Abstract
One of the most significant global challenges for humans is environmental pollution. The technology to control this problem is the utilization of semiconductors as photocatalysts. In the current study, iron-doped titania nanotubes (Fe/TiNTs) with increased photocatalytic effect were synthesized via a modified hydrothermal method. The products were characterized by X-ray powder diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), gas adsorption, electron spin resonance (ESR) and UV–Vis diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (DRS). TEM results indicated that Fe/TiNTs have a tubular and uniform structure with an average outer diameter of 23–48 nm and length of 10–15 µm. ESR and DRS revealed that Fe3+ ions were successfully introduced into the TiNT structure by replacing Ti4+ ions. An enhanced light absorption in the range of 400–600 nm additionally indicated successful doping. The band gap was narrowed as iron wt% was increased. The photocatalytic activity was evaluated by the degradation of methyl orange (MO) in the presence of Fe/TiNTs and TiTNs by monitoring the degradation of MO under UV light irradiation. An acceleration on the hydration of Portland cement was observed in the presence of 2.0 wt% Fe/TiNTs. Fe/TiNTs can be used as a nanomaterial in cement-based building materials to provide self-cleaning properties to the surface of concrete even in indoor environments.
1. Introduction
One serious outstanding concern and a global problem for humanity is environmental pollution and destruction, for instance, NOX, algae, and organic wastes. As the world’s population is increasing and the world becomes industrialized, the demand for a clean environment and natural energy sources is increasing. The release of industrial pollutants and toxic agents into the atmosphere and drinking water becomes a significant challenge facing the world. The promising technology to control environmental pollution and remedy air and water contamination is the utilization of semiconductor materials as a photocatalyst. TiO2 nanoparticles and nanotubes have interesting and excellent properties, which have attracted much attention in recent years. Due to its low cost, and chemical and thermal stability, TiO2 is an interesting and widely used semiconductor among the various photocatalysts. The history of applying TiO2 as a catalyst goes back to work carried out by Fujishima and Honda in 1972 by splitting water into oxygen and hydrogen [1]
Basically, TiO2 oxidizes organic and inorganic wastes through catalyzing the respective redox processes. However, the practical application of TiO2 as a photocatalyst is limited, due to its wide band gap (3.2 eV), as it is only able to utilize the UV range of solar light. The contribution of UV light to the total solar light is only 3–5% [2]. Furthermore, UV light cannot pass through window glass, limiting indoor use of TiO2 as a catalyst. Furthermore, the possibility of recombination of photogenerated electron and hole pairs is high in TiO2 due to the short charge separation distance within the particle [3]. To overcome these challenges and improve its activity under the range of UV and visible light, it is necessary to generate new sub-energy levels by doping TiO2 nanoparticles with foreign ions dopants. Numerous types of research have been conducted on the modification of TiO2 nanoparticles by doping and co-doping with various cations and anions so far. For example, J. Ma et al. [4] synthesized Fe-doped TiO2 nanoparticles by a facile co-precipitation method using Fe(NO3)3·9H2O and Ti(SO4)2 as a Ti precursor. They reported that doping TiO2 with Fe influenced the UV–Vis absorption, enhanced visible light absorption, and minimized electron–hole recombination caused by the incorporation of iron ions into the crystal lattice of TiO2. Ye Cong et al. [2] co-doped TiO2 with nitrogen and Fe3+ in a homogeneous precipitation hydrothermal process. They mentioned that the nitrogen and Fe3+-ions doping induced the formation of new states close to the valence band and conduction band, respectively, and this phenomenon leads to the narrowing of the band gap and greatly improves the photocatalytic activity in the visible light region. H. Khan et al. [3] synthesized Fe-TiO2 nanoparticles by a facile sol–gel method and stated that undoped TiO2 shows an absorption edge in the UV region while this was shifted towards the visible region in the case of Fe-doped TiO2 nanoparticles. They described that the shift was a result of the d−d transition of Fe3+ (2T2g → 2A2g, 2T1g) and the charge transfer transition between interacting iron ions (Fe3+ + Fe3+ → Fe4+ + Fe2+). L. Wen et al. [5] prepared the Fe-doped TiO2 by hydrothermal