Abstract
Potato production in the Andean highlands demands strategies that reduce dependence on synthetic inputs without sacrificing yield. We evaluated two microbial bioinputs—Bacillus subtilis and Trichoderma viride—applied once pre-plant to seed tubers, under three organo-mineral fertilization regimes (0%, 50%, and 100% of the recommended NPK rate) in two cultivars (INIA 303-Canchán and Yungay) in field conditions in Ayacucho, Peru, using a randomized complete block, split-plot design (three replicates). Agronomic traits (plant height, root dry weight, stems per plant, tubers per plant, and plot-level yield) were analyzed with robust two-way ANOVA and multivariate methods. Combining microbial inoculation with 50% NPK sustained growth responses comparable to 100% NPK for key traits: in Yungay with T. viride, plant height at 50% NPK (≈96.15 ± 1.71 cm) was not different from 100% NPK (≈98.87 ± 1.70 cm), and root dry weight at 50% NPK (≈28.50 ± 0.28 g) matched or exceeded 100% NPK (≈16.97–22.62 g depending on cultivar–treatment). Notably, T. viride increased root biomass even without mineral fertilizer (≈27.62 ± 0.29 g in Yungay), while B. subtilis enhanced canopy vigor and stem number at full NPK (≈4.5 ± 0.29 stems). Yungay out-yielded INIA 303-Canchán overall (≈57.5 ± 2.5 kg vs. ≈42.7 ± 2.5 kg per plot). The highest yields occurred with B. subtilis + 100% NPK (≈62.88 ± 6.07 kg per plot), followed by B. subtilis + 50% NPK (≈51.7 ± 6.07 kg per plot). Plant height was the strongest correlate of yield (Spearman ρ ≈ 0.60), underscoring its value as a proxy for productivity. Overall, a single pre-plant inoculation with B. subtilis or T. viride can halve mineral fertilizer inputs while maintaining growth and sustaining high, cultivar-dependent yields in highland potato systems.
1. Introduction
Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) is a pivotal food crop worldwide, valued both for its broad nutritional profile and for its remarkable capacity to adapt to a wide range of agroclimatic conditions [1,2,3]. Having arisen in the Peruvian Andes [4], the potato is a fundamental pillar of food security [5]. Against this backdrop, Peruvian agriculture confronts a steep rise in international demand [6]. National production reached 329,836 t in 2024, according to the National Institute of Statistics and Informatics [7]. In the Andean department of Ayacucho, favorable rainfall and temperature drove a 37.9% expansion during the 2023–2024 campaign relative to the preceding season [8].
Yet, these gains have been accompanied by the indiscriminate use of synthetic fertilizers, which accelerates soil degradation and contaminates water resources [9,10]. The utilization efficiency of mineral fertilizers rarely exceeds 40% [11], and the consistent absence of soil diagnostics before application further undermines long-term sustainability [12,13,14]. As a consequence, the optimal organic matter content of Andean soils is declining [15], jeopardizing their medium-term productive capacity.
Using plant growth-promoting microorganisms (PGPMs) can be a complementary strategy to conventional management based on mineral fertilization and chemical crop protection. These microorganisms improve nutrient acquisition, enhance resilience to biotic stress, and reduce reliance on external inputs [16,17]. Among plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR), Bacillus spp. (e.g., B. subtilis, B. amyloliquefaciens) have been shown to (i) increase available phosphorus by up to 30% through solubilization; (ii) reduce Fusarium spp. incidence by 45–60% via antifungal lipopeptides; (iii) mitigate drought stress [18,19,20]; and (iv) solubilize zinc and potassium, fix atmospheric nitrogen, and inhibit Rhizoctonia solani mycelial growth by 49.87% [21,22,23]. Foliar and soil applications of B. subtilis have also alleviated Potato virus Y (PVY) symptoms by 32.79–72.26% within days after inoculation, underscoring its antiviral biocontrol potential [24].
Fungal counterparts such as Trichoderma spp., particularly, T. viride, are likewise recognized as plant growth-promoting fungi (PGPF) that enhance soil fertility, improve nutrient uptake, and suppress soil-borne pathogens [25,26,27]. Foliar application of T. viride isolates to PVY-infected potatoes significantly promoted biomass accumulation, plant height, root development, and leaf number; at the same time, peroxidase, polyphenol oxidase, total protein, and chlorophyll levels increased 21 days after inoculation, and a reduction in PVY accumulation levels of up to 18.76 times was shown compared to untreated plants. [28]. Moreover, T. viride has proven effective against R. solani, improving yield parameters [29,30] and has been deployed to counter Alternaria solani by eliciting plant defense responses [31,32]. Integrating such microorganisms into crop management therefore fosters eco-efficient agriculture, reducing reliance on synthetic inputs while safeguarding soil ecosystem.
Despite mounting evidence of their benefits, studies examining the interaction among PGPMs, organo-mineral fertilization, and high-yielding potato cultivars in Ayacucho remain scarce. The present work addresses this gap by evaluating the inoculation of T. viride and B. subtilis in relevant potato varieties grown in Ayacucho. By assessing agronomic performance under limited-input conditions, we identify synergistic combinations that could reinforce future sustainable intensification strategies in the Andean highlands.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
The fieldwork was conducted during the 2024–2025 growing season on a 972 m2 experimental plot situated in Viscachayooc (74°12′07″ W, 13°04′48″ S; 2727 m.a.s.l.), managed by Canaán Agrarian Experimental Station of the National Institute for Agricultural Innovation (INIA) in the Andrés Avelino Cáceres Dorregaray District, Huamanga Province, Ayacucho, Peru (Figure 1). Key meteorological variables were logged by the INIA-Canaán automatic station operated jointly by SENAMHI and the Regional Government of Ayacucho. Mean air temperature traced a gentle downward trajectory, declining from 17.6 °C in November to 15.5 °C in April; minimum and maximum were 8.8 °C and 28.9 °C, respectively. In parallel, the ambient relative humidity increased steadily from 54.7% to 72.8%. Rainfall was modest daily (0.1–0.2 mm day−1 on average), yet convective events produced conspicuous spikes of 14.4 mm in February and of 9.8 mm in December. Instantaneous precipitation rates were therefore highly erratic, with mean values below 1.1 mm h−1 but an extreme of 96 mm h−1 recorded in February. Incoming solar radiation waned from 247.3 W m−2 at the onset of the season to 184 W m−2 by its close, although midday peaks consistently exceeded 983 W m−2 and occasionally reached 1178 W m−2, indicating ample photosynthetically active energy throughout.
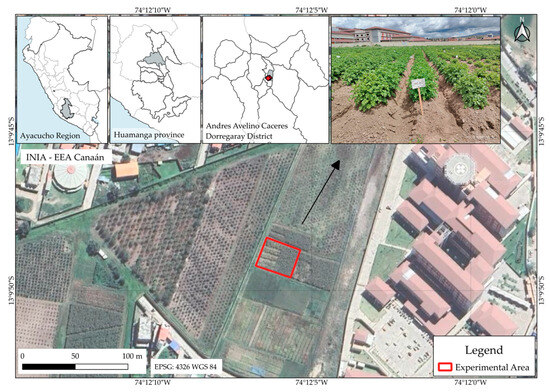
Figure 1.
Geographic location of the experimental site. Field trials were conducted on plots managed by Canaán Agrarian Experimental Station the National Institute for Agricultural Innovation (INIA) in the Andrés Avelino Cáceres Dorregaray District, Huamanga Province, Ayacucho, Peru.
2.2. Soil Physicochemical Properties
Immediately before experiment establishment, composite soil cores were taken from the 0–40 cm of depth. Samples were sealed and transported to the Soil, Water and Foliar Laboratory (LABSAF) at the Canaán Agricultural Research Station (INIA) for analysis. Soil parameters evaluated include soil texture, pH [33], electrical conductivity was measured according to Molua [34], organic matter content [35], and total nitrogen [36]. Cation exchange capacity, available phosphorus, and potassium were extracted, following Muindi [37] and Xu et al. [38], respectively.
