Nano-Silica-Modified Hydrophobic PDMS Encapsulation on CNT Thermoelectric Fibers for Waterproof Thermoelectric Textiles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Preparation of Gas-Phase Hydrophobic Nano-Silica and Investigation of PDMS Concentration
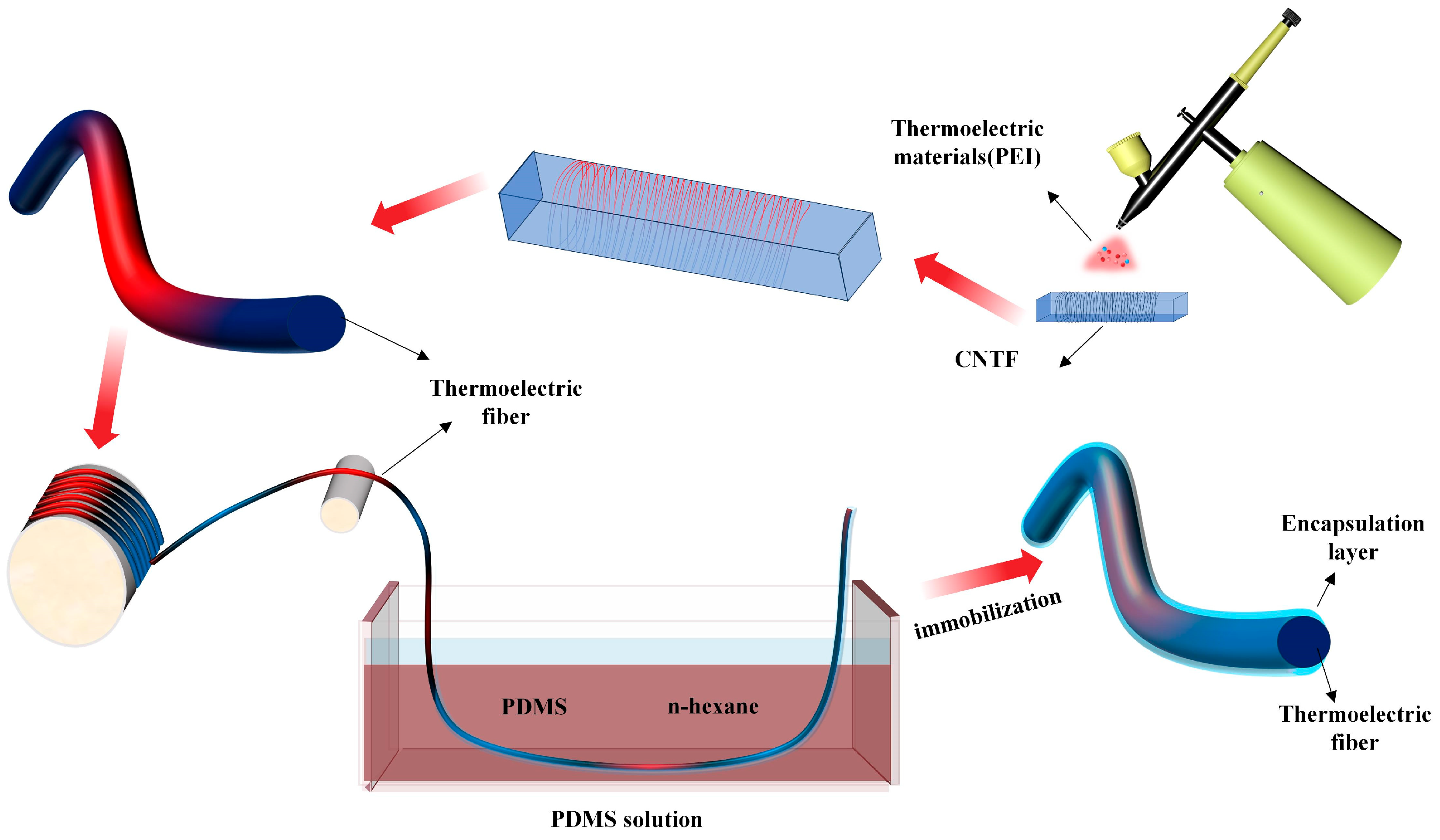
2.3. Encapsulation of Thermoelectric Fibers
2.4. Preparation of Thermal Electrical Components
2.5. Characterization and Performance Testing
3. Results and Discussion
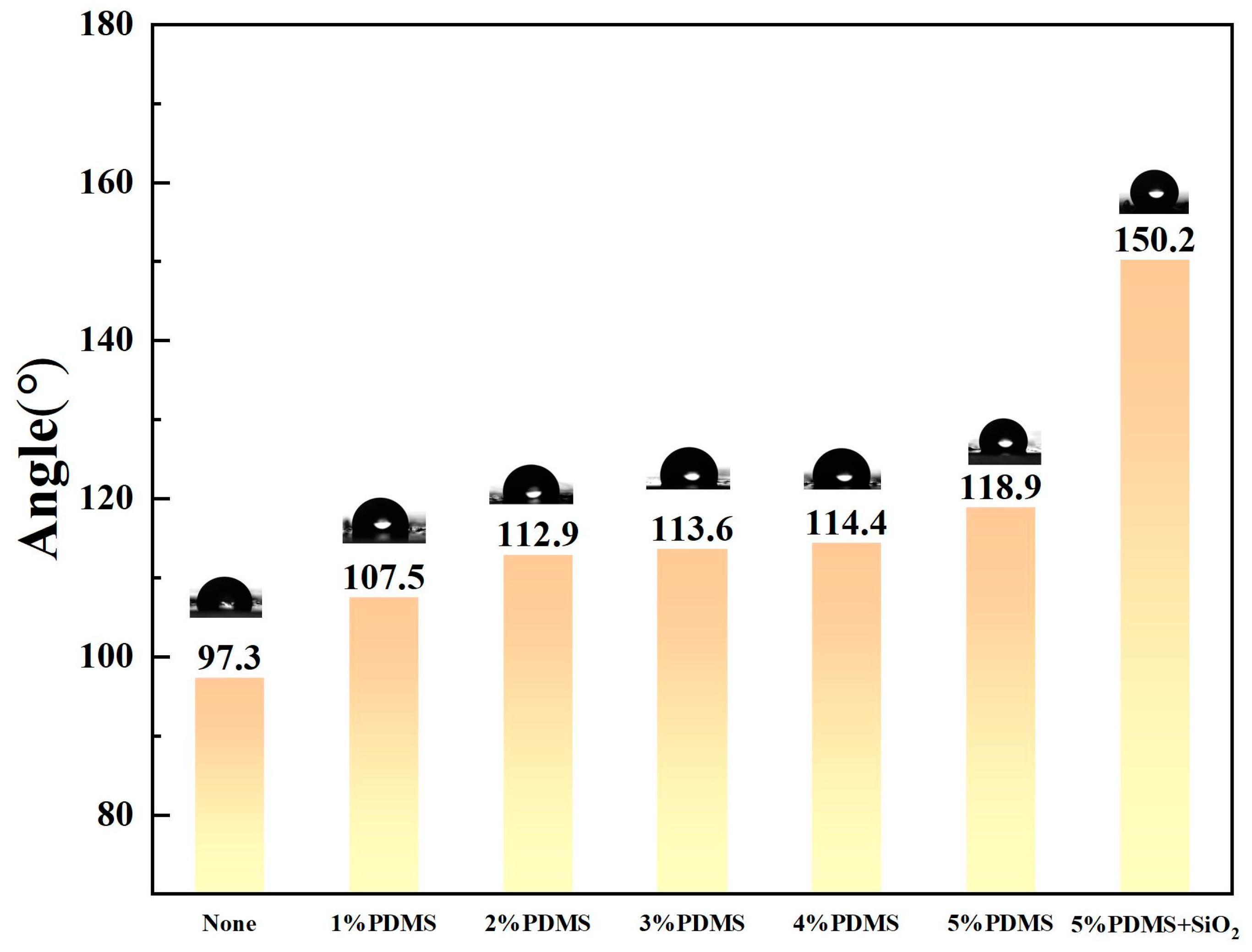
3.1. Coating Hydrophobicity and Fiber Mechanical Properties
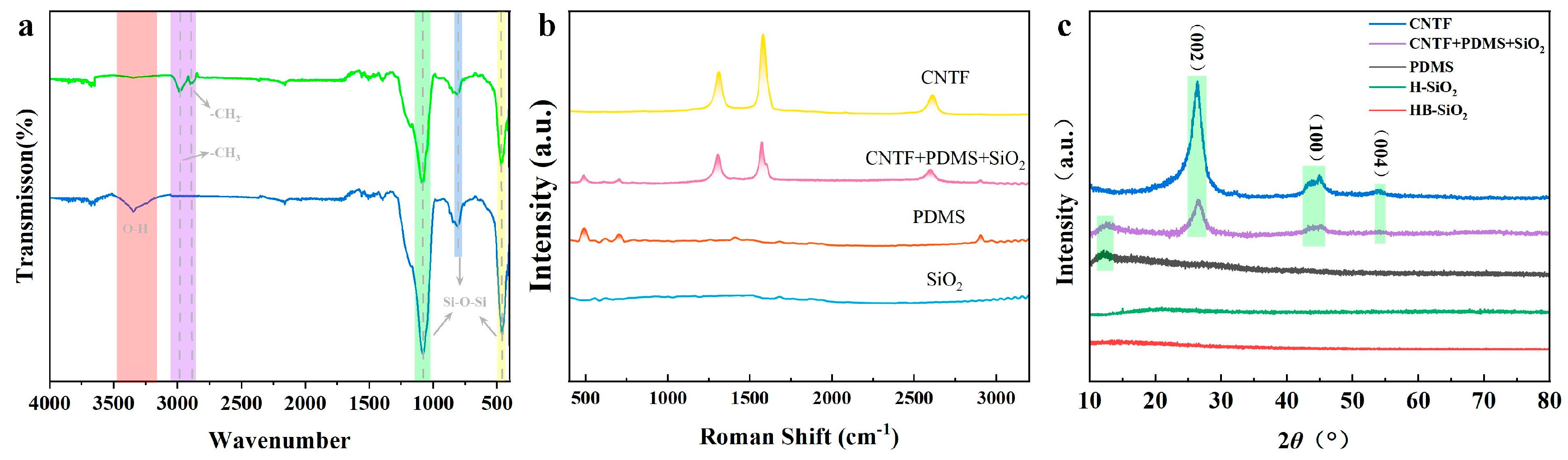
3.2. Form and Structure
3.3. Thermocouple Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shen, Y.; Han, X.; Zhang, P.; Chen, X.; Yang, X.; Liu, D.; Yang, X.; Zheng, X.; Chen, H.; Zhang, K.; et al. Review on Fiber-Based Thermoelectrics: Materials, Devices, and Textiles. Adv. Fiber. Mater. 2023, 5, 1105–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chen, J.; Liang, L.; Deng, L.; Chen, G. A PEDOT:PSS thermoelectric fiber generator. Nano Energy 2022, 102, 107678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lim, S.; Jeong, M.H.; Kim, W.; Baik, S.; Suk, J.W. Flexible thermocouple using a thermoelectric graphene fiber with a seamless junction. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2024, 172, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Guo, Y.; Wu, B.; Hou, C.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, H. Highly Integrable Thermoelectric Fiber. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2020, 12, 33297–33304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Zhang, B.X.; Hu, S.; Zhu, H.X.; Hu, H.J.; Chen, K.L.; Li, D.W.; Gu, P. Phase-Separated Ductile Eutectogels with Excellent Environmental Durability and Antibacterial Features for Thermoelectric Response and Highly Sensitive Wearable Sensors. Chem. Mater. 2025, 37, 7064–7078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, P.; Jiang, Q.; Jiang, F.; Liu, J.; Liu, G.; Liu, C.; Du, Y.; Xu, J. Organic/inorganic hybrid for flexible thermoelectric fibers. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 405, 126510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, T.; Chan, K.H.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.-Q.; Cheng, Y.; Li, T.; Ho, G.W. Scalable thermoelectric fibers for multifunctional textile-electronics. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, S.; Chen, Y.; Shi, W.; Wang, M.; Yao, Q.; Chen, L. Cotton-based wearable poly(3-hexylthiophene) electronic device for thermoelectric application with cross-plane temperature gradient. Thin Solid Film. 2018, 667, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, A.; Wu, Y.; Fenech-Salerno, B.; Torrisi, F.; Carmichael, T.B.; Müller, C. Conducting materials as building blocks for electronic textiles. MRS Bull. 2021, 46, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, B.; Hu, H.; Chen, K.; Li, H.; Birch, D.; Chen, Y.; Qiu, H.; Gu, P. Phase-Transition-Promoted Thermoelectric Textiles Based on Twin Surface-Modified CNT Fibers. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2024, 16, 18030–18039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, D.; Zhang, K.; Tian, G.; Jiang, B.; Huang, Y. Stretchable Electronics Based on PDMS Substrates. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2003155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, M.P.; Salieb-Beugelaar, G.B.; Hunziker, P. PDMS with designer functionalities—Properties, modifications strategies, and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2018, 83, 97–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Wei, H.; Zhou, W.; Soto Rodriguez, P.E.D.; Lin, C.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z. Advanced strategies for marine antifouling based on nanomaterial-enhanced functional PDMS coatings. Nano Mater. Sci. 2024, 6, 375–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, G.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Q.; Niu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Long, D. Detailed insights of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) degradation mechanism via ReaxFF MD and experiments. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 488, 150728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Kim, H.; Kim, T.S.; Kim, H.Y.; Mun, J.; Choi, G.; Jeong, H.E.; Yeo, J. Adhesive-free PDMS/PUA bilayer using selective photopolymerization for transparent, attachable, and wearable triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2024, 121, 109274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, F.; Huang, R.; Li, X.; Hu, J.; Lin, S. Facile Construction of Chestnut-Like Structural Fireproof PDMS/Mxene@BN for Advanced Thermal Management and Electromagnetic Shielding Applications. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2307482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojuroye, O.; Torah, R.; Beeby, S. Modified PDMS packaging of sensory e-textile circuit microsystems for improved robustness with washing. Microsyst. Technol. 2022, 28, 1467–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viegas, I.M.A.; Rinnan, Å.; Andersen, S.I. Effect of Isopropanol on the Fluorescence of Crude Oil-in-Water Dispersions. Energy Fuels 2023, 37, 5757–5765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Yue, G.; Hongjian, P.; Hongying, C. Dispersion stability of titanium dioxide in aqueous isopropanol with polymer dispersant. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2020, 17, 1083–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yu, L.; Wang, S.; Cai, H.; Ran, X.; Xie, J.; Guo, Z.; Chen, K.; Li, H.; Gu, P. In-Situ Growth of Self-Reduction MXene/AuNP-Decorated CNT Yarns (CNTYs) for One-Dimensional Textile Heaters with Exceptional Electrothermal Performance. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2025, 7, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyland, M.; Hunter, H.; Liu, J.; Veety, E.; Vashaee, D. Wearable thermoelectric generators for human body heat harvesting. Appl. Energy 2016, 182, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.; Park, K.T.; Lee, S.-S.; Kim, H. Highly stretchable three-dimensional thermoelectric fabrics exploiting woven structure deformability and passivation-induced fiber elasticity. Nano Energy 2022, 97, 107143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.T.; Lee, T.; Ko, Y.; Cho, Y.S.; Park, C.R.; Kim, H. High-Performance Thermoelectric Fabric Based on a Stitched Carbon Nanotube Fiber. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2021, 13, 6257–6264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, T.; Zhou, B.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, L.; Jiang, W.; Snyder, G.J. Stretchable fabric generates electric power from woven thermoelectric fibers. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmoughni, H.M.; Menon, A.K.; Wolfe, R.M.W.; Yee, S.K. A Textile-Integrated Polymer Thermoelectric Generator for Body Heat Harvesting. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1800708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.A.; Aliev, A.E.; Bykova, J.S.; de Andrade, M.J.; Kim, D.; Sim, H.J.; Lepró, X.; Zakhidov, A.A.; Lee, J.B.; Spinks, G.M.; et al. Woven-Yarn Thermoelectric Textiles. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 5038–5044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, B.; Ma, M.; Wang, S.; Cai, H.; Li, D.; Gu, P. Nano-Silica-Modified Hydrophobic PDMS Encapsulation on CNT Thermoelectric Fibers for Waterproof Thermoelectric Textiles. Textiles 2025, 5, 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/textiles5040052
Zhang B, Ma M, Wang S, Cai H, Li D, Gu P. Nano-Silica-Modified Hydrophobic PDMS Encapsulation on CNT Thermoelectric Fibers for Waterproof Thermoelectric Textiles. Textiles. 2025; 5(4):52. https://doi.org/10.3390/textiles5040052
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Boxuan, Mingyuan Ma, Shengyu Wang, Hanyu Cai, Dawei Li, and Peng Gu. 2025. "Nano-Silica-Modified Hydrophobic PDMS Encapsulation on CNT Thermoelectric Fibers for Waterproof Thermoelectric Textiles" Textiles 5, no. 4: 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/textiles5040052
APA StyleZhang, B., Ma, M., Wang, S., Cai, H., Li, D., & Gu, P. (2025). Nano-Silica-Modified Hydrophobic PDMS Encapsulation on CNT Thermoelectric Fibers for Waterproof Thermoelectric Textiles. Textiles, 5(4), 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/textiles5040052






