Wrinkling Controlled Shear and Draping, Based on Hierarchical Textile Models, Weaving Kind and Yarn Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
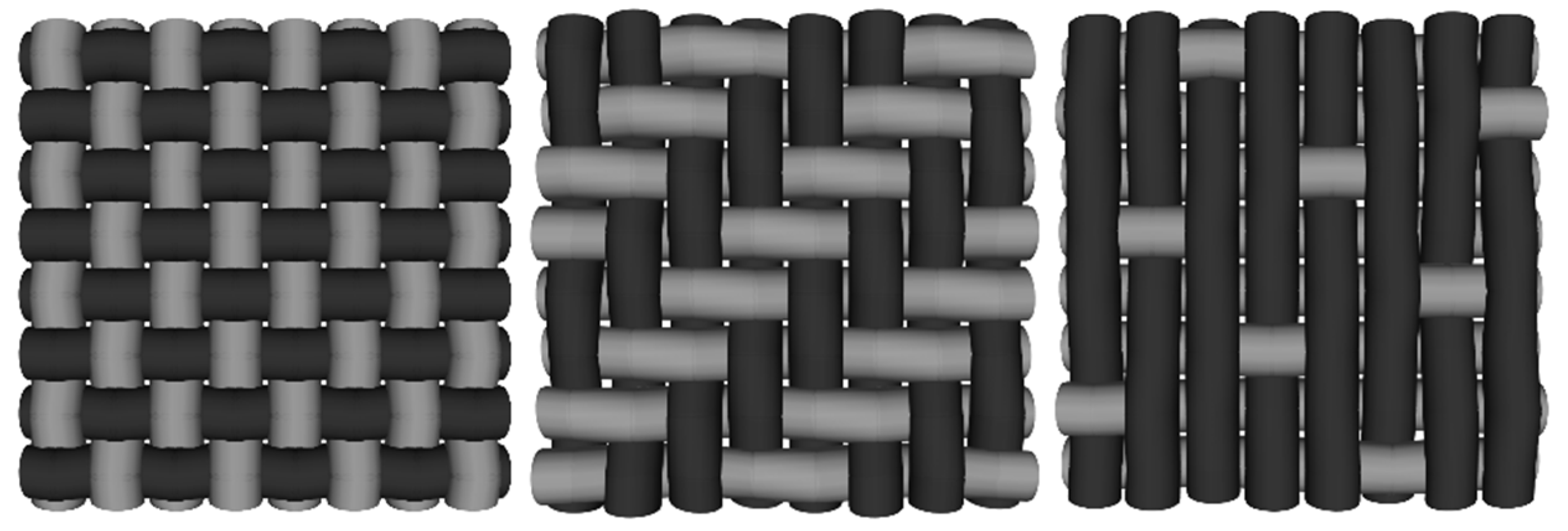
2. Main Parameters Influencing the Textile Behaviour
- The textile pattern;
- The yarn’s cross-sectional shape and size;
- The yarn’s elastic properties;
- The friction coefficient between fibres or rovings.
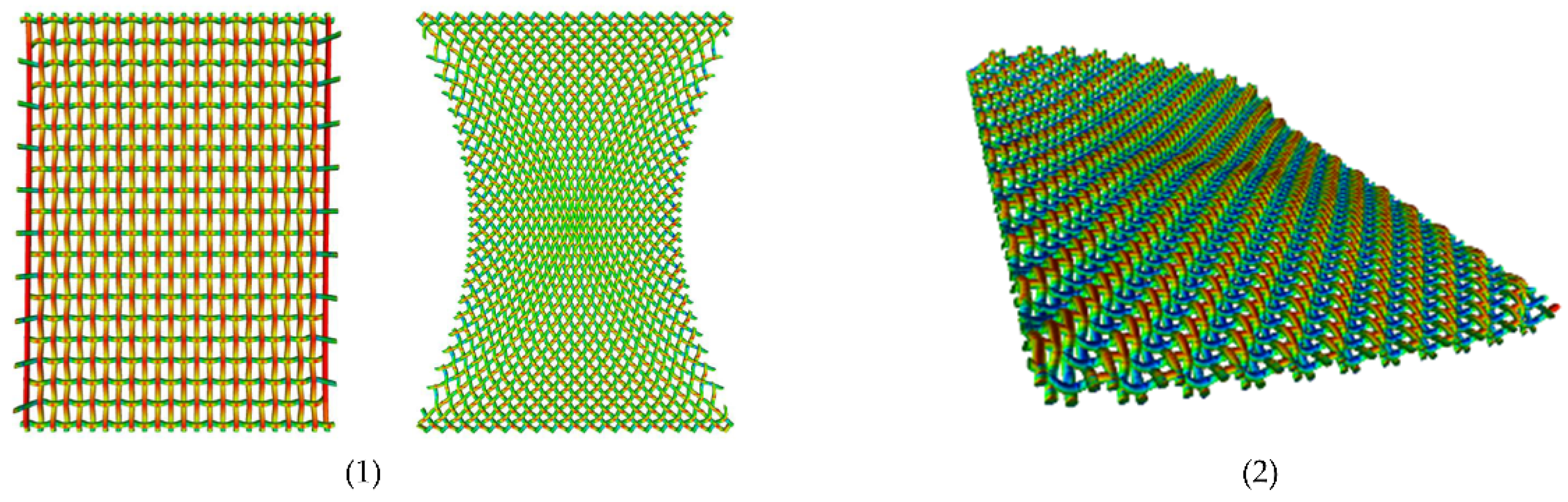
3. Shear Frame Experiment
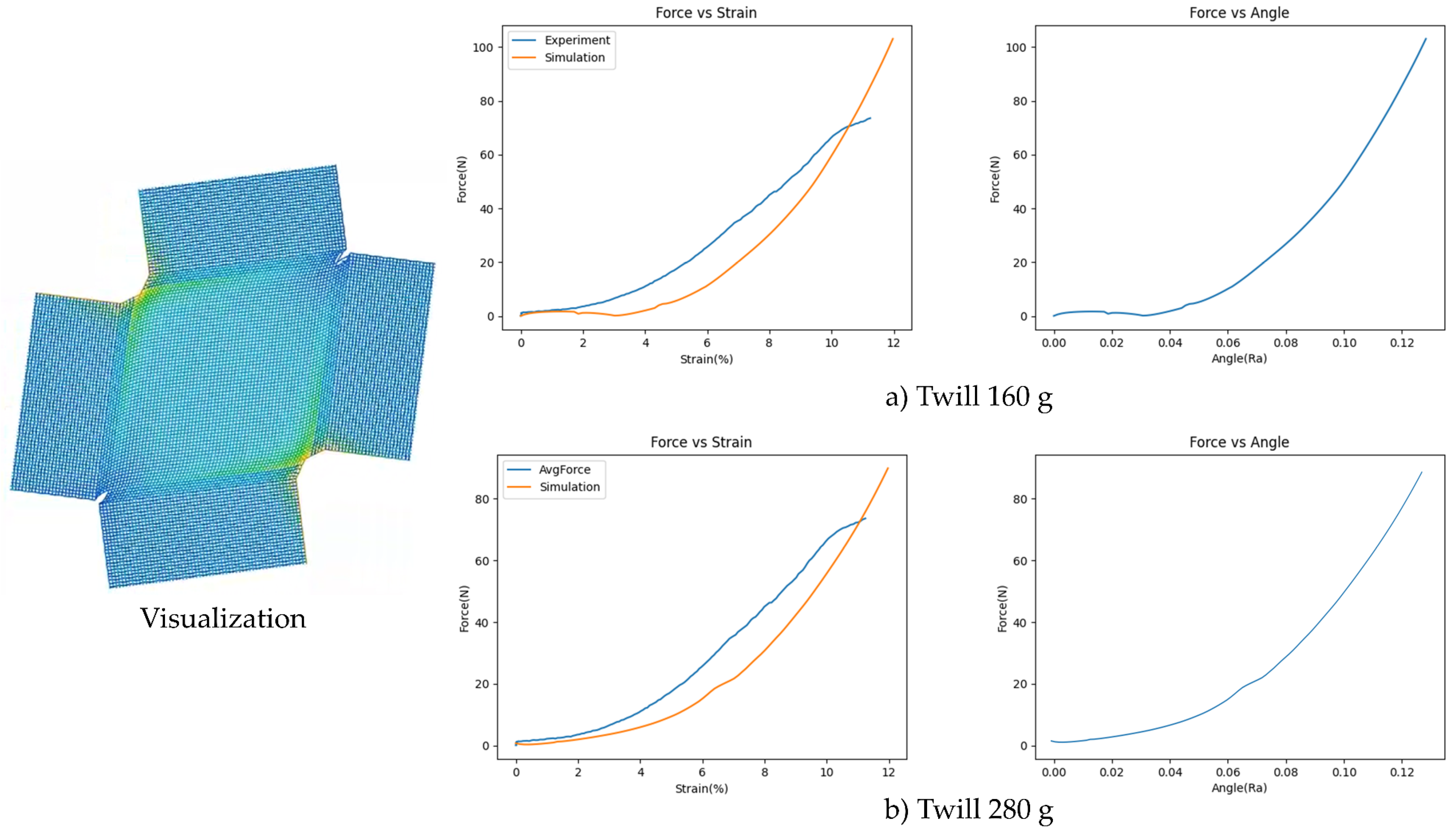
4. Shear Test Simulation and Validation
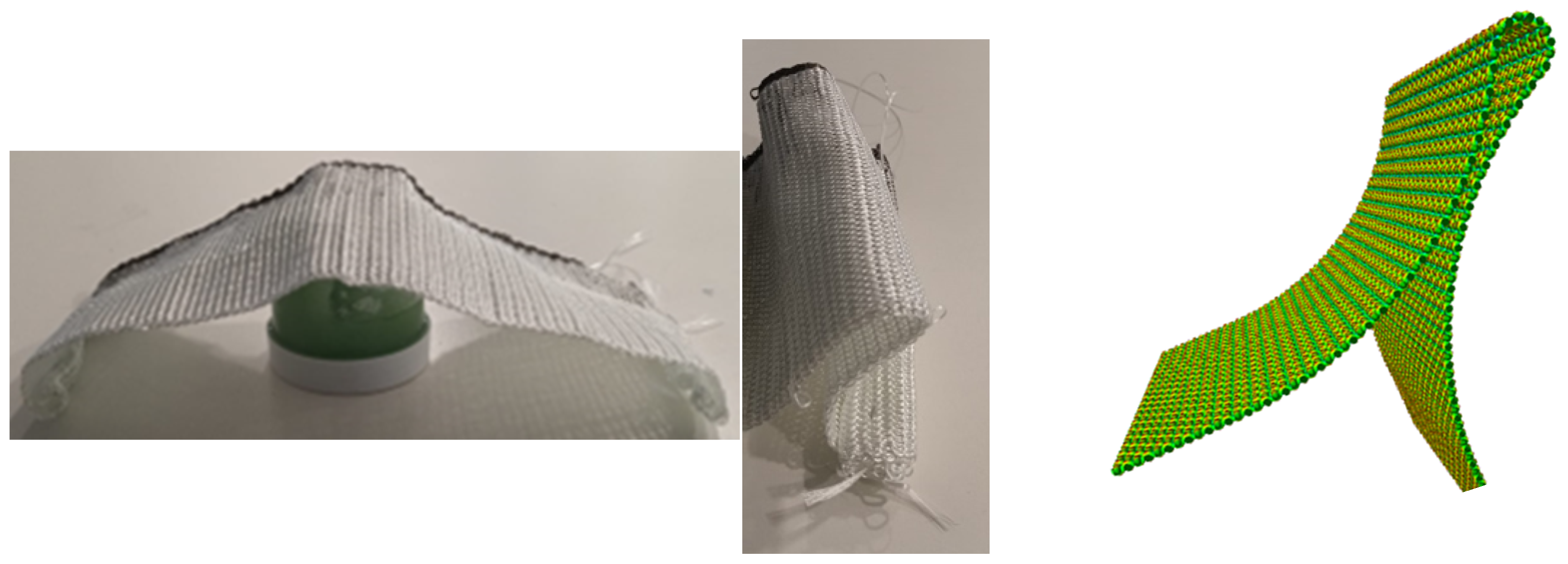
5. Draping Simulation: Relation Between Load Value and Yarn Thickness and Stiffness
5.1. Hierarchical Textile Models
5.2. Shear Compliance Due to Sliding on the Yarn Level
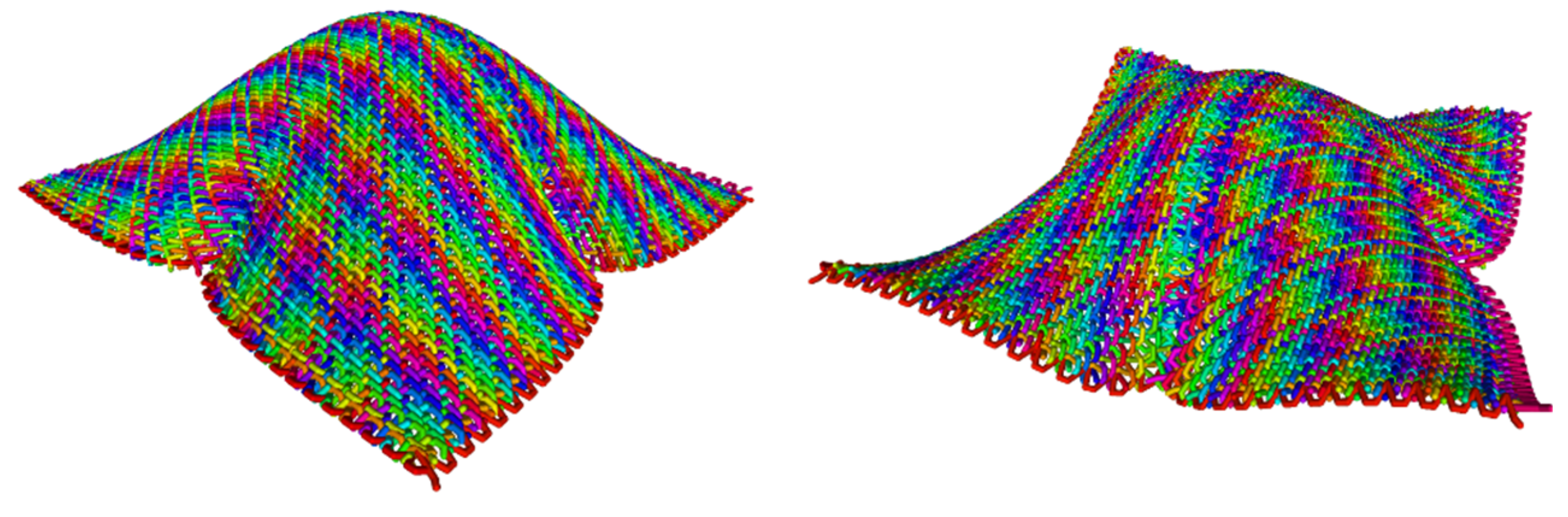
5.3. Wrinkling of the Effective 2D Plate
5.4. Dense Textiles in the Large Bending Regime
5.5. Textile in the Large Membrane Tension Regime
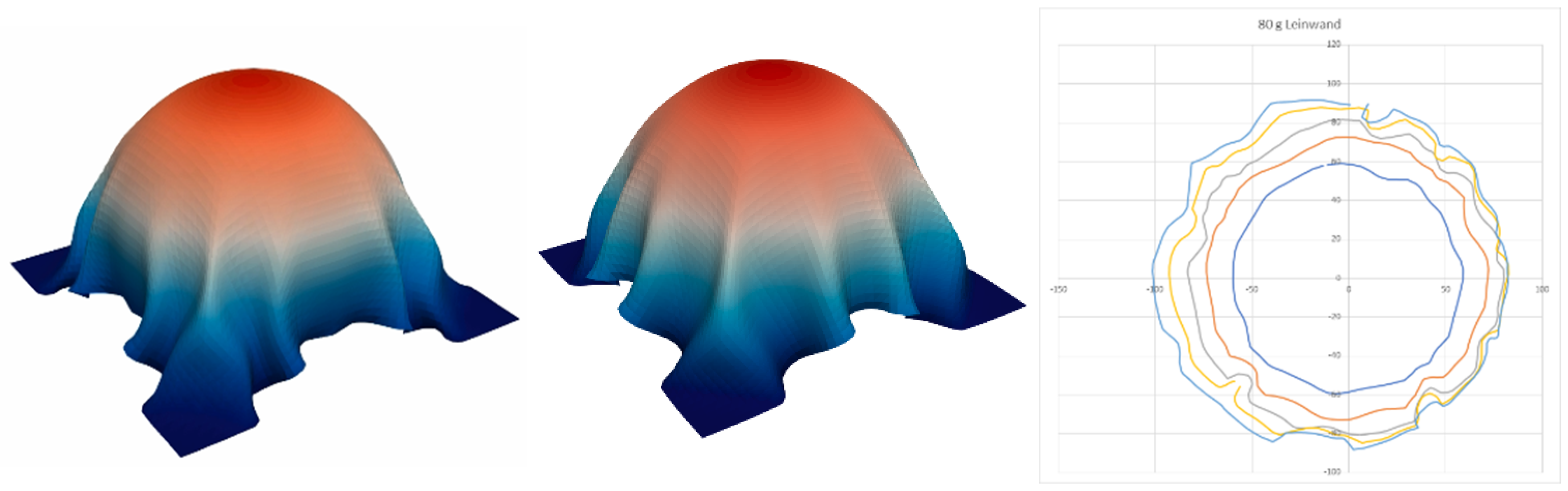
5.6. Penetration Test
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vassiliadis, S.; Kallivretaki, E.; Domvoglou, D.; Provatidis, C. Mechanical Analysis of Woven Fabrics:The State of the Art. In Advances in Modern Woven Fabrics Technology; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011; pp. 41–64. [Google Scholar]
