Climate Change and Its Positive and Negative Impacts on Irrigated Corn Yields in a Region of Colorado (USA)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Information
2.2. Long-Term Research Plots and Weather Analysis
2.3. Long-Term County Yields and Weather Analysis
3. Results and Conclusions
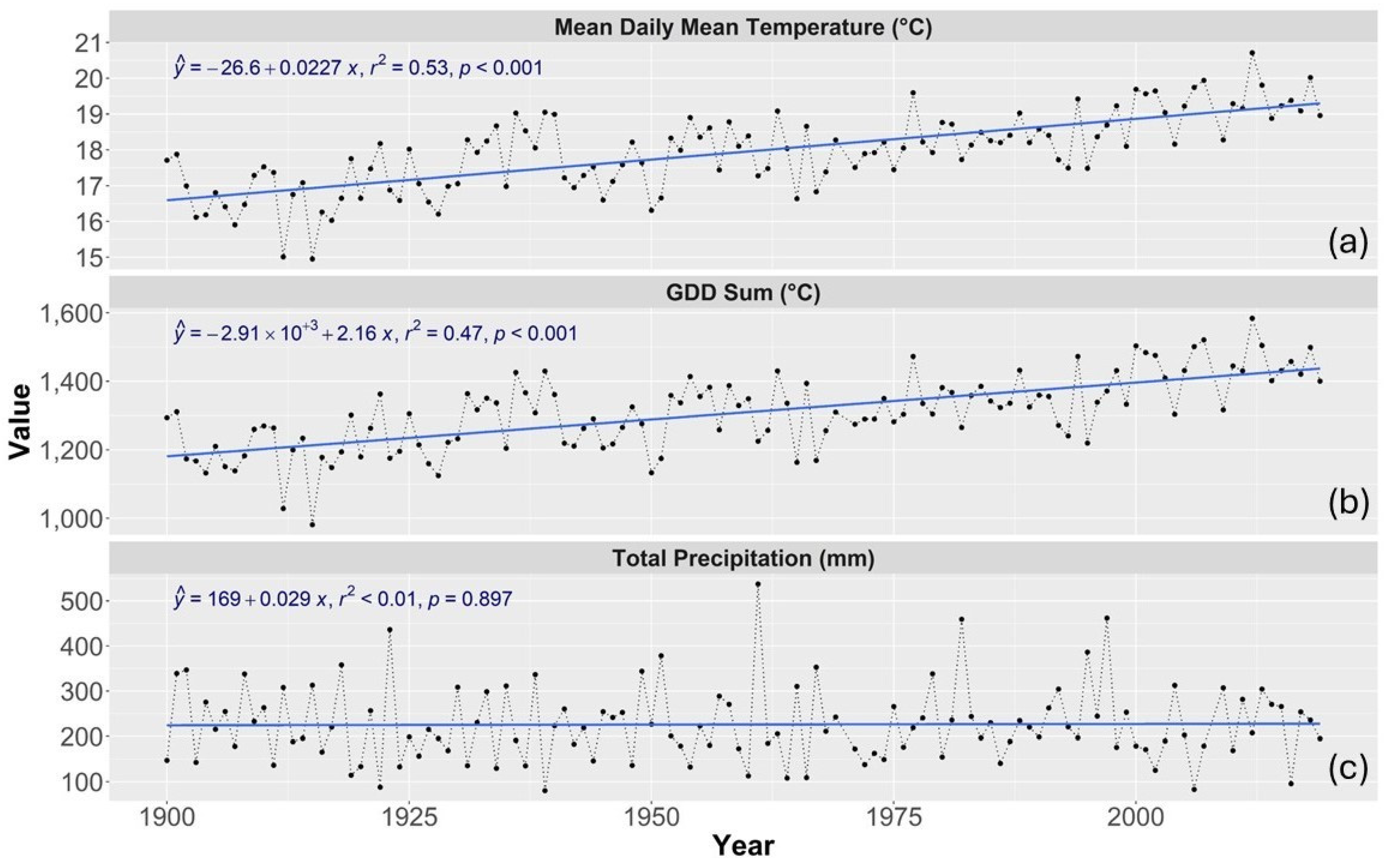
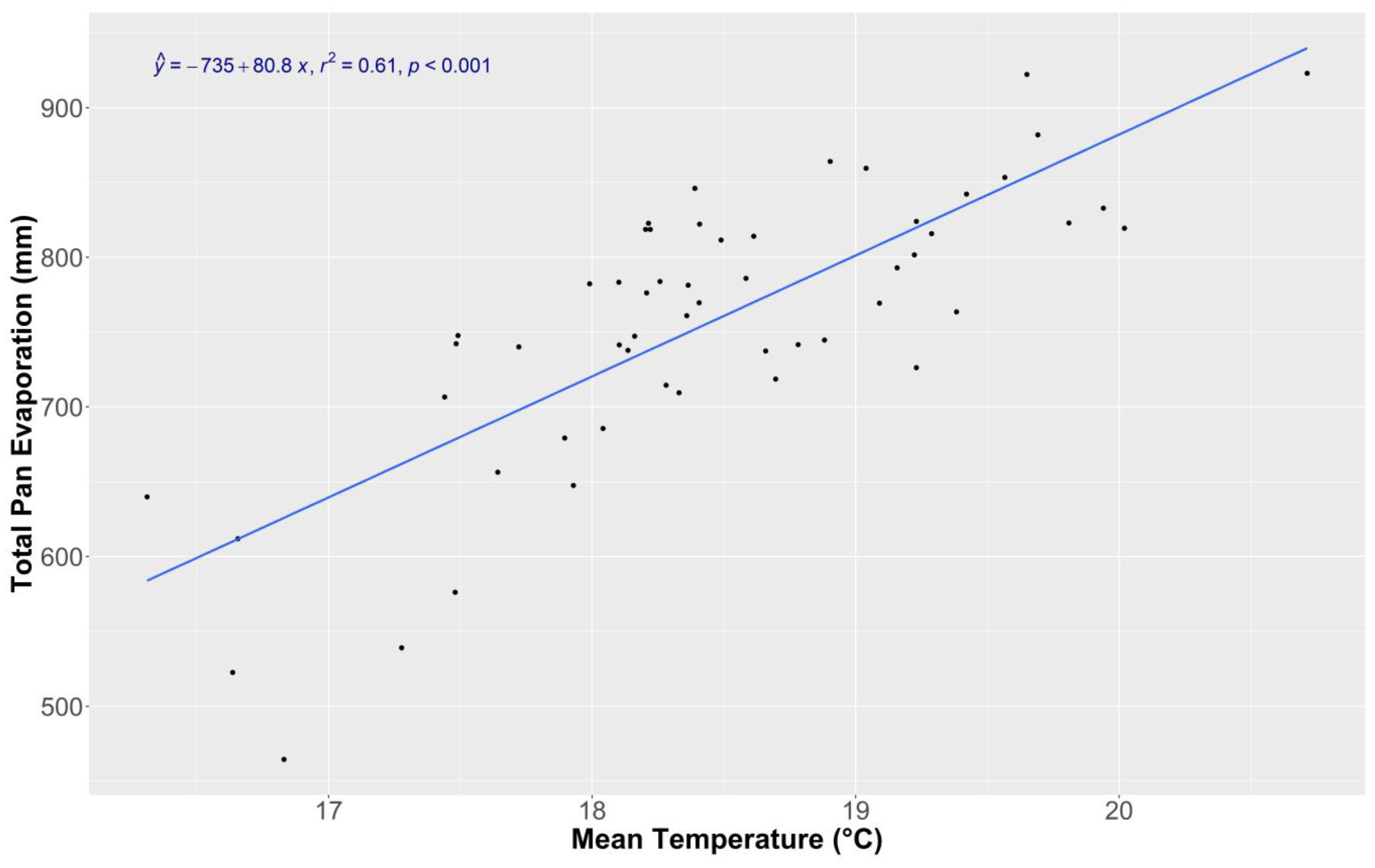
3.1. Climate Change
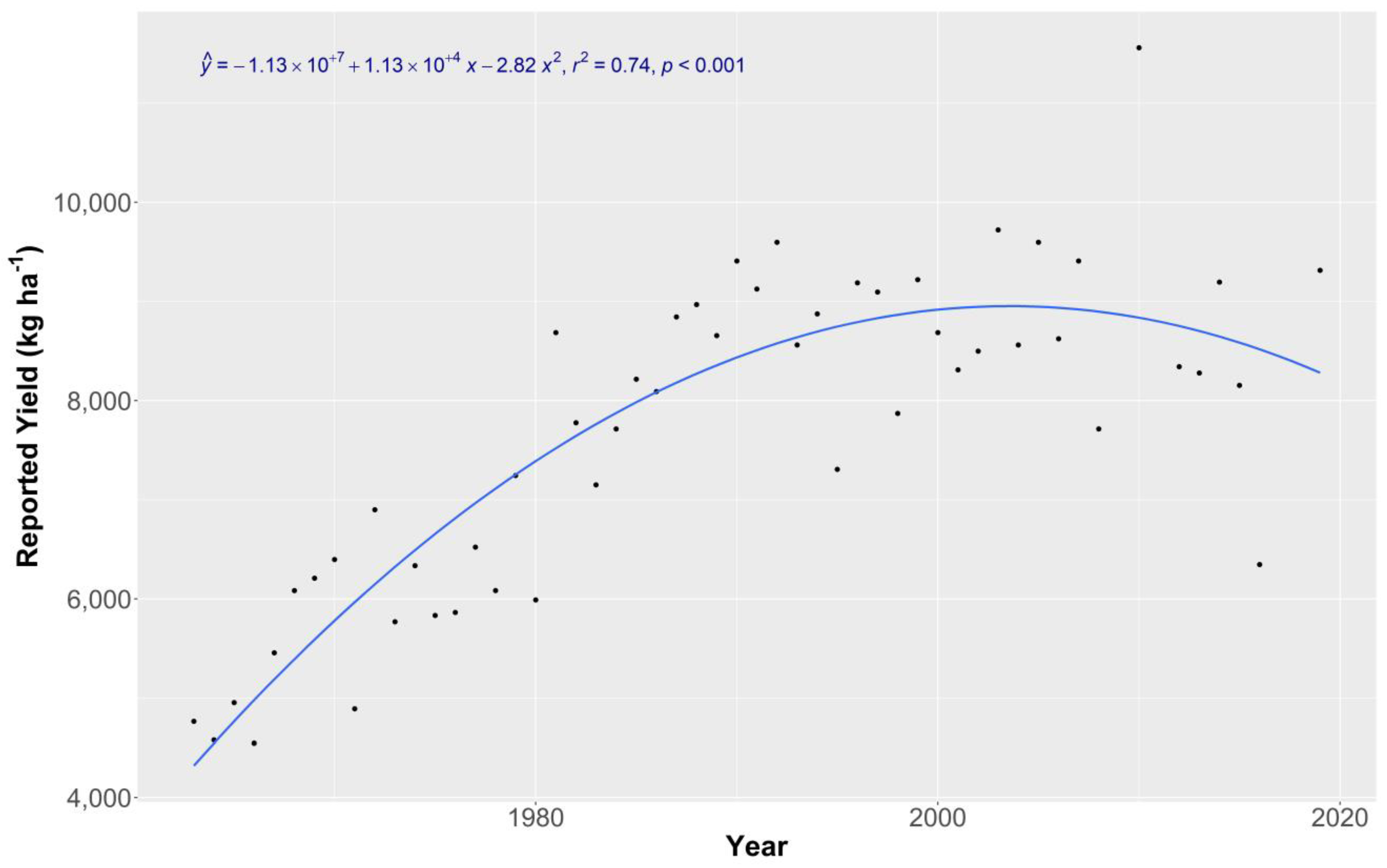
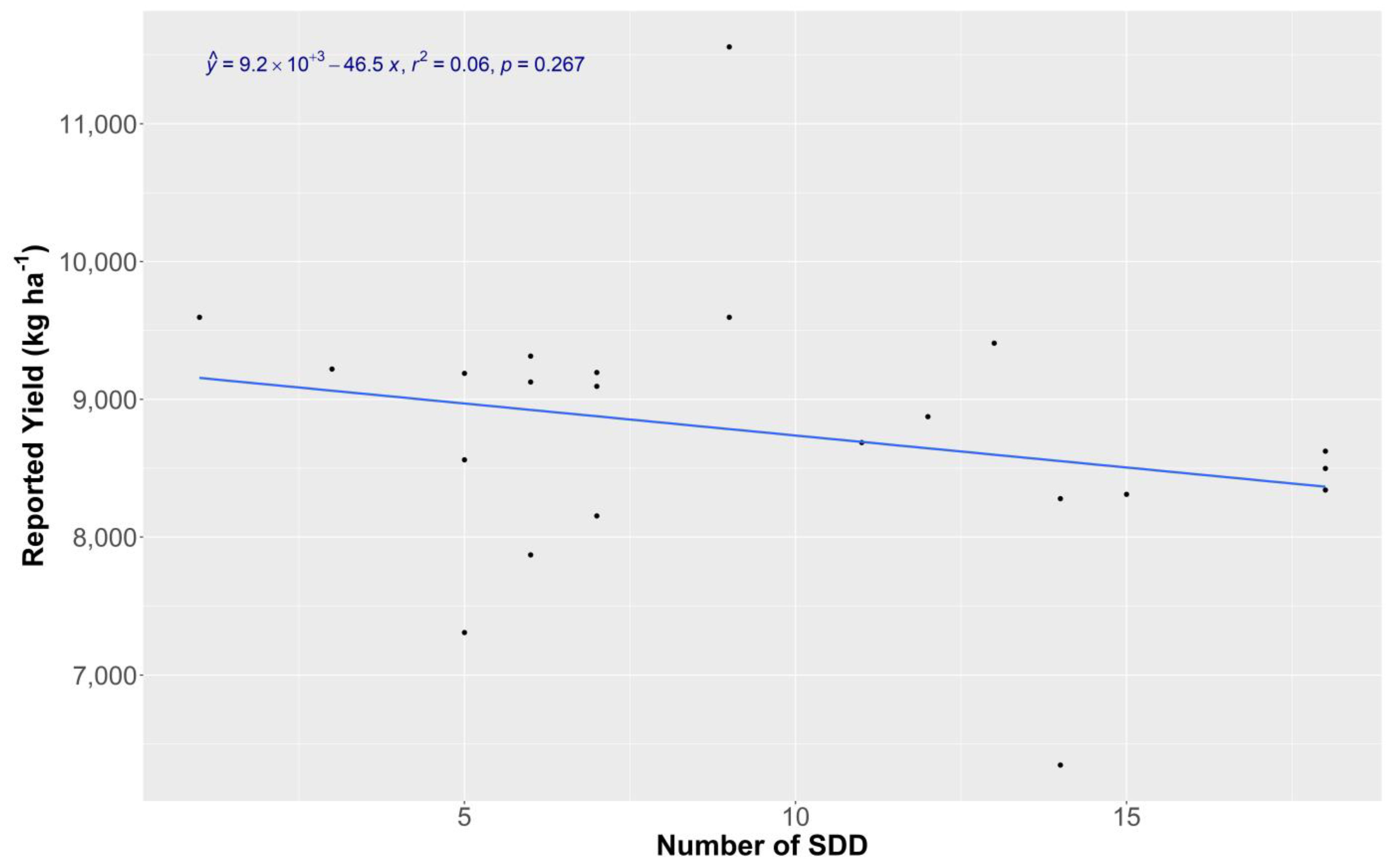
3.1.1. County Yields and Weather Analysis
3.1.2. Long-Term Research Plots and Weather Analysis
3.2. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Delgado, J.A.; Groffman, P.M.; Nearing, M.A.; Goddard, T.; Reicosky, D.; Lal, R.; Kitchen, N.R.; Rice, C.W.; Towery, D.; Salon, P. Conservation practices to mitigate and adapt to climate change. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2011, 66, 118A–129A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusser, S.; Bahlai, C.; Swinton, S.M.; Robertson, G.P.; Haddad, N.M. Long-term research avoids spurious and misleading trends in sustainability attributes of no-till. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2020, 26, 3715–3725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, J.A.; Halvorson, A.D.; D’Adamo, R.; Stewart, C.E.; Floyd, B.; Del Grosso, S. Long-term nitrogen balance of an irrigated no-till soil-corn system. J. Nutr. Cycl. 2023, 126, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Liu, B.; Piao, S.; Wang, X.; Lobell, D.B.; Huang, Y.; Huang, M.; Yao, Y.; Bassu, S.; Ciais, P.; et al. Temperature increase reduces global yields of major crops in four independent estimates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 9326–9331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatfield, J.L.; Boote, K.J.; Kimball, B.A.; Ziska, L.H.; Izaurralde, R.C.; Ort, D.; Thomson, A.M.; Wolfe, D. Climate impacts on agriculture: Implications for crop reduction. Agron. J. 2011, 103, 351–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatfield, J.L.; Dold, C. Climate change impacts on corn phenology and productivity. In Corn—Production and Human Health in a Changing Climate; Amanullah and Shah Fahad; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; pp. 95–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesen, J.E.; Bindi, M. Consequences of climate change for European agricultural productivity, land use and policy. Eur. J. Agron. 2002, 16, 239–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, A.M.; Brown, R.A.; Rosenberg, N.J.; Izaurralde, R.C.; Benson, V. Climate change impacts for the conterminous USA: An integrated assessment. Part. 3. Dryland production of grain and forage crops. Clim. Chang. 2005, 69, 43–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.H.; Ahuja, L.R.; Saseendran, S.A.; Green, T.R.; Ma, L.; Nielsen, D.C.; Walthall, C.L. Climate change impacts on dryland cropping systems in the Central Great Plains, USA. Clim. Chang. 2012, 111, 445–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, G. Evidence for a weakening strength of temperature-corn yield relation in the United States during 1980–2010. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 605–606, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Ma, X.; Pan, X.; Binxiang, H. Climate warming changed the planting boundaries of varieties of summer corn with different maturity levels in the North China Plain. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2019, 58, 2605–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.M. Heat Units for Corn in Southern Ontario; Food Factsheet Agdex 111.30: 4; Ontario Ministry of Agriculture: Guelph, ON, Canada, 1969.
