Proximate Composition and Nutritional Indices of Fenugreek Under Salinity Stress: The Role of Biocyclic Vegan and Other Organic Fertilization Systems in Forage Quality
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Experimental Site and Environmental Conditions
2.3. Plant Material
2.4. Crop Management and Agronomic Practices
2.5. Data Collection
2.5.1. Plant and Seed Composition
2.5.2. Nutritional Composition
2.5.3. Digestibility Indices
2.5.4. Forage Quality Indicators
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Nutritional Composition
3.2. Nutritional Composition
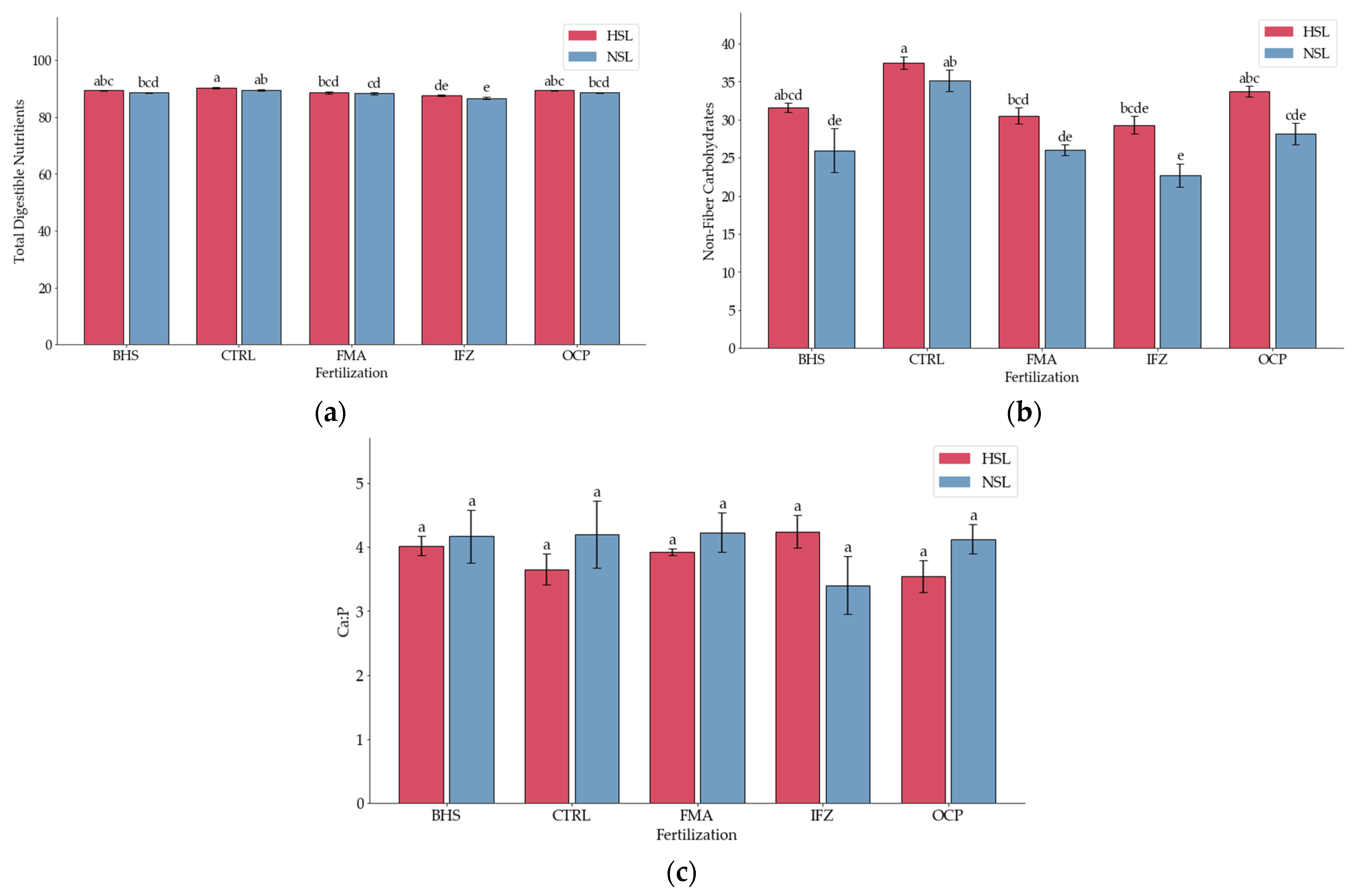
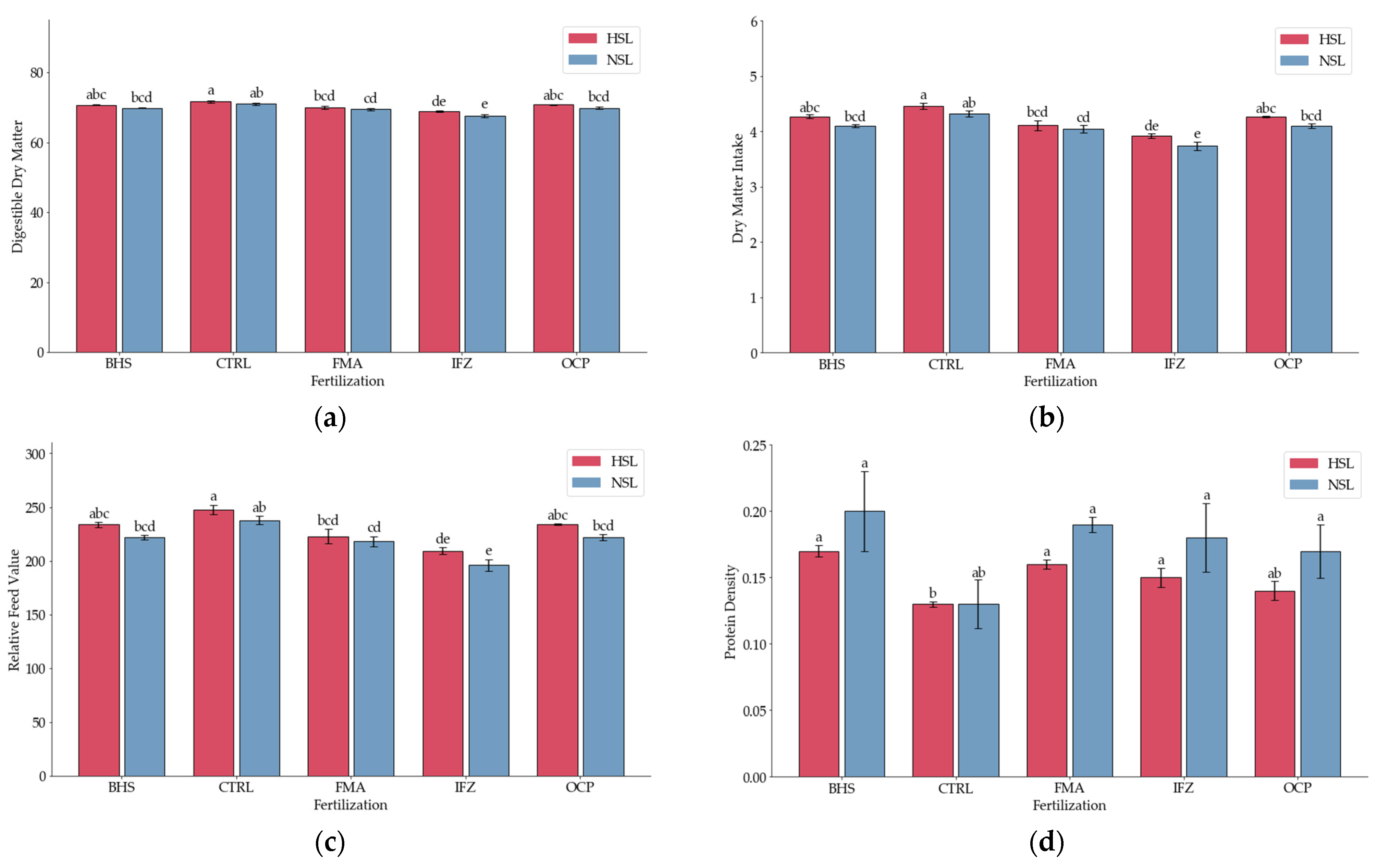
3.3. Digestibility Indices
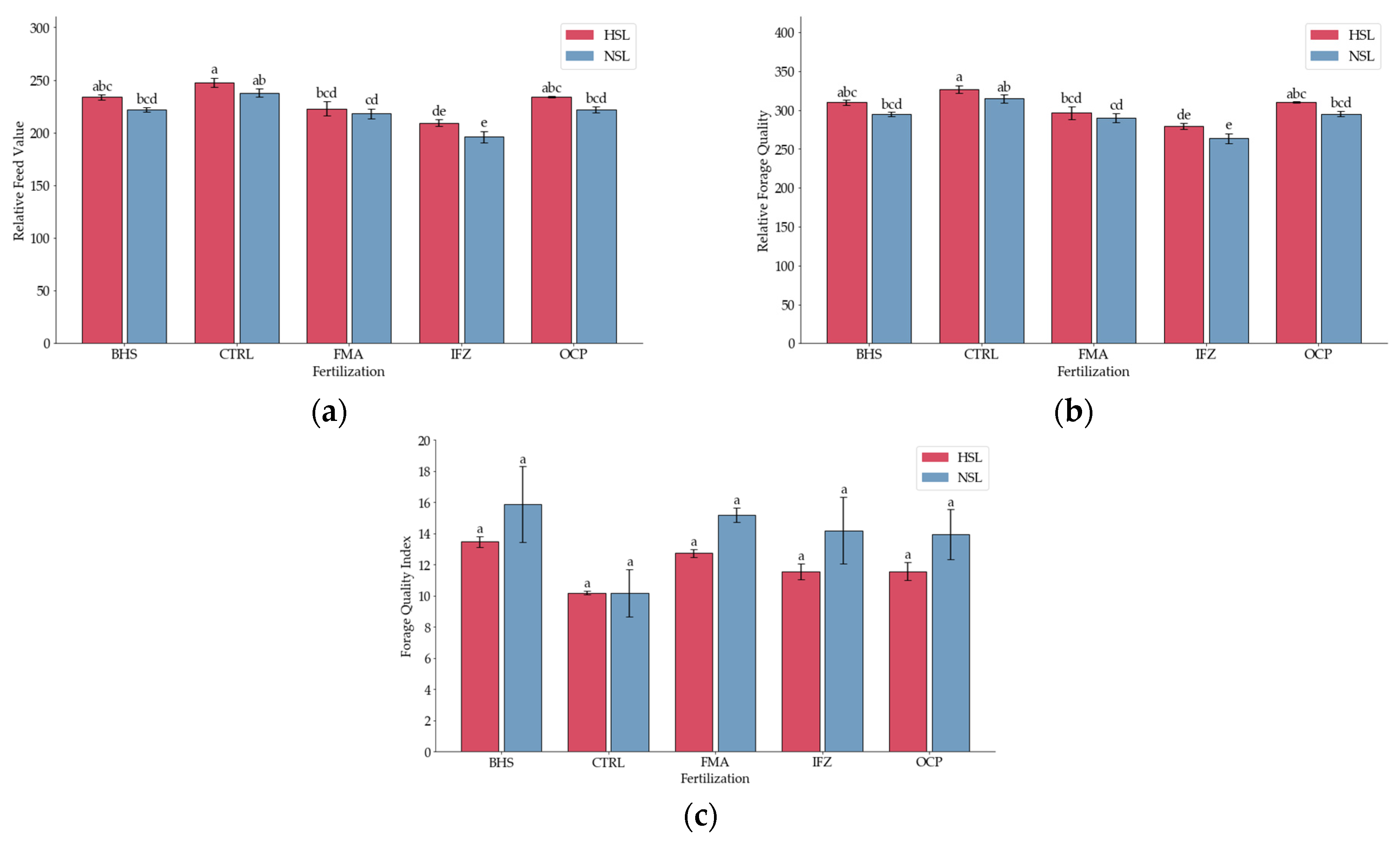
3.4. Forage Quality Indicators
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ritzema, H. Drain for Gain: Managing salinity in irrigated lands—A review. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 176, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otlewska, A.; Migliore, M.; Dybka-Stępień, K.; Manfredini, A.; Struszczyk-Świta, K.; Napoli, R.; Białkowska, A.; Canfora, L.; Pinzari, F. When salt meddles between plant, soil, and microorganisms. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 553087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenzuela, F.J.; Reineke, D.; Leventini, D.; Chen, C.C.L.; Barrett-Lennard, E.G.; Colmer, T.D.; Dodd, I.C.; Shabala, S.; Brown, P.; Bazihizina, N. Plant responses to heterogeneous salinity: Agronomic relevance and research priorities. Ann. Bot. 2022, 129, 499–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kefford, B.J.; Buchwalter, D.; Cañedo-Argüelles, M.; Davis, J.; Duncan, R.P.; Hoffmann, A.; Thompson, R. Salinized rivers: Degraded systems or new habitats for salt-tolerant faunas? Biol. Lett. 2016, 12, 20151072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.; Munns, R. Evolution of approaches to increase the salt tolerance of crops. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2022, 41, 128–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarolli, P.; Luo, J.; Park, E.; Barcaccia, G.; Masin, R. Soil salinization in agriculture: Mitigation and adaptation strategies combining nature-based solutions and bioengineering. iScience 2024, 27, 108830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irin, I.J.; Hasanuzzaman, M. Organic amendments: Enhancing plant tolerance to salinity and metal stress for improved agricultural productivity. Stresses 2024, 4, 185–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtaza, G.; Ahmed, Z.; Iqbal, R.; Deng, G. Biochar from agricultural waste as a strategic resource for promotion of crop growth and nutrient cycling of soil under drought and salinity stress conditions: A comprehensive review with context of climate change. J. Plant Nutr. 2025, 1–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, S. Could we stop killing?—Exploring a post-lethal vegan or vegetarian agriculture. World 2020, 1, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edberg, K. Farming Without Animals? The Outlook for Biocyclic Vegan Agriculture as an Alternative Approach to Food Production in Sweden. Master’s Thesis, LUCSUS (Lund University Centre for Sustainability Studies), Lund, Sweden, 2023. ID 9120376. [Google Scholar]
