Development of Natural Rubber-Based Elasto Ball as an Alternative Material to Substitute Pumice in the Garment Washing Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
2.2. Extraction of Silica and Silica–Lignin Hybrid from Rice Husk
2.3. Treatment Silanization of Silica and Silica–Lignin Hybrid
2.4. Compounding Process
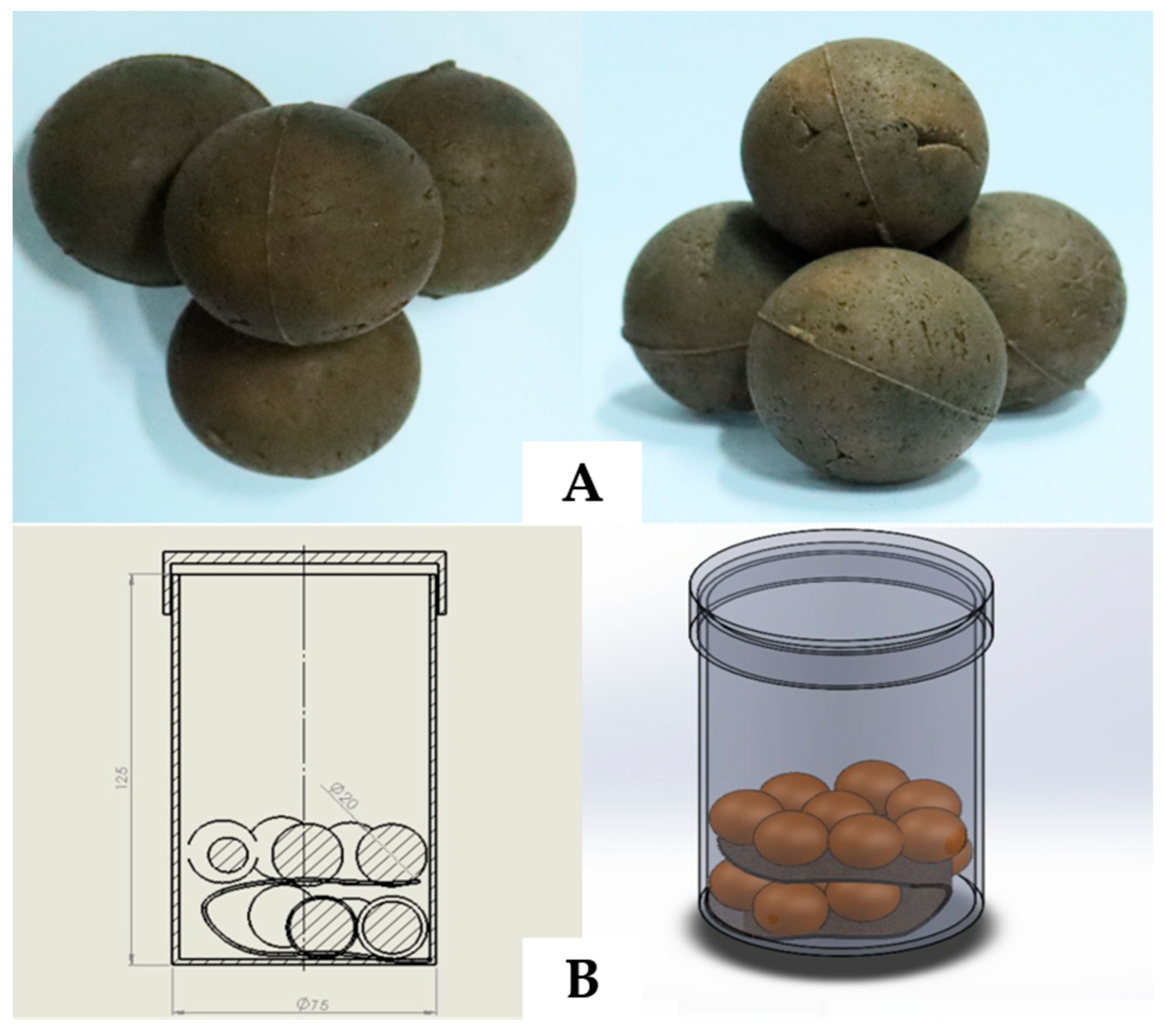
2.5. Manufacturing of Elasto Ball for Garment Washing Applications
2.6. Characterization
2.6.1. Characterization of Silica and Silica–Lignin Hybrid
2.6.2. Characterization of Rubber Elasto Ball
Porosity Measurement
Cell Size Measurement
Characterization of Hardness
2.7. Performance of Elasto Ball in the Garment Washing Process Using the Acid Washing Method
2.7.1. Characterization for Fading Color with Spectrophotometer
2.7.2. Characterization for Cotton Fiber After Washing
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Silica Filler and Silica–Lignin Hybrid Fillers
