Enterotoxin- and Antibiotic-Resistance-Encoding Genes Are Present in Both Coagulase-Positive and Coagulase-Negative Foodborne Staphylococcus Strains
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Identification of Staphylococcus
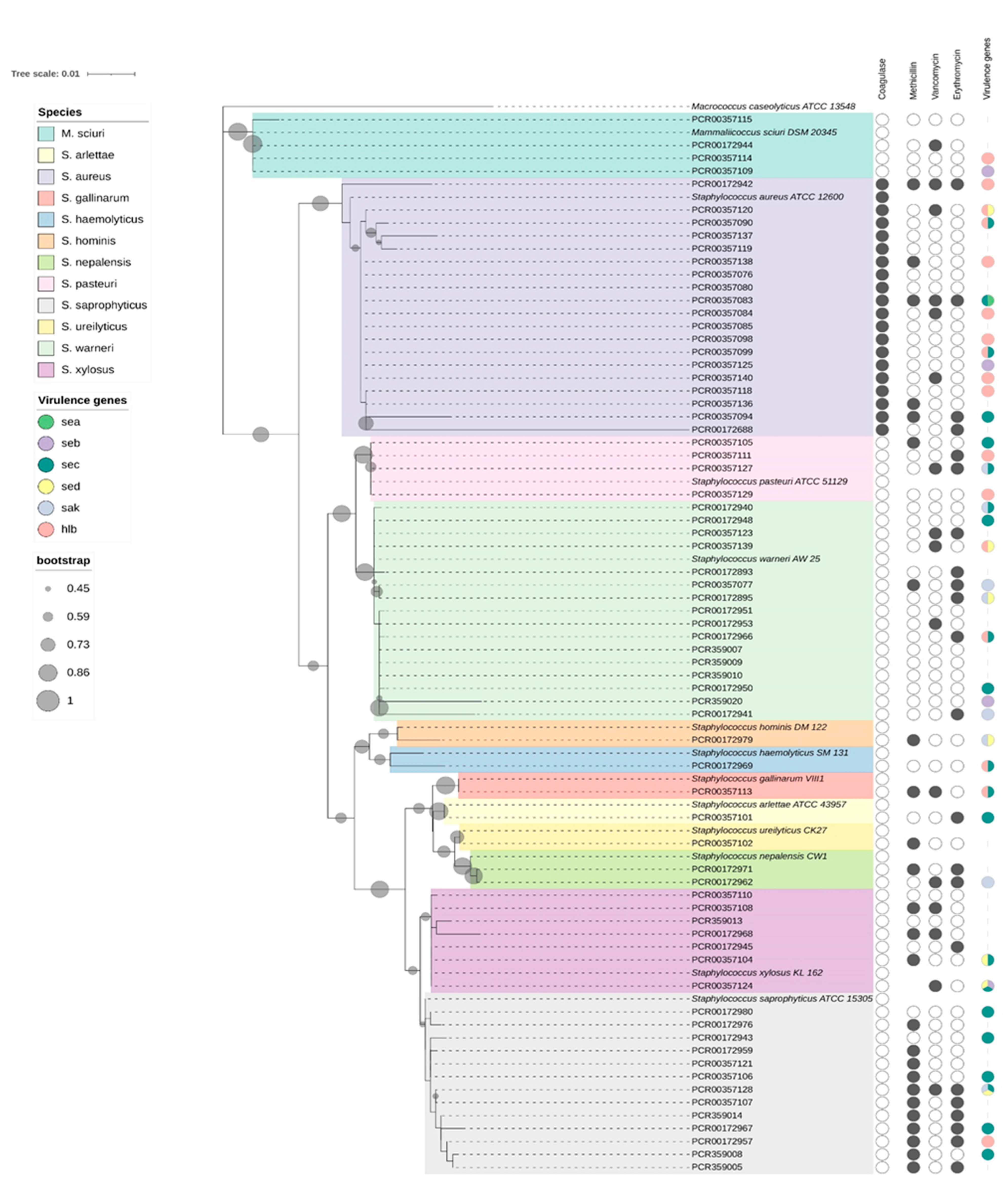
2.2. Species Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.3. PCR for the Identification of Virulence and Antibiotic Resistance Genes
2.4. Antimicrobial-Resistance Profile
2.5. Data Interpretation
3. Results
3.1. Detection of Virulence Genes
3.2. Antimicrobial-Resistance Profile
3.3. Antimicrobial-Resistance Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, J.D.; Negi, Y.K.; Gaur, A.; Khanna, D. Detection of virulence genes in Staphylococcus aureus isolated from paper currency. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 13, e450–e455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adame-Gómez, R.; Castro-Alarcón, N.; Vences-Velázquez, A.; Toribio-Jiménez, J.; Pérez-Valdespino, A.; Leyva-Vázquez, M.A.; Ramírez-Peralta, A. Genetic Diversity and Virulence Factors of S. aureus Isolated from Food, Humans and Animals. Int. J. Microbiol. 2020, 2020, 1048097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begović, J.; Jovčić, B.; Papić-Obradović, M.; Veljović, K.; Lukić, J.; Kojić, M.; Topisirović, L. Genotypic diversity and virulent factors of Staphylococcus epidermidis isolated from human breast milk. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 168, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coates, R.; Moran, J.; Horsburgh, M.J. Staphylococci: Colonizers and pathogens of human skin. Future Microbiol. 2014, 9, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sospedra, I.; Mañes, J.; Soriano, J.M. Report of toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 (TSST-1) from Staphylococcus aureus isolated in food handlers and surfaces from foodservice establishments. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 80, 288–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, D.; Wu, Q.; Xu, M.; Zhang, J.; Yu, S. Prevalence, Virulence Genes, Antimicrobial Susceptibility, and Genetic Diversity of Staphylococcus aureus from Retail Aquatic Products in China. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinchuk, I.V.; Beswick, E.J.; Reyes, V.E. Staphylococcal Enterotoxins. Toxins 2010, 2, 2177–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokarewa, M.I.; Jin, T.; Tarkowski, A. Staphylococcus aureus: Staphylokinase. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2006, 38, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, T.J. Immune evasion by staphylococci. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 948–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piechowicz, L.; Galiński, J.; Garbacz, K.; Haras, K. Bacteriophage analysis of staphylokinase-negative Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from people. J. Basic Microbiol. 2010, 50, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natsis, N.E.; Cohen, P.R. Coagulase-Negative Staphylococcus Skin and Soft Tissue Infections. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2018, 19, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Normanno, G.; La Salandra, G.; Dambrosio, A.; Quaglia, N.C.; Corrente, M.; Parisi, A.; Santagada, G.; Firinu, A.; Crisetti, E.; Celano, G.V. Occurrence, characterization and antimicrobial resistance of enterotoxigenic Staphylococcus aureus isolated from meat and dairy products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 115, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regenthal, P.; Hansen, J.S.; André, I.; Lindkvist-Petersson, K. Thermal stability and structural changes in bacterial toxins responsible for food poisoning. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsuura, S.; Murata, M. Temperature dependence of staphylococcal enterotoxin A production by Staphylococcus aureus. Nihon Rinsho. 2012, 70, 1323–1328. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Necidová, L.; Bursová, Š.; Haruštiaková, D.; Bogdanovičová, K.; Lačanin, I. Effect of heat treatment on activity of staphylococcal enterotoxins of type A, B, and C in milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 3924–3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennekinne, J.A.; De Buyser, M.L.; Dragacci, S. Staphylococcus aureus and its food poisoning toxins: Characterization and outbreak investigation. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 36, 815–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chajęcka-Wierzchowska, W.; Gajewska, J.; Wiśniewski, P.; Zadernowska, A. Enterotoxigenic Potential of Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci from Ready-to-Eat Food. Pathogens 2020, 9, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Martín, M.; Corbera, J.A.; Suárez-Bonnet, A.; Tejedor-Junco, M.T. Virulence factors in coagulase-positive staphylococci of veterinary interest other than Staphylococcus aureus. Vet. Q. 2020, 40, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soumya, K.R.; Philip, S.; Sugathan, S.; Mathew, J.; Radhakrishnan, E.K. Virulence factors associated with Coagulase Negative Staphylococci isolated from human infections. 3 BiotechBiotech 2017, 7, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallander, H.O.; Sanderson, H. Association of methicillin resistance to production of enterotoxin B and other factors in coagulase-positive and coagulase-negative staphylococci. Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Scand. Sect. B Microbiol. Immunol. 1972, 80, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyzik, E.; Marek, A.; Stȩpień-Pyśniak, D.; Urban-Chmiel, R.; Jarosz, L.S.; Jagiełło-Podȩbska, I. Detection of Antibiotic Resistance and Classical Enterotoxin Genes in Coagulase-negative Staphylococci Isolated from Poultry in Poland. J. Vet. Res. 2019, 63, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.Y.; Yang, S.J. Profiles of coagulase-positive and -negative staphylococci in retail pork: Prevalence, antimicrobial resistance, enterotoxigenicity, and virulence factors. Anim. Biosci. 2021, 34, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stapleton, P.D.; Taylor, P.W. Methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus: Mechanisms and modulation. Sci. Prog. 2002, 85, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peacock, S.J.; Paterson, G.K. Mechanisms of methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2015, 84, 577–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoseini Alfatemi, S.M.; Motamedifar, M.; Hadi, N.; Ebrahim Saraie, H.S. Analysis of virulence genes among methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) strains. Jundishapur J. Microbiol. 2014, 7, 10741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, C.J.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Robles Aguilar, G.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 6736, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Bai, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G. Pathogenicity and antibiotic resistance of coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from retailing chicken meat. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 90, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowoyo, P.T.; Ogunbanwo, S.T. Antimicrobial resistance in coagulase-negative staphylococci from Nigerian traditional fermented foods. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2017, 16, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, K.; Zhang, Y. Characterization of methicillin-resistant coagulase-negative staphylococci (MRCoNS) in retail meat. Food Microbiol. 2014, 42, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; He, T.; Schwarz, S.; Zhao, Q.; Shen, Z.; Wu, C.; Shen, J. Multidrug resistance gene cfr in methicillin-resistant coagulase-negative staphylococci from chickens, ducks, and pigs in China. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 303, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamandane, A.; Silva, A.C.; Brito, L.; Malfeito-Ferreira, M. Microbiological assessment of street foods at the point of sale in Maputo (Mozambique). Food Qual. Saf. 2021, 5, fyaa030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamandane, C.; Lobo, M.L.; Afonso, S.; Miambo, R.; Matos, O. Occurrence of intestinal parasites of public health significance in fresh horticultural products sold in Maputo markets and supermarkets, Mozambique. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salamandane, C.; Fonseca, F.; Afonso, S.; Lobo, M.L.; Antunes, F.; Matos, O. Handling of fresh vegetables: Knowledge, hygienic behavior of vendors, public health in Maputo markets, Mozambique. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salamandane, A.; Alves, S.; Chambel, L.; Malfeito-Ferreira, M.; Brito, L. Characterization of Escherichia coli from Water and Food Sold on the Streets of Maputo: Molecular Typing, Virulence Genes, and Antibiotic Resistance. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 2, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadariya, J.; Smith, T.C.; Thapaliya, D. Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcal Food-Borne Disease: An Ongoing Challenge in Public Health. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 827965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivakumar, M.; Dubal, Z.B.; Kumar, A.; Bhilegaonkar, K.; Vinodh Kumar, O.R.; Kumar, S.; Kadwalia, A.; Shagufta, B.; Grace, M.R.; Ramees, T.P.; et al. Virulent methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in street vended foods. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 1116–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamandane, A.; Vila-Boa, F.; Malfeito-Ferreira, M.; Brito, L. High fecal contamination and high levels of antibiotic-resistant Enterobacteriaceae in water consumed in the city of Maputo, Mozambique. Biology 2021, 10, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamandane, A.; Malfeito-Ferreira, M.; Brito, L. A high level of antibiotic resistance in Klebsiella and Aeromonas isolates from street water sold in Mozambique, associated with the prevalence of extended-spectrum and AmpC ß-lactamases. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2022, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Organization for Standardization ISO 6888-1; Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuffs—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Coagulase-Positive Staphylococci (Staphylococcus aureus and Other Species)—Part 1: Technique Using Baird-Parker Agar Medium—Amendmen. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1999.