- Eisenbach, L.D.; Folina, A.; Zisi, C.; Roussis, I.; Tabaxi, I.; Papastylianou, P.; Kakabouki, I.; Efthimiadou, A.; Bilalis, D.J. Effect of biocyclic humus soil on yield and quality parameters of sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas L.). Sci. Papers. Ser. A Agron. 2018, LXI, 210–217. [Google Scholar]
- Folina, A.; Tsementzi, K.; Stavropoulos, P.; Mavroeidis, A.; Kakabouki, I.; Bilalis, D. Impact of salinity and fertilization on soil properties, and root development in fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum) cultivation. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. Cluj-Napoca 2024, 52, 13868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shayeb, N.; Mabrouk, S. Utilisation of some edible and medicinal plants to inhibit aflatoxin formation. Nutr. Rep. Int. 1984, 29, 273–282. [Google Scholar]
- Bhat, B.G.; Sambaiah, K.; Chandrasekhara, N. The effect of feeding fenugreek and ginger on bile composition in the albino rat. Nutr. Rep. Int. 1985, 32, 1145–1151. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, R.C.; Srivastava, A.; Lall, R. Nutraceuticals in Veterinary Medicine; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; Volume 120. [Google Scholar]
- Acharya, S.; Basu, S.; Thomas, J. Medicinal properties of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.): A review of the evidence based information. Adv. Med. Plant Res. 2007, 2007, 81–122. [Google Scholar]
- Żuk-Gołaszewska, K.; Wierzbowska, J. Fenugreek: Productivity, nutritional value and uses. J. Elem. 2017, 22, 1067–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, Z.; Mir, P.; Acharya, S.; Zaman, M.; Taylor, W.; Mears, G.; McAllister, T.; Goonewardene, L. Comparison of alfalfa and fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum) silages supplemented with barley grain on performance of growing steers. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 1998, 78, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jat, H.; Taparia, A. Utilization of methi straw by cattle. Indian J. Anim. Sci. 1990, 60, 1380–1381. [Google Scholar]
- Attia-Ismail, S.A. Effect of fenugreek seeds (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.) as feed additive on 1 sheep performance in the north western coast of Egypt 2. Anal. Methods 2000, 32, 33. [Google Scholar]
- Solorio-Sánchez, F.; Solorio-Sánchez, B.; Basu, S.; Casanova-Lugo, F.; Sarabia-Salgado, L.; Ku-Vera, J.; Aguilar-Pérez, C.; Ramírez-Avilés, L.; Noguera-Savelli, E.; Cetzal-Ix, W. Opportunities to grow annual forage legume fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.) under mexican sylvopastoral system. Am. J. Soc. Issues Humanit. 2014, 86–95. [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery, J. The potential of Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum) as a Forage for Dairy Herds in Central Alberta. Master’s Thesis, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Alemu, A.; Doepel, L. Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.) as an alternative forage for dairy cows. Animal 2011, 5, 1370–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamalak, A.; Atalay, A.I.; Özkan, Ç.Ö.; Kaya, E.; Tatlıyer, A. Determination of potential nutritive value of Trigonella kotschi fenzl hay harvested at three different maturity stages. Kafkas Üniversitesi Vet. Fakültesi Derg. 2011, 17, 635–640. [Google Scholar]