treatment using TiCl4 and Fe(NO3)3 as the precursors of TiO2 and Fe ions. They claimed that Fe ions are more easily doped on the surface of TiO2 than in bulk. They noted that the ions on the surface can form an intermediate interfacial transfer pathway for electrons and holes. K. Elghniji et al. [6] also synthesized Fe-doped TiO2 nanoparticles by an acid-catalyzed sol–gel method. They confirmed by electron spin resonance analysis (ESR) that Fe3+ ions are successfully doped in the TiO2 lattice by substituting Ti4+. N. Roy et al. [7] synthesized Fe-doped TiO2 nanocrystals by hydrothermal treatment using titanium tetraisopropoxide and Fe-(SO4)·7H2O as the precursors of TiO2 and Fe ions. They reported the reduction in overpotential for the electrochemical oxygen evolution reaction (OER) using transition metal (TM)-doped TiO2 nanocrystals (NCs). They assigned reduction in overpotential to the splitting of d orbitals of doped TM in the TM-doped TiO2 NCs and, of course, their interactions with oxyradicals made the OEP possible. They also mentioned that the change in the original pearl color of undoped TiO2 NCs and UV–visible absorption spectra is an evident of orbital splitting of TM in TM-doped TiO2. R. Shwetharani et al. [8] synthesized a “Fe-induced titania” nanostructure at high calcination temperature through a wet impregnation technique. They stated that a highly reactive tetragonal anatase phase with a dispersed nanospheroid structure is existing in the Fe-induced titania which is a desired photocatalyst for water molecules. Their product exhibits a remarkably high photocatalytic capacity to evolve hydrogen, to an extent of 850 mmol/5 mg within 40 min. Next to these examples, a large number of other publications have published on the doping of TiO2 nanoparticles [9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20].
In addition to the work that has been carried out on the doping of TiO2 nanoparticles to date, there has also been some research on the modification of TiO2 nanotubes (TiNTs) by doping with foreign ions [21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30]. But few of them have used Fe3+ ions as doping agent [31,32,33,34,35,36,37]. Therefore, this paper deals with the study of TiNTs doped with Fe3+-ions via a modified hydrothermal process. A different synthesis process of hydrothermal approach was utilized to synthesize TiNTs. Without using an autoclave, TiNTs and Fe/TiNTs were synthesized in one step in a Teflon flask. This is a facile approach for the synthesis of Fe/TiNTs. Since the diameter of Fe3+-ions is almost identical to Ti4+, doping with Fe3+ -ions was preferred.
The authors of this work previously reported the applications of Fe-doped TiNTs (Fe/TiNTs) on the hydration of tricalcium silicates. An improvement in the hydration was observed and a strong interaction between Fe/TiNTs and Ca2+ was found [38]. This time, we applied to the Portland cement for the first time to investigate its reactivity during 24 h hydration. Also, it was revealed that TiNTs can improve the performance of concrete, especially of UHPC, for instance, mechanical and self-cleaning properties improvement due to the addition of TiO2 [39,40,41].
2. Experimental Procedure
2.1. Materials and Methods
The precursors were titanium (IV) oxide (anatase, 99.6% metal basis (Alfa Aesar, Haverhill, MA, USA)) and NaOH (Geyer Th. GmbH & Co., KG, Berlin, Germany). Fe(NO3)3·9H2O (Fluka AG, Darmstadt, Germany) were used as an iron source for doping and the deionized water and HCl ((37%), Fluka AG) were used for washing purposes. CEM I 52.5R (Dyckerhof GmbH, Wiesbaden, Germany) was used as a white cement source.
A modified hydrothermal method was utilized to fabricate both TiNTs and Fe/TiNTs, by using 3 g anatase powder with 200 mL of 10 M NaOH aqueous suspension in a 250 mL PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) flask in the presence and absence of Fe(NO3)3·9H2O. Samples with 0.0, 0.07, 0.1, 0.3, 1.0, and 2.00 wt% of iron percentages with respect to anatase were prepared and the mixtures were firstly stirred for 30 min. Then, they were sonicated for 20 min to obtain better dispersion. Prior to addition of Fe(NO3)3·9H2O to the dispersion, they were dissolved in 10 mL deionized water. Afterward, the dispersions were refluxed for 24 h by heating at 130 ± 5 °C in an oil bath. The products were fabricated after 24 h. Then they were firstly washed with deionized water till pH reached 7 and then washing was continued with a 0.1 M HCl solution. Afterward, once again, washing with deionized water was performed until pH reached 7. Finally, they were firstly dried at 80 °C for 8 h then calcinated at 400 °C for 1 h to assist the doping process.
