Conservation of Heritage Sites in Kathmandu, Nepal: Assessing the Corrosion Threat from Pigeon Excreta on Metal Monuments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
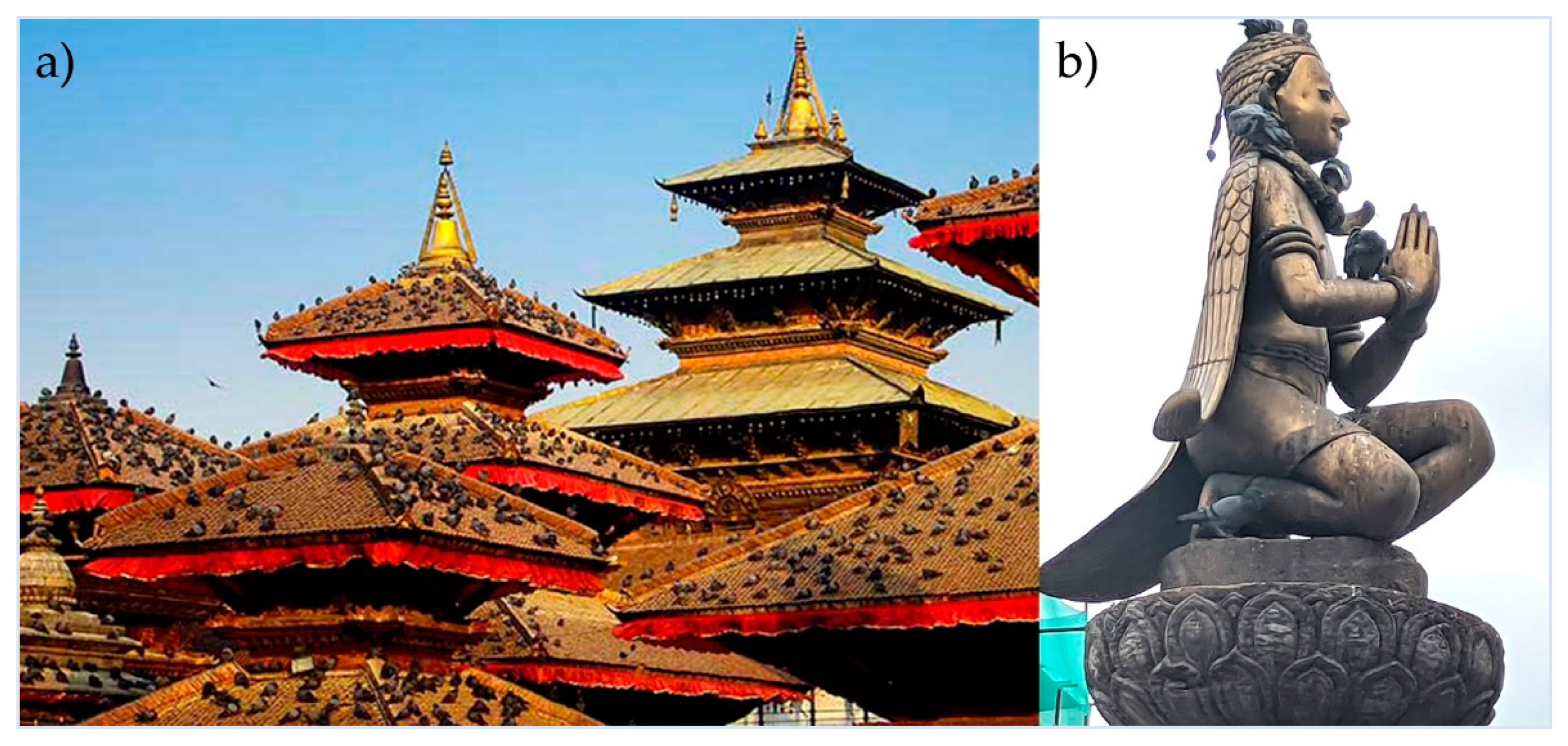
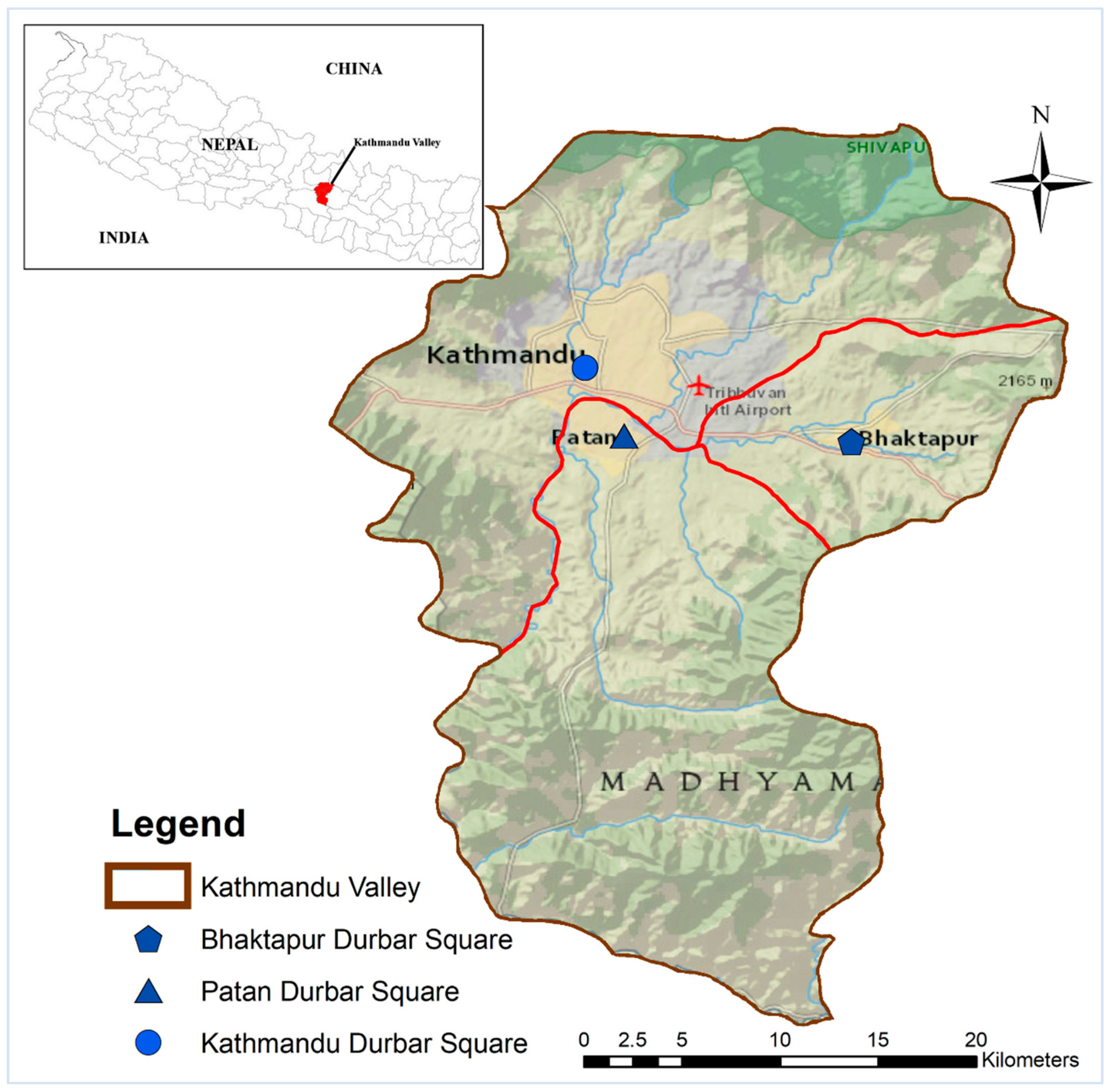
2.1. Sampling Sites
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Data Management and Analysis
3. Results
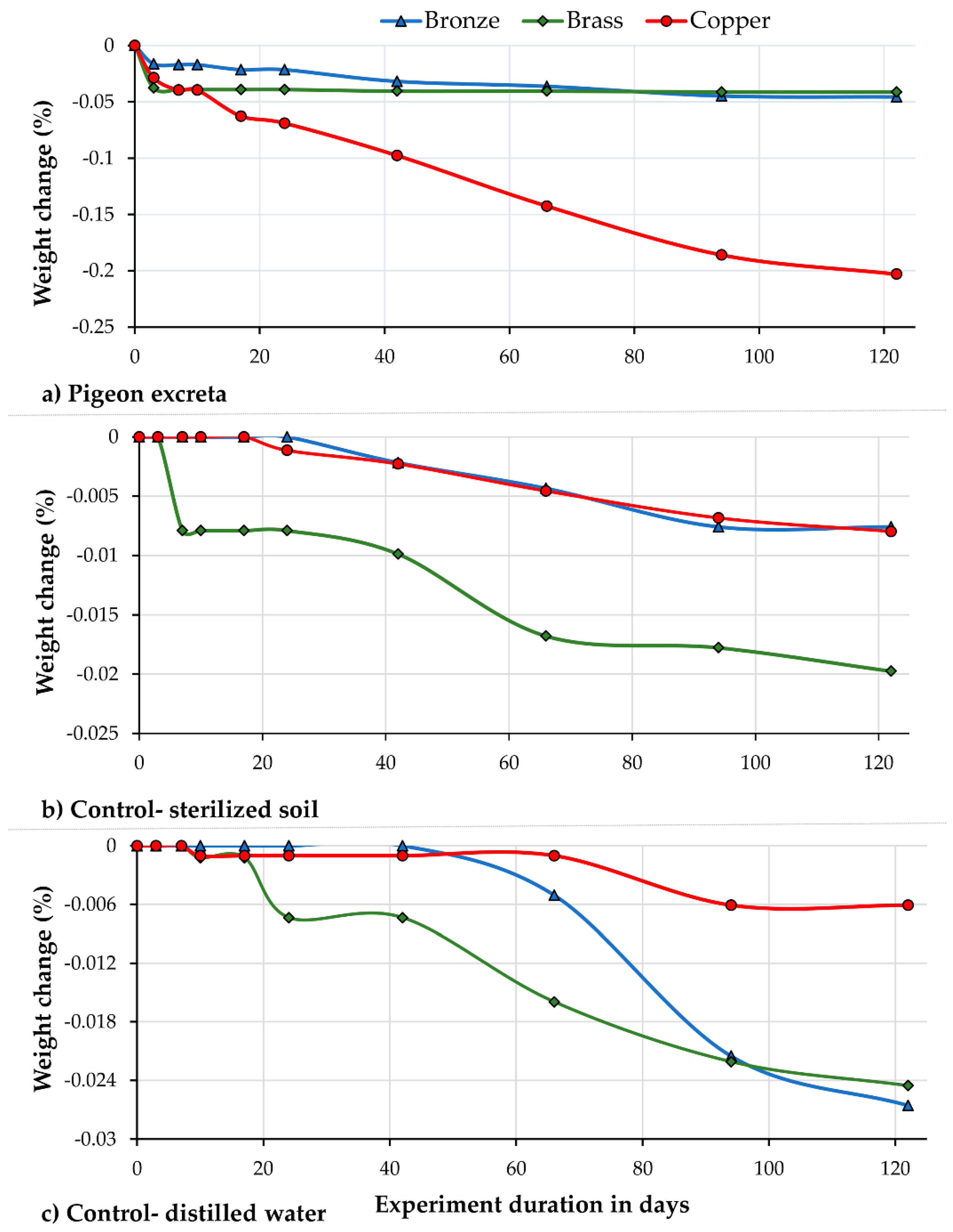
3.1. General Pattern of Weight Loss in Metal Samples
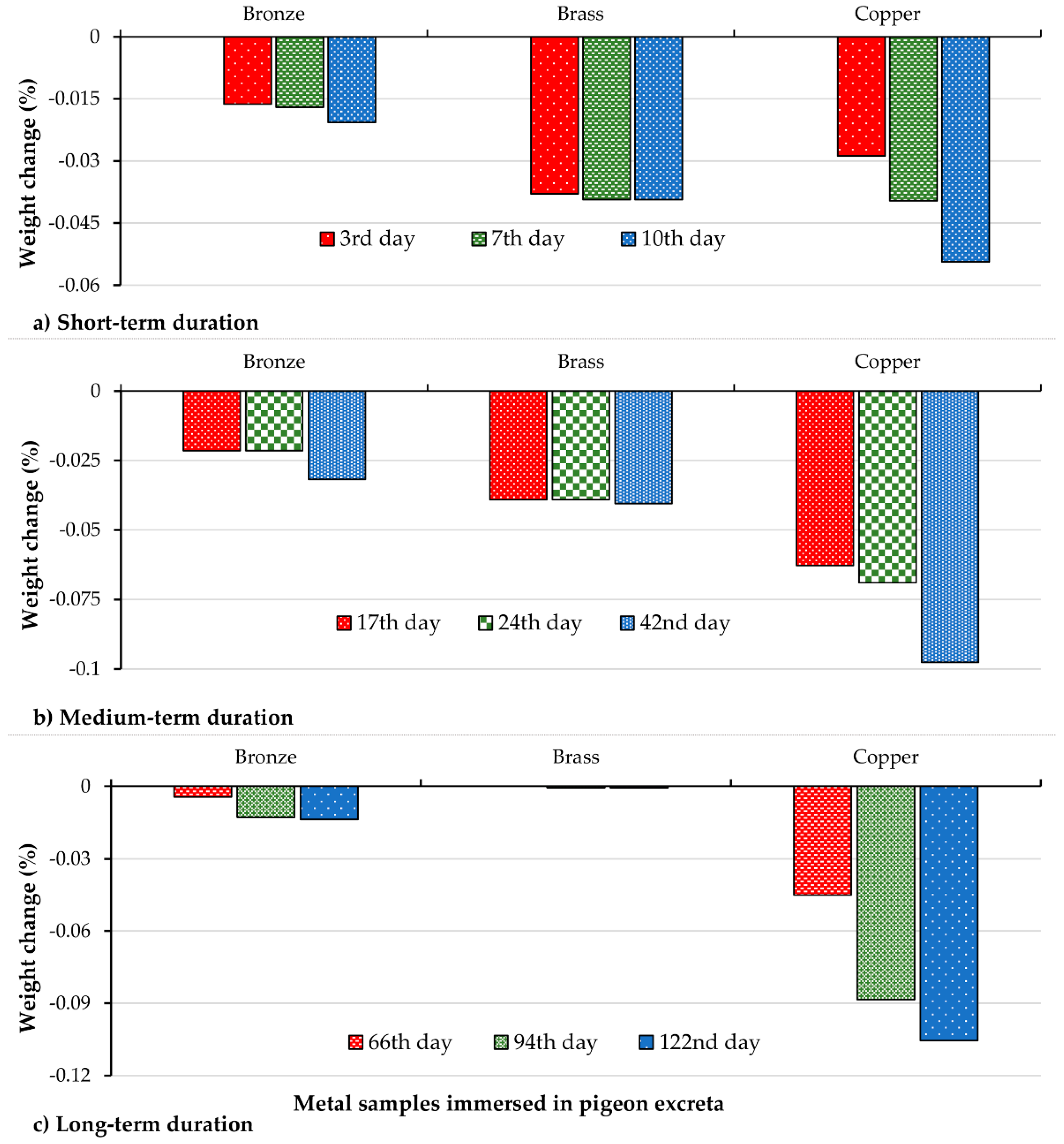
3.2. Weight Loss Patterns among Metal Samples by Study Conditions and Exposure Time
3.3. Weight Loss Pattern of Metal Samples in Pigeon Excreta as a Function of Exposure Duration
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bernardi, E.; Bowden, D.J.; Brimblecombe, P.; Kenneally, H.; Morselli, L. The effect of uric acid on outdoor copper and bronze. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 2383–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, D.; Prasad, J.; Pandey, A.K.; Upadhyay, M.K. A scientific approach to preservation of cultural heritage-Sibsagar (Assam) centrally protected monument. Int. J. Conserv. Sci. 2018, 9, 291–300. [Google Scholar]
- Agapiou, A.; Lysandrou, V.; Themistocleous, K.; Hadjimitsis, D.G. Risk assessment of cultural heritage sites clusters using satellite imagery and GIS: The case study of Paphos District, Cyprus. Nat. Hazards 2016, 83, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuertes-Gutiérrez, I.; García-Ortiz, E.; Fernández-Martínez, E. Anthropic threats to geological heritage: Characterization