- Mir, P.; Mir, Z.; Townley-Smith, L. Comparison of the nutrient content and in situ degradability of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum) and alfalfa hays. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 1993, 73, 993–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, Z.; Acharya, S.; Mir, P.; Taylor, W.; Zaman, M.; Mears, G.; Goonewardene, L. Nutrient composition, in vitro gas production and digestibility of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum) and alfalfa forages. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 1997, 77, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obour, A.; Obeng, E.; Holman, J. Influence of different seeding dates on fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.) forage yield and nutritive value. Kans. Agric. Exp. Stn. Res. Rep. 2015, 1, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zgher, M.S.; Mahde, A.H. Effect of seed radial, number of irrigation peroids and nitrogen levels on growth and forage yield of Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.). Al-Qadisiyah J. Pure Sci. 2015, 20, 89–100. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammed, S.R. Response of Two Fenugreek Trigonella foenum-graecum Varieties to Different Cutting Dates and Nitrogen Fertilizer for Growth and Forage Yield Traits under Rainfed Condition. Tikrit J. Sci. Agric. 2017, 17, 134–142. [Google Scholar]
- Basu, S.K.; Acharya, S.N.; Thomas, J.E. A report on powdery mildew infestations caused by Erysiphe polygoni DC in North American grown fenugreek. J. Mycopathol. Res. 2006, 44, 253–256. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammad, A.A.; Rezvani, M.P.; Fallahi, J.; Boroumand, R.Z. Effect of chemical and organic fertilizers on quantitative and qualitative characteristics of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.) forage. J. Agroecol. 2011, 3, 491–499. [Google Scholar]
- Ghanbari, S.; Telavat, M.M.; Siadat, A. Effect of manure application on forage yield and quality of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) and fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.) in intercropping. Iran. J. Crop Sci. 2015, 17, Pe315–Pe328. [Google Scholar]
- Abbasdokht, H.; Chaichi, M.R.; Asadi, S.; Nazari, M.; Manafi Noran, M.; Khademi, H.R. Effects of types of nitrogenous fertilizer (biological, chemical, integrative) and cropping mixes on some forage-medicine characteristics in additive intercropping of sorghum (Sorghum bicolor [L.] Moench) with fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.). Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2016, 62, 1741–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCartney, D.; Fraser, J. The potential role of annual forage legumes in Canada: A review. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2010, 90, 403–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahab, A.A.; Bayomy, H.M.; El-Salam, H.S.A.; Almasoudi, S.E.; Ozaybi, N.A.; Mahmoud, G.A.; Atteya, A.K.; El-Serafy, R.S. Seed disinfection treatments minimized microbial load and enhanced nutritional properties of fenugreek sprouts which alleviated diabetes-negative disorders in diabetic rats. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousallamy, A.; Samir, A. Effect of using dried Fenugreek seeds as natural feed additives on growth performance, feed utilization, whole-body composition and entropathogenic Aeromonas hydrophila-challinge of monsex Nile tilapia O. niloticus (L) fingerlings. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2009, 3, 1234–1245. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, J.; Gupta, K.; Arora, S. Changes in the anti-nutritional factors of developing seeds and pod walls of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum graecum L.). Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 1994, 46, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewari, A.; Brar, J.K.; Singh, R.; Singh, A. Agronomic biofortification of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum) seeds with chromium: Implication on nutritional, anti-nutritional, mineral and in-vitro protein digestibility. Food Biosci. 2024, 60, 104481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadresan, M.; Luthe, D.S.; Reddivari, L.; Chaichi, M.R.; Yazdani, D. Effect of salinity stress and surfactant treatment on physiological traits and nutrient absorption of fenugreek plant. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2015, 46, 2807–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punia, H.; Tokas, J.; Malik, A.; Yashveer, S. Reconnoitering bionanomaterials for mitigation of abiotic stress in plants. In Bionanotechnology: Emerging Applications of Bionanomaterials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 101–126. [Google Scholar]
- Odhong, C.; Wahome, R.; Vaarst, M.; Kiggundu, M.; Nalubwama, S.; Halberg, N.; Githigia, S. Challenges of conversion to organic dairy production and prospects of future development in integrated smallholder farms in Kenya. Livest. Res. Rural Dev. 2014, 26, 14–21. [Google Scholar]
- McBride, W.D.; Greene, C. The profitability of organic soybean production. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2009, 24, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakley, A.; Black, I.A. An examination of the Degtiareff methods for determining soil organic matter and a proposed modification of chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci. 1934, 37, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corwin, D.L.; Yemoto, K. Salinity: Electrical conductivity and total dissolved solids. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2020, 84, 1442–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Global Map of Salt Affected Soils Version 1.0; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- ISO11261; Soil Quality: Determination of Total Nitrogen: Modified Kjeldahl Method. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1995.
- Association of Official Analytical Chemists; Cunniff, P. Official Methods of Analysis of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Association of Official Analytical Chemists. Official methods of analysis of the AOAC International. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem. Int. 1995, 10, 15563657608988149. [Google Scholar]
- ISO11260; Soil Quality: Determination of Cation Exchange Capacity and Base Saturation Method Using Barium Chloride Solution. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1994.
