Metagenomic and Proxy Monitoring of Surfactant Degradation by Microbial Consortia from Oil-Contaminated Soil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microbial Enrichment and DNA Sequencing
2.2. Shotgun Metagenomics and Statistical Analysis of Enrichment Samples
2.3. Degradation Experiments and Physicochemical Analyses
2.4. Foaming Activity and Stability Measurements
2.5. Microbial Community Structure, Functional Abundance Predictions (PICRUSt)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Surfactant-Specific Selection of Microbial Consortia
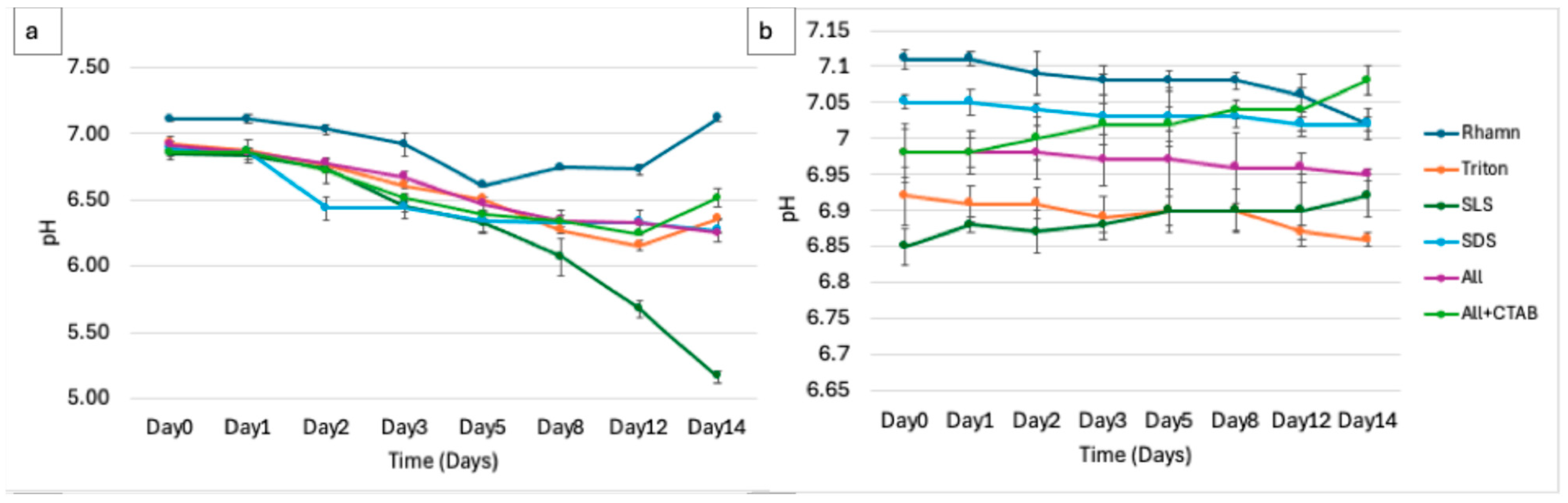
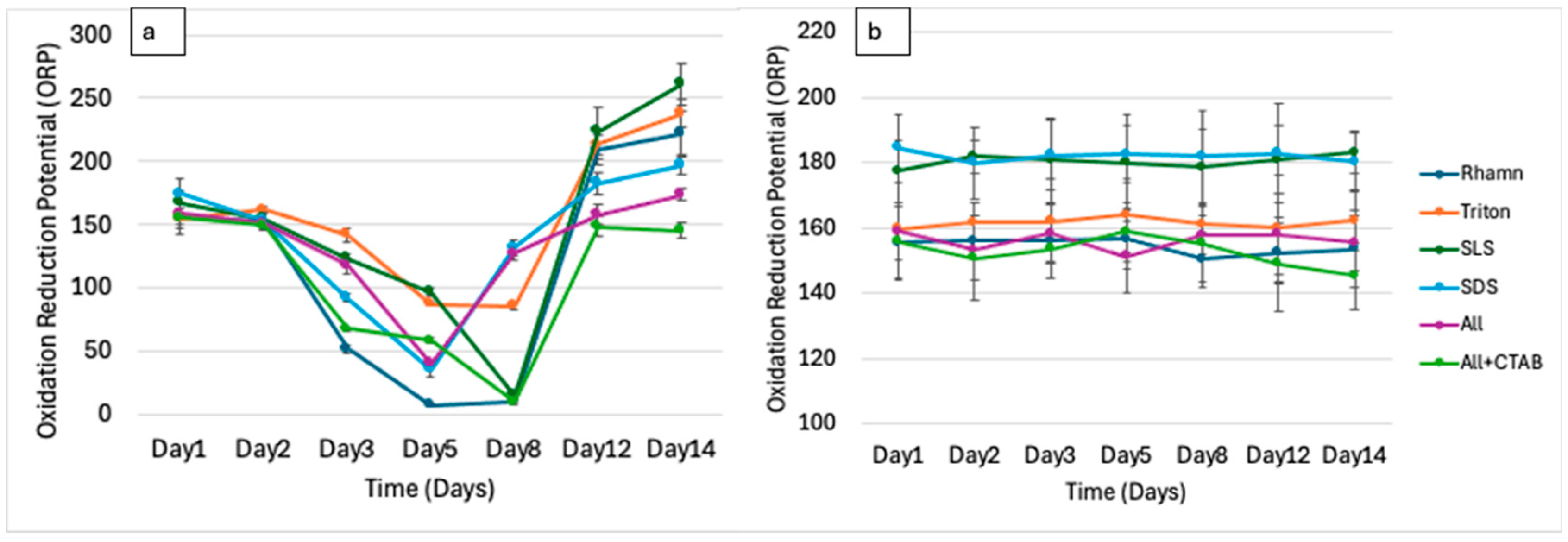
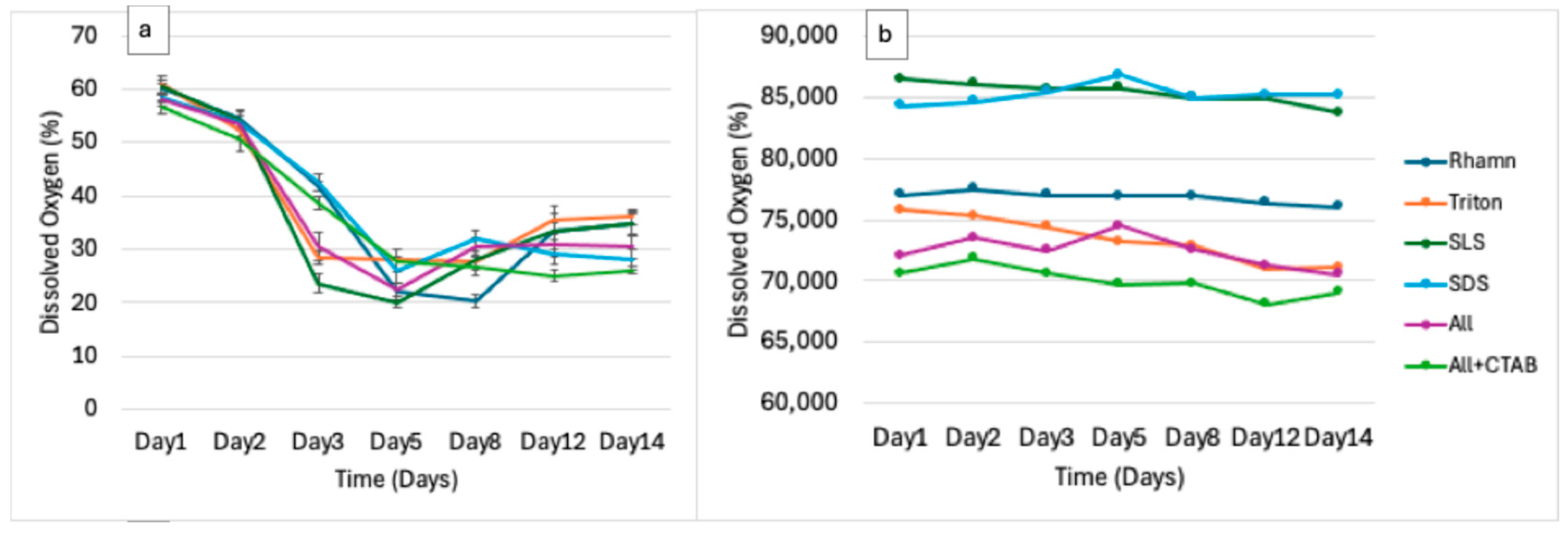
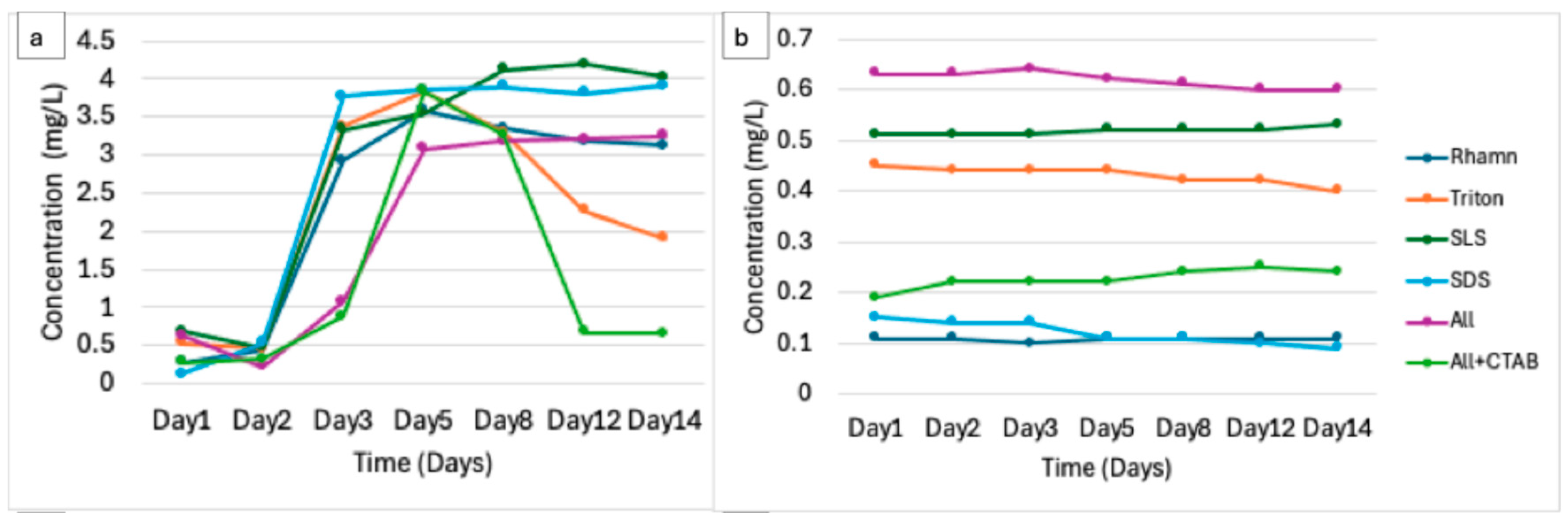
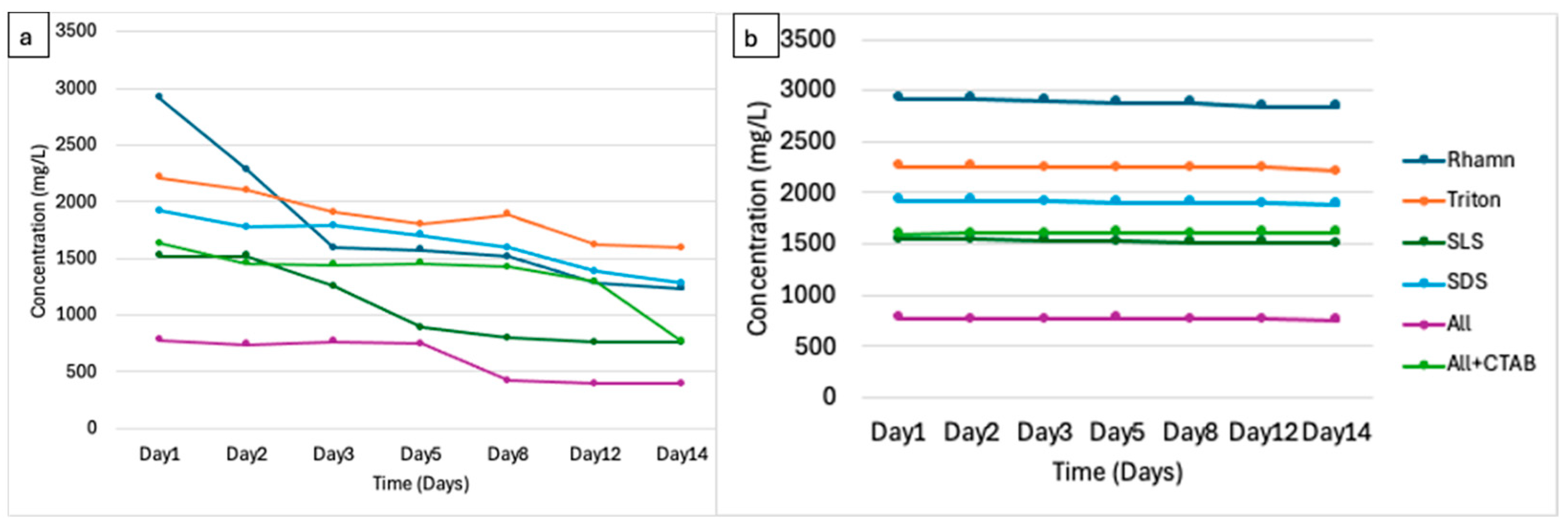
3.2. Physicochemical Dynamics Indicate Biodegradation
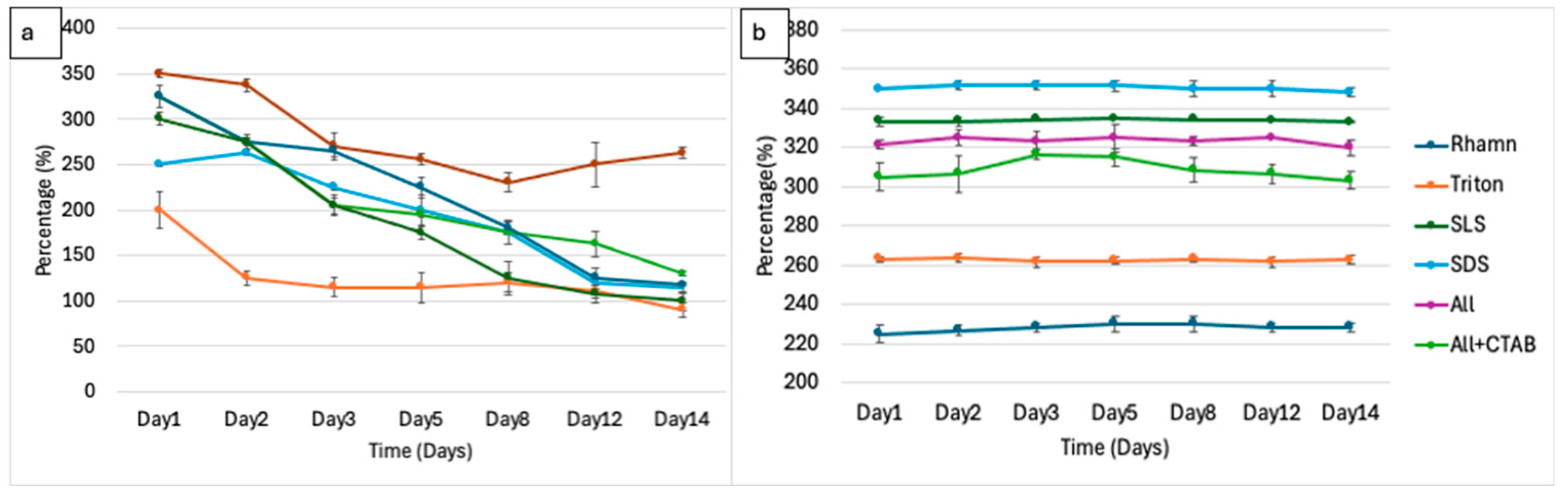
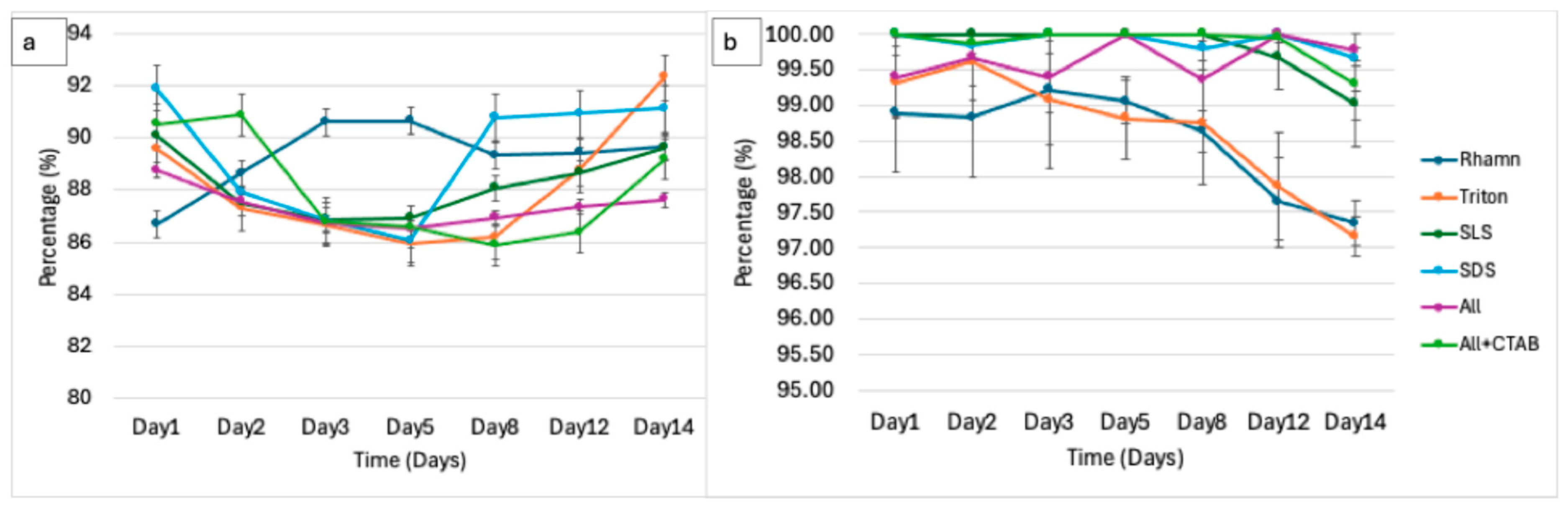
3.3. Foaming Activity and Stability as Direct Degradation Indicators
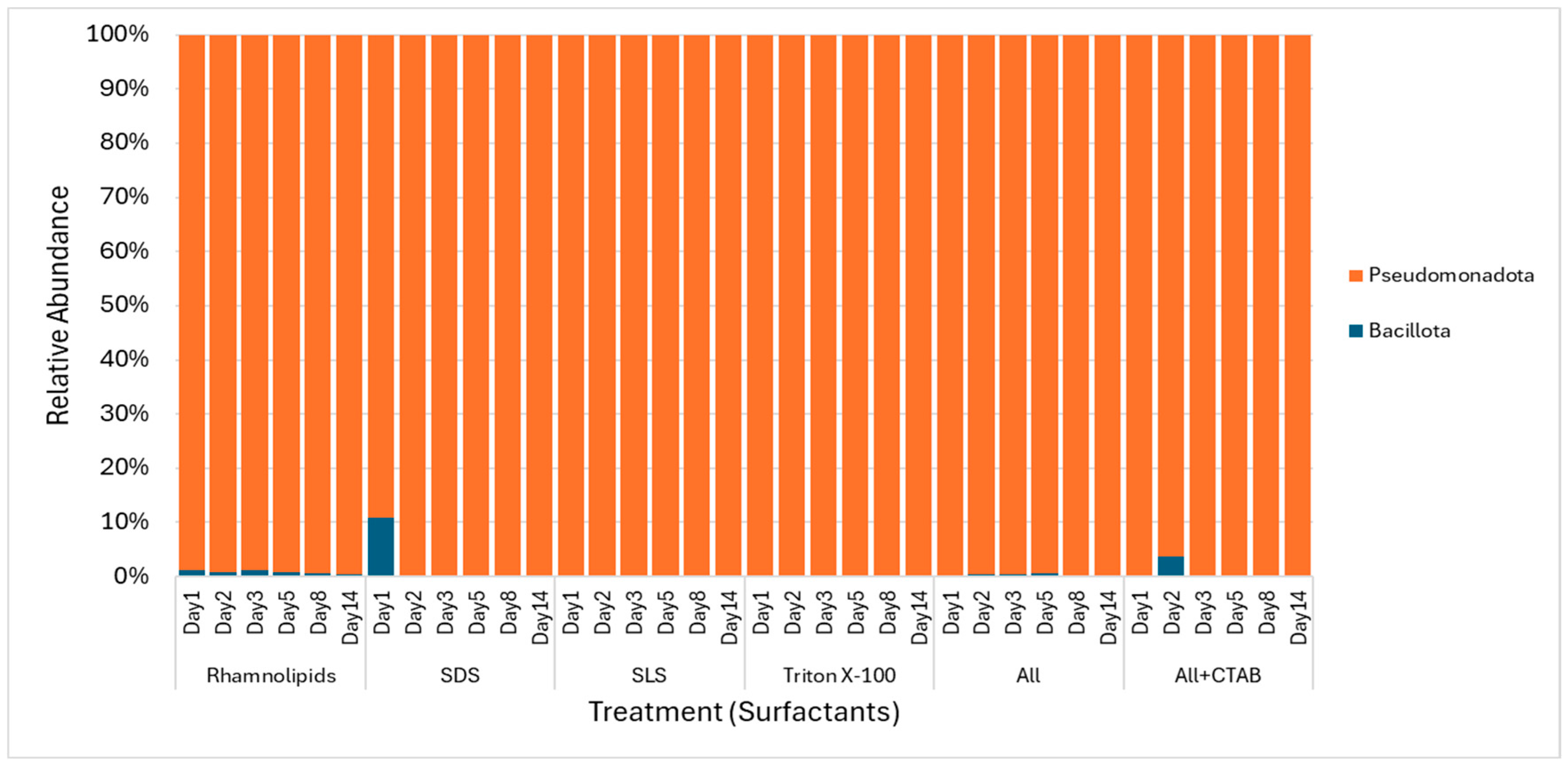
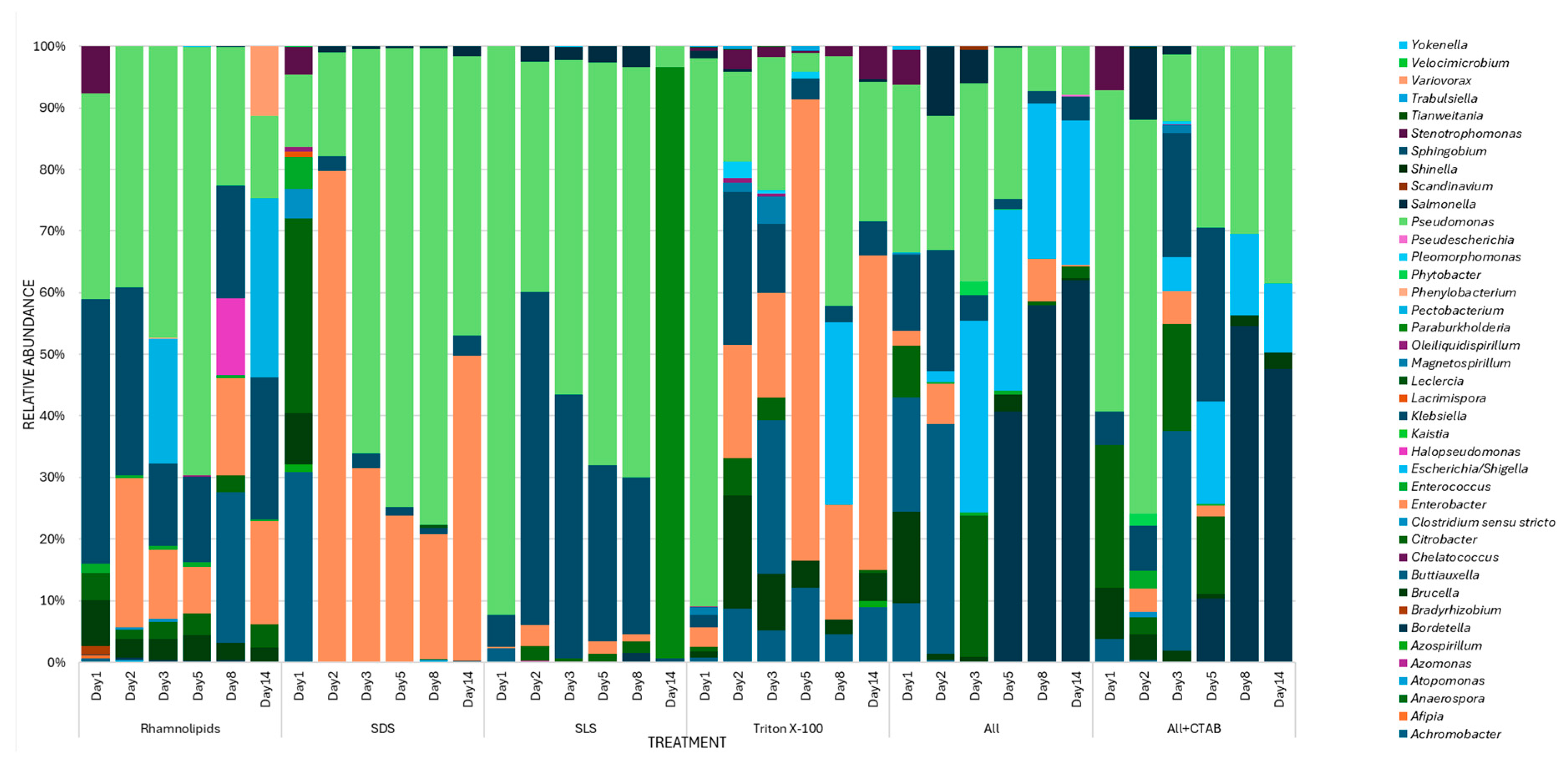
