Detection of Electron Beam-Irradiated Bone-Containing Foods Using a Robust Method of Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Spectrometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Irradiation of Samples
2.3. Preparation of Food Samples for EPR Cavity for Recording of Signals
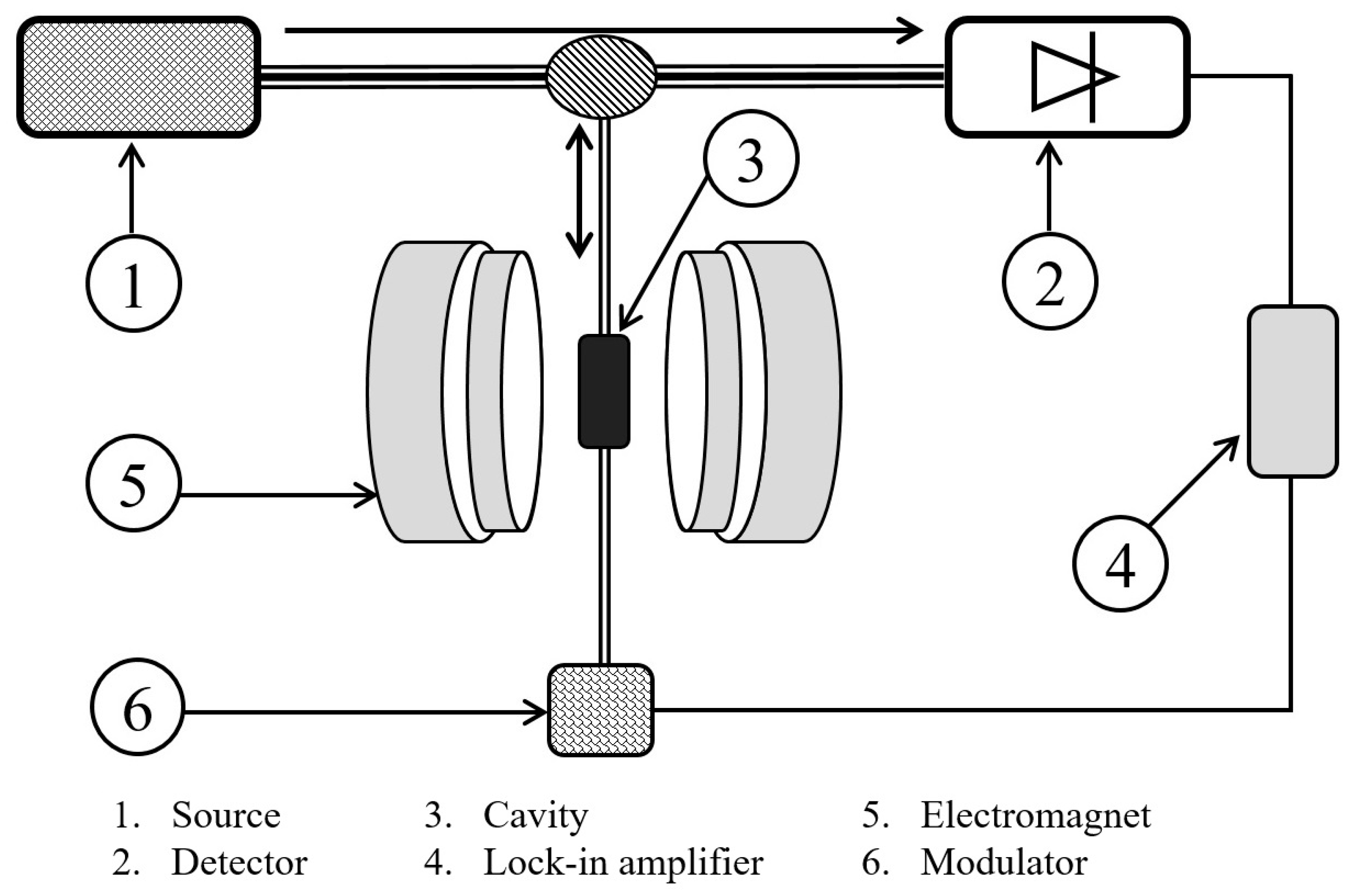
2.4. EPR Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
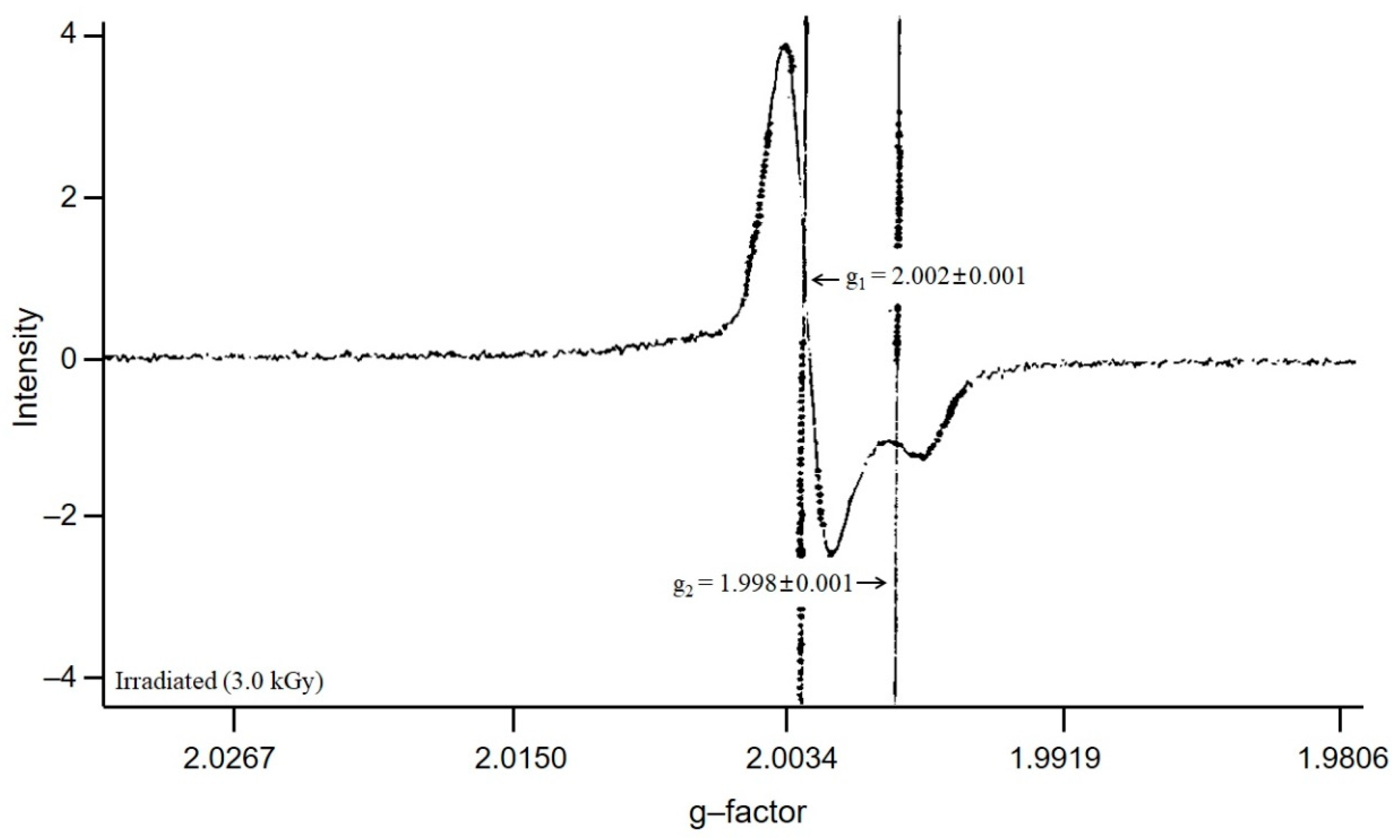
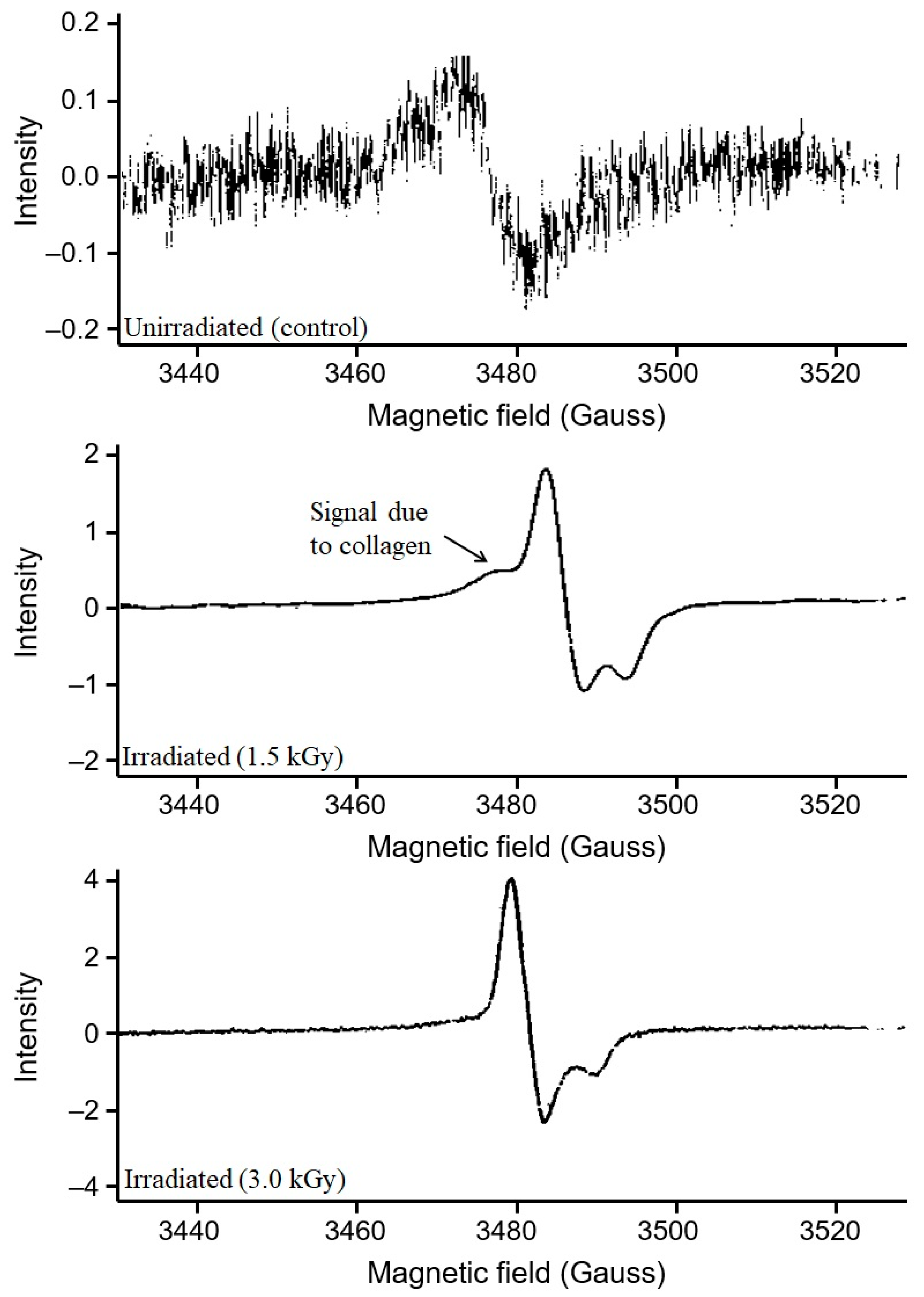
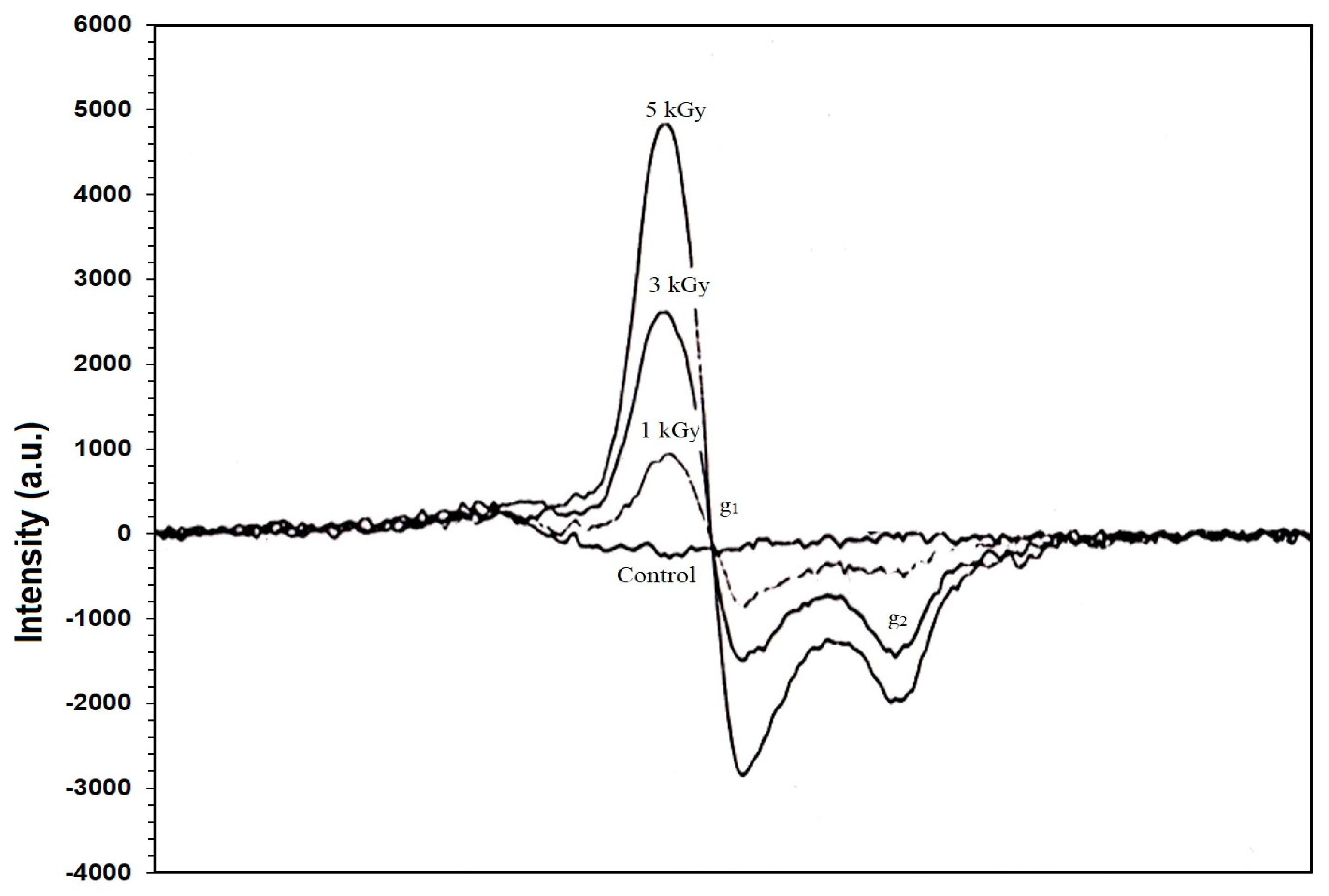
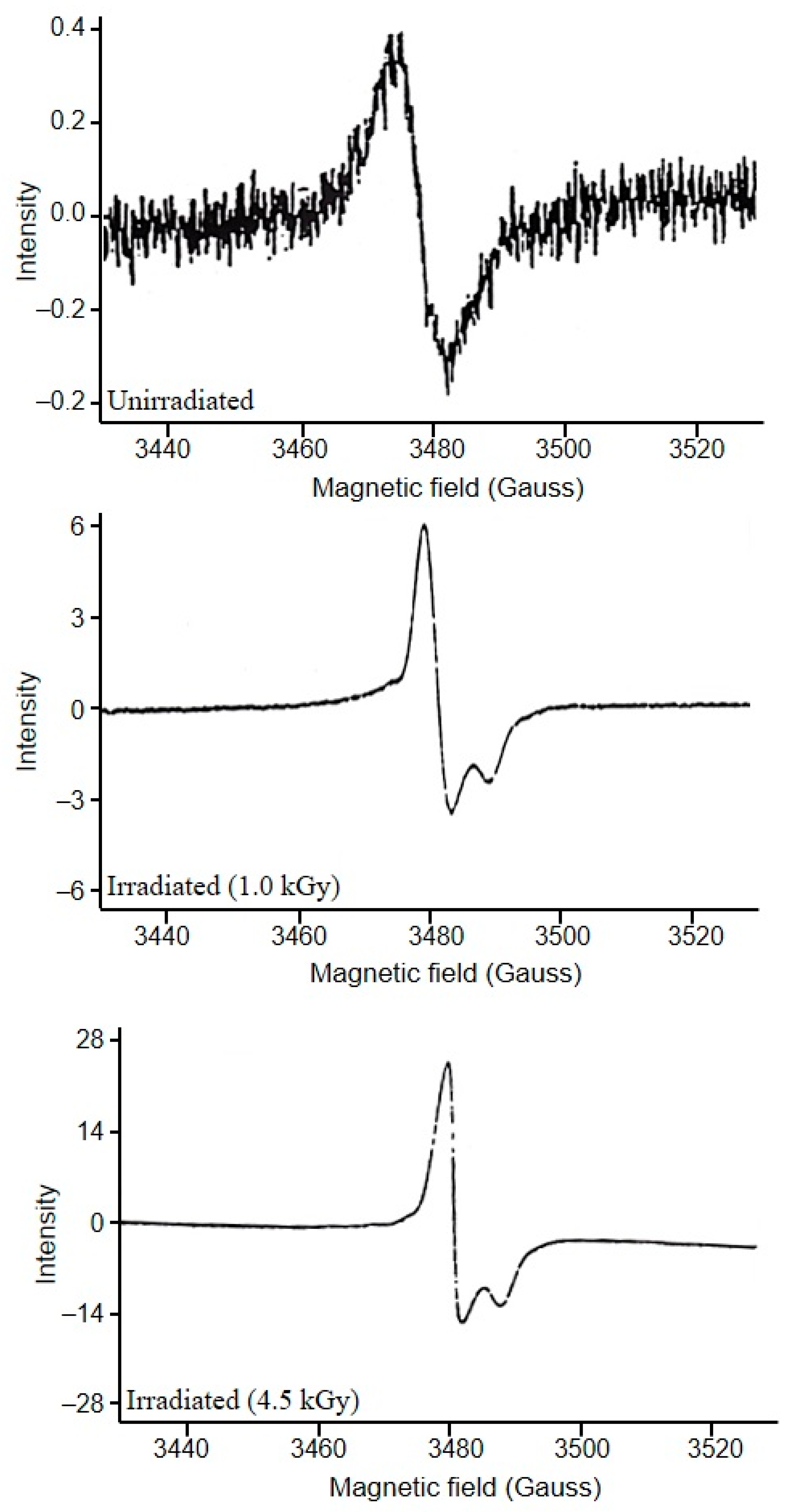
3.1. Assessment of EPR Signals from Bone Samples
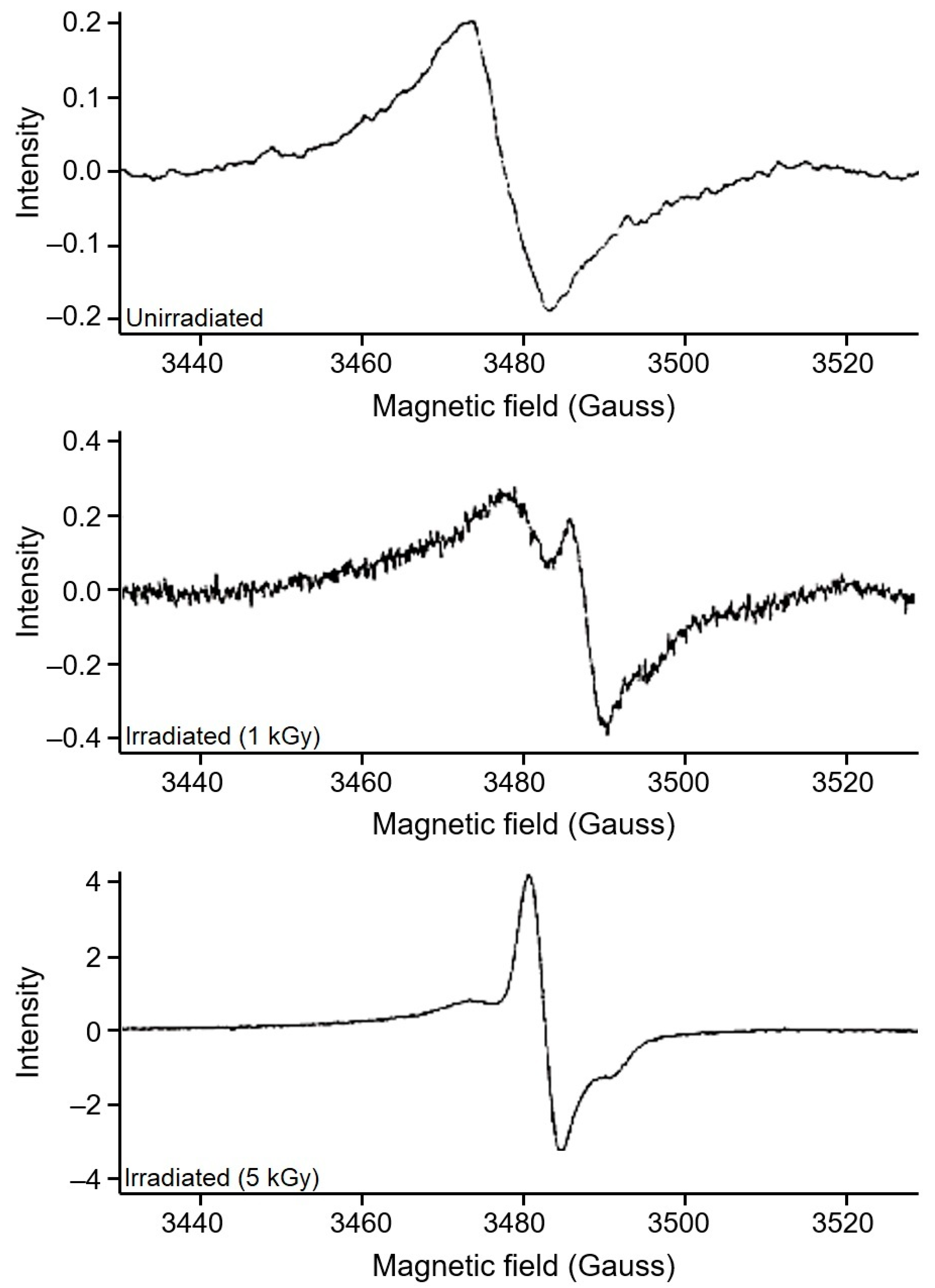
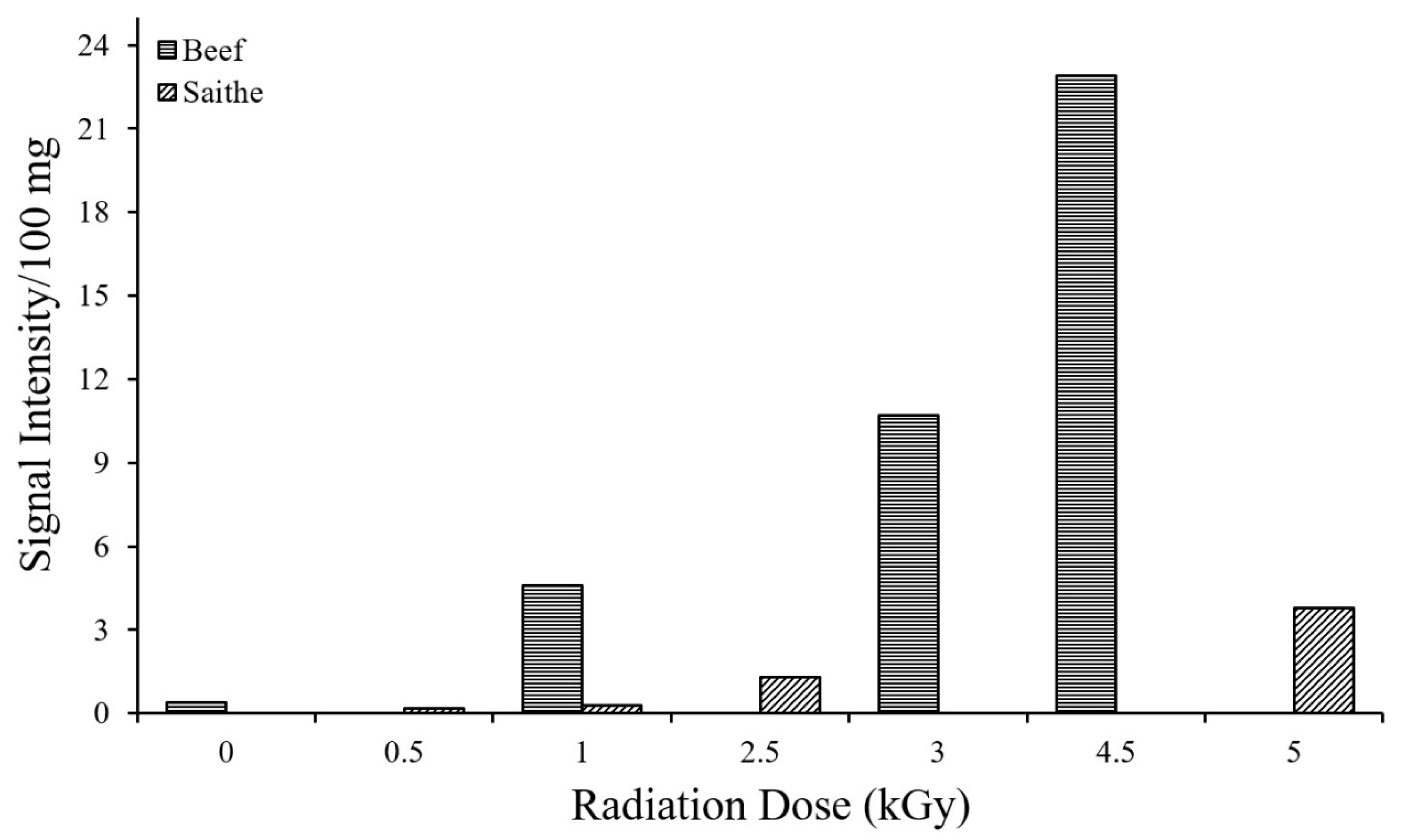
3.2. Identification of Irradiated Samples of Chicken, Beef, and Lamb’s Meat
