An Electrochemical Impedance Study of Alkaline Water Splitting Using Fe Doped NiO Nanosheets
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Catalyst Electrode Fabrication
2.3. Material Characterization
2.4. Electrochemical Measurements
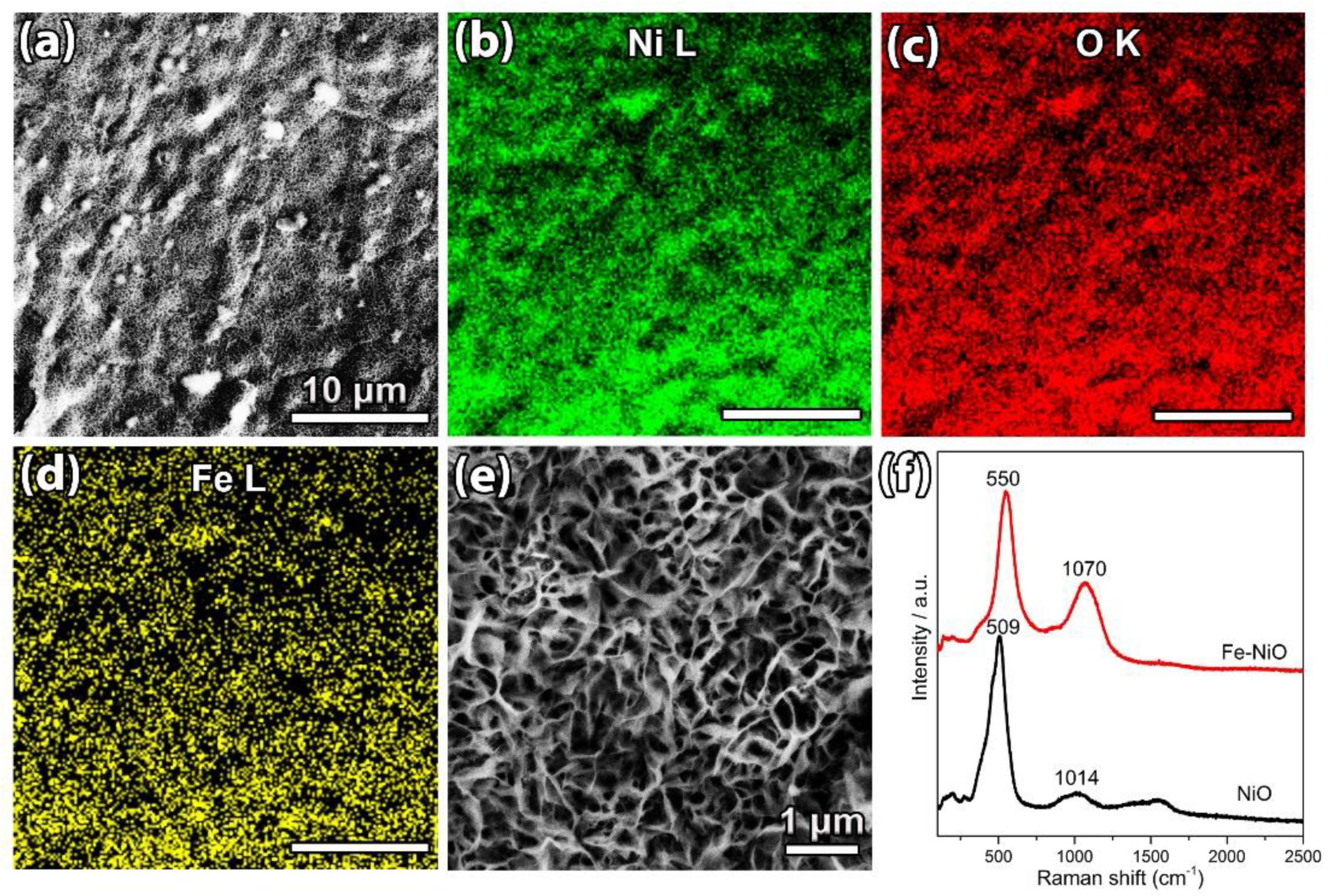
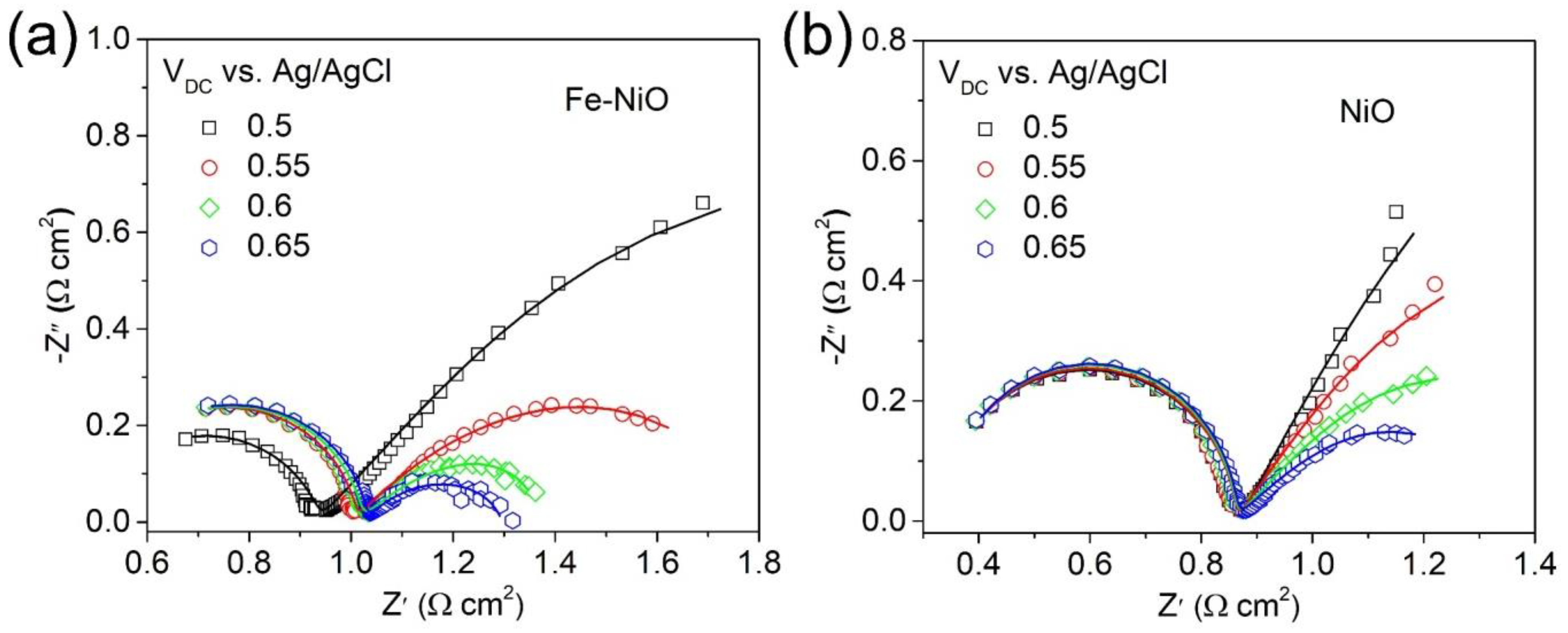
3. Result and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schlapbach, L.; Zuttel, A. Hydrogen-storage materials for mobile applications. Nature 2001, 414, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasteiger, H.A.; Markovic, N.M. Chemistry. Just a dream--or future reality? Science 2009, 324, 48–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardo, S.; Rivas, D.F.; Modestino, M.A.; Greiving, V.S.; Abdi, F.F.; Llado, E.A.; Artero, V.; Ayers, K.; Battaglia, C.; Becker, J.P.; et al. Pathways to electrochemical solar-hydrogen technologies. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 2768–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, B. Recent advances in transition metal phosphide nanomaterials: Synthesis and applications in hydrogen evolution reaction. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 1529–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anantharaj, S.; Ede, S.R.; Sakthikumar, K.; Karthick, K.; Mishra, S.; Kundu, S. Recent Trends and Perspectives in Electrochemical Water Splitting with an Emphasis on Sulfide, Selenide, and Phosphide Catalysts of Fe, Co, and Ni: A Review. ACS Catal 2016, 6, 8069–8097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Xia, B.Y.; Zhao, B.; Wang, X. A review on noble-metal-free bifunctional heterogeneous catalysts for overall electrochemical water splitting. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 17587–17603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corrigan, D.A. The Catalysis of the Oxygen Evolution Reaction by Iron Impurities in Thin-Film Nickel-Oxide Electrodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1987, 134, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, E.L. Electrochemical Behavior of Reactively Sputtered Iron-Doped Nickel Oxide. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1997, 144, 3072–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotochaud, L.; Young, S.L.; Ranney, J.K.; Boettcher, S.W. Nickel-iron oxyhydroxide oxygen-evolution electrocatalysts: The role of intentional and incidental iron incorporation. J. Am. Chem Soc. 2014, 136, 6744–6753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Pu, Z.; Li, Y.; Wu, L.; Tu, Z.; Jiang, M.; Kou, Z.; Amiinu, I.S.; Mu, S. Iron-Doped Nickel Phosphide Nanosheet Arrays: An Efficient Bifunctional Electrocatalyst for Water Splitting. ACS Appl Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 