Inhibitory Effects of Bacillus subtilis Isolated from Meju (Fermented Soybean Brick) on the Growth of Aspergillus parasiticus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Media
2.2. Preparation and Fermentation of Meiu Cakes
2.3. Enumeration and Isolation of Bacteria
2.4. Identification and Characterization of Bacillus Isolates
2.5. Genome Sequencing
2.6. Inoculum Preparation
2.7. Cultures with/without B. subtilis
2.8. Determination of Fungal Growth and Aflatoxin Production
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
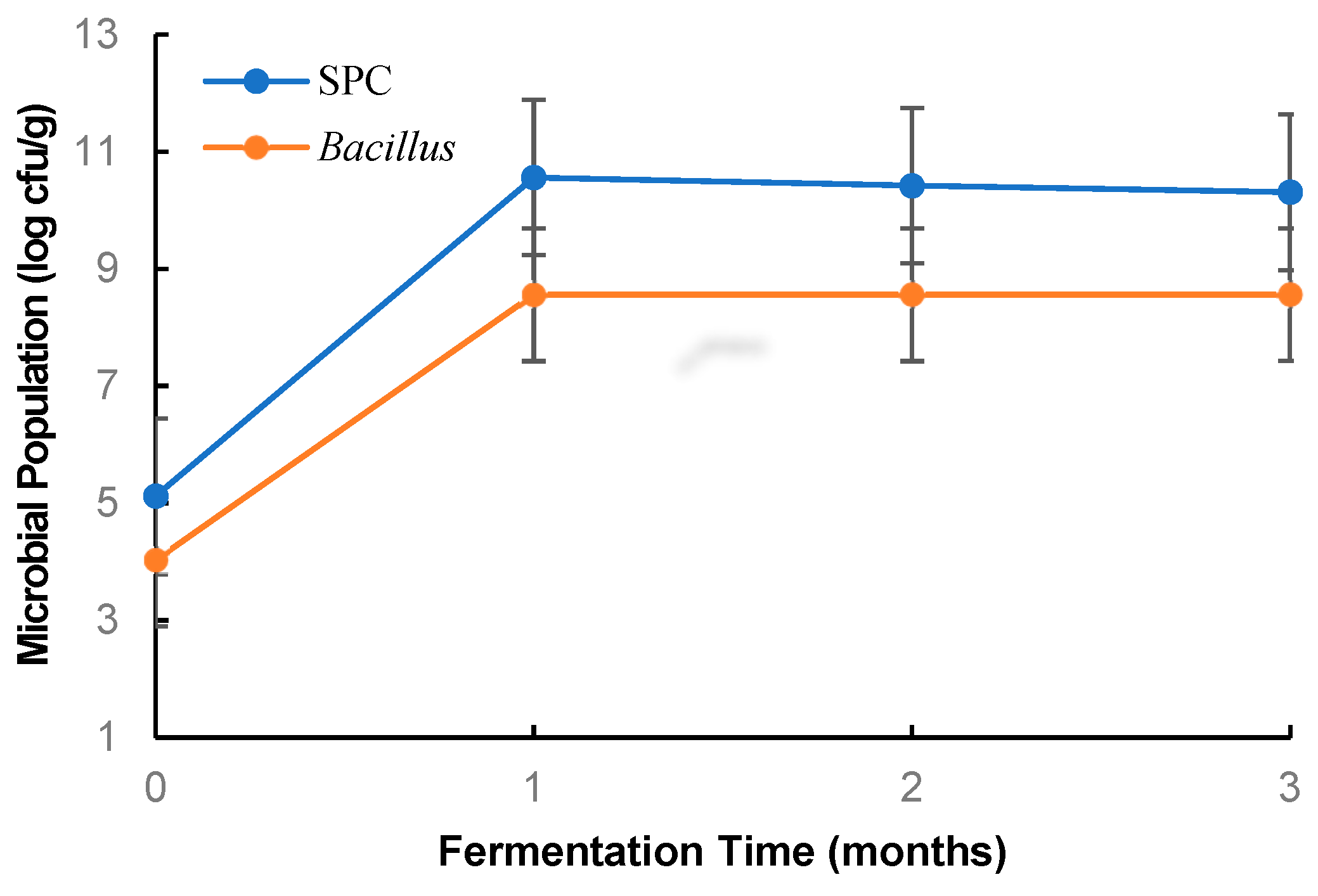
3.1. Changes in Bacillus Population
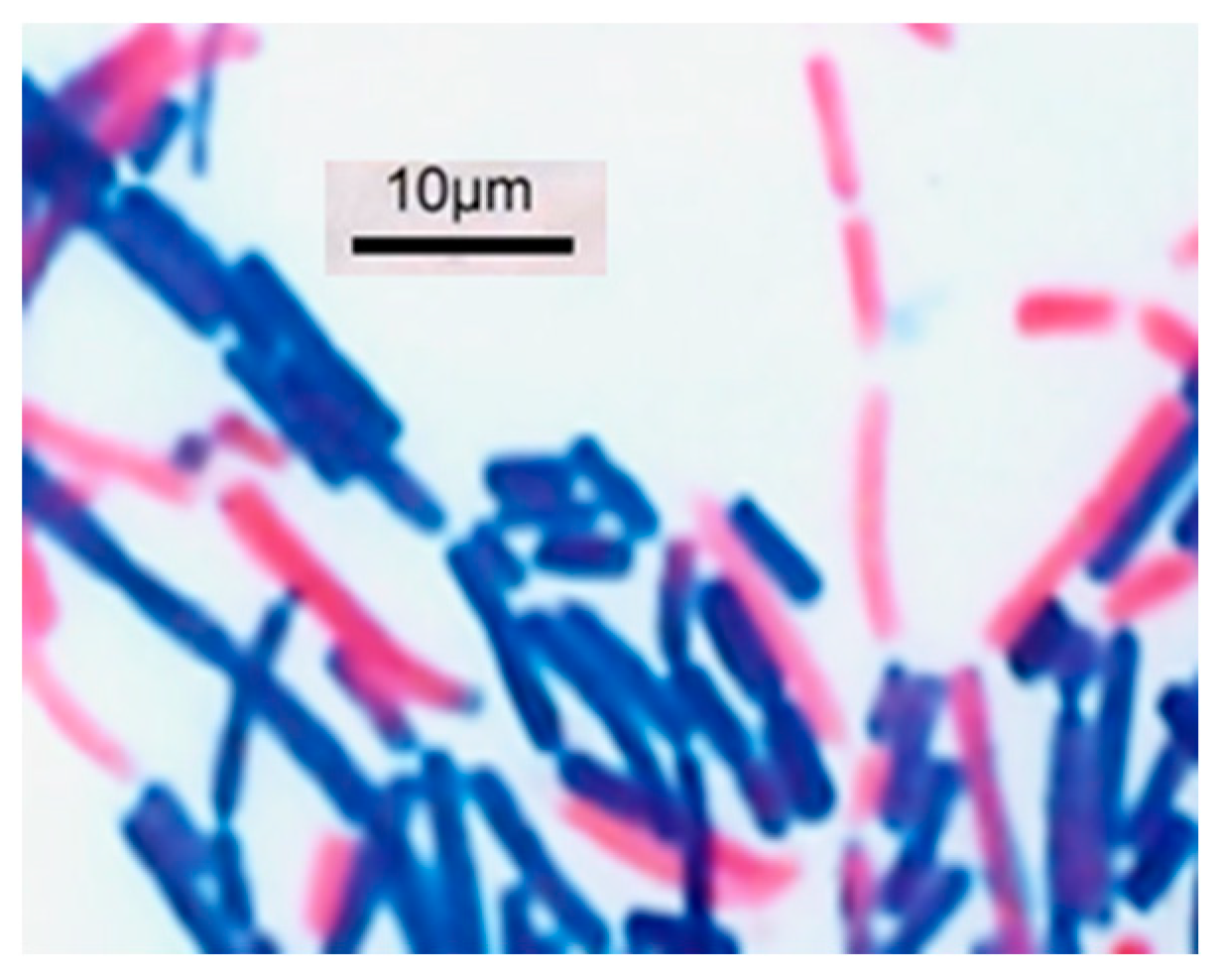
3.2. Characterization and Identification of Bacillus Strain
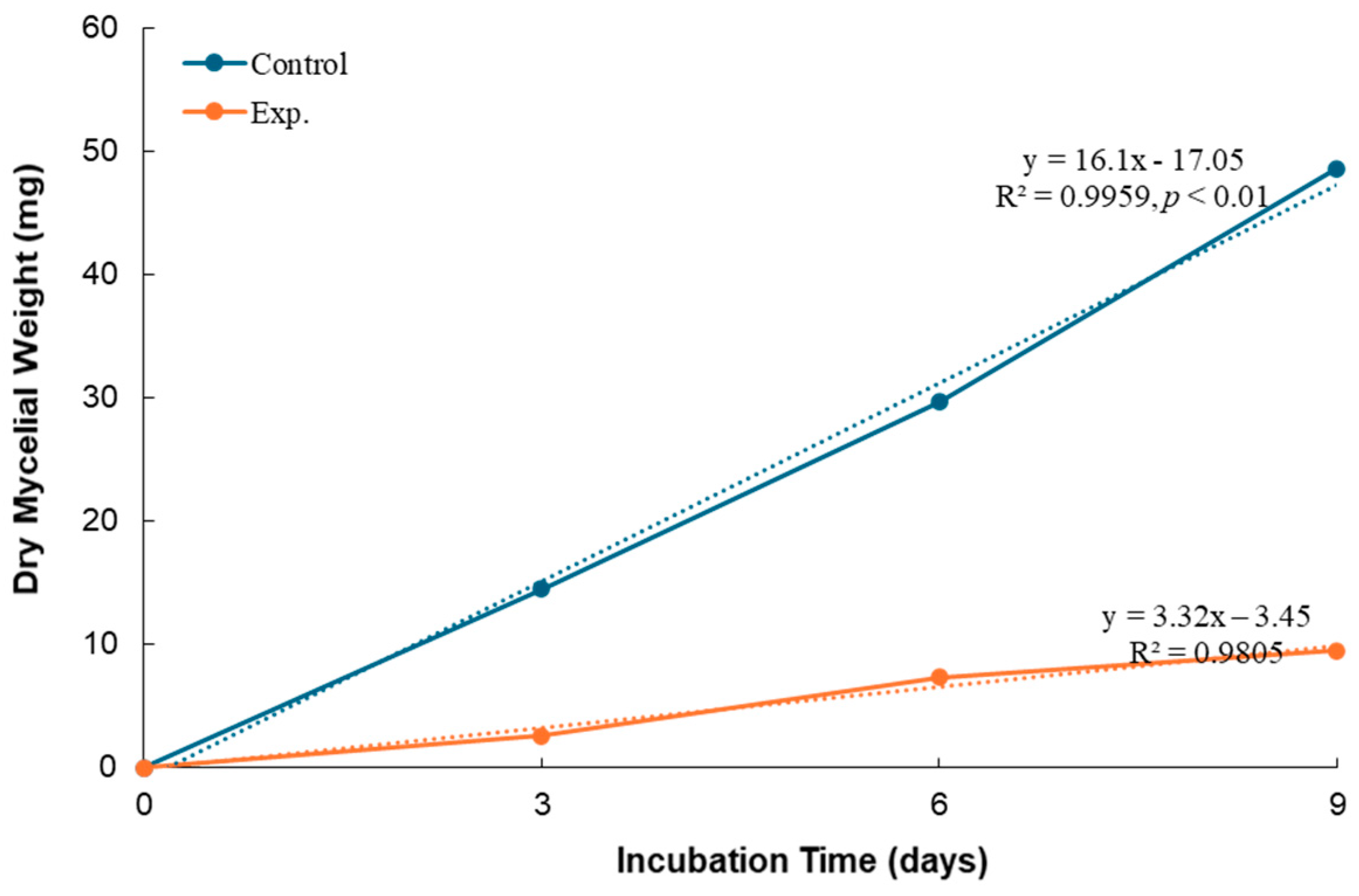
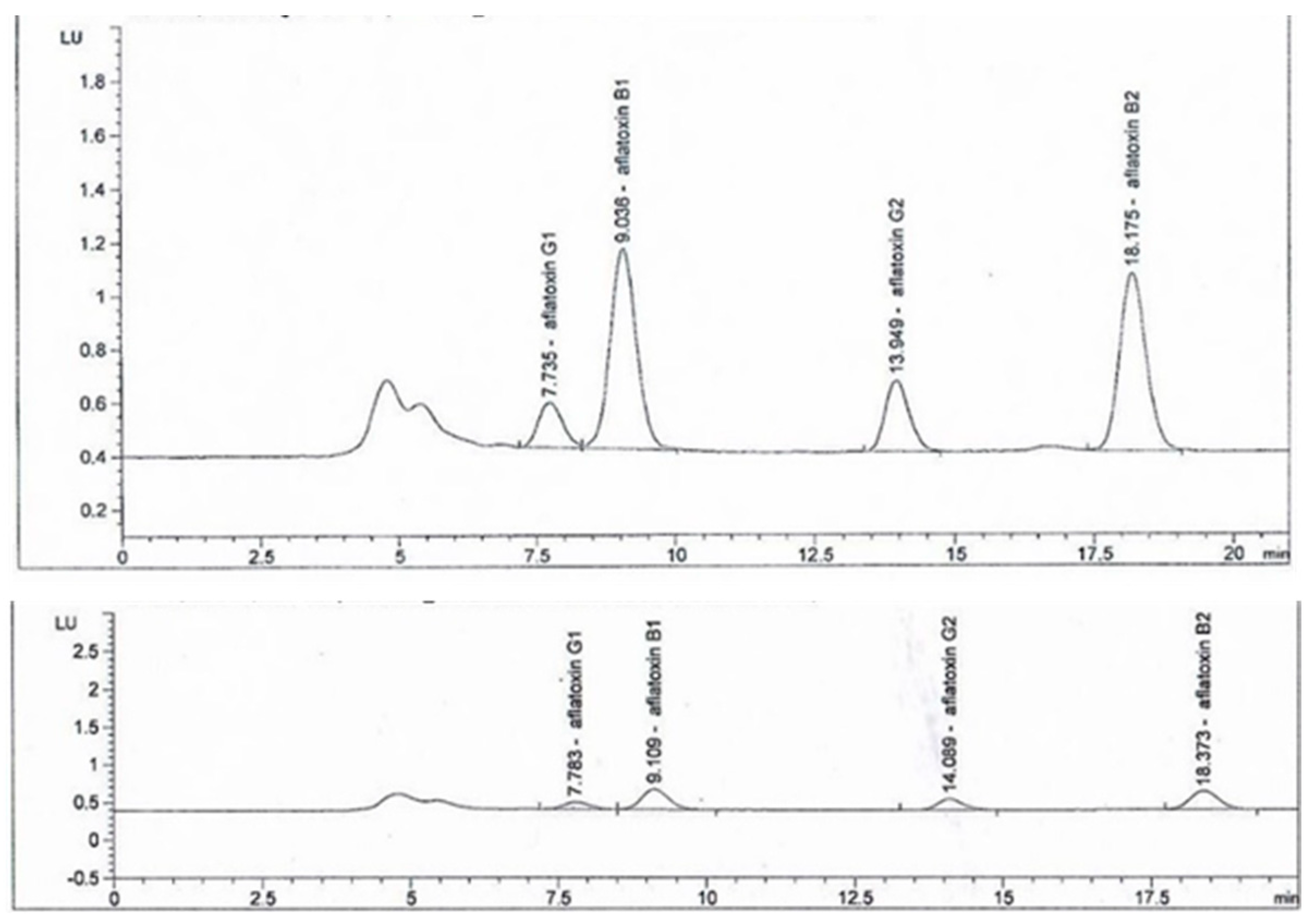
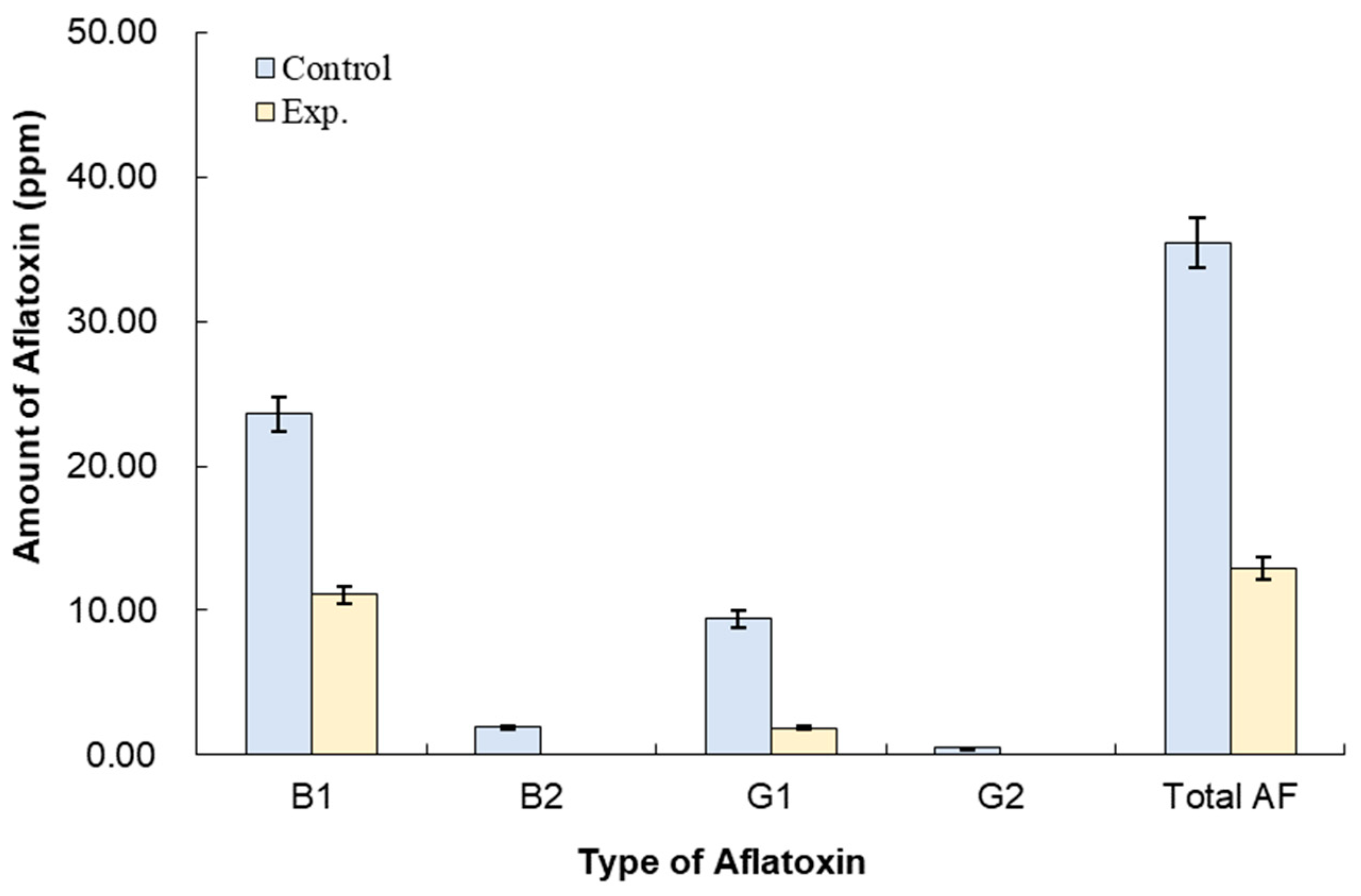
3.3. Effect of B. subtilis K-0924 on the Growth of A. parasiticus and Aflatoxin Production
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, I.K.; Kim, J.G. Effects of dietary supplementation of Korean soybean paste (doen-jang) on the lipid metabolism in rats fed a high fat and/or a high cholesterol diet. J. Korean Publ. Health Assoc. 2002, 28, 282–305. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.L.; Kim, J.G. Inhibitory effects of doen-jang (Korean fermented soybean paste) and soybean extracts on the growth of KB cells. Korean J. Environ. Health 2005, 31, 444–450. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.G.; Lee, Y.W.; Kim, P.G.; Roh, W.S.; Shintani, H. Reduction of aflatoxins by Korean soybean paste and its effect on cytotoxicity and reproductive toxicity-Part 3. Inhibitory effects of Korean soybean paste (doen-jang) on aflatoxin toxicity in laying hens and aflatoxin accumulation in their eggs. J. Food Prot. 2003, 66, 866–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.G. Antigenotoxic effects of water extract from Korean fermented soybean paste (doen-jang). J. Food Prot. 2004, 67, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.G. Changes of components affecting organoleptic quality during the ripening of traditional Korean soybean paste; amino nitrogen, amino acids, and color. Korean J. Environ. Health 2004, 30, 22–28. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, M.H.; Im, S.S.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, G.E. Antioxidative materials in domestic meju and doenjang-separation of hydrophilic brown pigment and their antioxidant activity. J. Korean Soc. Food Nutr. 1994, 23, 604–613. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, K.S.; Chung, H.C.; Choi, J.D.; Kwon, K.I.; Im, M.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Seo, J.S. Effects of meju manufacturing periods on the fermentation characteristics of kanjang. Korean traditional soy sauce. J. Korean Soc. Agric. Chem. Biotechnol. 1999, 42, 277–282. [Google Scholar]