and management: A case study in the Dinosaur Tracksites of La Rioja (Spain). Geoheritage 2016, 8, 135–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosher, L.; Kim, D.; Okubo, T.; Chmutina, K.; Jigyasu, R. Dealing with multiple hazards and threats on cultural heritage sites: An assessment of 80 case studies. Disaster Prev. Manag. 2020, 29, 109–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lane, P.J. Future urban growth and archaeological heritage management: Some implications for research activity in Africa. Conserv. Manag. Archaeol. Sites 2011, 13, 134–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaina, F. A risk assessment for cultural heritage in Southern Iraq: Framing drivers, threats and actions affecting archaeological sites. Conserv. Manag. Archaeol. Sites 2019, 21, 184–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.; Hassan, M.; Gull, F. Mycobial deterioration of stone monuments of Dharmarajika, Taxila. J. Microbiol. Exp. 2015, 2, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nwanko, E.A.; Obieluem, U.H.; Anozei, O.O. Monuments as living heritage: The challenges of safety and implications on lost memories. J. Tour. Herit. Stud. 2017, 6, 133–147. [Google Scholar]
- Spennemann, D.H.R.; Watson, M.J. Dietary habits of urban pigeons (Columba livia) and implications of excreta pH—A review. Eur. J. Ecol. 2017, 3, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skandrani, Z.; Lepetz, S.; Prévot-Julliard, A.C. Nuisance species: Beyond the ecological perspective. Ecol. Process 2014, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spennemann, D.H.R.; Pike, M.; Watson, M.J. Behaviour of Pigeon Excreta on Masonry Surfaces. Restor. Build. Monum. 