To ensure accuracy, analyses were performed with certified equipment. Soil pH and electrical conductivity were measured using a pH meter (WTW INOLAB, model pH 7310, Xylem Analytics Germany Sales GmbH & Co. KG., Weilheim in Oberbayern, Germany) and conductivity meter (WTW INOLAB, model Cond 7310, Xylem Analytics Germany Sales GmbH & Co. KG., Weilheim in Oberbayern, Germany), respectively. Organic matter content was quantified with a digital burette (BDeco, model DCB5000, Boeckel, Hamburg, Germany). Soil texture was determined using a hydrometer (THERMCO ASTM, model 152H, HB Instrument/Gilson Company Inc., Reading, PA, USA) and a mechanical dispenser (Hamilton Beach, model HMD400, Hamilton Company, Reno, NV, USA). Total nitrogen was measured employing a digestion system (BERT, model Heizblock K24, Heizbiac GmbH, Ulm, Germany) and distillation equipment (Wasserdam, model Destillere 52, Grupo WESDOM, Wenzhou, China). Available phosphorus was quantified colorimetrically using a spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific, model Genesys 150, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Rochester, NY, USA), while exchangeable bases and potassium were determined with an atomic emission spectrophotometer (Agilent Technologies, model 4210, Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). Mass determinations were carried out with an analytical balance (Bell, model M214Ai, BEL Engineering S.r.l., Monza, Italy) (Table 1).

Table 1.
Soil physicochemical characteristics before planting the potato crop.
2.3. Plant Material
Two contrasting potato cultivars were evaluated: INIA 303-Canchán and Yungay. INIA 303-Canchán is a medium-cycle variety (120 days), with average yields of 30 t ha−1 under farmer-managed conditions and horizontal resistance to Phytophthora infestans [39]. Yungay has a longer cycle (170–180 days), with yields > 45 t ha−1 under optimal management, and known tolerance to drought and resistance to Streptomyces scabies, Phytophthora erythroseptica, and Globodera spp., although it remains susceptible to late blight [40,41,42].
2.4. Experimental Design
The experiment employed a randomized complete-block experimental design (DBCA) with split-plot arrangement and three replications. The main factor was microbial inoculation with uninoculated control (m1), Trichoderma viride (m2) and Bacillus subtilis (m3), while the second factor was organo-mineral fertilizer at 0% (n1), 50% (n2) or 100% (n3), with a total of nine treatment combinations (Table 2). Each cultivar (INIA 303-Canchán and Yungay) was represented by 27 experimental units, giving 54 units overall; individual plots measured 15 m2 (3 rows of 5 m length, spaced 1 m between rows and 0.30 m between seedholes and accommodating 60 plants).

Table 2.
Factors and interactions.
2.5. Fertilization and Agronomic Management
Certified, registered-category seed tubers of the cultivars INIA 303-Canchán and Yungay were provided by the National Seed Project (PROSEM) of INIA. Sowing was carried out on 12 November 2024, coinciding with the first seasonal rains, by placing two tubers per seedhole at an in-row spacing of 0.30 m. A routine treatment during the vegetative stage was adopted against the principal insect pests of the experiment field: Epicauta spp., Phthorimaea operculella, and Epitrix spp. were suppressed with α-cypermethrin (60 mL 20 L−1 spray solution) applied at threshold levels, whereas disease management relied exclusively on the biological agents under evaluation. Both cultivars reached physiological maturity 130 days after sowing, at which point the crop was lifted and assessed. Fertilization was determined based on soil analysis and the nutritional requirements of the potato crop, the corresponding NPK doses were applied at sowing and during the first hilling, thereby establishing the three fertilization of NPK levels (n1, n2, n3) detailed in the previous sections.
2.6. Microbial Inoculation Procedure
The bioinoculant Bacillus subtilis strain AP-01 (Silvestre; 1 × 109 CFU g−1; SENASA-PBUA 176) and a granular formulation of Trichoderma viride produced on sterile, sporulated maize kernels (Solagro; 1 × 1012 conidia kg−1; SENASA-PBUA 393) were applied immediately prior to sowing. The microorganisms were reconstituted at the manufacturer-recommended rate of 20 g Bacillus and 30 g Trichoderma per 15 L of water. Agricultural oil (Wett Oil; Comercial Andina Industrial S.A.C., Peru) was added to each solution as a spreader/sticker to improve adhesion and reduce desiccation/UV exposure, and molasses (PROBIOLSUR; Productos Biológicos del Sur S.A.C., Peru) was included as a carbon source only to the treatments containing microbial propagules. The resulting suspensions were sprayed directly onto seed tubers already laid in open rows using a calibrated hand sprayer, applying approximately 100 mL of inoculum per linear meter, which corresponds to an estimated 2.5 mL per tuber. This application was performed only once, immediately prior to covering the rows with soil, following the manufacturer’s recommendation for both inoculants. A single pre-sowing treatment was chosen because previous studies have shown that seed or tuber inoculation with PGPR such as Bacillus subtilis and biocontrol fungi such as Trichoderma viride can be effective with a single intervention [43]. This approach also reflects the objective of reducing production costs while promoting sustainable agriculture and enhancing the natural fertility of soils [44,45,46]. All inoculations were carried out at predawn to minimize desiccation-related mortality. No pre-plant disinfectants, bactericides, or fungicides were used, following the inoculation protocols of Hao et al. [47] and Attia et al. [48].
2.7. Agronomic Measurements
Crop performance was monitored at four phenological checkpoints that were synchronized across both cultivars. These time points (30, 60, 75, and 120 days after sowing, DAS) were selected because they coincide with key growth stages of potato and thus allowed for timely and representative data collection. At 30 DAS, field emergence exceeded 95%, making this stage appropriate for counting established plants. At 60 DAS, early flowering and the appearance of initial stolons were recorded, while 75 DAS corresponded to the tuber bulking stage. The final observation occurred at 120 DAS, when both cultivars had reached physiological maturity and senescence.
Percentage of plant emergence (PER) was assessed by block at 30 DAS to account for potential spatial variation in initial plant establishment. Each experimental unit comprised three rows with a total of 48 plants; measurements were taken from plants (n = 7–10) in the central row. To minimize border effects, the first and last plants of each row were excluded from sampling, ensuring that only interior plants were considered for measurements of plant height, vigor, and root biomass. Plant height (PH) was measured at 60 DAS, while root-biomass weight (RW) was evaluated at 75 DAS on three plants from the same row. The number of sampled plants varied because in some treatments, particularly the uninoculated control, only 7–10 plants in the central row grew vigorously enough to be considered representative. Plant height was measured from the soil surface to the apical meristem measured with a ruler, following the protocols of Naawe et al. [49] and Nguyen [50]. Vigor was scored visually on a nine-point ordinal scale (3 = weak, 5 = moderate, 7 = vigorous, 9 = very vigorous) at 60 DAS [51]. To reduce observer bias, the assessment was performed simultaneously by three independent evaluators, and consensus scores were recorded for each plant. Root dry weight at 75 DAS was obtained by drying the root in an oven for 24 h, then they were weighed on a MEDILAB (model ALC-6100.1) precision scale. The final observation occurred at 120 DAS, number of main stems (NSP) and tubers (NTP) per plant were counted on the same tagged plants, and crop yield (YIELD) was recorded with a precision platform scale.
2.8. Statistical Analysis
All datasets were processed in RStudio (v. 2024.12.1 + 563). After exploratory screening with the ‘dplyr’ package [52], each response variable was tested for normality and homoscedasticity using the Shapiro–Wilk and Levene tests, respectively. As several traits violated one or both assumptions, a robust two-way ANOVA was conducted using the ‘WRS2’ package [53]. For pairwise comparisons, Sidák’s adjustment was applied using appropriate functions (RHSDB function) to control for family-wise error and to compute corrected confidence intervals [54]. Post hoc comparisons and estimation of marginal means were performed using the ‘emmeans’ package [55]. Additionally, multiple-comparison procedures were carried out with the ‘multcomp’ package [56], ensuring robust statistical inference across treatment groups.