- Baek, J.H.; So, K.-K.; Ko, Y.-H.; Kim, J.-M.; Kim, D.H. Mycoflora and enzymatic characterization of fungal isolates in commercial meju, starter for a Korean traditional fermented soybean product. Mycobiology 2014, 42, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Jeon, C.O. Microbial community dynamics during fermentation of doenjang-meju, traditional Korean fermented soybean. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 185, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Kim, M.C.; Kwon, S.W.; Kim, S.J.; Park, I.C.; Ka, J.O.; Weon, H.Y. Analyses of bacterial communities in meju, a Korean traditional fermented soybean bricks, by cultivation-based and pyrosequencing methods. J. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, S.; Lee, J.M.; Muthaiya, M.J.; Kim, B.S.; Oh, J.Y.; Song, C.K.; Jeon, E.J.; Ryu, H.S.; et al. Mass spectrometry-based metabolite profiling and bacterial diversity characterization of Korean traditional meju during fermentation. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 22, 1523–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.-A.; Kim, E.; Yang, S.M.; Lee, S.; Yoon, S.-R.; Jang, K.-S.; Kim, H. High-throughput sequencing of the microbial community associated with the physicochemical properties of meju (dried fermented soybean) and doenjang (traditional Korean fermented soybean paste). LWT 2021, 146, 111473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.M.; Baek, J.H.; Chun, B.H.; Jeon, C.O. Fermentative features of Bacillus velezensis and Leuconostoc mesenteroides in doenjang-meju, a Korean traditional fermented soybean brick. Food Microbiol. 2023, 110, 104186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, D.-W.; Heo, S.; Lee, B.; Lee, H.; Jeong, K.; Her, J.-Y.; Lee, K.-G.; Lee, J.-J.H. Effects of the predominant bacteria from meju and doenjang on the production of volatile compounds during soybean fermentation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 262, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, A.Y.; Kwon, B.; Kamala-Kannan, S.; Lee, K.J.; Oh, B.T.; Kim, D.H.; Yang, M.S.; Kim, J.H.; Park, S.M. Isolation and characterization of Bacillus polyfermenticus isolated from Meju, Korean soybean fermentation starter. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 26, 1099–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.R.; Ko, Y.J.; Kim, E.J.; Kim, I.H.; Shim, K.H.; Kim, Y.G.; Ryu, C.H. Quality characteristic of wheat Doenjang according to mixing ratio of Meju. Korean J. Food Preserv. 