Association and Interrelationship Among Agronomic Traits and Fungal Diseases of Sorghum, Anthracnose and Grain Mold
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Anthracnose Field Study
2.3. Grain Mold Field Study
2.4. Agronomic Traits
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Machine Learning Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frederiksen, R.; Odvody, G. Compendium of Sorghum Diseases, 2nd ed.; American Phytopathological Society (APS Press): St. Paul, MN, USA, 2000; ISBN 978-0-89054-240-8. [Google Scholar]
- Abreha, K.B.; Ortiz, R.; Carlsson, A.S.; Geleta, M. Understanding the sorghum–Colletotrichum sublineola interactions for enhanced host resistance. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 641969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, W.; Ali, A.; Arshad, M.S.; Afzal, F.; Akram, R.; Siddeeg, A.; Kousar, S.; Rahim, M.A.; Aziz, A.; Maqbool, Z. Nutrients and bioactive compounds of Sorghum bicolor L. used to prepare functional foods: A review on the efficacy against different chronic disorders. Int. J. Food Prop. 2022, 25, 1045–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirany, T.; Tadele, E.; Aregahegn, H.; Wale, D. Economic potentials and use dynamics of sorghum food system in Ethiopia: Its implications to resolve food deficit. Adv. Agric. 2022, 2022, 4580643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fall, R.; Cissé, M.; Sarr, F.; Kane, A.; Diatta, C.; Diouf, M. Production and use sorghum: A literature review. J. Nutr. Health Food Sci. 2016, 4, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundia, C.W.; Secchi, S.; Akamani, K.; Wang, G. A regional comparison of factors affecting global sorghum production: The case of North America, Asia and Africa’s Sahel. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyaya, H.D.; Reddy, K.N.; Vetriventhan, M.; Ahmed, M.I.; Krishna, G.M.; Reddy, M.T.; Singh, S.K. Sorghum germplasm from West and Central Africa maintained in the ICRISAT genebank: Status, gaps, and diversity. Crop J. 2017, 5, 518–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.S.; Islam, M.N.; Rahman, M.M.; Mostofa, M.G.; Khan, M.A.R. Sorghum: A prospective crop for climatic vulnerability, food and nutritional security. J. Agri. Food Res. 2022, 8, 100300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welderufael, S.; Abay, F.; Ayana, A.; Amede, T. Genetic diversity, correlation and genotype × yield × trait (GYT) analysis of grain yield and nutritional quality traits in sorghum (Sorghum bicolor [L.] Moench) genotypes in Tigray, northern Ethiopia. Discov. Agric. 