3. Results
3.1. Correlation Among Agronomic Variables
Spearman’s rank correlation analysis (Figure 2) revealed a clear hierarchy of agronomic drivers of marketable output. Plant height emerged as the prime predictor: taller canopies were strongly associated with higher yields (0.60).
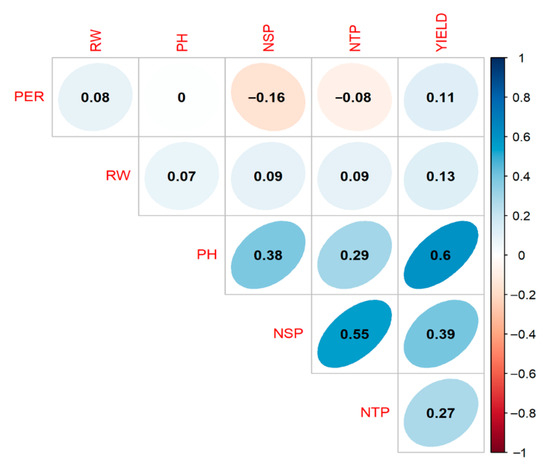
Figure 2.
Spearman correlation matrix for key agronomic traits in potato. PER, emergence percentage; RW, root dry weight; PH, plant height; NSP, number of main stems per plant; NTP, number of tubers per plant; YIELD, crop yield. Numeric entries are correlation coefficients (ρ). Cell color and ellipse orientation depict the strength and direction of the relationship, with blue for positive and red for negative associations, whereas unshaded cells correspond to non-significant correlations (p > 0.05).
A moderately tight link was detected between the number of main stems per plant (NSP) and the number of tubers per plant (NTP) (ρ = 0.55). Near to this correlation correspond to plant height (PH) and crop yield (YIELD) with 0.6. PH also covaried with stem density (NSP) (ρ = 0.38), underscoring the integrated nature of above-ground growth. Crop yield responded positively, though less sharply, to NSP (ρ = 0.39) and tuber set per plant (NTP) (ρ = 0.27), confirming the additive contribution of both source and sink components to final productivity. By contrast, plant emergence per row (PER) and root dry weight (RW) were only weakly related to yield with 0.11 and 0.13, respectively.
3.2. Plant Emergence per Block
According to the robust ANOVA performed using the WRS2 package, no statistically significant differences were detected among varieties (F = 2.76, p = 0.104), experimental units (F = 10.64, p = 0.338), or the variety × experimental unit interaction (F = 2.29, p = 0.977). These results suggest a consistent performance across varieties, regardless of the treatment applied. Specifically, the Yungay variety exhibited an average emergence of 14.30 ± 0.19 units, compared to 13.83 ± 0.18 units for Canchán. However, this apparent difference was not statistically significant (Figure 3 and Table S1). Similar results were found for treatments, and the highest values were observed for the non-inoculated control (14.58 ± 0.39) and T. viride without fertilization (14.53 ± 0.42), whereas the lowest values were recorded for 100% NPK and B. subtilis without fertilization with 13.58 ± 0.39 and 13.66 ± 0.42, respectively (Figure 4 and Table S2).
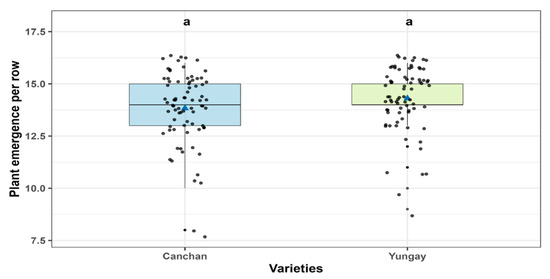
Figure 3.
Mean comparisons of plant emergence per row across the Canchán and Yungay varieties. According to Sidak-adjusted comparisons, no statistically significant differences were observed between treatments, as indicated by the shared letter “a” above the boxplots (p > 0.05). The solid black line within each box marks the median, while the blue triangle denotes the treatment mean and gray circles individual data points.
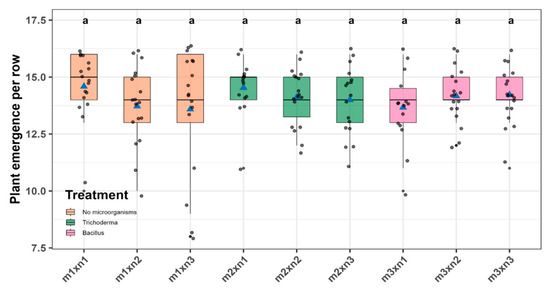
Figure 4.
Plant emergence per block across treatment combinations of microbial inoculation and NPK rates. Box-and-whisker plots show the distribution of observations for each treatment. Horizontal lines indicate medians, blue triangles represent treatment means, and gray dots individual data points. Same lowercase letters denote groups without significant differences according to Sidák’s test (p > 0.05).
3.3. Plant Height (cm)
Robust ANOVA (WRS2) revealed highly significant main effects for genotype, treatment, and their interaction (p = 0.001), confirming that plant height responded differentially to each genotype × treatment combination in INIA 303-Canchán and Yungay. Sidák-adjusted post hoc tests (Figure 3) revealed clear pairwise contrasts (p < 0.05). In both cultivars, the greatest heights were attained under the full NPK rate combined with microbial inoculation. For Yungay, Bacillus subtilis + 100% NPK treatment reached 102.11 ± 1.60 cm, followed by Trichoderma viride + 100% NPK at 98.87 ± 1.70 cm; the shortest plants occurred under Bacillus subtilis + 0% NPK at 60.57 ± 1.81 cm. Conversely, in INIA 303-Canchán the highest plants were recorded for Bacillus subtilis + 100% NPK at 90.20 ± 1.60 cm, followed by the uninoculated 100% NPK control at 84.00 ± 1.60 cm; the minimum was recorded for Trichoderma viride + 0% NPK at 45.42 ± 1.81 cm. In 0%NPK treatments, B. subtilis inoculated treatment in Canchán and T. viride inoculated treatment in Yungay outperformed their uninoculated counterparts, highlighting a cultivar-specific synergy between microbial inoculation and nutrient stress. However, it is noteworthy that in several cases, the combination of 50% NPK with PGPMs achieved plant heights statistically comparable to those with 100% NPK, particularly in Yungay. For instance, Trichoderma viride + 50% NPK in Yungay yielded 96.15 ± 1.71 cm, not significantly different from Trichoderma + 100% NPK (98.87 ± 1.70 cm; p > 0.05) (Figure 5 and Table S3).
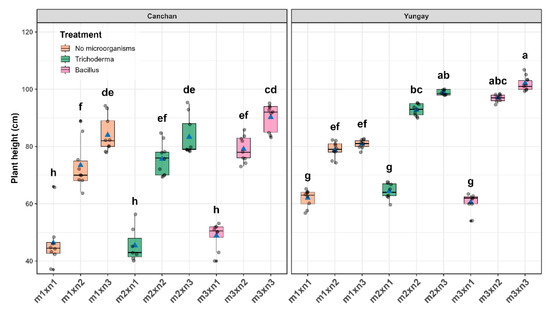
Figure 5.
Interactive effect of potato genotypes and treatment combinations (microbial inoculant plus NPK level) on plant height, measured 75 days after sowing (DAS). For each cultivar, box-and-whisker plots show the distribution of observations across the nine treatments. Horizontal lines represent the medians, blue triangles indicate the treatment means, and gray circles denote individual data points. Different lowercase letters above the boxes indicate statistically significant differences according to Sidák’s test (p < 0.05).