- International Organization for Standardization ISO 6888-2; Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuffs—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Coagulase-Positive and Other Species)—Staphylococci (Staphylococcus aureus Part 2: Technique Using Rabbit Plasma Fibrinogen Agar Medium. Türk Standartları Enstitüsü: Çankaya, Turkey, 2008.
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejaz, H.; Alzahrani, B.; Hamad, M.F.S.; Abosalif, K.O.A.; Junaid, K.; Abdalla, A.E.; Elamir, M.Y.M.; Aljaber, N.J.; Hamam, S.S.M.; Younas, S. Molecular analysis of the antibiotic resistant NDM-1 gene in clinical isolates of Enterobacteriaceae. Clin. Lab. 2020, 66, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarraud, S.; Mougel, C.; Thioulouse, J.; Lina, G.; Meugnier, H.; Forey, F.; Nesme, X.; Etienne, J.; Vandenesch, F. Relationships between Staphylococcus aureus genetic background, virulence factors, agr groups (alleles), and human disease. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prunier, A.-L.; Malbruny, B.; Laurans, M.; Brouard, J.; Duhamel, J.-F.O.; Leclercq, R. High Rate of Macrolide Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus Strains from Patients with Cystic Fibrosis Reveals High Proportions of Hypermutable Strains. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 187, 1709–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Amery, K.; Elhariri, M.; Elsayed, A.; El-Moghazy, G.; Elhelw, R.; El-Mahallawy, H.; Hariri, M.E.; Hamza, D. Vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from camel meat and slaughterhouse workers in Egypt. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2019, 8, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitkälä, A.; Salmikivi, L.; Bredbacka, P.; Myllyniemi, A.-L.; Koskinen, M.T. Comparison of Tests for Detection of-Lactamase-Producing Staphylococci. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 2031–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russi, N.B.; Maito, J.; Dieser, S.A.; Renna, M.S.; Signorini, M.L.; Camussone, C.; Neder, V.E.; Pol, M.; Tirante, L.; Odierno, L.M.; et al. Comparison of phenotypic tests for detecting penicillin G resistance with presence of blaZ gene in Staphylococcus aureus isolated from bovine intramammary infections. J. Dairy Res. 2015, 82, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milheiriço, C.; Oliveira, D.C.; De Lencastre, H. Update to the multiplex PCR strategy for assignment of mec element types in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 3374–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strommenger, B.; Kettlitz, C.; Werner, G.; Witte, W. Multiplex PCR assay for simultaneous detection of nine clinically relevant antibiotic resistance genes in Staphylococcus aureus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 4089–4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. M100 Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing an Informational Supplement for Global Application Developed through the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute Consensus Process; CLSI: Wayne, NJ, USA, 2021; Volume 27. [Google Scholar]
