Autonomous Sewing Technology and System: A New Strategy by Integrating Soft Fingers and Machine Vision Technology
Abstract
1. Introduction
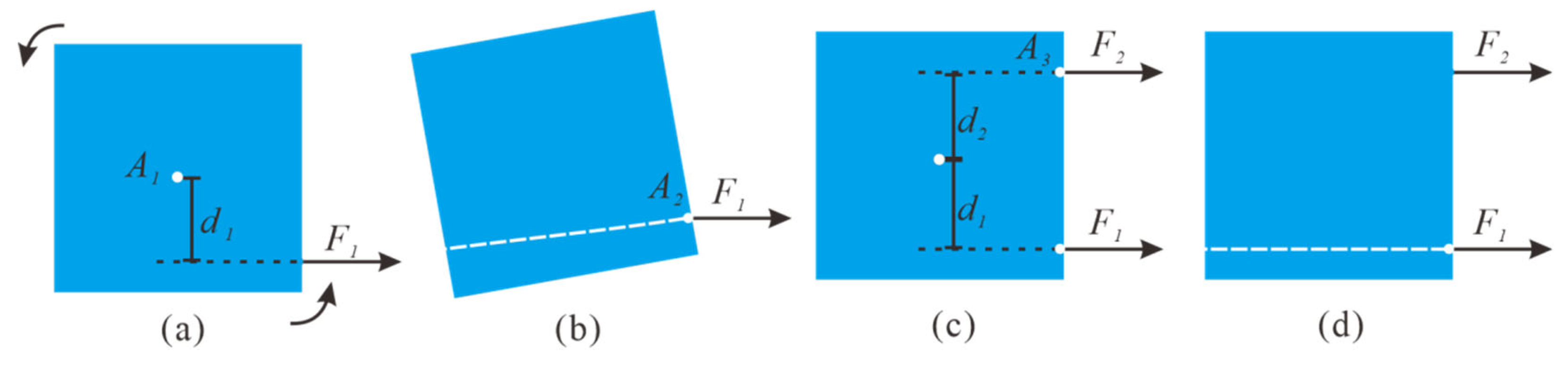
2. Theoretical Background
3. Experimental Method
3.1. Material and Devices
3.1.1. Fabric
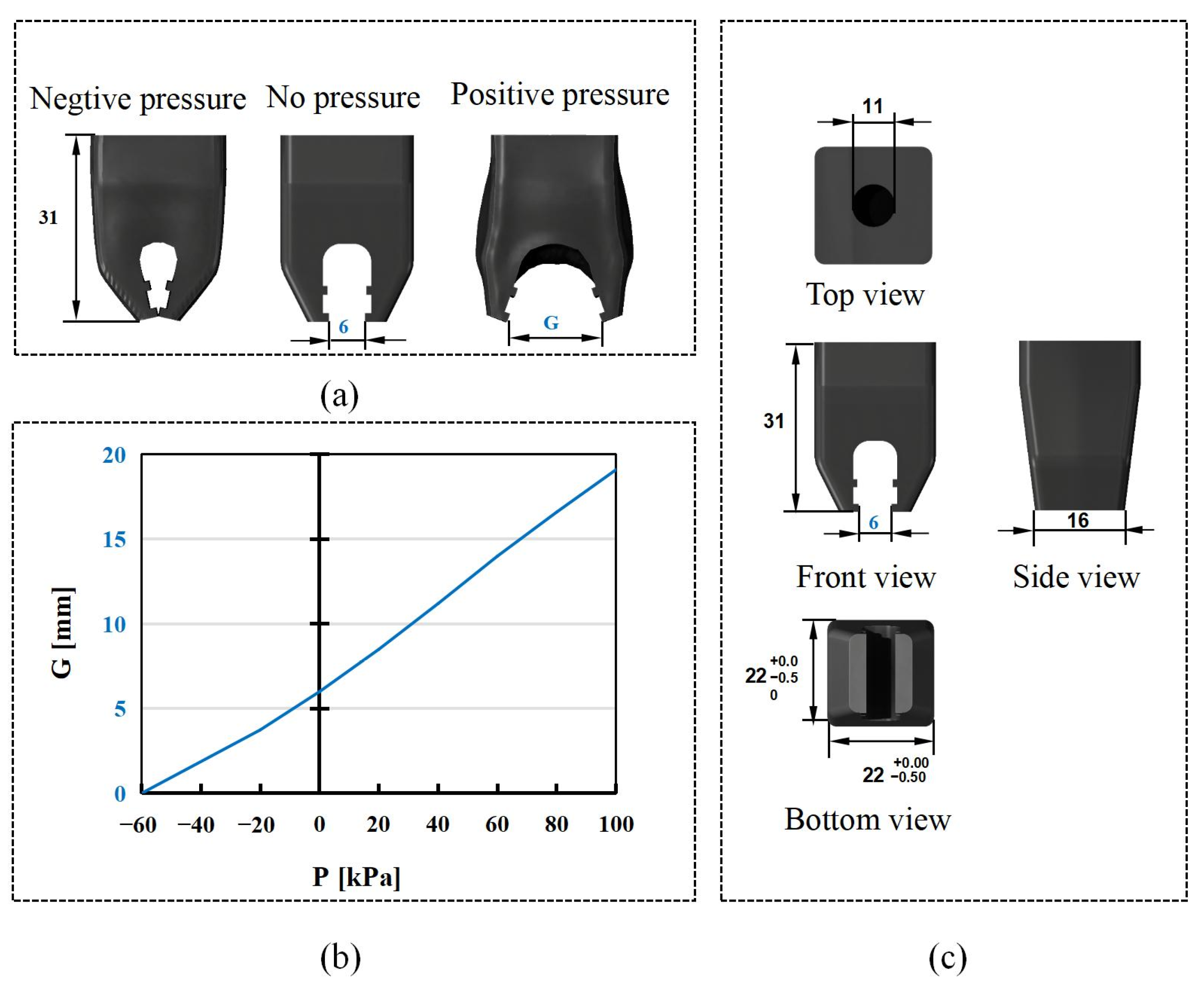
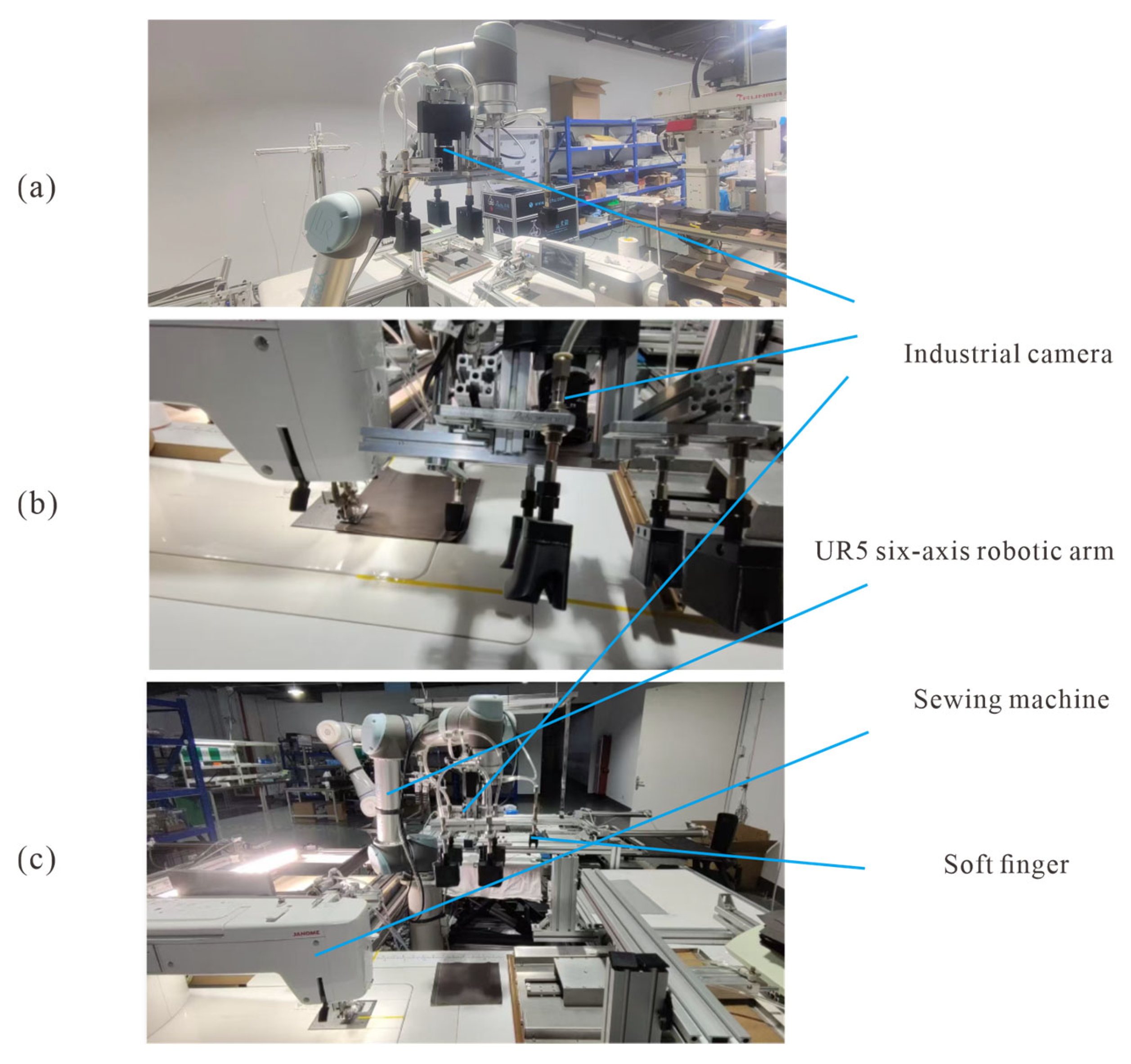
3.1.2. Soft Finger Robot
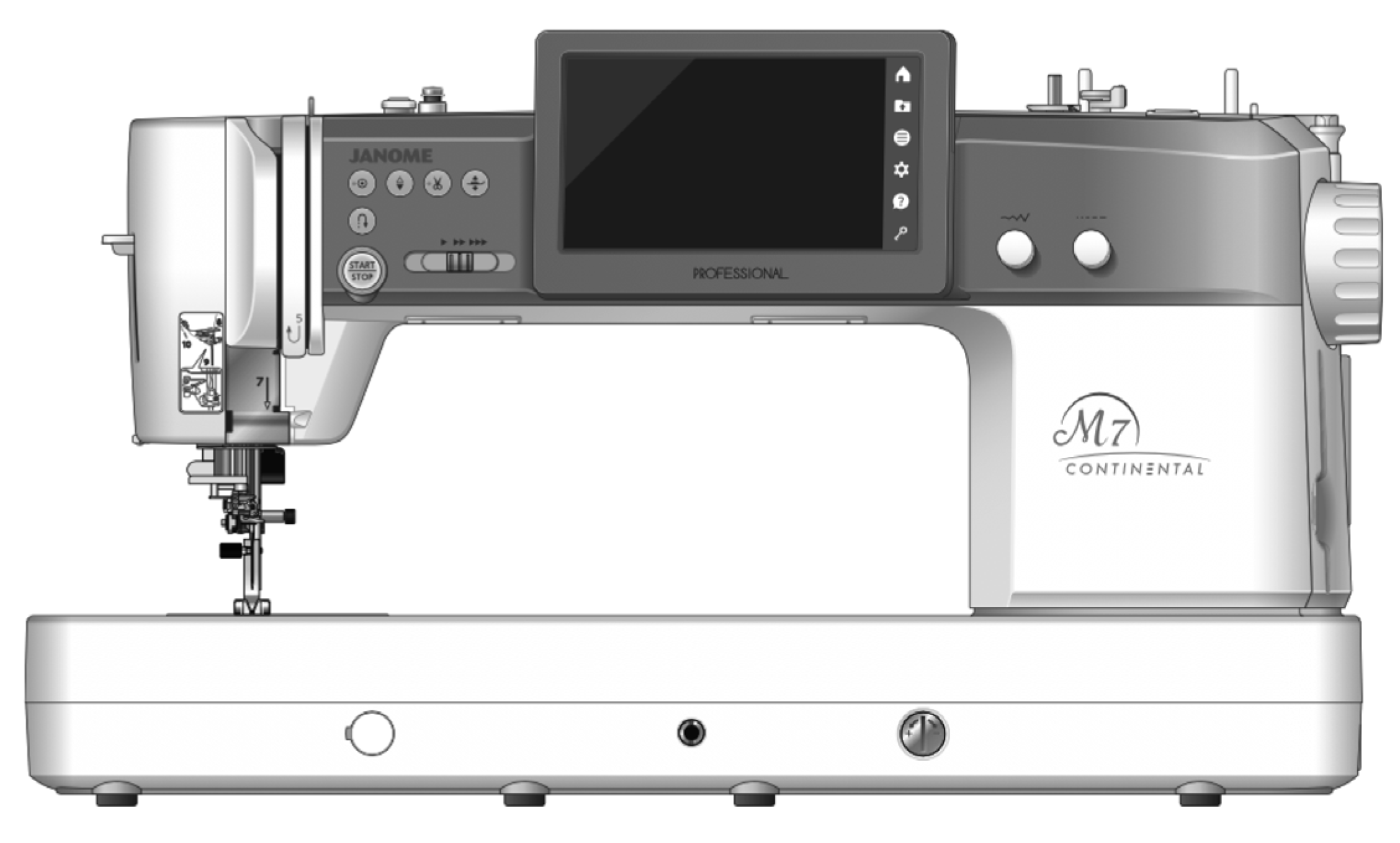
3.1.3. Sewing Machine
3.2. Method
3.2.1. Manual Sewing
- (1)
- Sewing-thread linear density: Three commercially produced cotton sewing threads (20 s/2, 40 s/2, 60 s/2) were pre-screened in a pilot study. The selection brackets the range recommended by the fabric weight interval (77–395 g·m−2) according to ISO 4915:2021 [26].
- (2)
- Needle size: Sizes 11, 14 and 16 are the most frequently used needles for light-, medium- and heavy-weight cotton fabrics in apparel production [27].
- (3)
- Stitch tension: The Continental M7’s “stitch tension” is displayed on the screen as a dimensionless relative value ranging from 0.0 to 7.0 (higher numbers give tighter needle thread); it has no physical units such as cN, g, or N. A preliminary “wide-range” test (0–7, step 0.5) on Fabric #5 showed that tension < 1.6 frequently produced looping on the bobbin side, whereas tension > 3.0 occasionally caused puckering. The interval was therefore discretized into three operative ranges: 0–1.6 (low), 1.6–3.0 (medium), 3.0–4.5 (high). These ranges coincide with the supplier’s manual and with the industrial practice reported by Nayak and Padhye [28].