2024, 2, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chala, A.; Brurberg, M.B.; Tronsmo, A.M. Incidence and severity of sorghum anthracnose in Ethiopia. Plant Pathol. J. 2010, 9, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Rao, V.P.; Upadhyaya, H.D.; Reddy, V.G.; Thakur, R.P. Resistance to Grain Mold and Downy Mildew in a Mini-Core Collection of Sorghum Sermplasm. Plant Dis. 2010, 94, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, A.; Wenndt, A.; Boyles, R. The Sorghum Grain Mold Disease Complex: Pathogens, Host Responses, and the Bioactive Metabolites at Play. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 660171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somantri, S.; Somantri, R.U. A bibliometric analysis of sorghum disease research using VOS viewer. AIP Conf. Proc. 2024, 2957, 090003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pande, S.; Harikrishnan, R.; Alegbejo, M.; Mughogho, L.; Karunakar, R.; Ajayi, O. Prevalence of sorghum diseases in Nigeria. Int. J. Pest. Manag. 1993, 39, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngugi, K.; King, B.; Abayo, O.; Reddy, R. Prevalence, incidence and severity of sorghum diseases in Western Kenya. J. Plant Dis. 2002, 86, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mims, C.W.; Vaillancourt, L.J. Ultrastructural characterization of infection and colonization of maize leaves by Colletotrichum graminicola, and by a C. graminicola pathogenicity mutant. Phytopathology 2002, 92, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, R.P.; Mathur, K. Anthracnose. In Compendium of Sorghum Diseases; Frederiksen, R.A., Odvody, G.N., Eds.; The American Phytopathological Society: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2000; pp. 10–12. [Google Scholar]
- Acharya, B.; O’Quinn, T.N.; Everman, W.; Mehl, H.L. Effectiveness of fungicides and their application timing for the management of sorghum foliar anthracnose in the mid-atlantic u.s. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 2804–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waniska, R.D.; Venkatesha, R.T.; Chandrashekar, A.; Krishnaveni, S.; Bejosano, F.P.; Jeoung, J.; Jayaraj, J.; Muthukrishnan, S.; Liang, G.H. Antifungal Proteins and Other Mechanisms in the Control of Sorghum Stalk Rot and Grain Mold. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 4732–4742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cota, L.V.; Souza, A.G.C.; Costa, R.V.; Silva, D.D.; Lanza, F.E.; Aguiar, F.M.; Figueiredo, J.E.F. Quantification of yield losses caused by leaf anthracnose on sorghum in Brazil. J. Phytopathol. 2017, 165, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prom, L.K.; Cuevas, H.E.; Ahn, E.; Isakeit, T.; Magill, C. Response of sorghum accessions from three African countries to anthracnose, grain mould, and rust. Plant Pathol. J. 2022, 21, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koima, I.N.; Kilalo, D.C.; Orek, C.O.; Wagacha, J.M.; Nyaboga, E.N. Identification and Characterization of Colletotrichum Species Causing Sorghum Anthracnose in Kenya and Screening of Sorghum Germplasm for Resistance to Anthracnose. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erpelding, J.E. Field Assessment of Anthracnose disease response for the Sorghum germplasm collection from the Mopti region. Am. J. Agri. Biol. Sci. 2010, 5, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengistu, G.; Shimelis, H.; Laing, M.; Lule, D. Assessment of sorghum genetic resources of Ethiopia for anthracnose (Colletotrichum sublineolum Henn.) resistance and agronomic traits. J. Phytopathol. 2019, 167, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Qin, P.; Jiang, Y.; Hu, L.; Liu, K.; Xu, X. Evaluation of sorghum germplasm resistance to anthracnose by Colletotrichum sublineolum in China. Crop Prot. 2020, 134, 105173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, K.; Arif, M.; Zhang, B.; Dong, L.; Wang, R.; Ren, M.; Xie, X. Response and disease resistance evaluation of sorghum seedlings under anthracnose stress. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 21978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erpelding, J.E. Inheritance of anthracnose resistance for the sorghum cultivar redlan. Plant Pathol. J. 2007, 6, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mehta, P.; Wiltse, C.; Rooney, W.; Collins, S.; Frederiksen, R.; Hess, D.; Chisi, M.; TeBeest, D.O. Classification and inheritance of genetic resistance to anthracnose in Sorghum Field. Crops Res. 2005, 93, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, R.; Chandrashekar, A. Biology and management of sorghum grain mold. In Proceedings of the Consultative Group Meeting on Technical and Institutional Options for Sorghum Grain Mold Management, Patancheru, India, 18–19 May 2000; Chandrashekar, A., Bandyopadhyay, R., Hall, A.J., Eds.; International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics: Patancheru, India, 2000; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Little, C.R.; Perumal, R.; Tesso, T.; Prom, L.K.; Odvody, G.N.; Magill, C.W. Sorghum pathology and biotechnology—A fungal disease perspective: Part I. grain mold, head smut, and ergot. Eur. J. Plant Sci. Biotechnol. 2012, 6, 10–30. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.D.; Bandyopadhyay, R. Grain Mold. In Compendium of Sorghum Diseases; Frederiksen, R.A., Odvody, G.N., Eds.; The American Phytopathological Society: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2000; pp. 38–40. [Google Scholar]
- Navi, S.S.; Bandyopadhyay, R.; Reddy, R.K.; Thakur, R.P.; Yang, X.B. Effects of wetness duration and grain development stages on sorghum grain mold infection. Plant Dis. 2005, 89, 872–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, I.K.; Aruna, C.; Tonapi, V.A. Sorghum grain mold. In ICAR-Indian Institute of Millet Research, Hyderrabad, India; ICAR: Hyderabad, India, 2020; 86p, ISBN 81-89335-93-6. [Google Scholar]