3.4. Root Dry Weight (RW)
Robust two-way ANOVA showed highly significant main effects of genotype, treatment and their interaction on root dry weight (p < 0.001). Yungay proved far more responsive than INIA 303-Canchán, obtaining a greater response in all treatments. The Sidak-adjusted contrasts singled out the T. viride + 50% NPK (28.50 ± 0.28 g) in Yungay as the standout performer, roughly 1.7-fold higher than the best treatment in INIA 303-Canchán (16.97 ± 0.43 g). Remarkably, Yungay maintained nearly the same root mass under Trichoderma with no mineral fertilizer (27.62 ± 0.29 g), underscoring a strong genotype–fungus synergy that is only marginally fertilizer-dependent. On the other hand, the poorest performance was recorded under B.subtilis combined with 50% NPK for Yungay (8.99 ± 0.28 g) and INIA 303-Canchán (9.17 ± 0.23 g). Collectively, the data indicate that moderate nutrient supply amplifies the root-promoting effect of T. viride in a cultivar-specific manner, whereas B. subtilis confers little benefit under the same conditions (Figure 6 and Table S4).
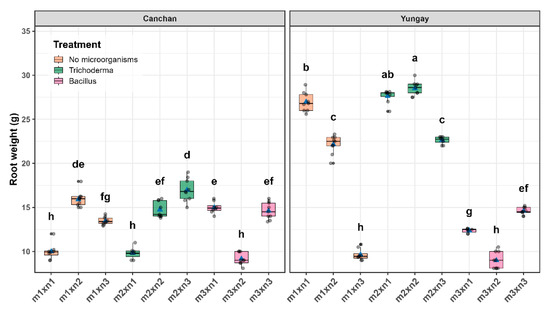
Figure 6.
Interactive effect of potato genotype and treatment combination (microbial inoculant × NPK level) on root dry weight at 75 days after sowing (DAS). Box-and-whisker plots show the distribution of values across the nine treatment combinations for INIA 303-Canchán (left panel) and Yungay (right panel). The horizontal line within each box represents the median, blue triangles indicate the mean, and gray dots correspond to individual plant measurements. Different lowercase letters above the boxes indicate statistically significant differences according to Sidák’s test (p < 0.05).
3.5. Number of Stems per Plant (NSP)
The robust ANOVA (WRS2) showed significant differences in the number of main stems between cultivars (p = 0.004) and combined treatments (p = 0.001); no significative effects were found for the interaction. Yungay (3.76 ± 0.16) exhibited an increase in stems was slightly higher and significant compared to INIA 303-Canchán with 3.17 ± 0.16 (Figure 7 and Table S5).
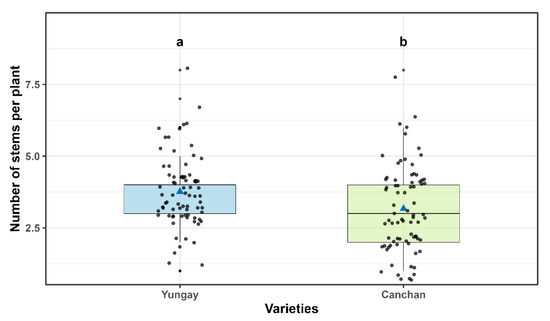
Figure 7.
Number of main stems per plant in INIA 303-Canchán and Yungay cultivars. Box-and-whisker plots display the distribution of observations for each cultivar. The horizontal line within each box represents the median, blue triangles indicate the mean, and gray dots correspond to individual plant measurements. Different lowercase letters above the boxes indicate statistically significant differences between cultivars according to Sidák’s test (p < 0.05).
The highest mean stem number was recorded for B. subtilis + 100% NPK (4.5 ± 0.29) stems, followed by 50% NPK (4.06 ± 0.30), while the lowest value occurred in the untreated control (2.18 ± 0.30) (Figure 8 and Table S6).
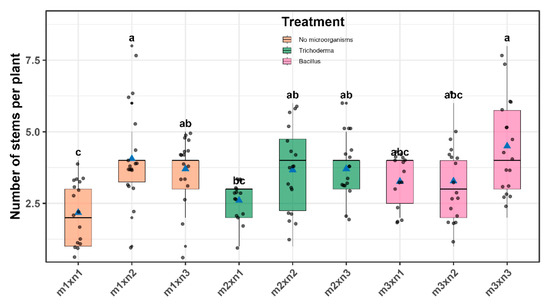
Figure 8.
Number of main stems per plant across treatment combinations of microbial inoculation and NPK levels. Box-and-whisker plots show the distribution of observations for each of the nine treatment combinations. Horizontal lines within boxes represent medians, blue triangles indicate treatment means, and gray dots correspond to individual plant measurements. Different lowercase letters above the boxes indicate statistically significant differences among treatments according to Sidák’s test (p < 0.05).
Similarly to the root dry weight variable, stem density did not always increase proportionally with NPK level. The uninoculated treatments + 50% NPK and + 100% NPK, both recorded 4.06 ± 0.30 and 3.70 ± 0.30 stems, respectively, without significant differences. This finding suggests that further increases beyond 50% NPK may not yield additional benefits in shoot proliferation, especially in the absence of microbial support. Such insights support a transition to reduced-input systems without compromising early canopy development.
3.6. Number of Tubers per Plant (NTP)
Factorial ANOVA detected a marked effect of combined treatment on the number of tubers per plant (NTP), with a significant cultivar × treatment interaction (p < 0.01) despite the absence of a cultivar effect (p = 0.45). In Yungay, with the treatment m1 × n2 showed the highest performance with (25.78 ± 0.30), followed by m2 × n2 (20.30 ± 2.12) and m3 × n2 (18.22 ± 1.99), while the worst performance was recorded when no fertilizer and no microbes were supplied (12.88 ± 1.99). In INIA 303-Canchán the response pattern shifted, and the combination of T. viride with the full NPK dose produced the greatest number of tubers (24.00 ± 1.99), followed by B. subtilis at the same nutrient level (20.60 ± 1.99), whereas the unfertilized control (10.60 ± 2.12) again ranked last (Figure 9 and Table S7).
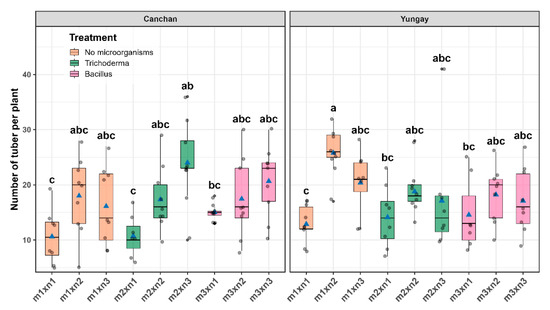
Figure 9.
Number of tubers per plant as affected by the interaction between microbial inoculation and NPK fertilization in two potato cultivars. Box-and-whisker plots illustrate the distribution of observations across nine treatment combinations for INIA 303-Canchán (left panel) and Yungay (right panel). The horizontal line within each box represents the median, blue triangles indicate the treatment mean, and gray dots represent individual plant measurements. Different lowercase letters above the boxes indicate statistically significant differences among treatments according to Sidák’s test (p < 0.05).
3.7. Vigor
The evaluation of plant vigor (PV) between 60 and 75 days after sowing (Figure 8) revealed that inoculations with Trichoderma and Bacillus, in combination with 100% NPK fertilization, significantly increased the relative proportion of highly vigorous plants (PV = 9). The B. subtilis + 100% NPK treatment showed the highest percentage of very vigorous plants (~70–80% at 75 days), followed by m2 × n3 (~60%). In contrast, the control treatment m1 × n1 (without microorganisms or fertilizer) predominantly exhibited plants with moderate vigor (PV = 5, ~80%) (Figure 10).
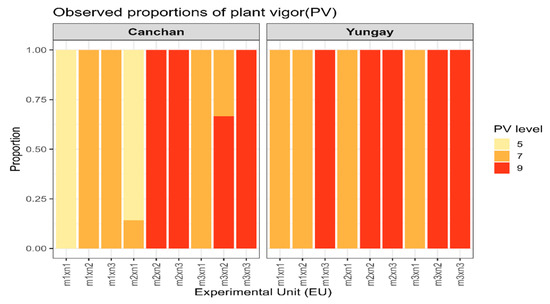
Figure 10.