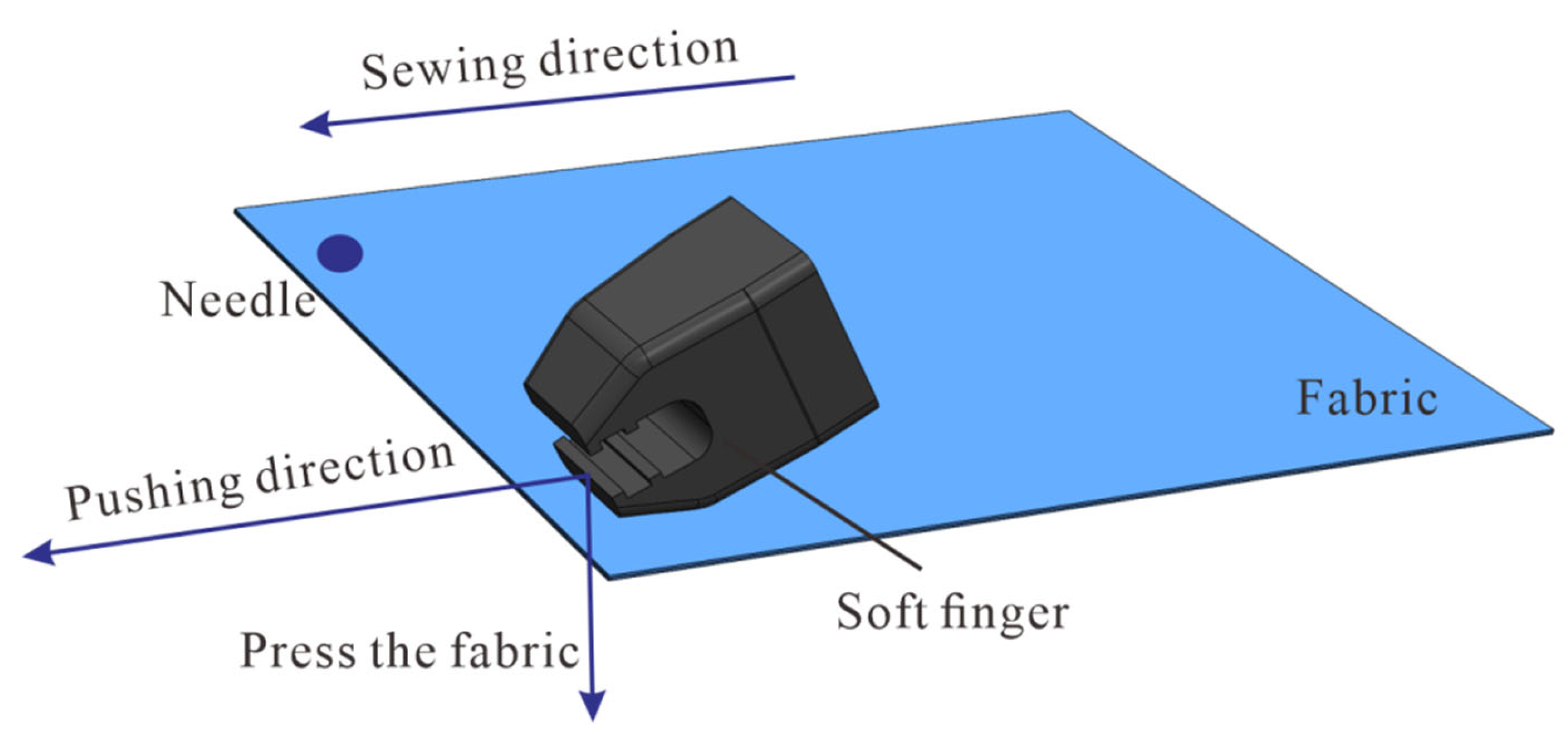
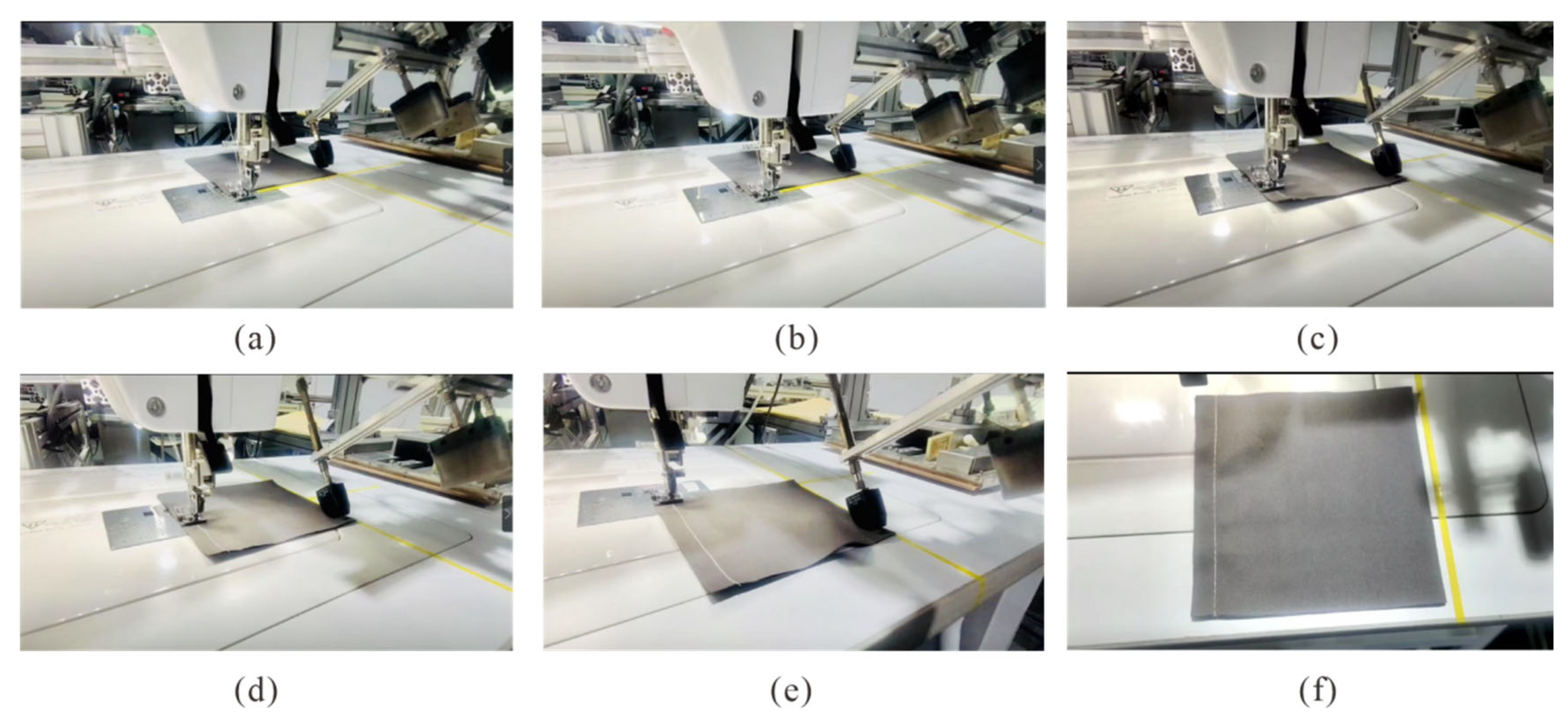
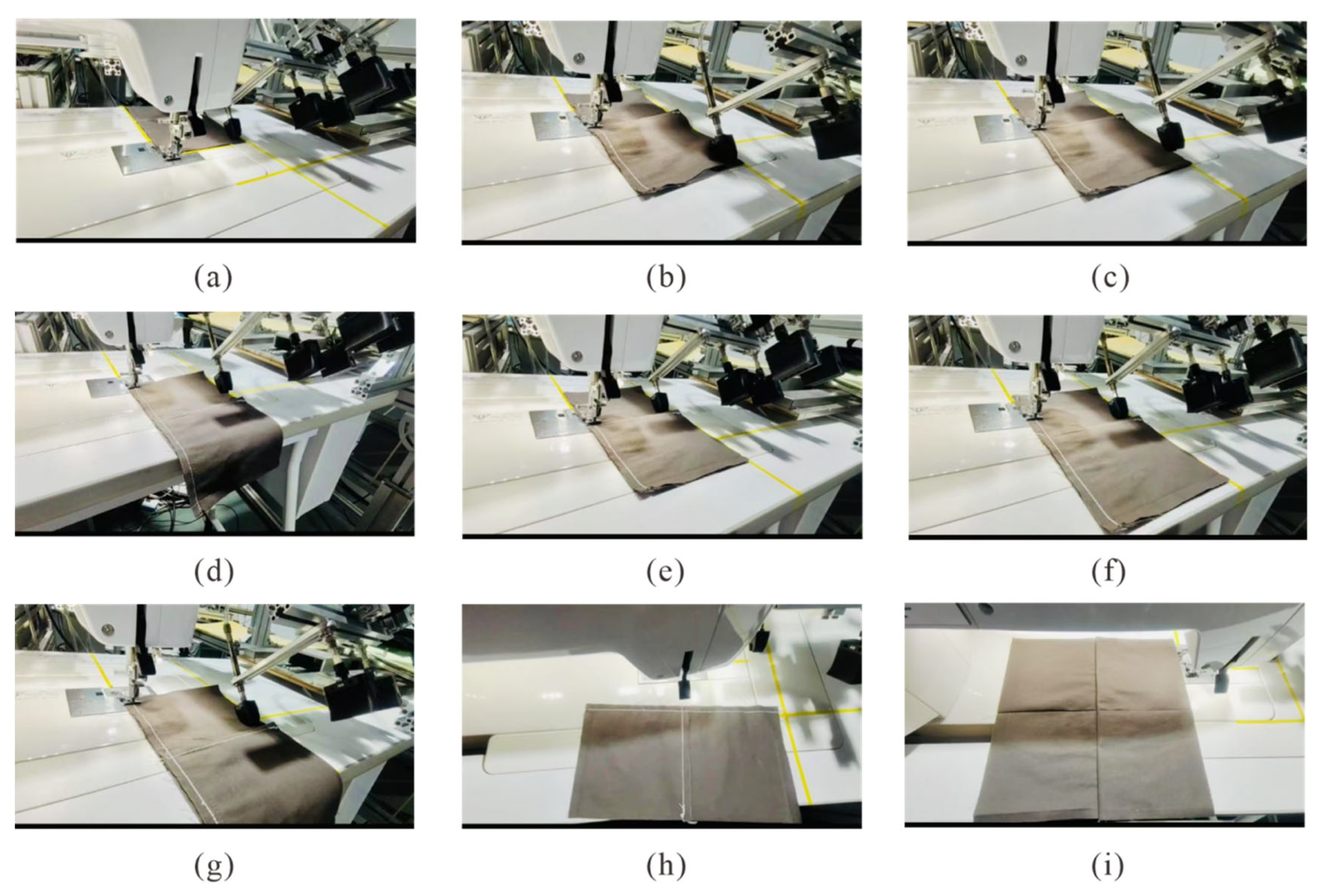
3.2.2. Sewing with Soft Finger
4. Results and Discussion
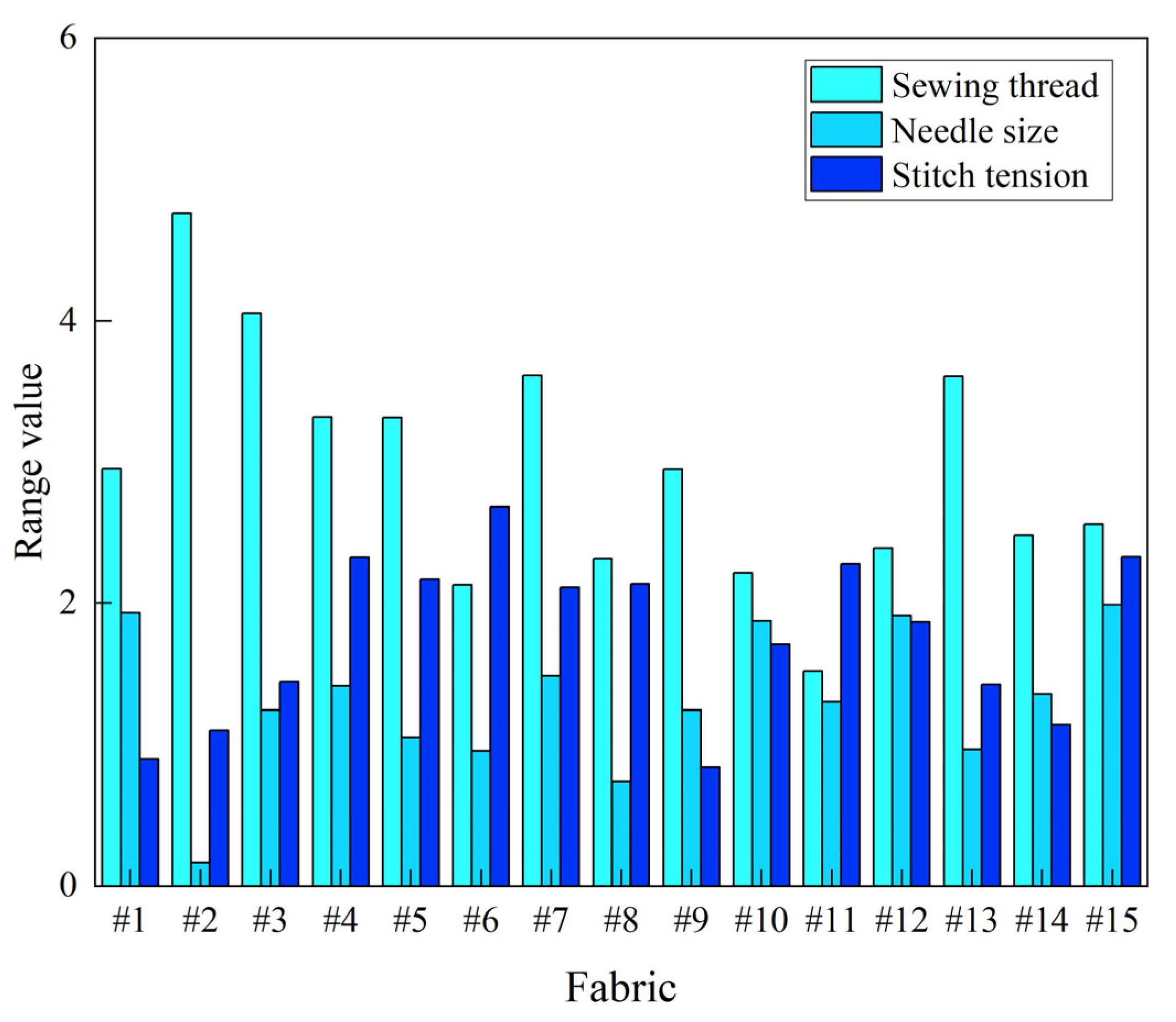
4.1. Optimal Sewing Parameters
4.2. The Sewing Model for the Soft Finger
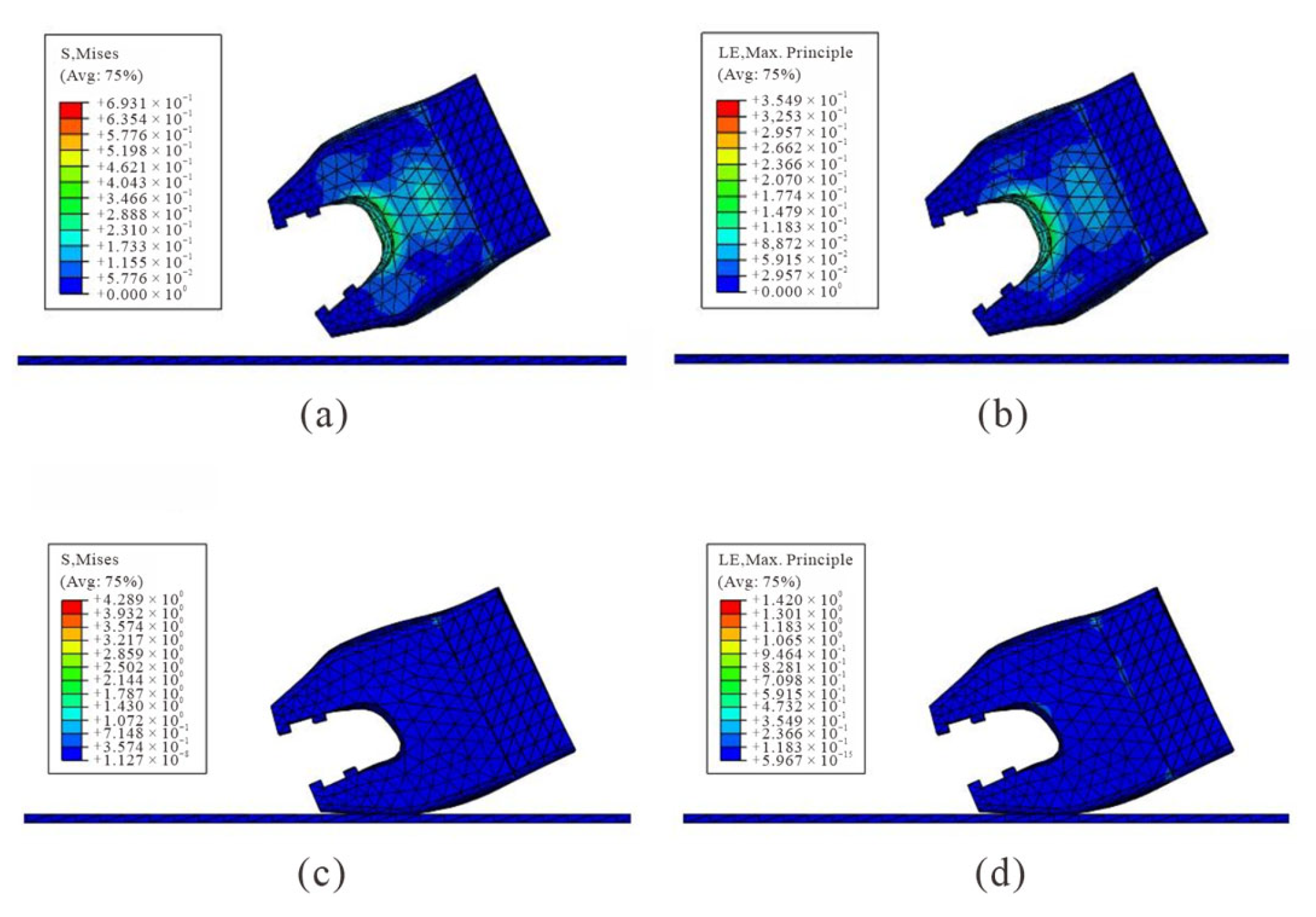
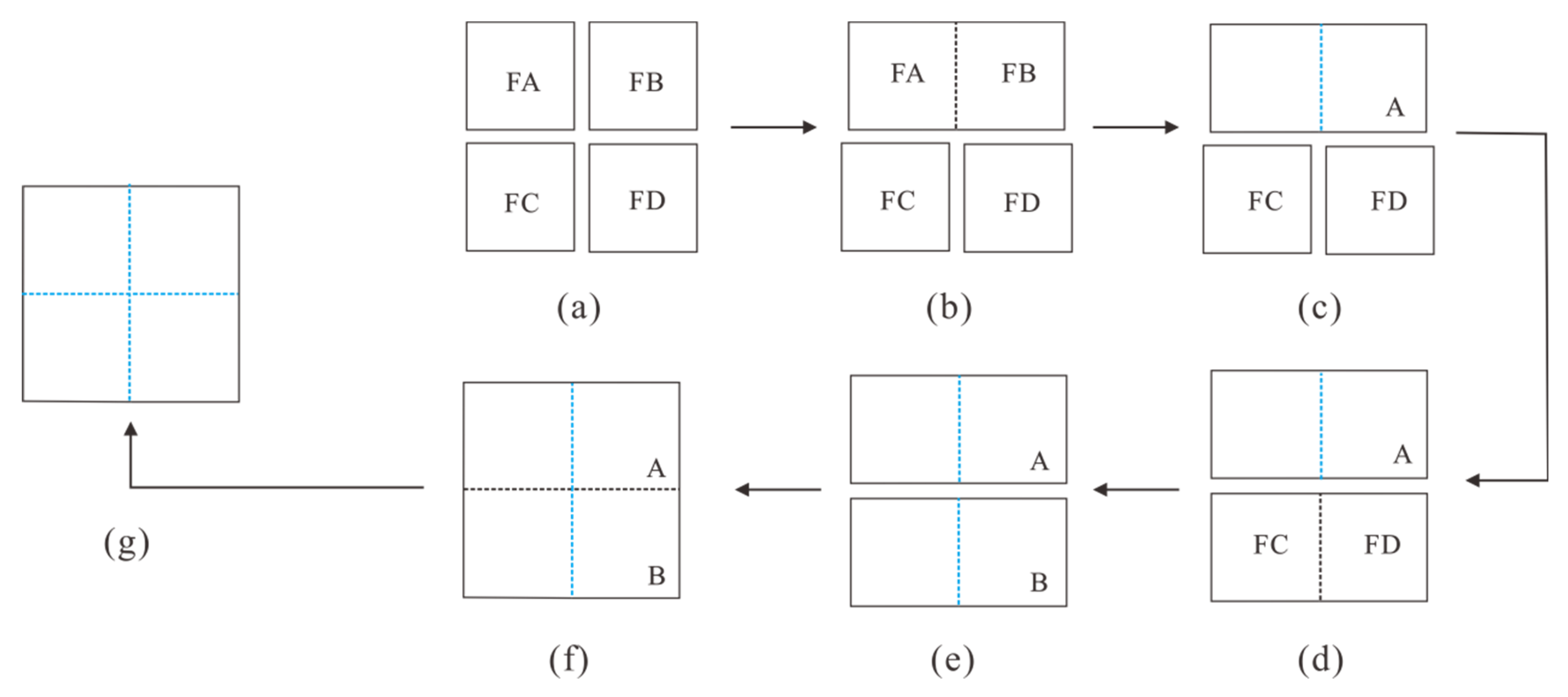
4.2.1. Sewing Model
4.2.2. Validation Test
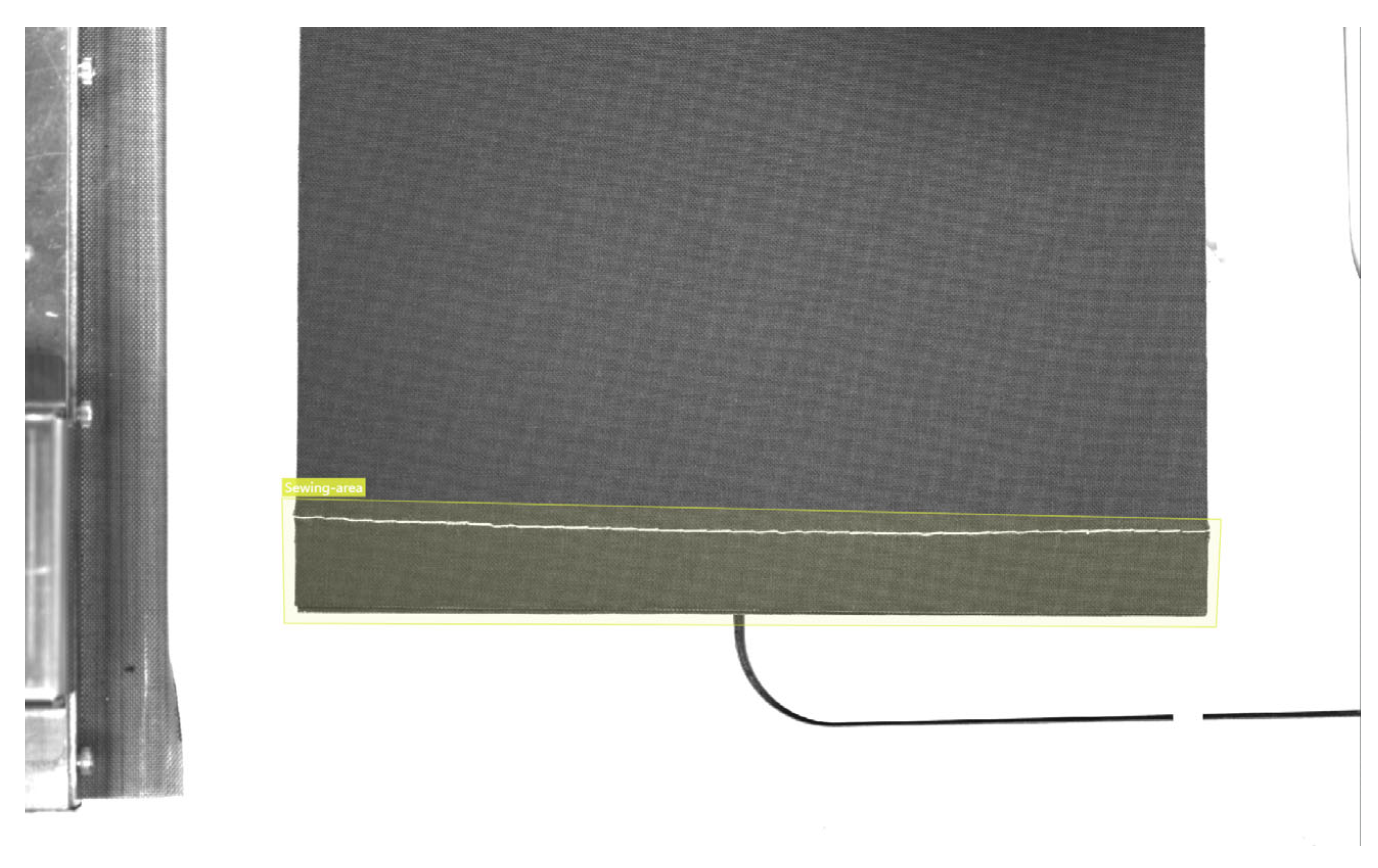
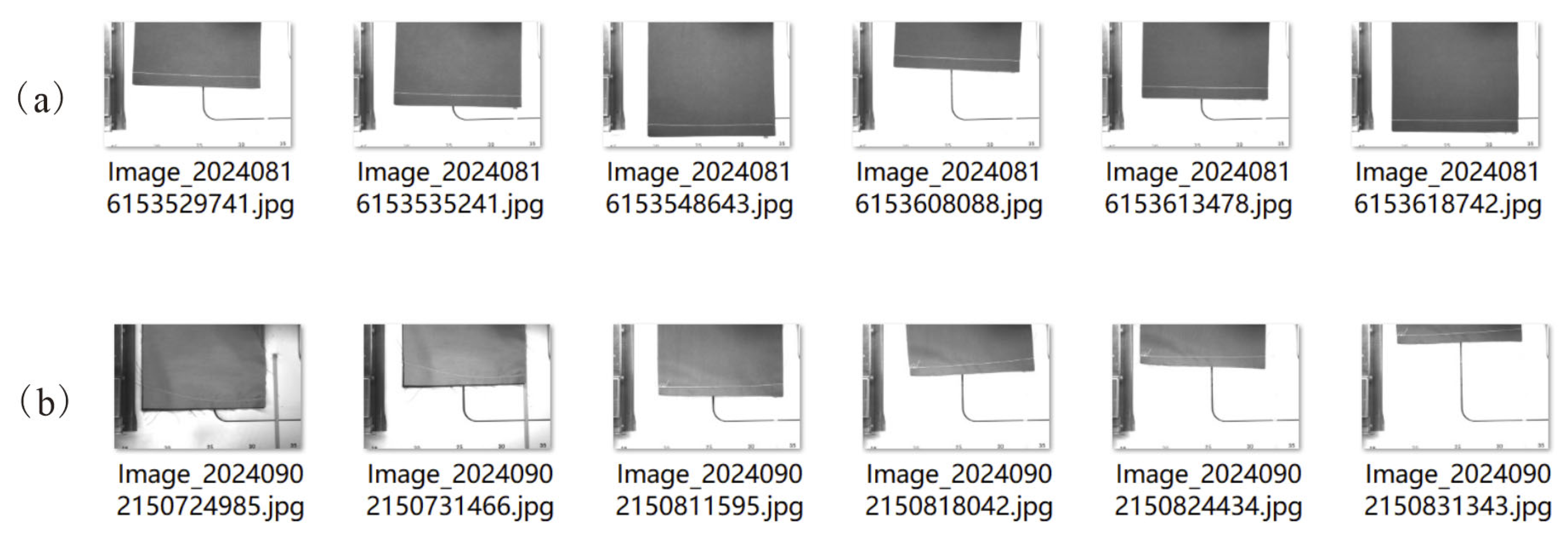
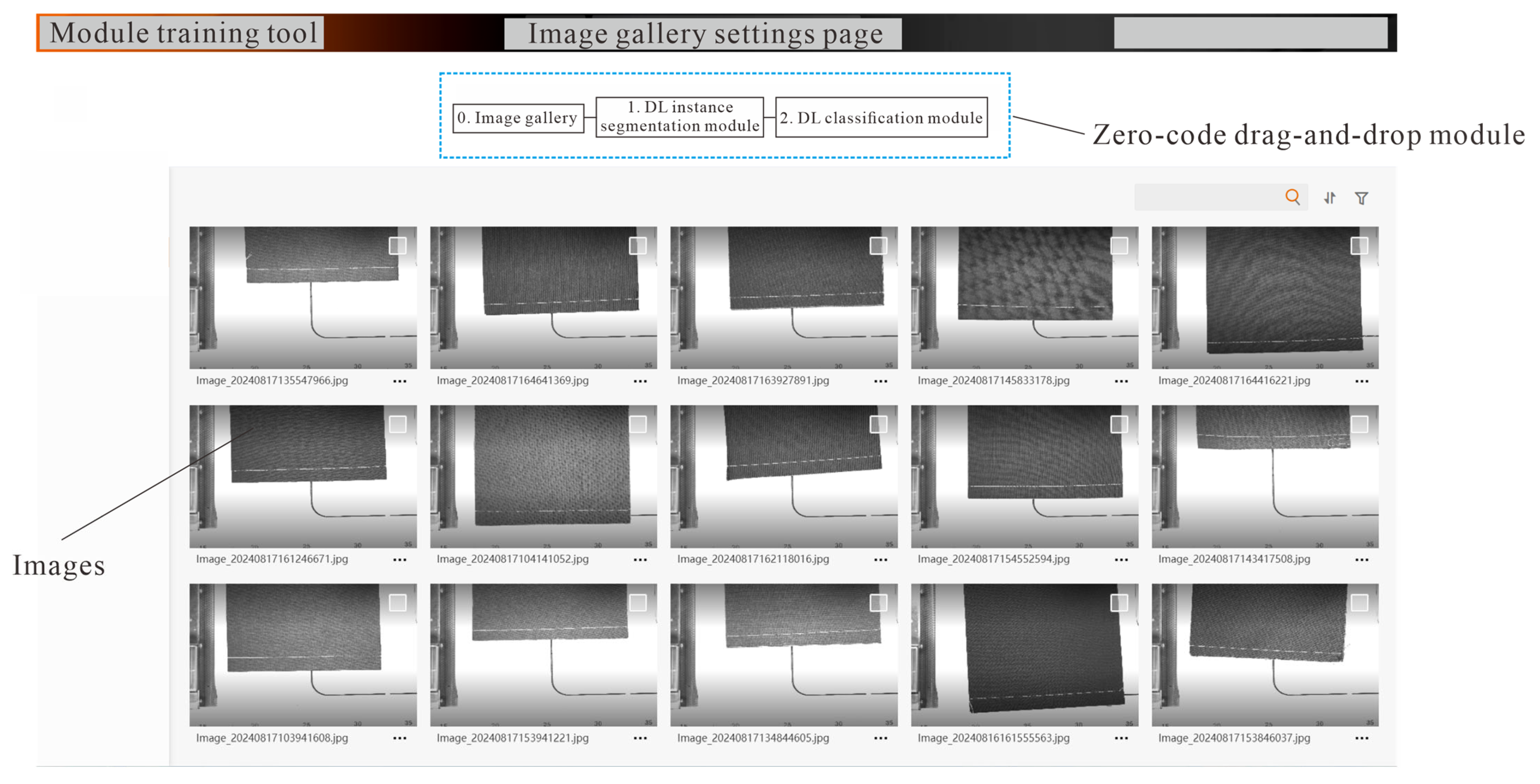
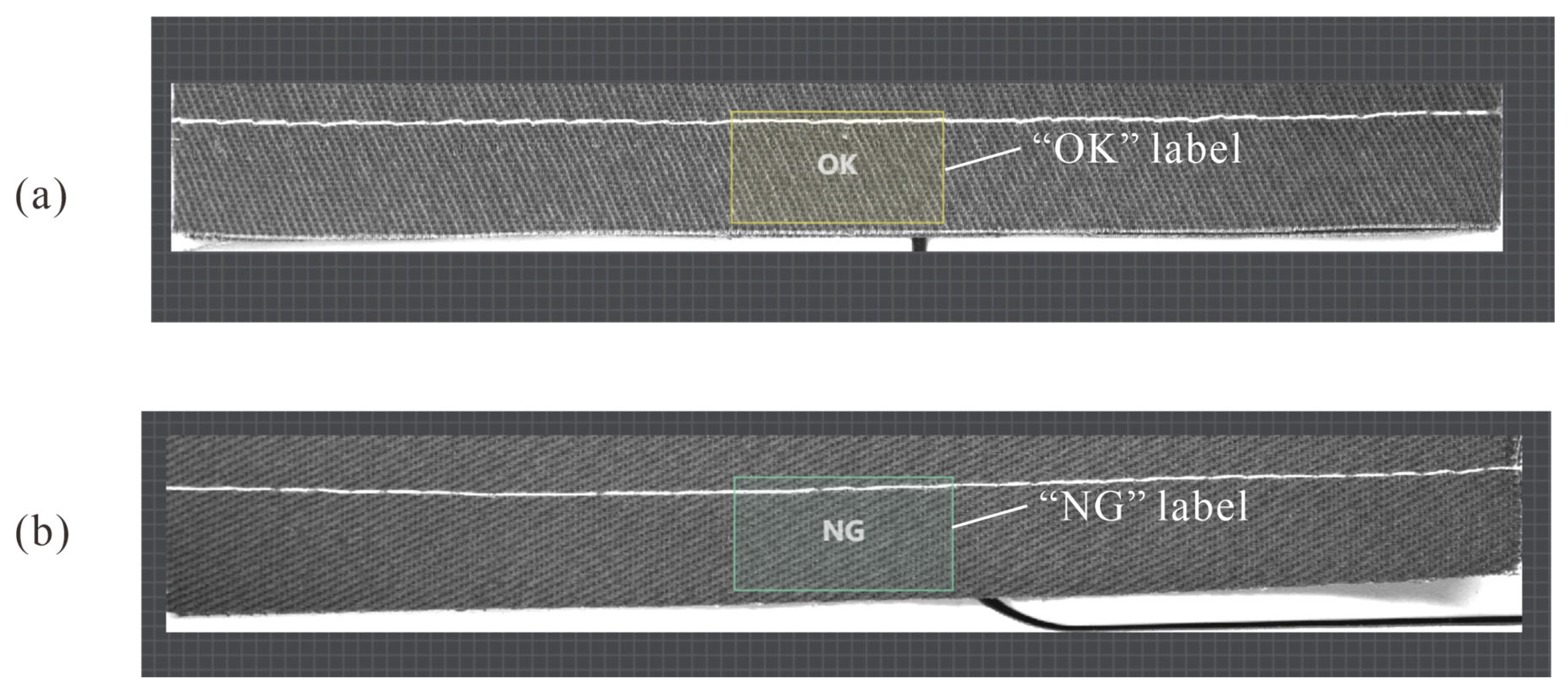
5. Quality Inspection
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haq, U.N.; Khan, M.M.R.; Khan, A.M.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Hossain, M.R. Global initiatives for industry 4.0 implementation and progress within the textile and apparel manufacturing sector: A comprehensive review. Int. J. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2025, 38, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiyan, W.; Zakaria, N. Technology integration to promote circular economy transformation of the garment industry: A systematic literature review. Autex Res. J. 2023, 24, 20230006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, A.; Saeed, M.A.; Ullah, T.; Uddin, Z.; Ullah Khan, R.M.W. A review of artificial intelligence applications in apparel industry. J. Text. Inst. 2022, 113, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Rho, S.; Lim, D.; Jeong, W. A Basic Study on Establishing the Automatic Sewing Process According to Textile Properties. Processes 2021, 9, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gershon, D. Strategies for robotic handling of flexible sheet material. Mechatronics 1993, 3, 611–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, M.; Nasu, Y.; Mitobe, K.; Borovac, B. Multi-arm robot control system for manipulation of flexible materials in sewing operation. Mechatronics 2000, 10, 371–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Shen, J.; Zhang, F. Grasping model of fabric cut pieces for robotic soft fingers. Text. Res. J. 2022, 92, 2223–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shen, J.; Yao, X.; Zhang, F. Research progress of automatic grasping methods for garment fabrics. Int. J. Cloth. Sci. Technol. 2023, 35, 997–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chi, X.; Ji, C.; Sun, Y. Analysis of grasping deformation of textile fabric based on fluid structure coupling. Text. Res. J. 2022, 92, 4374–4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, X.; Feng, W.; Wu, L.; Yuan, R. Grabbing performance of non-contact gripper based on Coanda effect for garment fabrics. J. Text. Res. 2022, 43, 208–213. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, W.; Hu, Y.; Li, X.R.; Liu, L. Robot end effector based on electrostatic adsorption for manipulating garment fabrics. Text. Res. J. 2022, 92, 691–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, K.; Abe, T. A Versatile End-Effector for Pick-and-Release of Fabric Parts. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 1431–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jilich, M.; Frascio, M.; Avalle, M.; Zoppi, M. Development of a gripper for garment handling designed for additive manufacturing. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2021, 235, 1799–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Wang, N.; Zhang, F. A design of bionic soft gripper for automatic fabric grasping in apparel manufacturing. Text. Res. J. 2023, 93, 1587–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, S.; Myeong, J.; Kim, H.-Y.; Park, Y.-L. Delicate Fabric Handling Using a Soft Robotic Gripper With Embedded Microneedles. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 4852–4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Shen, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, F.; Yao, X. A study on the formulation of process parameters for soft finger-assisted fabric stitching. Int. J. Cloth. Sci. Technol. 2024, 36, 1004–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhu, J. Intelligent Intercommunicating Multiscale Engineering: The Engineering of the Future. Engineering 2023, 30, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Wang, K.; Xiao, Z.; Han, Y. An information theory constrained unsupervised region of interest segmentation for active underwater small target detection. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2025, 157, 4119–4135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharia, P.; Aspragathos, N.; Mariolis, I.; Dermatas, E. A robotic system based on fuzzy visual servoing for handling flexible sheets lying on a table. Ind. Robot. Int. J. Robot. Res. Appl. 2009, 36, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Hou, D.; Fu, T.; Song, J.; He, W.; Song, R. Research on robot sewing method based on process modeling. Int. J. Intell. Robot. Appl. 2024, 8, 401–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokuda, F.; Murakami, R.; Seino, A.; Kobayashi, A.; Hayashibe, M.; Kosuge, K. Fixture-Free 2D Sewing Using a Dual-Arm Manipulator System. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2025, 22, 7927–7940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 3801:1977; Textiles—Woven Fabrics—Determination of Mass per Unit Length and Mass per Unit Area. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1977.
