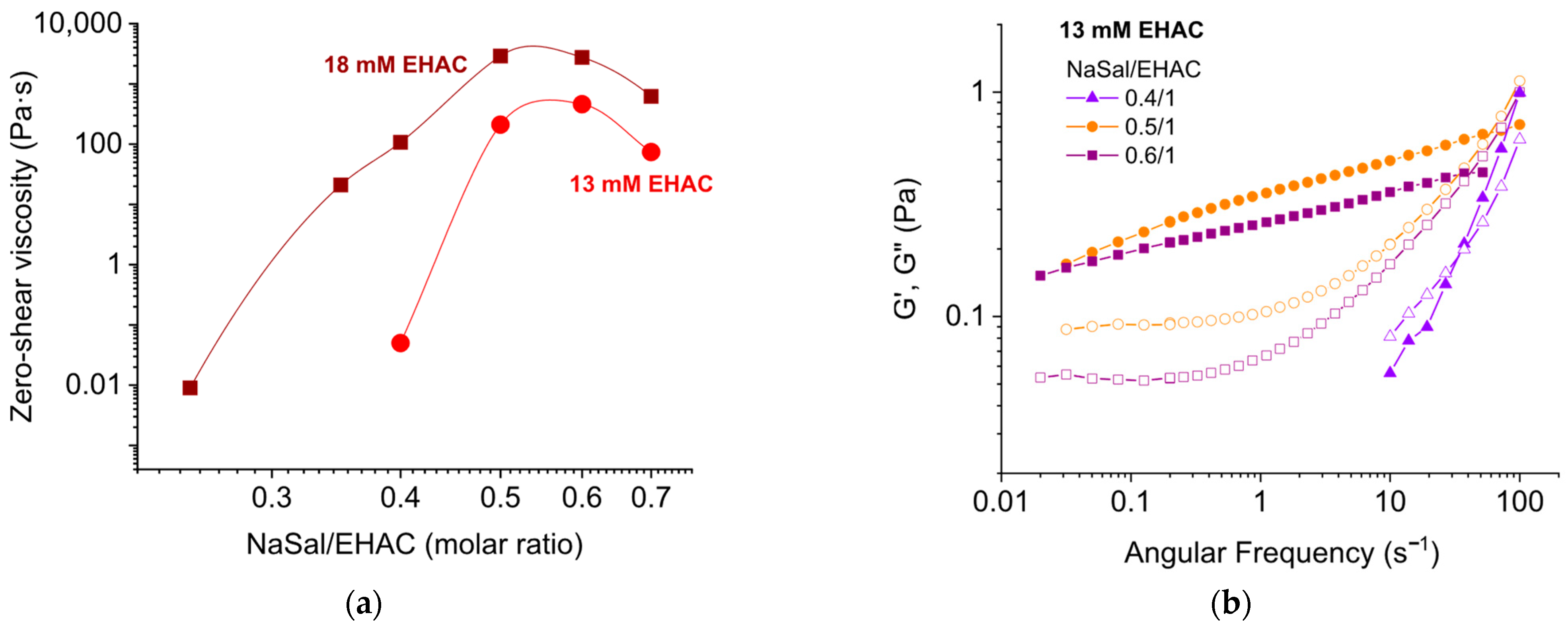
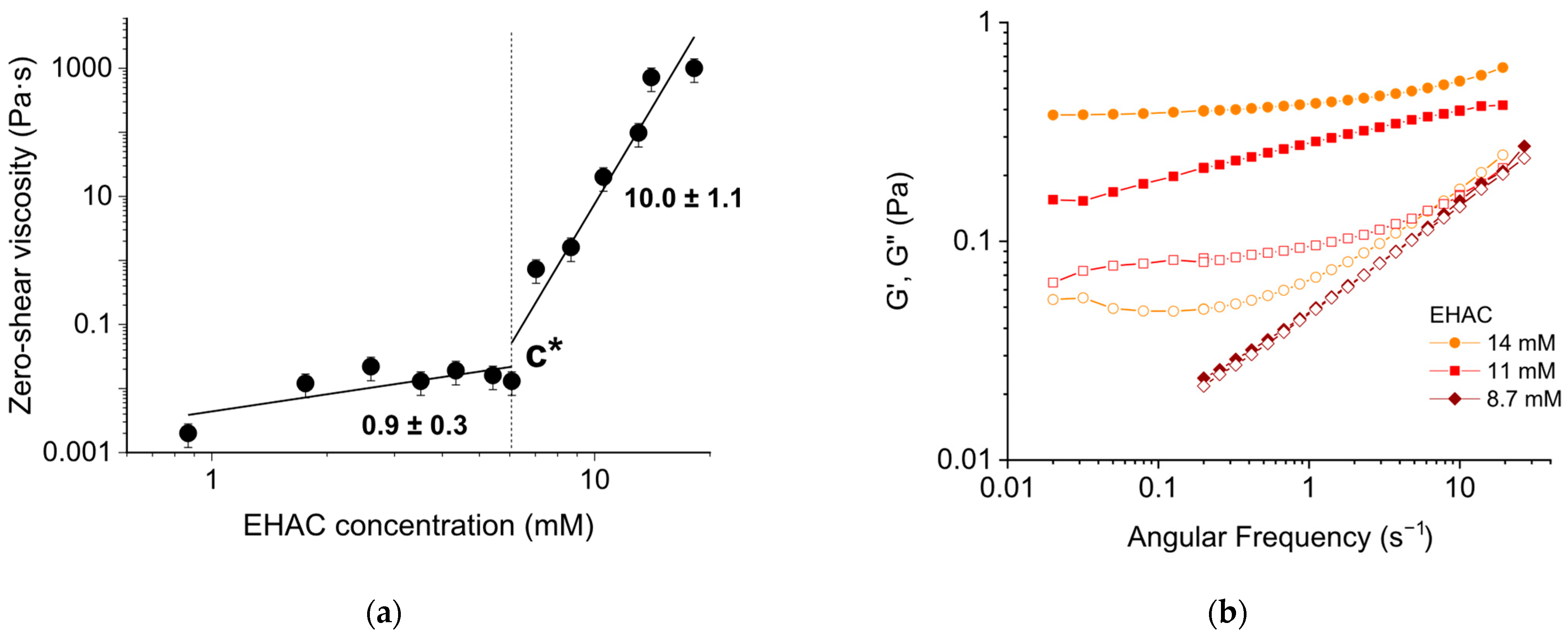
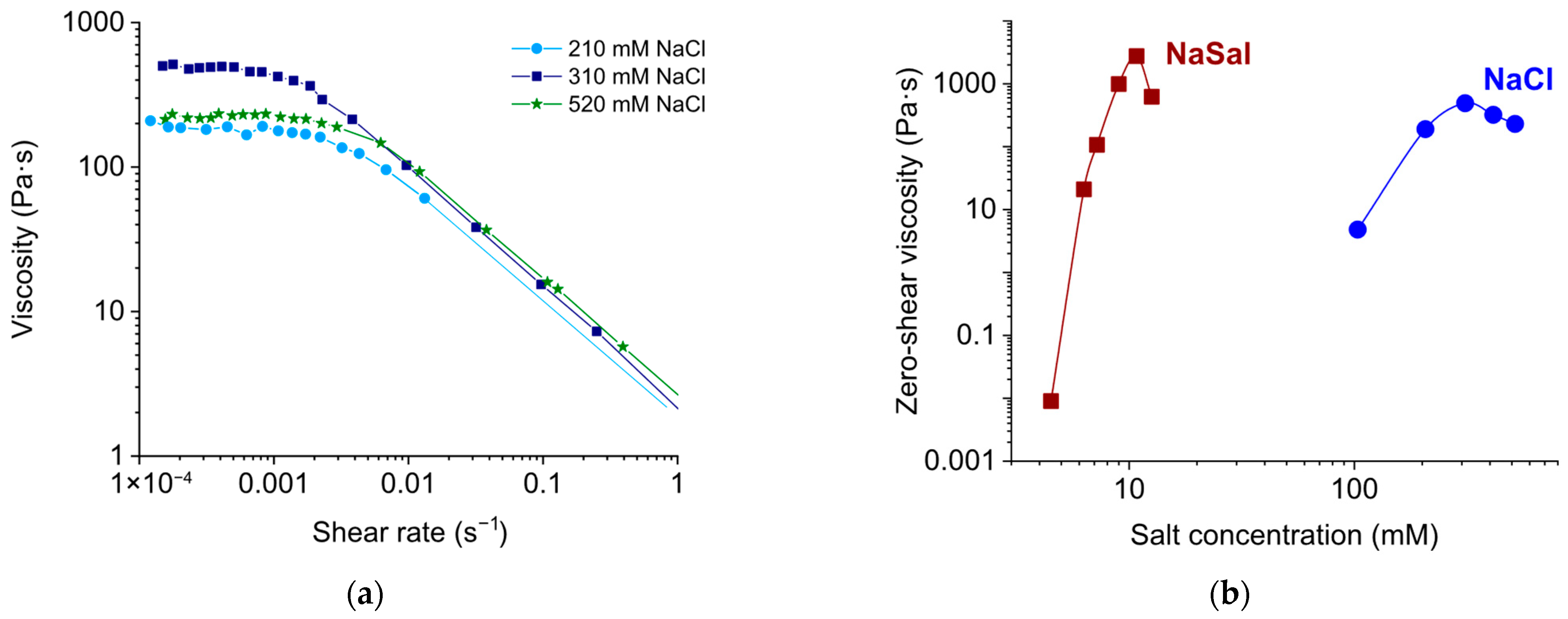
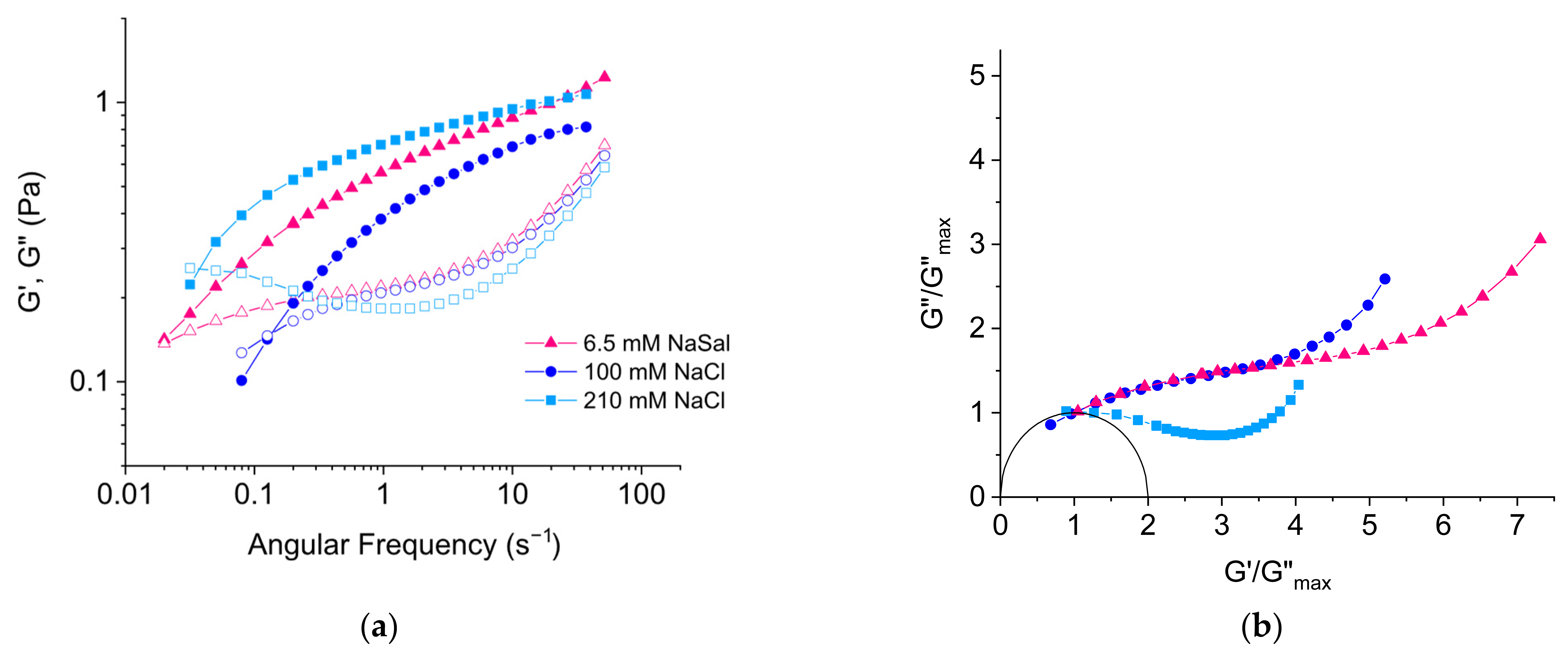
| Surfactant Concentration (mM) | Salt Type | Salt-to-Surfactant Molar Ratio | Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 13 | NaSal | 0.4–0.7 | 25 |
| 18 | NaSal | 0.25–0.7 | 25 |
| 0.9–19 | NaSal | 0.5 | 25 |
| 18 | NaCl | 5.6–29 | 25 |
| 13 | NaSal | 0.5 | 25–60 |
| 18 | NaSal | 0.36; 0.5 | 25–60 |
| 18 | NaCl | 5.6; 11.7 | 25–60 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shishkhanova, K.B.; Molchanov, V.S.; Philippova, O.E. Tuning of the Viscosity Maximum and the Temperature Effect on Wormlike Micelle Solutions Using Hydrotropic and Inorganic Salts. Liquids 2025, 5, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/liquids5040028
Shishkhanova KB, Molchanov VS, Philippova OE. Tuning of the Viscosity Maximum and the Temperature Effect on Wormlike Micelle Solutions Using Hydrotropic and Inorganic Salts. Liquids. 2025; 5(4):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/liquids5040028
Chicago/Turabian StyleShishkhanova, Kamilla B., Vyacheslav S. Molchanov, and Olga E. Philippova. 2025. "Tuning of the Viscosity Maximum and the Temperature Effect on Wormlike Micelle Solutions Using Hydrotropic and Inorganic Salts" Liquids 5, no. 4: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/liquids5040028
APA StyleShishkhanova, K. B., Molchanov, V. S., & Philippova, O. E. (2025). Tuning of the Viscosity Maximum and the Temperature Effect on Wormlike Micelle Solutions Using Hydrotropic and Inorganic Salts. Liquids, 5(4), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/liquids5040028