- Prom, L. The Effects of Fusarium thapsinum, Curvularia lunata, and Their Combination on Sorghum Germination and Seed Mycoflora. J. New Seeds 2004, 6, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, R.P.; Rao, V.P.; Reddy, B.V.S.; Reddy, S.P. Grain mold. In Screening Techniques for Sorghum Diseases; Thakur, R.P., Reddy, B.V.S., Mathur, K., Eds.; Bull. 76; ICRISAT: Patancheru, India, 2007; pp. 5–14. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, O.E.; Nyquist, W.E.; Axtell, J.D. Quantitative inheritance and correlations of agronomic and grain quality traits of sorghum. Crop Sci. 1985, 25, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siame, B.A.; Mpuchane, S.F.; Gashe, B.A.; Allotey, J.; Teffera, G. Occurrence of aflatoxins, fumonisin B1, and zearalenone in foods and feeds in Botswana. J. Food Prot. 1998, 61, 1670–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leslie, J.F.; Zeller, K.A.; Lamprecht, S.C.; Rheeder, J.P.; Marasas, W.F.O. Toxicity, pathogenicity, and genetic differentiation of five species of Fusarium from sorghum and millet. Phytopathology 2005, 95, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Audilakshmi, S.; Stenhouse, J.W.; Reddy, T.P. Genetic analysis of grain mold resistance in white seed sorghum genotypes. Euphytica 2005, 145, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpofu, L.T.; McLaren, N.W. Ergosterol concentration and variability in genotype-by-pathogen interaction for grain mold resistance in sorghum. Planta 2014, 240, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Aruna, C.; Das, I.K.; Reddy, P.S.; Ghorade, R.B.; Gulhane, A.R.; Kalpande, V.V.; Kajjidoni, S.T.; Hanamaratti, N.G.; Chattannavar, S.N.; Mehtre, S.; et al. Development of sorghum genotypes for improved yield and resistance to grain mold using population breeding approach. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 687332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tayea, W.; Dejene, M.; Ayalew, A.; Chala, A. Evaluation of sorghum genotypes for their reaction to major grain molds and mycotoxin-producing fungi in two climates of Ethiopia. Isr. J. Plant Sci. 2022, 69, 87–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nida, H.; Girma, G.; Mekonen, M.; Lee, S.; Seyoum, A.; Salegn, K.D.; Tadesse, T.; Ayana, G.; Senbetay, T.; Tesso, T.; et al. Identification of sorghum grain mold resistance loci through genome wide association mapping. J. Cereal Sci. 2019, 85, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olatoye, M.O.; Hu, Z.; Morris, G.P. Genome-wide mapping and prediction of plant architecture in a sorghum nested association mapping population. Plant Genome 2020, 