Animals Traded for Traditional Medicine Purposes in the Kumasi Central Market, Ghana: Conservation Implications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling Procedure and Data Collection
2.3. Data Analysis
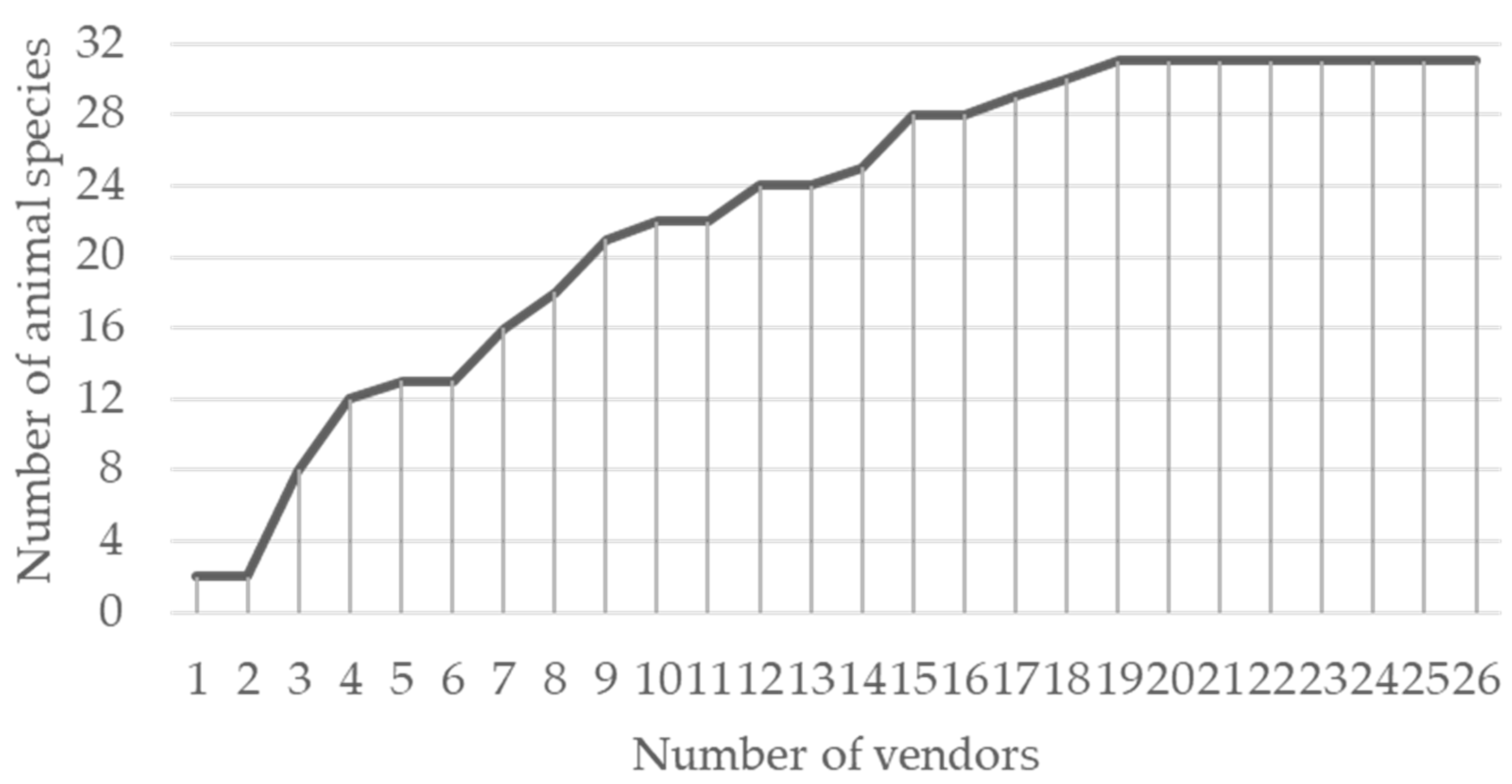
3. Results
3.1. Animal Trade
3.2. Conservation Implications
4. Discussion
4.1. Animal Trade
4.2. Conservation Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Albuquerque, U.P.; Monteiro, J.M.; Ramos, M.A.; de Amorim, E.L.C. Medicinal and Magic Plants from a Public Market in Northeastern Brazil. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 110, 76–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, U.P.; Monteiro, J.M.; Ramos, M.A.; de Amorim, E.L.C.; Alves, R.R.N. Ethnobiological Research in Public Markets. In Methods and Techniques in Ethnobiology and Ethnoecology; Albuquerque, U., Cruz da Cunha, L., de Lucena, R., Alves, R., Eds.; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Cruze, N.; Assou, D.; Coulthard, E.; Norrey, J.; Megson, D.; Macdonald, D.W.; Harrington, L.A.; Ronfot, D.; Segniagbeto, G.H.; Auliya, M. Snake Oil and Pangolin Scales: Insights into Wild Animal Use at “Marché Des Fétiches” Traditional Medicine Market, Togo. Nat. Conserv. 2020, 39, 45–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, F.S.; Fernandes-Ferreira, H.; Léo Neto, N.A.; Brito, S.V.; Alves, R.R.N. The Trade of Medicinal Animals in Brazil: Current Status and Perspectives. Biodivers. Conserv. 2013, 839–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, E.S.; Torres, D.F.; Brooks, S.E.; Alves, R.R.N. The Medicinal Animal Markets in the Metropolitan Region of Natal City, Northeastern Brazil. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 130, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segniagbeto, G.H.; Petrozzi, F.; Aïdam, A.; Luiselli, L. Reptiles Traded in the Fetish Market of Lomé, Togo (West Africa). Herpetol. Conserv. Biol. 2013, 8, 400–408. [Google Scholar]
- Whiting, M.J.; Williams, V.L.; Hibbitts, T.J. Animals Traded for Traditional Medicine at the Faraday Market in South Africa: Species Diversity and Conservation Implications. In Animals in Traditional Folk Medicine: Implications for Conservation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 421–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, V.L.; Moshoeu, T.J.; Alexander, G.J.; Williams, V. Reptiles Sold as Traditional Medicine in Xipamanine and Xiquelene Markets (Maputo, Mozambique). S. Afr. J. Sci. 2016, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, V.; Whiting, M. A picture of health? Animal use and the Faraday Traditional Medicine Market, South Africa. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 179, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, R.R.N.; Rosa, I.L. Trade of Animals Used in Brazilian Traditional Medicine: Trends and Implications for Conservation. Hum. Ecol. 2010, 38, 691–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, R.R.N.; Rosa, I.L.; Albuquerque, U.P.; Cunningham, A.B. Medicine from the Wild: An Overview of the Use and Trade of Animal Products in Traditional Medicines. In Animals in Traditional Folk Medicine: Implications for Conservation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, V.L.; Cunningham, A.B.; Kemp, A.C.; Bruyns, R.K. Risks to Birds Traded for African Traditional Medicine: A Quantitative Assessment. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 105397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hua, N.; Sun, S. Wildlife Trade, Consumption and Conservation Awareness in Southwest China. Biodivers. Conserv. 2008, 17, 1493–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djagoun, C.A.M.S.; Akpona, H.A.; Mensah, G.A.; Nuttman, C.; Sinsin, B. Wild Mammals Trade for Zootherapeutic and Mythic Purposes in Benin (West Africa): Capitalizing Species Involved, Provision Sources, and Implications for Conservation. In Animals in Traditional Folk Medicine: Implications for Conservation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 367–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obiri, B.; Addai, A. People and Plants: A Survey of Economic Botanicals on the Kumasi Central Market. Ghana J. For. 2010, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoye, V. Street Vendor Exclusion in “Modern” Market Planning: A Case Study from Kumasi, Ghana; WIEGO: Manchester, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Solomon-Ayeh, B.; Adams, I.; Decardi-Nelson, I.; Farhan, S. Informal Commerce: Aspects of Congestion in Kumasi Central Market, Ghana. Int. J. Environ. Ecol. Fam. Urban. Stud. 2016, 6, 11–22. [Google Scholar]
- Asase, A.; Oppong-Mensah, G. Traditional Antimalarial Phytotherapy Remedies in Herbal Markets in Southern Ghana. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 126, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falconer, J. Non-Timber Forest Products in Southern Ghana. Main Report; Natural Resources Institute: Chatham, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Van Andel, T.; Myren, B.; Van Onselen, S. Ghana’s Herbal Market. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 140, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boakye, M.K.; Pietersen, D.W.; Kotzé, A.; Dalton, D.L.; Jansen, R. Knowledge and Uses of African Pangolins as a Source of Traditional Medicine in Ghana. PLoS ONE 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boakye, M.K.; Wiafe, E.D.; Ziekah, M.Y. Ethnomedicinal Use of Vultures by Traditional Medicinal Practitioners in Ghana. Ostrich 2019, 90, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boakye, M.K. Influence of Ethnicity on Cultural Use of Pangolins in Ghana and Its Implications on Their Conservation. Ethnobiol. Conserv. 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghana Statistical Service 2010 Population & Housing Census. District Analytical Report: Kumasi Metropolitan. 2014. Available online: https://www2.statsghana.gov.gh/docfiles/2010_District_Report/Ashanti/KMA.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2021).