- Moore, J.E.; Undersander, D.J. Relative forage quality: An alternative to relative feed value and quality index. In Proceedings of the 13th Annual Florida Ruminant Nutrition Symposium, Gainesville, FL, USA, 10–11 January 2002; pp. 16–29. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, M. Calculation of Non-Neutral Detergent Fiber Carbohydrate Content of Feeds that Contain Non-Protein Nitrogen; University of Florida: Gainesville, FL, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- McDowell, L.R. Minerals in Animal and Human Nutrition; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder, J.W. Interpreting Forage Analysis; North Dakota State University: Fargo, ND, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Undersander, D.; Mertens, D.; Thiex, N. Forage Analyses; Information Systems Division, National Agricultural Library (United States of America) NAL/USDA: Beltsville, MD, USA, 1993; p. 10301. [Google Scholar]
- Olaiya, C.O.; Soetan, K.O. A review of the health benefits of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.): Nutritional, Biochemical and pharmaceutical perspectives. Am. J. Soc. Issues Humanit 2014, 4, 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Tunçtürk, R.; Celen, A.E.; Tunçtürk, M. The effects of nitrogen and sulphur fertilizers on the yield and quality of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.). Turk. J. Field Crops 2011, 16, 69–75. [Google Scholar]
- Tuncturk, R. Salinity exposure modifies nutrient concentrations in fenugreek (Trigonella foenum graecum L.). Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2011, 6, 3685–3690. [Google Scholar]
- El Nasri, N.A.; El Tinay, A. Functional properties of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum graecum) protein concentrate. Food Chem. 2007, 103, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.U.; Sharma, R. An evaluation of protein quality of fenugreek seeds (Trigonella foenum graecum) and their supplementary effects. Food Chem. 1987, 24, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, N.; Kumar, P.; Wani, S.A. Effect of extraction parameters on the isolation of fenugreek seed protein and characterization of fenugreek protein concentrate. Qual. Assur. Saf. Crops Foods 2022, 14, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzbowska, J.; Zuk-Golaszewska, K. The impact of nitrogen fertilization and Rhizobium inoculation on the yield and quality of Trigonella foenum-graecum L. J. Elem. 2014, 19, 1109–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, S.; Mehta, R.; Bairwa, M.; Meena, R. productivity and profitability of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum l.) As influenced by bio-fertilizers and plant growth regulators. Legume Res.-Int. J. 2014, 37, 646–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.H.; Li, S.X.; Malhi, S. Effects of fertilization and other agronomic measures on nutritional quality of crops. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2008, 88, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folina, A.; Mavroeidis, A.; Stavropoulos, P.; Eisenbach, L.; Kakabouki, I.; Bilalis, D. Comparison of Organic and Inorganic Fertilization in Fenugreek Cultivation Using Nitrogen Indicators. Nitrogen 2024, 5, 712–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okon, O.G. Effect of salinity on physiological processes in plants. In Microorganisms in Saline Environments: Strategies and Functions; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 237–262. [Google Scholar]