3.4. Microbial Community Distribution During Degradation
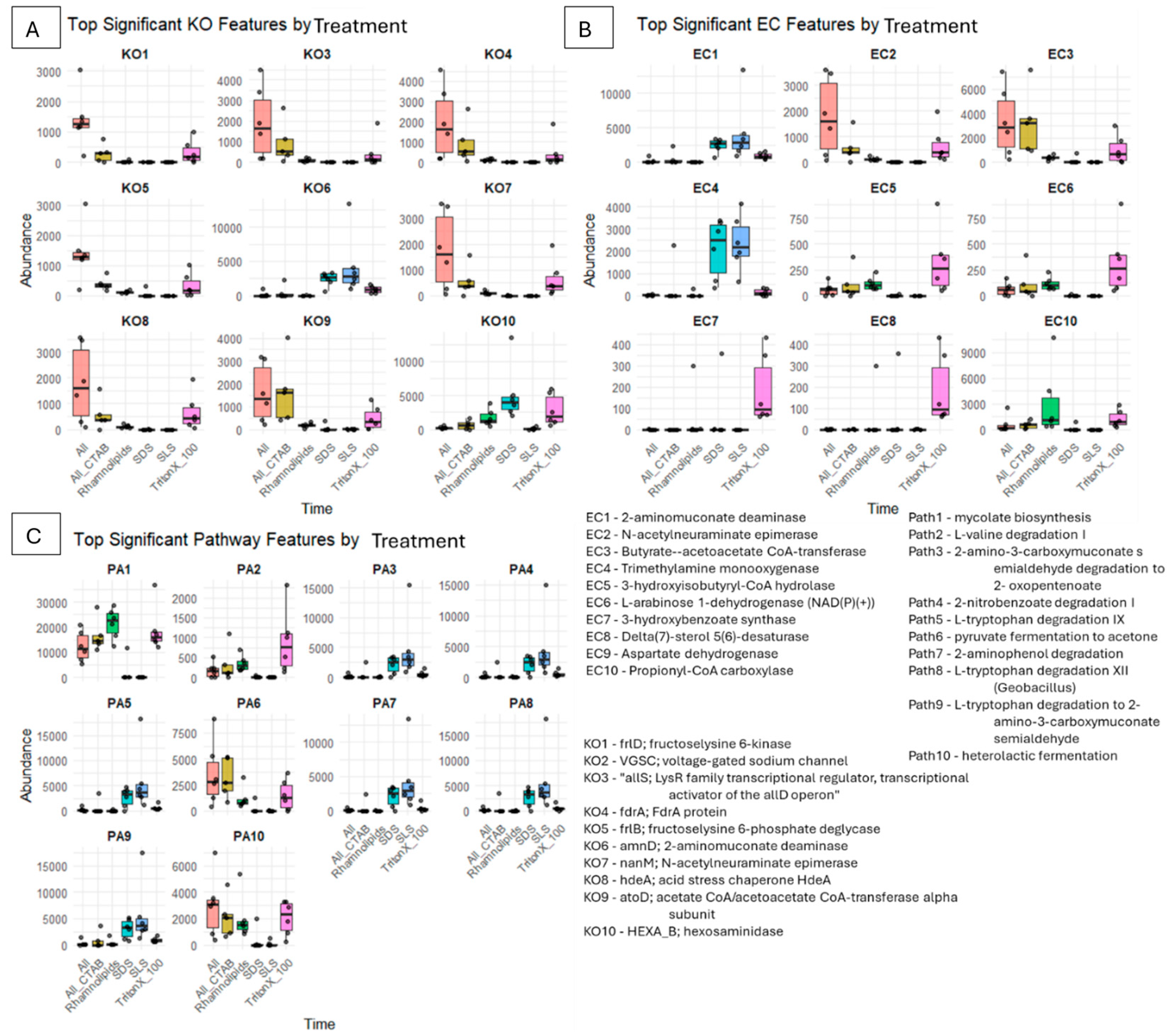
3.5. Microbial Functional Potential and Mechanistic Degradation Insights Using PICRUSt2
3.5.1. Degradation of SLS
3.5.2. Degradation of SDS
3.5.3. Degradation of Rhamnolipids
3.5.4. Degradation of Triton X-100
3.5.5. Degradation of Surfactant Mixture (ALL)
3.5.6. Degradation of Surfactant Mixture (ALL) with 1% CTAB
3.6. The Implications and Limitations of the Study
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gonçalves, R.A.; Holmberg, K.; Lindman, B. Cationic surfactants: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 375, 121335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Jiang, R.; Xiao, W.; Yu, J. Use of surfactants for the remediation of contaminated soils: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 285, 419–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaban, S.M.; Kang, J.; Kim, D.H. Surfactants: Recent advances and their applications. Compos. Commun. 