2.2. Methods and Sample Preparation
Synthesized Fe/TiNTs and TiNTs were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM-Quanta 250 FEG ESEM, FEI Deutschland GmbH, Dreieich, Germany) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM-FEI Talos F200X) to study the morphology and dimension of Fe/TiNTs and TiNTs. The Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area of the TiNTs was determined by using Micromeritics ASAP 2020 (Micromeritics GmbH, Unterschleißheim, Germany). The specific surface was derived from the N2-isotherms, and pore size distributions of the samples were evaluated using the Barrett–Joyner–Halenda (BJH) method. To check the phase composition of Fe/TiNTs and TiNTs, Powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD) diffractograms were recorded at room temperature on an STOE Stadi P powder diffractometer (STOE, Darmstadt, Germany) in Debye–Scherrer setup (capillary inner diameter: 0.48 mm) by using Ge (111)-monochromated Cu-Kα1 radiation (154.0596 pm) and a position-sensitive detector. ESR measurements were carried out using an X-band MiniScope MS5000 spectrometer (Magnettech by Freiberg Instruments) with field homogeneity of ±5 μT within the sample region, 0.2 mT field modulation, and 100 kHz modulation frequency. The specimens were filled in 50 µL capillary tubes and measured at room temperature acquiring three scans, each for 600 s at 50 mW microwave power. The background was measured under the same conditions and subtracted from the spectra. The diffuse reflectance spectra of both TiNTs and Fe/TiNTs were measured to study the possible absorption of light in visible region due to doping and also to determine the optical band gap. The measurements were carried out with an UV/VIS/NIR photospectrometer Cary 5000 from Varian (Agilent Technology, Germany) equipped with an integrating sphere for diffuse