3.1.1. Characterization of Silica Filler and Silica–Lignin Hybrid Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectrophotometer
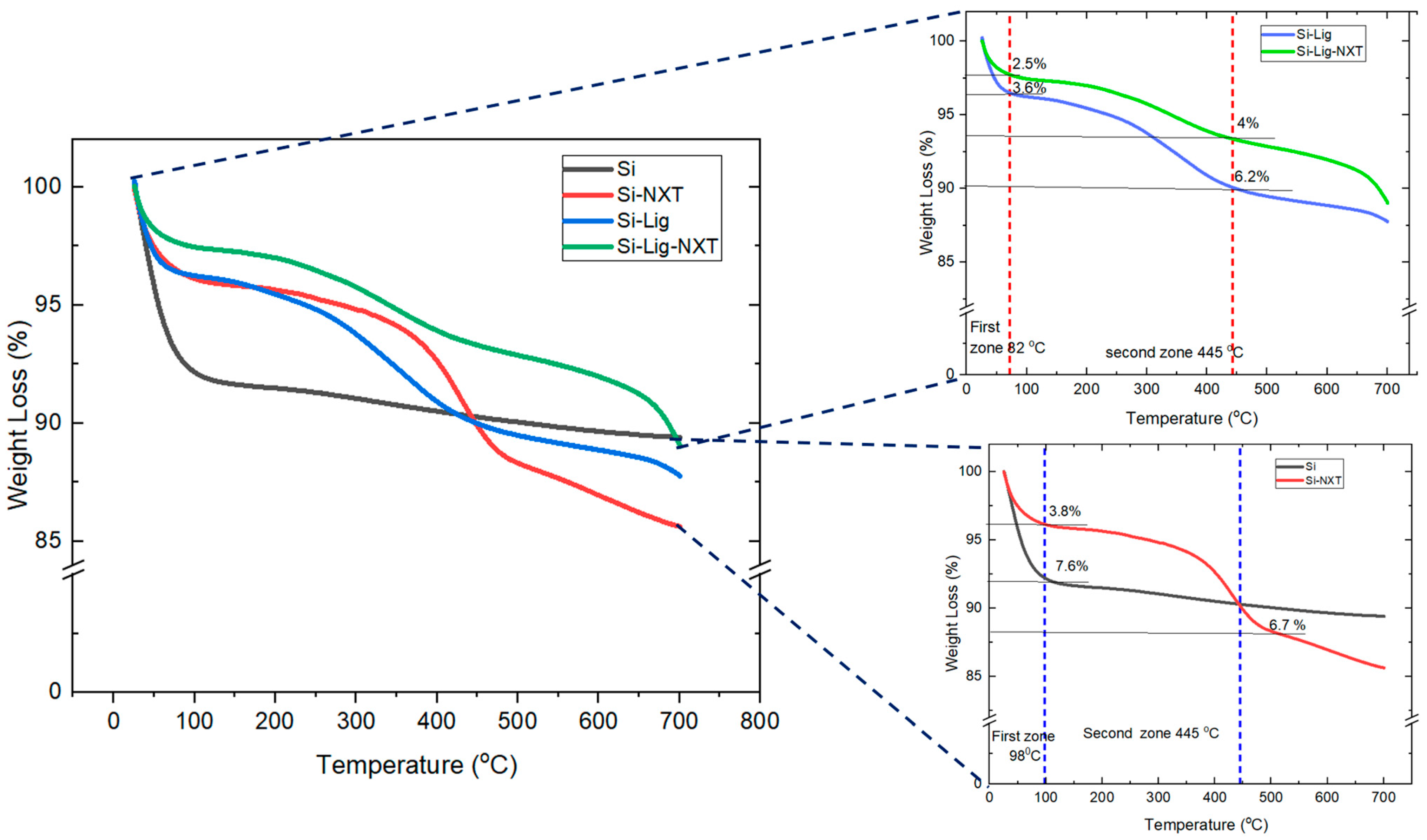
3.1.2. Thermogravimetry–Derivative Thermogravimetry (TG–DTA)
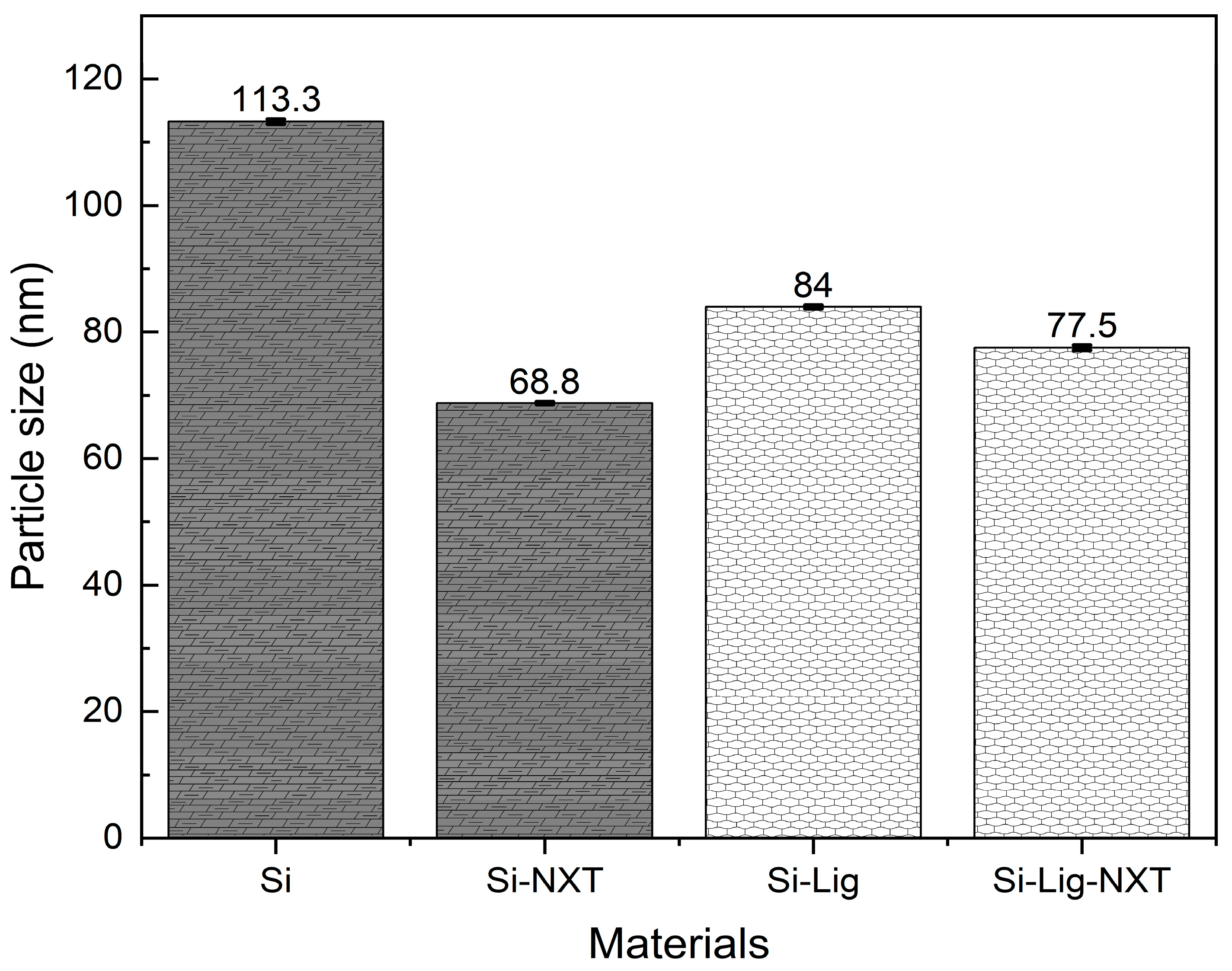
3.1.3. Particle Size Analysis (PSA)
3.2. Characterization of Natural Rubber Filler (NRF), Silica, and Silica–Lignin Hybrid Fillers
3.2.1. Cure Characteristic of Natural Rubber Compound
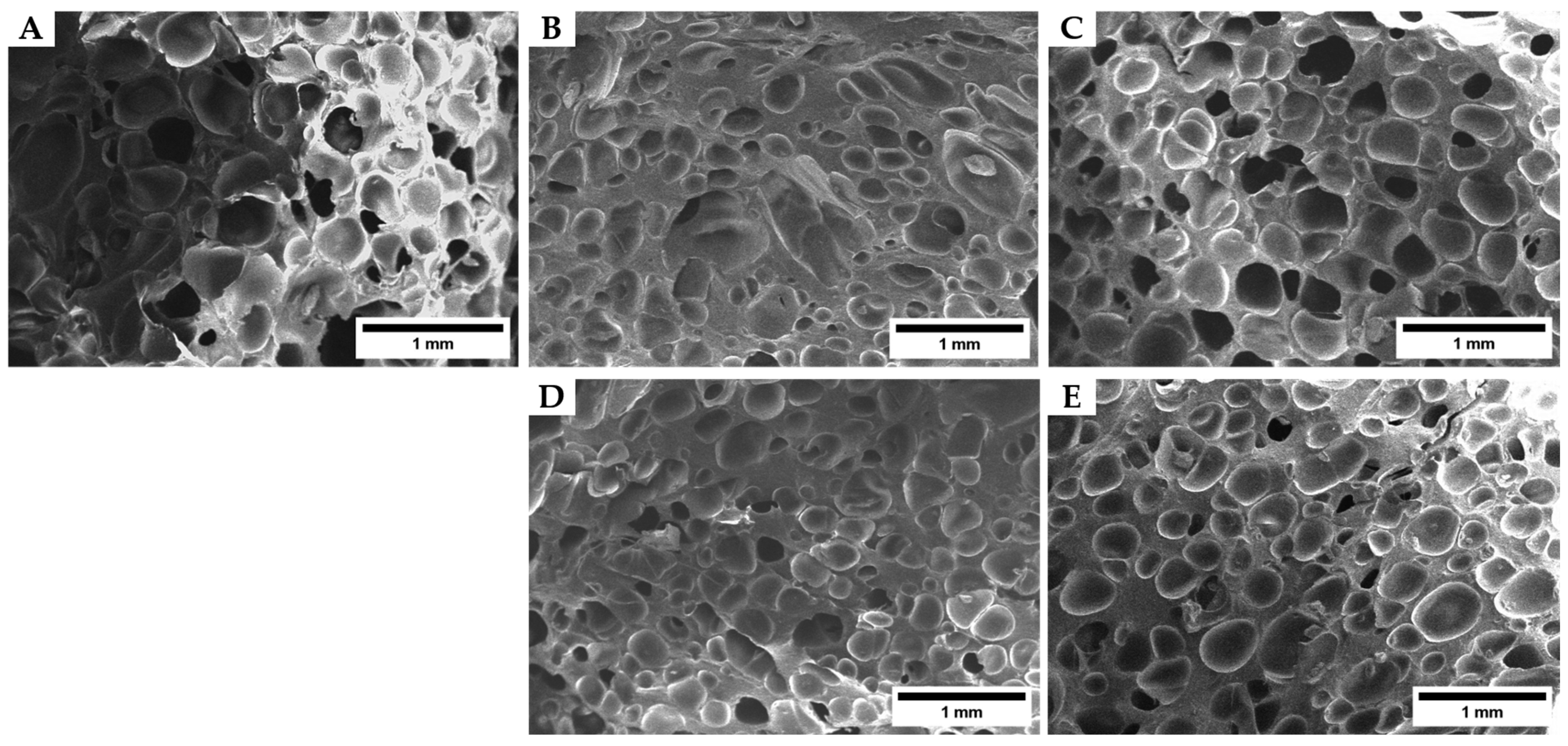
3.2.2. Density Dan Cellular Structure
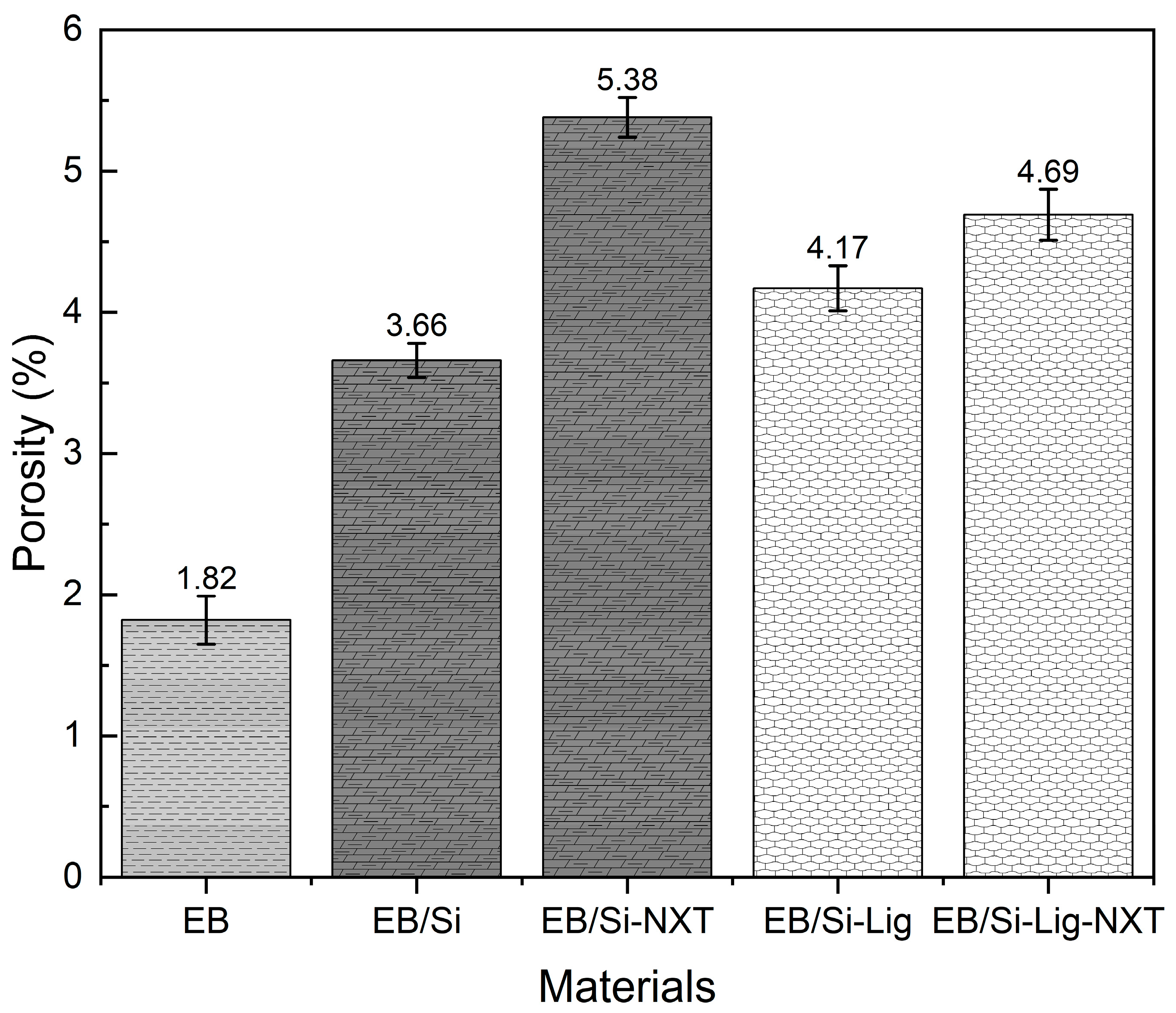
3.2.3. Porosity
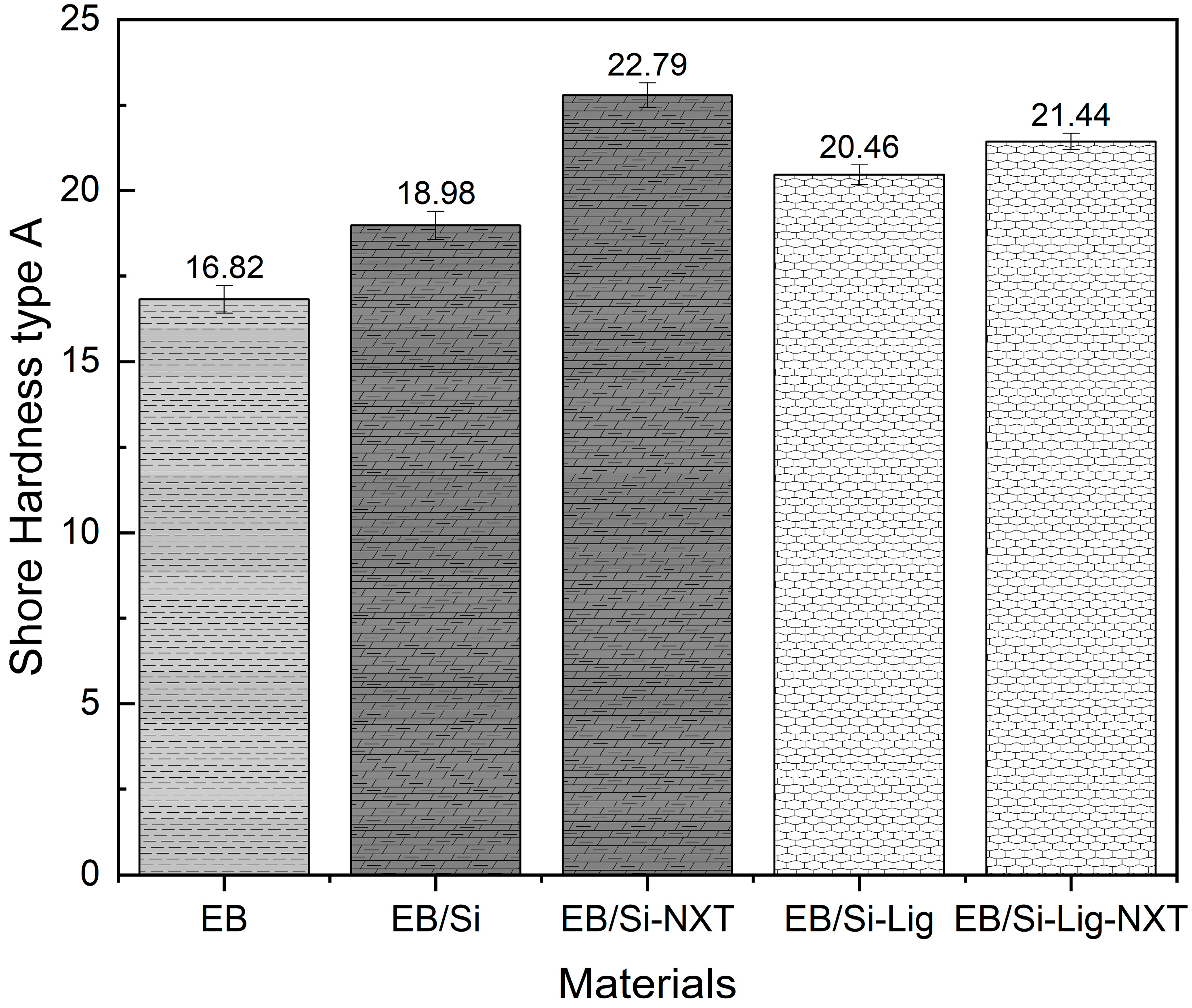
3.2.4. Hardness Analysis of Elasto Ball
3.3. Application of Rubber Washing Balls/Elasto Balls in Garment Washing Process
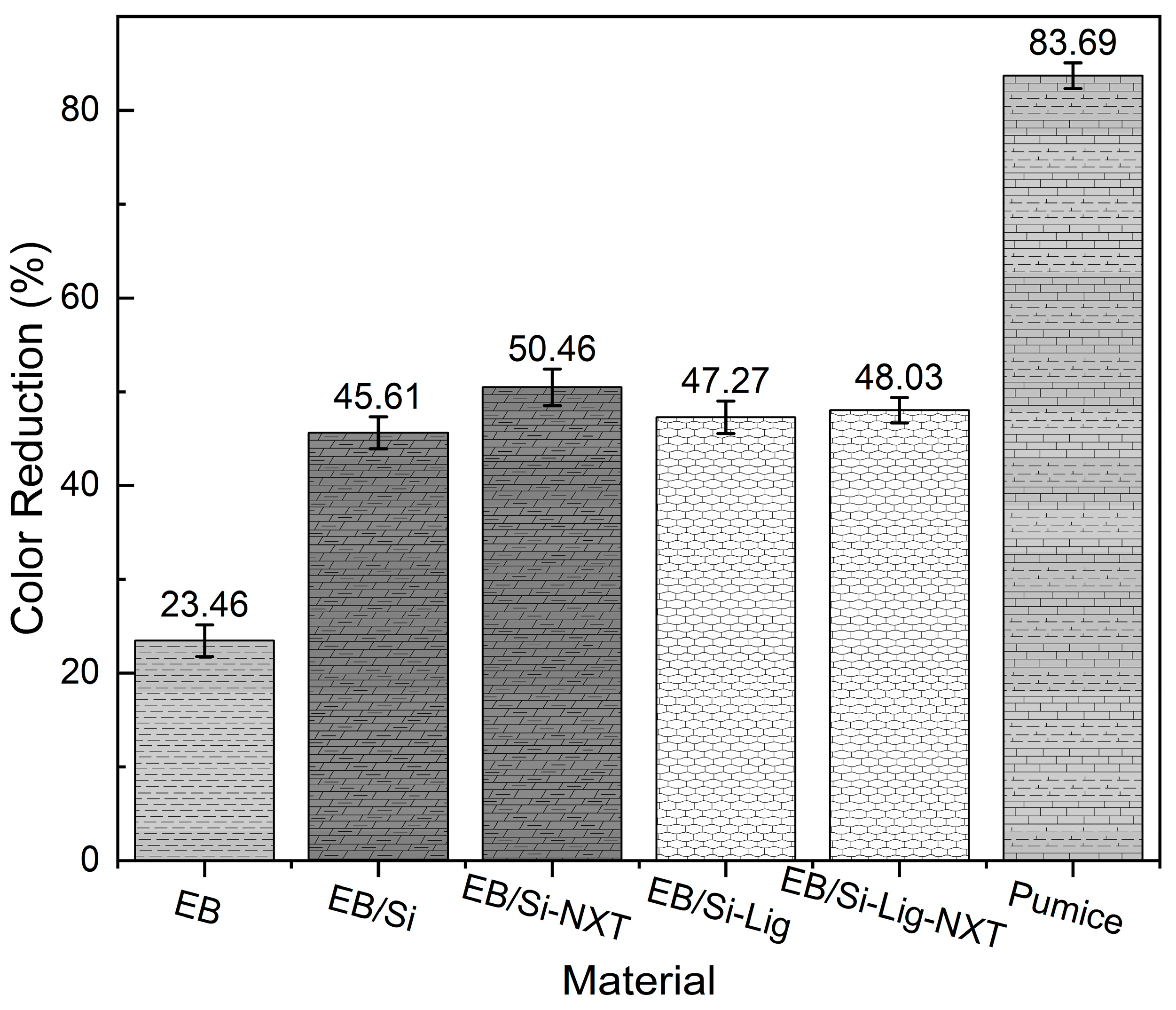
3.3.1. Color Degradation Analysis
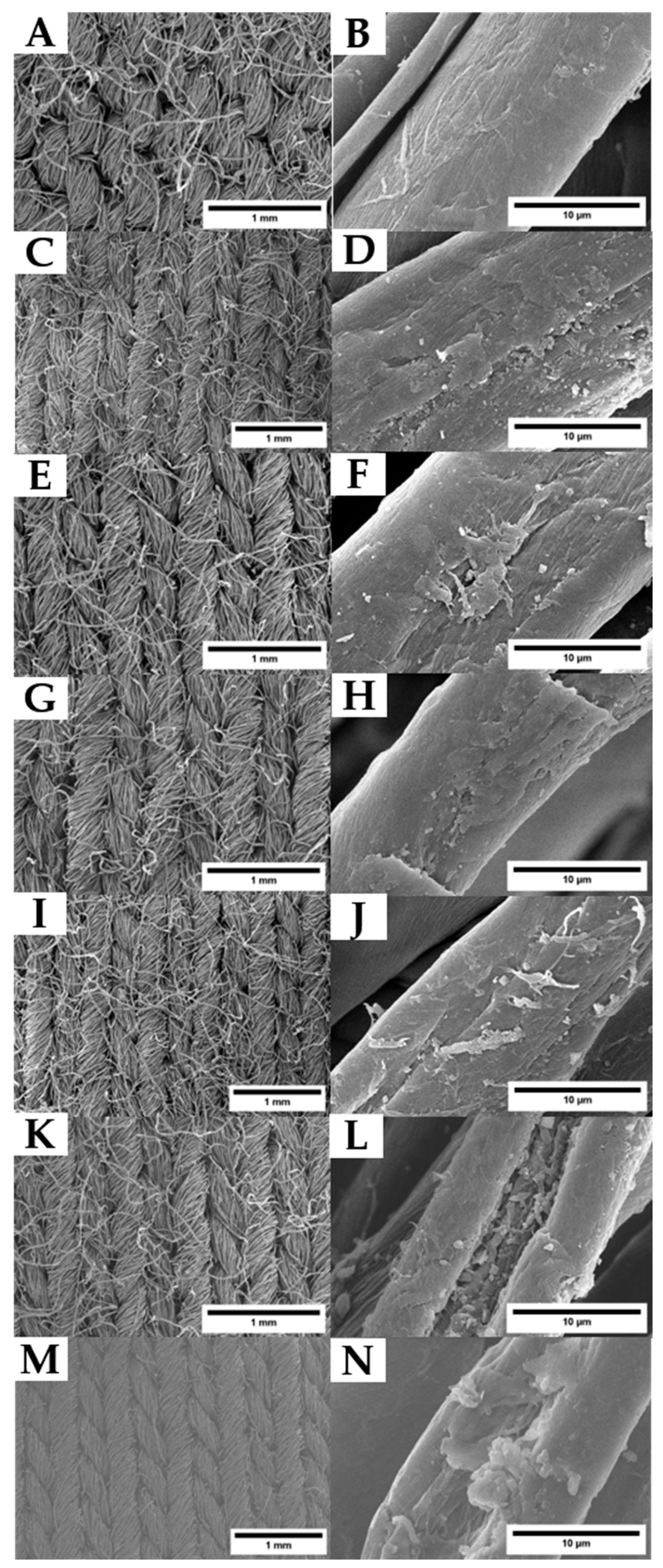
