Response of Prokaryotic Communities to Freshwater Salinization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.2. Sampling and Physicochemical Measurements
2.3. Filtration, DNA Extraction, and dPCR
2.4. Sequencing and Sequence Processing
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Archaeal Absolute Abundance and 16S rRNA Gene Diversity
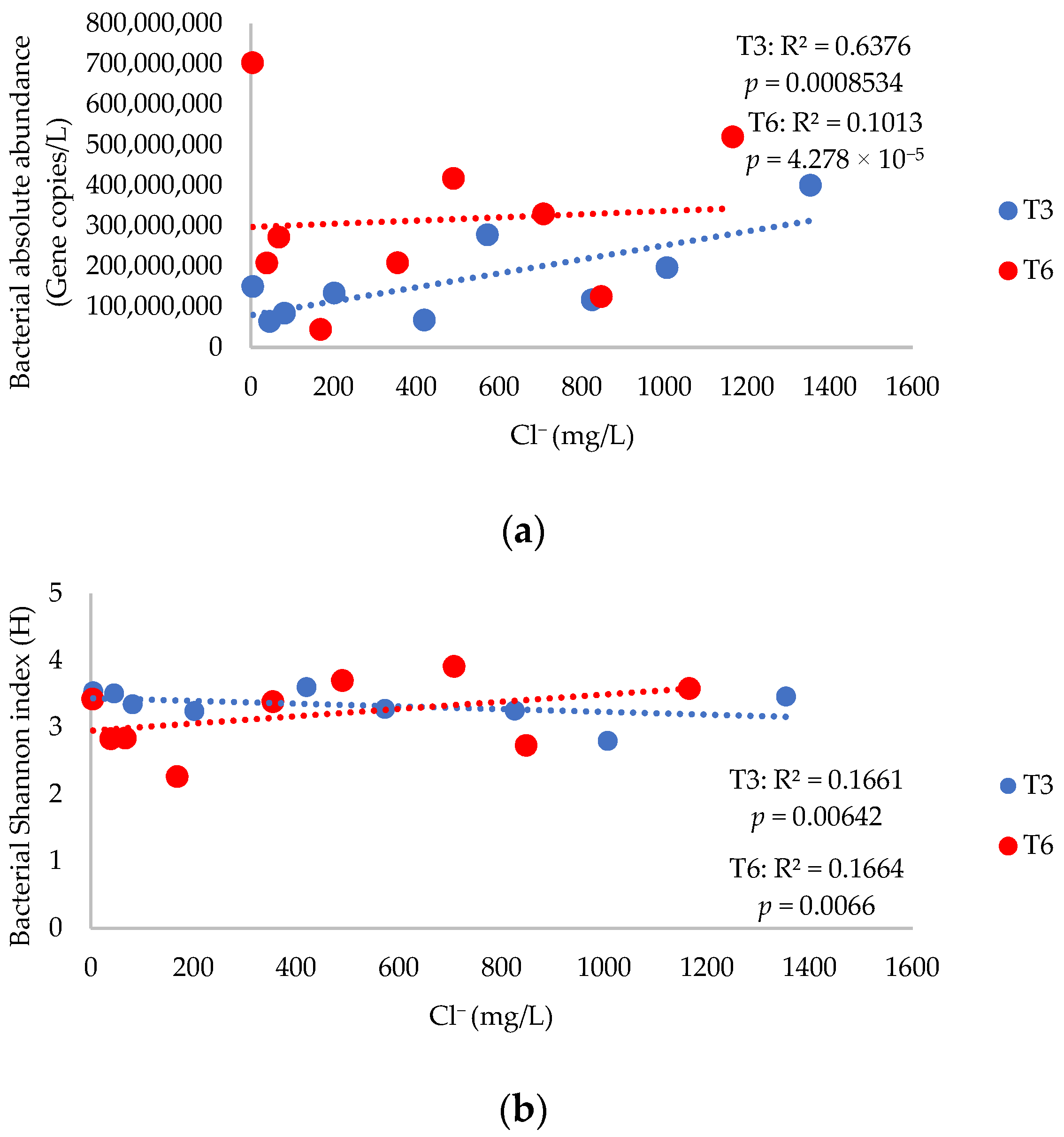
3.2. Bacterial Absolute Abundance, Alpha Diversity Indices, and 16S rRNA Gene Diversity