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, N.; Xu, L.; Zhu, J.; Tao, H.; Huang, S.; Wang, P. Late harvest and foliar fungicide acted together to minimize climate change effects on summer maize yield in the North China Plain during 1954–2015. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 265, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Hu, Q. Changes in agro-meteorological indicators in the contiguous United States: 1951–2000. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2004, 78, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlenker, W.; Roberts, M.J. Nonlinear temperature effects indicate severe damages to U.S. crop yields under climate change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 15594–15598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, L.K. Impact of climate change on twenty-first century crop yields in the U.S. Climate 2019, 7, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Yang, J.Y.; Drury, C.F.; Smith, W.N.; Grant, B.B.; He, P.; Qian, B.; Zhou, W.; Hoogenboomd, G. Estimating the impacts of climate change on crop yields and N2O emissions for conventional and no-tillage in Southwestern Ontario, Canada. Agric. Syst. 2018, 159, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drury, C.F.; Tan, C.S.; Welacky, T.W.; Oloya, T.O.; Hamill, A.F.; Weaver, S.E. Red clover and tillage influence on soil temperature, water content, and corn emergence. Agron. J. 1999, 91, 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Q.; Buyanovsky, G. Climate effects on corn yield in Missouri. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2003, 42, 1626–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearl, J. Causality: Models, Reasoning and Inference, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021; Available online: https://www.R-project.org (accessed on 4 August 2024).
- Mix, K.; Lopez, V.L.; Rast, W. Annual and growing season temperature changes in the San Luis Valley, Colorado. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2011, 220, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ABC News. Record-Breaking Temperatures across Country. 21 June 2022. ABC News YouTube Channel. 2022. Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wvWN5-Sa1ds (accessed on 21 June 2022).