- ISO 5084:1996; Textiles—Determination of Thickness of Textiles and Textile Products. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996.
- ISO 9073-7:1995; Textiles—Test Methods for Nonwovens—Part 7: Determination of Bending Length. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1995.
- ISO 8295:1995; Plastics—Film and Sheeting—Determination of the Coefficients of Friction. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1995.
- ISO 4915:2021; Textiles—Stitch Types—Classification and Terminology. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- Cooklin, G. Garment Technology for Fashion Designers, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Nayak, R.; Padhye, R. Automation in Garment Manufacturing; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery, D.C. Design and Analysis of Experiments, 9th ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.; Ramírez-Gómez, Á.; Wang, J.; Zhang, F.; Li, Y. Intelligent and Precise Textile Drop-Off: A New Strategy for Integrating Soft Fingers and Machine Vision Technology. Textiles 2025, 5, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahimipirehgalin, M.; Trunzer, E.; Odenweller, M.; Vogel-Heuser, B. Automatic Visual Leakage Detection and Localization from Pipelines in Chemical Process Plants Using Machine Vision Techniques. Engineering 2021, 7, 758–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Lei, B.; Liu, L.; Li, S.X.; Ni, D.; Wang, T. Deep Learning in Medical Ultrasound Analysis: A Review. Engineering 2019, 5, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Fabric | Weight [g/m2] | Thickness [mm] | Bending Stiffness [mN·cm] | Friction Coefficient | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Warp | Weft | Static | Dynamic | |||
| #1 | 258.68 | 0.611 | 24.23 | 51.57 | 0.69 | 0.66 |
| #2 | 82.94 | 0.348 | 15.87 | 30.80 | 0.32 | 0.31 |
| #3 | 251.51 | 0.581 | 21.17 | 29.50 | 0.72 | 0.55 |
| #4 | 297.74 | 0.648 | 29.77 | 26.13 | 0.70 | 0.68 |
| #5 | 159.98 | 0.407 | 20.20 | 18.30 | 0.47 | 0.39 |
| #6 | 395.19 | 0.867 | 18.10 | 22.00 | 0.95 | 0.66 |
| #7 | 131.92 | 0.351 | 17.23 | 28.07 | 0.30 | 0.18 |
| #8 | 253.13 | 0.579 | 36.27 | 50.50 | 0.17 | 0.18 |
| #9 | 275.53 | 0.666 | 25.03 | 50.50 | 0.62 | 0.54 |
| #10 | 378.68 | 0.997 | 48.47 | 36.03 | 1.04 | 0.88 |
| #11 | 302.10 | 0.760 | 24.60 | 26.83 | 1.00 | 0.70 |
| #12 | 113.88 | 0.354 | 26.10 | 26.43 | 0.89 | 0.65 |
| #13 | 174.51 | 0.508 | 22.87 | 20.73 | 1.07 | 0.84 |