2013, 20, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, H.M.; Han, D.M.; Baek, J.H.; Chun, B.H.; Jeon, C.O. Dynamics and correlation of microbial communities and metabolic compounds in doenjang-meju, a Korean traditional soybean brick. Food Res. Int. 2022, 155, 111085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Choi, H.S.; Hwang, K.A.; Song, J. Quality changes in doenjang upon fermentation with two different Bacillus subtilis strains. J. East Asian Soc. Diet. Life 2016, 26, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.-J.; Park, J.-H.; Cho, J.-I. Control of aflatoxin and characteristics of the quality in doenjang (soybean paste) prepared with antifungal bacteria. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 2000, 32, 1258–1265. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, K.M.; Math, R.K.; Hong, S.Y.; Asraful Islam, S.M.; Mandanna, D.K.; Cho, J.J.; Yun, M.G.; Kim, J.M.; Yun, H.D. Iturin produced by Bacillus pumilus HY1 from Korean soybean sauce (kanjang) inhibits growth of aflatoxin producing fungi. Food Control 2009, 20, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.B.; Lee, M.; Kim, D.H.; Chung, S.H.; Shin, H.D.; Samson, R.A. The proportion of non-aflatoxigenic strains of the Aspergillus flavus/oryzae complex from meju by analyses of the aflatoxin biosynthetic genes. J. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Y.H.; Hyun, M.W.; Suh, D.Y.; Kim, Y.M.; Kim, S.H. Identification and Characterization of Eurotium rubrum isolated from meju in Korea. Mycobiology 2009, 37, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, F.; Freire, F.; Guedes, M.I.F. Mycotoxins and their effects on human and animal health. Food Control 2014, 36, 159–165. [Google Scholar]
