Influence of Ion Generation–Recombination on Dielectric Relaxation Time in Electrolytes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Model
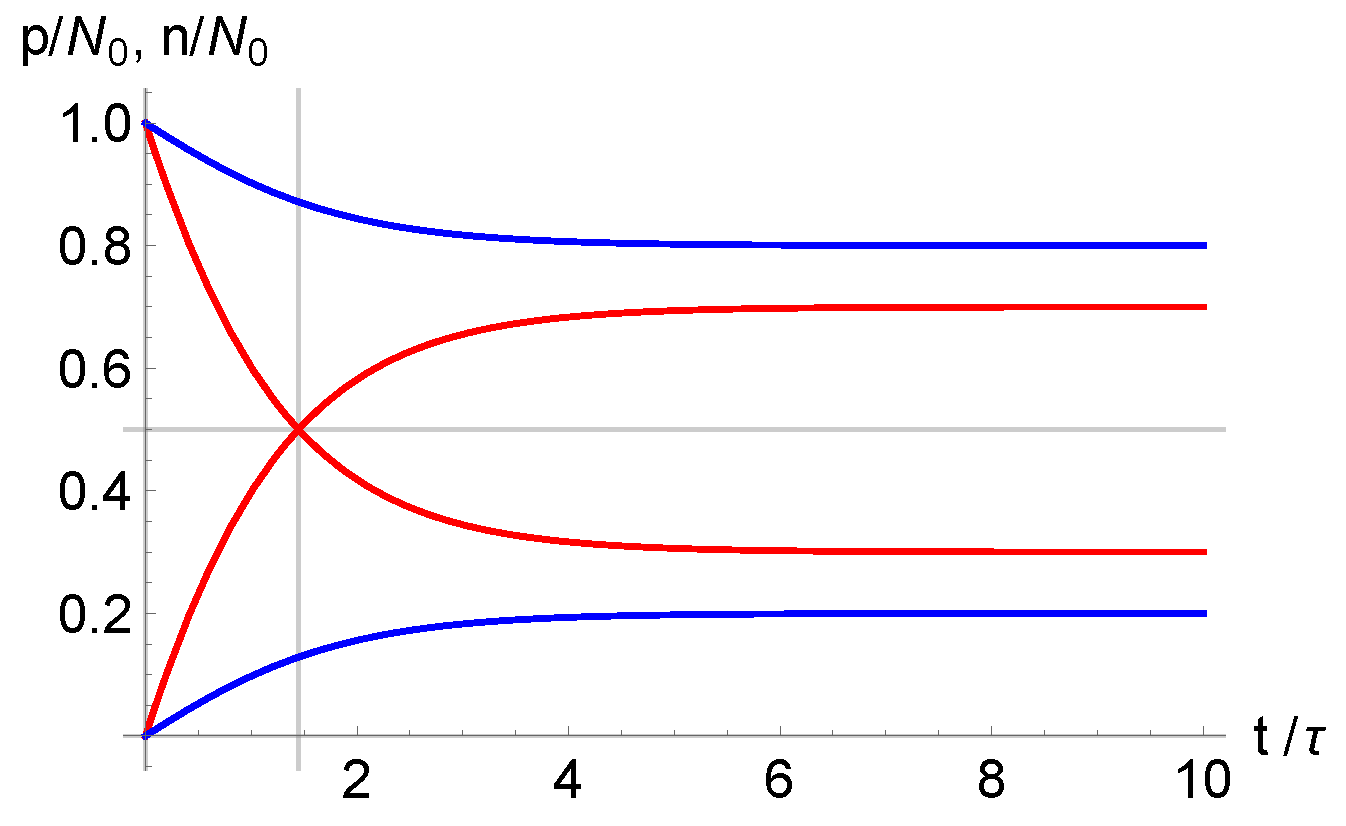
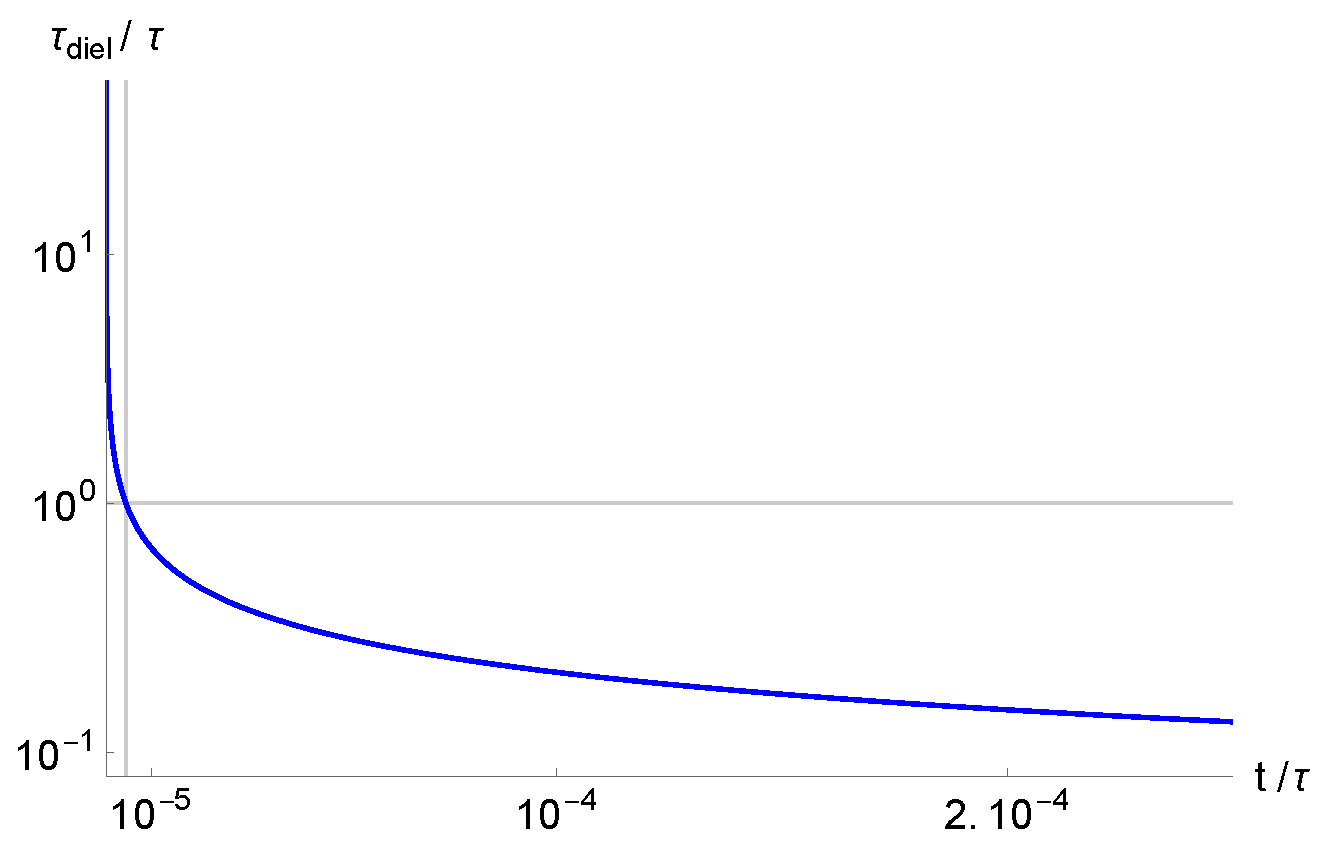
3. Debye Length and Dielectric Relaxation Time
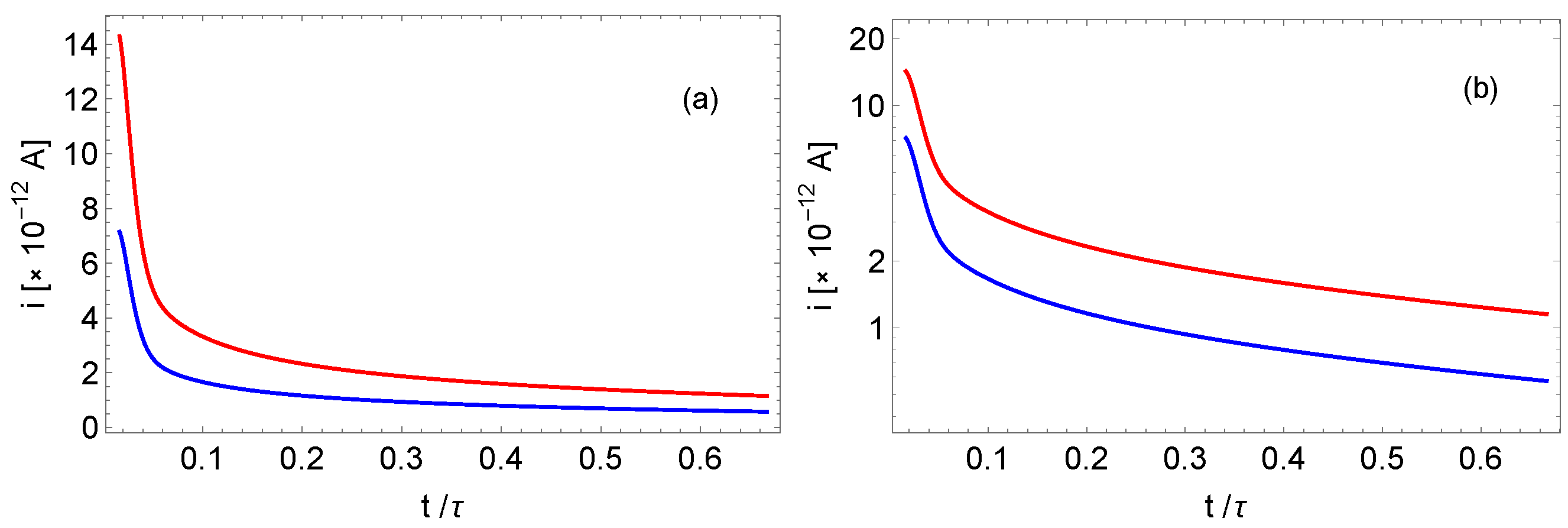
4. Electric Current Relaxation in a Cell Limited by Blocking Electrodes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nernst, W. On the kinetics of bodies in solution. Z. Phys. Chem. 1888, 2U, 613. [Google Scholar]
- Planck, M. On the potential difference between two dilute solutions of binary electrolytes. Ann. Phys. 1890, 276, 561. [Google Scholar]
- Barsoukov, E.; Macdonald, J.R. Impedance Spectroscopy: Theory, Experiment, and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Evangelista, L.R.; Lenzi, E.K. Fractional Diffusion Equations and Anomalous Diffusion; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Coelho, R. Physics of Dielectrics for the Engineer; Elsevier Science Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Q.; Wei, W. Poisson-Boltzmann-Nernst-Planck model. J. Chem. Phys. 2011, 134, 194101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sze, S.M. Semiconductor Devices: Physics and Technology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Sluythers-Rehbach, M.; Sluythers, J.H. Comprehensive Treatise of Electrochemistry; Yeager, E., Bockris, J.O.M., Conway, B.A., Sarangapani, S., Eds.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1984; Volume 9. [Google Scholar]
- Leijtens, T.; Eperon, G.E.; Barker, A.J.; Grancini, G.; Zhang, W.; Kandada, A.R.S.; Snaith, H.J.; Petrozza, A. Carrier trapping and recombination: The role of defect physics in enhancing the open circuit voltage of metal halide perovskite solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 3472. [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg, B. Ionic channels in biological membranes—Electrostatic analysis of a natural nanotube. Contemp. Phys. 1998, 39, 447. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Z.; Cao, X.; Huang, H. Electroneutral models for dynamic Poisson-Nernst-Planck systems. Phys. Rev. E 2018, 97, 012411. [Google Scholar]
- Row, H.; Fernandes, J.B.; Mandadapu, K.K.; Shekhar, K. Spatiotemporal dynamics of ionic reorganization near biological membrane interfaces. Phys. Rev. Res. 2025, 7, 013185. [Google Scholar]
- Tedesco, M.; Hamelers, H.; Biesheuvel, P. Nernst-Planck transport theory for (reverse) electrodialysis: I. Effect of Coion transport through the membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 510, 370. [Google Scholar]
- Alexe-Ionescu, A.L.; Barbero, G.; Lelidis, I.; Scalerandi, M. Relaxation times of an electrolytic cell subject to an external electric field: Role of ambipolar and free diffusion phenomena. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 13287. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, D.; Bazant, M.Z.; Biesheuvel, P.M.; Pugh, M.C.; Dawson, F.P. Theory of linear sweep voltammetry with diffuse charge: Unsupported electrolytes, thin films, and leaky membrane. Phys. Rev. E 2017, 95, 033303. [Google Scholar]
- Yavarian, M.; Melnik, R.; Miskovic, Z.L. Frequency Response of the Diffuse-Charge Dynamics in Electrochemical Systems with a Graphene Electrode. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2024, 171, 086501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazant, M.Z.; Thorton, K.; Adjadari, A. Diffuse-charge dynamics in electrochemical systems. Phys. Rev. E 2004, 70, 021506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lelidis, I.; Barbero, G. Effect of different anionic and cationic mobilities on the impedance spectroscopy measurements. Phy. Lett. A 2005, 343, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelidis, I.; Barbero, G. A generalization of the linear adsorption model to include electrosorption. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 678, 132440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross Macdonald, J. Theory of ac Space-Charge Polarization Effects in Photoconductors, Semiconductors, and Electrolytes. Phys. Rev. 1953, 92, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbero, G.; Lelidis, I. Electrical Response of a Medium Containing Dissociable Impurities. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelidis, I.; Barbero, G.; Sfarna, A. Comparison of two generation-recombination terms in the Poisson-Nernst-Planck model. J. Chem. Phys. 2012, 137, 154104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Chen, S.; Huang, J. Understanding Dynamics of Electrochemical Double Layers via a Modified Concentrated Solution Theory. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 013519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic, M.S.; Bazant, M.Z.; Ajdari, A. Steric effects in the dynamics of electrolytes at large applied voltages. I. Double-layer charging. Phys. Rev. E 2007, 75, 021502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Garcia, J.J.; Horno, J.; Grosse, C. Impedance-Frequency Response of Closed Electrolytic Cells. Micromachines 2023, 14, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, M. Curvature affects electrolyte relaxation: Studies of spherical and cylindrical electrodes. Phys. Rev. E 2019, 100, 042602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisquert, J. Theory of the Impedance of Electron Diffusion and Recombination in a Thin Layer. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabregat-Santiago, F.; Garcia-Belmonte, G.; Bisquert, J.; Zaban, A.; Salvador, P. Decoupling of Transport, Charge Storage, and Interfacial Charge Transfer in the Nanocrystalline TiO2/Electrolyte System by Impedance Methods. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, P.W. Physical Chemistry, 5th ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Hunter, R.J. Foundations of Colloidal Science, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Russel, W.B.; Saville, D.; Schowalter, W.R. Colloidal Dispersions; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Lyklema, J. Fundamentals of Interface and Colloid Science; Academic: New York, NY, USA, 1995; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Lelidis, I.; Alexe-Ionescu, A.L.; Barbero, G. Drift-Diffusion Phenomenon in the Presence of Reversible Trapping Reaction. J. Phys. Chem. C 2024, 128, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lelidis, I.; Barbero, G. Influence of Ion Generation–Recombination on Dielectric Relaxation Time in Electrolytes. Liquids 2025, 5, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/liquids5020010
Lelidis I, Barbero G. Influence of Ion Generation–Recombination on Dielectric Relaxation Time in Electrolytes. Liquids. 2025; 5(2):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/liquids5020010
Chicago/Turabian StyleLelidis, Ioannis, and Giovanni Barbero. 2025. "Influence of Ion Generation–Recombination on Dielectric Relaxation Time in Electrolytes" Liquids 5, no. 2: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/liquids5020010
APA StyleLelidis, I., & Barbero, G. (2025). Influence of Ion Generation–Recombination on Dielectric Relaxation Time in Electrolytes. Liquids, 5(2), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/liquids5020010






