The Effect of Antibiotic Treatment and Gene Expression of Mex B Efflux Transporters on the Resistance in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Biofilms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search
2.2. Planktonic Cell Growth
2.3. Determination of Minimal Bacterial Concentration (MBC) and Minimal Inhibition Concentration (MIC)
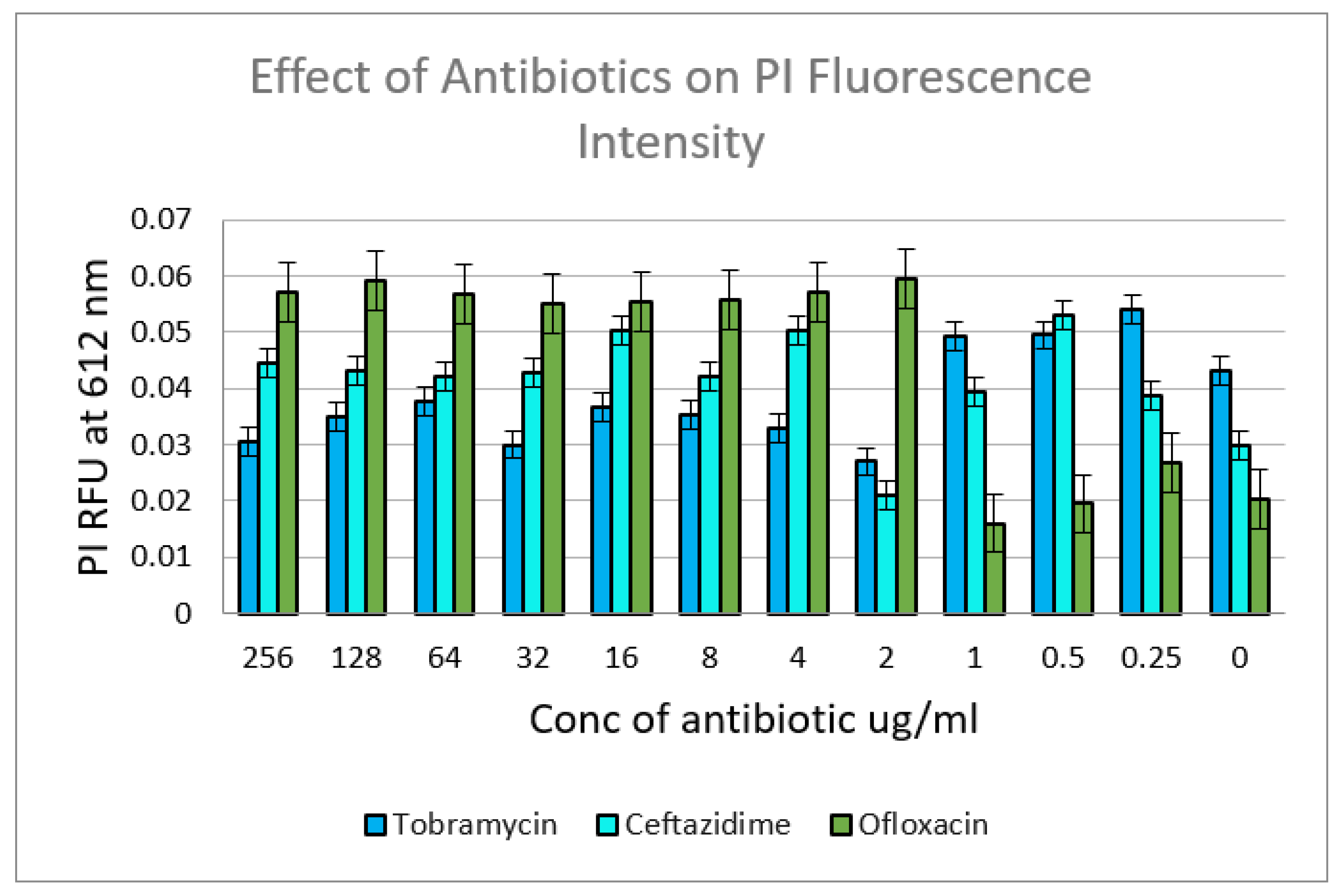
2.4. Viability Assay Using Spectrofluorometric Analysis
2.5. Gene Expression Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Selection of Primers for Gene Expression Studies
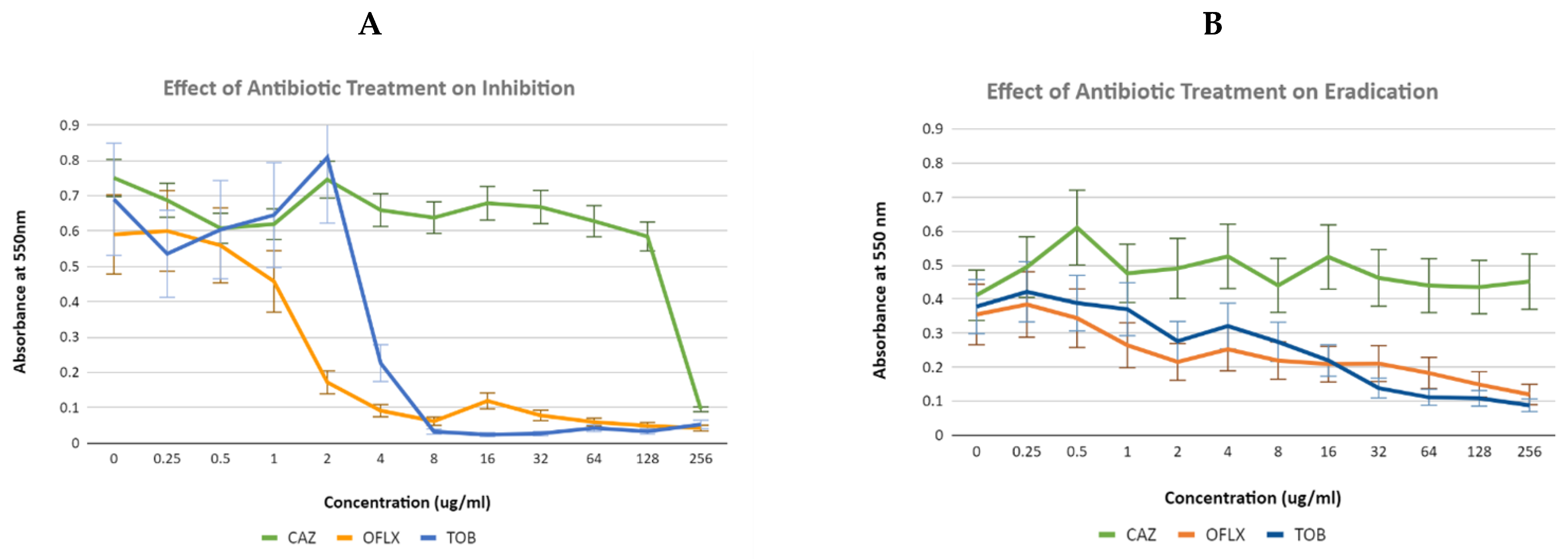
3.2. Effectiveness of Different Antibiotics for Inhibition and Eradication of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Biofilm
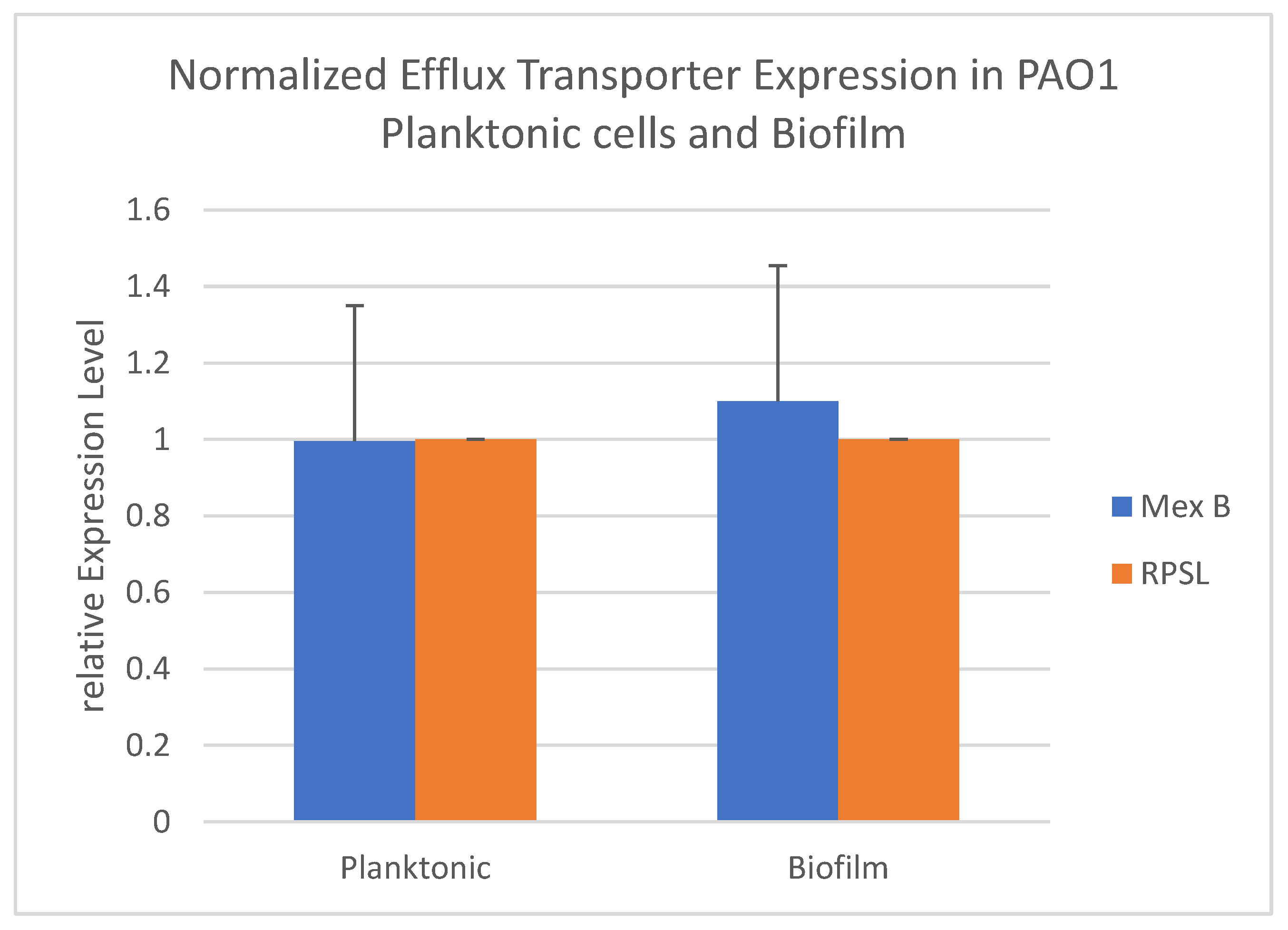
3.3. Changes in Expression of Efflux Transporter Genes in P. aeruginosa during Biofilm Formation
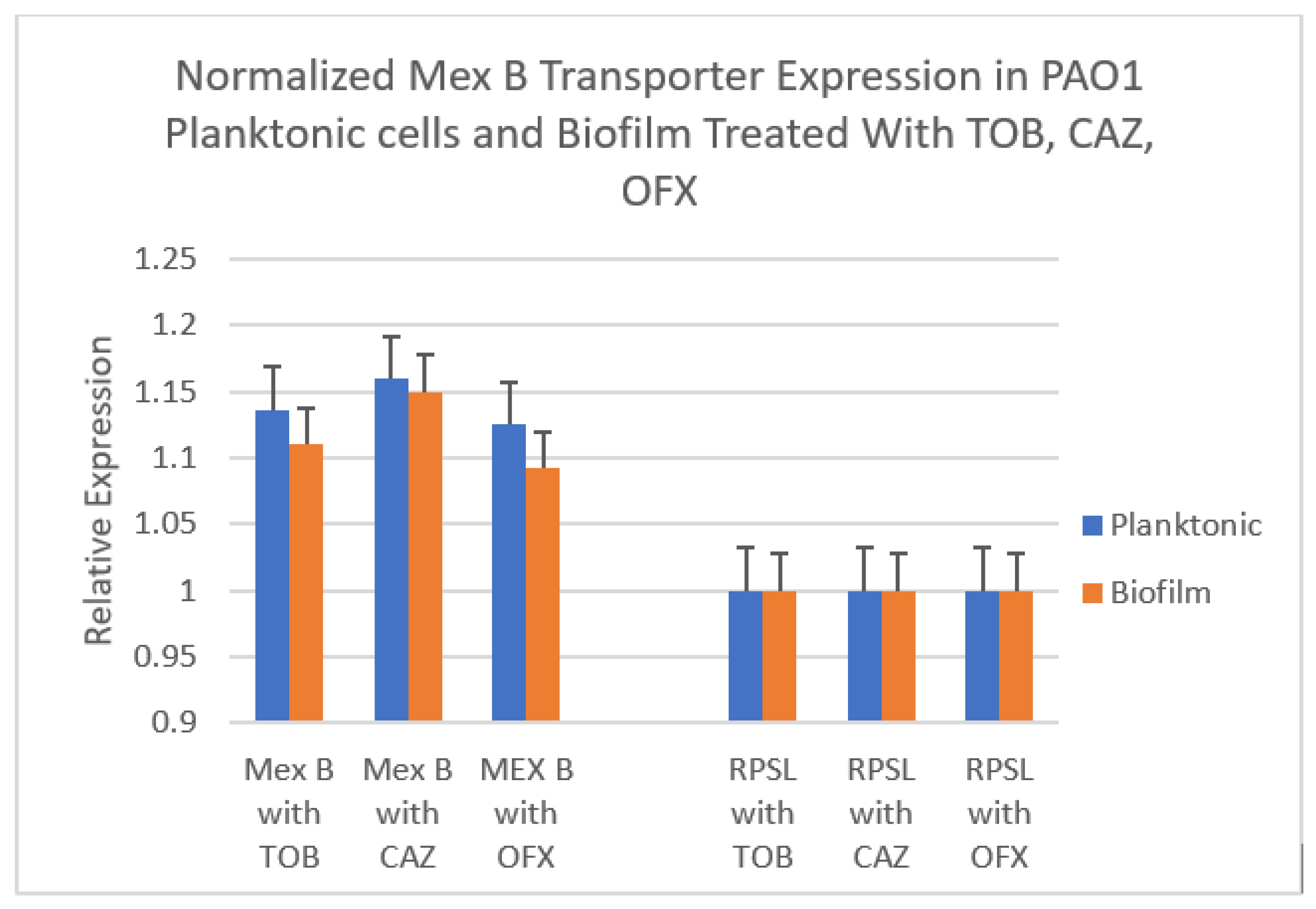
3.4. Effect of Various Antibiotics on Expression of Efflux Transporter Genes in Inhibition and Eradication Phases
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sousa, A.M.; Pereira, M.O. Pseudomonas aeruginosa diversification during infection development in cystic fibrosis Lungs—A review. Pathogens 2014, 3, 680–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walker, J.; Moore, G. Pseudomonas aeruginosa in hospital water systems: Biofilms, guidelines, and practicalities. J. Hosp. Infect. 2014, 89, 324–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lund-Palau, H.; Turnbull, A.R.; Bush, A.; Bardin, E.; Cameron, L.; Soren, O.; Wierre-Gore, N.; Alton, E.W.F.W.; Bundy, J.G.; Connett, G.; et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in cystic fibrosis: Pathophysiological mechanisms and therapeutic approaches. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2016, 10, 685–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourakbari, B.; Yaslianifard, S.; Yaslianifard, S.; Mahmoudi, S.; Keshavarz-Valian, S.; Mamishi, S. Evaluation of efflux pumps gene expression in resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates in an Iranian referral hospital. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2016, 8, 249–256. [Google Scholar]