- Peles, F.; Sipos, P.; Győri, Z.; Pfliegler, W.P.; Giacometti, F.; Serraino, A.; Pócsi, I. Adverse effects, transformation, and channeling of aflatoxins into food raw materials in livestock. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Mahato, D.K.; Kamle, M.; Mohanta, T.K.; Kang, S.G. Aflatoxins: A global concern for food safety, human health, and their management. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO/IARC (World Health Organization/International Agency for Research on Cancer). Agents Classified by the IARC Monographs. Volume 1–134. Available online: http://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php (accessed on 30 January 2023).
- Binder, E.M.; Tan, L.M.; Chin, L.J.; Handl, J.; Richard, J. Worldwide occurrence of mycotoxins in commodities, feeds and feed ingredients. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2007, 137, 265–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Yan, Q.; Chen, N.; Ling, T.; Wang, J.; Jiang, H. Detoxification of aflatoxin B1 by Stenotrophomonas sp. CW117 and characterization the thermophilic degradation process. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 261, 114178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorner, J.W. Combined effects of biological control formulations, cultivars, and fungicides on preharvest colonization and aflatoxin contamination of peanuts by Aspergillus species. Peanut Sci. 2004, 31, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Moyne, A.L.; Shelby, R.; Cleveland, T.E.; Tuzun, S. Bacillomycin D: An iturin with antifungal activity against Aspergillus flavus. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 90, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Rural Development Administration of Korea. Korean Food Composition Database. Wanjugun, Korea. Available online: https://koreanfood.rda.go.kr/eng/fctFoodSrchEng/list (accessed on 5 January 2024).
- Korea Food Research Institute. Recommended Method of Preparing Korean Meju Cakes and Soybean Paste; Korea Food Research Institute: Sungnam, Korea, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Bergey, D.H.; Holt, J.G. Bergey’s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology, 9th ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Sneath, P.H.A. Endospore-forming Gram-positive rods and cocci. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology; Sneath, P.H.A., Mair, N.S., Sharpe, M.E., Holt, J.G., Eds.; Williams & Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1986; Volume 2, pp. 1104–1139. [Google Scholar]
- bioMérieux. api web. May 2016. Available online: https://apiweb.biomerieux.com (accessed on 30 January 2023).