Observed proportions of plant vigor (PV) levels in potato across microbial inoculation and NPK fertilization treatments. Stacked bar charts display the relative frequency of plants assigned to three vigor categories (PV = 5, 7, or 9) for each treatment combination in INIA 303-Canchán (left panel) and Yungay (right panel). Colors represent vigor scores, with darker shades indicating higher levels of plant vigor. Each bar reflects the proportion of plants within a given treatment.
3.8. Crop Yield
The ANOVA-WRS2 analysis for yield revealed significant effects of variety (p = 0.001) and experimental unit (p = 0.015), with no significant variety × treatment interaction (p = 0.975), indicating a consistent varietal response across treatments. The Yungay variety exhibited a significantly higher yield (57.5 ± 2.5 kg) compared to INIA-Canchán (42.7 ± 2.5 kg), with p = 0.0016, highlighting its greater productive potential under the experimental conditions (Figure 11 and Table S8).
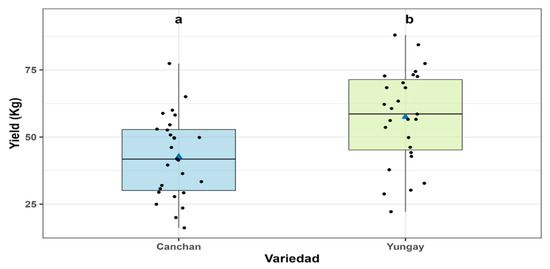
Figure 11.
Crop yield (YIELD) in INIA 303-Canchán and Yungay cultivars. Box-and-whisker plots show the distribution of yield values for each cultivar. The horizontal line within each box represents the median, blue triangles indicate the mean, and black dots represent individual plot measurements. Different lowercase letters above the boxes indicate statistically significant differences between cultivars according to Sidák’s test (p < 0.05).
The Sidak multiple comparison analysis revealed significant differences among treatments. The highest yields were observed in the Bacillus + 100% NPK treatment (62.88 ± 6.07 kg) and Bacillus + 50% NPK (51.7 ± 6.07 kg), both significantly superior to the unfertilized and uninoculated control (35.43 ± 6.07 kg). T. viride + 100% NPK (61.73 ± 6.07 kg), and T. viride + 50% NPK (52.06 ± 6.07 kg) showed intermediate yields (Figure 12 and Table S9).
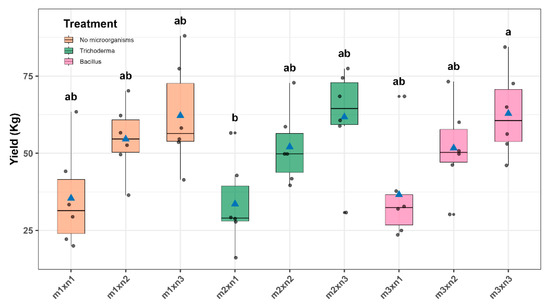
Figure 12.
Crop yield (YIELD) across treatment combinations of microbial inoculation and NPK fertilization. Box-and-whisker plots display the distribution of yield values for each of the nine treatment combinations. The horizontal line within each box represents the median, blue triangles indicate the mean, and black dots correspond to individual plot measurements. Different lowercase letters above the boxes indicate statistically significant differences among treatments according to Sidák’s test (p < 0.05).
3.9. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
The principal component analysis (PCA) explained 75.66% of the total variability across the first three axes: PC1 (42.02%) was associated with productive variables; PC2 (18.8%) was linked to the number of emerged plants per furrow and root weight; and PC3 (14.84%) contrasted these same variables. The concentration ellipses revealed a clear separation between cultivars, with greater dispersion observed in Yungay (green triangles) and a more compact distribution in Canchán (Figure 13).
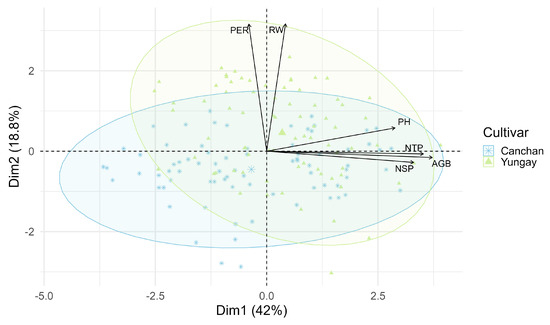
Figure 13.
Principal component analysis (PCA) of agronomic traits evaluated in potato. The biplot shows the two-dimensional distribution of individual observations based on the first two principal components (Dim1: 42.0%, Dim2: 18.8%). Arrows represent the loading vectors of six agronomic variables: plant emergence per row (PER), root dry weight (RW), plant height (PH), number of stems per plant (NSP), number of tubers per plant (NTP), and total yield (WTP). Cultivar identity is indicated by point shape and color, with ellipses showing the 95% confidence dispersion for INIA 303-Canchán and Yungay.
4. Discussion
This study confirmed that full fertilization substantially contributes to potato yield. However, the application of Bacillus subtilis and Trichoderma viride was able to potentiate growth, vigor, and productivity even under 50% NPK, enabling comparable or superior results to full chemical fertilization [22,57,58]. Particularly in the Yungay cultivar, known for its high responsiveness and physiological plasticity, these microbial inoculants maximized yield, suggesting that integrating PGPMs into fertilization regimes can significantly improve nutrient use efficiency (NUE) and promote sustainable intensification in highland agroecosystems [59,60].
Consistent with recent reports [61], Bacillus subtilis and Trichoderma viride enhanced rhizosphere activity by stimulating nutrient solubilization, modulating soil enzyme activities (e.g., urease, dehydrogenase, alkaline phosphatase), and improving root system architecture [27,62,63]. These functions are critical in nutrient-depleted soils, as they increase the bioavailability of N, P, and K through organic acid excretion and enzymatic mineralization [27,64]. In our study, Spearman correlation analysis identified plant height (ρ = 0.60) as the best yield predictor [65,66], followed by number of stems (ρ = 0.39) [67,68] and tubers per plant (ρ = 0.27) [69]—variables directly influenced by microbial stimulation of shoot and root development [60].
Under B. subtilis + 100% NPK, Yungay achieved the highest yield (62.88 kg/plot), while T. viride + 100% NPK yielded 61.73 kg. Importantly, yields under 50% NPK with inoculants—51.7 kg with Bacillus and 52.06 kg with Trichoderma—did not differ significantly from full NPK treatments (p > 0.05), highlighting the functional equivalence between microbial bioactivation and chemical inputs [61]. This reflects findings from greenhouse and field trials where microbial inoculation improved tuber number and weight under reduced fertilization [70].
In terms of plant physiology, the enhanced aerial growth and increased number of stems observed in plants inoculated with Bacillus subtilis—particularly under full fertilization (m3 × n3)—may be explained by mechanisms previously reported in the literature, such as the microbial production of phytohormones like indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), and the solubilization of key nutrients including phosphorus and zinc [71,72]. Although IAA production was not directly quantified in the present study, the significant increases in plant height (up to 102.11 ± 1.60 cm) and stem number (4.5 ± 0.29) compared to the uninoculated control suggest that B. subtilis may enhance shoot development through hormonal modulation and improved nutrient bioavailability [73]. These physiological effects likely contributed to the greater canopy vigor and tuber initiation potential observed in Bacillus-treated plots, reinforcing its role as an effective biofertilizer under both full and reduced NPK regimes [74].
Meanwhile, T. viride exerted stronger effects on root biomass, even under nutrient limitation [75]. In Yungay, T. viride + 50% NPK achieved 28.5 g root weight, which is statistically equivalent to T. viride + 100% NPK. This result is aligned with studies indicating that Trichoderma alters soil pH, increases phosphorus solubility, synthesizes auxins and gibberellins, and triggers systemic resistance against pathogens like Rhizoctonia solani [76,77,78]. Its dual biofertilizer–biocontrol role explains why it sustained root development and yield under constrained NPK availability [79].
PCA results further supported these interactions: PC1 (42.02% of variance) was heavily loaded with PH, NSP, NTP, and YIELD. Yungay was associated with greater dispersion and stronger correlation to these variables, confirming its higher responsiveness. This suggests that genotype–inoculant compatibility is critical for optimizing microbial fertilization strategies [80,81].