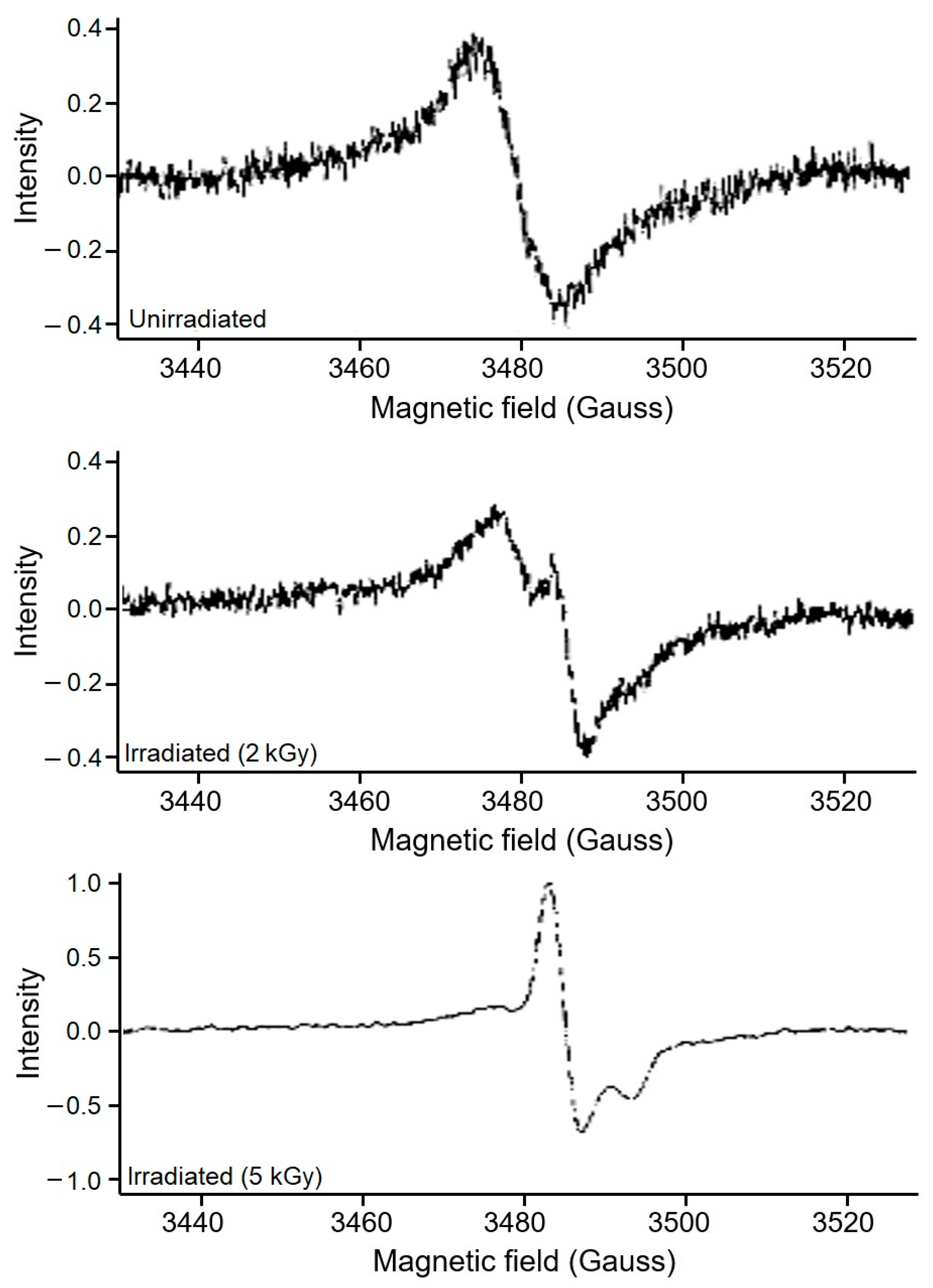
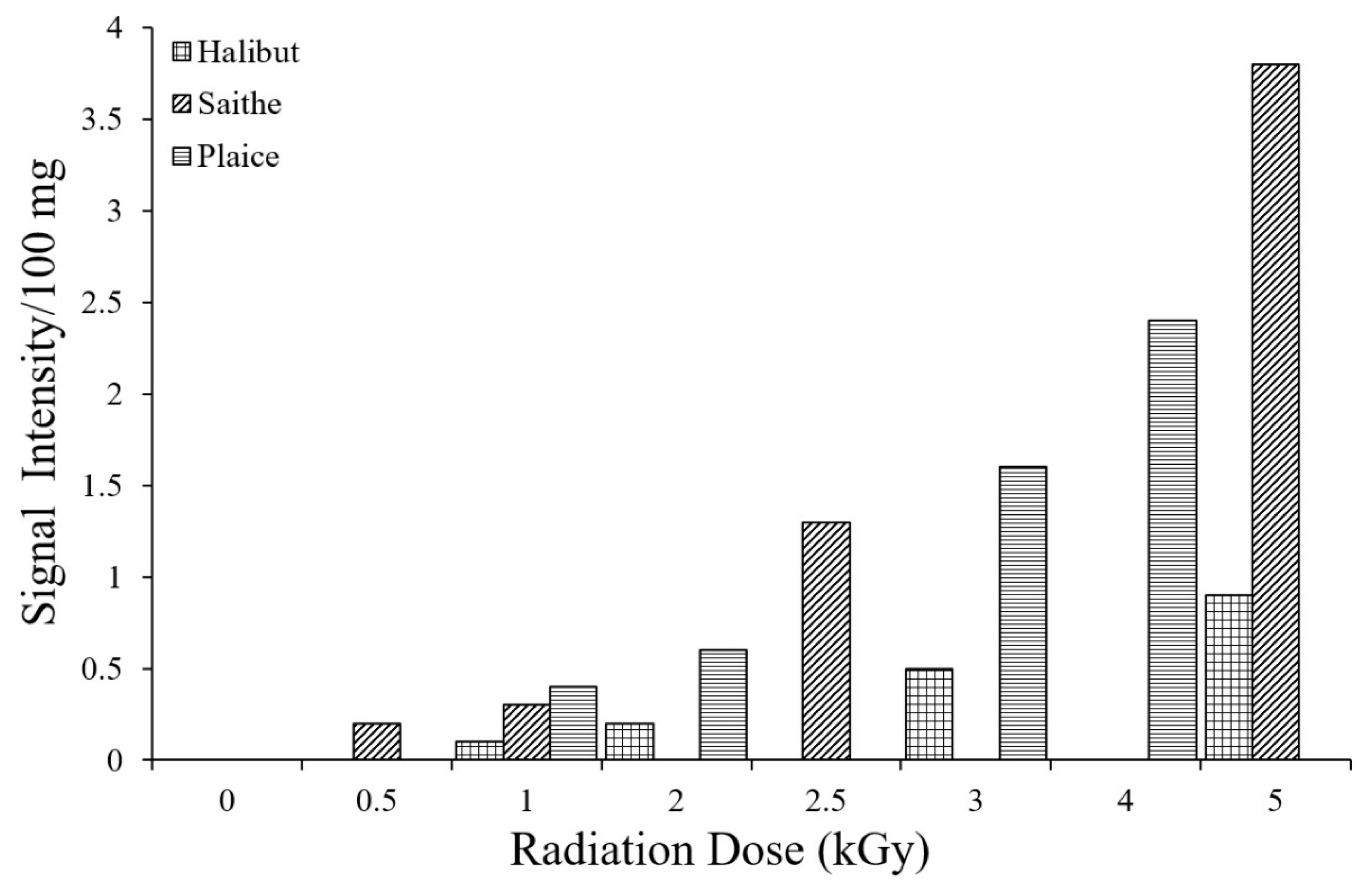
3.3. Identification of Irradiated Seafood
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sahoo, M.; Aradwad, P.; Panigrahi, C.; Kumar, V.; Naik, S.N. Irradiation of Food. In Novel Technologies in Food Science; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 333–373. ISBN 9781119776376. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasa, U.M.; Sruthi, P.; Rastogi, N.K.; Naidu, M.M. Application of Irradiation in the Food Industry. In A Volume in Unit Operations and Processing Equipment in the Food Industry; Jafari, S.M., Therdthai, N., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2023; pp. 221–253. ISBN 978-0-12-818717-3. [Google Scholar]