| #14 | 77.46 | 0.356 | 24.13 | 18.37 | 0.82 | 0.72 |
| #15 | 175.37 | 0.433 | 18.43 | 25.57 | 0.90 | 0.69 |
| Repetitive Precision | Recommended Load | Lifetime | Safe Pressure | Frequency | External Gripping Force | Contact Temperature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ±0.05 mm | 30 g | 1.5 million times | +80 kPa | 6 times/s | 0–0.3 N | 180 °C |
| Column | Factor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Test Number | I Sewing Thread | II Needle Size | ERROR | IV Stitch Tension | |
| 1 | 1 (20S/2) | 1 (11) | 1 | 1 | |
| 2 | 1 | 2 (14) | 2 | 2 | |
| 3 | 1 | 3 (16) | 3 | 3 | |
| 4 | 2 (40S/2) | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| 5 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 | |
| 6 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | |
| 7 | 3 (60S/2) | 1 | 3 | 2 | |
| 8 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | |
| 9 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | |
| P | S | Score |
|---|---|---|
| worst | worst | 0–2 |
| worse | worse | 2–4 |
| good | good | 4–6 |
| better | better | 6–8 |
| best | best | 8–10 |
| Fabric | Test Number | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | |
| #1 | 4.44 | 5.23 | 6.50 | 9.43 | 6.38 | 9.22 | 9.14 | 6.41 | 8.10 |
| #2 | 3.47 | 4.79 | 4.93 | 9.76 | 8.16 | 8.52 | 9.38 | 8.97 | 8.92 |
| #3 | 4.10 | 4.67 | 6.49 | 9.44 | 8.98 | 9.00 | 9.33 | 5.74 | 5.59 |
| #4 | 4.22 | 5.91 | 6.13 | 9.84 | 6.69 | 9.68 | 9.35 | 6.57 | 7.05 |
| #5 | 3.94 | 5.56 | 7.02 | 9.86 | 8.25 | 8.36 | 9.84 | 6.93 | 5.11 |
| #6 | 4.00 | 6.66 | 9.14 | 9.53 | 7.63 | 9.03 | 9.45 | 7.20 | 6.19 |
| #7 | 3.26 | 6.37 | 4.73 | 9.83 | 4.94 | 5.39 | 9.40 | 7.89 | 7.91 |
| #8 | 4.06 | 5.75 | 7.23 | 9.44 | 7.49 | 7.06 | 9.53 | 7.81 | 6.52 |
| #9 | 4.41 | 5.87 | 7.24 | 9.70 | 8.59 | 8.07 | 9.87 | 5.78 | 8.29 |
| #10 | 4.58 | 5.91 | 9.63 | 9.67 | 8.26 | 8.84 | 9.56 | 7.59 | 8.92 |
| #11 | 4.95 | 6.07 | 9.74 | 9.53 | 8.19 | 7.49 | 9.58 | 5.89 | 5.18 |
| #12 | 3.87 | 5.74 | 5.27 | 9.82 | 5.94 | 6.27 | 9.73 | 6.00 | 6.32 |
| #13 | 3.87 | 5.64 | 6.03 | 9.90 | 7.67 | 6.45 | 9.90 | 8.17 | 8.29 |
| #14 | 4.01 | 5.58 | 5.85 | 7.95 | 7.54 | 5.72 | 9.90 | 6.77 | 6.22 |
| #15 | 3.87 | 5.64 | 6.03 | 9.90 | 5.61 | 7.71 | 9.90 | 6.46 | 6.78 |
| Index | Sewing Thread | Needle Size | Stitch Tension |
|---|---|---|---|
| k1 | 5.507 | 7.880 | 5.767 |
| k2 | 8.823 | 6.913 | 7.920 |
| k3 | 7.293 | 6.830 | 7.937 |
| R | 3.316 | 1.050 | 2.170 |
| Fabric | Sewing Thread | Needle Size | Stitch Tension |
|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | 40 s/2 | 16 | 1.6–3.0 |
| #2 | 60 s/2 | 11 | 3.0–4.5 |