3.3.2. Surface Analysis of Washed Samples Using SEM
3.3.3. Analysis for Bursting Testing for Cotton Fabric
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haq, U.N.; Khan, M.M.R. Technology of acid wash on woven denim apparel with damp pumice stone. Int. J. Sci. Environ. Technol. 2014, 3, 2090–2095. [Google Scholar]
- Rasel, M.S.; Awal, Z.B.A.; Khan, M.R.; Das, D. Analysis of the influence of enzyme wash, acid wash, ice wash analysis of the influence of enzyme wash, acid wash, ice wash and pigment wash on the properties of knit garment. Int. J. Sci. Res. Eng. Dev. 2020, 3, 213–218. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, M.Z.; Rahaman, M.T.; Islam, T.; Pranta, A.D. An empirical analysis of sustainable denim washing technology in the apparel industries. Int. J. Ind. Manuf. Syst. Eng. 2021, 6, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, U.N. Behaviors of physical and mechanical characteristics of denim apparel after acid wash treatment. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2014, 3, 696–701. [Google Scholar]
- Fergusson, S.M.A. Garment-Finishing Techniques. In Garment Manufacturing Technology, 1st ed.; Nayak, R., Padhye, R., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2015; pp. 387–403. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M. Effect of pumice stone and its substitutes on denim garments during acid wash. J. Text. Appar. Technol. Manag. 2021, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, J.; Khalil, E.; Solaiman, M. Effect of enzyme washing combined with pumice stone on the physical, mechanical and color properties of denim garments. Int. J. Res. Advent Technol. 2014, 2, 65–68. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, E. Study on properties analysis of knitwear after acid wash. AASCIT Commun. 2016, 3, 102–106. [Google Scholar]