- Tahergorabi, R.; Matak, K.E.; Jaczynski, J. Application of Electron Beam to Inactivate Salmonella in Food: Recent Developments. Food Res. Int. 2012, 45, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, J.; Mohácsi-Farkas, C. History and Future of Food Irradiation. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 22, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.A.; Shahid, M.K. Detection of Radiation Treatment of Spices Using Electron Spin Resonance Spectroscopy Technique. J. Spices Aromat. Crops 2021, 30, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swallow, A.J. Can We Tell If Our Food Has Been Irradiated. Chem. Br. 1988, 24, 102–103. [Google Scholar]
- Vazirov, R.A.; Narkhova, A.A.; Vazirova, E.N.; Sokovnin, S.Y. Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Signal in Wheat Seeds Irradiated with Low-Energy Electron Beam. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2023, 208, 110934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coghlan, A. Irradiated Food: Too Hot to Handle? New Sci. 1990, 125, 28–29. [Google Scholar]
- Vazirov, R.A.; Sokovnin, S.Y.; Agdantseva, E.N.; Tsmokalyuk, A.N. Investigation of Radiation-Induced Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Signal of an Eggshell after Electron Beam Irradiation. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2022, 192, 109882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roessler, M.M.; Salvadori, E. Principles and Applications of EPR Spectroscopy in the Chemical Sciences. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 2534–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murrieta, H.S.; Muñoz, E.P.; Adem, E.; Burillo, G.; Vazquez, M.; Cabrera, E.B. Effect of Irradiation Dose, Storage Time and Temperature on the ESR Signal in Irradiated Oat, and Corn and Wheat. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1996, 47, 1657–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, M.; Polat, M. Free Radical Kinetics of Irradiated Durum Wheat. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2000, 58, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontanesi, L. Meat Authenticity and Traceability. In Woodhead Publishing Series in Food Science, Technology and Nutrition; Toldra’, F., Eighth, E., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2017; pp. 585–633. ISBN 978-0-08-100694-8. [Google Scholar]
- Tomaiuolo, M.; Chiaravalle, A.E.; Mangiacotti, M.; Petrella, A.; Di Taranto, A.; Iammarino, M. Innovative Techniques for Identifying a Mechanically Separated Meat: Sample Irradiation Coupled to Electronic Spin Resonance. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 2331–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchioni, E.; Horvatovich, P.; Charon, H.; Kuntz, F. Detection of Irradiated Ingredients Included in Low Quantity in Non-Irradiated Food Matrix. 2. ESR Analysis of Mechanically Recovered Poultry Meat and TL Analysis of Spices. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 3774–3778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, S.K.; Kumar, R.; Nadanasabapathy, S.; Bawa, A.S. Detection Methods for Irradiated Foods. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2009, 8, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzik, G.P.; Stachowicz, W. Advanced Analytical Methods for the Detection of Irradiated Foods. In Advanced Spectroscopic Techniques for Food Quality; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2022; Volume 32, p. 80. ISBN 978-1-83916-404-0. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.A.; Shahid, M.K. Identification of Radiation Processing of Different Plant Foods of Pakistan Origin Using the Rapid Technique of Electron Spin Resonance (ESR) Spectrometry. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2022, 204, 110667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN1786; Detection of Irradiated Food Containing Bone, Method by ESR Spectroscopy. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 1996.