- Takano, N.; Uetsuji, Y.; Kashiwagi, Y.; Zako, M. Hierarchical modelling of textile composite materials and structures by the homogenization method. Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1999, 7, 207–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargar, M.; Payvandy, P.; Mozafary, V. Simulation of Draping Behavior of Woven Fabrics with an Optimized Yarn-Level Numerical Model. Fibers Polym. 2023, 24, 2503–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirio, G.; Lopez-Moreno, J.; Miraut, D.; Otaduy, M.A. Yarn-level simulation of woven cloth. ACM Trans. Graph. 2014, 33, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaldor, J.; James, D.; Marschner, S. Simulating knitted cloth at the yarn level. ACM Trans. Graph. 2008, 27, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provot, X. Deformation Constraints in a Mass-Spring Model to Describe Rigid Cloth Behavior. In Proceedings of the Graphics Interface, Quebec, QC, Canada, 17–19 May 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Baraff, D.; Witkin, A. Large steps in cloth simulation. In Proceedings of the Computer Graphics Proceedings, Orlando, FL, USA, 19–24 July 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Etzmuss, O.; Gross, J.; Strasser, W. Deriving a Particle System from Continuum Mechanics for the Animation of Deformable Objects. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2003, 9, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etzmuss, O.; Keckeisen, M.; Strasser, W. A fast finite element solution for cloth modelling. In Proceedings of the 11th Pacific Conference on Computer Graphics and Applications, Canmore, AB, Canada, 8–10 October 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Boisse, P.; Borr, M.; Buet, K.; Cherouat, A. Finite element simulations of textile composite forming including the biaxial fabric behavior. Compos. Part B Eng. 1997, 28, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, H.; Zhang, H.; Gröger, B.; Hornig, A.; Gude, M. Characterization and Numerical Modelling of Through-Thickness Metal-lic-Pin-Reinforced Fibre/Thermoplastic Composites under Bending Loading. J. Compos. Sci. 2020, 4, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioranescu, D.; Damlamian, A.; Orlik, J. Two-scale analysis for homogenization of multi-scale contact problems in elasticity. Asymptot. Anal. 2013, 82, 201–232. [Google Scholar]