reflectance measurements. The influence on the Portland cement hydration of Fe-doped TiNTs was compared to undoped TiNTs by using an isothermal calorimetry analysis device (DCA ToniCalHexa, Technik Baustoffprüfsysteme GmbH, Berlin, Germany) at 25 °C. Sample preparation was carried out by the addition of 2.0 wt% of both Fe/TiNTs and TiNTs in Portland cement. Pure Portland cement was used as a control, the water-to-cement ratio (w/c) was set to 0.5, and the measurement was carried out for 24 h.
The photocatalytic activities of the 2.0 wt% Fe-doped TiO2 and TiNTs samples under UV light were evaluated based on the degradation rate of methyl orange (MO). A methyl orange solution (10 mg L−1, analytic grade, Merck) in deionized water (<0.16 μS) was chosen as the test solution. The cylinders were filled with a mixture of 10 mg of photocatalyst in 10 mL of dye solution. The mixture was magnetically stirred and illuminated. For illumination, a light-emitting diode (LED)–UV lamp (365 nm, 680 mW cm−2, SPCM-0800, DUSA) was used. After intervals of 2 h and 8 h, 2 mL of the mixture was taken out, centrifuged with 5000 rpm for 10 min, and then the solution was analyzed with an ultraviolet–visible (UV–Vis) spectrometer (Lambda XLS+; Perkin Elmer, Rodgau, Germany).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Synthesized Fe/TiNTs
- Morphology analysis
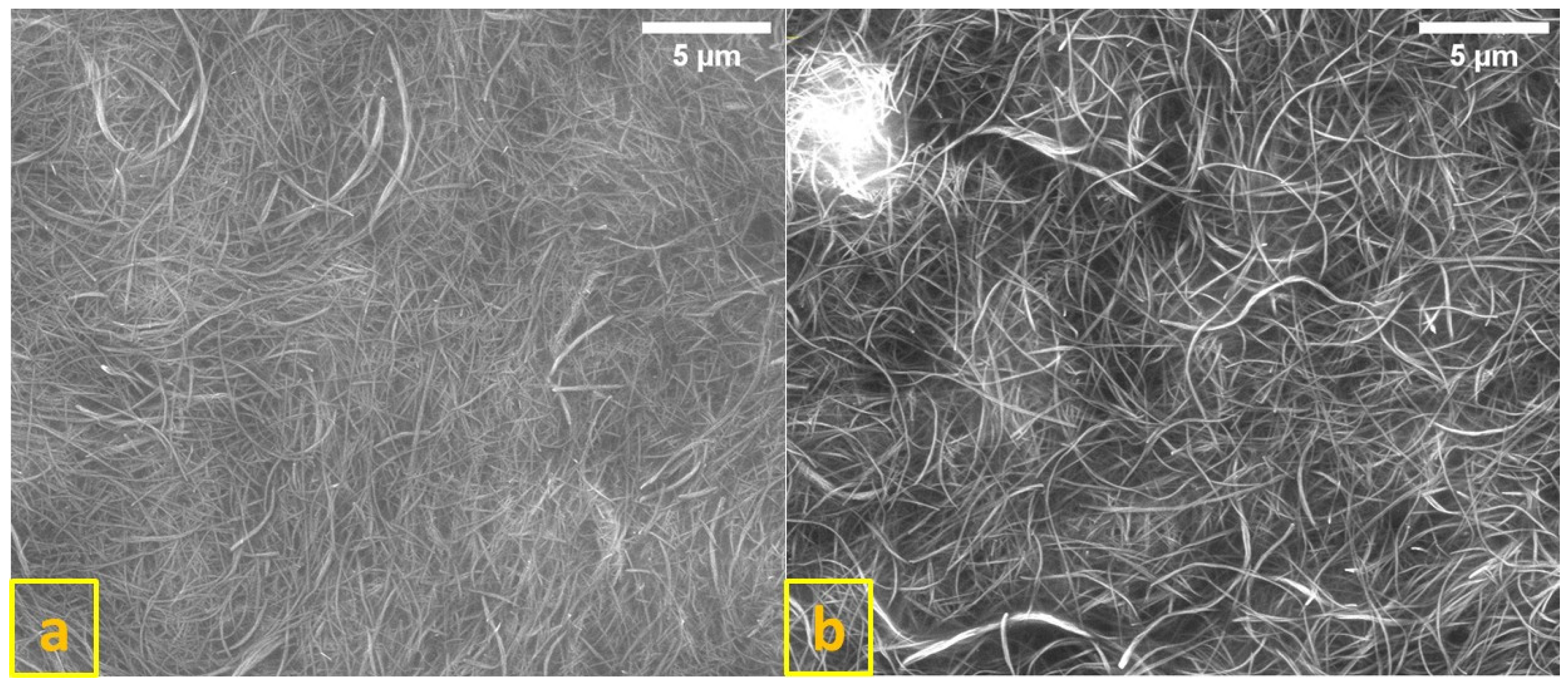
Figure 1 shows SEM images of TiNTs and Fe/TiNTs synthesized with 1.0 wt% of Fe3+-ions. There are no differences in the average morphology of both TiNTs and Fe/TiNTs, having a tubular and uniform structure with an average outer diameter of 23–48 nm and length of 10–15 µm, respectively. This indicates that the doping process does not change the morphology of nanotubes.
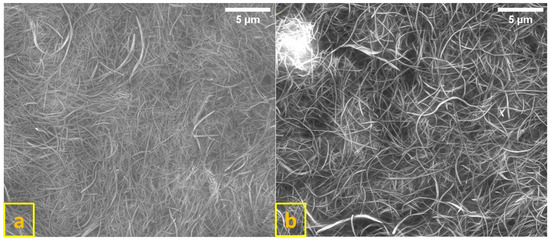
Figure 1.
SEM images of TiNTs (a) and 1.0 wt% Fe/TiNTs (b).