13, e20038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gichile, H. Review on sorghum grain mold and its sustainable management methods through host resistance. J. Agric. Res. Advs. 2023, 5, 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Birhanu, C.; Girma, G.; Mekbib, F.; Nida, H.; Tirfessa, A.; Lule, D.; Bekeko, Z.; Ayana, G.; Bejiga, T.; Bedada, G.; et al. Exploring the genetic basis of anthracnose resistance in Ethiopian sorghum through a genome-wide association study. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, M.; Singh, Y.; Srivastava, D.; Srivastava, S. Effect of weather parameters on the severity of sorghum anthracnose. Environ. Ecology 2021, 39, 1236–1241. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, G.P.; Ramu, P.; Deshpande, S.P.; Hash, C.T.; Shah, T.; Upadhyaya, H.D.; Riera-Lizarazu, O.; Brown, P.J.; Acharya, C.B.; Mitchell, S.E.; et al. Population genomic and genome-wide association studies of agroclimatic traits in sorghum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 110, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, D.H.; Hoffmann, L.; Rooney, W.L.; Herald, T.J.; Bean, S.; Boyles, R.; Brenton, Z.W.; Kresovich, S. Genetic architecture of kernel composition in global sorghum germplasm. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Srinivasan, S.; Mirnezami, S.V.; Kusmec, A.; Fu, Q.; Attigala, L.; Fernandez, M.G.S.; Ganapathysubramanian, B.; Schnable, P.S. Semiautomated Feature Extraction from RGB Images for Sorghum Panicle Architecture GWAS. Plant Physiol. 2019, 179, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girma, G.; Nida, H.; Seyoum, A.; Mekonen, M.; Nega, A.; Lule, D.; Mengiste, T. A large-scale genome-wide association analyses of Ethiopian sorghum landrace collection reveal loci associated with important traits. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariscal-Amaro, L.A.; Héctor, E.; Villaseñor-Mir, H.E.; Solís-Moya, E.; Hortelano-Santa Rosa, R.; Martínez-Cruz, E. Effect of fungicides on agronomic traits, yield and leaf blights in rainfed wheat in Mexico. Rev. Fitotec. Mex. 2020, 43, 71–78. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, N.D.; Maziero, S.M. Environmental variability in indirect selection for grain yield in common bean lines. Sci. Agric. 2023, 80, e20220082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laidig, F.; Feike, T.; Macholdt, J.; Miedaner, T.; Rentel, D.; Piepho, H.P. Yield Reduction Due to Diseases and Lodging and Impact of Input Intensity on Yield in Variety Trials in Five Cereal Crops. Euphytica 2022, 218, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dendi, A.; Khan, M.A.; Mir, R.R.; Bhat, M.A.; Wani, F.J.; Bhat, M.A. Trait phenotyping and Inheritance of leaf blight resistance in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) under temperate conditions of Kashmir valley. J. Cereal Sci. 2023, 15, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.M.; Liu, P.; Zhao, J.H.; Su, L.Y.N.; Zhao, M.Y.; Jiang, Z.J.