Abstract
Conductive tracks are key constituents of wearable electronics and e-textiles, as they form the interconnective links between wearable electrical devices/systems. They are made by coating or printing conductive patterns or tracks on textiles or by weaving, knitting, or embroidering conductive yarns into textiles. Screen printing is a mature and cost-effective fabrication method that is used in the textile industry. It allows a high degree of geometric freedom for the design of conductive patterns or tracks. Current screen-printed conductive textiles have the limitations of low durability when washed or when placed under bending, and they typically require encapsulation layers to protect the printed conductor. This paper presents a printable paste formulation and fabrication process based on screen printing for achieving a flexible and durable conductive polyester-cotton textile using an inexpensive carbon as the conductor. The process does not require an interface, the smoothing of the textile, or an encapsulation layer to protect the conductor on the textile. A resistivity of 4 × 10−2 Ω·m was achieved. The textile remains conductive after 20 standard washes, resulting in the conductor’s resistance increasing by 140%. The conductive textile demonstrated less than ±10% resistance variation after bending for 2000 cycles.
1. Introduction
Smart textiles, which are also known as intelligent or electronic textiles (e-textiles), combine electronic functionality with textiles [1] and are important in the area of flexible electronics. Textiles with integrated conductors are essential for many e-textile devices, such as printed circuits [2], sensors (e.g., gas [3], pressure [4]), thin-film transistors [5], wireless power transfer [6], energy harvesters [7], and electrical storage devices [8,9]. Conductive textiles should ideally be flexible, washable, and chemically and mechanically stable in order to meet the requirements of most textile-related applications, such as in sports/fitness training and for workwear.
Conductivity is implemented in a nonconductive textile by adding electrically conductive materials. It can be achieved by weaving, knitting, or embroidering conductive yarns into textiles [10] or by printing. Potential yarn materials include metal wires and fibers with coatings of conductive materials, which are achieved through casting or spinning. For printing, typical conductive materials are conductive polymers [11] or metal-polymer composites [12].
In the case of weaving, since the yarn forms the structure of the textile, conductive yarns can only be added orthogonally following the warp and weft within the textile. This significantly limits the options for the placement of interconnections. Similarly, for knitting, the structure of the textile/garment defines the route that the yarn must follow. Embroidery overcomes this limitation, since an embroidered conductor can have any orientation within the textile. However, embroidery—like weaving/knitting—adds each conductor in turn in a serial process. This significantly slows the manufacturing process, particularly as the number of conductors increases, and this results in complex circuits with many interconnections, making it impractical. Further, if a conductor pattern is repeated, each pattern is formed one after the other, potentially reducing the repeatability. Screen printing overcomes these limitations—the conductors can have any orientation with respect to the underlying textile; further, all conductors are printed simultaneously in a single print pass, which speeds up the printing process, makes complex circuits feasible, and increases the repeatability.
The screen printing of conductive materials on textiles to achieve a conductor therefore offers a flexible and scalable solution. Hong et al. [13] presented a screen-printed conductive circuit on a textile that was achieved by printing a UV-curable silver material that was formulated into a screen-printable paste. The paste contained silver nanoflakes, an ultraviolet (UV)-curing binder system consisting of polyurethane acrylate, trimethylolpropane triacrylate and tripropylene glycol diacrylate as diluents, 1-(2-hydroxy-5-methylphenyl)-1-propanone as a photoinitiator, and other functional additives for improving the print quality. The conductive textile achieved a resistivity of 16.6 μΩ·cm. However, as silver reacts with oxygen, its electrical and mechanical performance changes over time. Further, the read distance of a textile RFID antenna that was made using this paste was reduced to ~40% after five washes, which was attributed to mechanical deformation during washing. Lakshitha et al. [14] implemented a stretchable conductive textile by screen printing a carbon black dispersion and a stretchable polyurethane coating, achieving a liner resistance of less than 71 Ω·cm−1, which was stable up to 25% strain. However, washing the carbon-black-based conductive textile twice with detergent at 40 °C for 30 min at a spin speed of 645 rpm caused a 16% resistance increase due to the poor adhesion of the carbon black to the textile. Ali et al. [15] demonstrated a conductive textile using screen-printed carbon black paste printed with different thicknesses on a textile. The conductive textiles all demonstrated a sheet resistivity of less than 100 Ω/sq.