Moreover, Bacillus and Trichoderma are not only efficient individually but synergistic when co-applied. Reports show that their combined action improves rhizosphere conditions, enzyme activity, and nutrient cycling, even more so when used alongside organic amendments such as compost or farmyard manure [42,82]. This synergism enables nutrient recovery and retention, enhancing NUE while lowering the environmental footprint of conventional fertilization [58,83].
In conclusion, our results—and those corroborated by multiple field and greenhouse studies—clearly indicate that the integration of PGPMs into potato nutrient management programs allows for the reduction of chemical fertilizers by up to 50% without compromising yield or quality. The implications are far-reaching: improved soil health, reduced input costs, resilience to nutrient stress, and alignment with sustainable agriculture goals. Future research should prioritize strain–genotype matching, long-term soil microbiome monitoring, and large-scale implementation protocols adapted to diverse agroecological zones.
Further large-scale field trials across contrasting edaphoclimatic conditions are recommended to validate the consistency of the combined effects of Bacillus subtilis and Trichoderma viride. Future studies should also address their long-term impacts on soil fertility, rhizosphere microbial communities, and postharvest tuber quality. In addition, evaluating different formulations and application methods could help optimize their effectiveness under reduced fertilization schemes, thereby strengthening their adoption in sustainable potato production systems.
5. Conclusions
The present study demonstrated that the combined use of Bacillus subtilis and Trichoderma viride significantly enhances growth, vigor, and yield in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.), particularly in the Yungay cultivar, even under reduced fertilization conditions. Treatments with 50% NPK plus microbial inoculants achieved yields statistically comparable to full NPK fertilization, highlighting their potential to improve nutrient use efficiency and promote eco-efficient intensification. The observed increases in plant height, stem number, and root biomass—strongly correlated with yield—suggest that microbial stimulation of nutrient solubilization and probable phytohormonal effects, as reported by other authors, contribute to these outcomes. These findings support the strategic integration of microbial biofertilizers into nutrient management programs as a sustainable alternative to reduce agrochemical inputs, enhance crop performance, and improve soil health in highland potato systems.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/applmicrobiol5040112/s1, Table S1. Mean comparisons of plant emergence per row across the Canchán and Yungay cultivars; Table S2. Mean comparisons of plant emergence per row across the Canchán and Yungay varieties; Table S3. Interactive effect of potato genotypes and treatment combinations (microbial inoculant plus NPK level) on plant height, measured 75 days after sowing (DAS); Table S4. Interactive effect of potato genotype and treatment combination (microbial inoculant × NPK level) on root dry weight at 75 days after sowing (DAS); Table S5. Number of main stems per plant in INIA 303-Canchán and Yungay cultivars; Table S6. Number of main stems per plant across treatment combinations of microbial inoculation and NPK levels; Table S7. Number of tubers per plant as affected by the interaction between microbial inoculation and NPK fertilization in two potato cultivars; Table S8. Crop yield (YIELD) in INIA 303-Canchán and Yungay cultivars; Table S9. Crop yield (YIELD) across treatment combinations of microbial inoculation and NPK fertilization.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.T. and M.V.; methodology, M.T., M.V., and G.P.; software, M.T.; validation, M.T., and H.C.; formal analysis, M.T., H.C., and D.M.; investigation, J.V.; resources, O.P. and J.V.; data curation, M.T. and D.M.; writing—original draft preparation, H.C.-S. and D.M.; writing—review and editing, H.C.-S. and D.M.; visualization, M.T. and D.M.; supervision, D.M.; project administration, O.P. and J.V.; funding acquisition, O.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
“Eco-Efficient Intensification with Trichoderma viride and Bacillus subtilis Enhances Yield and Growth of Potato (Solanum Tuberosum L.) under Differential Organo-Mineral Nutrition in Peru” was funded by the investment project 2361771: “Improving the availability, access, and use of quality seeds for potato, amylaceous maize, grain legumes, and cereals in the regions of Junín, Ayacucho, Cusco, and Puno (4 departments)”, supported by Instituto Nacional de Innovación Agraria, (INIA) Perú.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| INIA | Instituto Nacional de Innovación Agraria |
| RW | Root-biomass weight |
| PH | Plant height |
| NSP | Number of main stems per plant |
| NTP | Tubers per plant |
| YIELD | Crop yield |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
References
- Camire, M.E.; Kubow, S.; Donnelly, D.J. Potatoes and human health. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2009, 49, 823–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, H.; Ortiz, O. (Eds.) The Potato Crop: Its Agricultural, Nutritional and Social Contribution to Humankind; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadu, T.; Abdullahi, A.; Ahmad, K. The role of crop protection in sustainable potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) production to alleviate global starvation. In Solanum tuberosum—A Promising Crop for Starvation Problem; Yildiz, M., Ozgen, Y., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spooner, D.M.; McLean, K.; Ramsay, G.; Waugh, R.; Bryan, G.J. A single domestication for potato revealed by AFLP genotyping. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 14694–14699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adekanmbi, T.; Wang, X.; Basheer, S.; Liu, S.; Yang, A.; Cheng, H. Climate change impacts on global potato yields: A review. Environ. Res. Clim. 2024, 3, 012001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaux, A.; Goffart, J.-P.; Kromann, P.; Andrade-Piedra, J.; Polar, V.; Hareau, G. The potato of the future: Opportunities and challenges in sustainable agri-food systems. Potato Res. 2021, 64, 681–720, Erratum in Potato Res. 2022, 65, 209–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- INEI. Perú: Producción Nacional de los Principales Cultivos 2024; Instituto Nacional de Estadística e Informática: Lima, Perú, 2024. Available online: https://www.inei.gob.pe/ (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Pérez, C.R.S. Boletín Estadístico Mensual: Valor Bruto de la Producción Agropecuaria; Ministerio de Desarrollo Agrario y Riego: Lima, Peru, 2024; pp. 1–7.