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, X.P. Correlation of microbiomes in “plant-insect-soil” ecosystem. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1088532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porch, T.G.; Valentin, S.; Estevez de Jensen, C.; Beaver, J.S. Identification of soil-borne pathogens in a common bean root rot nursery in Isabela, Puerto Rico. J. Agric. Univ. Puerto Rico 2014, 98, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prom, L.; Perumal, R.; Erpelding, J.; Isakeit, T.; Montes, N.; Magill, C. A pictorial technique for mass screening of sorghum germplasm for anthracnose (Colletotrichum sublineolum) resistance. Open Agric. 2009, 3, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prom, L.K.; Ahn, E.; Isakeit, T.; Magill, C. Correlations among grain mold severity, seed weight, and germination rate of sorghum association panel lines inoculated with Alternaria alternata, Fusarium thapsinum, and Curvularia lunata. J. Agric. Crops 2022, 8, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Romo, J.T. Seed weight and germination time affect growth of two shrubs. J. Range Manag. 1998, 51, 699–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, P.; Guo, L.; Gao, Y.; Qi, L.; Cao, B. Effects of seed size and sand burial on germination and early growth of seedlings for coastal Pinus thunbergii Parl. in the Northern Shandong Peninsula, China. Forests 2019, 10, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.; Mandal, S.M.; Chakraborty, D. Seed Size Variation: Influence on Germination and Subsequent Seedling Performance in Hyptis suaveolens (Lamiaceae). Res. J. Seed Sci. 2008, 1, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKersie, B.D.; Tomes, D.T.; Yamamoto, S. Effect of seed size on germination, seedling vigor, electrolyte leakage, and establishment of Bird’s- Foot Trefoil [Lotus corniculatus (L.)]. Can. J. Plant Sci. 1981, 61, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Mantilla Perez, M.B.; Hu, J.; Salas Fernandez, M.G. Genome-wide association study for nine plant architecture traits in sorghum. Plant Genome 2016, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adepoju, A.F.; Adenuga, O.O.; Dada, K.E.; Odey, C.F.; Balogun, S.T.; Nitsa, M.B. Association and interrelationship of yield and agronomic characters in coffee (Coffea sp L). J. Plant Breed. Crop Sci. 2020, 12, 299–309. [Google Scholar]
- Garud, T.B.; Ismail, S.; Shinde, B.M. Effect of two mold-causing fungi on germination of sorghum seed. Intern. Sorghum and Millet Newl. 2000, 41, 54. [Google Scholar]