The key limitations of a screen-printed conductor on a textile are its mechanical durability under bending and its ability to withstand washing, both of which are particularly important for wearable e-textiles. Previously, these limitations were addressed by implementing a screen-printed three-layer design. The three layers were a polymer interface layer, which was first printed on the textile to overcome the textile’s surface roughness, the conductive layer, and then an encapsulation layer for mechanical protection and electrical insulation. The encapsulated silver tracks remained undamaged after eight washes in a washing machine with liquid detergent, and they demonstrated good flexibility [16]. Therefore, to avoid a multiple-layer design and improve the conductive textile’s mechanical durability under bending and washing, a single conductive layer printed on a textile must be mechanically flexible, overcome the surface roughness of the textile, achieve an acceptable electrical conductivity, demonstrate good adhesion to the textile, and have excellent resistance to chemical detergents. These factors are important for achieving a flexible, washable, and conductive textile consisting of a single layer, thus avoiding the need for additional interface and encapsulation layers.
This work demonstrates a textile with a single screen-printed conductive carbon black layer that is washable and bendable. The carbon black paste used ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) as the binder and was printed directly on the textile, without the need for pre-coating or a printed interface layer, which is often used to smooth the textile, or an encapsulation or protection layer. The developed paste can be used in many e-textile applications where conductive tracks are required to connect electronic components or as an active component on its own.
In this paper, the justifications of the conductor and binder materials are presented in Section 2 on the materials and methods. The paste formulation and the textile that were selected are detailed, and the methods that were used are also presented. In Section 3, the printed conductive textile samples are examined with a scanning electron microscope (SEM), and six different conductive material paste formulations that were printed on textiles with four curing methods are investigated. The influence of the conductive textile track’s resistivity as a function of the carbon concentration is also investigated. These samples were bent for 2000 cycles and washed 20 times in a washing machine using everyday washing liquid. The application of the screen-printed conductive textile is demonstrated via an LED-based light-emitting textile. The conclusions are presented in Section 4.
2. Materials and Methods
The conductive paste in this work was formulated from carbon, the EVA polymer, and a low-flammability solvent, 1,2,4-Trichlorobenzene, with a flash point at 110 °C.
2.1. Justification of the Conductive Material
Examples of conductive materials include gold [17], silver [18], nickel [19], conductive polymers, such as poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene): poly (styrene sulfonate) [20], and carbonized materials, such as carbon nanotubes [21], graphene [22], graphite [23], and carbon black [24]. Among these materials, conductive textiles made with coated micro- or nano-scaled metal particles achieve an extremely low resistivity (less than 1 × 10−7 Ω·m [25]) when compared with carbonized materials and conductive polymers, but they require complex processes, such as metal particle synthesis and/or purification. Conductive polymer approaches have poor processability, so they are not suitable for large-scale application [26]. Carbon black is inexpensive and has a high thermal stability, is non-toxic, and offers UV degradation resistance. Carbon black offers an alternative to carbon nanotubes, graphene, and graphene oxide, which are of a significantly higher cost and have a lower electrochemical stability [27]. Rashedul et al. [28] reported a simple, low-cost, and scalable way of implementing a conductive cotton textile through dip coating with a carbon-black-based ink/paste. The conductive textile achieved a sheet resistivity of between 25 and 28 kΩ/sq, and its resistance did not increase after bending for 1000 cycles; after 12 washes, its resistance increased to 5 times.
The conductive carbon black powder with a medium particle diameter of 35 nm used in this work was supplied by Smart Fabric Inks, UK [29].
2.2. Justification of the Binder Material Selection
Various carbon black pastes using polymer binder formulations have been developed to fabricate conductive textiles. Examples of polymer binders include polyaniline [21], polyamide [30], polypyrrole [19], and polyurethane [15]. Examples of additive agents are sodium/cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide [20] and the anionic wetting and dispersing agent DELTA- DC 4242 [31]. The binder and agent are used to formulate a uniform and stable carbon black paste by using an appropriate solvent. EVA is a copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate. It has good adhesion to textiles, demonstrates good mechanical properties and chemical stability, and is non-toxic and hydrophobic.
Previously, EVA has been applied in flexible electrical devices, such as spray-coated conductive films for solar cell electrodes [32], spin-coated transparent electrodes [33], screen-printed conductors for paper-based electronics [34], and a dip-coated conductive membrane for energy storage [35]. This environmentally friendly copolymer is also widely used in food packaging, as an encapsulation material for flexible photovoltaic devices [36], as a hot-melt adhesive [37], and as a flexible adhesive layer between textile insole pads [38]. EVA is soluble in organic solvents, including xylene [33], butyl acetate [32], toluene [39], and chlorobenzene [29]. However, these solvents are flammable with flash points below 40 °C, which limits the paste’s curing temperature.
EVA beads (vinyl acetate 25 wt%) and the solvents, 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene and isopropyl alcohol, were supplied by Sigma-Aldrich. All chemicals used in this study were of analytic grade without any further purification or treatment.