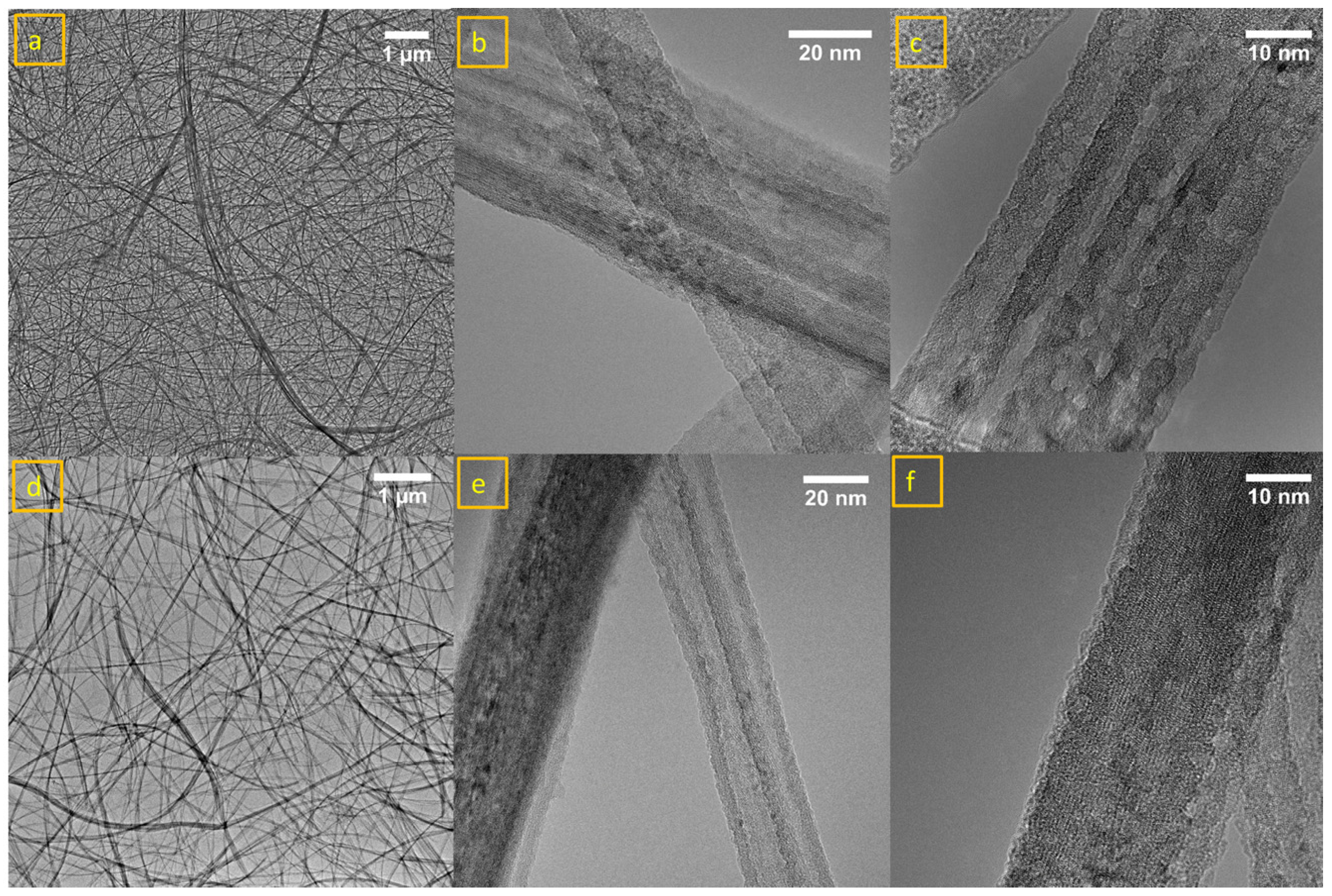
TEM images in Figure 2 confirmed the SEM results and also proved that nanotubes were hollow and tubular in structure. Furthermore, it is observed from TEM images that nanotubes were multilayered and showed a variance in diameters for both TiNTs (a, b, c) and Fe/TiNTs (d, e, f).
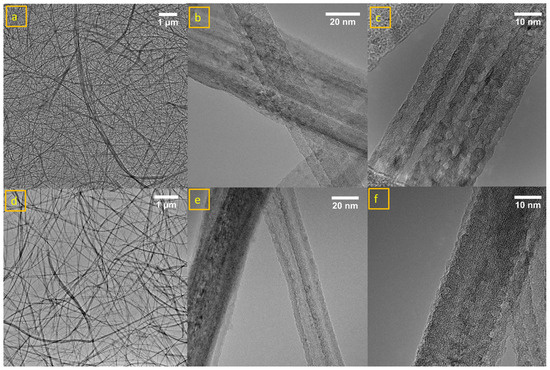
Figure 2.
TEM images of TiNTs (a–c) and 1.0 wt% Fe/TiNTs (d–f).
Figure 2c clearly shows the multilayered structure of the TiNTs. The dispersion of the nanotubes can be depicted in Figure 2a,d for TiNTs and 1.0 wt% of Fe/TiNTs. While the shape and structure of the Fe/TiNTs is comparable to the TiNTs and within the deviations observed within the single sample sets, a slightly improved dispersion is observed with the doped sample. The diameters of nanotubes for TiNTs in one region is 23–24 nm and 47–48 nm shown in Figure 2b, while this in another region is 35 nm, as shown in Figure 2c. In the case of Fe/TiNTs in one region is 24–29 nm and 39–42 nm, shown in Figure 2e, and in the other region, it is 32 nm, shown in Figure 2f. TEM shows smaller diameter for Fe/TiNTs compared to TiNTs, and interspaces between the layers of Fe/TiNTs are too close, and are not clearly visible. On the other hand, in the case of TiNTs, the layers of nanotube are clearly visible.