2018, 23, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abegg, M.A.; Cella, F.L.; Faganello, J.; Valente, P.; Schrank, A.; Vainstein, M.H. Cryptococcus neoformans and Cryptococcus gattii isolated from the excreta of psittaciformes in a Southern Brazilian Zoological Garden. Mycopathologia 2006, 161, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasiliu, A.; Buruiana, D. Are birds a menace to outdoor monuments? Int. J. Conserv. Sci. 2010, 1, 83–92. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, M.A.; Ali, M.F.; Bader, N.A.; Khalaphallah, R. The effect of wild pigeon excreta on the wall painting of Ramses II Temple at Aedinet Habu, Luxor. Sci. Cult. 2021, 7, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knotkova, D.; Kreislova, K. Atmospheric corrosion and conservation of copper and bronze. Trans. State Art Sci. Eng. 2007, 28, 107–142. [Google Scholar]
- Spennemann, D.H.; Watson, M. Experimental studies on the impact of bird excreta on architectural metals. APT Bull. J. Preserv. Technol. 2018, 49, 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- Balogh, K.; Slížková, Z.; Kreislová, K. The effects of bird excrements on copper and bronze. In Structural Analysis of Historical Constructions; Aguilar, R., Torrealva, D., Moreira, S., Pando, M.A., Ramos, L.F., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 1940–1948. [Google Scholar]