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI): National Library of Medicine (US). Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Kim, J.G.; Lee, Y.W.; Kim, P.G.; Roh, W.S.; Shintani, H. Reduction of aflatoxins by Korean soybean paste and its effect on cytotoxicity and reproductive toxicity-Part 1. Inhibition of growth and aflatoxin production of Aspergillus parasiticus by Korean soybean paste (doen-jang) and identification of the active component. J. Food Prot. 2000, 63, 1295–1298. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.I.; Kim, H.K.; Yoo, J.T. Characteristics of protease produced by Bacillus subtilis PCA 20-3 isolated from Korean traditional meju. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 2000, 32, 154–160. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, S.I.; Yoo, J.T. Purification of a protease produced by Bacillus subtilis PCA 20-3 isolated from Korean traditional meju. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 1999, 31, 1635–1641. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.S.; Kim, J.K. The identification of Bacillus sp. PM3 fermenting traditional Korean soybean paste. J. Resour. Dev. 2002, 21, 17–30. [Google Scholar]
- Amoa-Awua, W.K.; Terlabie, N.N.; Sakyi-Dawson, E. Screening of 42 Bacillus isolates for ability to ferment soybeans into dawadawa. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2006, 106, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogbadu, L.; Okagbue, R.N. Bacterial fermentation of soya bean for ‘daddawa’ production. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1988, 65, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omafuvbe, B.O.; Shonukan, O.O.; Abiose, S.H. Microbiological and biochemical changes in the traditional fermentation of soybean for soy-daddawa-Nigerian food condiment. Food Microbiol. 2000, 17, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terlbie, N.N.; Sasyi-Dawson, E.; Amoa-Awua, W.K. The comparative ability of four isolates of Bacillus subtilis to ferment soybeans into dawadawa. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2006, 106, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakwa, S.; Sakyi-Dawson, E.; Diako, C.; Annan, N.T.; Amoa-Awua, W.K. Effect of boiling and roasting on the fermentation of soybeans into dawadawa (soy-dawadawa). Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2005, 104, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter of Characteristics | Results | Parameter of Characteristics | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cell diameter > 1.0 Spores round Endospore Gram stain Form Sporangium swollen Parasporal crystals Catalase Anaerobic growth Voges–Proskauer test pH in V-P broth <6 >7 Gas from glucose Indole Acetyl methyl carbinol Citrate | - - + + Rod - - + - + +/- - - + + - | Acids from D-glucose L-arabinose D-xylose D-mannitol Hydrolysis of Casein Gelatin Starch Nitrate reduction Growth 5 °C 20 °C 30 °C 50 °C 60 °C | + + + + + + + + - + + + + |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.-G.; Park, J.-Y. Inhibitory Effects of Bacillus subtilis Isolated from Meju (Fermented Soybean Brick) on the Growth of Aspergillus parasiticus. Appl. Microbiol. 2024, 4, 354-363. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol4010024
Kim J-G, Park J-Y. Inhibitory Effects of Bacillus subtilis Isolated from Meju (Fermented Soybean Brick) on the Growth of Aspergillus parasiticus. Applied Microbiology. 2024; 4(1):354-363. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol4010024
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jong-Gyu, and Jeong-Yeong Park. 2024. "Inhibitory Effects of Bacillus subtilis Isolated from Meju (Fermented Soybean Brick) on the Growth of Aspergillus parasiticus" Applied Microbiology 4, no. 1: 354-363. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol4010024
APA StyleKim, J.-G., & Park, J.-Y. (2024). Inhibitory Effects of Bacillus subtilis Isolated from Meju (Fermented Soybean Brick) on the Growth of Aspergillus parasiticus. Applied Microbiology, 4(1), 354-363. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol4010024