- Tripathi, S.; Srivastava, P.; Devi, R.S.; Bhadouria, R. Influence of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides on soil health. In Agrochemicals Detection, Treatment and Remediation; Gurusamy, A., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 25–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashitha, R.; Mathew, J. Fate of conventional fertilizers in the environment. In Controlled Release Fertilizers for Sustainable Agriculture; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaz, T.M.; Dobermann, A.; Lyons, S.E.; Thomson, A.M. Research and innovation on novel fertilizers for crop nutrition. NPJ Sustain. Agric. 2025, 3, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B. Are nitrogen fertilizers deleterious to soil health? Agronomy 2018, 8, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisht, N.; Singh Chauhan, P. Excessive and disproportionate use of chemicals causes soil contamination and nutritional stress. In Soil Contamination—Threats and Sustainable Solutions; Larramendy, M.L., Soloneski, S., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeni, O.; Teoman, Ö. The Agriculture–Environment Relationship and Environment-based Agricultural Support Instruments in Turkey. Eur. Rev. 2022, 30, 194–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abebe, T.G.; Tamtam, M.R.; Abebe, A.A.; Abtemariam, K.A.; Shigut, T.G.; Dejen, Y.A.; Haile, E.G. Growing use and impacts of chemical fertilizers and assessing alternative organic fertilizer sources in Ethiopia. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2022, 2022, 4738416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Raish, S.M.; Sourani, O.M.; Abu-Elsaoud, A.M. Plant growth-promoting microorganisms as biocontrol agents: Mechanisms, challenges, and future prospects. Appl. Microbiol. 2025, 5, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuhoff, D.; Neumann, G.; Weinmann, M. Testing plant growth promoting microorganisms in the field—A proposal for standards. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 14, 1324665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chabbi, N.; Chafiki, S.; Telmoudi, M.; Labbassi, S.; Bouharroud, R.; Tahiri, A.; Mentag, R.; El Amri, M.; Bendiab, K.; Hsissou, D.; et al. Plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria improve seeds germination and growth of Argania spinosa. Plants 2024, 13, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Daim, I.A.A.; Meijer, J. Bacillus velezensis 5113 induces metabolic reprogramming during abiotic-stress tolerance in wheat. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 52567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.R.; Ali, Q.; Ayaz, M.; Bilal, M.S.; Sheikh, T.M.M.; Gu, Q.; Wu, H.; Gao, X. Plant–Microbes Interaction: Exploring the Impact of Cold-Tolerant Bacillus Strains RJGP41 and GBAC46 Volatiles on Tomato Growth Promotion through Different Mechanisms. Biology 2023, 12, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtyamova, Z.; Arkhipova, T.; Martynenko, E.; Nuzhnaya, T.; Kuzmina, L.; Kudoyarova, G.; Veselov, D. Growth-promoting effect of Rhizobacterium (Bacillus subtilis IB22) in salt-stressed barley depends on abscisic acid accumulation in the roots. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehmood, S.; Muneer, M.A.; Tahir, M.; Javed, M.T.; Mahmood, T.; Afridi, M.S.; Pakar, N.P.; Abbasi, H.A.; Munis, M.F.H.; Chaudhary, H.J. Deciphering distinct biological control and growth promoting potential of multi-stress tolerant Bacillus subtilis PM32 for potato stem canker. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2021, 27, 2101–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, I.; Kaushik, P.; Al-Huqail, A.A.; Khan, F.; Siddiqui, M.H. Effect of the diverse combinations of useful microbes and chemical fertilizers on important traits of potato. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 2641–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, H.A.; El Kammar, H.F.; Saied, S.M.; Soliman, A.M. Effect of Bacillus subtilis on Potato virus Y resistance and growth promotion in potato. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2023, 167, 743–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heflish, A.A.; Abdelkhalek, A.; Al-Askar, A.A.; Behiry, S.I. Protective and curative effects of Trichoderma asperelloides on tomato root-rot. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakibuzzaman, M.; Akand, M.H.; Siddika, M.; Uddin, A.F.M.J. Impact of Trichoderma application as bio-stimulator on disease suppression, growth and yield of potato. J. Biosci. Agric. Res. 2021, 27, 2252–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.L.; Hermosa, R.; Lorito, M.; Monte, E. Trichoderma: A multipurpose, plant-beneficial microorganism for eco-sustainable agriculture. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 312–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.; Ashfaq, M.; Rao, M.J.; Khan, K.S.; Malik, A.H.; Mehmood, M.A.; Fawaz, M.S.; Abbas, A.; Shakeel, M.T.; Naqvi, S.A.H.; et al. Trichoderma viride: An eco-friendly biocontrol solution against soil-borne pathogens in vegetables. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aseel, D.G.; Soliman, S.A.; Al-Askar, A.A.; Elkelish, A.; Elbeaino, T.; Abdelkhalek, A. Trichoderma viride isolate Tvd44 enhances potato growth and stimulates defence against Potato virus Y. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, A.; Hussain, S.; Saeedullah, S.; Akbar, A.; Ahmad, Z.; Tariq, M.; Karim, R.; Huzaifa, M. Soil moisture levels and Trichoderma viride for controlling black scurf of potato. Sarhad J. Agric. 2021, 38, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purwantisari, S.; Ferniah, R.S.; Nurchayati, Y.; Jannah, S.N. Effects of Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria and Trichoderma sp. On Potato Growth on Medium Plains. KnE Life Sci. 2022, 7, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Chandra, R.; Behera, L.; Chetan, K.; Estibaliz, S. Elevation of systemic defence in potato against Alternaria solani by a consortium of Trichoderma spp. In Review, 2021; submitted. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neina, D. Role of soil pH in plant nutrition and soil remediation. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2019, 2019, 5794869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molua, C.O. Investigating the Influence of Soil Electrical Conductivity on Crop Yield for Precision Agriculture Advancements. Int. J. Agric. Anim. Prod. 2021, 12, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.E.; Ali, G.A.; Gillespie, A.W.; Wagner-Riddle, C. Soil organic matter as catalyst of crop resource capture. Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Jabeen, N.; Farruhbek, R.; Chachar, Z.; Laghari, A.A.; Chachar, S.; Ahmed, N.; Ahmed, S.; Yang, Z. Enhancing Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Agriculture by Integrating Agronomic Practices and Genetic Advances. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 16, 1543714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muindi, E.M. Understanding soil phosphorus. Int. J. Plant Soil Sci. 2019, 31, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Du, X.; Wang, F.; Sha, J.; Chen, Q.; Tian, G.; Zhu, Z.; Ge, S.; Jiang, Y. Effects of Potassium Levels on Plant Growth, Accumulation and Distribution of Carbon, and Nitrate Metabolism in Apple Dwarf Rootstock Seedlings. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, J.; Alania, D.; Ninalaya, E.N.; Gastelo, M.; Bastos, C. Nuevos cultivares de papa con resistencia a la rancha [Phytophthora infestans (Mont.) De Bary] y adaptación al cambio climático. Rev. Latinoam. Papa 2019, 22, 66–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakır, E.; Ertek, T.S.; Katırcıoğlu, Y.Z.; Maden, S. Occurrence of potato pink rot caused by Phytophthora erythroseptica in Turkey. Australas. Plant Dis. Notes 2020, 15, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagöz, K.; Dadasoğlu, F.; Alaylar, B.; Kotan, R. Evaluation of molecular typing methods for some scab-causing Streptomyces strains from Turkey. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 40, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gartner, U.; Armstrong, M.R.; Sharma, S.K.; Jones, J.T.; Blok, V.C.; Hein, I.; Bryan, G.J. Characterisation and mapping of a Globodera pallida resistance derived from the wild potato species Solanum spegazzinii. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2024, 137, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yobo, K.S.; Laing, M.D.; Hunter, C.H. Effects of single and combined inoculations of selected Trichoderma and Bacillus isolates on growth of dry bean and biological control of Rhizoctonia solani damping-off. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 8746–8756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naqqash, T.; Malik, K.A.; Imran, A.; Hameed, S.; Shahid, M.; Hanif, M.K.; Majeed, A.; Iqbal, M.J.; Qaisrani, M.M.; van Elsas, J.D. Inoculation with Azospirillum spp. Acts as the Liming Source for Improving Growth and Nitrogen Use Efficiency of Potato. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 929114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overbeek, W.; Jeanne, T.; Hogue, R.; Smith, D.L. Effects of Microbial Consortia, Applied as Fertilizer Coating, on Soil and Rhizosphere Microbial Communities and Potato Yield. Front. Agron. 2021, 3, 714700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, B.; Stringam, B.L.; Darapuneni, M.K.; Lombard, K.A.; Sanogo, S.; Higgins, C.; Djaman, K. Effect of irrigation and nitrogen management on potato growth, yield, and water and nitrogen use efficiencies. Agronomy 2024, 14, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, S.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhou, H. Inhibition of potato Fusarium wilt by Bacillus subtilis ZWZ-19 and Trichoderma asperellum PT-29. Plants. 2024, 13, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, M.S.; El-Wakil, D.A.; Hashem, A.H.; Al-Askar, A.A.; AbdElgawad, H.; Alotaibi, R.S.; Abdel-Kader, S.A.; Abdelaziz, A.M. Investigating the activity of Bacillus subtilis and Trichoderma harzianum to mitigate Fusarium wilt disease of diverse cultivars of Vicia faba. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 16093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naawe, E.K.; Köken, I.; Aytekin, R.I.; Gleku, O.D.; Çalişkan, S.; Çalişkan, M.E. Effects of Elevated Temperature on Agronomic, Morphological, Physiological and Biochemical Characteristics of Potato Genotypes: 1. Agronomic and Morphological traits. Potato Res. 2024, 68, 2167–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozentsvet, O.; Bogdanova, E.; Nesterov, V.; Bakunov, A.; Milekhin, A.; Rubtsov, S.; Rozentsvet, V. Phenotyping of Potato Plants Using Morphological and Physiological Tools. Plants 2024, 13, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, D.; Dong, H.; Bai, S.; Wu, Y. Mapping QTLs for Spring Green-Up, Plant Vigor, and Plant Biomass in Two Lowland Switchgrass Populations. Mol. Breed. 2022, 42, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H.; Francois, R.; Henry, L.; Müller, K. dplyr: A Grammar of Data Manipulation, R Package, version 1.1.4; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2023.