- Loto, C.; Joseph, O.; Loto, R. Adsorption and inhibitive properties of Camellia sinensis for aluminium alloy in HCI. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2014, 9, 3637–3649. [Google Scholar]
- Bonapace, C.; Sestini, V. Traditional Materials and Construction Technologies Used in the Kathmandu Valley; United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization: Paris, France, 2012; 180p. [Google Scholar]
- Del Monte, M.; Sabbioni, C.J. Chemical and biological weathering of an historical building: Reggio Emilia Cathedral. Sci. Total Environ. 1986, 50, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spennemann, D.H.R.; Pike, M.; Watson, M.J. Effects of acid pigeon excreta on building conservation. Int. J. Build. Pathol. Adapt. 2017, 35, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassi, M.; Chiatante, D. The role of pigeon excrement in stone biodeterioration. Int. Biodeterior. Bull. 1976, 12, 73–79. [Google Scholar]
- Adam, M.; Grübl, P.J. Influence of Pigeon Droppings on the Surface of Building Materials; Audit report No. 195.04 dated August 26, 2004; Technical University of Darmstadt, Institute for Solid Construction: Darmstadt, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ramezanzadeh, B.; Mohseni, M.; Yari, H.; Sabbaghian, S. An evaluation of an automotive clear coat performance exposed to bird droppings under different testing approaches. Prog. Org. Coat. 2009, 66, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Lavenburg, G. Impacts of Bird Droppings and Deicing Salts on Highway Structures: Monitoring, Diagnosis, Prevention; Delaware Center for Transportation, University of Delaware DCT: Newark, DE, USA, 2011; 221p. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, H.E.; Khattab, S.A.; Al-Mukhtar, M. The effect of biodeterioration by bird droppings on the degradation of stone built. In Engineering Geology for Society and Territory; Lollino, G., Giordan, D., Marunteanu, C., Christaras, B., Yoshinori, I., Margottini, C., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 8, pp. 515–520. [Google Scholar]
- Ginez, M.A.; Espinoza-Vázquez, A.; Rodríguez-Gómez, F.J. Evaluation of corrosion in standard bronze with uric acid, chlorides and a mixture of both compounds. ECS Trans. 2018, 84, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spennemann, D.H.R.; Pike, M.; Watson, M.J. Bird impacts on heritage buildings. J. Cult. Herit. Manag. Sustain. Dev. 2018, 8, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Heras, M.; Benavente, D.; de Buergo, M.Á.; Fort, R. Soluble salt minerals from pigeon droppings as potential contributors to the decay of stone based Cultural Heritage. Eur. J. Mineral. 2004, 16, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, T. Deterioration of stone and concrete exposed to bird excreta–examination of the role of glyoxylic acid. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 125, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pudelkiewicz, W.; Stutz, M.; Matterson, L.J. Determination of uric acid in avian excreta by the use of uricase and differential spectrophotometry. Poult. Sci. J. 1968, 47, 