2.3. Textile Material
The textile used in this research was selected as typical of that used for the realization of clothing. It was obtained from Klopman, Italy [40], and was woven from cotton and polyester with fiber diameters of 12 and 15 µm, respectively. The textile was plain weave with 16.5 ends per inch or 9.05 picks per inch without further treatment. The thickness of the textile selected was 150 µm.
2.4. Formulation of the Carbon Black Paste
The screen-printable carbon paste was prepared by adding 0.66 g of EVA polymer beads and 1 g of carbon black into 6 mL of the solvent 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene. In this combination, there was 60% of carbon black by weight in the mixed carbon paste after solvent evaporation. Six different carbon pastes were prepared, resulting in a range of 30% to 80% of carbon black in the dried paste. The carbon black/EVA paste was mixed using a magnetic stirring bar at 80 °C on a hotplate for 6 h. The paste formulation process was performed in a fume cabinet with an air ventilation system.
2.5. Printing of the Carbon Black Paste
The fabrication process of the conductive textile is shown in Figure 1. The carbon black paste was printed onto the textile using a standard DEK248 semi-automatic screen printer. The textile was mounted on an alumina tile to provide a flat and rigid support for screen printing. A stainless-steel screen with a mesh size of 250 μm was used. The printing gap was 1 mm and the printing pressure was equivalent to 5.5 kg weight over the squeegee area. Each carbon composite film consisted of 4 depositions. The printing process was undertaken with an air ventilation system.
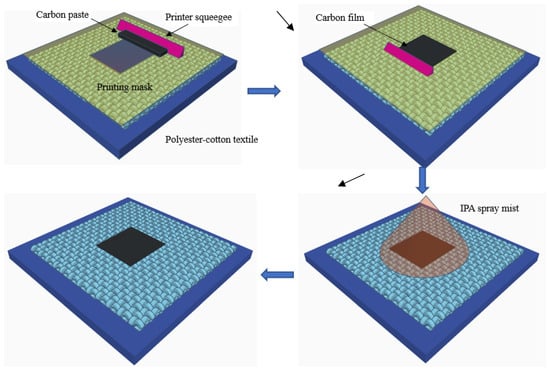
Figure 1.
Fabrication process of the carbon black conductive textile.
After printing, the printed carbon composite film was sprayed with isopropyl alcohol (IPA) solution for 30 s. IPA solution is one of the anti-solvents used in the phase inversion process for polymer membrane preparation [41,42], and the same anti-solvent was used because the EVA polymer is not soluble in IPA and because the 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene solvent is sparingly soluble in IPA. The IPA spray helps the carbon black/EVA to solidify before subsequent heating evaporates the solvent. It also prevents the carbon black/EVA composite conductive film from penetrating deeper into the textile, effectively stopping the conductive pattern from spreading during curing. After the evaporation of IPA at room temperature (23 °C) for 10 min, the textile samples were cured in a fan oven at 130 °C for 5 min. A carbon composite film with a thickness of ~50 μm was achieved on the surface of the polyester-cotton textile. In addition, to evaluate the electrical performance of only the conductive paste, it was also printed in 1, 2, 3, and 4 layers on a polyurethane-coated polyester-cotton textile. The polyurethane film was used to smooth the surface of the textile before subsequent printing while maintaining good flexibility [43]. This allowed the evaluation of the intrinsic electrical performance of the carbon film. It should be noted that the interface was not required for the carbon film that was printed directly on the textile for all of the results, except for those presented in the last paragraph in Section 3.2.
Three alternative curing methods were evaluated: room temperature (23 °C) drying in air for 6 h, fan oven curing at 130 °C for 5 or 15 min, and vacuum oven curing at 50 mbar pressure at 100 °C for 2 h.
2.6. Electrical Conductivity and Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Testing
The electrical resistivity (Ω·m) of the carbon composite conductive film on the textile was measured in 5 samples that were 50 mm in length, , and 40 mm in width, , both on the textile and on the polyurethane-film-coated polyester-cotton textile. The sample thickness, , varied with the curing conditions, the number of layers, and the carbon paste formulation. SEM views of the polyester-cotton textile were obtained using a Zeiss EVO LS25 scanning electron microscope. The conductor’s thickness was measured by using the cross-sectional SEM views for the textile samples or by using a micrometer for the carbon composite film on the polyurethane-film-coated textile. The resistance of the conductor was measured using a digital multimeter model Keithley 2100 6 1/2. The electrical resistivity was calculated using Equation (1)
where R is the average resistance, which was measured 5 times along the length of the conductive carbon composite film. Twenty samples were tested to obtain an average result.