26001–26007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Im, J.H.; Mayer, M.T.; Schreier, M.; Nazeeruddin, M.K.; Park, N.G.; Tilley, S.D.; Fan, H.J.; Gratzel, M. Water photolysis at 12.3% efficiency via perovskite photovoltaics and Earth-abundant catalysts. Science 2014, 345, 1593–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.D.; Prevot, M.S.; Fagan, R.D.; Trudel, S.; Berlinguette, C.P. Water oxidation catalysis: Electrocatalytic response to metal stoichiometry in amorphous metal oxide films containing iron, cobalt, and nickel. J. Am. Chem Soc. 2013, 135, 11580–11586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fillol, J.L.; Codola, Z.; Garcia-Bosch, I.; Gomez, L.; Pla, J.J.; Costas, M. Efficient water oxidation catalysts based on readily available iron coordination complexes. Nat. Chem 2011, 3, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Chang, S.L.Y.; Hocking, R.K.; Bach, U.; Spiccia, L. Highly active nickel oxide water oxidation catalysts deposited from molecular complexes. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Młynarek, G.; Paszkiewicz, M.; Radniecka, A. The effect of ferric ions on the behaviour of a nickelous hydroxide electrode. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1984, 14, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, D.; Minakshi, M.; Kim, D.J.; Kyeong, C. Influence of the Oxide Content in the Catalytic Power of Raney Nickel in Hydrogen Generation. Anal. Lett. 2017, 50, 2386–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friebel, D.; Louie, M.W.; Bajdich, M.; Sanwald, K.E.; Cai, Y.; Wise, A.M.; Cheng, M.-J.; Sokaras, D.; Weng, T.-C.; Alonso-Mori, R.; et al. Identification of Highly Active Fe Sites in (Ni,Fe)OOH for Electrocatalytic Water Splitting. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 1305–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.; Tryk, D.A.; Antonio, M.R.; Carr, R.; Scherson, D. In situ x-ray absorption fine structure studies of foreign metal ions in nickel hydrous oxide electrodes in alkaline electrolytes. J. Phys. Chem. 1994, 98, 10269–10276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Arco, M.; Malet, P.; Trujillano, R.; Rives, V. Synthesis and Characterization of Hydrotalcites Containing Ni(II) and Fe(III) and Their Calcination Products. Chem. Mater. 1999, 11, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Y.C.; Dang, L.; Liang, H.; Bi, W.; Gerken, J.B.; Jin, S.; Alp, E.E.; Stahl, S.S. Operando Analysis of NiFe and Fe Oxyhydroxide Electrocatalysts for Water Oxidation: Detection of Fe4+ by Mössbauer Spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 15090–15093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Tai, C.