A Snapshot of the Influent and Effluent Bacterial Populations in a Wastewater Treatment Plant in the North-West Province, South Africa
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and DNA Extraction
2.2. DNA Sequencing and Sequence Analysis
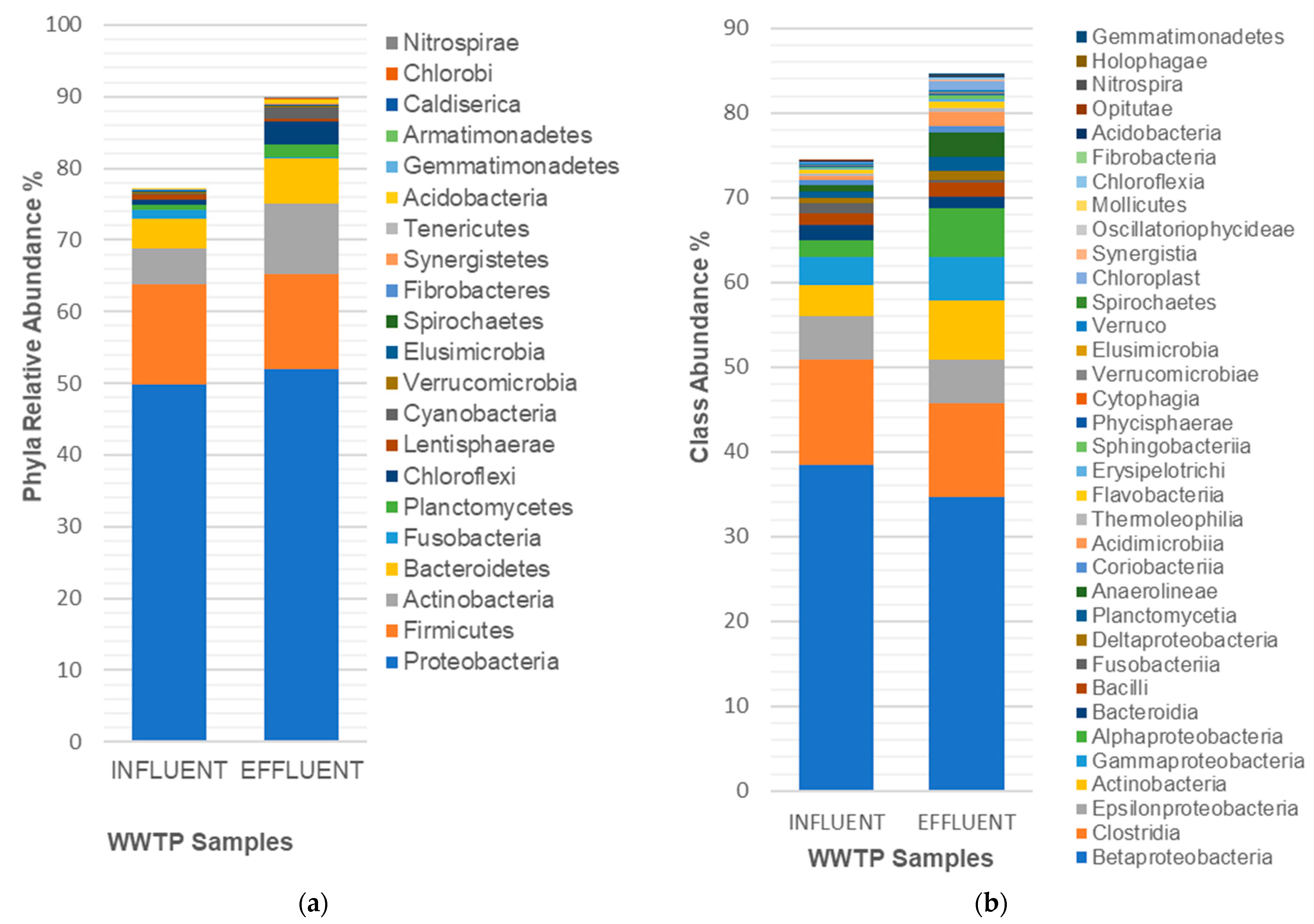
3. Results and Discussion
| Phylum | Class | Genera | Species | Role in Wastewater Treatment Process | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proteobacteria | Betaproteobacteria | Comamonas | C. testosteroni | Denitrification | [43,44] |
| Nitrosomonas | N. marina | Nitrification | [4] | ||
| N. eutropha | Nitrification | ||||
| Gammaproteobacteria | Acinetobacter | A. calcoaceticus | Phosphate removal | [45] | |
| Pseudomonas | P. aeruginosa | Denitrification | [38,40,41,46] | ||
| P. stutzeri | Denitrification | ||||
| P. fluorescens | Phosphate removal | [39,45] | |||
| P. mendocina | Phosphate removal | ||||
| P. Puti4da | Phosphate removal | ||||
| Aeromonas | A. hydrophila | Phosphate removal | [47] | ||
| Alphaproteobacteria | Rhodobacter | R. capsulatus | Denitrification | [48] | |
| Paracoccus | P. denitrificans | Denitrification | [40,49] | ||
| Hyphomicrobium | H. vulgare | Denitrification | [50] | ||
| H. methylovorum | Denitrification | ||||
| Deltaproteobacteria | Desulfovibrio | D. vulgaris | Sulfate removal | [51] | |
| D. oxamicus | Sulfate removal | ||||
| D. longus | Sulfate removal | ||||
| Bacteroidetes | Flavobacteriia | Flavobacterium | F. columnare | Denitrification | [42] |
| F. johnsoniae | Denitrification | ||||
| Firmicutes | Bacilli | Staphylococcus | S. aureus | Phosphate removal | [52] |
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Numberger, D.; Ganzert, L.; Zoccarato, L.; Mühldorfer, K.; Sauer, S.; Grossart, H.-P.; Greenwood, A.D. Characterization of bacterial communities in wastewater with enhanced taxonomic resolution by full-length 16S rRNA sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Makuwa, S.; Tlou, M.; Fosso-Kankeu, E.; Green, E. Evaluation of fecal coliform prevalence and physicochemical indicators in the effluent from a wastewater treatment plant in the north-west province, south africa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, M.; Sharma, N.R. Metagenomic Applications of Wastewater Treatment. In Metagenomics: Techniques, Applications, Challenges and Opportunities; Chopra, R.S., Chopra, C., Sharma, N.R., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, T.; Zhang, B.; Li, F.; Toure, B.; Omosa, I.B.; Chiramba, T.; Abdel-Monem, M.; Pradhan, M. Water and Wastewater Treatment in Africa—Current Practices and Challenges. Clean-Soil Air Water 2014, 42, 1029–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makuwa, S.; Tlou, M.; Fosso-Kankeu, E.; Green, E. The effects of dry versus wet season on the performance of a wastewater treatment plant in North West Province, South Africa. Water SA 2022, 48, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, K.; Barnard, T. The occurrence of pathogenic Escherichia coli in South African wastewater treatment plants as detected by multiplex PCR. Water SA 2010, 36, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jagals, P. Stormwater runoff from typical developed and developing South African urban developments: Definitely not for swimming. Water Sci. Technol. 1997, 35, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collivignarelli, M.C.; Abbà, A.; Alloisio, G.; Gozio, E.; Benigna, I. Disinfection in wastewater treatment plants: Evaluation of effectiveness and acute toxicity effects. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blatchley, E.R. Numerical modelling of UV intensity: Application to collimated-beam reactors and continuous-flow systems. Water Res. 1997, 31, 2205–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendricks, R.; Pool, E.J. The effectiveness of sewage treatment processes to remove faecal pathogens and antibiotic residues. J. Environ. Sci. Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng. 2012, 47, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anastasi, E.M.; Matthews, B.; Stratton, H.M.; Katouli, M. Pathogenic Escherichia coli found in sewage treatment plants and environmental waters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 5536–5541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adefisoye, M.A.; Okoh, A.I. Identification and antimicrobial resistance prevalence of pathogenic Escherichia coli strains from treated wastewater effluents in Eastern Cape, South Africa. Microbiologyopen 2016, 5, 143–151, PMCID:PMC4767426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhi, S.; Banting, G.; Li, Q.; Edge, T.A.; Topp, E.; Sokurenko, M.; Scott, C.; Braithwaite, S.; Ruecker, N.J.; Yasui, Y.; et al. Evidence of naturalized stress-tolerant strains of Escherichia coli in municipal wastewater treatment plants. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 5505–5518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tong, C.; Hu, H.; Chen, G.; Li, Z.; Li, A.; Zhang, J. Chlorine disinfectants promote microbial resistance in Pseudomonas sp. Environ. Res. 2021, 199, 111296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Shuai, X.; Xu, L.; Sun, Y.; Lin, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Meng, L.; Chen, H. Mechanisms underlying the effect of chlorination and UV disinfection on VBNC state Escherichia coli isolated from hospital wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 423, 127228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerva, I.; Remmas, N.; Kagalou, I.; Melidis, P.; Ariantsi, M.; Sylaios, G.; Ntougias, S. Effect of chlorination on microbiological quality of effluent of a full-scale wastewater treatment plant. Life 2021, 11, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannoni, S.J.; Britschgi, T.B.; Moyer, C.L.; Field, K.G. Genetic diversity in Sargasso Sea bacterioplankton. Nature 1990, 345, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugenholtz, P.; Goebel, B.M.; Pace, N.R. Impact of culture-independent studies on the emerging phylogenetic view of bacterial diversity. J. Bacteriol. 1998, 180, 4765–4774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Whitman, W.B.; Coleman, D.C.; Wiebe, W.J. Prokaryotes: The unseen majority. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 6578–6583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenn, T.C. Field guide to next-generation DNA sequencers. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2011, 11, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droege, M.; Hill, B. The Genome Sequencer FLX™ System—Longer reads, more applications, straight forward bioinformatics and more complete data sets. J. Biotechnol. 2008, 136, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qian, P.-Y. Conserved Regions in 16S Ribosome RNA Sequences and Primer Design for Studies of Environmental Microbes. In Encyclopedia of Metagenomics; Nelson, K., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claesson, M.J.; O’Sullivan, O.; Wang, Q.; Nikkilä, J.; Marchesi, J.R.; Smidt, H.; De Vos, W.M.; Paul Ross, R.; O’Toole, P.W. Comparative analysis of pyrosequencing and a phylogenetic microarray for exploring microbial community structures in the human distal intestine. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- García-Moyano, A.; Austnes, A.E.; Lanzén, A.; González-Toril, E.; Aguilera, Á.; Øvreås, L. Novel and Unexpected Microbial Diversity in Acid Mine Drainage in Svalbard (78° N), Revealed by Culture-Independent Approaches. Microorganisms 2015, 3, 667–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cydzik-Kwiatkowska, A.; Zielińska, M. Bacterial communities in full-scale wastewater treatment systems. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 32, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ye, L.; Zhang, T. Bacterial communities in different sections of a municipal wastewater treatment plant revealed by 16S rDNA 454 pyrosequencing. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 2681–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuśmirek, W.; Franus, W.; Nowak, R. Linking de novo assembly results with long DNA reads using the DNAasm-link application. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 7847064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulski, J.K. Next-Generation Sequencing—An Overview of the History, Tools, and “Omic” Applications. Next Gener. Seq.-Adv. Appl. Chall. 2015, 10, 61964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kukurba, K.R.; Montgomery, S.B. RNA sequencing and analysis. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2015, 2015, 951–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Acharya, K.; Halla, F.F.; Massawa, S.M.; Mgana, S.M.; Komar, T.; Davenport, R.J.; Werner, D. Chlorination effects on DNA based characterization of water microbiomes and implications for the interpretation of data from disinfected systems. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 276, 111319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, B.F.; Ng, C.M.; Nshimyimana, J.P.; Loh, L.L.; Gin, K.Y.-H.; Thompson, J.R. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) for assessment of microbial water quality: Current progress, challenges, and future opportunities. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, T.; Shao, M.-F.; Ye, L. 454 Pyrosequencing reveals bacterial diversity of activated sludge from 14 sewage treatment plants. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1137–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Osunmakinde, C.O.; Selvarajan, R.; Mamba, B.; Msagati, T.A.M. Viral communities distribution and diversity in a wastewater treatment plants using high-throughput sequencing analysis. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2021, 30, 3189–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Smith, S.R. Enzyme Recovery from Biological Wastewater Treatment. Waste Biomass Valorization 2021, 12, 4185–4211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasir, M. Analysis of microbial communities and pathogen detection in domestic sewage using metagenomic sequencing. Diversity 2021, 13, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.; Hokajärvi, A.-M.; Domingo, J.S.; Elk, M.; Jayaprakash, B.; Ryu, H.; Siponen, S.; Vepsäläinen, A.; Kauppinen, A.; Puurunen, O.; et al. Bacterial diversity and predicted enzymatic function in a multipurpose surface water system—From wastewater effluent discharges to drinking water production. Environ. Microbiome 2021, 16, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimann, S.; Grattepanche, F.; Rezzonico, E.; Lacroix, C. Development of a real-time RT-PCR method for enumeration of viable Bifidobacterium longum cells in different morphologies. Food Microbiol. 2010, 27, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyahara, M.; Kim, S.-W.; Fushinobu, S.; Takaki, K.; Yamada, T.; Watanabe, A.; Miyauchi, K.; Endo, G.; Wakagi, T.; Shoun, H. Potential of aerobic denitrification by Pseudomonas stutzeri TR2 to reduce nitrous oxide emissions from wastewater treatment plants. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 4619–4625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tian-Ming, C.; Li-Bo, G.; Li-Wei, C.; Shu, C.; Xiao-Dan, L.; Zhong-Li, C.; Shun-Peng, L. Enhanced Biological Phosphorus Removal with Pseudomonas putida GM6 from Activated sludge. Pedosphere 2007, 17, 624–629. [Google Scholar]