- Fraj, A.B.; Jaouachi, B.; Adolphe, D. Effect of stone washing parameters on denim behavior bagging. J. Nat. Fibers. 2021, 19, 5116–5132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ucar, N.; Realff, M.L.; Radhakrishnaiah, P.; Ucar, M. Objective subjective analysis of knitted fabric. Text. Res. J. 2002, 72, 977–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, E.; Rana, M.; Faria, J.; Islam, M.A.A.; Rana, M.S. Investigation on effect of acid wash with thermocol ball on physical properties of knitted garments. J. Text. Sci. Technol. 2016, 2, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohjiya, S.; Ikeda, Y. Chemistry, Manufacture and Applications of Natural Rubber; Woodhead Publishing in Materials: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sakdapipanich, J.T.; Rojruthai, P. Chapter 2: Natural Rubber: Biosynthesis, Structure, Properties and Application. In Natural Rubber Materials; RSC: London, UK, 2013; Volume 1, pp. 28–52. [Google Scholar]
- Mardiyati, Y.; Fauza, A.N.; Rachman, O.A.; Steven, S.; Santosa, S.P. A silica–lignin hybrid filler in a natural rubber foam composite as a green oil spill absorbent. Polymers 2022, 14, 2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zou, B.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Rong, C.; Wang, Z. A novel mesoporous lignin/silica hybrid from rice husk produced by a sol-gel method. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 8402–8405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umam, K.; Sagita, F.; Pramono, E.; Ledyastuti, M.; Kadja, G.T.M.; Radiman, C.L. Polyvinylidenefluoride (PVDF)/surface functionalized-mordenite mixed matrix membran. JCIS Open 2023, 11, 100093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D2240; Standard Test Method for Rubber Property—Durometer Hardness. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1964.