- Phase analysis
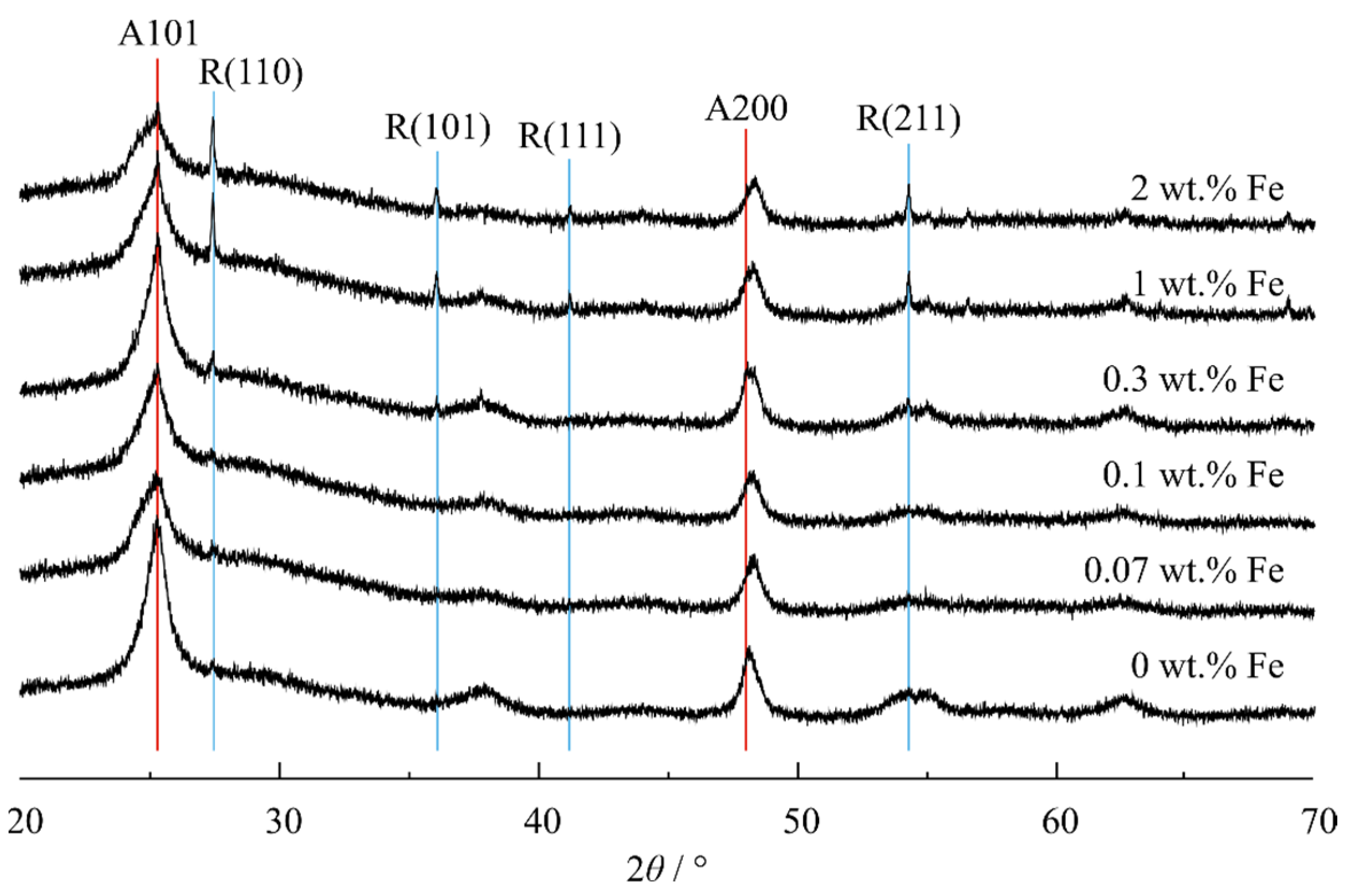
The PXRD diffractograms (represented in Figure 3) for the Fe/TiNTs with different Fe(III) content, which were heat-treated at 400 °C in air for an hour, show the presence of anatase TiO2 (ICSD coll. code 154604), and at high Fe3+ concentration, the presence of rutile.