- Nkansah, M.A.; Hayford, S.T.; Borquaye, L.S.; Ephraim, J.H. Heavy Metal Contents of Some Medicinal Herbs from Kumasi, Ghana. Cogent Environ. Sci. 2016, 2, 1234660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, V.L.; Witkowski, E.T.F.; Balkwill, K. Application of Diversity Indices to Appraise Plant Availability in the Traditional Medicinal Markets of Johannesburg, South Africa. Biodivers. Conserv. 2005, 14, 2971–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUCN. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2020-3. 2020. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/ (accessed on 30 January 2021).
- CITES. The CITES Species. 2021. Available online: https://cites.org/eng/disc/species.php (accessed on 30 January 2021).
- Sodeinde, O.A.; Soewu, D.A. Pilot Study of the Traditional Medicine Trade in Nigeria. TRAFFIC Bull. 1999, 18, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Gbogbo, F.; Daniels, J.K. Trade in Wildlife for Traditional Medicine in Ghana: Therapeutic Values, Zoonoses Considerations, and Implications for Biodiversity Conservation. Hum. Dimens. Wildl. 2019, 24, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, R.; Lopez, L.C.S. An Ethnozoological Survey of Medicinal Animals Commercialized in the Markets of Campina Grande, NE Brazil. Hum. Ecol. Rev. 2010, 17, 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Ntiamoa-Baidu, Y. Wildlife and Food Security in Africa; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Boakye, M.K.; Kotzé, A.; Dalton, D.L.; Jansen, R. Unravelling the Pangolin Bushmeat Commodity Chain and the Extent of Trade in Ghana. Hum. Ecol. 2016, 44, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djagoun, C.A.M.S.; Sogbohossou, E.A.; Kassa, B.; Akpona, H.A.; Amahowe, I.O.; Djagoun, R.; Sinsin, B. Trade in Primate Species for Medicinal Purposes in Southern Benin: Implications for Conservation. TRAFFIC Bull. 2018, 30, 48–56. [Google Scholar]
- Ntiamoa-Baidu, Y. Conservation Education in Threatened Species Management in Africa. Bird Conserv. Int. 1995, 5, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soewu, D.A. Wild Animals in Ethnozoological Practices Among the Yorubas of Southwestern Nigeria and the Implications for Biodiversity Conservation. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2008, 3, 421–427. [Google Scholar]

| Class | Family | Scientific Name | Common Name | Parts Sold | IUCN Status | CITES Appendix | Ghana Schedule |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actinopterygii | Malapteruridae | Malapterurus electricus | Electric fish | Skin | Least Concern | Not Listed | Not Listed |
| Aves | Accipitridae | Aquila spp. | Eagle | Head and feathers | Appendix II | I | |
| Aves | Accipitridae | Necrosyrtes monachus | Hooded vulture | Head, claw, beak | Critically Endangered | Appendix II | I |
| Aves | Accipitridae | Milvus migrans | Black kite | Whole (dried) | Least Concern | Appendix II | I |
| Aves | Columbidae | Spilopelia senegalensis | Laughing dove | Whole (live) | Least Concern | Not Listed | II |
| Aves | Columbidae | Streptopelia semitorquata | Red-eyed dove | Whole (live) | Least Concern | Not Listed | II |
| Aves | Corvidae | Corvus albus | Pied crow | Beak, feathers | Least Concern | Not Listed | |
| Aves | Phasianidae | Gallus domesticus | Domestic chicken | Whole (live), eggs | Domesticated | Not Listed | |
| Aves | Psittacidae | Psittacus erithacus | African grey parrot | Whole (live) | Endangered | Appendix I | II |
