Improved Measurement Method of Human Skin Temperature Based on Human Skin-like Gradient Standard Radiation Source
Abstract
1. Introduction
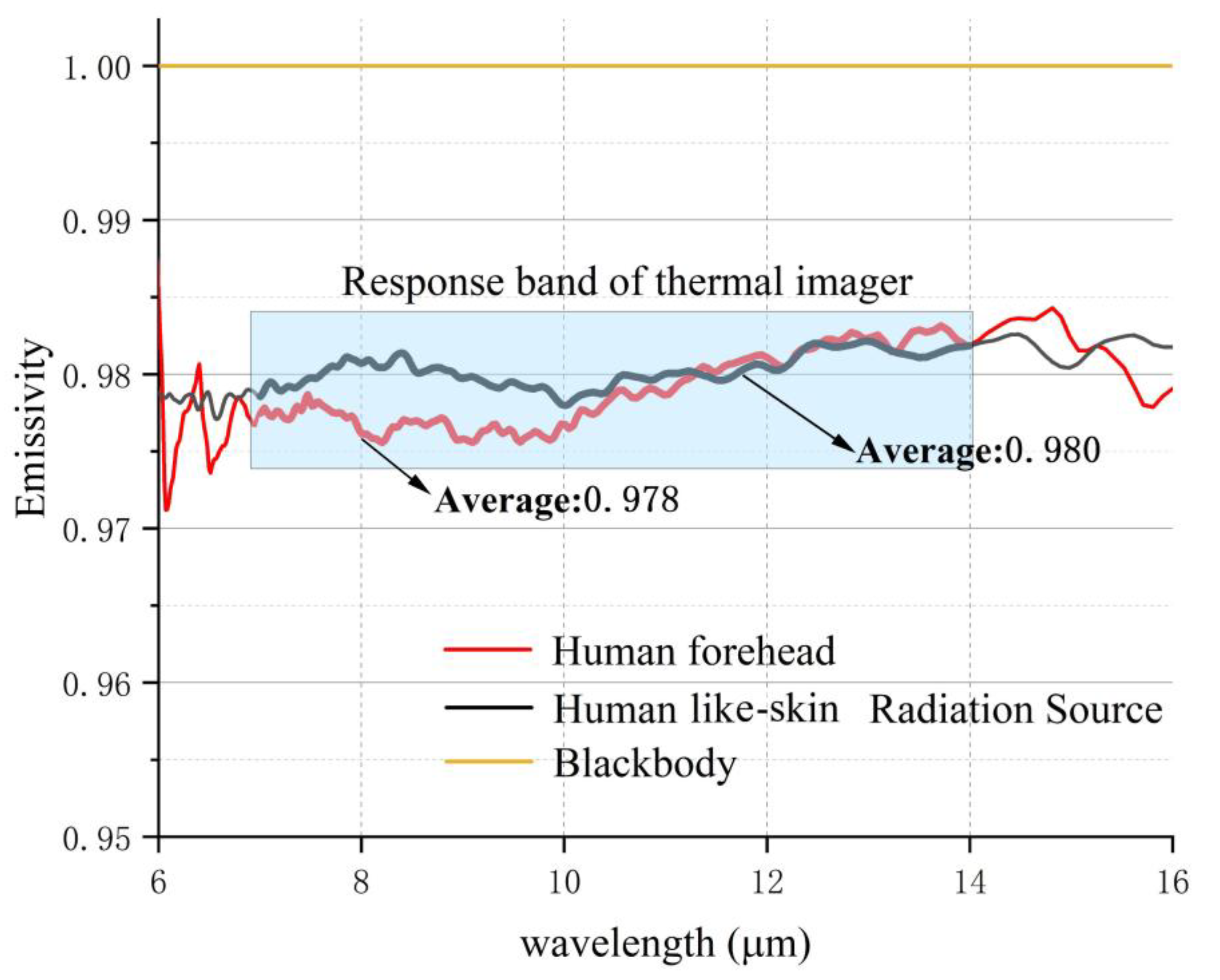
2. Theoretical Analysis
3. Experimental
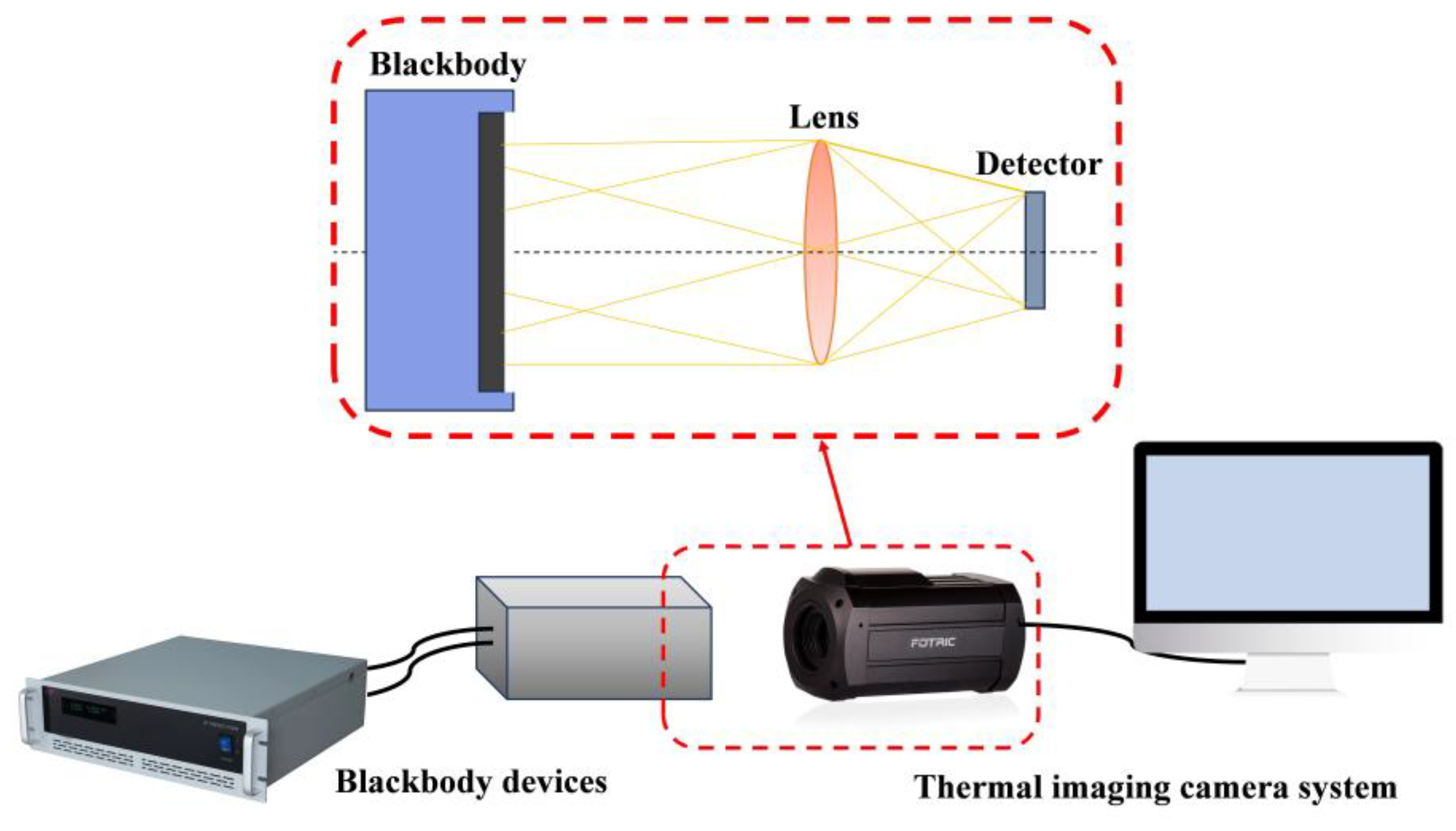
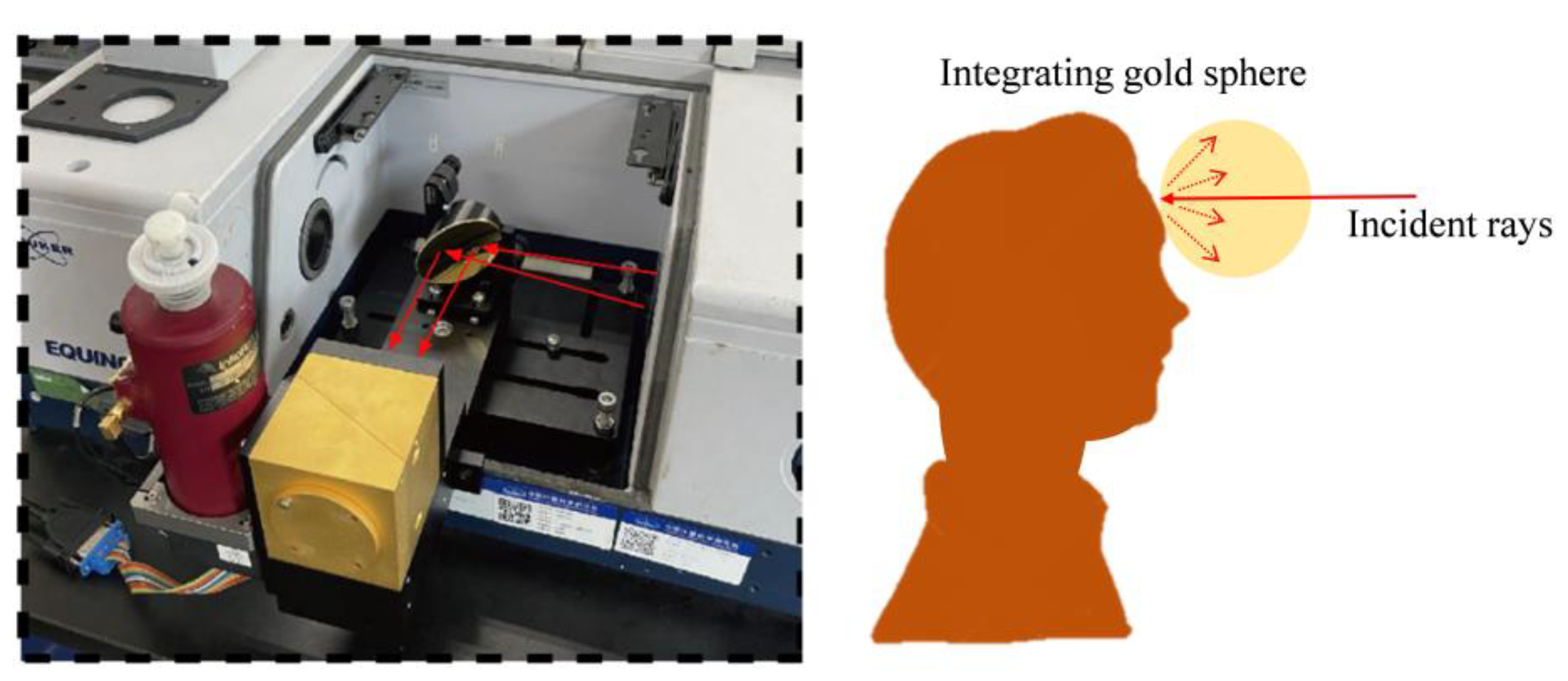
3.1. Experimental Setup
3.2. Accuracy
3.3. Uniformity
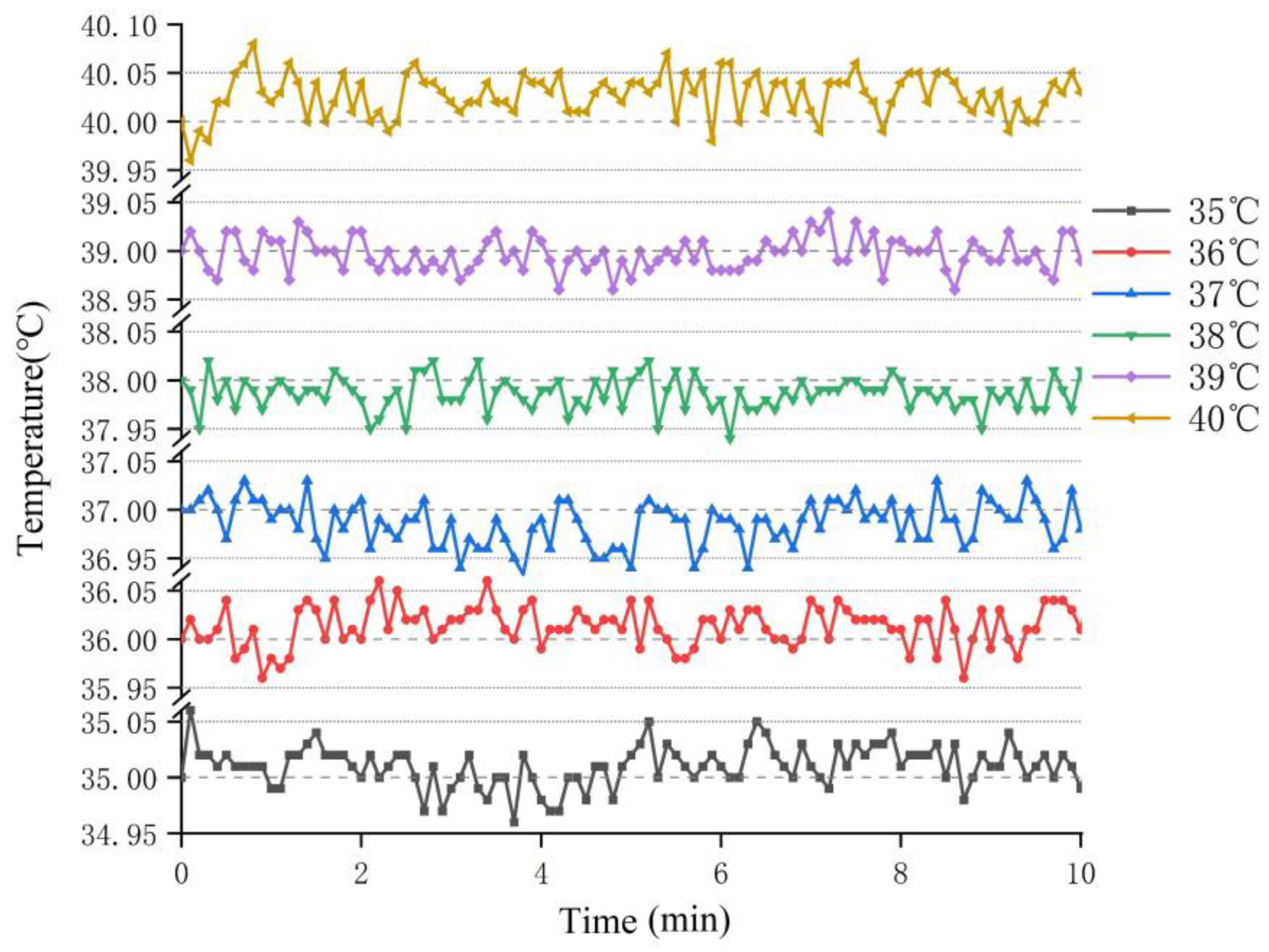
3.4. Repeatability
3.5. Spatial Distribution
3.6. Uncertainty
4. Practical Applications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, L.; Cui, Y.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, P.; Wang, C. Review: Radiation temperature measurement methods for engine turbine blades and environment influence. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2022, 123, 104204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.Y.; Fang, L.; Liu, W.W. The influencing factors and an error correction method of the use of infrared thermography in human facial skin temperature. Build. Environ. 2023, 244, 110736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundstrom, H.; Mattsson, M. Radiation influence on indoor air temperature sensors: Experimental evaluation of measurement errors and improvement methods. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2020, 115, 110082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.H.; Kim, M.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, B.J.; Lee, J. Precise infrared thermometry with considering background radiation for gas turbine air cooling application. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2020, 158, 106534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, C.L.; Wang, C.H.; Su, Y.L. Real-time Face Mask-Wearing Detection and Temperature Measurement based on a Deep Learning Model. J. Imaging Sci. Technol. 2022, 66, 010403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghassemi, P.; Pfefer, T.J.; Casamento, J.P.; Simpson, R.; Wang, Q. Best practices for standardized performance testing of infrared thermographs intended for fever screening. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Dai, C.H.; Wu, Z.F.; Wang, Y.F. Laboratory Calibration and Temperature Research of Spectral Radiometric Instruments. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2019, 39, 1965–1969. [Google Scholar]
- Mlacnik, V.; Pusnik, I. A Traceable Spectral Radiation Model of Radiation Thermometry. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, V.; Kumar, V.; Dubey, S.K.; Khan, G.S.; Shakher, C. Noncontact temperature measurement of human hand skin using volume phase holographic optical element based digital holographic interferometer. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2022, 151, 106886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, V.; Agarwal, S.; Kumar, V.; Shakher, C. Holographic optical element based digital holographic interferometer for the study of macro flames, micro flames and their temperature instability. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2019, 122, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Rastogi, V.; Agarwal, S.; Shakher, C. Investigation of temperature profile and temperature stability of micro diffusion flame under the influence of magnetic field by use of a holo-shear lens-based interferometer. Opt. Eng. 2020, 59, 064107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Chávez, O.; Cárdenas-Garcia, D.; Karaman, S.; Lizarraga, M.; Salas, J. Radiometric Calibration of Digital Counts of Infrared Thermal Cameras. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2019, 68, 4387–4399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.C.; Sun, X.G.; Xing, J. Research of Multi Points and Multi Spectral Calibration in Two-Dimensional Temperature Field Reconstruction Based on CCD. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2017, 37, 2283–2287. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, S.L.; Xing, J. Research on Calibration Method of Infrared Temperature Measurement System Near Room Temperature Field. Front. Phys. 2022, 9, 786443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.L.; Sun, X.G.; Wang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Xing, J. A data processing method on infrared temperature measurement of non-lambert body in a non-uniform environment. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2022, 123, 104187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-C.; Chen, Y.-M.; Luo, C. A method for improving temperature measurement precision on the uncooled infrared thermal imager. Measurement 2015, 74, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monier, R.; Thumerel, F.; Chapuis, J.; Soulié, F.; Bordreuil, C. Liquid metals surface temperature fields measurements with a two-colour pyrometer. Measurement 2017, 101, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhao, C.H.; Chen, L.W.; Jiang, J.; Yu, P.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, C. Error analysis and reflection correction for radiation temperature measurements at high background temperatures. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2021, 32, 055003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, I.; Otamendi, U.; Olaizola, I.G.; Solsona, R.; Maiza, M.; Viles, E.; Fernandez, A.; Arzua, I. A novel method for error analysis in radiation thermometry with application to industrial furnaces. Measurement 2022, 190, 110646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, P.Y.; Wang, G.; Gao, Z.; Liu, X.; Liu, W. Measurements of Temperature Distribution for High Temperature Steel Plates Based on Digital Image Correlation. Materials 2019, 12, 3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, W.H.; Ju, X.P.; Yan, C.X.; Yang, B.; Zhang, J. Self-correction of alignment errors and retardations for a channeled spectropolarimeter. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, 7857–7864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisaka, M. Noncontact localized internal infrared radiation measurement using an infrared point detector. Opt. Rev. 2018, 25, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poissenot-Arrigoni, C.; Marcon, B.; Rossi, F.; Fromentin, G. Fast and easy radiometric calibration method integration time insensitive for infrared thermography. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2023, 133, 104741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisiecka, E. Reduction of the impact of emissivity on high temperature measurements in non-contact thermometric devices. Opt. Appl. 2017, 47, 373–381. [Google Scholar]
- Owda, A.Y.; Salmon, N.; Harmer, S.W.; Shylo, S.; Bowring, N.J.; Rezgui, N.D.; Shah, M. Millimeter-wave emissivity as a metric for the non-contact diagnosis of human skin conditions. Bioelectromagnetics 2017, 38, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
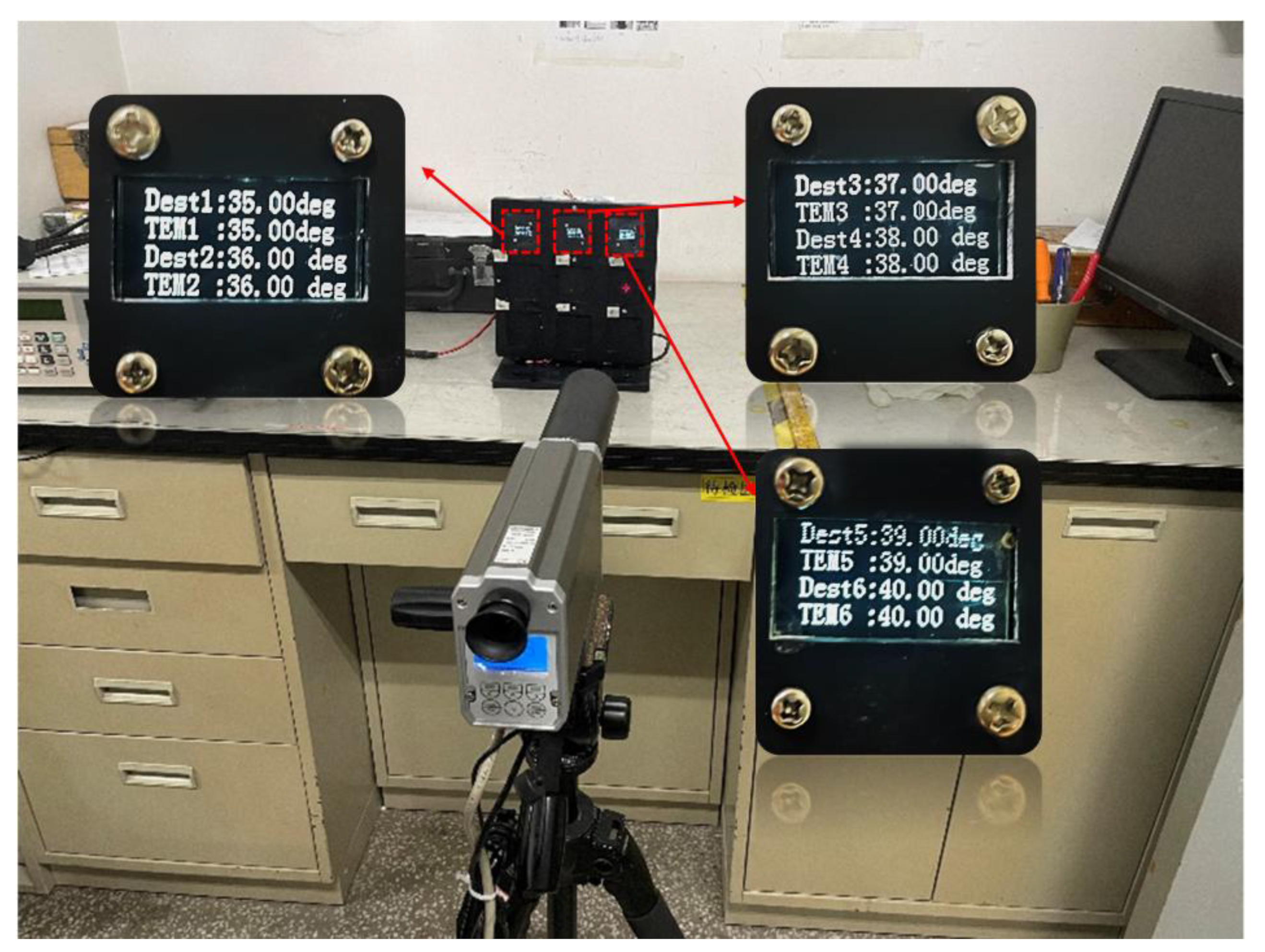


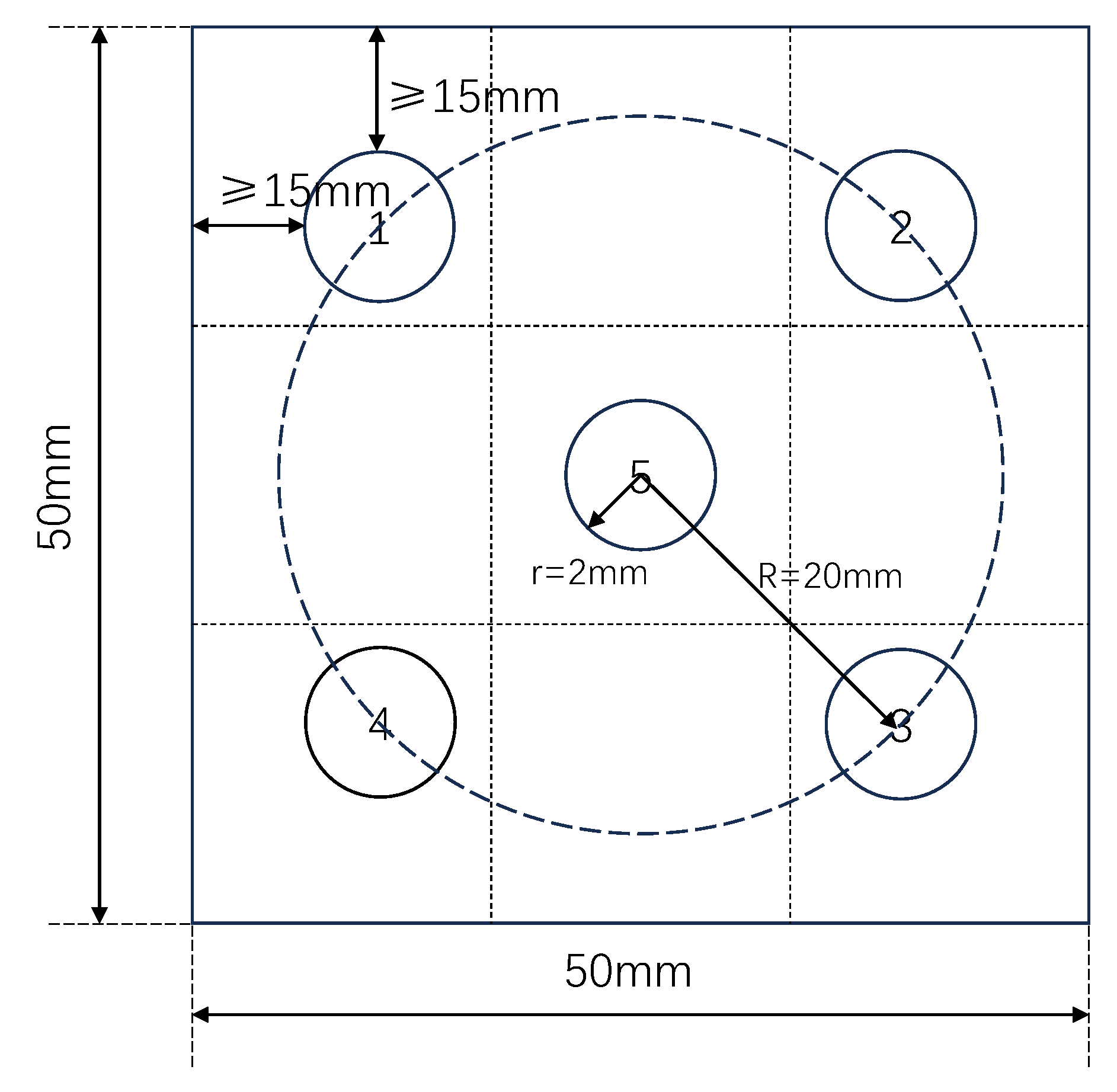

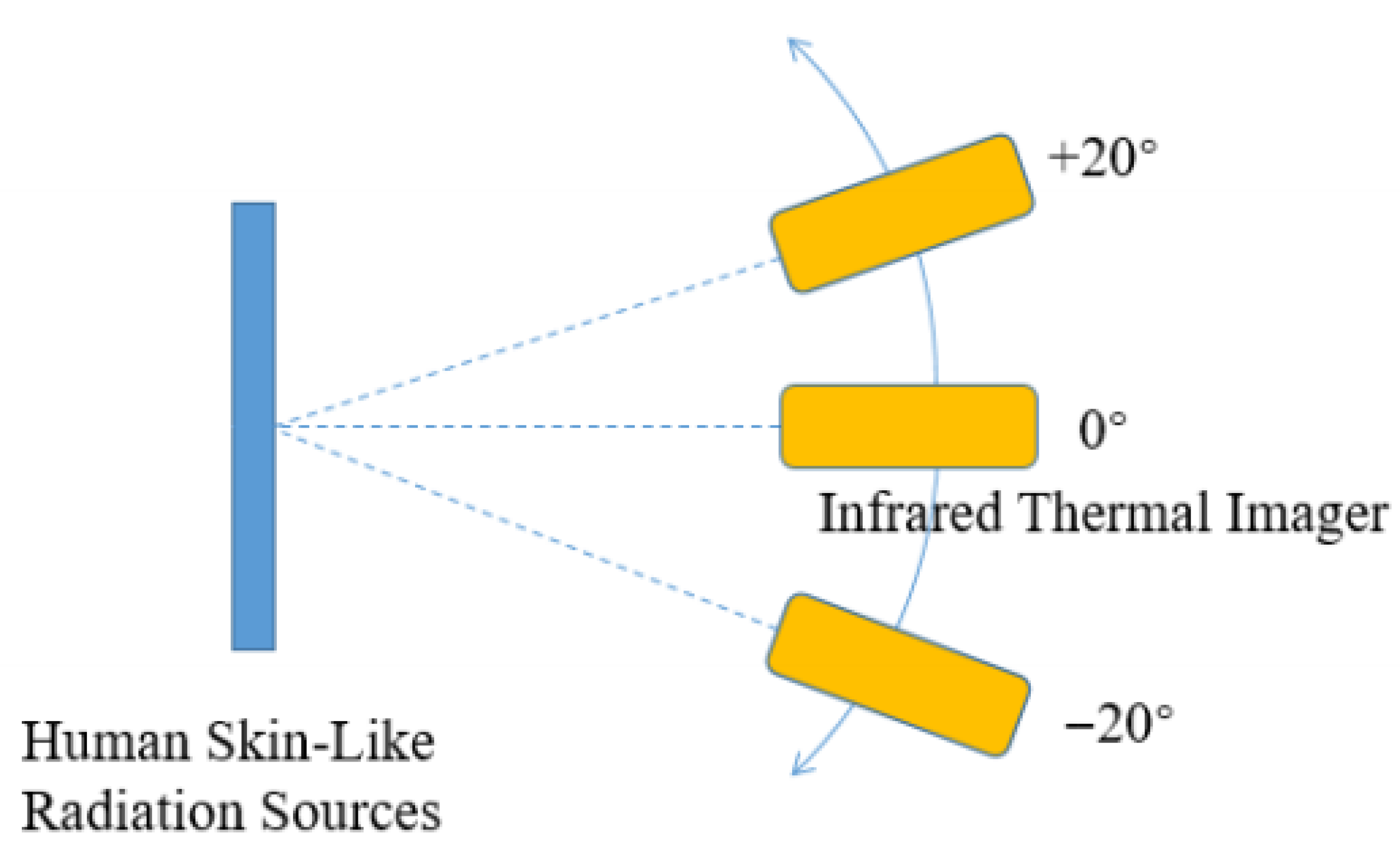

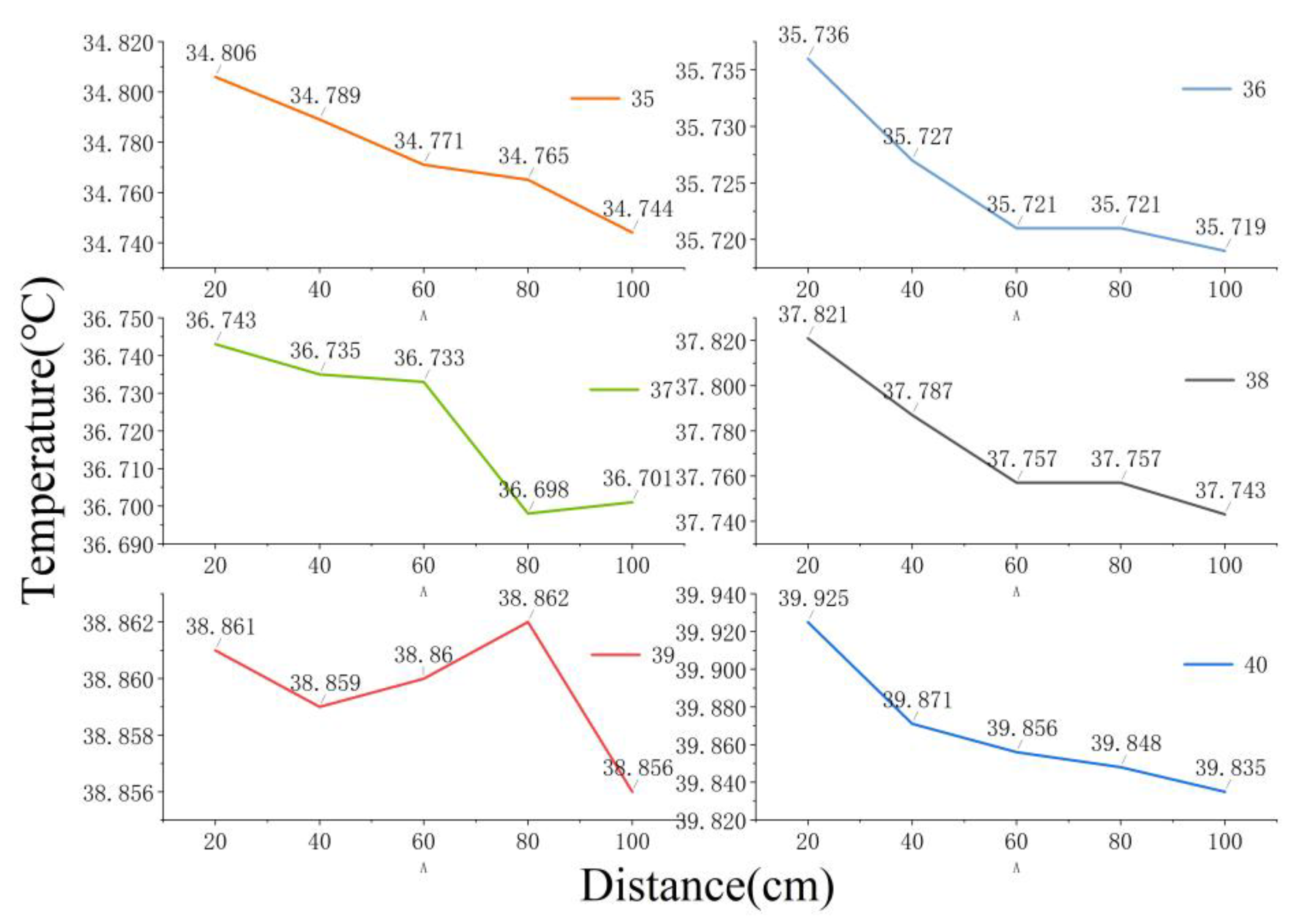
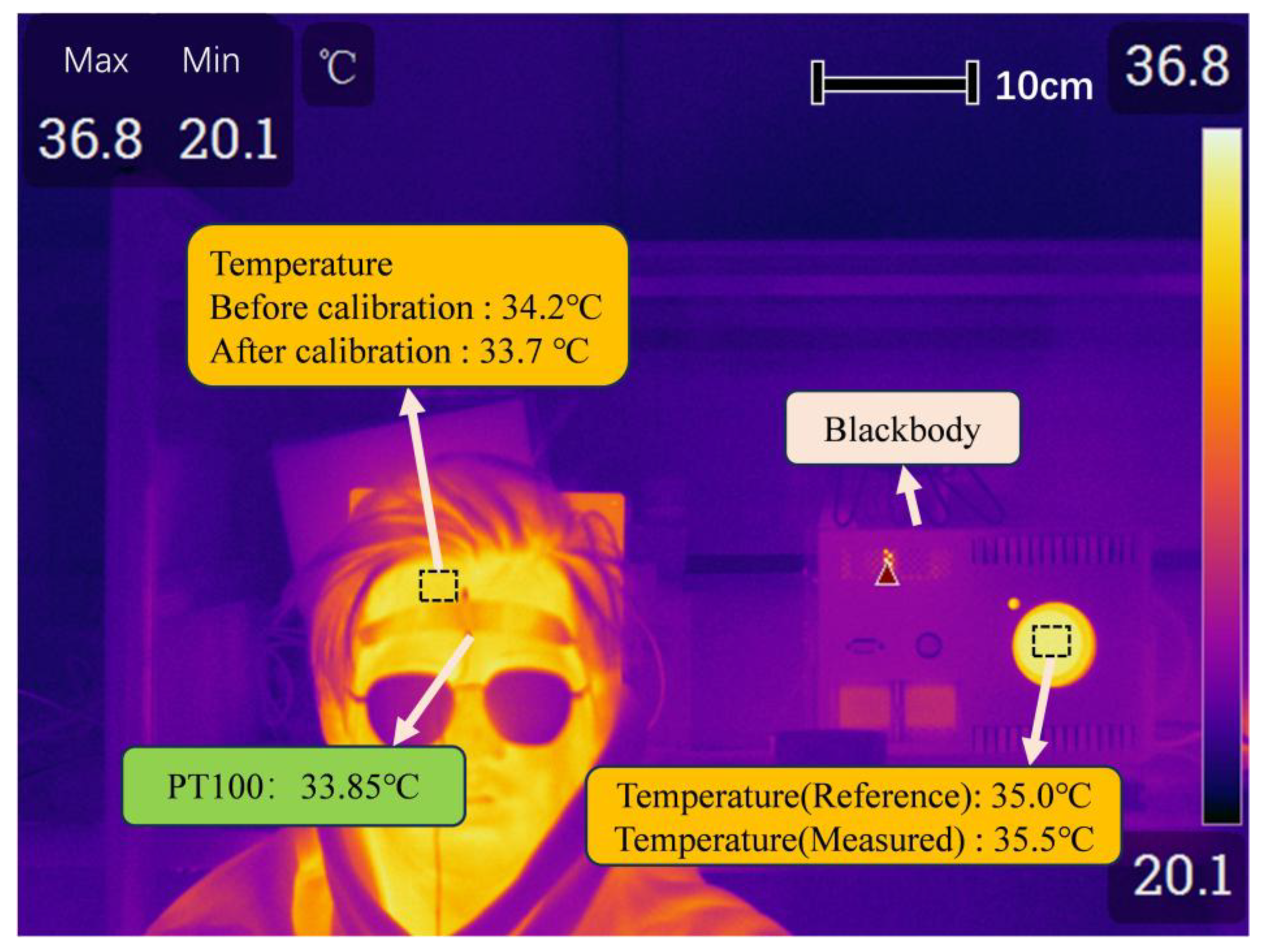
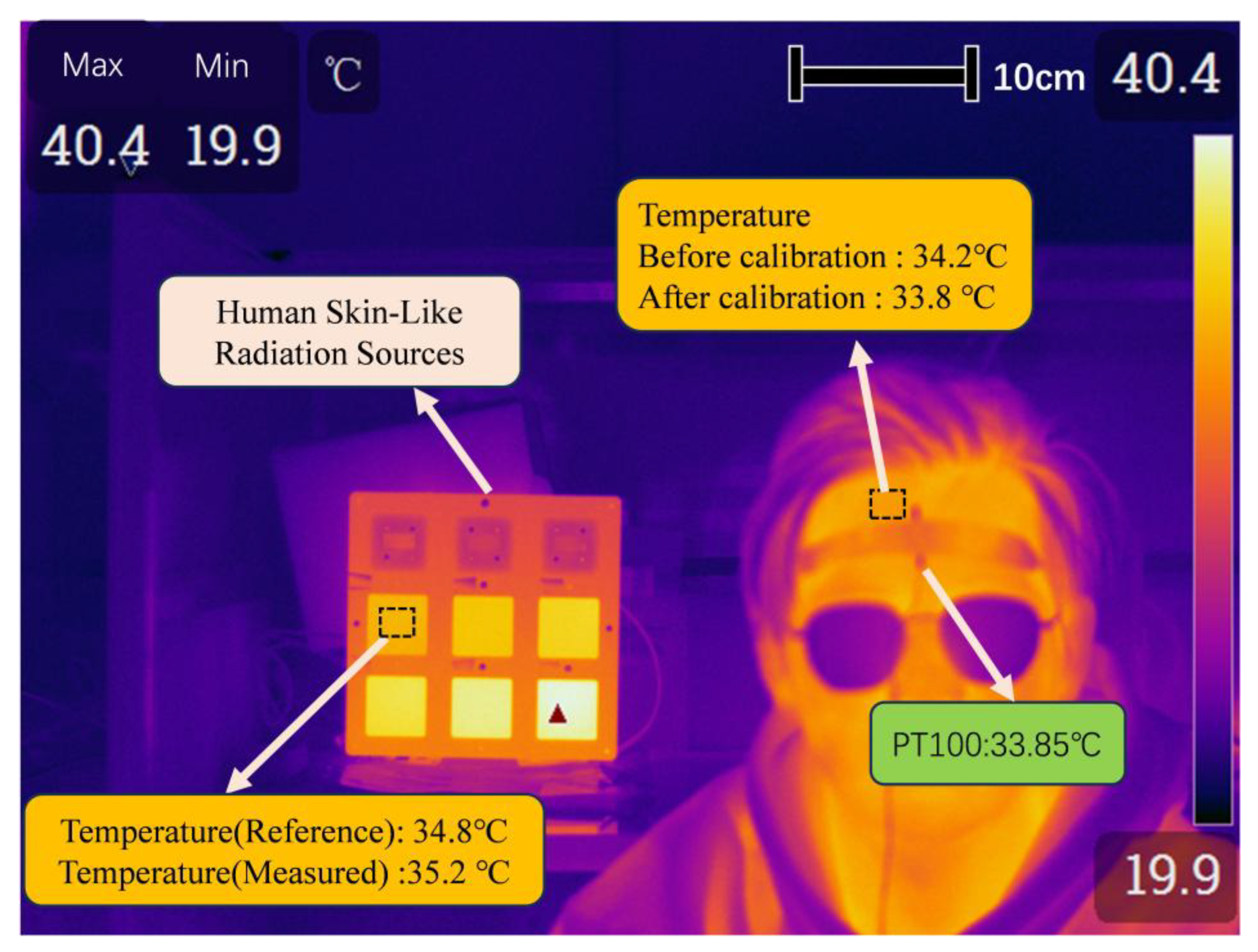
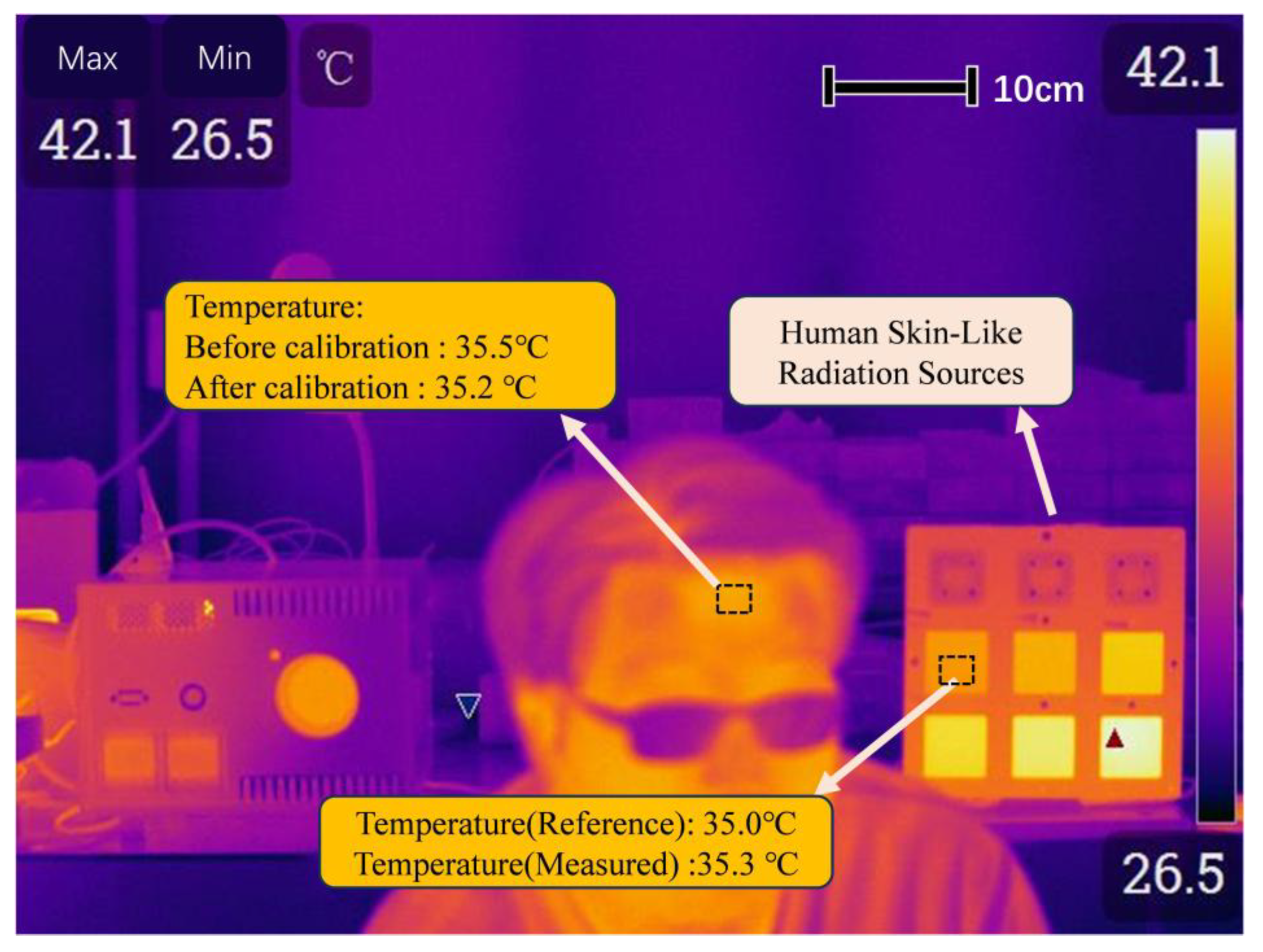
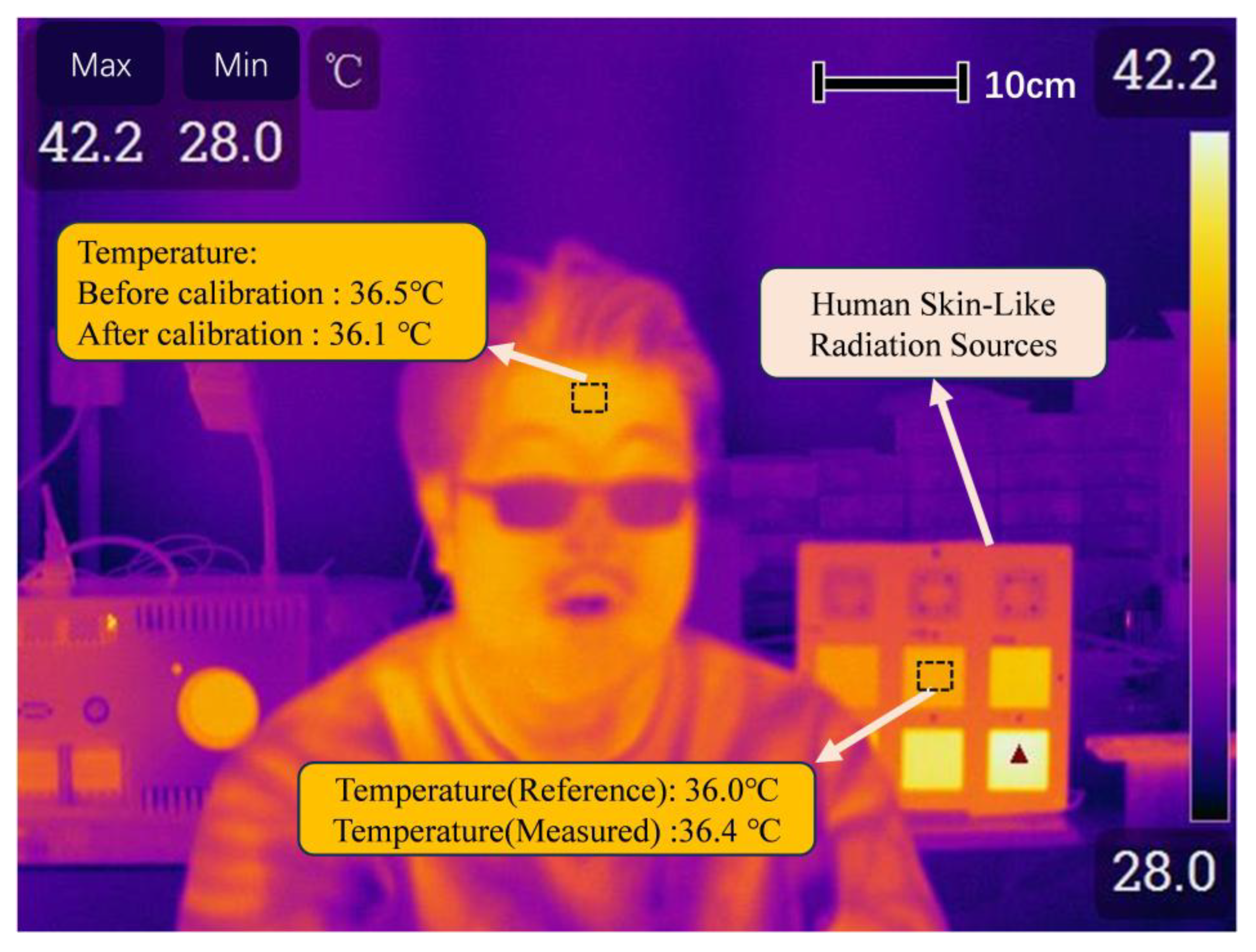
| Area ID | Setting/°C | Measured/°C | Measured-Setting/°C |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1# | 35.00 | 34.81 | −0.19 |
| 2# | 36.00 | 35.71 | −0.29 |
| 3# | 37.00 | 36.50 | −0.50 |
| 4# | 38.00 | 37.76 | −0.24 |
| 5# | 39.00 | 38.84 | −0.16 |