- Bessalah, S.; Jebahi, S.; Faraz, A.; Raoufi, A.; Tirink, C.; Dridi, W.; Daouad, M.; Keskes, H.; Khorchani, T.; Farah, K. Effect of Gamma Radiation on Novel Gelatin Extracted from Camel Skin for Pharmaceutical Application. Pak. J. Zool. 2023, 55, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinnikova, E.; Sadovnikova, M.; Rodionov, A.; Murzakhanov, F.; Grishin, P. Analysis of the Osseointegration Process of Dental Implants by Electron Paramagnetic Resonance: An In Vivo Study. Dent. J. 2022, 10, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escudero, R.; Segura, J.; Velasco, R.; Valhondo, M.; Romero de Ávila, M.D.; Garcia-Garcia, A.B.; Cambero, M.I. Electron Spin Resonance (ESR) Spectroscopy Study of Cheese Treated with Accelerated Electrons. Food Chem. 2019, 276, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonor, S.J.; Gómez, J.A.; Kinoshita, A.; Calandreli, I.; Tfouni, E.; Baffa, O. ESR Spectroscopic Properties of Irradiated Gum Arabic. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 1860–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marciniec, B.; Stawny, M.; Kozak, M.; Naskrent, M. The Influence of Radiation Sterilization on Thiamphenicol. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2008, 69, 865–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffi, J.; Stocker, P. Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Detection of Irradiated Foodstuffs. Appl. Magn. Reson. 1996, 10, 357–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desrosiers, M.F. Current Status of the EPR Method to Detect Irradiated Food. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1996, 47, 1621–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzik, G.P.; Stachowicz, W.; Michalik, J. Aspects of the EPR Study on Mineralized Tissues as Related to Medicine, Dosimetry, and Dating. In Experimental Methods in the Physical Sciences; Shukla, A.K., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; Volume 50, pp. 115–127. ISBN 1079-4042. [Google Scholar]
- Chawla, S.P.; Thomas, P.; Bongirwar, D.R. Factors Influencing the Yield of Radiation Induced Electron Spin Resonance (ESR) Signal in Lamb Bones. Food Res. Int. 2002, 35, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minea, R.; Pascanu, S. Identification of Irradiated Foods I Detection Methods Based on Physical Changes Induced by Irradiation in the Food Samples. Rom. Rep. Phys. 1996, 49, 107–131. [Google Scholar]
- Empis, J.M.A.; Silva, H.A.; Nunes, M.L.; Andrade, E.M. Detection of Irradiated Fish Using EPR of Fish Bone; Signal Intensity and Stability. Fish. Res. 1995, 21, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, E.; Sami, A.; Mansour, A.; Maghraby, A. EPR study of irradiated bovine bone: Application to radiation dosimetry. Radiat. Eff. Defects Solids 2025, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Type of Food | Absorbed Radiation Doses (kGy) |
|---|---|
| Beef | 0, 1, 3, 4.5 |
| Chicken | 0, 1, 1.5, 2.7, 3, 5 |
| Meat of Lamb | 0, 0.5, 1.5 |
| Halibut fish | 0, 1, 2, 3, 5 |
| Plaice fish | 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 |
| Saithe fish | 0, 0.5, 1, 2.5, 5 |
| Salmon fish | 0, 0.5, 1, 2.5, 5 |
| Spectrometric Settings | Values |
|---|---|
| Microwave radiation | |
| Microwave frequency | 9.78 GHz. |
| Microwave power | 9.95 mW |
| Magnetic field | |
| Centre field | 348 mT (3480 Gauss) |
| Sweep width | 10 mT (100 Gauss) |
| Signal Channel | |
| Modulation frequency | 50 kHz |
| Modulation amplitude | 0.4 mT (4 Gauss) |
| Time constant (Filter t.c) | 10.24 ms (bones) |
| 40.96 ms (fish bones) | |
| Sweep time | 42 s/sweep (bones) |
| 84 s/sweep (fish bones) | |
| No of sweeps | 5 (bones) |
| 10 (fish bones) | |
| Receiver gain | 50 dB (bones) |
| 60 dB (fish bones) | |
| Temperature | Room temperature |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, A.A.; Shahid, M.K. Detection of Electron Beam-Irradiated Bone-Containing Foods Using a Robust Method of Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Spectrometry. Physchem 2025, 5, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/physchem5030024
Khan AA, Shahid MK. Detection of Electron Beam-Irradiated Bone-Containing Foods Using a Robust Method of Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Spectrometry. Physchem. 2025; 5(3):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/physchem5030024
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Ashfaq Ahmad, and Muhammad Kashif Shahid. 2025. "Detection of Electron Beam-Irradiated Bone-Containing Foods Using a Robust Method of Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Spectrometry" Physchem 5, no. 3: 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/physchem5030024
APA StyleKhan, A. A., & Shahid, M. K. (2025). Detection of Electron Beam-Irradiated Bone-Containing Foods Using a Robust Method of Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Spectrometry. Physchem, 5(3), 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/physchem5030024