| Gastropoda | Achatinidae | Achatina spp. | Giant African snail | Shell | Least Concern | Not Listed | |
| Reptilia | Chamaeleonidae | Chamaeleon spp. | Chameleon | Whole (dried) | Least Concern | Appendix II | |
| Reptile | Crocodylidae | Crocodylia spp. | Crocodile | Skin, eggs | Appendix II | I | |
| Reptilia | Pythonidae | Python sebae | African Rock python | Skin, fat, bones | Least Concern | Appendix II | II |
| Reptilia | Pythonidae | Python regius | Royal (ball) Python | Skin, fat, bones | Least Concern | Appendix II | II |
| Reptilia | Testudinidae | Kinixys | Tortoise | Shell, head (dried), eggs | Appendix II | II | |
| Mammalia | Bovidae | Tragelaphus scriptus | Bushbuck | Skin, horn | Least Concern | Not Listed | II |
| Mammalia | Bovidae | Bos taurus | Bull | Horn | Domesticated | Not Listed | |
| Mammalia | Camelidae | Camelus dromedarius | Camel | Skin, skull, bones | Domesticated | Not Listed | |
| Mammalia | Cercopithecidae | Chlorocebus sabaeus | Green monkey | Skin | Least Concern | Appendix II | II |
| Mammalia | Cercopithecidae | Erythrocebus patas | Patas monkey | Skin | Near Threatened | Appendix II | II |
| Mammalia | Cercopithecidae | Papio anubis | Olive baboon | Skin | Least Concern | Appendix II | III |
| Mammalia | Civettictis | Civettictis civetta | African civet | Skin | Least Concern | Appendix III | II |
| Mammalia | Elephantidae | Loxodonta africana | African bush elephant | Skin, bones | Vulnerable | Appendix II | I |
| Mammalia | Equidae | Equus asinus | Donkey | Skin | Domesticated | Appendix I | |
| Mammalia | Equidae | Equus caballus | Horse | Skin, tail(hair) | Domesticated | ||
| Mammalia | Felidae | Panthera leo | Lion | Skin, bones | Vulnerable | Appendix II | I |
| Mammalia | Felidae | Panthera pardus | Leopard | Skin, bones | Vulnerable | Appendix I | I |
| Mammalia | Herpestidae | Crocuta crocuta | Spotted hyena | Skin, bones | Least Concern | Not Listed | II |
| Mammalia | Hystrix | Hystrix cristata | Crested porcupine | Quill | Least Concern | Not Listed | II |
| Mammalia | Manidae | Phataginus tricuspis | White-bellied pangolin | Scales | Endangered | Appendix I | I |
| Mammalia | Pteropodidae | Eidolon helvum | Straw-coloured fruit bat | Whole (dried) | Near Threatened | Not Listed |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boakye, M.K.; Agyemang, A.O.; Wiafe, E.D.; Dossou-Yovo, H.O.; Ziekah, M. Animals Traded for Traditional Medicine Purposes in the Kumasi Central Market, Ghana: Conservation Implications. Conservation 2021, 1, 113-120. https://doi.org/10.3390/conservation1020010
Boakye MK, Agyemang AO, Wiafe ED, Dossou-Yovo HO, Ziekah M. Animals Traded for Traditional Medicine Purposes in the Kumasi Central Market, Ghana: Conservation Implications. Conservation. 2021; 1(2):113-120. https://doi.org/10.3390/conservation1020010
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoakye, Maxwell Kwame, Alfred Ofori Agyemang, Edward Debrah Wiafe, Hubert Olivier Dossou-Yovo, and Meyir Ziekah. 2021. "Animals Traded for Traditional Medicine Purposes in the Kumasi Central Market, Ghana: Conservation Implications" Conservation 1, no. 2: 113-120. https://doi.org/10.3390/conservation1020010
APA StyleBoakye, M. K., Agyemang, A. O., Wiafe, E. D., Dossou-Yovo, H. O., & Ziekah, M. (2021). Animals Traded for Traditional Medicine Purposes in the Kumasi Central Market, Ghana: Conservation Implications. Conservation, 1(2), 113-120. https://doi.org/10.3390/conservation1020010