- Nawaz, F.; Shehzad, M.A.; Majeed, S.; Ahmad, K.S.; Aqib, M.; Usmani, M.M.; Shabbir, R.N. Role of mineral nutrition in improving drought and salinity tolerance in field crops. In Agronomic Crops: Volume 3: Stress Responses and Tolerance; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 129–147. [Google Scholar]
- Weisany, W.; Sohrabi, Y.; Heidari, G.; Siosemardeh, A.; Badakhshan, H. Effects of zinc application on growth, absorption and distribution of mineral nutrients under salinity stress in soybean (Glycine max L.). J. Plant Nutr. 2014, 37, 2255–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilalis, D.; Tabaxi, I.; Zervas, G.; Tsiplakou, E.; Travlos, I.S.; Kakabouki, I.; Tsioros, S. Chia (Salvia hispanica) fodder yield and quality as affected by sowing rates and organic fertilization. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2016, 47, 1764–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehtaiwesh, A.F. The effect of salinity on nutrient availability and uptake in crop plants. Sci. J. Appl. Sci. Sabratha Univ. 2022, 9, 55–73. [Google Scholar]
- National Research Council; Committee on Animal Nutrition Subcommittee on Dairy Cattle Nutrition. Nutrient Requirements of Dairy Cattle: 2001; National Academies Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Fields, M.W.; Hise, A.; Lohman, E.J.; Bell, T.; Gardner, R.D.; Corredor, L.; Moll, K.; Peyton, B.M.; Characklis, G.W.; Gerlach, R. Sources and resources: Importance of nutrients, resource allocation, and ecology in microalgal cultivation for lipid accumulation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 4805–4816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, S.; Bukhari, S.A.; Ashraf, M.Y.; Mahmood, S.; Iftikhar, T. Effect of salinity on growth, biochemical parameters and fatty acid composition in safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.). Pak. J. Bot. 2014, 46, 1153–1158. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, J.; Jiang, C.; Wang, X.; Zhuo, R.; Lu, M.-Z.; Zhang, J. Lignin biosynthesis and accumulation in response to abiotic stresses in woody plants. For. Res. 2022, 2, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Hussain, M.A.; Nawaz, H.; Muhammad, G.; Lang, I.; Ashraf, U. Physiological Interventions of Antioxidants in Crop Plants Under Multiple Abiotic Stresses. In Sustainable Agriculture in the Era of the OMICs Revolution; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 431–471. [Google Scholar]
- Lambers, H.; Chapin, F.S.; Pons, T.L. Plant Physiological Ecology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Doepel, L.; Montgomery, J.; Beauchemin, K.; King, J.; Acharya, S. Ruminal degradability and whole-tract digestibility of protein and fibre fractions in fenugreek haylage. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 2012, 92, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamadi, E.M.; Ebrahimi, A.; Amerian, M.R.; Alipour, H. Melatonin confers fenugreek tolerance to salinity stress by stimulating the biosynthesis processes of enzymatic, non-enzymatic antioxidants, and diosgenin content. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 890613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherney, J.H.; Cherney, D.J. Impact of fertilization on forage production and animal performance. In Proceedings of the Colloque sur les Plantes Fourrageres, Drummondville, QC, Canada, 9 December 2015; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Norman, H.C.; Masters, D.G.; Barrett-Lennard, E.G. Halophytes as forages in saline landscapes: Interactions between plant genotype and environment change their feeding value to ruminants. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2013, 92, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onte, S.; Singh, M.; Meena, V.; Kumar, S.; Meena, B.; Dutta, S. Organic Nutrient Management in Context to Sustainable Fodder Production: A Review. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci 2019, 8, 2434–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Näsholm, T.; Kielland, K.; Ganeteg, U. Uptake of organic nitrogen by plants. New Phytol. 2009, 182, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayal, G.; Patel, M.; Singh, H. 13. Plant nutrient. Basic introduction of soil science. 157.
- Tokas, J.; Punia, H.; Malik, A.; Sangwan, S.; Devi, S.; Malik, S. Growth performance, nutritional status, forage yield and photosynthetic use efficiency of sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench] under salt stress. Range Manag. Agrofor. 2021, 42, 59–70. [Google Scholar]
- Mäder, P.; Fliessbach, A.; Dubois, D.; Gunst, L.; Fried, P.; Niggli, U. Soil fertility and biodiversity in organic farming. Science 2002, 296, 1694–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmeades, D.C. The long-term effects of manures and fertilisers on soil productivity and quality: A review. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosystems 2003, 66, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Kumar, J.; Singh, S.; Singh, V.P.; Prasad, S.M. Roles of osmoprotectants in improving salinity and drought tolerance in plants: A review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2015, 14, 407–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattanagul, W.; Thitisaksakul, M. Effect of salinity stress on growth and carbohydrate metabolism in three rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars differing in salinity tolerance. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2008, 46, 736–742. [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel, P.; Gutzwiller, A. Dietary calcium to digestible phosphorus ratio for optimal growth performance and bone mineralization in growing and finishing pigs. Animals 2020, 10, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
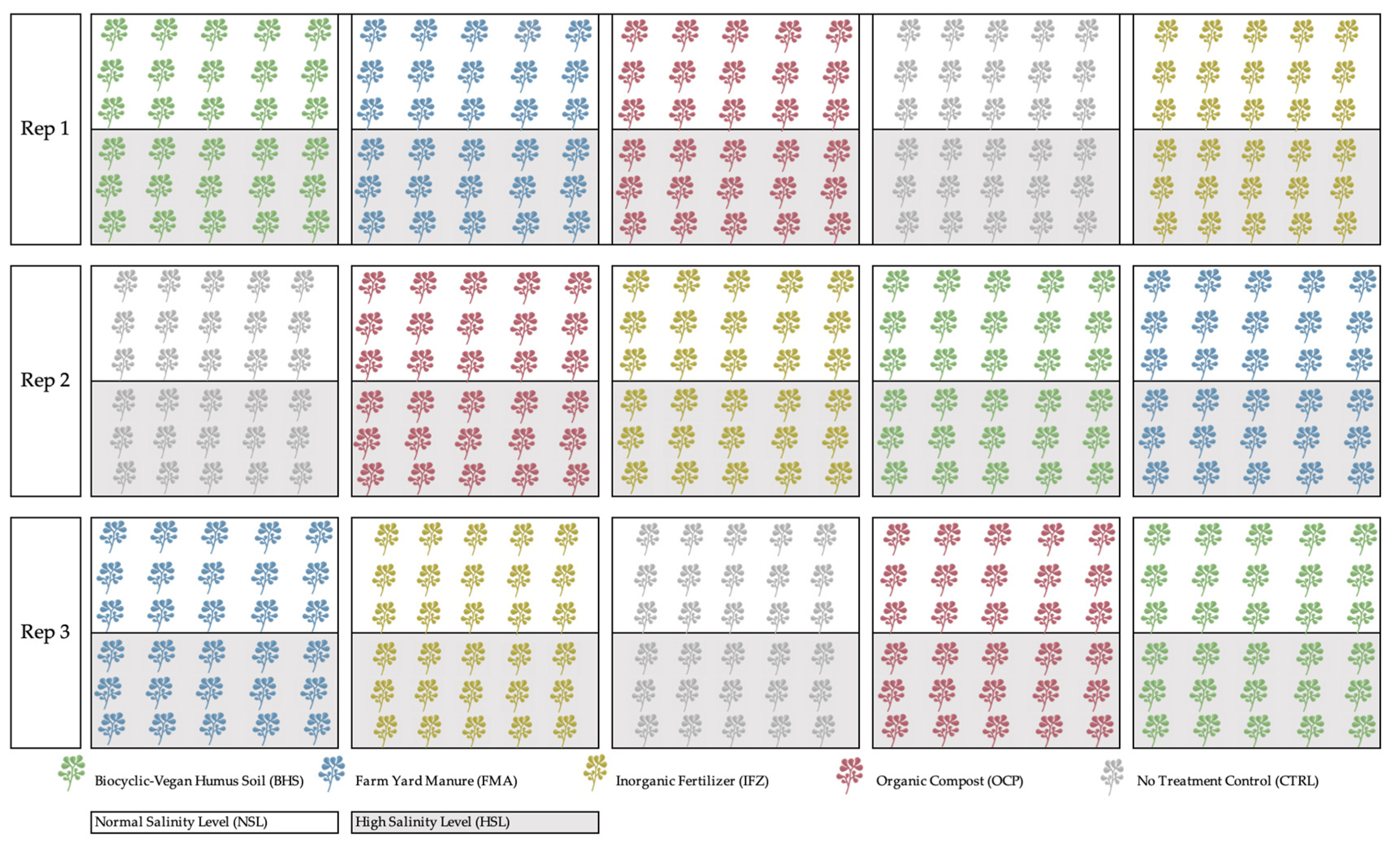
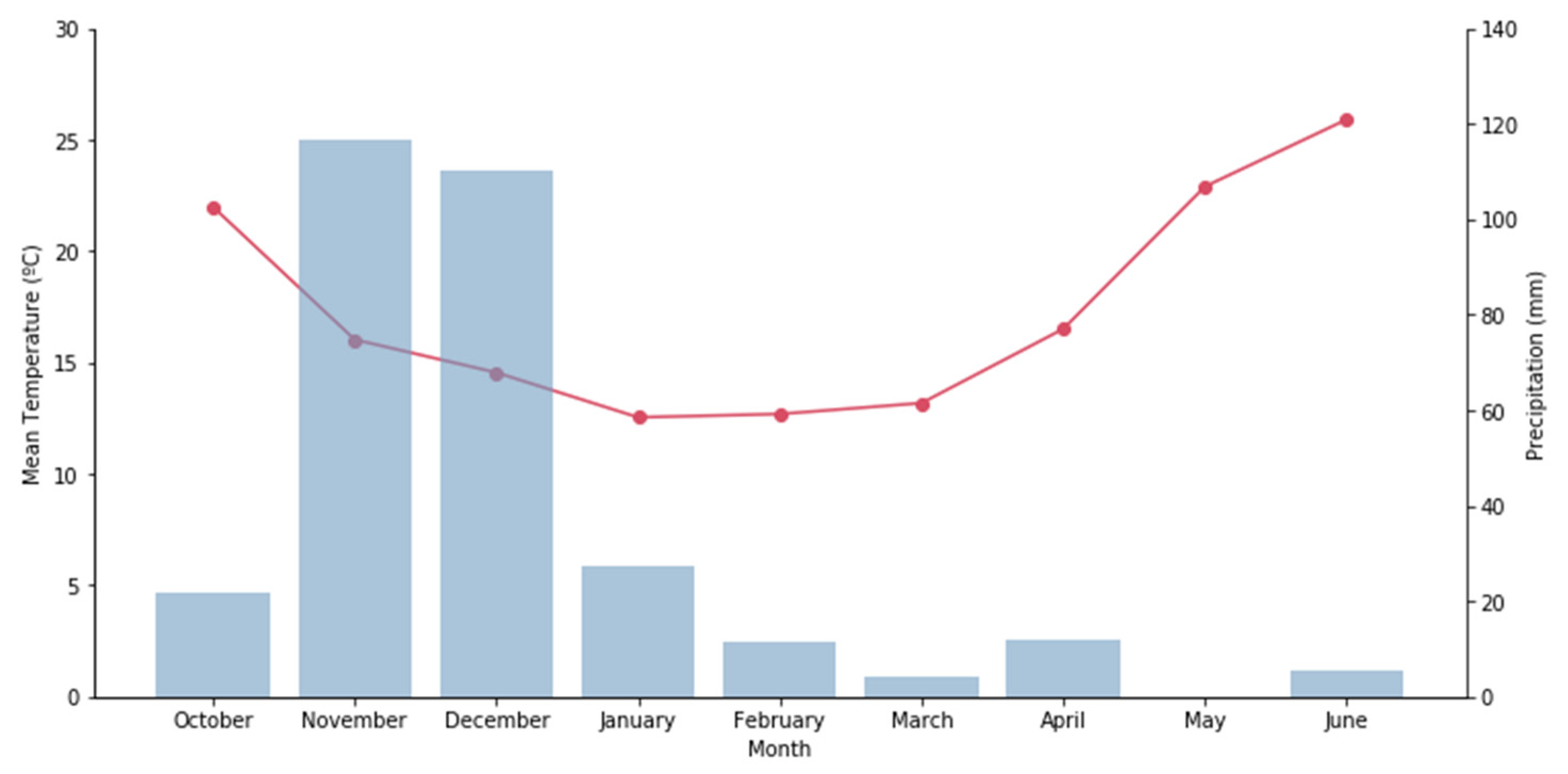

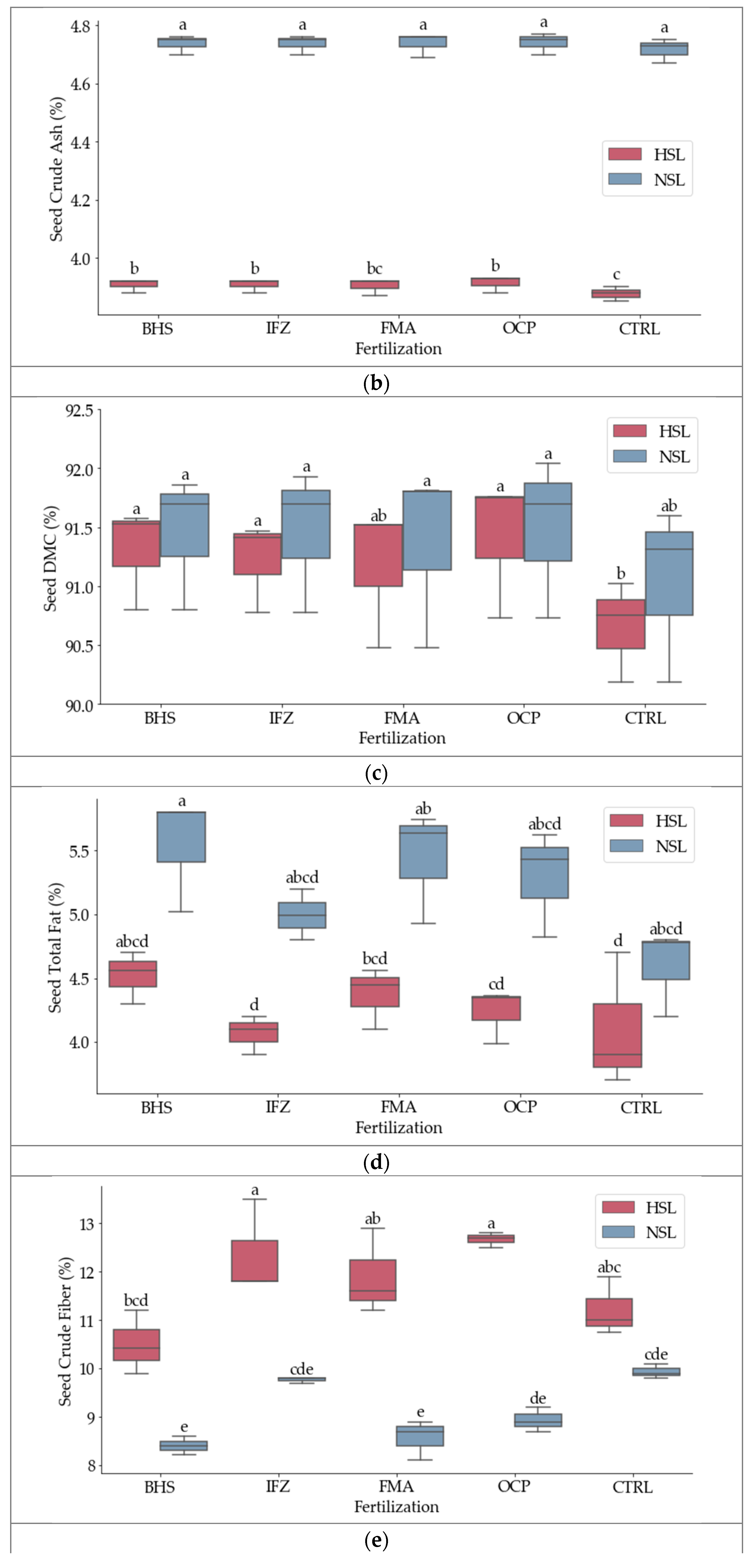

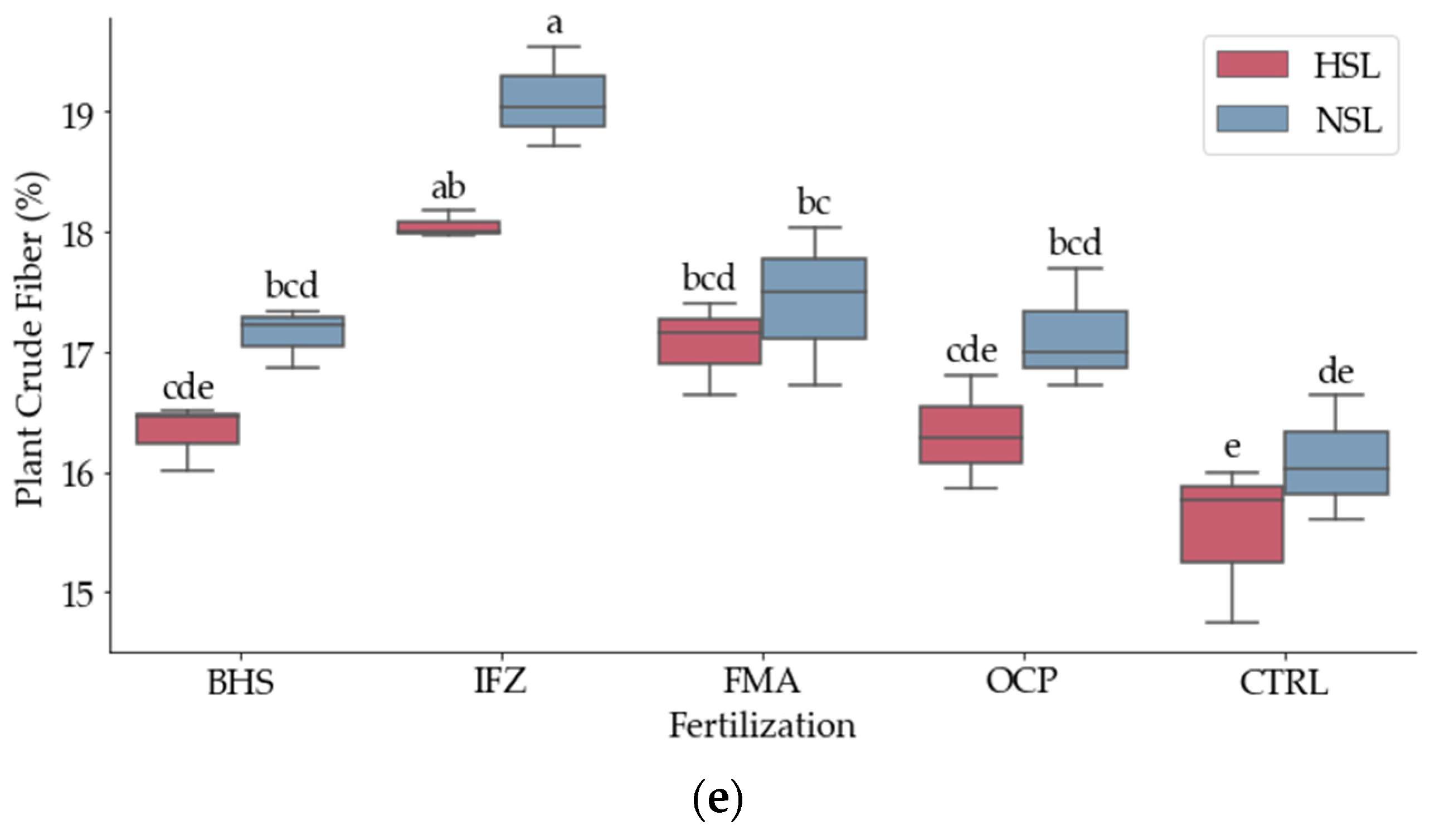
| Parameter | Unit | Analysis Method/Equation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen (N) | (%) | ISO, 1995 (11,261) | [46] |
| Crude Protein (CP) | (%) | Multiplying N concentration by 6.25 | [47,48] |
| Crude Ash (CA) | (%) | 924.05 | [47,48] |
| Dry Matter Content (DMC) | (%) | 943.01 | [47,48] |
| Total Fat (TF) | (%) | 920.39 | [47,48] |
| Crude Fiber (CF) | (%) | 978.10 | [47,48] |
| ADF | 978.10 | [47,48] | |
| NDF | 978.10 | [47,48] | |
| Calcium (Ca) | (g/100) | ISO, 1994 (11,260) | [49] |
| Phosphorus (P) | (%) | ISO, 1994 (11,263) | [49] |
| Source | DF | Seed CP (%) | Seed CA (%) | Seed DMC (%) | Seed TF (%) | Seed CF (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANOVA | ||||||
| Repitatio (A) | 2 | |||||
| Fertiliza (B) | 4 | 107.07 *** | 16.86 *** | 16.76 *** | 11.8 ** | 10.46 ** |
| Error A*B | 8 | |||||
| Salinity (C) | 1 | 5.89 * | 59,495.62 *** | 10.2 *** | 34.3 *** | 136.39 *** |