1274–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lettieri, M.; Masieri, M.; Frigione, M. Durability to simulated bird guano of nano-filled oleo/hydrophobic coatings for the protection of stone materials. Prog. Org. Coat. 2020, 148, 105900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilieș, D.C.; Marcu, F.; Caciora, T.; Indrie, L.; Ilieș, A.; Albu, A.; Costea, M.; Burtă, L.; Baias, Ș.; Ilieș, M.; et al. Investigations of Museum Indoor Microclimate and Air Quality. Case Study from Romania. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shrestha, S.; Khanal, L.; Pandey, N.; Kyes, R.C. Conservation of Heritage Sites in Kathmandu, Nepal: Assessing the Corrosion Threat from Pigeon Excreta on Metal Monuments. Conservation 2022, 2, 233-243. https://doi.org/10.3390/conservation2020015
Shrestha S, Khanal L, Pandey N, Kyes RC. Conservation of Heritage Sites in Kathmandu, Nepal: Assessing the Corrosion Threat from Pigeon Excreta on Metal Monuments. Conservation. 2022; 2(2):233-243. https://doi.org/10.3390/conservation2020015
Chicago/Turabian StyleShrestha, Saroj, Laxman Khanal, Naresh Pandey, and Randall C. Kyes. 2022. "Conservation of Heritage Sites in Kathmandu, Nepal: Assessing the Corrosion Threat from Pigeon Excreta on Metal Monuments" Conservation 2, no. 2: 233-243. https://doi.org/10.3390/conservation2020015
APA StyleShrestha, S., Khanal, L., Pandey, N., & Kyes, R. C. (2022). Conservation of Heritage Sites in Kathmandu, Nepal: Assessing the Corrosion Threat from Pigeon Excreta on Metal Monuments. Conservation, 2(2), 233-243. https://doi.org/10.3390/conservation2020015