- Mah, T.F.; O’Toole, G.A. Mechanisms of biofilm resistance to antimicrobial agents. Trends Microbiol. 2001, 9, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Plésiat, P.; Nikaido, H. The challenge of efflux-mediated antibiotic resistance in gram-negative bacteria. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 337–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quddus, S.; Liaqat, Z.; Azam, S.; Haq, M.U.; Ahmad, S.; Alharbi, M.; Khan, I. Identification of Efflux Pump Mutations in Pseudomonas aeruginosa from Clinical Samples. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquez, B. Bacterial efflux systems and efflux pumps inhibitors. Biochimie 2005, 87, 1137–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goli, H.R.; Nahaei, M.R.; Rezaee, M.A.; Hasani, A.; Kafil, H.S.; Aghazadeh, M.; Nikbakht, M.; Khalili, Y. Role of MexAB-OprM and MexXY-OprM efflux pumps and class 1 integrons in resistance to antibiotics in burn and intensive care unit isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Infect. Public Health 2018, 11, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, Y.; Tomida, J.; Kawamura, Y. MexXY multidrug efflux system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hassuna, N.A.; Darwish, M.K.; Sayed, M.; Ibrahem, R.A. Molecular epidemiology and mechanisms of high-level resistance to meropenem and imipenem in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arabestani, M.R.; Rajabpour, M.; Yousefi Mashouf, R.; Alikhani, M.Y.; Mousavi, S.M. Expression of efflux pump MexAB-OprM and OprD of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from clinical samples using qRT-PCR. Arch. Iran. Med. 2015, 18, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alav, I.; Sutton, J.M.; Rahman, K.M. Role of bacterial efflux pumps in biofilm formation. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 2003–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Horna, G.; López, M.; Guerra, H.; Saénz, Y.; Ruiz, J. Interplay between MexAB-OprM and MexEF-OprN in Clinical Isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Llanes, C.; Köhler, T.; Patry, I.; Dehecq, B.; van Delden, C.; Plésiat, P. Role of the MexEF-OprN efflux system in low-level resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to ciprofloxacin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 5676–5684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poole, K. Efflux-mediated antimicrobial resistance. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2005, 56, 20–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masuda, N.; Sakagawa, E.; Ohya, S.; Gotoh, N.; Tsujimoto, H.; Nishino, T. Contribution of the MexX-MexY-OprM efflux system to intrinsic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 2242–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhandari, S.; Adhikari, S.; Karki, D.; Chand, A.B.; Sapkota, S.; Dhungel, B.; Banjara, M.R.; Joshi, P.; Lekhak, B.; Rijal, K.R. Antibiotic Resistance, Biofilm Formation and Detection of mexA/mexB Efflux-Pump Genes Among Clinical Isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a Tertiary Care Hospital, Nepal. Front. Trop. Dis. 2022, 17, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorusso, A.B.; Carrara, J.A.; Barroso, C.D.N.; Tuon, F.F.; Faoro, H. Role of Efflux Pumps on Antimicrobial Resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishk, R.M.; Abdalla, M.O.; Hashish, A.A.; Nemr, N.A.; El Nahhas, N.; Alkahtani, S.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Kishk, S.M. Efflux MexAB-Mediated Resistance in P. aeruginosa Isolated from Patients with Healthcare Associated Infections. Pathogens 2020, 9, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangiaterra, G.; Cedraro, N.; Vaiasicca, S.; Citterio, B.; Galeazzi, R.; Laudadio, E.; Mobbili, G.; Minnelli, C.; Bizzaro, D.; Biavasco, F. Role of Tobramycin in the Induction and Maintenance of Viable but Non-Culturable Pseudomonas aeruginosa in an In Vitro Biofilm Model. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köhler, T.; Michea-Hamzehpour, M.; Henze, U.; Gotoh, N.; Curty, L.K.; Pechère, J.C. Characterization of MexE-MexF-OprN, a positively regulated multidrug efflux system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol. Microbiol. 1997, 23, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumas, J.L.; van Delden, C.; Perron, K.; Köhler, T. Analysis of antibiotic resistance gene expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by quantitative real-time-PCR. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006, 254, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paul, M.; Carmeli, Y. Combination antimicrobial therapy for gram-negative infections. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2008, 14, 230–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huttner, B.; Harbarth, S. Combination antibiotic therapy versus monotherapy for gram-negative bacteraemia: A commentary. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2015, 46, 262–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamma, P.D.; Cosgrove, S.E. Antimicrobial stewardship. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 26, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, D.; Sen, P.; Hlaing, Y.; Boadu, M.; Saadeh, B.; Basu, P. Antimicrobial Resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 15, 2520–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Zhang, L. The hierarchy quorum sensing network in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Protein Cell 2014, 6, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qu, L.; She, P.; Wang, Y.; Liu, F.; Zhang, D.; Chen, L.; Luo, Z.; Xu, H.; Qi, Y.; Wu, Y. Effects of norspermidine on Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation and eradication. MicrobiologyOpen 2016, 5, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rutherford, S.T.; Bassler, B.L. Bacterial quorum sensing: Its role in virulence and possibilities for its control. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a012427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.S.; Iglewski, B.H. Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing as a potential antimicrobial target. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1460–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakhour, J.; Sharara, S.L.; Hindy, J.-R.; Haddad, S.F.; Kanj, S.S. Antimicrobial Treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Severe Sepsis. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahedi Bialvaei, A.; Rahbar, M.; Hamidi-Farahani, R.; Asgari, A.; Esmailkhani, A.; Mardani Dashti, Y.; Soleiman-Meigooni, S. Expression of RND efflux pumps mediated antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical strains. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 153, 104789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Protein | Function | Role in Antibiotic Resistance | Primer Sequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multidrug Resistant Efflux Pump MexA | Resistance- Nodulation- Cell Division (RND) multidrug efflux Periplasmic membrane fusion protein precursor | Transports structurally varied molecules, including antibiotics, out of the bacterial cell | F: 5′-acctacgaggccgactaccaga-3′ R: 5′-gttggtcaccagggcgcctc-3′ |
| Multidrug Resistant Efflux Pump MexB | Resistance- Nodulation- Cell Division (RND) Inner membrane multidrug efflux Transporter protein | Transports structurally varied molecules, including antibiotics, out of the bacterial cell | F: 5′-gtgttcggctcgcagtactc-3′ R: 5′-aaccgtcgggattgaccttg-3′ |
| Outer Membrane Protein OprM | Major intrinsic multiple antibiotic resistance efflux outer membrane protein OprM precursor | Channel-forming outer membrane protein | F: 5′-ccatgagccgccaactgtc-3′ R: 5′-cctggaacgccgtctggat-3′ |
| Multidrug Resistant Efflux Pump MexX | Resistance- Nodulation- Cell Division (RND) multidrug efflux membrane fusion protein MexX precursor | Transports structurally varied molecules, including antibiotics, out of the bacterial cell | F: 5′-tgtacgcgtattcggaacaaggcgtctgc-3′ R: 5′-ttctgctagcgatgtgcatgggtgtccctc-3′ |