3.3. Correlation between Bacterial Taxa Relative Abundances and Chloride Levels
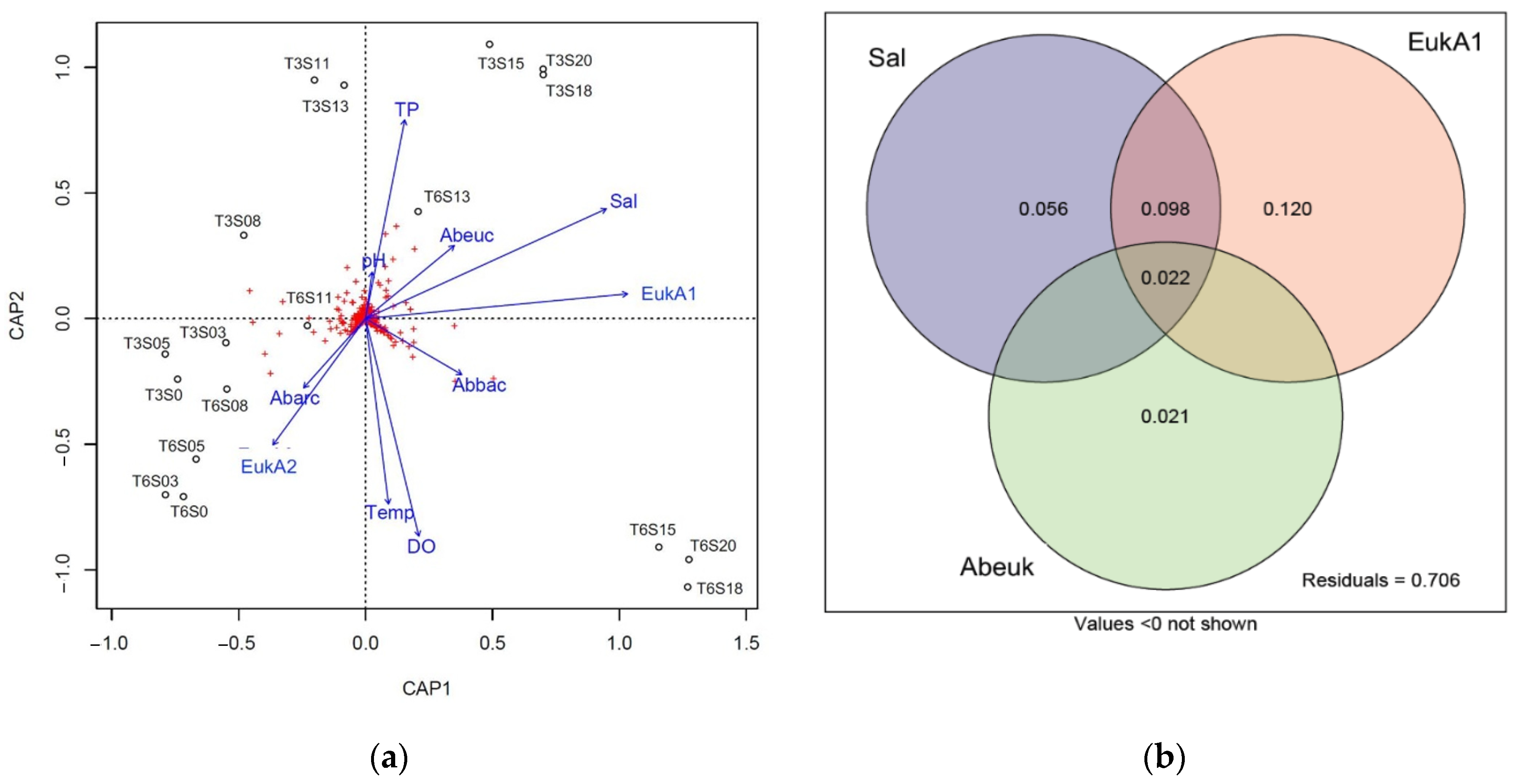
3.4. Correlation between Bacterial Beta Diversity and Abiotic Factors
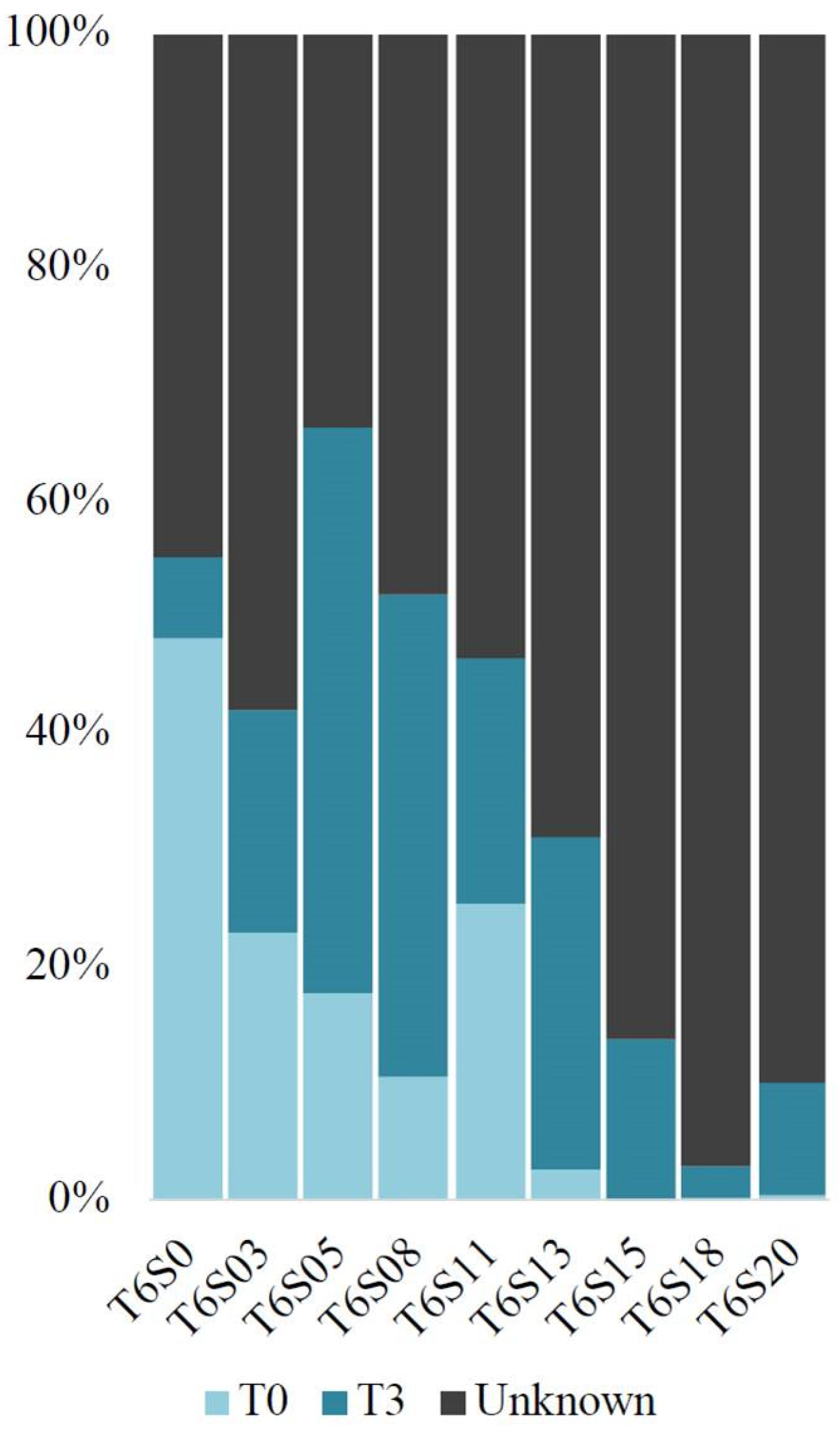
3.5. Microbial Source Tracking
3.6. Significantly Different OTUs between Bacterial Sample Groups
4. Discussion
4.1. Direct and Indirect Effect of Salinity on Prokaryotic Communities
4.2. Influence of Salinity on Bacterial Community Transition
4.3. Microbial Source Tracking and Overall Procaryotic Transitional Community Trends
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gouvernement of Canada. Code de Pratique de la Gestion Environnementale des sels de Voirie. 2018. Available online: https://www.canada.ca/fr/environnement-changement-climatique/services/polluants/sels-voirie/code-pratique-gestion-environnementale.html (accessed on 18 September 2020).