2.7. Wash Testing
The washing of the conductive textiles was undertaken in a washing machine (WME 7247 Model from Beko.plc) using a standard everyday wash setting (39 min, 1400 rpm, 30 °C) with an everyday washing liquid (brand name: FAIRY non-bio). Ten samples were washed simultaneously. These samples were then dried in a fan oven at room temperature for 1 h under air ventilation before the resistance measurement. Ten samples were tested to obtain an average result.
2.8. Bend Testing
As shown in Figure 2, the mechanical durability of the carbon composite conductive films on the textile was investigated under bending. The textile samples, which were tensioned with a weight of 100 g, were repetitively bent around a 3-mm-diameter mandrel. The samples were bent 2000 times with a rotational motor speed of 60 rpm. Twenty samples were tested to obtain an average result.
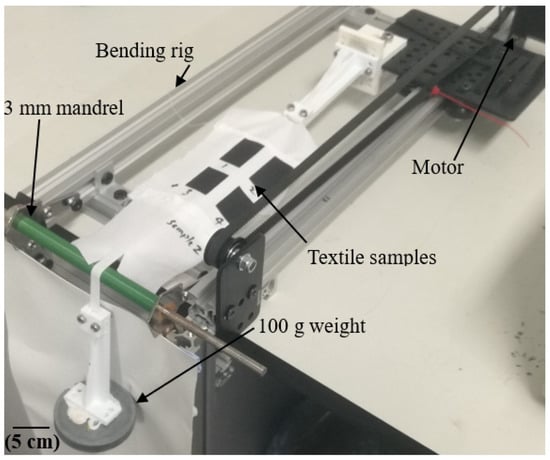
Figure 2.
Bending test setup.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. SEM Analysis
Figure 3a shows an SEM image of the textile before screen printing; the cotton and polyester fibers, when woven together, formed a textile with a rough and uneven surface. Figure 3b is an SEM image of the textile with one printed carbon black conductive layer. The printed material formed a continuous layer on the polyester-cotton textile, creating a smoother and flatter conductive surface. Figure 3c,d show the cross-sectional SEM images of the textile and the textile with one conductive coated layer, indicating that the carbon black film had a maximum thickness of ~50 μm. The carbon black/EVA composite adhered to the textile, but did not penetrate deeply into the textile. The printed textile surface was therefore conductive, but the opposite side of the textile was insulating. Further layers could be printed on top of the initial carbon black film to increase its conductivity.
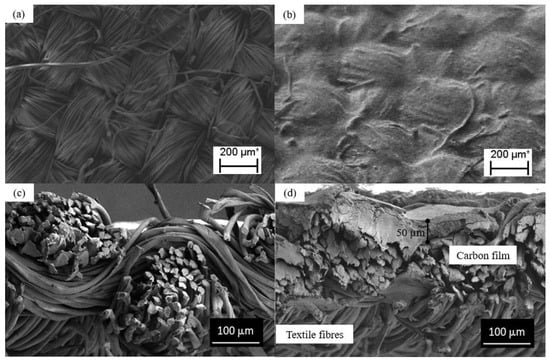
Figure 3.
SEM images of the textile. (a) Plan view of textile before screen printing, (b) plan view of the conductive textile, (c) cross-sectional view of the textile before screen printing, and (d) cross-sectional view of the conductive textile.
3.2. Electrical Conductivity and Mechanical Properties of the Conductive Textile
The relationship of the resistivity of carbon black/EVA composite that was printed directly on the polyester-cotton textile with the percentage weight of carbon black powder loading is shown in Figure 4. The resistivity of the conductor decreased with an increasing percentage of carbon black in the printed composite; at 60 wt%, the carbon black composite printed on the textile demonstrated the lowest resistivity of 0.04 Ω·m. As the percentage was further increased to 70 and 80 wt%, the resistivity increased slightly, since there was less binder holding the carbon particles together. Further, with less binder and more carbon, achieving a uniform mixing of the paste became challenging. In addition, the carbon black/EVA composite became less flexible.
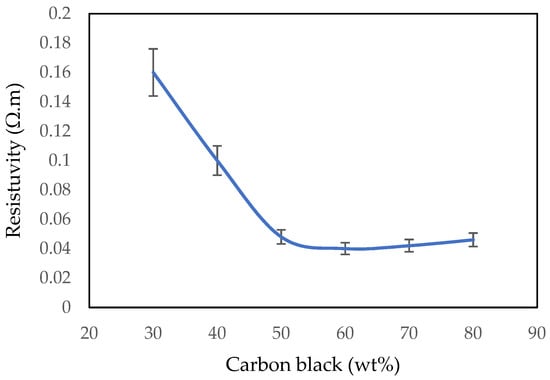
Figure 4.