- Cherif, C. Drapierbarkeitssimulation von Verstärkungstextilien für den Einsatz in Faserverbundkunststoffen mit der Finite-Elemente-Methode; Shaker: Aachen, Germany, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Wriggers, P. Computational Contact Mechanics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Zavarise, G.; Wriggers, P. Contact with friction between beams in 3-d space. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2000, 49, 977–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbagallo, G.; Madeo, A.; Azehaf, I.; Giorgio, I.; Morestin, F.; Boisse, P. Bias extension test on an unbalanced woven composite reinforcement: Experiments and modeling via a second gradient continuum approach. J. Compos. Mater. 2016, 51, 153–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisse, P.; Hamila, N.; Madeo, A. The difficulties in modeling the mechanical behavior of textile composite reinforcements with standard continuum mechanics of Cauchy. Some possible remedies. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2018, 154, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durville, D. Modeling frictional contact interactions in fibre assemblies. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Computational Contact Mechanics, Lecce, Italy, 10–12 July 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bare, D.; Orlik, J.; Panasenko, G. Asymptotic dimension reduction of a Robin-type elasticity boundary value problem in thin beams. Appl. Anal. 2013, 93, 1217–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griso, G.; Orlik, J.; Wackerle, S. Asymptotic behavior for textiles. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 2020, 52, 1639–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlik, J.; Falconi, R.; Griso, G.; Wackerle, S. Asymptotic behavior for textiles with loose contact. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 2023, 46, 17082–17127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlik, J.; Andrä, H.; Argatov, I.; Staub, S. Does the weaving and knitting pattern of a fabric determine its relaxation time? Q. J. Mech. Appl. Math. 2017, 70, 337–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlik, J.; Krier, M.; Neusius, D.; Pietsch, K.; Sivak, O.; Steiner, K. Recent efforts in modeling and simulation of textiles. Textiles 2021, 1, 322–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wackerle, S.; Orlik, J.; Hauck, M.; Lykhachova, O.; Steiner, K. The Way to Design a Textile with Required Critical Folding Deformation. Procedia Manuf. 