| #3 | 40 s/2 | 11 | 1.6–3.0 |
| #4 | 40 s/2 | 11 | 1.6–3.0 |
| #5 | 40 s/2 | 11 | 3.0–4.5 |
| 40 s/2 | 11 | 1.6–3.0 | |
| #6 | 40 s/2 | 16 | 3.0–4.5 |
| #7 | 60 s/2 | 11 | 3.0–4.5 |
| #8 | 40 s/2 | 11 | 3.0–4.5 |
| 60 s/2 | 11 | 3.0–4.5 | |
| #9 | 40 s/2 | 11 | 3.0–4.5 |
| #10 | 40 s/2 | 16 | 3.0–4.5 |
| #11 | 40 s/2 | 11 | 3.0–4.5 |
| #12 | 40 s/2 | 11 | 1.6–3.0 |
| 60 s/2 | 11 | 1.6–3.0 | |
| #13 | 60 s/2 | 11 | 3.0–4.5 |
| #14 | 60 s/2 | 11 | 1.6–3.0 |
| #15 | 40 s/2 | 11 | 1.6–3.0 |
| 60 s/2 | 11 | 1.6–3.0 |
| Sewing Speed r/min | Stitch Density | Pushing Speed [mm/s] | Latency Time [s] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Speed | Final Speed | |||
| 250 | 2.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 | 0.3 |
| 2.5 | 10.0 | 10.0 | ||
| 3.0 | 12.0 | 12.0 | ||
| 3.5 | 13.4 | 13.4 | ||
| 4.0 | 14.5 | 14.5 | ||
| 4.5 | 17.0 | 17.0 | ||
| 5.0 | 18.0 | 18.0 | ||
| 375 | 2.0 | 12.6 | 12.6 | 0.3 |
| 2.5 | 15.5 | 15.5 | ||
| 3.0 | 18.5 | 18.5 | ||
| 3.5 | 20.5 | 20.5 | ||
| 4.0 | 23.5 | 23.5 | ||
| 4.5 | 26.0 | 26.0 | ||
| 5.0 | 28.0 | 28.0 | ||
| 690 | 2.0 | 21.0 | 21.0 | 0.5 |
| 2.5 | 26.0 | 26.0 | ||
| 3.0 | 30.0 | 30.0 | ||
| 3.5 | 34.5 | 34.5 | ||
| 4.0 | 38.5 | 38.5 | ||
| 4.5 | 43.5 | 43.5 | ||
| 5.0 | 46.0 | 46.0 | ||
| 780 | 2.0 | 23.5 | 31 | 0.55 |
| 2.5 | 28 | 35 | ||
| 3.0 | 29.5 | 42.5 | ||
| 3.5 | 31 | 48.5 | ||
| 4.0 | 33 | 55 | ||
| 4.5 | 37 | 57 | ||
| 5.0 | 39 | 61 | ||
| 900 | 2.0 | 26 | 37.5 | 0.6 |
| 2.5 | 28 | 44 | ||
| 3.0 | 30 | 47 | ||
| 3.5 | 32 | 51 | ||
| 4.0 | 34 | 57 | ||
| 4.5 | 36 | 62 | ||
| 5.0 | 38 | 63.5 | ||
| 1350 | 2.0 | 27 | 43.5 | 0.7 |
| 2.5 | 30.5 | 47 | ||
| 3.0 | 33 | 49 | ||
| 3.5 | 35.5 | 53 | ||
| 4.0 | 39 | 58 | ||
| 4.5 | 42 | 60 | ||
| 5.0 | 45 | 65 | ||
| Factors | Initial Pushing Speed | Final Pushing Speed | Latency Time | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pearson Correlation | Significance | Pearson Correlation | Significance | Pearson Correlation | Significance | |
| Weight | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 |
| Thickness | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 |
| Warp bending | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 |
| Weft bending | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 |
| Static friction coefficient | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 |
| Dynamic friction Coefficient | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 |
| Sewing speed | 0.715 ** | <0.01 | 0.824 ** | <0.01 | 0.970 ** | 0.00 |
| Stitch density | 0.534 ** | <0.01 | 0.419 ** | <0.01 | 0.000 | 1.000 |