Resistivity as a function of carbon black wt% in the printed conductive textile.
According to Table 1, the conductive textile samples cured in the fan and vacuum ovens and without the IPA rinse demonstrated higher resistance than the samples cured at room temperature with the same carbon wt%. This is because EVA is a thermoplastic material, so it will liquefy, melt, or soften at temperatures >80 °C; thus, part of the film will melt into the textile and the conductive track will spread. The part of the film that melts into the textile reduces the thickness of the pure carbon film left on the textile surface and provides a lower conductivity, since it is now mixed with the textile substrate, which is not conductive. The spreading of the conductive carbon black composite on the textile also reduced the film thickness of the pure carbon/EVA layer. Therefore, the fan and vacuum oven curing methods without an IPA rinse resulted in significantly increased resistance compared with the room-temperature curing.

Table 1.
Conductive textile (50 mm × 40 mm × 0.05 mm × × ) resistance variation (Ω) for different curing methods and carbon black weight %.
As shown in Figure 5a, there was no noticeable spreading in the sample that was sprayed with IPA and cured in the fan oven for a shorter time (5 min compared with 15 min). Without the IPA rinse, the sample was not cured after 5 min at 130 °C; visual and touch examination indicated that the carbon layer on top of the textile was still sticky. The purpose of the IPA rinse was to reduce the curing time so that the sample was fully cured before the EVA melted and spread. Figure 5b shows the sample cured in the fan oven at 130 °C for 15 min, illustrating the spreading of the conductor that occurred without the IPA rinse. Figure 5a, when compared with Figure 5b–d, shows that the IPA spray reduced the spreading of the conductor as a result of the phase inversion of the paste, causing the carbon black/EVA to demix from the solvent, therefore reducing the mobility; it also reduced the curing time. The material formulation and process therefore allowed the fabrication of narrow and long conductive tracks on the textile, as shown at the bottom right in Figure 5a, with a width of 4 mm and a length of 40 mm, as well as a resistivity of 0.04 Ω·m.
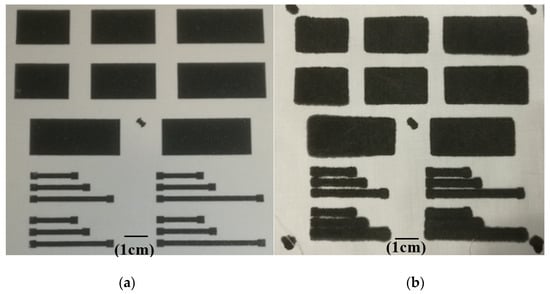
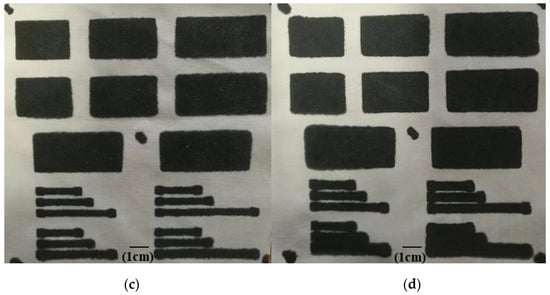
Figure 5.
(a) Screen-printed carbon conductive film patterns without any spreading. The carbon conductive film spreading patterns achieved (b) with the fan oven at 130 °C for 15 min, (c) at room temperature for 6 h, and (d) with the vacuum oven at 100 °C for 2 h.
The electrical resistivity of the printed composite conductive films is shown in Table 2. These were printed using the 60 wt% carbon black paste on the polyurethane-film-coated textile. After four depositions, the initial layer thickness of the carbon black/EVA composite was ~44 μm. The resistivity was reduced as the number of layers increased, as each new layer compressed the previous layers and filled in any gaps or voids in the previously deposited and cured layers.

Table 2.
Resistivity variation of the printed conductive layers on the polyurethane film.
3.3. Bending and Washing Results
The resistivity variation over 2000 bending cycles for the optimally coated sample is shown in Figure 6 (60% carbon black printed directly on the textile, IPA rinsed, and cured at 130 °C for 5 min). The carbon composite conductive films on the textiles exhibited less than ±10% resistivity variation, demonstrating the flexibility and durability of the carbon films on the textiles.
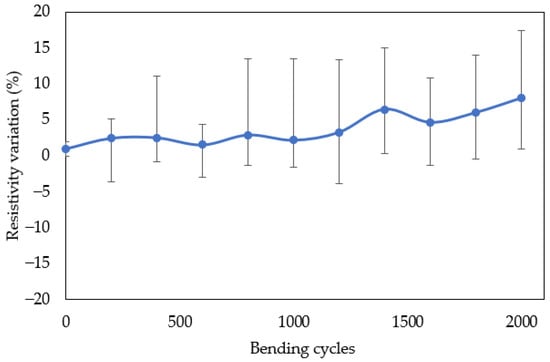
Figure 6.