2020, 22, 100537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badmus, S.O.; Amusa, H.K.; Oyehan, T.A.; Saleh, T.A. Environmental risks and toxicity of surfactants: Overview of analysis, assessment, and remediation techniques. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 62085–62104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spaniol, O.; Bergheim, M.; Dawick, J.; Kötter, D.; McDonough, K.; Schowanek, D.; Stanton, K.; Wheeler, J.; Willing, A. Comparing the European Union System for the Evaluation of Substances (EUSES) environmental exposure calculations with monitoring data for alkyl sulphate surfactants. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2021, 33, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.; Trybala, A.; Starov, V.; Pinfield, V.J. Effect of synthetic surfactants on the environment and the potential for substitution by biosurfactants. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 288, 102340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, G.; Dutta, K.; Daverey, A. Surfactants in water and wastewater (greywater): Environmental toxicity and treatment options. Chemosphere 2023, 341, 140082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Oba, B.T.; Shen, C.; Rong, L.; Zhang, B.; Huang, L.; Feng, L.; Liu, J.; Du, T.; Deng, Y. Effect of the bacterial community assembly process on the microbial remediation of petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated soil. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1196610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collivignarelli, M.C.; Baldi, M.; Abbà, A.; Caccamo, F.M.; Miino, M.C.; Rada, E.C.; Torretta, V. Foams in wastewater treatment plants: From causes to control methods. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siyal, A.A.; Shamsuddin, M.R.; Low, A.; Rabat, N.E. A review on recent developments in the adsorption of surfactants from wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 254, 109797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, D.; Jaspal, D. Surfactants in waste water: Development, current status and associated challenges. Mater. Today Proc. 2023. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S2214785323050939 (accessed on 9 July 2025).