- Takaya, N.; Catalan-Sakairi, M.A.B.; Sakaguchi, Y.; Kato, I.; Zhou, Z.; Shoun, H. Aerobic denitrifying bacteria that produce low levels of nitrous oxide. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 3152–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drysdale, G.D.; Kasan, H.C.; Bux, F. Denitrification by heterotrophic bacteria during activated sludge treatment. Water SA 1999, 25, 357–362. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelhamed, H.; Nho, S.; Karsi, A.; Lawrence, M. The role of denitrification genes in anaerobic growth and virulence of Flavobacterium columnare. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 130, 1062–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, T.; Aoi, T.; Miyazato, N.; Hatamoto, M.; Fuchigami, S.; Yamaguchi, T.; Watanabe, Y. Diversity and abundance of denitrifying bacteria in a simultaneously nitrifying and denitrifying rotating biological contactor treating real wastewater at low temperatures. H2Open J. 2019, 2, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, J.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Hu, Z.; Liang, S.; Fan, J.; Liu, H. A review on the sustainability of constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment: Design and operation. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 175, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidat, M.; Bux, F.; Kasan, H.C. Polyphosphate accumulation by bacteria isolated from activated sludge. Water SA 1999, 25, 175–179. [Google Scholar]
- Arat, S.; Bullerjahn, G.S.; Laubenbacher, R. A network biology approach to denitrification in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jha, V.; Chande, S.P.; Purohit, H.J. Seqestration Options for Phosphorus in Wastewater. In Optimization and Applicability of Bioprocesses; Purohit, H., Kalia, V., Vaidya, A., Khardenavis, A., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 115–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, S.; Ganzerli, S.; Rugiero, I.; Pellizzari, S.; Pedrini, P.; Tamburini, E. Potential of Rhodobacter capsulatus grown in anaerobic-light or aerobic-dark conditions as bioremediation agent for biological wastewater treatments. Water 2017, 9, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Medhi, K.; Gupta, A.; Thakur, I.S. Biological nitrogen removal from wastewater by Paracoccus denitrificans ISTOD1: Optimization of process parameters using response surface methodology. J. Energy Environ. Sustain. 2018, 5, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rissanen, A.J.; Ojala, A.; Fred, T.; Toivonen, J.; Tiirola, M. Methylophilaceae and Hyphomicrobium as target taxonomic groups in monitoring the function of methanol-fed denitrification biofilters in municipal wastewater treatment plants. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 44, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torbaghan, M.E.; Torghabeh, G.H.K. Biological removal of iron and sulfate from synthetic wastewater of cotton delinting factory by using halophilic sulfate-reducing bacteria. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sumathi, M.; Vasudevan, N. Removal of phosphate by Staphylococcus aureus under aerobic and alternating anaerobic–aerobic conditions. Environ. Technol. 2018, 39, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chahal, C.; Akker, B.V.D.; Young, F.; Franco, C.; Blackbeard, J.; Monis, P. Pathogen and Particle Associations in Wastewater: Significance and Implications for Treatment and Disinfection Processes. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 97, 63–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanks, O.C.; Newton, R.J.; Kelty, C.A.; Huse, S.M.; Sogin, M.L.; McLellan, S.L. Comparison of the microbial community structures of untreated wastewaters from different geographic locales. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 2906–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jia, S.; Zhang, X. Chapter 3—Biological HRPs in wastewater. In High-risk pollutants in wastewater; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 41–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevik, T.K.; Aa, K.; Ausland, G.; Hanssen, J.F. Retention and removal of pathogenic bacteria in wastewater percolating through porous media: A review. Water Res. 2004, 38, 1355–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coronel-Olivares, C.; Reyes-Gómez, L.M.; Hernández-Muñoz, A.; Martínez-Falcón, A.P.; Vázquez-Rodríguez, G.A.; Iturbe, U. Chlorine disinfection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Total coliforms, Escherichia coli and Enterococcus faecalis: Revisiting reclaimed water regulations. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 64, 2151–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dungeni, M.; Van der Merwe, R.; Momba, M. Abundance of pathogenic bacteria and viral indicators in chlorinated effluents produced by four wastewater treatment plants in the Gauteng Province, South Africa. Water SA 2010, 36, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Phylum | Class | Genus | Species |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proteobacteria | Gammaproteobacteria | Escherichia | E. coli |
| E. fergusonii | |||
| Serratia | S. liquefaciens | ||
| S. odorifera | |||
| S. marcescens | |||
| Aeromonas | A. hydrophila | ||
| A. media | |||
| A. jandaei | |||
| Legionella | L. pneumophila | ||
| L. jamestowniensis | |||
| L. erythra | |||
| Pseudomonas | P. fluorescens | ||
| P. stutzeri | |||
| P. aeruginosa | |||
| Actinobacteria | Actinobacteria | Mycobacterium | M. tuberculosis |
| M. leprae | |||
| Firmicutes | Clostridia | Clostridium | C. septicum |
| C. butyricum | |||
| C. botulinum | |||
| Bacilli | Staphylococcus | S. aureus | |
| S. epidermidis | |||
| S. haemolyticus | |||
| Streptococcus | S. salivarius |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Makuwa, S.; Green, E.; Fosso-Kankeu, E.; Moroaswi, V.; Tlou, M. A Snapshot of the Influent and Effluent Bacterial Populations in a Wastewater Treatment Plant in the North-West Province, South Africa. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 3, 764-773. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol3030053
Makuwa S, Green E, Fosso-Kankeu E, Moroaswi V, Tlou M. A Snapshot of the Influent and Effluent Bacterial Populations in a Wastewater Treatment Plant in the North-West Province, South Africa. Applied Microbiology. 2023; 3(3):764-773. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol3030053
Chicago/Turabian StyleMakuwa, Stenly, Ezekiel Green, Elvis Fosso-Kankeu, Victor Moroaswi, and Matsobane Tlou. 2023. "A Snapshot of the Influent and Effluent Bacterial Populations in a Wastewater Treatment Plant in the North-West Province, South Africa" Applied Microbiology 3, no. 3: 764-773. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol3030053
APA StyleMakuwa, S., Green, E., Fosso-Kankeu, E., Moroaswi, V., & Tlou, M. (2023). A Snapshot of the Influent and Effluent Bacterial Populations in a Wastewater Treatment Plant in the North-West Province, South Africa. Applied Microbiology, 3(3), 764-773. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol3030053