| B*C | 4 | ns | ns | ns | ns | 3.8 * |
| Error A*B*C | 10 | |||||
| Total | 29 | |||||
| CV | ||||||
| Grand Mean | 32,063 | 4.3183 | 91,257 | 4.7147 | 10,426 | |
| CV (Repit*Fertil) | 3.54 | 0.17 | 0.16 | 4.19 | 4.53 | |
| CV (Repit*Fertil*Sal) | 6.24 | 0.22 | 0.2 | 9.06 | 5.87 | |
| Source | DF | Plant CP (%) | Plant CA (%) | Plant DMC (%) | Plant TF (%) | Plant CF (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANOVA | ||||||
| Repitatio (A) | 2 | |||||
| Fertiliza (B) | 4 | 15.06 *** | 16.86 *** | 16.86 *** | 14.11 ** | 50.24 *** |
| Error A*B | 8 | |||||
| Salinity (C) | 1 | 5.83 * | 14,206.33 *** | 10.2 ** | 80.72 *** | 31.31 *** |
| B*C | 4 | ns | ns | ns | 5.57 * | ns |
| Error A*B*C | 10 | |||||
| Total | 29 | |||||
| CV | ||||||
| Grand Mean | 14.55 | 9.2767 | 90,087 | 1.7633 | 17,016 | |
| CV(Repit*Fertil) | 8.59 | 0.17 | 0.16 | 3.28 | 2.07 | |
| CV(Repit*Fertil*Sal) | 18.19 | 0.21 | 0.2 | 3.94 | 2.09 | |
| Source | DF | DDM | DMI | RFV | FPR | Protein Density | TDN | RGQ | FQI | NFC | Ca:P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANOVA | |||||||||||
| Repitatio (A) | 2 | ||||||||||
| Fertiliza (B) | 4 | 50.24 *** | 39.69 *** | 39.69 *** | 17.12 *** | 14.95 *** | 50.24 *** | 39.69 *** | 13.74 ** | 57.89 *** | ns |
| Error A*B | 8 | ||||||||||
| Salinity (C) | 1 | 31.31 *** | 31.15 *** | 31.15 *** | ns | 5.71 * | 31.31 *** | 31.15 *** | 5.16 * | 36.12 *** | ns |
| B*C | 4 | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| Error A*B*C | 10 | ||||||||||
| Total | 29 | ||||||||||
| CV | |||||||||||
| Grand Mean | 69,964 | 4.1335 | 224.37 | 1.2066 | 0.1614 | 88.67 | 298.16 | 12,892 | 30,049 | 3.949 | |
| CV(Repit*Fertil) | 0.56 | 1.91 | 2.52 | 6.82 | 8.51 | 0.38 | 2.33 | 8.73 | 4.17 | 7.26 | |
| CV(Repit*Fertil*Salin) | 0.56 | 1.73 | 2.29 | 15.3 | 18.07 | 0.39 | 2.11 | 18.37 | 7.49 | 8.38 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Folina, A.; Kakabouki, I.; Stavropoulos, P.; Mavroeidis, A.; Tsiplakou, E.; Bilalis, D. Proximate Composition and Nutritional Indices of Fenugreek Under Salinity Stress: The Role of Biocyclic Vegan and Other Organic Fertilization Systems in Forage Quality. Crops 2025, 5, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/crops5030024
Folina A, Kakabouki I, Stavropoulos P, Mavroeidis A, Tsiplakou E, Bilalis D. Proximate Composition and Nutritional Indices of Fenugreek Under Salinity Stress: The Role of Biocyclic Vegan and Other Organic Fertilization Systems in Forage Quality. Crops. 2025; 5(3):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/crops5030024
Chicago/Turabian StyleFolina, Antigolena, Ioanna Kakabouki, Panteleimon Stavropoulos, Antonios Mavroeidis, Eleni Tsiplakou, and Dimitrios Bilalis. 2025. "Proximate Composition and Nutritional Indices of Fenugreek Under Salinity Stress: The Role of Biocyclic Vegan and Other Organic Fertilization Systems in Forage Quality" Crops 5, no. 3: 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/crops5030024
APA StyleFolina, A., Kakabouki, I., Stavropoulos, P., Mavroeidis, A., Tsiplakou, E., & Bilalis, D. (2025). Proximate Composition and Nutritional Indices of Fenugreek Under Salinity Stress: The Role of Biocyclic Vegan and Other Organic Fertilization Systems in Forage Quality. Crops, 5(3), 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/crops5030024