- Schuler, M.S.; Cañedo-Argüelles, M.; Hintz, W.D.; Dyack, B.; Birk, S.; Relyea, R.A. Regulations are needed to protect freshwater ecosystems from salinization. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 374, 20180019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- CCME-Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment. Scientific Criteria Document for the Development of the Canadian Water Quality Guidelines for the Protection of Aquatic Life: Chloride Ion; Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment: Winnipeg, BC, Canada, 2011; ISBN 9781-896997-77-3. PN 1460. [Google Scholar]
- Galella, J.G.; Kaushal, S.; Wood, K.L.; Reed, L. Freshwater Salinization Syndrome: Anthropogenic effects of road salting over land use and time. In AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts; American, Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; p. H43Q-2319. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, V.R.; Findlay, S.E.G.; Weathers, K.C. Road Salt: The Problem, the Solution, and How to Get There; Cary Institute of Ecosystem Studies: Millbrook, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Astorg, L.; Gagnon, J.; Lazar, C.S.; Derry, A.M. Effects of freshwater salinization on a salt-naïve planktonic eukaryote community. Limnol. Oceanogr. Lett. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionard, M.; Muylaert, K.; Gansbeke, D.V.; Vyverman, W. Influence of changes in salinity and light intensity on growth of phytoplankton communities from the Schelde river and estuary (Belgium/The Netherlands). Hydrobiologia 2005, 540, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavsanoglu, U.N.; Maleki, R.; Akbulut, N. Effects of Salinity on the Zooplankton Community Structure in Two Maar Lakes and One Freshwater Lake in the Konya Closed Basin, Turkey. Ekoloji Derg. 2015, 24, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschini, J. Exploring the Impacts of Increased Salinity on Zooplankton Communities in Sturgeon Lake. Bachelor’s Thesis, Wilfrid Laurier University, Waterloo, ON, Canada, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Moffett, E.R.; Baker, H.K.; Bonadonna, C.C.; Shurin, J.B.; Symons, C.C. Cascading effects of freshwater salinization on plankton communities in the Sierra Nevada. Limnol. Oceanogr. Lett. 2020, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, D.L.; Brock, M.A.; Vogel, M.; Petrie, R. From fresh to saline: A comparison of zooplankton and plant communities developing under a gradient of salinity with communities developing under constant salinity levels. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2008, 59, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hintz, W.D.; Jones, D.K.; Relyea, R.A. Evolved tolerance to freshwater salinization in zooplankton: Life-history trade-offs, cross-tolerance and reducing cascading effects. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 374, 20180012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coldsnow, K.D.; Mattes, B.M.; Hintz, W.D.; Relyea, R.A. Rapid evolution of tolerance to road salt in zooplankton. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 222, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishika, T.; Bahri, P.A.; Laird, D.W.; Moheimani, N.R. The effect of gradual increase in salinity on the biomass productivity and biochemical composition of several marine, halotolerant, and halophilic microalgae. J. Appl. Phycol. 2018, 30, 1453–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottrell, M.; Kirchman, D. Single-cell analysis of bacterial growth, cell size, and community structure in the Delaware estuary. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2004, 34, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouvier, T.C.; del Giorgio, P. Compositional changes in free-living bacterial communities along a salinity gradient in two temperate estuaries. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2002, 47, 453–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herlemann, D.P.R.; Labrenz, M.; Jürgens, K.; Bertilsson, S.; Waniek, J.J.; Andersson, A.F. Transitions in bacterial communities along the 2000 km salinity gradient of the Baltic Sea. ISME J. 2011, 5, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henriques, I.S.; Alves, A.; Tacão, M.; Almeida, A.; Cunha, A.; Correia, A. Seasonal and spatial variability of free-living bacterial community composition along an estuarine gradient (Ria de Aveiro, Portugal). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2006, 68, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolomé, M.C.; D’ors, A.; Sánchez-Fortún, S. Toxic effects induced by salt stress on selected freshwater prokaryotic and eukaryotic microalgal species. Ecotoxicology 2009, 18, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kartal, B.; Koleva, M.; Arsov, R.; van der Star, W.; Jetten, M.S.; Strous, M. Adaptation of a freshwater anammox population to high salinity wastewater. J. Biotechnol. 2006, 126, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushal, S.S.; Likens, G.E.; Pace, M.L.; Reimer, J.E.; Maas, C.M.; Galella, J.G.; Utz, R.M.; Duan, S.; Kryger, J.R.; Yaculak, A.M.; et al. Freshwater salinization syndrome: From emerging global problem to managing risks. Biodegradation 2021, 154, 255–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushal, S.S.; Groffman, P.M.; Likens, G.E.; Belt, K.T.; Stack, W.P.; Kelly, V.R.; Band, L.E.; Fisher, G.T. Increased salinization of fresh water in the northeastern United States. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 13517–13520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dugan, H.A.; Bartlett, S.L.; Burke, S.M.; Doubek, J.P.; Krivak-Tetley, F.E.; Skaff, N.K.; Summers, J.C.; Farrell, K.J.; McCullough, I.M.; Morales-Williams, A.M.; et al. Salting our freshwater lakes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 4453–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Statistics Canada. Canada’s Core Public Infrastructure Survey: Interactive Dashboard. Gouvernement du Canada, 2018. Available online: https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/n1/pub/71-607-x/71-607-x2021002-eng.htm (accessed on 26 October 2020).
- Wetzel, R.G.; Likens, G.E. Limnological Analyses, 3rd ed.; Springer Press: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 97–98. ISBN 978-1-4757-3250-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaff, J.D. Method 300.0 Determination of Inorganic Anions by Ion Chromatography; US Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Research and Development, Environmental Monitoring Systems Laboratory: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Qiagen. DNeasy® PowerWater® Kit Handbook; HB-2267-001 © 2017; QIAGEN: Hilden, Germany, 2017; all rights reserved. [Google Scholar]
- ThermoFisher Scientific. N.D. QuantStudio™ 3D Digital PCR System User Manual; Applied Biosystems: Waltham, MA, USA, 2021; PN MAN0007720; Available online: https://assets.thermofisher.com/TFS-Assets/LSG/manuals/MAN0007720.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2019).
- ThermoFisher Scientific. Target Quantification Using SYBR® Green I Dye on the QuantStudio™ 3D Digital PCR System; Demonstrated Protocol; Applied Biosystems: Waltham, MA, USA, 2014; CO35063 0414. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Zhong, S.; Deng, B.; Jin, Q.; Wu, J.; Huo, J.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y. Impact of Phellinus gilvus mycelia on growth, immunity and fecal microbiota in weaned piglets. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, C.; Stoll, W.; Lehmann, R.; Herrmann, M.; Schwab, V.F.; Akob, D.M.; Nawaz, A.; Wubet, T.; Buscot, F.; Totsche, K.-U.; et al. Archaeal Diversity and CO2Fixers in Carbonate-/Siliciclastic-Rock Groundwater Ecosystems. Archaea 2017, 2017, 2136287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing mothur: Open-Source, Platform-Independent, Community-Supported Software for Describing and Comparing Microbial Communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Li, M.; Castelle, C.; Probst, A.; Zhou, Z.; Pan, J.; Liu, Y.; Banfield, J.; Gu, J.-D. Insights into the ecology, evolution, and metabolism of the widespread Woesearchaeotal lineages. Microbiome 2018, 6, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Pan, J.; Wang, F.; Gu, J.-D.; Li, M. Bathyarchaeota: Globally distributed metabolic generalists in anoxic environments. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 42, 639–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Team, R. RStudio: Integrated Development for R. RStudio, Inc. Available online: http://www.rstudio.com (accessed on 20 January 2019).
