Catalytic Effects of Different Metal Salts on Cotton Waste Textiles by Pyrolysis: Pyrolysis Behavior and Properties of Activated Carbon
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Pyrolysis Behavior
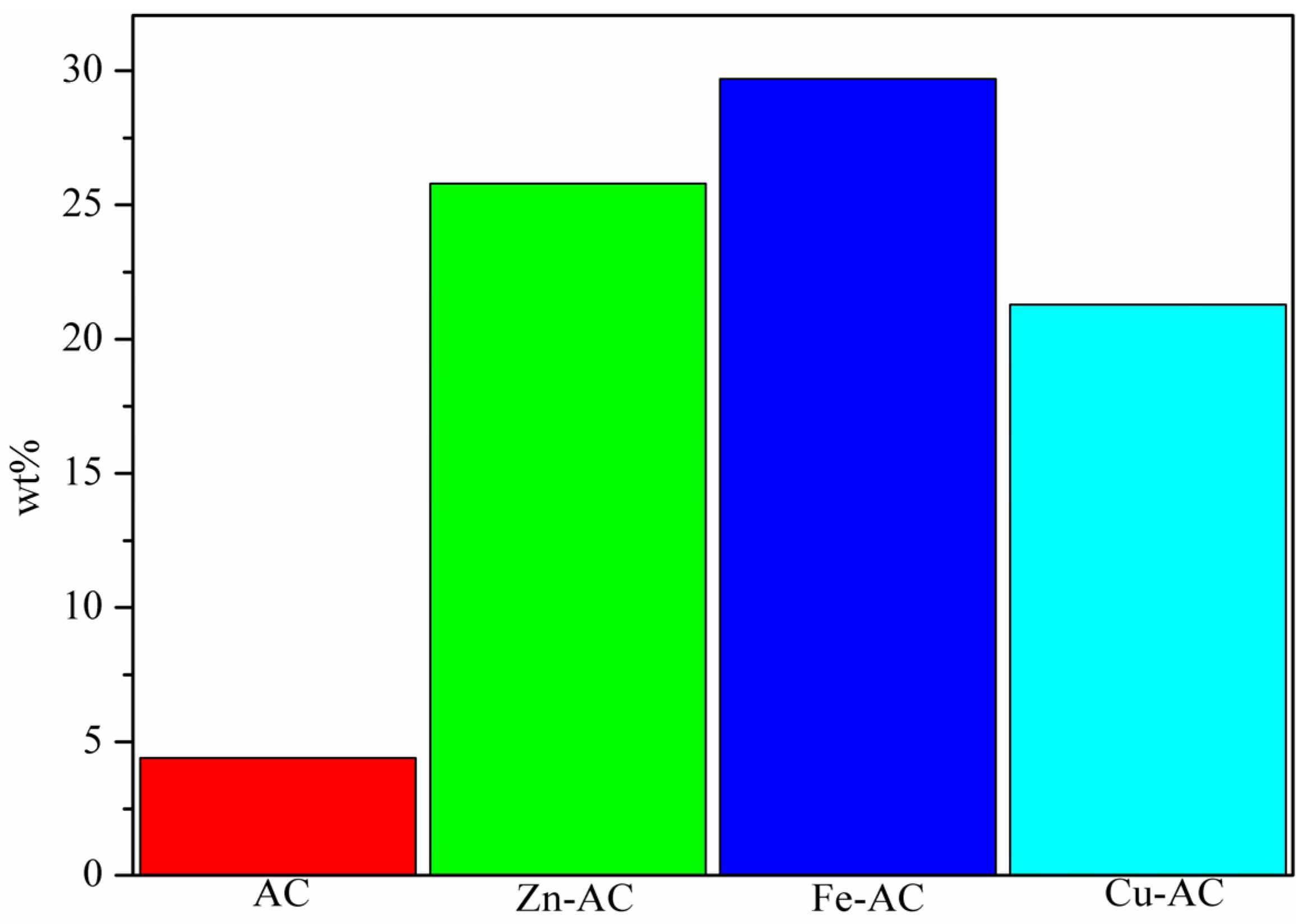
3.1.1. AC Yield
3.1.2. Pyrolysis Process
3.2. AC Characteristics
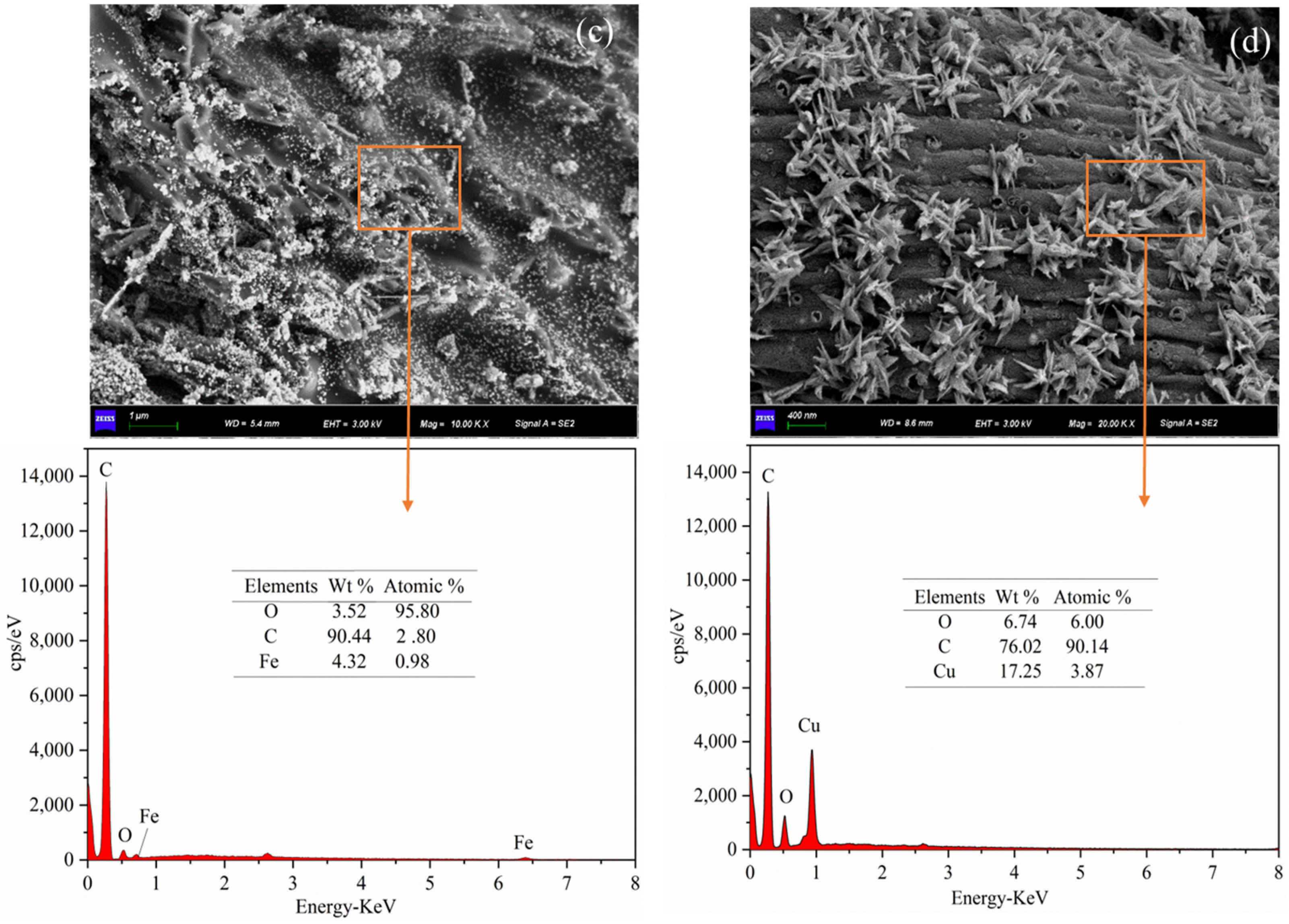
3.2.1. Morphology
3.2.2. Specific Surface Area and Aperture Distribution
3.2.3. Surface Functional Groups
3.2.4. Surface Molecular Structures and Atomic Valence States
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pensupa, N.; Leu, S.Y.; Hu, Y.Z.; Du, C.Y.; Liu, H.; Jing, H.D.; Wang, H.M.; Lin, C.S.K. Recent Trends in Sustainable Textile Waste Recycling Methods: Current Situation and Future Prospects. Top. Curr. Chem. 2017, 375, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Ma, H.R.; Li, Z.; Yan, S.C.; Ma, L.; Yu, F.; Wang, G.; Guo, X.H.; Ma, Y.Q.; Wong, C.P. Flute type micropores activated carbon from cotton stalk for high performance supercapacitors. J. Power Sources 2017, 359, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopatina, A.; Anugwom, I.; Blot, H.; Conde, A.S.; Mänttäri, M.; Kallioinen, M. Re-use of waste cotton textile as an ultrafiltration membrane. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeVoy, J.E.; Congiusta, E.; Lundberg, D.J.; Findeisen, S.; Bhattacharya, S. Post-Consumer textile waste and disposal: Differences by socioeconomic, demographic, and retail factors. Waste Manag. 2021, 136, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rago, Y.P.; Surroop, D.; Mohee, R. Torrefaction of textile waste for production of energy-dense biochar using mass loss as a synthetic indicator. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bert, V.; Allemon, J.; Sajet, P.; Dieu, S.; Papin, A.; Collet, S.; Gaucher, R.; Chalot, M.; Michiels, B.; Raventos, C. Torrefaction and pyrolysis of metal-enriched poplars from phytotechnologies: Effect of temperature and biomass chlorine content on metal distribution in end-products and valorization options. Biomass Bioenergy 2017, 96, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.R.; Lu, T.; Zhao, D.D.; Huang, H.Y.; Noriyuki, K.; Chen, Y. Influence of temperature on product distribution and biochar properties by municipal sludge pyrolysis. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2013, 15, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.F.; Lu, T.Y.; Meng, Y.; Han, S.Y.; Jiang, J.G. Pyrolysis characteristics of excavated waste and generation mechanism of gas products. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 370, 133489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerzak, W.; Acha, E.; Li, B. Comprehensive Review of Biomass Pyrolysis: Conventional and Advanced Technologies, Reactor Designs, Product Compositions and Yields, and Techno-Economic Analysis. Energies 2024, 17, 5082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.W.; Yu, Z.S.; Lin, Y.; Lin, Y.S.; Fan, Y.L.; Liao, Y.F.; Ma, X.Q. Effects of additives on the co-pyrolysis of municipal solid waste and paper sludge by using thermogravimetric analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 209, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, D.; Yi, S.; Jung, S.; Kwon, E.E.; Eilhann, E. Valorization of synthetic textile waste using CO2 as a raw material in the catalytic pyrolysis process. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Wen, C.; Chen, X.P.; Jiang, G.D.; Liu, G.N.; Liu, D. Catalytic pyrolysis and gasification of waste textile under carbon dioxide atmosphere with composite Zn-Fe catalyst. Fuel Process. Technol. 2017, 166, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanoğlu, A.; Çay, A.; Yanık, J. Production of biochars from textile fibres through torrefaction and their characterization. Energy 2019, 166, 664–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.T.; Li, Y.Q.; Chi, D.C.; Wu, Q. Efficient removal of ammonium in aqueous solution by ultrasonic magniesium-modified biochar. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 461, 142972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.; Yang, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.X.; Pan, J.F. Preparation of microwave-activated magnetic bio-char adsorbent and study on removal of elemental mercury from flue gas. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 134049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.G.; Cho, Y.J.; Song, P.S.; Kang, Y.; Kim, J.S.; Choi, M.J. Effects of temperature distribution on the catalytic pyrolysis of polystyrene waste in a swirling fluidized-bed reactor. Catal. Today 2003, 79–80, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, F.; Lopes, H.; Andre, R.N. Effect of catalysts in the quality of syngas and by-products obtained by co-gasification of coal and wastes. 