-W.; Niklasson, G.A.; Edvinsson, T. Direct observation of active catalyst surface phases and the effect of dynamic self-optimization in NiFe-layered double hydroxides for alkaline water splitting. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.F.; Selloni, A. Mechanism and Activity of Water Oxidation on Selected Surfaces of Pure and Fe-Doped NiOx. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 1148–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Ma, Y.; Edvinsson, T. In operando Raman investigation of Fe doping influence on catalytic NiO intermediates for enhanced overall water splitting. Nano Energy 2019, 66, 104118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lvovich, V.F. Impedance Spectroscopy: Applications to Electrochemical and Dielectric Phenomena; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Barsoukov, E.; Macdonald, J.R. Impedance Spectroscopy: Theory, Experiment, and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Harrington, D.A.; Conway, B.E. ac Impedance of Faradaic reactions involving electrosorbed intermediates—I. Kinetic theory. Electrochim. Acta 1987, 32, 1703–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Z.C.; Zou, Z.X.; Huang, J.S.; Gao, F. Fe-doped NiO mesoporous nanosheets array for highly efficient overall water splitting. J. Catal. 2018, 358, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.H.; Jia, J.F.; Wang, J.; Liu, S.J.; Wang, X.C.; Song, H.Z.; Hu, X. Synthesis of Fe-doped NiO nanofibers using electrospinning method and their ferromagnetic properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 2070–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fominykh, K.; Chernev, P.; Zaharieva, I.; Sicklinger, J.; Stefanic, G.; Doblinger, M.; Muller, A.; Pokharel, A.; Bocklein, S.; Scheu, C.; et al. Iron-doped nickel oxide nanocrystals as highly efficient electrocatalysts for alkaline water splitting. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 5180–5188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, R.E.; Parisot, G.I.; Meixner, A.E. Infrared Absorption and Raman Scattering by Two-Magnon Processes in NiO. Phys. Rev. B 1971, 4, 2302–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleury, P.A.; Loudon, R. Scattering of Light by One- and Two-Magnon Excitations. Phys. Rev. 1968, 166, 514–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aytan, E.; Debnath, B.; Kargar, F.; Barlas, Y.; Lacerda, M.M.; Li, J.X.; Lake, R.K.; Shi, J.; Balandin, A.A. Spin-Phonon Coupling in Antiferromagnetic Nickel Oxide. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 111, 252402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mironova-Ulmane, N.; Kuzmin, A.; Steins, I.; Grabis, J.; Sildos, I.; Pärs, M. Raman Scattering in Nanosized Nickel Oxide NiO. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2007, 93, 012039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funkenbusch, E.F.; Cornilsen, B.C. Two-Magnon Raman Scattering in Calcium Doped NiO. Solid State Commun. 1981, 40, 707–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Cai, J.; Lin, Y.-H.; Nan, C.-W. Room-Temperature Ferromagnetism Observed in Fe-Doped NiO. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 87, 202501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnusamy, P.M.; Agilan, S.; Muthukumarasamy, N.; Senthil, T.S.; Rajesh, G.; Venkatraman, M.R.; Velauthapillai, D. Structural, optical and magnetic properties of undoped NiO and Fe-doped NiO nanoparticles synthesized by wet-chemical process. Mater. Charact. 2016, 114, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Conway, B.E. AC Impedance of Faradaic Reactions Involving Electrosorbed Intermediates: Examination of Conditions Leading to Pseudoinductive Behavior Represented in Three-Dimensional Impedance Spectroscopy Diagrams. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1991, 138, 2897–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brug, G.J.; Van den Eeden, A.L.G.; Sluyters-Rehbach, M.; Sluyters, J.H. The Analysis of Electrode Impedances Complicated by the Presence of a Constant Phase Element. J. Electroanal Chem 1984, 176, 275–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diard, J.P.; LeGorrec, B.; Montella, C. Non-linear impedance for a two-step electrode reaction with an intermediate adsorbed species. Electrochim. Acta 1997, 42, 1053–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, C.T.; Jain, A.; de Arquer, F.P.G.; De Luna, P.; Li, J.; Wang, N.; Zheng, X.L.; Cai, J.; Gregory, B.Z.; Voznyy, O.; et al. Multi-site electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution in neutral media by destabilization of water molecules. Nat. Energy 2019, 4, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, B.E.; Tilak, B.V. Behavior and characterization of kinetically involved chemisorbed intermediates in electrocatalysis of gas evolution reactions. In Advances in Catalysis; Eley, D.D., Pines, H., Weisz, P.B., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1992; Volume 38, pp. 1–147. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, C.H.; Mansfeld, F. Technical Note: Concerning the Conversion of the Constant Phase Element Parameter Y0 into a Capacitance. Corrosion 2001, 57, 747–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elezović, N.R.; Jović, V.D.; Krstajić, N.V. Kinetics of the hydrogen evolution reaction on Fe–Mo film deposited on mild steel support in alkaline solution. Electrochim. Acta 