| Weight [g/m2] | Thickness [mm] | Bending Stiffness [mN·cm] | Friction Coefficient | Sewing Thread | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Warp | Weft | Warp | Weft | |||
| 190.467 | 0.391 | 18.26 | 25.48 | 0.195 | 0.205 | 40 s/2 |
| Needle size | Stitch tension | Sewing speed | Stitch density | IS | FS | LT |
| 14 | 1.6–3.0 | 800 | 3.0 | 27.038 | 44.083 | 0.510 |
| Training Report | |
|---|---|
| Task ID | 1732_9_20250906184108903 |
| Model Version | V8 |
| Training Images | 1780 |
| Training Time | 48 min 38 s |
| Incremental Model | NO |
| Release | VM500 |
| Model Type | High-precision |
| Epochs | 89 |
| Rotation Range | 180° |
| Base Learning Rate | 0.0001 |
| Batch Size | 8 |
| Model Precision Mode | Fast |
| Model UID | 1732_124106 |
| Data Augmentation | Default Configuration |
| Predicted Sewing Area | Predicted Background | |
|---|---|---|
| Actual sewing area | 367 | 1 |
| Actual background | 1 | 0 |
| Training Report | |
|---|---|
| Task ID | 2437_1_20250906184058992 |
| Model Version | V3 |
| Training Images | 1503 |
| Training Time | 28 min 25 s |
| Incremental Model | NO |
| Release | VM500 |
| Model Type | High-precision |
| Epochs | 100 |
| Base Learning Rate | 0.0001 |
| Batch Size | 32 |
| Model UID | 2437_123923 |
| Data Augmentation | Default Configuration |
| ROI Perturbation | Enabled |
| Width/Height Jitter | [0.9, 1.2] |
| Rotation Jitter | [−3°, 3°] |
| Number of Perturbations | 3 |
| Predicted NG | Predicted OK | |
|---|---|---|
| Actual NG | 41 | 8 |
| Actual OK | 8 | 592 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, J.; Ramírez-Gómez, Á.; Wang, J.; Zhang, F. Autonomous Sewing Technology and System: A New Strategy by Integrating Soft Fingers and Machine Vision Technology. Textiles 2025, 5, 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/textiles5040045
Shen J, Ramírez-Gómez Á, Wang J, Zhang F. Autonomous Sewing Technology and System: A New Strategy by Integrating Soft Fingers and Machine Vision Technology. Textiles. 2025; 5(4):45. https://doi.org/10.3390/textiles5040045
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Jinzhu, Álvaro Ramírez-Gómez, Jianping Wang, and Fan Zhang. 2025. "Autonomous Sewing Technology and System: A New Strategy by Integrating Soft Fingers and Machine Vision Technology" Textiles 5, no. 4: 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/textiles5040045
APA StyleShen, J., Ramírez-Gómez, Á., Wang, J., & Zhang, F. (2025). Autonomous Sewing Technology and System: A New Strategy by Integrating Soft Fingers and Machine Vision Technology. Textiles, 5(4), 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/textiles5040045