- Gali, K.K.; Sackville, A.; Tafesse, E.G.; Lachagari, V.; McPhee, K.; Hybl, M.; Miki’c, A.; Smýkal, P.; McGee, R.; Burstin, J.; et al. Genome-wide association mapping for agronomic and seed quality traits of field pea (Pisum sativum L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, X.; Hathorn, A.; Hunt, C.; Cruickshank, A.W.; van Oosterom, E.J.; Godwin, I.D.; Mace, E.S.; Jordan, D.R. Large-scale GWAS in sorghum reveals common genetic control of grain size among cereals. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 1093–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czembor, J.H.; Czembor, E. Genome-Wide Association Study of Agronomic Traits in European Spring Barley from Polish Gene Bank. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikshit, H.K.; Manjunatha, P.B.; Aski, M.S.; Mishra, G.P.; Gupta, S.; Devate, N.B.; Singh, A.; Bansal, R.; Kumar, S.; Nair, R.M. Genome-wide association studies for phenological and agronomic traits in mungbean (Vigna radiata L. Wilczek). Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1209288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Soto, R.I.; Mora, F.; de Oliveira, M.A.R.; Higashi, W.; Scapim, C.A.; Schuster, I. A genome-wide association study for agronomic traits in soybean using SNP markers and SNP-based haplotype analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suruliandi, A.; Mariammal, G.; Raja, S.P. Crop Prediction Based on Soil and Environmental Characteristics Using Feature Selection Techniques. Math. Comput. Model. Dyn. Syst. 2021, 27, 117–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesami, M.; Naderi, R.; Tohidfar, M.; Yoosefzadeh-Najafabadi, M. Development of support vector machine-based model and comparative analysis with artificial neural network for modeling the plant tissue culture procedures: Effect of plant growth regulators on somatic embryogenesis of chrysanthemum, as a case study. Plant Methods 2020, 16, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biau, G.; Scornet, E. A random forest guided tour. Test 2016, 25, 197–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

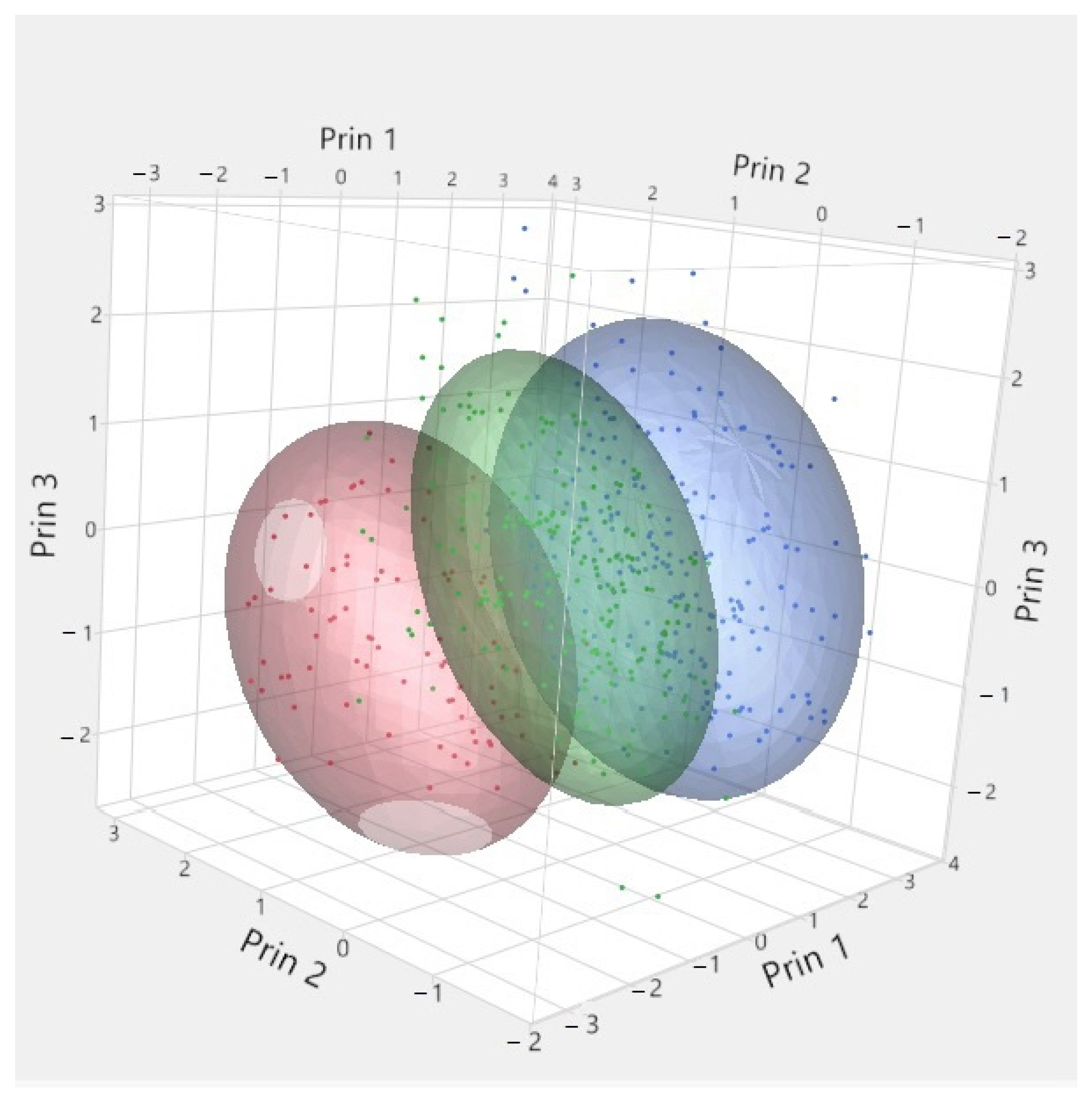
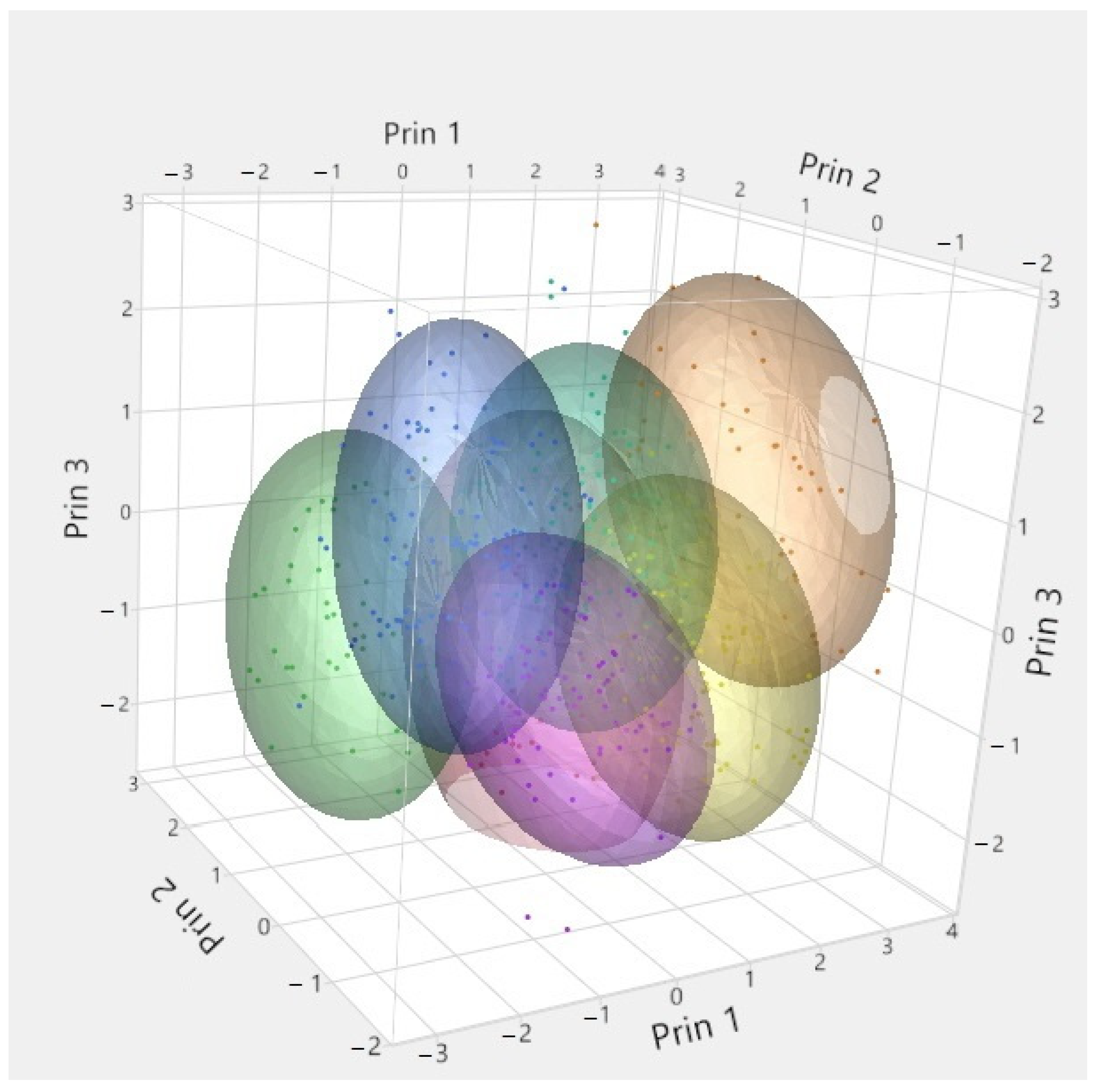
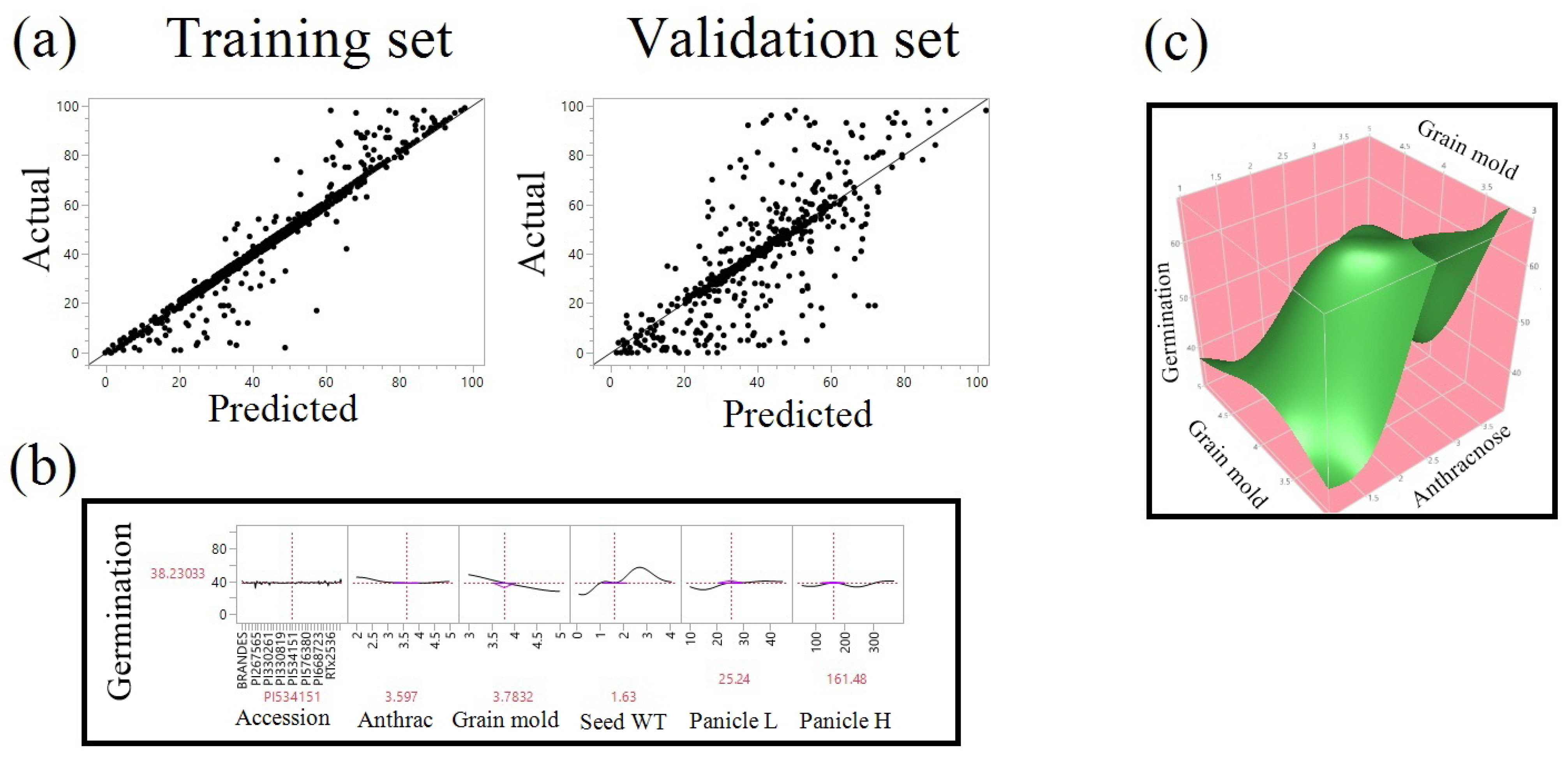
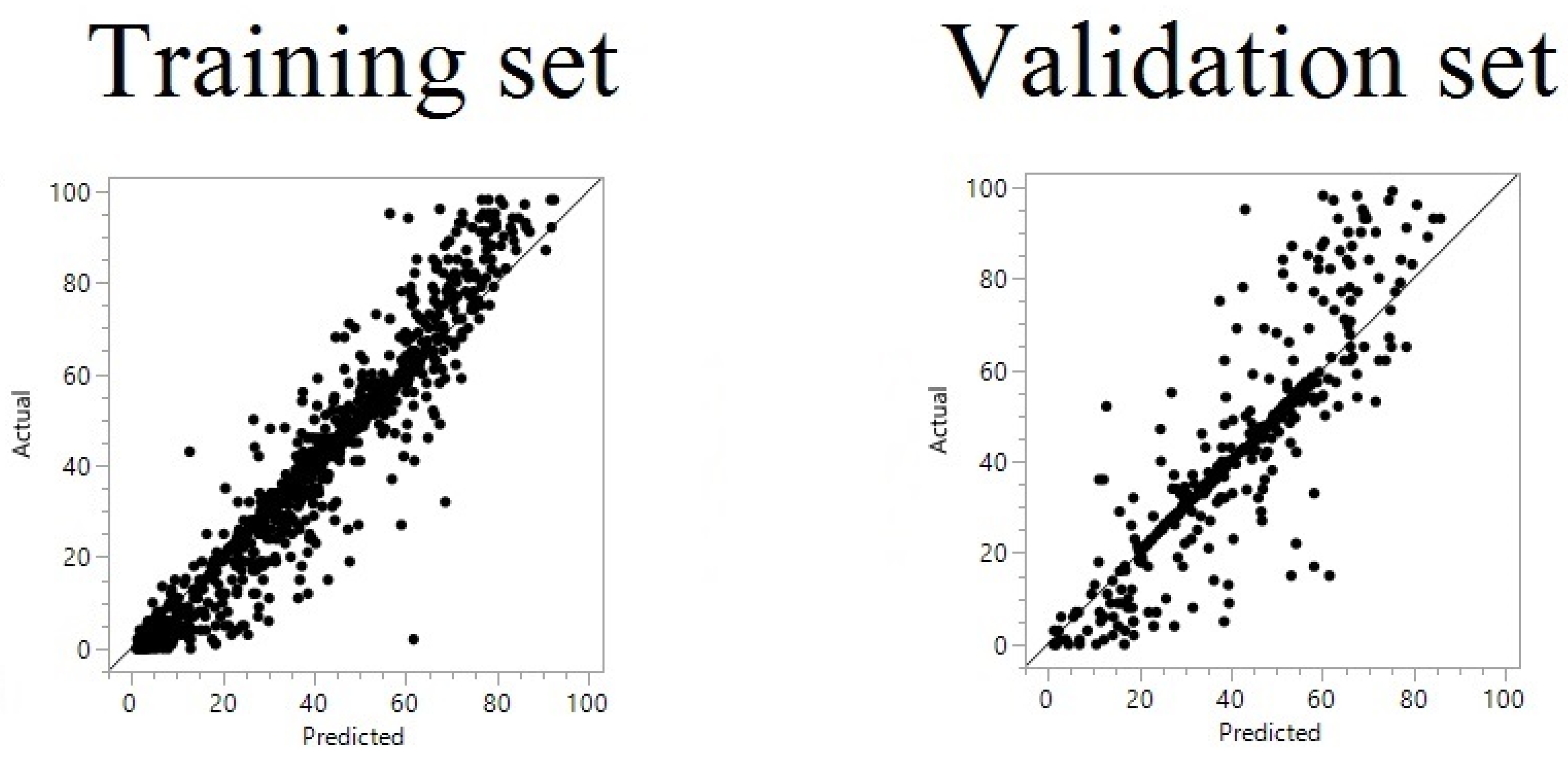
| Year/Month | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | Air temperature | 22.7 | 22.9 | - a | 24.4 | 24.7 | 25.8 | 26.1 | 26.0 | 26.2 | 25.4 | 25.3 | 24.3 |
| Total rainfall | 52.3 | 46.2 | - | 67.3 | 226.1 | 60.5 | 30.5 | 108.7 | 189.5 | 133.1 | 7.1 | 68.8 | |
| 2020 | Air temperature | 23.4 | 23.6 | 23.4 | 24.8 | 25.3 | 26.6 | 26.3 | 26.5 | 25.7 | 25.4 | 24.3 | 23.4 |
| Total rainfall | 157.7 | 68.8 | 182.9 | 71.1 | 94.2 | 14.7 | 93.0 | 97.5 | 51.3 | 23.4 | 182.9 | 25.9 |
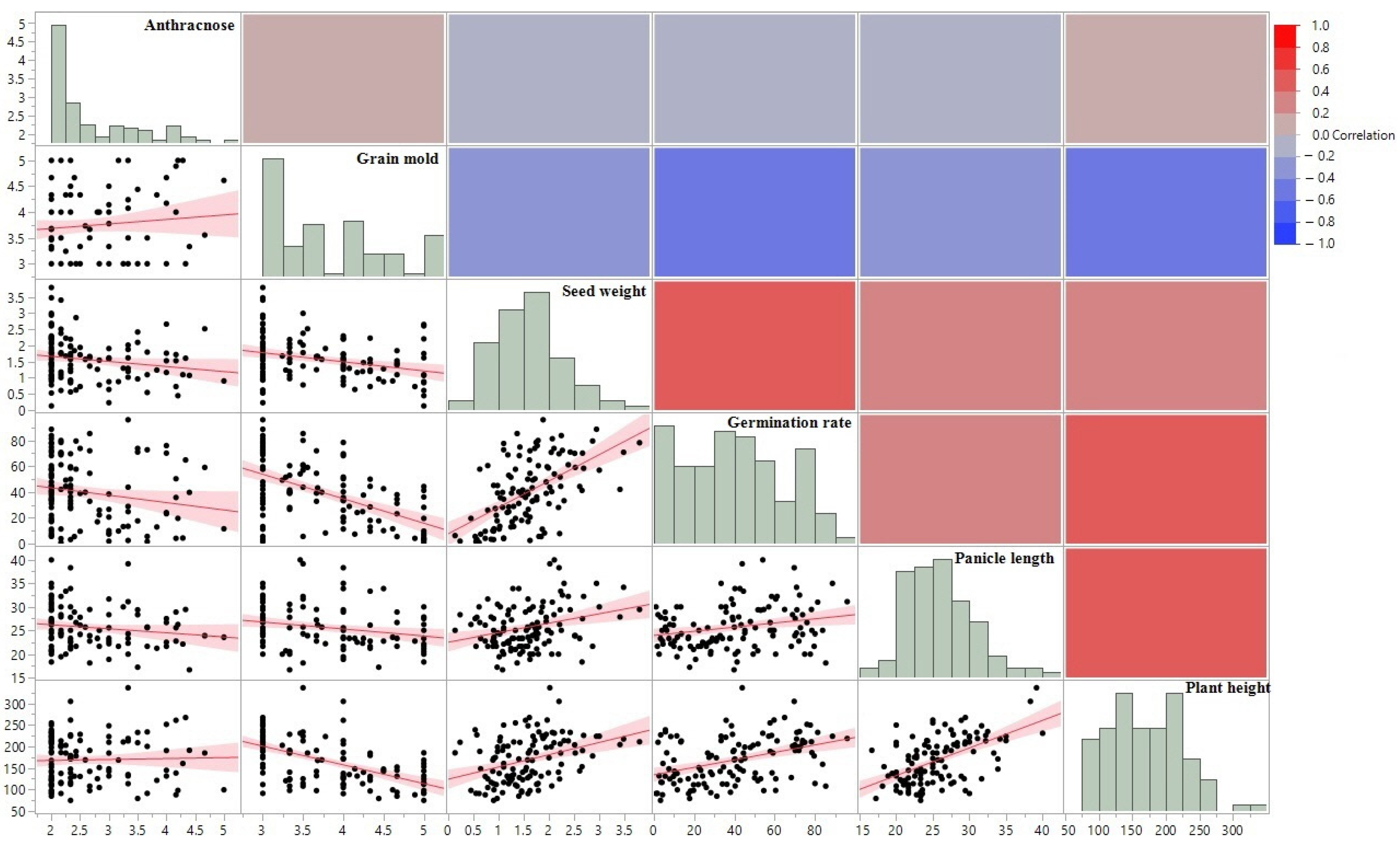
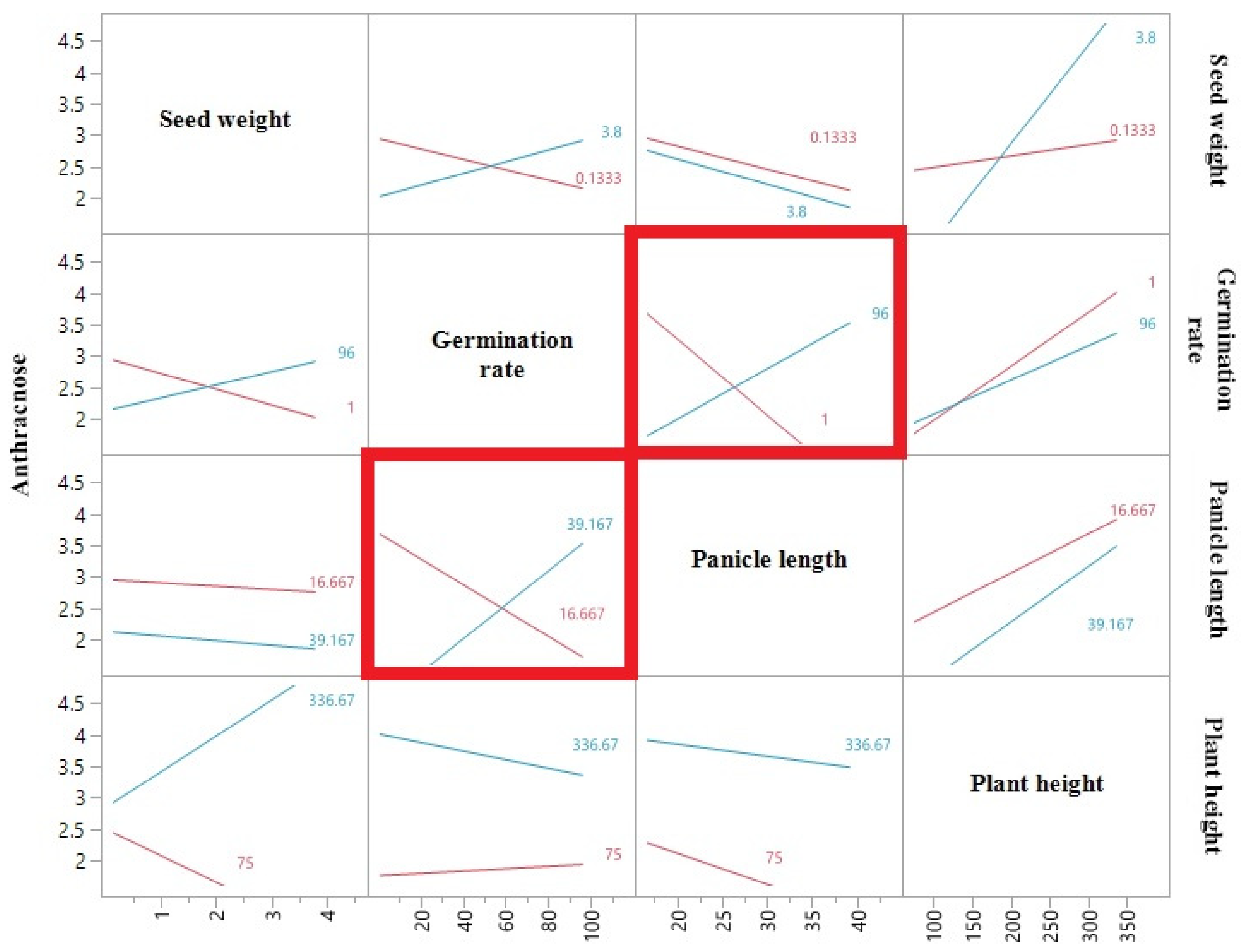