Resistivity variation of the carbon black layer on the polyester-cotton textile during the bending test.
Figure 7 shows the resistivity variation over 20 washes. The carbon composite conductive films on the textiles (60% carbon black printed directly on the textile, IPA rinsed, and cured at 130 °C for 5 min) showed no visual damage, indicating that the majority of the carbon composite remained on the textile. After 20 washes, the composite film remained conductive, and the overall resistivity of the carbon composite conductive films increased by 140%. EVA is a hydrophobic and chemically stable material, so its dimensions and adhesion with the textile were not strongly affected by the water, washing, or washing liquid.
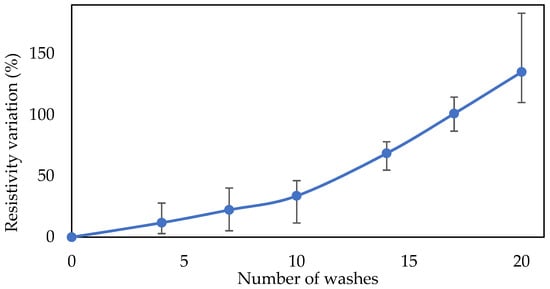
Figure 7.
Resistivity variation of the carbon black layer on the polyester-cotton textile after 20 washes.
Figure 8 shows the flexible conductive textile after screen printing, followed by an IPA rinse and curing in a fan oven at 130 °C for 5 min; the conductive patterns show sharp edges, indicating that the conductive carbon black/EVA composite did not spread during curing. LEDs were attached between the conductive tracks by using adhesive tape. The LED display on the textile, which is shown in Figure 9a, was encapsulated with a 100-μm-thick layer of EVA, which reduced the contact resistance between the LEDs and the conductive tracks. All of the LEDs operated at a voltage of ~2 V (±0.3 V).

Figure 8.
Screen-printed conductive textile pattern.
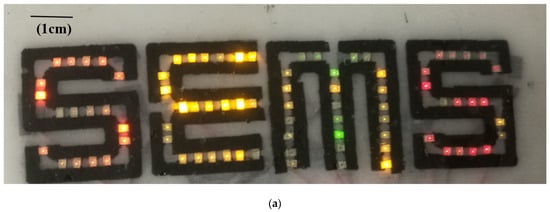
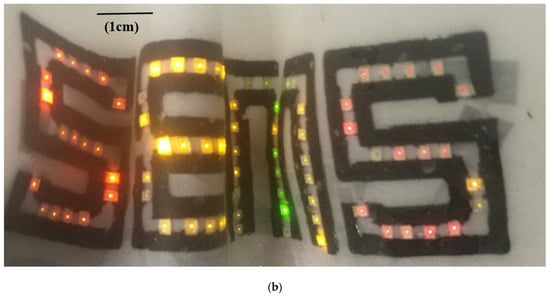
Figure 9.
(a) LED display made by the conductive textile pattern; (b) bent LED display after washing the textile.
The LED display on the textile was washed three times in the washing machine with the same standard washing liquid, and it remained functional, as shown in Figure 9b. Although a resistance change of 140% after 20 washes would result in the LEDs becoming proportionally less bright with each wash, they still functioned. However, some LEDs turned off after four washes. This was because the LED textile did not just rely on the conductive tracks to operate. It also required a reliable connection between the LEDs and the conductive tracks. This was achieved by using an encapsulation layer. Unfortunately, the encapsulation layer degraded, leading to the failure of the connection, so some LEDs did not turn on after four washes. Future work will develop a reliable encapsulation in order to improve the durability of LED textiles.
4. Conclusions
Electrically conductive textiles were achieved based on an inexpensive new formulation of a carbon black/EVA composite. This solution-processed composite was screen printed on a polyester-cotton substrate. The carbon black particles were linked by EVA polymer and formed a conductive network that was absorbed into the pores of the textile. This resulted in a strong bond between the carbon black/EVA composite film and the textile, thus creating a washable and bendable conductive textile.
The influence of the carbon percentage and curing regime on the resistivity was also evaluated. When the conductive composite was rinsed in IPA, then cured in a high-temperature oven, and the percentage of carbon black paste was 60 wt%, the lowest resistivity of 0.04 Ω·m was achieved.
The conductive composite layer on the textile achieved less than ±10% resistance variation after bending for 2000 cycles and remained conductive after 20 standard washes, after which the conductor’s resistance increased by 140%. The application was demonstrated in an LED display textile in which the printed conductive tracks were used as interconnections.