2: Heavy metals, sulphur and halogen compounds abatement. Fuel 2007, 86, 2052–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.H.; Luo, C.; Yan, F.; Yang, Y.; Guo, B.; Wang, L.; Xu, S.Q.; Wu, F.; Ji, P.H. Remediation of Pb(II) and Cd(II) in polluted waters with calcium thioglycolate-modified straw biochar. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 338, 122638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.J.; Liu, H.Y.; Lu, H.F.; Zhang, Z.K.; Chen, Y.F. High Selectivity of Cyclohexane Dehydrogenation for H2 Evolution Over Cu/SBA-15 Catalyst. Catal. Lett. 2017, 147, 1295–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emara, M.M.; Ali, S.H.; Kassem, T.S.E.; Van Patten, P.G. Catalysis of sugarcane-bagasse pyrolysis by Co, Ni, and Cu single and mixed oxide nanocomposites. J. Nanoparticle Res. Interdiscip. Forum Nanoscale Sci. Technol. 2020, 22, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.H.; Xu, Z.H.; Zhang, D.F.; Chen, W.F.; Zhang, T.Q.; Huang, Y.X.; Gu, L.; Deng, H.X.; Tian, D.Q. Box-Behnken design approach towardsoptimization of activated carbon synthesized by co-pyrolysis of waste polyester textiles and MgCl2. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 427, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Park, C.Y.; Lee, J. Reduction of polycyclic compounds and biphenyls generated by pyrolysis of industrial plastic waste by using supported metal catalysts: A case study of polyethylene terephthalate treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 392, 122464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Q.W.; Wang, L.; Jiang, J.J.; Ma, S.D.; Liu, L.Y.; Zhou, Z.L.; Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Bai, J. Catalytic pyrolysis of oil-based drill cuttings over metal oxides: The product properties and environmental risk assessment of heavy metals in char. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 159, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhong, M.Q.; Wang, T.; Liu, J.X.; Mei, M.; Chen, S.; Li, J.P. Study on the Pyrolysis and Adsorption Behavior of Activated Carbon Derived from Waste Polyester Textiles with Different Metal Salts. Materials 2023, 15, 7112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.H.; Zhang, H.P.; Yan, Y. Gradient porous Co–Cu–Mn mixed oxides modified ZSM-5 membranes as high efficiency catalyst for the catalytic oxidation of isopropanol. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 111, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.D.; Guo, D.W.; Shang, Q.; Zhao, Y.J.; Zhang, L.Y.; Guo, X.; Cheng, J.; Chang, G.Z.; Guo, Q.J.; Sun, S.Z. Mechanism of biochar-gas-tar-soot formation during pyrolysis of different biomass feedstocks: Effect of inherent metal species. Fuel 2021, 293, 120409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rufford, T.E.; Hulicova-Jurcakova, D.; Zhu, Z.H.; Lu, G.Q. A comparative study of chemical treatment by FeCl3, MgCl2, and ZnCl2 on microstructure, surface chemistry, and double-layercapacitance of carbons from waste biomass. J. Mater. Res. 2010, 25, 1451–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, N.; Kawamoto, H.; Saka, S. Different action of alkali/alkaline earth metal chlorides on cellulose pyrolysis. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2008, 81, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tazibet, S.; Velasco, L.F.; Lodewyckx, P.; M’Hamed, D.A.; Boucheffa, Y. Systematic study of the role played by ZnCl2 during the carbonization of a chemically activated carbon by TG–MS and DSC. J. Therm. Anal. Calorimetrt 2018, 134, 1395–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.J.; Jiang, W.; Li, S.; Zhang, X.W.; Wang, W.Q. Preparation and analysis of straw activated carbon synergetic catalyzed by ZnCl2-H3PO4 through hydrothermal carbonization combined with ultrasonic assisted immersion pyrolysis. Waste Manag. 2019, 89, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.H.; Sun, Z.H.; Zhou, Y.W.; Chen, W.F.; Zhang, T.Q.; Huang, Y.X.; Zhang, D.F. Insights into the pyrolysis behavior and adsorption properties of activated carbon from waste cotton textiles by FeCl3-activation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 582, 123934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.D.; Liu, Y.C.; Luo, G.; Qian, F.; Zhang, S.C.; Chen, J.M. Facile Fabrication of Magnetic Carbon Composites from Hydrochar via Simultaneous Activation and Magnetization for Triclosan Adsorption. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 5840–5848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solak, A.; Rutkowski, P. Bio-oil production by fast pyrolysis of cellulose/polyethylene mixtures in the presence of metal chloride. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2014, 16, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terakado, O.; Amano, A.; Hirasawa, M. Explosive degradation of woody biomass under the presence of metal nitrates. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2009, 85, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.Q.; Chen, S.; Wang, T.; Liu, J.X.; Mei, M.; Li, J.P. Co-pyrolysis of polyester and cotton via thermogravimetric analysis and adsorption mechanism of Cr(VI) removal by carbon in aqueous solution. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 354, 118902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.T.; Liu, D.M.; Cai, Y.D.; Wang, Y.P.; Teng, J. Adsorption pore structure and its fractal characteristics of coals by N2 adsorption/desorption and FESEM image analyses. Fuel 2019, 257, 116031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mel, M.S. Application of the simple Bayesian classifier for the N2 (77 K) adsorption/desorption hysteresis loop recognition. Adsorption 2023, 29, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.F.; Yue, Q.Y.; Gao, B.Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q. Activated carbon from tomato stem by chemical activation with FeCl2. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 529, 842–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezoti, O.; Cazetta, A.L.; Bedin, K.C.; Souza, L.S.; Martins, A.C.; Silva, T.L.; Júnior, O.O.S.; Visentainer, J.V.; Almeida, V.C. NaOH-activated carbon of high surface area produced from guava seeds as a high-efficiency adsorbent for amoxicillin removal: Kinetic, isotherm and thermodynamic studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 288, 778–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Chen, Y.C.; Li, J.P.; Xue, Y.J.; Liu, J.X.; Mei, M.; Hou, H.B.; Chen, S. Co-pyrolysis behavior of sewage sludge and rice husk by TG-MS and residue analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 250, 119557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, K.L.; Ng, D.H.L. Synthesis and characterization of cotton-made