| 6# | 40.00 | 39.73 | −0.27 |
| No | Setting (°C) | Position 5 (°C) | Position 1 | Position 2 | Position 3 | Position 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position X-Position 5 (°C) | ||||||
| 1 | 35.00 | 34.97 | 0.05 | 0.08 | −0.21 | −0.16 |
| 2 | 36.00 | 36.00 | 0.02 | 0.03 | −0.02 | −0.03 |
| 3 | 37.00 | 37.00 | 0.01 | 0.12 | −0.04 | −0.10 |
| 4 | 38.00 | 37.97 | −0.06 | 0.14 | −0.17 | −0.29 |
| 5 | 39.00 | 39.04 | −0.04 | 0.05 | −0.11 | −0.11 |
| 6 | 40.00 | 39.99 | 0.10 | 0.00 | −0.32 | −0.31 |
| Source of Uncertainty | 35 °C | 36 °C | 37 °C | 38 °C | 39 °C | 40 °C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature accuracy | 0.030 | <0.010 | <0.010 | 0.030 | 0.040 | 0.010 |
| Temperature stability | 0.018 | 0.020 | 0.024 | 0.017 | 0.017 | 0.022 |
| Surface uniformity | 0.146 | 0.029 | 0.093 | 0.183 | 0.076 | 0.215 |
| Uncertainty of radiation thermometers | 0.035 | 0.035 | 0.035 | 0.035 | 0.035 | 0.035 |
| Difference between standard plate emissivity and human forehead skin emissivity | 0.010 | 0.010 | 0.010 | 0.010 | 0.010 | 0.010 |
| Uncertainty of spatial distribution | 0.040 | 0.045 | 0.052 | 0.043 | 0.050 | 0.052 |
| Other imponderables | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.005 |
| Total standard uncertainty | 0.160 | 0.051 | 0.103 | 0.190 | 0.095 | 0.219 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, T.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, G.; Chen, X.; Hao, Z. Improved Measurement Method of Human Skin Temperature Based on Human Skin-like Gradient Standard Radiation Source. Thermo 2025, 5, 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/thermo5040038
Li T, Zhang Z, Feng G, Chen X, Hao Z. Improved Measurement Method of Human Skin Temperature Based on Human Skin-like Gradient Standard Radiation Source. Thermo. 2025; 5(4):38. https://doi.org/10.3390/thermo5040038
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Tianshuo, Zhenyuan Zhang, Guojin Feng, Xinhua Chen, and Ziqi Hao. 2025. "Improved Measurement Method of Human Skin Temperature Based on Human Skin-like Gradient Standard Radiation Source" Thermo 5, no. 4: 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/thermo5040038
APA StyleLi, T., Zhang, Z., Feng, G., Chen, X., & Hao, Z. (2025). Improved Measurement Method of Human Skin Temperature Based on Human Skin-like Gradient Standard Radiation Source. Thermo, 5(4), 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/thermo5040038