| Multidrug Resistant Efflux Pump MexY | Resistance- Nodulation- Cell Division (RND) multidrug efflux transporter MexY | Transports structurally varied molecules, including antibiotics, out of the bacterial cell | F: 5′-tgtactagttgatgcccctagcgaaactctc-3′ R: 5′-tttaagcttgacctacaggacgctgctg-3′ |
| Ribosomal Subunit RPSL | Ribosomal subunit binding rRNA and tRNA, expressed constitutively | Structural constituent of ribosome which serves as Internal control | F: 5′-gctgcaaaactgcccgcaacg-3′ R: 5′-acccgaggtggtccagcgaacc-3′ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kello, E.; Greenberg, R.; Li, W.; Polansky, S.; Maldonado, R.; Peter, Y.; Basu, P. The Effect of Antibiotic Treatment and Gene Expression of Mex B Efflux Transporters on the Resistance in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Biofilms. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 3, 709-721. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol3030049
Kello E, Greenberg R, Li W, Polansky S, Maldonado R, Peter Y, Basu P. The Effect of Antibiotic Treatment and Gene Expression of Mex B Efflux Transporters on the Resistance in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Biofilms. Applied Microbiology. 2023; 3(3):709-721. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol3030049
Chicago/Turabian StyleKello, Evan, Rochelle Greenberg, Weiqi Li, Shaya Polansky, Roberto Maldonado, Yakov Peter, and Paramita Basu. 2023. "The Effect of Antibiotic Treatment and Gene Expression of Mex B Efflux Transporters on the Resistance in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Biofilms" Applied Microbiology 3, no. 3: 709-721. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol3030049
APA StyleKello, E., Greenberg, R., Li, W., Polansky, S., Maldonado, R., Peter, Y., & Basu, P. (2023). The Effect of Antibiotic Treatment and Gene Expression of Mex B Efflux Transporters on the Resistance in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Biofilms. Applied Microbiology, 3(3), 709-721. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol3030049