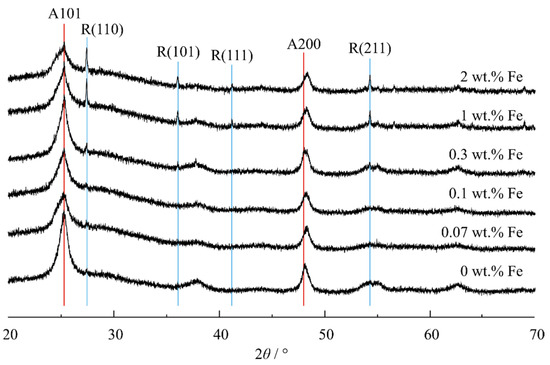
Figure 3.
XRD patterns of Fe/TiNTs and TiNTs.
The TiNTs (undoped) annealed at 400 °C show only anatase reflections (ICSD Coll. Code 63711) with broad reflections but starting at 0.30 wt% Fe, the presence of rutile (ICSD Coll. Code 63710) is already very obvious, suggesting that Fe3+ promotes a phase transformation to a rutile phase which is bulk, i.e., a phase separation from nanocrystalline anatase forming bulk rutile. The FWHM of the (101) anatase plane increases from ~1° in the undoped TiNT to ~1.4° in the Fe/TiNT sample with 2.00 wt% Fe. Furthermore, the anatase (200) reflection shifts by ~0.2° to the right from the undoped to the doped sample with the highest Fe content, indicating a contraction of the unit cell along the a and b dimensions due to a slightly smaller Fe3+ ionic radius (0.64 Å) than Ti4+ (0.68 Å). Thus, in the synthetic route used for doping of Fe into anatase TiNTs, a phase separation of rutile (presumably free of Fe3+ and other defects) occurred simultaneously at higher Fe3+ concentration. No reflection for eventually formed crystalline Fe2O3 was observed in the XRD pattern, which indicates that the iron atoms are incorporated into the structure of TiO2. The presence of amorphous Fe2O3 is unlikely, because after a heat treatment over 150 °C, any possibly formed amorphous Fe2O3 should be converted into a crystalline form [42].
The formation of rutile could be due to the surface oxygen vacancy concentration of anatase grains increasing in Fe/TiNTs [43]. Mixed phases of anatase and rutile have previously been shown to outperform pure anatase or pure rutile materials in photocatalytic applications, which was attributed to a band alignment between the polymorphs. The combination of the added states by the dopant and the induced band alignment, thus, are promising an enhanced photocatalytic performance of the Fe/TiNTs.
- Specific surface area and pore size distribution
The specific surface area of the hydrothermal Fe/TiNTs and TiNTs was determined by both the Brunauer–Emmet–Teller and Barrett–Joyner–Halenda methods, and the latter is specifically useful for the determination of pore diameters from gas sorption isotherms.
Table 1 shows the BET-specific surface area and BJH surface area of pores of TiNTs doped with different weight percentages of Fe3+.

Table 1.
Specific surface area (BET) and surface area of pores (BJH) of Fe/TiNTs.