activated carbon fiber and its adsorption of methylene blue in water treatment. Biomass Bioenergy 2012, 46, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Sun, J.S.; Li, M.; Wang, S.H.; Pei, H.S.; Zhang, J.S. Enhanced enzymatic hydrolysis and structural features of corn stover by FeCl3 pretreatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 5853–5858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naik, D.K.; Monika, K.; Prabhakar, S.; Parthasarathy, R.; Satyavathi, B. Pyrolysis of sorghum bagasse biomass into bio-char and bio-oil products: A thorough physicochemical characterization. J. Therm. Anal. Calorimetrt 2017, 127, 1277–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


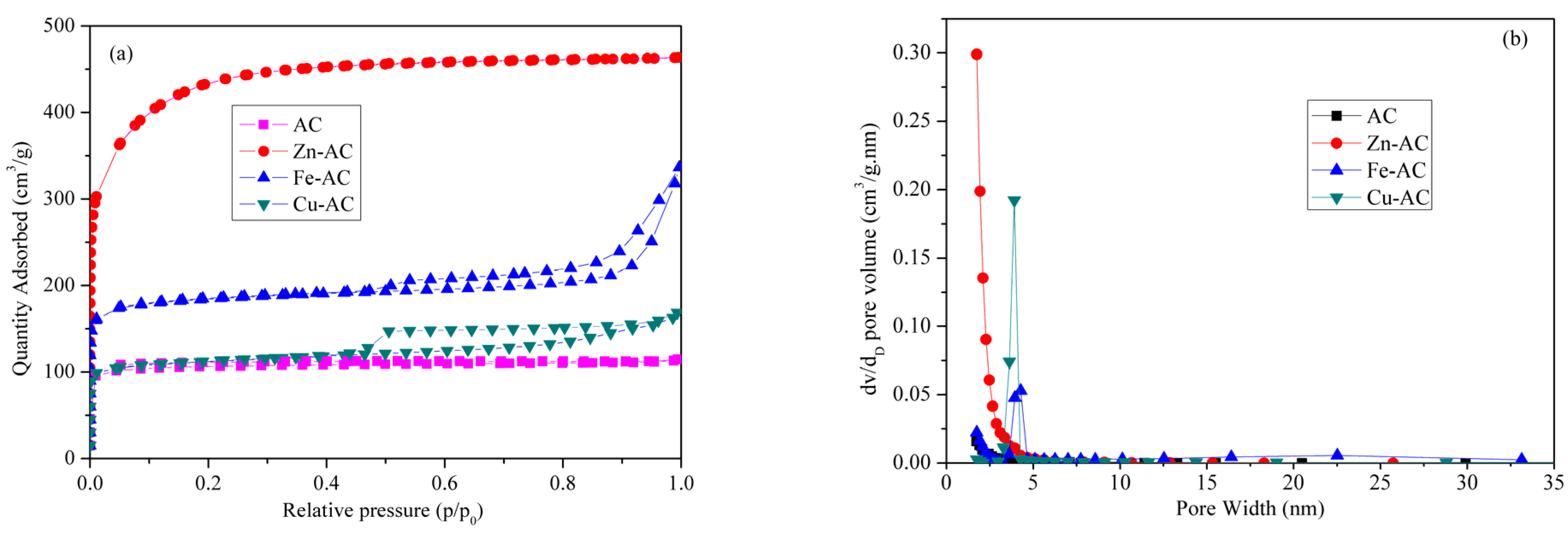

| Sample | SBET (m2/g) | Smic (m2/g) | Smic/SBET (%) | Sext (m2/g) | Sext/SBET (%) | Vt (cm3/g) | Vmic (cm3/g) | Dp (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AC | 422.95 | 382.58 | 90.46 | 40.36 | 9.54 | 0.17 | 0.15 | 1.63 |
| Zn-AC | 1621.53 | 1050.00 | 64.75 | 571.53 | 35.25 | 0.72 | 0.42 | 1.76 |
| Fe-AC | 712.05 | 603.59 | 84.77 | 108.47 | 15.23 | 0.39 | 0.23 | 2.18 |
| Cu-AC | 436.58 | 352.43 | 80.73 | 84.15 | 19.27 | 0.24 | 0.13 | 2.18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Chen, S. Catalytic Effects of Different Metal Salts on Cotton Waste Textiles by Pyrolysis: Pyrolysis Behavior and Properties of Activated Carbon. Textiles 2025, 5, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/textiles5010004
Zhang Y, Zhao X, Chen S. Catalytic Effects of Different Metal Salts on Cotton Waste Textiles by Pyrolysis: Pyrolysis Behavior and Properties of Activated Carbon. Textiles. 2025; 5(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/textiles5010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yixiao, Xingjie Zhao, and Si Chen. 2025. "Catalytic Effects of Different Metal Salts on Cotton Waste Textiles by Pyrolysis: Pyrolysis Behavior and Properties of Activated Carbon" Textiles 5, no. 1: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/textiles5010004
APA StyleZhang, Y., Zhao, X., & Chen, S. (2025). Catalytic Effects of Different Metal Salts on Cotton Waste Textiles by Pyrolysis: Pyrolysis Behavior and Properties of Activated Carbon. Textiles, 5(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/textiles5010004