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. phyloseq: An R package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, S. Phylosmith: An R-package for reproducible and efficient microbiome analysis with phyloseq-objects. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R.; Gorley, R.N. PRIMER v6. User manual/tutorial. In Plymouth Routine in Mulitvariate Ecological Research; Plymouth Marine Laboratory: Plymouth, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, K.; Green, R. Statistical design and analysis for a ’biological effects’ study. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1988, 46, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R.; Somerfield, P.; Gorley, R.N. Testing of null hypotheses in exploratory community analyses: Similarity profiles and biota-environment linkage. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2008, 366, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J. Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Communities in R: Vegan Tutorial; Univ. of Oulu: Oulu, FI, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Steinberger, A. Asteinberger9/Seq_Scripts, Version v1.1; Zenodo, 2020. Available online: https://zenodo.org/record/4270481#.YoXBqqBByUk (accessed on 20 January 2019). [CrossRef]
- Shenhav, L.; Thompson, M.; Joseph, T.A.; Briscoe, L.; Furman, O.; Bogumil, D.; Mizrahi, I.; Pe’er, I.; Halperin, E. FEAST: Fast expectation-maximization for microbial source tracking. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MTQ. Ministère des transports du Québec Stratégie québécoise pour une gestion environnementale des sels de voirie. In Direction de L’environnement et de la Recherche; Dépôt Légal—Bibliothèque et Archives Nationales du Québec; Publications du Québec: Montréal, QC, Canada, 2019; ISBN 978-2-550-60045. [Google Scholar]
- Pernthaler, J. Predation on prokaryotes in the water column and its ecological implications. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jousset, A. Ecological and evolutive implications of bacterial defences against predators. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 14, 1830–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.; Liu, H.; Li, M. Community, Distribution, and Ecological Roles of Estuarine Archaea. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 2060, PMCID: PMC7484942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, E.S.; Reysenbach, A.L. Nanoarchaeota. In Encyclopedia of Microbiology, 4th ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 274–279. ISBN 9780128117378. [Google Scholar]
- Jarrell, K.F.; Albers, S.J. Archaellum. In Encyclopedia of Microbiology, 4th ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 253–261. ISBN 9780128117378. [Google Scholar]
- Leoni, C.; Volpicella, M.; Fosso, B.; Manzari, C.; Piancone, E.; Dileo, M.C.G.; Arcadi, E.; Yakimov, M.; Pesole, G.; Ceci, L.R. A Differential Metabarcoding Approach to Describe Taxonomy Profiles of Bacteria and Archaea in the Saltern of Margherita di Savoia (Italy). Microorganisms 2020, 8, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.; Liang, Q.; Niu, M.; Wang, F. High occurrence of Bathyarchaeota (MCG) in the deep-sea sediments of South China Sea quantified using newly designed PCR primers. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2017, 9, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prosser, J.I.; Nicol, G.W. Candidatus nitrosotalea. In Bergey’s Man. Syst. Archaea Bact. April; 2015; pp. 1–7. ISBN 9781118960608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.-L.; Yang, J.; Chen, X.-L.; Wang, P.; Zhao, H.-L.; Su, H.-N.; Li, C.-Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhong, S.; Wang, L.; et al. A predator-prey interaction between a marine Pseudoalteromonas sp. and Gram-positive bacteria. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickman, M.; Gochnauer, M. Impact of sodium chloride on the microbiota of a small stream. Environ. Pollut. (1970) 1978, 17, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañedo-Argüelles, M.; Kefford, B.; Piscart, C.; Prat, N.; Schäfer, R.; Schulz, C.-J. Salinisation of rivers: An urgent ecological issue. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 173, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañedo-Argüelles, M.; Hawkins, C.P.; Kefford, B.J.; Schäfer, R.B.; Dyack, B.J.; Brucet, S.; Buchwalter, D.; Dunlop, J.; Frör, O.; Lazorchak, J.; et al. Saving freshwater from salts. Science 2016, 351, 914–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environment Canada. Priority Substances List Assessment Report: Road Salts. In Canadian Environmental Protection Act 1999; Environment Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2001; ISBN 0-662-31018-7. [Google Scholar]