- ISO 13938-1:2019; Textiles—Bursting properties of fabrics Part 1: Hydraulic method for determination of bursting strength and bursting distension. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
- Das, S.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Dhanania, S.; Bhowmick, A.K. Reactive grafting of 3-octanoylthio-1-propyltriethoxysilane in styrene butadiene rubber: Characterization and its effect on silica reinforced tire composites. Polymer 2019, 179, 121693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srisuwan, L.; Jarukumjorn, K.; Suppakarn, N. Effect of silane treatment methods on physical properties of rice husk flour/natural rubber composites. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 2018, 4583974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Dhanania, S.; Bhowmick, A.K. Improved dispersion and physico-mechanical properties of rubber/silica composites through new silane grafting. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2020, 60, 3115–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayichelaeh, C.; Reuvekamp, L.A.E.M.; Dierkes, W.K.; Blume, A.; Noordermeer, J.W.M.; Sahakaro, K. Enhancing the silanization reaction of the silica-silane system by different amines in model and practical silica-filled natural rubber compounds. Polymer 2018, 10, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anbealagan, L.D.; Chew, T.L.; Yeong, Y.F.; Jawad, Z.A.; Ho, C.D. Synthesis and characterization of (3-aminopropyl) triethoxysilane (APTES) functionalized zeolite AlPO-18. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; Volume 1195. [Google Scholar]
- Park, N.; Ahn, B.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, W.; Moon, H.; Kim, W. Effect of organosilane agents on the vulcanizate structure and physical properties of silica-filled solution styrene butadiene rubber compounds. Compos. Interfaces 2017, 25, 259–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano, M.; Marsano, E.; Turturro, A.; Conzatti, L.; Busca, G. Dependence of surface properties of silylated silica on the length of silane arms. Adsorption 2012, 18, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jembere, A.L.; Fanta, S.W. Studies on the synthesis of silica powder from rice husk ash as reinforcement filler in rubber tire tread part: Replacement of commercial precipitated silica. Int. J. Mater. Sci. Appl. 2017, 6, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Ren, F.; Zhu, C.; Feng, J.; Cheng, Q.; Chen, S.; Shen, G.; Wang, F. Hybrid silane technology in silica-reinforced tread compound. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2019, 92, 310–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnnarongchai, W.; Chaochanchaikul, K. Effect of blowing agent on cell morphology and acoustic absorption of natural rubber foam. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2015, 804, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoeythornkhajhornchai, P.; Samthong, C.; Boonkerd, K.; Somwangthanaroj, A. Effect of azodicarbonamide on microstructure, cure kinetics and physical properties of natural rubber foam. J. Cell. Plast. 2017, 53, 287–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najib, N.N.; Ariff, Z.M.; Manan, N.A.; Bakar, A.A.; Sipaut, C.S. Effect of blowing agent concentration on cell morphology and impact properties of natural rubber foam. J. Phys. Sci. 2009, 20, 13–25. [Google Scholar]
- Bayat, H.; Fasihi, M.; Zare, Y.; Rhee, K.Y. An experimental study on one-step and two-step foaming of natural rubber/silica nanocomposites. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2020, 9, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami-Tapeh-Esmaeil, E.; Vahidifar, A.; Esmizadeh, E.; Rodrigue, D. Chemistry, processing, properties, and applications of rubber foams. Polymers 2021, 13, 1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poompradub, S.; Thirakulrati, M.; Prasassarakich, P. In situ generated silica in natural rubber latex via the sol-gel technique and properties of the silica rubber composites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2014, 144, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provost, M.; Raulin, K.; Maindron, T.; Gaud, V. Influence of silane coupling agent on the properties of UV curable SiO2-PMMA hybrid nanocomposite. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2018, 89, 796–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, X.; Tang, Z.; Lu, S.; Tan, Y.; Wang, C.; Yang, L.; Shi, X. Effect of rice husk ash surface modification by silane coupling agents on damping capacity of cement-based pastes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 296, 123730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakir, F.; Almaamori, M.H.; Hamood, F.J. Effect of silica on the mechanical properties of rubber reclaim composite. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 2016, 9, 325–333. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.K.R.; Jintun, S. Sustainability issues of various denim washing methods. Text. Leather Rev. 2021, 4, 96–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.; Patel, S.; Mishra, B.K. Oxidation by permanganate: Synthetic and mechanistic aspects. Tetrahedron. 2009, 65, 707–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sever, K.; Atagür, M.; Tunçalp, M.; Altay, L.; Seki, Y.; Sarıkanat, M. The effect of pumice powder on mechanical and thermal properties of polypropylene. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2018, 32, 1092–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knežević, M.; Kramar, A.; Hajnrih, T.; Korica, M.; Nikolic, T.; Zekic, A.; Kostic, M. Influence of potassium permanganate oxidation on structure and properties of cotton. J. Nat. Fibers. 2020, 19, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezeamaku, U.L.; Ezekannagha, C.; Eze, O.I.; Odimegwu, N.; Nwakaudu, A.; Okafor, A.; Ekuma, I.; Onukwuli, O.D. The impact of potassium permanganate (KMnO4) treatment on the tensile strength of pineapple leaf fiber reinforced with tapioca-based bio resin. Arab Gulf J. Sci. Res. 2023, 41, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karande, A. Coating of technical textiles. Asian Dryer 2021, 17, 50–54. [Google Scholar]