| Traits | Spearman ρ | Prob > |ρ| |
|---|---|---|
| Anthracnose–Grain mold | 0.0708 | 0.4311 |
| Anthracnose–Seed weight | −0.1903 | 0.0328 |
| Anthracnose–Germination rate | −0.2067 | 0.0202 |
| Anthracnose–Panicle length | −0.1113 | 0.2145 |
| Anthracnose–Plant height | 0.0356 | 0.6926 |
| Germination rate–Grain mold | −0.5159 | <0.0001 |
| Germination rate–Plant height | 0.4031 | <0.0001 |
| Germination rate–Panicle length | 0.2274 | 0.0105 |
| Germination rate–Seed weight | 0.5615 | <0.0001 |
| Grain mold–Plant height | −0.6113 | <0.0001 |
| Grain mold–Panicle length | −0.2701 | 0.0022 |
| Grain mold–Seed weight | −0.289 | 0.001 |
| Plant height–Seed weight | 0.389 | <0.0001 |
| Plant height–Panicle length | 0.525 | <0.0001 |
| Panicle length–Seed weight | 0.2575 | 0.0036 |
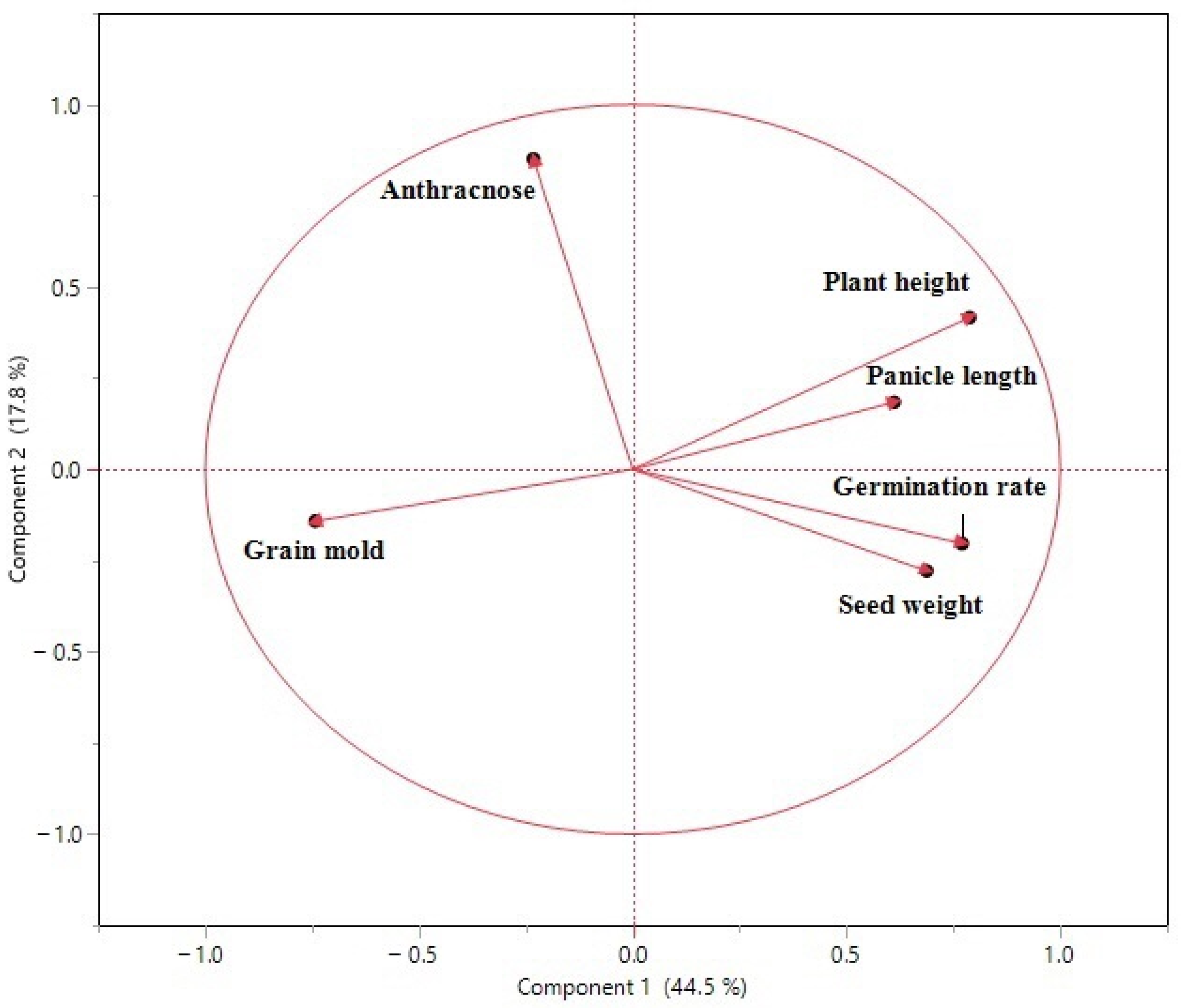
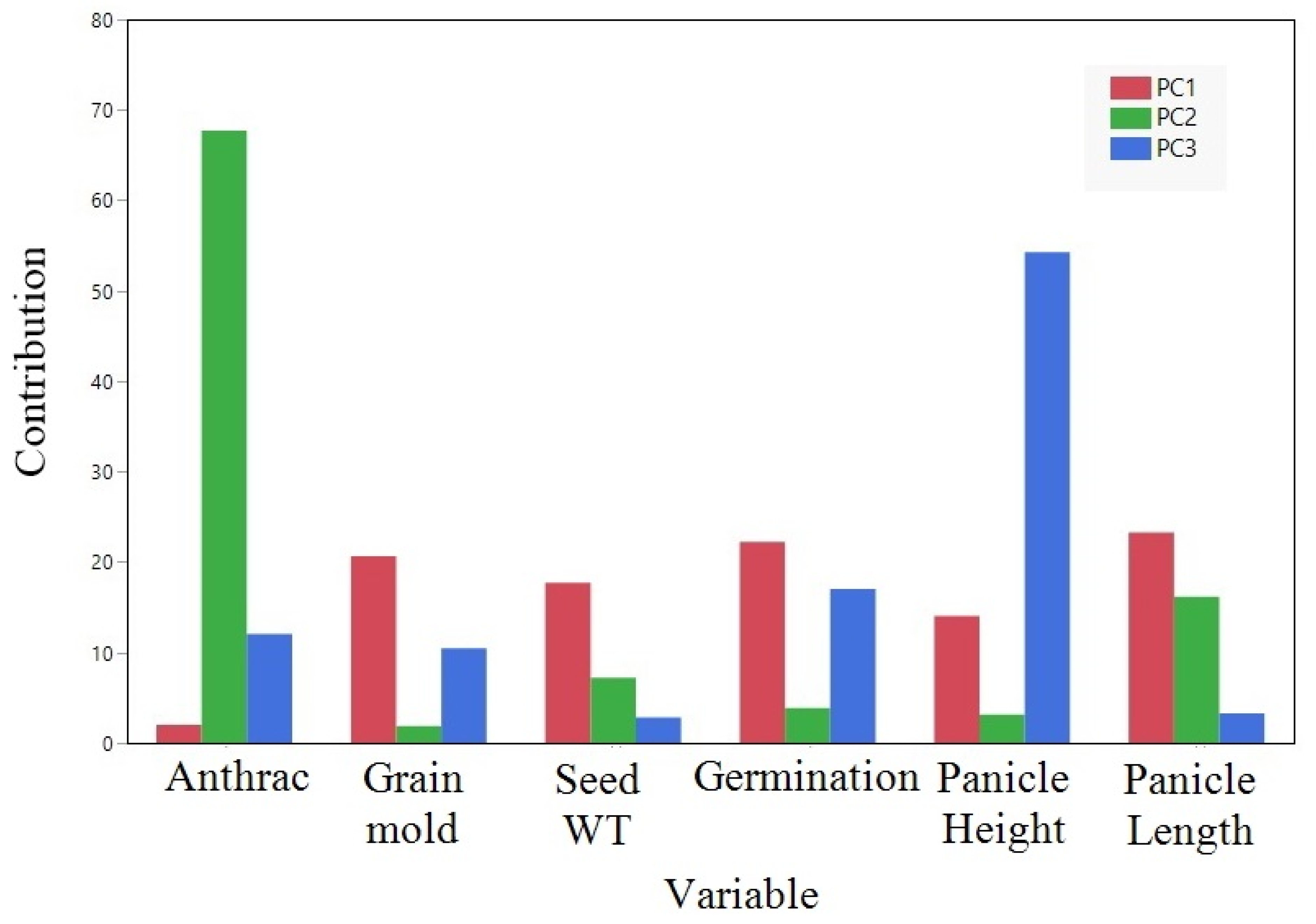
| Cluster | Members | R-Square with Its Own Cluster | R-Square with the Next Closest | 1-R-Square Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Plant height | 0.653 | 0.001 | 0.348 |
| Germination rate | 0.586 | 0.03 | 0.427 | |
| Grain mold | 0.56 | 0.009 | 0.443 | |
| Seed weight | 0.463 | 0.032 | 0.555 | |
| Panicle length | 0.372 | 0.02 | 0.64 | |
| 2 | Anthracnose | 1 | 0.021 | 0 |
| Term | Number of Splits | Sum of Squares | Importance | Portion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grain mold | 616 | 120,944.23 |  | 0.3396 |
| Accession | 1447 | 108,634.499 |  | 0.3051 |
| Seed weight | 1086 | 64,907.3179 |  | 0.1823 |
| Panicle height | 789 | 36,383.6986 |  | 0.1022 |
| Panicle length | 639 | 13,592.7099 |  | 0.0382 |
| Anthracnose | 665 | 11,649.3571 |  | 0.0327 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prom, L.K.; Ahn, E.J.S.; Cuevas, H.E.; Liu, J.; Isakeit, T.S.; Magill, C.W. Association and Interrelationship Among Agronomic Traits and Fungal Diseases of Sorghum, Anthracnose and Grain Mold. Crops 2024, 4, 651-666. https://doi.org/10.3390/crops4040045
Prom LK, Ahn EJS, Cuevas HE, Liu J, Isakeit TS, Magill CW. Association and Interrelationship Among Agronomic Traits and Fungal Diseases of Sorghum, Anthracnose and Grain Mold. Crops. 2024; 4(4):651-666. https://doi.org/10.3390/crops4040045
Chicago/Turabian StyleProm, Louis K., Ezekiel J. S. Ahn, Hugo E. Cuevas, Jinggao Liu, Thomas S. Isakeit, and Clint W. Magill. 2024. "Association and Interrelationship Among Agronomic Traits and Fungal Diseases of Sorghum, Anthracnose and Grain Mold" Crops 4, no. 4: 651-666. https://doi.org/10.3390/crops4040045
APA StyleProm, L. K., Ahn, E. J. S., Cuevas, H. E., Liu, J., Isakeit, T. S., & Magill, C. W. (2024). Association and Interrelationship Among Agronomic Traits and Fungal Diseases of Sorghum, Anthracnose and Grain Mold. Crops, 4(4), 651-666. https://doi.org/10.3390/crops4040045