- Delgado, J.A.; Floyd, B.; Brandt, A.D.; D’Adamo, R. Use of narrow rows in sprinkler-irrigated corn systems to increase grain yields, aboveground biomass, and water and nitrogen use efficiencies. Agronomy 2022, 12, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| VARIABLES | Regression Yield (kg ha−1) |
|---|---|
| Total Applied N (kg ha−1) | 20.4 *** |
| (0.9) | |
| Total Water | 15.2 ** |
| (6.0) | |
| Dekalb DKC42-91 RR/YG a | 686.0 |
| (574.7) | |
| Dekalb DKC42-72 RR/YG a | −1797.3 |
| (1112.4) | |
| Dekalb DKC42-72 RR/YGVT a | −862.0 *** |
| (324.2) | |
| Dekalb DKC42-72 RR/YGVT3 a | −2492.4 *** |
| (846.6) | |
| Dekalb DKC43-48 RIB GENVT3P a | −1633.6 ** |
| (745.6) | |
| Channel 192-09VT3PRIB Blend w/A250 a | −3759.2 ** |
| (1494.7) | |
| Channel 193-53 STXRIB | −2879.7 ** |
| (1166.4) | |
| Sum of GDD (°C) b | 17.6 *** |
| (6.4) | |
| Constant | −25,349.5 ** |
| (11,379.6) | |
| Observations | 148 |
| R-squared | 0.79 |
| Corn Growing Period | Temperature | Intercept (bo) (°C) | Slope (b1) (°C yr−1) | Coefficient of Determination (r2) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| September (CoAgMET) | Maximum | −265 | 0.144 | 0.13 | 0.256 |
| Minimum | −267 | 0.137 | 0.27 | 0.086 |
| Nitrogen Treatment | Growing Period | Minimum Temperature | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| kg N ha−1 | Intercept (bo) (kg ha−1) | Slope (b1)
(kg ha−1 °C−1) | Coefficient of Determination (r2) | p Value | Delta Yield (kg ha−1) | |
| 0 | Planting Through maturity (R6) | 3402 | 175 | 0.05 | 0.222 | 404 |
| 67 | Planting Through maturity (R6) | 3001 | 477 | 0.21 | 0.010 | 1100 |
| 134 | Planting Through maturity (R6) | 799 | 866 | 0.36 | <0.001 | 1998 |
| 202 | Planting Through maturity (R6) | 4231 | 559 | 0.22 | 0.011 | 1290 |
| 246 | Planting Through maturity (R6) | 6968 | 332 | 0.13 | 0.060 | 766 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Delgado, J.A.; D’Adamo, R.E.; Villacis, A.H.; Halvorson, A.D.; Stewart, C.E.; Alwang, J.; Del Grosso, S.J.; Manter, D.K.; Floyd, B.A. Climate Change and Its Positive and Negative Impacts on Irrigated Corn Yields in a Region of Colorado (USA). Crops 2024, 4, 366-378. https://doi.org/10.3390/crops4030026
Delgado JA, D’Adamo RE, Villacis AH, Halvorson AD, Stewart CE, Alwang J, Del Grosso SJ, Manter DK, Floyd BA. Climate Change and Its Positive and Negative Impacts on Irrigated Corn Yields in a Region of Colorado (USA). Crops. 2024; 4(3):366-378. https://doi.org/10.3390/crops4030026
Chicago/Turabian StyleDelgado, Jorge A., Robert E. D’Adamo, Alexis H. Villacis, Ardell D. Halvorson, Catherine E. Stewart, Jeffrey Alwang, Stephen J. Del Grosso, Daniel K. Manter, and Bradley A. Floyd. 2024. "Climate Change and Its Positive and Negative Impacts on Irrigated Corn Yields in a Region of Colorado (USA)" Crops 4, no. 3: 366-378. https://doi.org/10.3390/crops4030026
APA StyleDelgado, J. A., D’Adamo, R. E., Villacis, A. H., Halvorson, A. D., Stewart, C. E., Alwang, J., Del Grosso, S. J., Manter, D. K., & Floyd, B. A. (2024). Climate Change and Its Positive and Negative Impacts on Irrigated Corn Yields in a Region of Colorado (USA). Crops, 4(3), 366-378. https://doi.org/10.3390/crops4030026