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grispoldi, L.; Karama, M.; Armani, A.; Hadjicharalambous, C.; Cenci-Goga, B.T. Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin in food of animal origin and staphylococcal food poisoning risk assessment from farm to table. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 20, 677–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, T.; Campos, F.; D’azevedo, P.; Sand, S.; Franco, A.; Frazzon, J.; Frazzon, A. Prevalence of enterotoxin-encoding genes and antimicrobial resistance in coagulase-negative and coagulase-positive Staphylococcus isolates from black pudding. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2012, 45, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasaj, M.; Saeidi, Z.; Tahmasebi, H.; Dehbashi, S.; Arabestani, M.R. Prevalence and distribution of resistance and enterotoxins/enterotoxin-like genes in different clinical isolates of coagulase-negative Staphylococcus. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2020, 25, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Divyakolu, S.; Chikkala, R.; Ratnakar, K.S.; Sritharan, V.; Divyakolu, S.; Chikkala, R.; Ratnakar, K.S.; Sritharan, V. Hemolysins of Staphylococcus aureus—An Update on Their Biology, Role in Pathogenesis and as Targets for Anti-Virulence Therapy. Adv. Infect. Dis. 2019, 9, 80–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vubil, D.; Garrine, M.; Ruffing, U.; Acácio, S.; Sigaúque, B.; Alonso, P.L.; von Müller, L.; Herrmann, M.; Mandomando, I. Molecular Characterization of Community Acquired Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia in Young Children in Southern Mozambique, 2001–2009. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaumburg, F.; Alabi, A.S.; Peters, G.; Becker, K. New epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus infection in Africa. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nhatsave, N.; Garrine, M.; Messa, A.; Massinga, A.; Cossa, A.; Vaz, R.; Ombi, A.; Zimba, T.; Alfredo, H.; Mandomando, I.; et al. Molecular characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from raw Milk samples of dairy cows in Manhiça district, southern Mozambique. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergelidis, D.; Abrahim, A.; Papadopoulos, T.; Soultos, N.; Martziou, E.; Koulourida, V.; Govaris, A.; Pexara, A.; Zdragas, A.; Papa, A. Isolation of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus spp. from ready-to-eat fish products. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 59, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oosthuysen, W.F.; Orth, H.; Lombard, C.J.; Sinha, B.; Wasserman, E. Population structure analyses of Staphylococcus aureus at Tygerberg Hospital, South Africa, reveals a diverse population, a high prevalence of Panton–Valentine leukocidin genes, and unique local methicillin-resistant S. aureus clones. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Moremi, N.; Claus, H.; Vogel, U.; Mshana, S.E. The role of patients and healthcare workers Staphylococcus aureus nasal colonization in occurrence of surgical site infection among patients admitted in two centers in Tanzania. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2019, 8, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kateete, D.P.; Bwanga, F.; Seni, J.; Mayanja, R.; Kigozi, E.; Mujuni, B.; Ashaba, F.K.; Baluku, H.; Najjuka, C.F.; Källander, K.; et al. CA-MRSA and HA-MRSA coexist in community and hospital settings in Uganda. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2019, 8, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govender, V.; Madoroba, E.; Magwedere, K.; Fosgate, G.; Kuonza, L. Prevalence and risk factors contributing to antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from poultry meat products in South Africa, 2015–2016. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 2019, 90, e1–e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seng, R.; Kitti, T.; Thummeepak, R.; Kongthai, P.; Leungtongkam, U.; Wannalerdsakun, S.; Sitthisak, S. Biofilm formation of methicillin-resistant coagulase negative staphylococci (MR-CoNS) isolated from community and hospital environments. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Shah, H.N.; Misra, R.; Chen, J.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Cutler, R.R.; Mkrtchyan, H.V. The prevalence, antibiotic resistance and mecA characterization of coagulase negative staphylococci recovered from non-healthcare settings in London, UK. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2018, 7, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Lin, J.; Li, L.; Cai, W.; Ye, J.; He, S.; Zhang, W.; Liu, N.; Gong, Z.; Ye, X.; et al. Methicillin-Resistant Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci Carriage is a Protective Factor of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Nasal Colonization in HIV-Infected Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2021, 2021, 5717413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asante, J.; Hetsa, B.; Amoakoo, D.; Abia, A.; Bester, L.; Essack, S. Multidrug-Resistant Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci Isolated from Bloodstream in the uMgungundlovu District of KwaZulu-Natal Province in South Africa: Emerging Pathogens. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Sabokroo, N.; Wang, Y.; Hashemian, M.; Karamollahi, S.; Kouhsari, E. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the epidemiology of vancomycin-resistance Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2021, 10, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandomando, I.; Sigaúque, B.; Morais, L.; Espasa, M.; Vallès, X.; Sacarlal, J.; Macete, E.; Aide, P.; Quintò, L.; Nhampossa, T.; et al. Antimicrobial drug resistance trends of bacteremia isolates in a rural hospital in southern Mozambique. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 83, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deurenberg, R.H.; Vink, C.; Kalenic, S.; Friedrich, A.W.; Bruggeman, C.A.; Stobberingh, E.E. The molecular evolution of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2007, 13, 222–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowy, F.D. Antimicrobial resistance: The example of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Clin. Investg. 2003, 111, 1265–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Virulence Factor (Target Gene) | Primer Sequence (5′–3′) | Amplicon Size (bp) | Annealing Temperature (°C)/Time (s) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enterotoxin A (sea) | seaF | TGCAGGGAACAGCTTTAGGC | 250 | 52/30 |
| seaR | GTGTACCACCCGCACATTGA | |||
| Enterotoxin B (seb) | sebF | ATTCTATTAAGGACACTAAGTTAGGG | 400 | 52/45 |
| sebR | ATCCCGTTTCATAAGGCGAGT | |||
| Enterotoxin C (sec) | secF | GTAAAGTTACAGGTGGCAAAACTTG | 297 | 52/45 |
| secR | CATATCATACCAAAAAGTATTGCCGT | |||
| Enterotoxin D (sed) | sedF | GAATTAAGTAGTACCGCGCTAAATAATATG | 492 | 52/45 |
| sedR | GCTGTATTTTTCCTCCGAGAGT | |||
| Enterotoxin E (see) | seeF | CAAAGAAATGCTTTAAGCAATCTTAGGC | 480 | 52/30 |
| seeR | CACCTTACCGCCCAAAGCTG | |||
| Hemolysin (hlb) | hlbF | GTGCACTTACTGACAATAGTGC | 300 | 52/30 |
| hlbR | GTTGATGAGTAGCTACCTTCAGT | |||
| Staphylokinase (sak) | sakF | ATCCCGTTTCATAAGGCGAGT | 260 | 52/45 |
| sakR | CACCTTACCGCCCAAAGCTG | |||
| Resistance to the Antibiotic | Primer for the Target Gene | Primer Sequence (5′–3′) | Amplicon Size (bp) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Penicillin | blaZ-F | AAGAGATTTGCCTATGCTTC | 170 | [46,47] |
| blaZ-R | GCTTGACCACTTTTATCAGC | |||
| Methicillin | mecA-F | TCCAGATTACAACTTCACCAGG | 180 | [48] |
| mecA-R | CCACTTCATATCTTGTAACG | |||
| Erythromycin | ermA-F | AAGCGGTAAACCCCTCTGA | 190 | [49] |