- de Carvalho, R.C.; Feijão, E.; Matos, A.R.; Cabrita, M.T.; Utkin, A.B.; Novais, S.C.; Lemos, M.F.L.; Caçador, I.; Marques, J.C.; Reis-Santos, P.; et al. Ecotoxicological Effects of the Anionic Surfactant Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS) in Two Marine Primary Producers: Phaeodactylum tricornutum and Ulva lactuca. Toxics 2022, 10, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayaprakash, P.O.; Mekala, C.; Priyan, M.V. Subsurface Based Contaminant Transport Modelling of SDS Nac12h25so4. Int. J. Eng. Adv. Technol. 2020, 9, 4412–4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Cervilla, R.; Santos, A.; Romero, A.; Lorenzo, D. Partition of a mixture of chlorinated organic compounds in real contaminated soils between soil and aqueous phase using surfactants: Influence of pH and surfactant type. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacarias-Salinas, M.; Vaca, M.; Flores, M.A.; Bandala, E.R.; Torres, L.G. Surfactant-Enhanced Washing of Soils Contaminated with Wasted-Automotive Oils and the Quality of the Produced Wastewater. J. Environ. Prot. 2013, 4, 1495–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.L.; Musin, E.V.; Dubrovskii, A.V.; Tikhonenko, S.A. Qualitative and quantitative methods detection of SDS based on polyelectrolyte microcapsules. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmer, N.; Gore, D.; Sanders, D.; Gouin, T.; Droge, S.T.J. Toxicity mitigation and bioaccessibility of the cationic surfactant cetyltrimethylammonium bromide in a sorbent-modified biodegradation study. Chemosphere 2019, 222, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Xu, Z.; Yin, D.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, X.; Song, L. Toxic effects of sodium dodecyl sulfate on planarian Dugesia japonica. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, R.; Chatterjee, A.; Chatterjee, S.; Saha, N.C. Acute toxicity and impact of sublethal exposure to commonly used surfactants sodium dodecyl sulphate, cetylpyridinium chloride and sodium laureth sulphate on oxidative stress enzymes in oligochaete worm Branchiura sowerbyi (Beddard, 1892). Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 6367–6379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jho, E.H.; Yun, S.H.; Thapa, P.; Nam, J.-W. Changes in the aquatic ecotoxicological effects of Triton X-100 after UV photodegradation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 11224–11232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.Y.; Wei, X.P.; Yang, Y.T.; Ni, H.G. Prediction and mechanism of combined toxicity of surfactants and antibiotics in aquatic environment based on in silico method. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 488, 137390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, R.F.; Teixeira, A.C.S.C. An overview on surfactants as pollutants of concern: Occurrence, impacts and persulfate-based remediation technologies. Chemosphere 2022, 300, 134507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, M.; Eadsforth, C.; Schowanek, D.; Delfosse, T.; Riddle, A.; Budgen, N. Comprehensive review of several surfactants in marine environments: Fate and ecotoxicity. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, I.G.S.; de Almeida, F.C.G.; da Rocha e Silva, N.M.P.; Casazza, A.A.; Converti, A.; Sarubbo, L.A. Soil bioremediation: Overview of technologies and trends. Energies 2020, 13, 4664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, R.; Shafiq, I.; Akhter, P.; Muhammad; Iqbal, J.; Hussain, M. A state-of-the-art review on wastewater treatment techniques: The effectiveness of adsorption method. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 9050–9066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panasia, G.; Oetermann, S.; Steinbüchel, A.; Philipp, B. Sulfate ester detergent degradation in pseudomonas aeruginosa is subject to both positive and negative regulation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e01352-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zamili, H.A.A.; Al-Mayaly, I.K. Biodegradation of sodium lauryl ether sulfate (SLES) contamination by Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates. J. Degrad. Min. Lands Manag. 2024, 11, 6319–6327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulo, A.M.S.; Aydin, R.; Dimitrov, M.R.; Vreeling, H.; Cavaleiro, A.J.; García-Encina, P.A.; Stams, A.J.M.; Plugge, C.M. Sodium lauryl ether sulfate (SLES) degradation by nitrate-reducing bacteria. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 5163–5173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, T.T.; Kiefer, R.; Nguyen, N.T. Isolation and characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa VK30 capable of degradation of Triton X-100. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2024, 1368, 012003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyrwas, B.; Dymaczewski, Z.; Zgoła-Grześkowiak, A.; Szymański, A.; Frańska, M.; Kruszelnicka, I.; Ginter-Kramarczyk, D.; Cyplik, P.; Ławniczak, Ł.; Chrzanowski, Ł. Biodegradation of Triton X-100 and its primary metabolites by a bacterial community isolated from activated sludge. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 128, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, C.W.; Lai, Y.J.S.; Luo, Y.H.; Cai, Y.; Wu, W.; Rittmann, B.E. A two-stage design enhanced biodegradation of high concentrations of a C16-alkyl quaternary ammonium compound in oxygen-based membrane biofilm reactors. Water Res. 2024, 250, 120963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.W.; Luo, Y.H.; Sean Lai, Y.J.; Ilhan, Z.E.; Ontiveros-Valencia, A.; Krajmalnik-Brown, R.; Jin, Y.; Gu, H.; Long, X.; Zhou, D.; et al. Identifying biodegradation pathways of cetrimonium bromide (CTAB) using metagenome, metatranscriptome, and metabolome tri-omics integration. Water Res. 2023, 246, 120738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, T.M.S.; Procópio, L.C.; Brandão, F.D.; Carvalho, A.M.X.; Tótola, M.R.; Borges, A.C. Biodegradability of bacterial surfactants. Biodegradation 2011, 22, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccolo, A.; De Martino, A.; Scognamiglio, F.; Ricci, R.; Spaccini, R. Efficient simultaneous removal of heavy metals and polychlorobiphenyls from a polluted industrial site by washing the soil with natural humic surfactants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 25748–25757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Wang, W.; Li, F.; Zhu, L. Mixed-surfactant-enhanced phytoremediation of PAHs in soil: Bioavailability of PAHs and responses of microbial community structure. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 653, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.Q.; Li, Y.Q.; He, Q.S.; Li, B.Z.; Yuan, Y.J.; Wen, J.P. Effects of different surfactants on the degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons by mixed-bacteria. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2022, 97, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cierniak, D.; Cierniak, D.; Woźniak-Karczewska, M.; Parus, A.; Wyrwas, B.; Loibner, A.P.; Heipieper, H.J.; Ławniczak, Ł.; Chrzanowski, Ł. How to accurately assess surfactant biodegradation-impact of sorption on the validity of results. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.W.; Luo, Y.H.; Long, X.; Gu, H.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, L.; Sean Lai, Y.J.; Rittmann, B.E. The structure of biodegradable surfactants shaped the microbial community, antimicrobial resistance, and potential for horizontal gene transfer. Water Res. 2023, 236, 119944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, H. Synergistic solubilization of phenanthrene by mixed micelles composed of biosurfactants and a conventional non-ionic surfactant. Molecules 2020, 25, 4327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Lin, J.; Lin, J.; Wang, W.; Li, S. Biodegradation of petroleum hydrocarbons by Bacillus subtilis BL-27, a strain with weak hydrophobicity. Molecules 2019, 24, 3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, L.; García, M.T.; Pinazo, A.; Pérez-Matas, E.; Hafidi, Z.; Bautista, E. Cationic Surfactants Based on Arginine-Phenylalanine and Arginine-Tryptophan: Synthesis, Aggregation Behavior, Antimicrobial Activity, and Biodegradation. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patowary, K.; Kalita, M.C.; Deka, S. Degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) employing biosurfactant producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa KS3. Indian J. Biotechnol. 2015, 14, 208–215. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.; He, J.; Li, M.; Peng, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y.; Deng, F. Unlocking the Potential of Metagenomics with the PacBio High-Fidelity Sequencing Technology. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, S.B.; Corpuz, R.L.; Simmonds, T.J.; Geib, S.M. HiFiAdapterFilt, a memory efficient read processing pipeline, prevents occurrence of adapter sequence in PacBio HiFi reads and their negative impacts on genome assembly. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Yang, C.; Sun, Y.; Igarashi, Y.; Jin, T.; Luo, F. PacBio Long Reads Improve Metagenomic Assemblies, Gene Catalogs, and Genome Binning. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 516269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, A.R.; Van Dam, A.R. Metagenomic binning of PacBio HiFi data prior to assembly reveals a complete genome of Cosmopolites sordidus (Germar) (Coleopterea: Curculionidae, Dryophthorinae) the most damaging arthropod pest of bananas and plantains. PeerJ 2023, 11, e16276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portik, D.M.; Brown, C.T.; Pierce-Ward, N.T. Evaluation of taxonomic classification and profiling methods for long-read shotgun metagenomic sequencing datasets. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainguy, J.; Vienne, M.; Fourquet, J.; Darbot, V. metagWGS, a comprehensive workflow to analyze metagenomic data using Illumina or PacBio HiFi reads. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huson, D.H.; Albrecht, B.; Bağcı, C.; Bessarab, I.; Górska, A.; Jolic, D.; Williams, R.B.H. MEGAN-LR: New algorithms allow accurate binning and easy interactive exploration of metagenomic long reads and contigs. Biol. Direct 2018, 13, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nlshloka, G.M.; Ross, S.; Kornbrekke, R.E. Fundamental Methods for Measuring Foam Stability. In Foams; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 1996; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Lunkenheimer, K.; Malysa, K.; Winsel, K.; Geggel, K.; Siegel, S. Novel method and parameters for testing and characterization of foam stability. Langmuir 2010, 26, 3883–3888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Genome analysis Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Li, T.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J. An independent evaluation in a CRC patient cohort of microbiome 16S rRNA sequence analysis methods: OTU clustering, DADA2, and Deblur. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1178744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Mai, J.; Cao, X.; Burberry, A.; Cominelli, F.; Zhang, L. ggpicrust2: An R package for PICRUSt2 predicted functional profile analysis and visualization. Bioinformatics 2023, 39, btad470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisneros-León, D.G.; Espinoza-Montero, P.J.; Bolaños-Mendez, D.; Alvarez-Paguay, J.; Fernández, L.; Saavedra-Alulema, P.F.; Lopez, K.; Astorga, D.; Piñeiros, J.L. Electrochemical degradation of surfactants in domestic wastewater using a DiaClean® cell equipped with a boron-doped diamond electrode. Front. Chem. 2023, 11, 900670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanta, C.L.P.S.; Friedrich, L.C.; Machulek, A.; Higa, K.M.; Quina, F.H. Surfactant degradation by a catechol-driven Fenton reaction. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 178, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aonyas, M.M.; Dojčinović, B.P.; Dolić, S.D.; Obradović, B.M.; Manojlović, D.D.; Marković, D.D.; Roglić, G.M. Degradation of anionic surfactants using the reactor based on dielectric barrier discharge. J. Serbian Chem. Soc. 2016, 81, 1097–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado, E.; Fernndez-Serrano, M.; Ros, F.; Lechug, M. Aerobic Biodegradation of Surfactants. In Biodegradation—Life of Science; InTech: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, L.D.; Tsai, P.C.; Nguyen, T.N.; Chen, C.C.; Huang, S.L. Growth and gene expression of Pseudomonas nitroreducens TX1 on octylphenol polyethoxylate surfactants. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2025, 109, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, L.; He, L.; Kong, C.; Weng, J.; Ma, J.; Liu, F. Effect of Surfactants on Microbial Metabolic Activity and Community Structure in Oil Field–Produced Water Systems. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardhi, D.S.; Panchal1, R.R.; Raval, V.H.; Raval, V.H.; Joshi, R.G.; Poczai, P.; Almalki, W.H.; Rajput, K.N. Microbial surfactants: A journey from fundamentals to recent advances. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 982603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, G.; Fu, H.; Zhong, H.; Yuan, X.; Fu, M.; Wang, W.; Huang, G. Co-degradation with glucose of four surfactants, CTAB, Triton X-100, SDS and Rhamnolipid, in liquid culture media and compost matrix. Biodegradation 2007, 18, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutosławski, K.; Ryznar-Luty, A.; Cibis, E. Efficiency of aerobic biodegradation of sugar beet distillery stillage under dissolved oxygen tension-controlled conditions. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0306330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staninska-Pięta, J.; Piotrowska-Cyplik, A.; Juzwa, W.; Zgoła-Grześkowiak, A.; Wolko, Ł.; Sydow, Z.; Kaczorowski, Ł.; Powierska-Czarny, J.; Cyplik, P. The impact of natural and synthetic surfactants on bacterial community during hydrocarbon biodegradation. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2019, 142, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekonnen, B.A.; Aragaw, T.A.; Genet, M.B. Bioremediation of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soil: A review on principles, degradation mechanisms, and advancements. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1354422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Chen, N.; Piao, H.; Sun, D.; Ratnaweera, H.; Maletskyi, Z.; Bi, X. Characterization of Oxidation-Reduction Potential Variations in Biological Wastewater Treatment Processes: A Study from Mechanism to Application. Processes 2022, 10, 2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chebbi, A.; Franzetti, A.; Formicola, F.; Ambaye, T.G.; Gomez, F.H.; Murena, B.; De Marco, E.; Beltrani, T.; Sbaffoni, S.; Vaccari, M. Insights into rhamnolipid-based soil remediation technologies by safe microorganisms: A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 367, 133088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frindte, K.; Allgaier, M.; Grossart, H.P.; Eckert, W. Microbial response to experimentally controlled redox transitions at the sediment water interface. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, 0143428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata-Sandoval, J.C.; Karns, J.; Torrents, A. Influence of rhamnolipids and triton X-100 on the biodegradation of three pesticides in aqueous phase and soil slurries. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 3296–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Meng, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L. The potential linkage between sediment oxygen demand and microbes and its contribution to the dissolved oxygen depletion in the Gan River. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1413447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Song, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, S. Effects of two surfactants on microbial diversity of a PCE-degrading microbial consortium. Chemosphere 2020, 261, 127685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.; Jasmine, J.; Mukherji, S. Practical considerations and challenges involved in surfactant enhanced bioremediation of oil. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 328608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinçer, A.R. Increasing BOD5/COD ratio of non-biodegradable compound (reactive black 5) with ozone and catalase enzyme combination. SN Appl. Sci 2020, 2, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurshid, S.; Quaff, A.R.; Jha, R. Integrated Method of Ozonation and Anaerobic Process for Treatment of Atrazine bearing Wastewater. Nat. Environ. Pollut. Technol. 2023, 22, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, P.; Tiwari, S.; Tiwari, H.; Sonwani, R.K.; Singh, R.S. Techno-economic assessment of coupling ozonation and biodegradation process for the dye wastewater treatment. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 56, 104286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junior, R.M.; Passoni, C.M.; Santos, F.M.; Bernardes, F.S.; Filho, F.J.C.M.; Paulo, P.L. Assessment of Surfactant Removal Capacity and Microbial Community Diversity in a Greywater-Treating Constructed Wetland. Resources 2023, 12, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacalamita, D.; Mongioví, C.; Crini, G. Chemical oxygen demand and biochemical oxygen demand analysis of discharge waters from laundry industry: Monitoring, temporal variability, and biodegradability. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1387041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onadeji, A.; Sani, B.S.; Abubakar, U.A. Response surface methodology optimization of the effect of pH, contact time, and microbial concentration on chemical oxygen removal potential of vegetable oil industrial effluents. Water Environ. Res. 2024, 96, e10963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishaq, A.; Said, M.I.M.; Azman, S.B.; Houmsi, M.R.; Isah, A.S.; Jagun, Z.T.; Mohammad, S.J.; Bello, A.A.D.; Abubakar, U.A. The influence of various chemical oxygen demands on microbial fuel cells performance using leachate as a substrate. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 32, 27467–27482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozitis, D.; Strade, E. COD reduction ability of microorganisms isolated from highly loaded pharmaceutical wastewater pre-treatment process. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2015, 6, 507–512. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Nguyen, A.V.; Farrokhpay, S. Foamability of sodium dodecyl sulfate solutions: Anomalous effect of dodecanol unexplained by conventional theories. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 495, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zheng, N.; Yang, Z.; Li, X.; Lei, T. Experimental study on the foam-stabilizing advantages and foam stabilization mechanism of novel microbial polysaccharides. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 385, 122428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, M.; Castilla-Alcántara, J.C.; Garbayo, I.; Vílchez, C.; Cuaresma, M. Potential impact of biodegradable surfactants on foam-based microalgal cultures. Processes 2020, 8, 1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, R.; Singha, L.P.; Shukla, P. Biotechnological potential of microbial bio-surfactants, their significance, and diverse applications. FEMS Microbes 2023, 4, xtad015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollenbach, R.; Oeppling, S.; Delavault, A.; Völp, A.R.; Willenbacher, N.; Rudat, J.; Ochsenreither, K.; Syldatka, C. Comparative study on interfacial and foaming properties of glycolipids in relation to the gas applied for foam generation. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 34235–34244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Liu, S.; Xu, L.; Zhou, J.; Xin, F.; Zhang, W.; Qian, X.; Li, M.; Dong, W.; Jiang, M. Enhanced rhamnolipids production using a novel bioreactor system based on integrated foam-control and repeated fed-batch fermentation strategy. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2020, 13, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, J.; Biswas, R.; Chauhan, A.; Ranjan, A.; Rajput, V.D. Surfactant pollution, an emerging threat to ecosystem: Approaches for effective bacterial degradation. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 133, 1229–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phulpoto, I.A.; Qi, Z.; Qazi, M.A.; Yu, Z. Biosurfactants-based mixed polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degradation: From microbial community structure toward non-targeted metabolomic profile determination. Environ. Int. 2024, 184, 108448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, F.; Zhan, Y.; Zhu, L. Shifts in microbial community structure during in situ surfactant-enhanced bioremediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-contaminated soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 14451–14461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, S.P.; Hunter, W.R.; Coulson, L.E.; Banat, I.M.; Schelker, J. Synthetic and biological surfactant effects on freshwater biofilm community composition and metabolic activity. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 6847–6859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, H.; Hou, J.; Du, M.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.; Christie, P.; Luo, Y. Surfactant-enhanced bioremediation of petroleum-contaminated soil and microbial community response: A field study. Chemosphere 2023, 322, 138225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, N.; Simarro, R.; Molina, M.C.; Bautista, L.F.; Delgado, L.; Villa, J.A. Effect of surfactants on PAH biodegradation by a bacterial consortium and on the dynamics of the bacterial community during the process. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 9438–9446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecotti, M.; Coppotelli, B.M.; Mora, V.C.; Viera, M.; Morelli, I.S. Efficiency of surfactant-enhanced bioremediation of aged polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-contaminated soil: Link with bioavailability and the dynamics of the bacterial community. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhu, L.; Wang, L.; Zhan, Y. Gene expression of an arthrobacter in surfactant-enhanced biodegradation of a hydrophobic organic compound. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 3698–3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, P.; Tang, H.; Zhang, A.; Liu, Z.; Li, Z. Optimization and regulation effects of microbial community on the efficient degradation of aromatic hydrocarbons. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 59, 105020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Li, P.; Zhang, A.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wei, C.; Yang, Z.; Li, Z. Optimizing carbon sources regulation in the biochemical treatment systems for coal chemical wastewater: Aromatic compounds biodegradation and microbial response strategies. Water Res. 2024, 256, 121627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Fan, Z.; Miao, K.; Wei, W.; Ye, C.; Li, C. Response of soil microbial community to surfactant Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS) contamination in lake-terrestrial ecotone: Structural and functional changes. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 32, 103281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najim, A.A.; Ismail, Z.Z.; Hummadi, K.K. Biodegradation potential of sodium dodecyl sulphate (SDS) by mixed cells in domestic and non-domestic actual wastewaters: Experimental and kinetic studies. Biochem. Eng. J. 2022, 180, 108374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awi, A.A.M.; Yasid, N.A.; Shukor, M.Y. Characterization of Sodium Dodecyl Sulphate–degrading Enterobacter cloacae sp. STRAIN AaMa. J. Environ. Microbiol. Toxicol. 2023, 11, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambily, P.S.; Jisha, M.S. Metabolic profile of sodium dodecyl sulphate (SDS) biodegradation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa (MTCC 10311). J. Environ. Biol. 2014, 35, 827–831. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Q.; Fan, Z.; Zeng, L.; Li, C.; Ye, C.; Zheng, R. Effect of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) on microbial community structure and function in lake–terrestrial ecotones: A simulation experiment. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2024, 34, 103594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Yang, J.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; Lin, Y.; Zheng, S.; Liang, S.; Han, S. Multiple cellular responses guarantee yeast survival in presence of the cell membrane/wall interfering agent sodium dodecyl sulfate. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 527, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Ma, L.; Xu, X.; Peng, Q.; Zhong, H.; Gong, Y.; Shi, L.; He, M.; Shi, B.; Qiao, Y. Physiological and Transcriptomic Analyses of Escherichia coli Serotype O157:H7 in Response to Rhamnolipid Treatment. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grether, J.; Dittmann, H.; Willems, L.; Schmiegelt, T.; Perino, E.H.B.; Hubel, P.; Lilge, L.; Hausmann, R. Bioprocess exploitation of microaerobic auto-induction using the example of rhamnolipid biosynthesis in Pseudomonas putida KT2440. J. Biol. Eng. 2025, 19, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandoval, N.R.; Papoutsakis, E.T. Engineering membrane and cell-wall programs for tolerance to toxic chemicals: Beyond solo genes. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2016, 33, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadati, F.; Shahryari, S.; Sani, N.M.; Farajzadeh, D.; Zahiri, H.S.; Vali, H.; Noghabi, K.A. Effect of MA01 rhamnolipid on cell viability and expression of quorum-sensing (QS) genes involved in biofilm formation by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; He, S.; Gao, Z.; Feng, L.; Jiang, J.; Zhao, Q.; Wei, L. Micro-mechanism of rhamnolipid promoting acid production during anaerobic digestion: Protein structures, metagenomics and molecular dynamics simulations. Water Res. 2025, 283, 123795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, N.; Liu, L. Microbial response to acid stress: Mechanisms and applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhatib, S.A.; Arya, S.; Islayem, D.; Nyadzayo, R.M.; Mohamed, S.; Yousef, A.F.; Hernandez, H.H.; Pappa, A.M. Revealing bioremediation potential of novel indigenous bacteria from oil-contaminated sites in the UAE: A combined bioinformatics and experimental validation. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0329515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, Y.K.; Zhang, W.; Liang, Y. Effect of surfactant assisted ultrasonic pretreatment on production of volatile fatty acids from mixed food waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 368, 128340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Li, Y.; He, Q.; Li, B.; Yuan, Y.; Wen, J. Effects of Different Surfactants to Petroleum Hydrocarbons Degradation of Mixed-bacteria. Res. Sq. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Fang, S.; Huang, W.; Wang, F.; Zhang, L.; Fang, F.; Cao, J.; Wu, Y.; Wang, D. New insights into different surfactants’ impacts on sludge fermentation: Focusing on the particular metabolic processes and microbial genetic traits. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2022, 16, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Zhang, L.; Wei, Z.; Liu, X.; Shi, X.; Liu, X.; Cao, J.; Feng, Q.; Fang, F.; Luo, J. Overlooked roles of improved substrates functions in remodeling microbial community and driving metabolic traits during sludge fermentation triggered by surfactants and antibiotics co-existence. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 482, 136617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Wang, K.; Chen, M.; Fan, J.; Han, S.; Hou, J.; Chi, L.; Liu, Y.; Wei, T. Profiling the composition and metabolic activities of microbial community in fermented grain for the Chinese strong-flavor Baijiu production by using the metatranscriptome, high-throughput 16S rRNA and ITS gene sequencings. Food Res. Int. 2020, 138, 109765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Usman, M.; Zheng, Z.; Zhao, X.; Meng, X.; Hu, K.; Shen, X.; Wang, X.; Cai, Y. Two microbial consortia obtained through purposive acclimatization as biological additives to relieve ammonia inhibition in anaerobic digestion. Water Res. 2023, 230, 119583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, M.; Wang, H.; Ren, Y.; Qiu, J.; Cheng, M.; Hong, Q. McbG, a LysR Family Transcriptional Regulator, Activates the mcbBCDEF Gene Cluster Involved in the Upstream Pathway of Carbaryl Degradation in Pseudomonas sp. Strain XWY-1. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, e02970-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, D.C.; Cryder, Z.; Gan, J. Soil bacterial community dynamics following surfactant addition and bioaugmentation in pyrene-contaminated soils. Chemosphere 2019, 231, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Saino, M.; Bai, X. Study on the bio-methane yield and microbial community structure in enzyme enhanced anaerobic co-digestion of cow manure and corn straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 219, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colores, G.M.; Macur, R.E.; Ward, D.M.; Inskeep, W.P. Molecular Analysis of Surfactant-Driven Microbial Population Shifts in Hydrocarbon-Contaminated Soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 2959–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furmanczyk, E.M.; Lipinski, L.; Dziembowski, A.; Sobczak, A. Genomic and functional characterization of environmental strains of SDS-degrading Pseudomonas spp., providing a source of new sulfatases. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, E.M.; Rebello, S.; Asok, A.K.; Jisha, M.S. Pseudomonas plecoglossicida S5, a novel nonpathogenic isolate for sodium dodecyl sulfate degradation. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2015, 13, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Yan, W.; Ding, M.; Yuan, Y. Construction of microbial consortia for microbial degradation of complex compounds. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 1051233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Borjigin, Q.; Gao, J.L.; Yu, X.F.; Hu, S.P.; Zhang, B.Z.; Han, S.C. Community succession and functional prediction of microbial consortium with straw degradation during subculture at low temperature. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffries, T.C.; Rayu, S.; NielsenUffe, U.N.; Lai, K.; Ijaz, A.; Nazaries, L.; Singh, B.K. Metagenomic functional potential predicts degradation rates of a model organophosphorus xenobiotic in pesticide contaminated soils. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeij, H.B.; Etemadifar, Z.; Kilbane, J.; Karimi-Jafari, M.H.; Mofidifar, S. Unraveling the metabolic landscape of Exophiala spinifera strain FM: Model reconstruction, insights into biodesulfurization and beyond. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0317796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliphant, K.; Allen-Vercoe, E. Macronutrient metabolism by the human gut microbiome: Major fermentation by-products and their impact on host health. Microbiome 2019, 7, 175225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Duan, T.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, W.; Wang, X.; Han, J. Impact mechanisms of various surfactants on the biodegradation of phenanthrene in soil: Bioavailability and microbial community responses. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 950, 175225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, T.; Zhou, Z.; Shen, X.; Qiao, W.; Jiang, L.; Pan, W.; Zhou, J. Effects of dissolved oxygen on performance and microbial community structure in a micro-aerobic hydrolysis sludge in situ reduction process. Water Res. 2016, 90, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Q.; He, K.; Collins, G.; De Vrieze, J.; Wu, G. Microbial strategies driving low concentration substrate degradation for sustainable remediation solutions. NPJ Clean Water 2024, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Jones, R.B.; Fodor, A.A. Inference-based accuracy of metagenome prediction tools varies across sample types and functional categories. Microbiome 2020, 8, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, G.M.; Maffei, V.J.; Zaneveld, J.; Yurgel, S.N.; Brown, J.R.; Taylor, C.M.; Huttenhower, C.; Langille, M.G.I. PICRUSt2: An improved and customizable approach for metagenome inference. bioRxiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koolivand, A.; Coulon, F.; Ball, A.S.; Ismail, N.I.; Khudur, L.S.; ParsiMehr, M.; Gao, G.; Godini, K. Challenges with Bioaugmentation and Field-Scale Application of Bioremediation Processes for Petroleum-Contaminated Sites: A Review. Indian J. Microbiol. 2024, 1–17. Available online: https://dspace.lib.cranfield.ac.uk/server/api/core/bitstreams/37143f38-9a85-46c2-b5c9-b34fd0018010/content (accessed on 9 July 2025).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Mokoena, M.I.; Nkuna, R.; Matambo, T.S. Metagenomic and Proxy Monitoring of Surfactant Degradation by Microbial Consortia from Oil-Contaminated Soil. Appl. Microbiol. 2026, 6, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol6010003
Mokoena MI, Nkuna R, Matambo TS. Metagenomic and Proxy Monitoring of Surfactant Degradation by Microbial Consortia from Oil-Contaminated Soil. Applied Microbiology. 2026; 6(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol6010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleMokoena, Morena India, Rosina Nkuna, and Tonderayi Sylvester Matambo. 2026. "Metagenomic and Proxy Monitoring of Surfactant Degradation by Microbial Consortia from Oil-Contaminated Soil" Applied Microbiology 6, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol6010003
APA StyleMokoena, M. I., Nkuna, R., & Matambo, T. S. (2026). Metagenomic and Proxy Monitoring of Surfactant Degradation by Microbial Consortia from Oil-Contaminated Soil. Applied Microbiology, 6(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol6010003