Author Contributions
Methodology, S.Y. and K.Y.; resources, A.K. and M.L.; data curation, S.Y. and A.K.; writing—original draft preparation, S.Y.; writing—review and editing, K.Y. and J.T.; English language check, J.T.; supervision, K.Y.; funding acquisition, K.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by EPSRC under grant number EP/S001654/1.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
K.Y. and J.T. are Directors of Smart Fabric Inks Limited. The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Fernández-Caramés, T.; Fraga-Lamas, P. Towards the internet of smart clothing: A review on IoT wearables and garments for creating intelligent connected e-textiles. Electronics 2018, 7, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komolafe, A.; Torah, R.; Wei, Y.; Nunes-Matos, H.; Li, M.; Hardy, D.; Dias, T.; Tudor, M.; Beeby, S. Integrating Flexible Filament Circuits for E-Textile Applications. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1900176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Jung, H.G.; Jang, J.W.; Park, D.; Lee, D.; Kim, I.; Kim, Y.; Cheong, D.Y.; Lee, G.; Yoon, D.S. Graphene-Based Electronic Textile Sheet for Highly Sensitive Detection of NO2 and NH3. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 345, 130361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Yao, D.; Hu, S.; Du, D.; Shao, W.; Tang, B.; Fan, J.-M.; Tang, X.-G.; Gao, J. Highly conductive, washable and super-hydrophobic wearable carbon nanotubes e-textile for vacuum pressure sensors. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020, 303, 111710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamedi, M.; Herlogsson, L.; Crispin, X.; Marcilla, R.; Berggren, M.; Inganäs, O. Fiber-embedded electrolyte-gated field-effect transistors for e-textiles. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Medeiros, M.S.; Goswami, D.; Chanci, D.; Moreno, C.; Martinez, R.V. Washable, breathable, and stretchable e-textiles wirelessly powered by omniphobic silk-based coils. Nano Energy 2021, 87, 106155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, S.; Shi, J.; Beeby, S. Wearable Textile Power Module Based on Flexible Ferroelectret and Supercapacitor. Energy Technol. 2019, 7, 1800938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, S.; Owen, J.; Beeby, S. Solid-State Supercapacitor Fabricated in a Single Woven Textile Layer for E-Textiles Applications. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2018, 20, 1700860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Jiang, L.; Tu, H.; Hu, J.; Moon, K.-S.; Yan, X.; Wong, C.-P. Rational design and evaluation of UV curable nano-silver ink applied in highly conductive textile-based electrodes and flexible silver-zinc batteries. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castano, L.; Flayau, A. Smart fabric sensors and e-textile technologies: A review. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 053001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achilli, A.; Pani, D.; Bonfiglio, A. Characterization of Screen-Printed Textile Electrodes Based on Conductive Polymer for ECG Acquisition. In Proceedings of the 2017 Computing in Cardiology Conference (CinC), Rennes, France, 24–27 September 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Jari, S.; Toni, B.; Mahmoud, M.; Timo, K.; Pekka, I.; Leena, U.; Jukka, V.; Matti, M. Screen-printing fabrication and characterization of stretchable electronics. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25784. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, H.; Hu, J.; Yan, X. UV Curable Conductive Ink for the Fabrication of Textile-Based Conductive Circuits and Wearable UHF RFID Tags. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 27318–27326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshitha, R.; Induni, W.; Nadeeka, D.; Ruchira, N.; Nalin, S. Carbon black functionalized stretchable conductive fabrics for wearable heating applications. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 19174–19180. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.; Lin, L.; Cartridge, D. High electrical conductivity waterborne inks for textile printing. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2019, 16, 1337–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Meadmore, K.; Freeman, C.T.; Grabham, N.J.; Hughes, A.-M.; Wei, Y.; Torah, R.N.; Glanc-Gostkiewicz, M.; Beeby, S.P.; Tudor, J. Development of User-Friendly Wearable Electronic Textiles for Healthcare Applications. Sensors 2018, 18, 2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudem, B.; Kim, D.H.; Yu, J.S. Triboelectric nanogenerators with gold-thin-film-coated conductive textile as floating electrode for scavenging wind energy. Nano Res. 2017, 11, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.-C.; Ding, K.-Q.; Ma, R.-J.; Wang, H.-L.; Sun, W.-J.; Yan, D.-X.; Li, B.; Li, Z.-M. Highly Conductive and Machine-Washable Textiles for Efficient Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1800503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narian, E.; Arami, M.; Bahrami, H.; Pajootan, E. Modification of Nickel Ferrite with Cationic Surfactant: Dye Removal from Textile Wastewater Using Magnetic Separation. J. Environ. Eng. 2015, 141, 05014006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Xin, B.; Shen, C. Preparation and characterization of PSA/PEDOT conductive composite yarns. Text. Res. J. 2016, 87, 528–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Cho, G. Polyurethane nanoweb-based textile sensors treated with single-walled carbon nanotubes and silver nanowire. Text. Res. J. 2018, 89, 2938–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Luo, M.; He, P.; Yang, J. Washable and flexible screen printed graphene electrode on textiles for wearable healthcare monitoring. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2020, 53, 125402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäl, P.; Junger, I.J.; Grimmelsmann, N.; Ehrmann, A. Development of graphite-based conductive textile coatings. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2018, 15, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva, R.; Ganta, D.; Guzman, C. Mechanical, in-situ electrical and thermal properties of wearable conductive textile yarn coated with polypyrrole/carbon black composite. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 6, 016307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yehia, E. Elmogahzy, Engineering Textiles, 2nd ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2020; Chapter 14.2.1; ISBN 978-0-08-102488-1. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, A.K. Conducting Polymers: Concepts and Applications. J. At. Mol. Condens. Nano Phys. 2018, 5, 159–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinti, S.; Arduini, F.; Carbone, M.; Sansone, L.; Cacciotti, I.; Moscone, D.; Palleschi, G. Screen-Printed Electrodes Modified with Carbon Nanomaterials: A Comparison among Carbon Black, Carbon Nanotubes and Graphene. Electroanalysis 2015, 27, 2230–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashedul, I.; Nipa, K.; Dewan, M.A.; Hasan, S. Fabrication of low cost and scalable carbon-based conductive ink for E-textile applications. Mater. Today Commun. 2019, 19, 32–38. [Google Scholar]
- Smart Fabric Lnks Ltd. Available online: https://www.fabinks.com/ (accessed on 18 June 2021).
- Toghchi, M.J.; Campagne, C.; Cayla, A.; Bruniaux, P.; Loghin, C.; Cristian, I.; Burgnies, L.; Chen, Y. Electrical conductivity enhancement of hybrid PA6,6 composite containing multiwall carbon nanotube and carbon black for shielding effectiveness application in textiles. Synth. Met. 2019, 251, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gultekin, N.D. Investigation of Thermal and Electrical Conductivity Properties of Carbon Black Coated Cotton Fabrics. Marmara Fen Bilim. Derg. 2015, 27, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mazzotta, G.; Dollmann, M.; Habisreutinger, S.N.; Christoforo, M.G.; Wang, Z.; Snaith, H.J.; Riede, M.K.; Nicholas, R.J. Solubilization of Carbon Nanotubes with Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate for Solution-Processed Conductive Films and Charge Extraction Layers in Perovskite Solar Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 1185–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Guo, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Tang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Y. Facile preparation of graphene nanowalls/EVA hybrid film for ultraflexible transparent electrodes. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2019, 23, 1473–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Lei, Z.; Liu, Y.; Feng, W.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, H. Solvent-free electrically conductive Ag/ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) composites for paper-based printable electronics. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 19501–19507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, D.; Li, C.; Wei, L. Highly conductive ethylene evinyl acetate copolymer/carbon nanotube paper for lightweight and flexible supercapacitors. J. Power Sources 2014, 248, 1248–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Wang, K.; Zhang, H.; Ding, Y.; Yu, Q. Encapsulation of PV Modules Using Ethylene Vinyl Acetate Copolymer as the Encapsulant. Macromol. React. Eng. 2015, 9, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuzakhanov, R.M.; Kapitskaya, Y.V.; Stoyanov, O.V.; Nikitina, N.N. Adhesive compositions based on modified ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymers. Polym. Sci. Ser. C 2007, 49, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, W.-T.; Wong, D.P.; Yick, K.-L.; Ng, S.P.; Yip, J. The biomechanical effects and perceived comfort of textile-fabricated insoles during straight line walking. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 2018, 42, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhai, T.; Lu, X.; Yu, M.; Tong, Y.; Mai, K. Conductive membranes of EVA filled with carbon black and carbon nanotubes for flexible energy-storage devices. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klopman. Available online: https://www.klopman.com/ (accessed on 18 June 2021).
- Agnieszka, K.; Vankelecom, F. Understanding and guiding the phase inversion process for synthesis of solvent resistant nanofiltration membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 42130. [Google Scholar]
- Vandezande, P.; Li, X.; Gevers, L.; Vankelecom, I.F. High throughput study of phase inversion parameters for polyimide-based SRNF membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 330, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Freeman, C.; Torah, R.; Beeby, S.; Tudor, J. Screen printed fabric electrode array for wearable functional electrical stimulation. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2014, 213, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).