| ermA-R | TTCGCAAATCCCTTCTCAAC | |||
| ermB-F | TCAAAACATAATATAGATAAA | 642 | [44] | |
| ermB-R | GCTAATATTGTTTAAATCGTCAAT | |||
| ermC-F | AATCGTCAATTCCTGCATGT | 299 | [49] | |
| ermC-R | TAATCGTGGAATACGGGTTTG | |||
| Vancomycin | vancA-F | GGCAAGTCAGGTGAAGATG | 713 | [45] |
| vancA-R | ATCAAGCGGTCAATCAGTTC | |||
| vancB-F | GTGACAAACCGGAGGCGAGGA | 430 | ||
| vancB-R | CCGCCATCCTCCTGCAAAAAA |
| Virulence Genes | CPS (n = 19) | CNS (n = 47) | Total (n = 66) |
|---|---|---|---|
| sea * | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| seb * | 1 | 3 (6.4%) | 4 (6.1%) |
| sec * | 3 (15.8%) | 17 (36.2%) | 20 (30.3%) |
| sed * | 2 | 6 (12.8%) | 8 (12.1%) |
| see * | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| hlb | 9 (47.4%) | 7 (14.9%) | 16 (24.2%) |
| sak | 0 | 8 (17%) | 8 (12.1%) |
| Total | 16 (84.2%) | 41 (87.2%) | 57 (86.4%) |
| Antibiotic Group | Antibiotic | CPS (n = 19) | CNS (n = 47) | Total (n = 66) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| β-lactam | FOX (30 μg) | 5 (26.3%) | 20 (42.6%) | 25 (37.9%) |
| AMP (10 μg) | 5 (26.3%) | 6 (12.8%) | 11 (16.7%) | |
| MET (5 μg) | 5 (26.3%) | 20 (42.6%) | 25 (37.9%) | |
| VAN (5 μg) | 5 (26.3%) | 10 (21.3%) | 15 (27.7%) | |
| PEN (10 μg) | 11 (57.9%) | 44 (93.6%) | 55 (83.3%) | |
| Non- β-lactam | CHL (30 μg) | 0 | 2 (4.3%) | 2 (3%) |
| TET (30 μg) | 1 | 3 (6.4%) | 4 (6.1%) | |
| GEN (10 μg) | 0 | 2 (4.3%) | 2 (3%) | |
| SXT (23.75/1.25 μg) | 0 | 4 (8.5%) | 4 (6.1%) | |
| ERY (16 μg) | 4 (21.1%) | 18 (38.3%) | 22 (33.3%) | |
| CIP (5 μg) | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| LVX (5 μg) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Antibiotic-Resistance Gene | CPS (n = 19) | CNS (n = 47) | Total (n = 66) |
|---|---|---|---|
| bla-Z | 8 (42.1%) | 41 (87.2%) | 49 (74.2%) |
| mecA | 7 (36.8%) | 22 (46.8%) | 29 (43.9%) |
| vancA | 6 (31.6%) | 22 (46.8%) | 28 (42.4%) |
| vancB | 0 | 7 (14.9%) | 7 (10.6%) |
| ermA | 4 (21.1%) | 3 (6.4%) | 7 (10.6%) |
| ermB | 1 | 7 (14.9%) | 8 (12.1%) |
| ermC | 5 (26.3%) | 2 (4.3%) | 7 (10.6%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salamandane, A.; Oliveira, J.; Coelho, M.; Ramos, B.; Cunha, M.V.; Malfeito-Ferreira, M.; Brito, L. Enterotoxin- and Antibiotic-Resistance-Encoding Genes Are Present in Both Coagulase-Positive and Coagulase-Negative Foodborne Staphylococcus Strains. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 2, 367-380. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol2020028
Salamandane A, Oliveira J, Coelho M, Ramos B, Cunha MV, Malfeito-Ferreira M, Brito L. Enterotoxin- and Antibiotic-Resistance-Encoding Genes Are Present in Both Coagulase-Positive and Coagulase-Negative Foodborne Staphylococcus Strains. Applied Microbiology. 2022; 2(2):367-380. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol2020028
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalamandane, Acácio, Jessica Oliveira, Miguel Coelho, Beatriz Ramos, Mónica V. Cunha, Manuel Malfeito-Ferreira, and Luisa Brito. 2022. "Enterotoxin- and Antibiotic-Resistance-Encoding Genes Are Present in Both Coagulase-Positive and Coagulase-Negative Foodborne Staphylococcus Strains" Applied Microbiology 2, no. 2: 367-380. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol2020028
APA StyleSalamandane, A., Oliveira, J., Coelho, M., Ramos, B., Cunha, M. V., Malfeito-Ferreira, M., & Brito, L. (2022). Enterotoxin- and Antibiotic-Resistance-Encoding Genes Are Present in Both Coagulase-Positive and Coagulase-Negative Foodborne Staphylococcus Strains. Applied Microbiology, 2(2), 367-380. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol2020028