- Jahan, T.; Khan, J. Impact of stone enzyme wash and acid wash based on denim garments. J. Text. Sci. Technol. 2022, 8, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Kim, T.H.; Liu, K.; Ma, M.G.; Choi, S.E.; Si, C. Multifunctional lignin-based composite materials for emerging applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 708976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abisha, M.; Priya, R.K.; Arunachalam, K.P.; Avudaiappan, S.; Flores, E.I.S.; Parra, P.F. Biodegradable green composites: Effects of potassium permanganate (KMnO4) treatment on thermal, mechanical, and morphological behavior of butea parviflora (BP) fibers. Polymers 2023, 15, 2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, E. Effect of processing time and concentration of potassium permanganate on physico-mechanical properties of denim jeans during stone washing. Sci. Innov. 2015, 3, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Hailong, W.; Yongjiannan, A.; Aize, L. Research on strength distribution of natural pumice concrete based on precast porosity. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 657, 012095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Formulation (phr) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BL-0 (a) | Si (b) | Si-NXT (c) | Si-Lig (d) | Si-Lig-NXT (e) | |
| RSS1 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Afflux 42M | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Silica | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Silica silane NXT | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
| Silica–lignin hybrid | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| Silica–lignin hybrid silane NXT | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| ZnO | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Azodicarbonamide | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| CBS | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| Sulfur | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Functional Group | Wavenumber (cm−1) | References [19,20,21,22] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experiment | |||||
| Before Silane NXT | After Silane NXT | ||||
| Silica (Si) | Silica–Lignin Hybrid (Si-Lig) | Silica Silane NXT (Si-NXT) | Silica–Lignin Hybrid-NXT (Si-Lig-NXT) | ||
| O-H stretching (silica–lignin) | 3318 | 3327 | 3333 | 3340 | 3450 |
| C-H asym bending in CH3 in Si-O-CH2-CH3 | 2627 | 2728 | 2856 | 2849 | 2844 |
| C=O stretch | 1634 | 1681 | 1645 | 1692 | 1693 |
| C-H stretching of methyl and methylene groups Aromatic skeletal vibration of lignin | 1508 | 1510 | 1513 | 1571 | 1641 |
| C-O stretching peak of the Si-O-CH2-CH3 group of silanes | 1065 | 1062 | 1086 | 1097 | 1075 |
| Si-C-stretching vibration | 795 | 794 | 799 | 797 | 798 |
| Si-O bending vibration | 611 | 613 | 612 | 616 | 568 |
| Si-OH | 965 | 974 | 966 | 987 | 964 |
| Sample | Wt Loss % from TGA (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| 25–200 °C | 200–700 °C | |
| Si | 7.6 | - |
| Si-NXT | 3.8 | 6.7 |
| Si-Lig | 3.6 | 6.2 |
| Si-Lig-NXT | 2.5 | 4 |
| Sample Code | ML (dNm) | MH (dNm) | (dNm) | ts2 (min) | t90 (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BL (blanko) | 0.19 | 7.34 | 7.15 | 6.39 | 14.22 |
| S (Silica no silane) | 0.60 | 7.28 | 6.68 | 8.42 | 16.53 |
| Si-NXT (silica silane NXT) | 0.46 | 6.92 | 6.46 | 9.12 | 19.29 |
| Si-Lig (silica–lignin hybrid) | 0.45 | 7.19 | 6.74 | 8.37 | 18.15 |
| Si-Lig-NXT (silica–lignin hybrid silane NXT | 0.56 | 6.49 | 5.93 | 8.29 | 18.03 |
| Parameters | BL | Si | Si-NXT | Si-Lig | Si-Lig-NXT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.8616 | 0.6728 | 0.6058 | 0.4266 | 0.5252 | |
| ER | 1.16 | 1.49 | 1.32 | 1.69 | 1.58 |
| x (mm) | 0.62 ± 0.19 | 0.99 ± 0.12 | 0.82 ± 0.21 | 0.87 ± 0.26 | 0.66 ± 0.14 |
| y (mm) | 0.55 ± 0.18 | 0.86 ± 0.14 | 0.71 ± 0.23 | 0.72 ±0.23 | 0.57 ± 0.22 |
| Sample Code | Element (%) After Acid Washing | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | O | S | Si | Mn | |
| EB/Si | 64.03 | 32.4 | 3.24 | 0.26 | 0.12 |
| EB/Si-NXT | 63.45 | 32.01 | 4.05 | 0.09 | 0.39 |
| EB/Si-Lig | 72.04 | 20.63 | 5.36 | 1.76 | 0.09 |
| EB/Si-Lig-NXT | 72.66 | 23.55 | 3.18 | 0.51 | 0.21 |
| Pumice stone | 66.45 | 29.44 | 3.6 | 0.38 | 0.14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Komalasari, M.; Rachman, O.A.; Ardy, H.; Asri, L.A.T.W.; Mardiyati, Y. Development of Natural Rubber-Based Elasto Ball as an Alternative Material to Substitute Pumice in the Garment Washing Process. Textiles 2025, 5, 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/textiles5040047
Komalasari M, Rachman OA, Ardy H, Asri LATW, Mardiyati Y. Development of Natural Rubber-Based Elasto Ball as an Alternative Material to Substitute Pumice in the Garment Washing Process. Textiles. 2025; 5(4):47. https://doi.org/10.3390/textiles5040047
Chicago/Turabian StyleKomalasari, Maya, Onny Aulia Rachman, Husaini Ardy, Lia A. T. W. Asri, and Yati Mardiyati. 2025. "Development of Natural Rubber-Based Elasto Ball as an Alternative Material to Substitute Pumice in the Garment Washing Process" Textiles 5, no. 4: 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/textiles5040047
APA StyleKomalasari, M., Rachman, O. A., Ardy, H., Asri, L. A. T. W., & Mardiyati, Y. (2025). Development of Natural Rubber-Based Elasto Ball as an Alternative Material to Substitute Pumice in the Garment Washing Process. Textiles, 5(4), 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/textiles5040047