2020, 47, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiryaev, V.; Orlik, J. A one-dimensional computational model for hyperelastic string structures with Coulomb friction. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 2017, 40, 741–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falconi, R.; Griso, G.; Orlik, J. Asymptotic behavior for nonlinear textiles with glued yarns. Anal. Appl. 2024. accepted for publication. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlik, J.; Neusius, D.; Steiner, K. Modelling and Simulation of Technical Textiles by TexMath. Fraunhofer Institute for Industrial Mathematics. 2023. [Online]. Available online: https://www.itwm.fraunhofer.de/de/abteilungen/sms/produkte-und-leistungen/texmath.html (accessed on 3 December 2024).
- Griso, G.; Orlik, J.; Wackerle, S. Asymptotic behavior for textiles in von-Kármán regime. J. Math. Pures Appl. 2020, 144, 164–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griso, G.; Khilkova, L.; Orlik, J.; Sivak, O. Homogenization of perforated elastic structures. J. Elast. 2020, 141, 181–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlik, J.; Panasenko, G.; Shiryaev, V. Optimization of textile-like materials via homogenization and beam approximations. Multiscale Model. Simul. 2016, 14, 637–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wackerle, S.; Pinnau, R.; Orlik, J. Optimization of buckling for textiles. In Progress in Industrial Mathematics at ECMI; Springer: Budapest, Hungary, 2018. [Google Scholar]


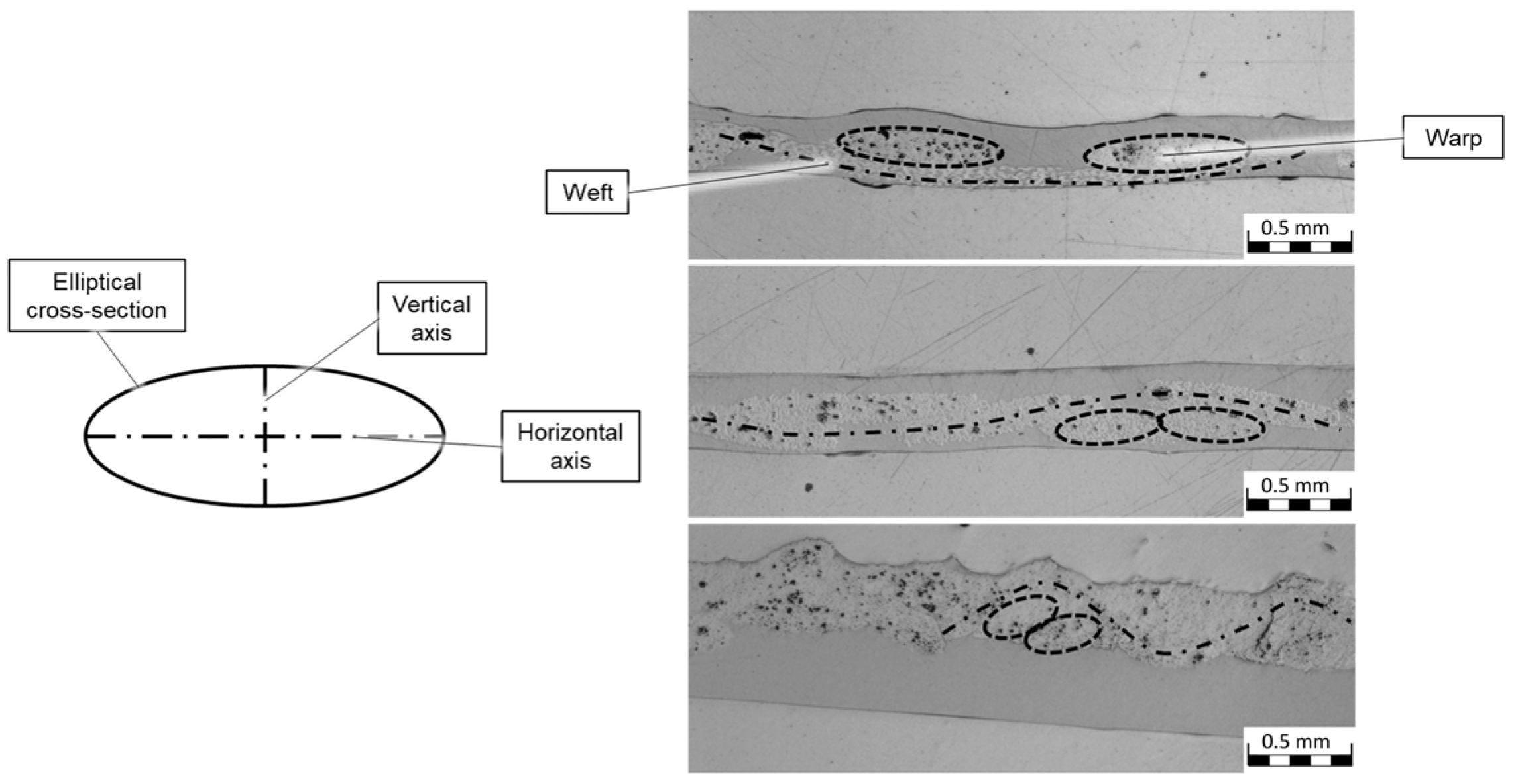
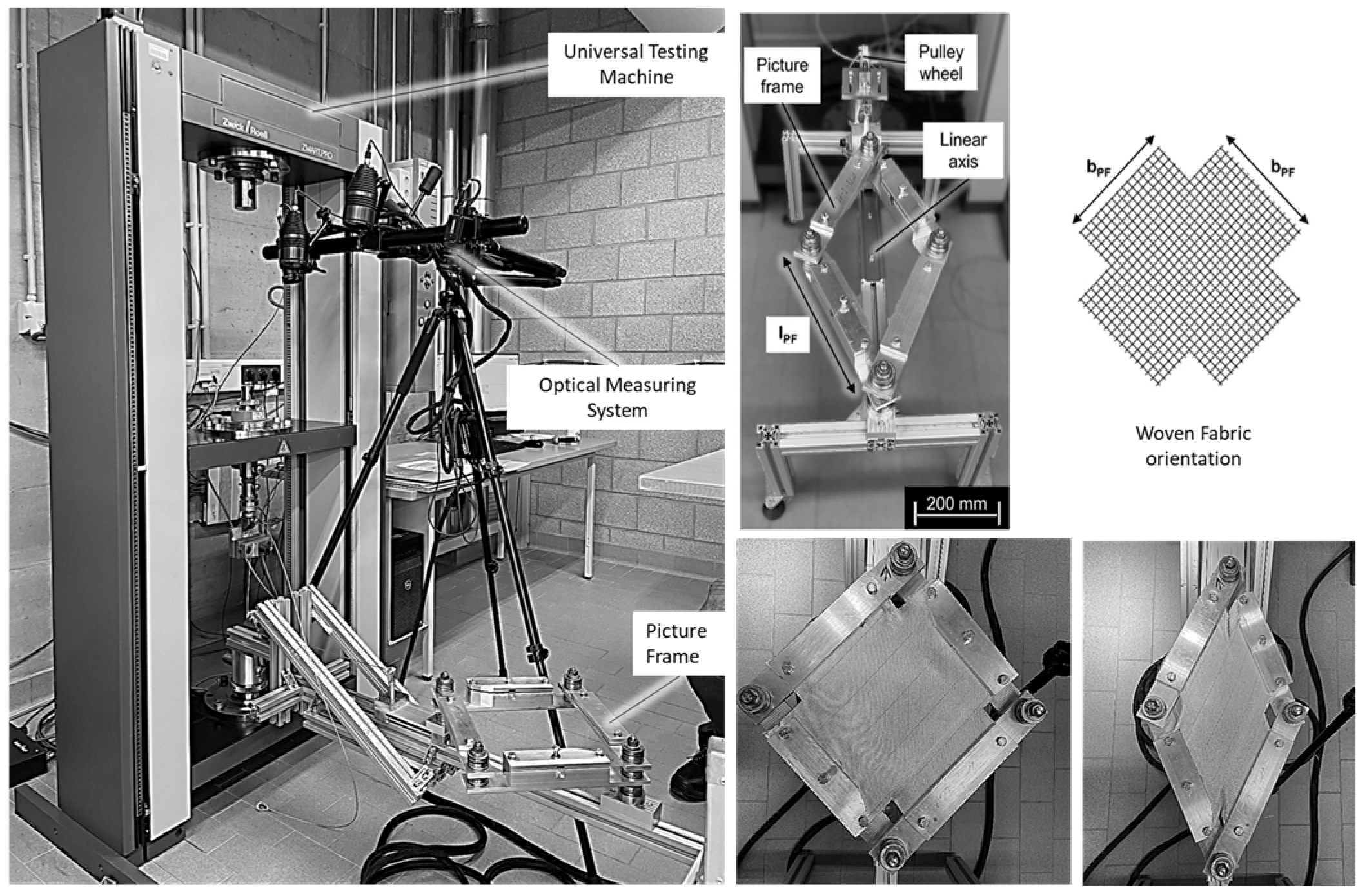
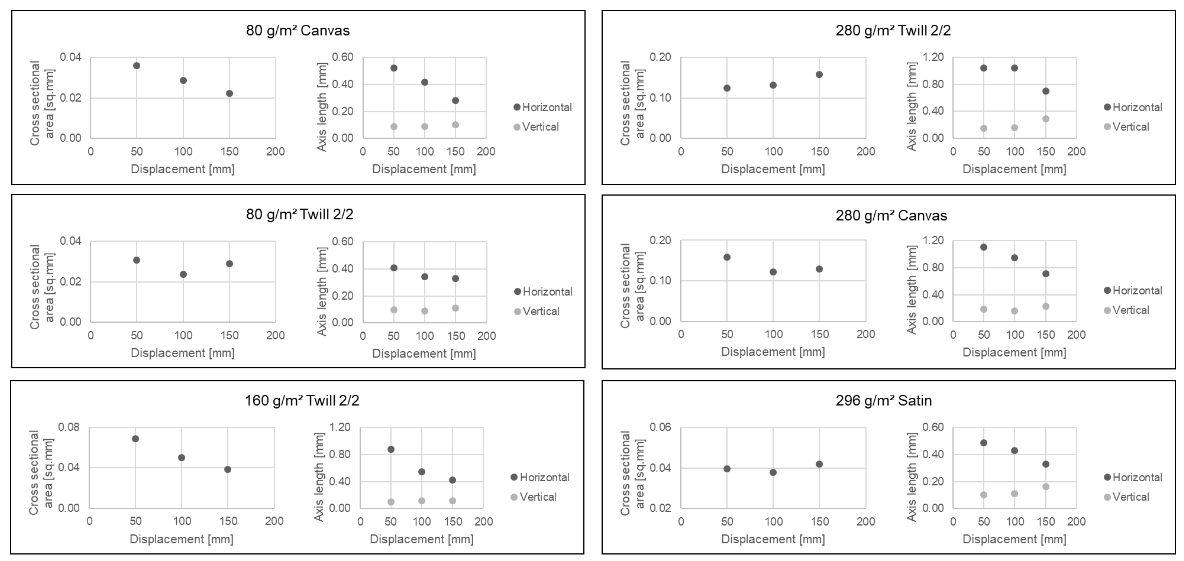
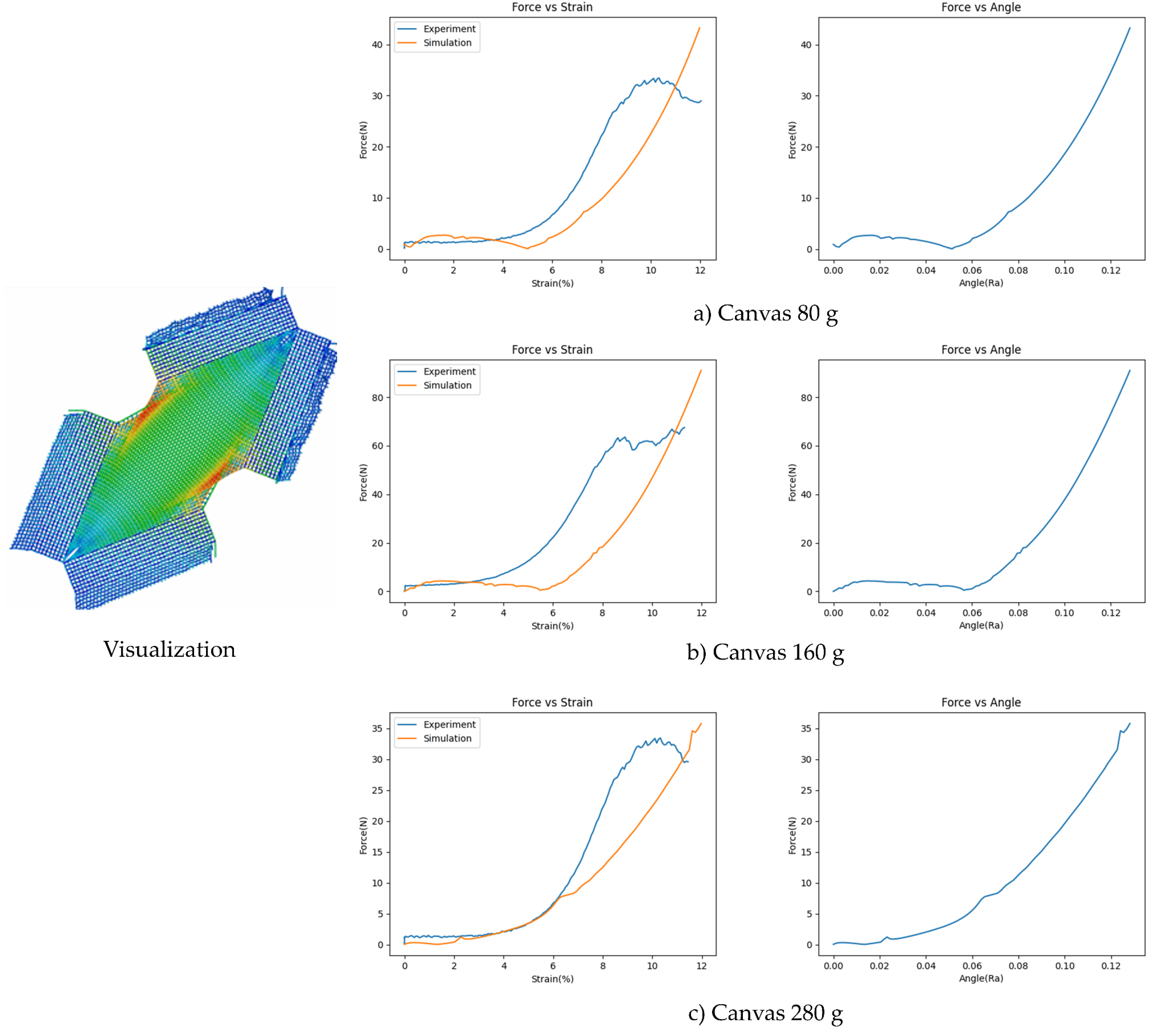






| Type of Woven | Yarn’s Cross-Sectional Area [mm²] | Yarn’s E-Modulus [GPa] | Yarn Diameter [mm] | Weaving Distance [mm] | Friction Coefficient [1] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Canvas 80 g | 0.03 | 31.333 | 0.2 | 0.58 | 0.3 |
| Twill 80 g | 0.03 | 33.283 | 0.2 | 0.55 | 0.31 |
| Canvas 160 g | 0.05 | 32.887 | 0.24 | 0.41 | 0.26 |
| Twill 160 g | 0.06 | 27.222 | 0.29 | 0.47 | 0.3 |
| Canvas 280 g | 0.12 | 36.709 | 0.39 | 0.61 | 0.4 |
| Twill 280 g | 0.13 | 32.804 | 0.41 | 0.72 | 0.28 |
| Satin 296 g | 0.05 | 32.667 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.34 |
| Strain | 2D-Plate Model | |
|---|---|---|
| Kirchhoff plate | ||
| Karman plate | ||
| Large bending deformation | ||