- Pernthaler, J.; Posch, T.; Simek, K.; Vrba, J.; Amann, R.; Psenner, R. Contrasting bacterial strategies to coexist with a flagellate predator in an experimental microbial assemblage. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez, J.M.; Sherr, E.B.; Sherr, B.F. Size-selective grazing on bacteria by natural assemblages of estuarine flagellates and ciliates. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1990, 56, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jezbera, J.; Horňák, K.; Imek, K. Food selection by bacterivorous protists: Insight from the analysis of the food vacuole content by means of fluorescence in situ hybridization. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2005, 52, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jackrel, S.; Gilbert, J.A.; Wootton, J.T. The Origin, Succession, and Predicted Metabolism of Bacterial Communities Associated with Leaf Decomposition. mBio 2019, 10, e01703-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alonso, C.; Warnecke, F.; Amann, R.; Pernthaler, J. High local and global diversity of Flavobacteria in marine plankton. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 1253–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchman, D.L. The ecology of Cytophaga-Flavobacteria in aquatic environments. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2002, 39, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Zhang, J.; Nawaz, M.Z.; Mahboob, S.; Al-Ghanim, K.A.; Khan, I.A.; Lu, Z.; Chen, T. Seasonal succession and spatial distribution of bacterial community structure in a eutrophic freshwater Lake, Lake Taihu. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 669, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goecke, F.R.; Thiel, V.; Wiese, J.; Labes, A.; Imhoff, J.F. Algae as an important environment for bacteria–phylogenetic relationships among new bacterial species isolated from algae. Phycologia 2013, 52, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabarova, T.; Salcher, M.M.; Porcal, P.; Znachor, P.; Nedoma, J.; Grossart, H.-P.; Seďa, J.; Hejzlar, J.; Šimek, K. Recovery of freshwater microbial communities after extreme rain events is mediated by cyclic succession. Nat. Microbiol. 2021, 6, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Barber, M.; Lu, J.; Goel, R. Microbial community successions and their dynamic functions during harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a freshwater lake. Water Res. 2020, 185, 116292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennon, J.T.; Jones, S.E. Microbial seed banks: The ecological and evolutionary implications of dormancy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 9, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisnoski, N.I.; Lennon, J.T. Stabilising role of seed banks and the maintenance of bacterial diversity. Ecol. Lett. 2021, 24, 2328–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Bai, C.; Cai, J.; Shao, K.; Tang, X.; Gao, G. Low recovery of bacterial community after an extreme salinization-desalinization cycle. BMC Microbiol. 2018, 18, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandeparker, L.; Eswaran, R.; Gardade, L.; Kuchi, N.; Mapari, K.; Naik, S.D.; Anil, A.C. Elucidation of the tidal influence on bacterial populations in a monsoon influenced estuary through simultaneous observations. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 189, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemos, L.N.; de Carvalho, F.M.; Gerber, A.; Guimarães, A.P.C.; Jonck, C.R.; Ciapina, L.P.; de Vasconcelos, A.T.R. Genome-centric metagenomics reveals insights into the evolution and metabolism of a new free-living group in Rhizobiales. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gagnon, J.-C.; Astorg, L.; Derry, A.M.; Lazar, C.S. Response of Prokaryotic Communities to Freshwater Salinization. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 2, 330-346. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol2020025
Gagnon J-C, Astorg L, Derry AM, Lazar CS. Response of Prokaryotic Communities to Freshwater Salinization. Applied Microbiology. 2022; 2(2):330-346. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol2020025
Chicago/Turabian StyleGagnon, Jean-Christophe, Louis Astorg, Alison M. Derry, and Cassandre Sara Lazar. 2022. "Response of Prokaryotic Communities to Freshwater Salinization" Applied Microbiology 2, no. 2: 330-346. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol2020025
APA StyleGagnon, J.-C., Astorg, L., Derry, A. M., & Lazar, C. S. (2022). Response of Prokaryotic Communities to Freshwater Salinization. Applied Microbiology, 2(2), 330-346. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol2020025