2005, 50, 5594–5601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L. Study of the Kinetics of Hydrogen Evolution Reaction on Nickel-Zinc Alloy Electrodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1991, 138, 3321–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Schaftinghen, T.; Deslouis, C.; Hubin, A.; Terryn, H. Influence of the surface pre-treatment prior to the film synthesis, on the corrosion protection of iron with polypyrrole films. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 51, 1695–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, T.M.J.; Niklasson, G.A. Comparison of dielectric and optical properties of nickel-oxide-based electrochromic coatings. Proc. Spie 1990, 1272, 129–138. [Google Scholar]
- Biju, V.; Khadar, M.A. Dielectric properties of nanostructured nickel oxide. J. Mater. Sci. 2003, 38, 4055–4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diard, J.P.; LeGorrec, B.; Maximovitch, S. Etude de l’activation du degagement d’hydrogene sur electrode d’oxyde de nickel par spectroscopie d’impedance. Electrochim. Acta 1990, 35, 1099–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Zhang, W.; Xiang, R.; Liu, K.; Wang, H.-Y.; Chen, M.; Han, Y.; Cao, R. Porous Nickel–Iron Oxide as a Highly Efficient Electrocatalyst for Oxygen Evolution Reaction. Adv. Sci. 2015, 2, 1500199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pebley, A.C.; Decolvenaere, E.; Pollock, T.M.; Gordon, M.J. Oxygen evolution on Fe-doped NiO electrocatalysts deposited via microplasma. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 15070–15082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, M.; Dai, H. A mini review of NiFe-based materials as highly active oxygen evolution reaction electrocatalysts. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiu, Z.; Ma, Y.; Niklasson, G.A.; Edvinsson, T. An Electrochemical Impedance Study of Alkaline Water Splitting Using Fe Doped NiO Nanosheets. Physchem 2021, 1, 69-81. https://doi.org/10.3390/physchem1010005
Qiu Z, Ma Y, Niklasson GA, Edvinsson T. An Electrochemical Impedance Study of Alkaline Water Splitting Using Fe Doped NiO Nanosheets. Physchem. 2021; 1(1):69-81. https://doi.org/10.3390/physchem1010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiu, Zhen, Yue Ma, Gunnar A. Niklasson, and Tomas Edvinsson. 2021. "An Electrochemical Impedance Study of Alkaline Water Splitting Using Fe Doped NiO Nanosheets" Physchem 1, no. 1: 69-81. https://doi.org/10.3390/physchem1010005
APA StyleQiu, Z., Ma, Y., Niklasson, G. A., & Edvinsson, T. (2021). An Electrochemical Impedance Study of Alkaline Water Splitting Using Fe Doped NiO Nanosheets. Physchem, 1(1), 69-81. https://doi.org/10.3390/physchem1010005