- Mair, P.; Wilcox, R. WRS2: Robust Statistical Methods, R Package, version 1.14; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2023.
- Zhicheng, D.; Feng, H. RHSD: Ryan-Hom Step-Down Banferroni or Sidak, R Package, version 0.2.0; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022.
- Lenth, R. emmeans: Estimated Marginal Means, Aka Least-Squares Means, R Package, version 1.8.6; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2023.
- Hothorn, T.; Bretz, F.; Westfall, P. multcomp: Simultaneous Inference in General Parametric Models, R Package, version 1.4.25; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2008.
- De Lima Gonilha, D.B.; Santos, C.H.B.; Frezarin, E.T.; Siqueira, J.S.; Rigobelo, E.C. Biological Strategies to Minimize Fertilizer Use in Maize: Efficacy of Trichoderma harzianum and Bacillus subtilis. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 15, 2261–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, P.H.V.; Souza, A.G.V.; De Araujo, L.D.; Frezarin, E.T.; De Souza, G.V.L.; Da Silveira, C.M.; Rigobelo, E.C. Trichoderma harzianum and Bacillus subtilis in Association with Rock Powder for the Initial Development of Maize Plants. Agronomy 2023, 13, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroz, N.; Colvin, B.; Jayasinghe, S.; Gleason, C.; Tanaka, K. Phytocytokine StPep1-secreting bacteria suppress potato powdery scab disease. Phytopathology® 2024, 114, 2055–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantar, F.; Uysal, A. Effect of Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens culture on the growth and yield of off-season potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Acta Agron. 2020, 69, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirado-Malaver, R.H.; Tirado-Lara, R. Biofertilization with beneficial microorganisms and low rates of chemical fertilization in potatoes (Solanum tuberosum L.) management for sustainable agriculture. Braz. J. Biol. 2025, 85, e286059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Montañez, R.; Calero-Rios, E.; Quispe, K.; Huasasquiche, L.; Lastra, S.; La Torre, B.; Solórzano, R. Synergy Between Microbial Inoculants and Mineral Fertilization to Enhance the Yield and Nutritional Quality of Maize on the Peruvian Coast. Appl. Microbiol. 2024, 4, 1757–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelina, E.; Papatheodorou, E.M.; Demirtzoglou, T.; Monokrousos, N. Effects of Bacillus subtilis and Pseudomonas fluorescens Inoculation on Attributes of the Lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) Soil Rhizosphere Microbial Community: The Role of the Management System. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, M.I.; Mujawar, L.H.; Shahzad, T.; Almeelbi, T.; Ismail, I.M.I.; Oves, M. Bacteria and fungi can contribute to nutrients bioavailability and aggregate formation in degraded soils. Microbiol. Res. 2016, 183, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aishwarya, K.R.; Singh, D.; Pradeep, S.D.; Mehta, T.; Singh, K.; Fandan, R.; Nitwal, R.; Singh, J.P. Correlation and Path Coefficient Analysis among Yield and Yield Associated Traits in Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) Accessions in the ‘Terai’ Region of Uttarakhand. J. Sci. Res. Rep. 2024, 30, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsumi, K.; Usami, T. Plant-level prediction of potato yield using machine learning and unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) multispectral imagery. Discov. Appl. Sci. 2024, 6, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowles, N.R.; Knowles, L.O. Manipulating Stem Number, Tuber Set, and Yield Relationships for Northern- and Southern-Grown Potato Seed Lots. Crop Sci. 2006, 46, 284–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shayanowako, A.; Mangani, R.; Mtaita, T.; Mazarura, U. Influence of Main Stem Density on Irish Potato Growth and Yield: A Review. Annu. Res. Rev. Biol. 2015, 5, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussan, A.J.; Mitchell, P.D.; Copas, M.E.; Drilias, M.J. Evaluation of the Effect of Density on Potato Yield and Tuber Size Distribution. Crop Sci. 2007, 47, 2462–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marjanović, J.; Zubairu, A.M.; Varga, S.; Turdalieva, S.; Ramos-Diaz, F.; Ujj, A. Demonstrating agroecological practices in potato production with conservation tillage and Pseudomonas spp., Azotobacter spp., Bacillus spp. bacterial inoculants—Evidence from Hungary. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, C.; Christensen, M.N.; Kovács, Á.T. Molecular Aspects of Plant Growth Promotion and Protection by Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2021, 34, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, C.N.G.; Pang, J.K.Y.; Gottardi, M.; Kračun, S.K.; Svendsen, B.A.; Nielsen, K.F.; Kovács, Á.T.; Moelbak, L.; Fimognari, L.; Husted, S.; et al. Bacillus subtilis promotes plant phosphorus (P) acquisition through P solubilization and stimulation of root and root hair growth. Physiol. Plant. 2024, 176, e14338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, C.B.; Dos Santos, R.M.; De Souza Buzo, F.; De Andrade Da Silva, M.S.R.; Rigobelo, E.C. Effects of Chemical Fertilization and Microbial Inoculum on Bacillus subtilis Colonization in Soybean and Maize Plants. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 901157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhuang, L.; Yu, Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, J.; Wang, Q. A microbial consortium-based product promotes potato yield by recruiting rhizosphere bacteria involved in nitrogen and carbon metabolisms. Microb. Biotechnol. 2021, 14, 1961–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Lin, X.; Wei, X.; Zeng, Q.; Mu, C.; Zhou, X. Trichoderma viride improves phosphorus uptake and the growth of Chloris virgata under phosphorus-deficient conditions. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1425034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelagio-Flores, R.; Esparza-Reynoso, S.; Garnica-Vergara, A.; López-Bucio, J.; Herrera-Estrella, A. Trichoderma-induced acidification is an early trigger for changes in Arabidopsis root growth and determines fungal phytostimulation. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Cornejo, H.A.; Macías-Rodríguez, L.; del-Val, E.; Larsen, J. Ecological Functions of Trichoderma spp. and Their Secondary Metabolites in the Rhizosphere: Interactions with Plants. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2016, 92, fiw036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, A.; Mubeen, M.; Zheng, H.; Sohail, M.A.; Shakeel, Q.; Solanki, M.K.; Iftikhar, Y.; Sharma, S.; Kashyap, B.K.; Hussain, S.; et al. Trichoderma spp. Genes Involved in the Biocontrol Activity Against Rhizoctonia solani. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 884469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhandari, S.; Pandey, K.R.; Joshi, Y.R.; Lamichhane, S.K. An overview of multifaceted role of Trichoderma spp. for sustainable agriculture. Arch. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2021, 6, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreote, F.D.; Rocha, U.N.D.; Araújo, W.L.; Azevedo, J.L.; Van Overbeek, L.S. Effect of bacterial inoculation, plant genotype and developmental stage on root-associated and endophytic bacterial communities in potato (Solanum tuberosum). Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2010, 97, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortiello, M.; Milc, J.; Sanfelici, A.; Martini, S.; Tagliazucchi, D.; Caccialupi, G.; Ben Hassine, M.; Giovanardi, D.; Francia, E.; Caradonia, F. Genotype and Plant Biostimulant Treatments Influence Tuber Size and Quality of Potato Grown in the Pedoclimatic Conditions in Northern Apennines in Italy. Int. J. Plant Prod. 2024, 18, 579–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poveda, J.; Eugui, D. Combined use of Trichoderma and beneficial bacteria (mainly Bacillus and Pseudomonas): Development of microbial synergistic bio-inoculants in sustainable agriculture. Biol. Control 2022, 176, 105100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, S.D.A.D.; Cardoso, A.F.; Castro, G.L.S.D.; Júnior, D.D.D.S.; Silva, T.C.D.; Silva, G.B.D. Co-Inoculation of Trichoderma asperellum with Bacillus subtilis to Promote Growth and Nutrient Absorption in Marandu Grass. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2022, 2022, 3228594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).