| Large membrane deformation |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Orlik, J.; Neusius, D.; Krier, M.; Steiner, K.; Backes, S.; Bhat, S.; Gries, T. Wrinkling Controlled Shear and Draping, Based on Hierarchical Textile Models, Weaving Kind and Yarn Properties. Textiles 2024, 4, 582-595. https://doi.org/10.3390/textiles4040034
Orlik J, Neusius D, Krier M, Steiner K, Backes S, Bhat S, Gries T. Wrinkling Controlled Shear and Draping, Based on Hierarchical Textile Models, Weaving Kind and Yarn Properties. Textiles. 2024; 4(4):582-595. https://doi.org/10.3390/textiles4040034
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrlik, Julia, David Neusius, Maxime Krier, Konrad Steiner, Sebastian Backes, Shantanu Bhat, and Thomas Gries. 2024. "Wrinkling Controlled Shear and Draping, Based on Hierarchical Textile Models, Weaving Kind and Yarn Properties" Textiles 4, no. 4: 582-595. https://doi.org/10.3390/textiles4040034
APA StyleOrlik, J., Neusius, D., Krier, M., Steiner, K., Backes, S., Bhat, S., & Gries, T. (2024). Wrinkling Controlled Shear and Draping, Based on Hierarchical Textile Models, Weaving Kind and Yarn Properties. Textiles, 4(4), 582-595. https://doi.org/10.3390/textiles4040034