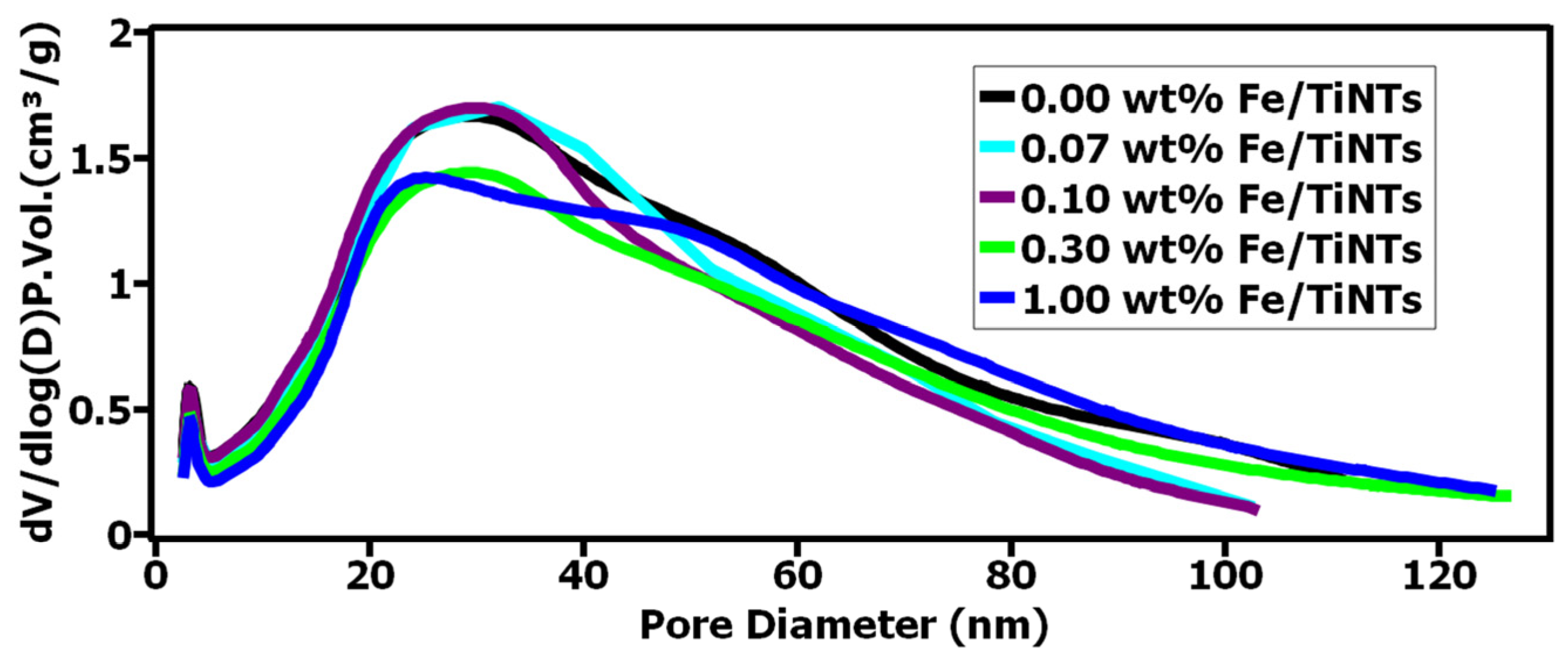
A decrease in the BET-specific surface area was observed when the concentration of Fe3+ ions was increased due to the doping process. The doping caused the formation of nanotubes with smaller diameters confirmed by isotherm plots (explained at the end of this part). Changes in the diameter of some nanotubes could have caused such a decrease in BET-specific surface area. The high values of BET are due to a multilayer of nanotubes which were verified with TEM analysis. Figure 4 shows the pore size distribution of Fe/TiNTs and TiNTs using the BJH method. It indicates that most of the pores have diameters in the range of 20–40 nm and these pores are attributed to empty spaces as a result of hollow nanotubes, and pores with bigger diameters could be due to agglomeration and generated bundles of nanotubes. Similarly, if we look at the pore diameter between 20–40 nm, a decrease in the pore diameter occurs at a critical dopant concentration of 1.0 wt% Fe, with a change in the line shape to coalesced bimodal, starting at 0.3 wt%. This is in good agreement with TEM results. TEM shows that overall diameters of 1.00 wt% Fe/TiNTs are smaller than normal TiNTs. The pore volume was also decreased at this particular range of diameters for higher-doped samples. Two possible reasons might be caused by these phenomena. The first one is some blockage of Fe/TiNTs might have occurred during the washing process by the free iron ions. The second possibility could be the formation of thicker layers of Fe/TiNTs generating smaller interspaces between layers. As a result of these findings, the BET surface area of Fe/TiNTs was decreased compared to TiNTs, which is in good agreement with the findings.
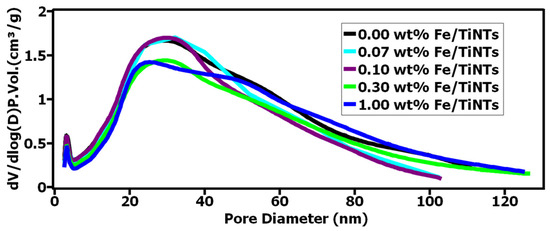
Figure 4.
Barrett–Joyner–Halenda (BJH) pore size and volume analysis of Fe/TiNTs and TiNTs.
From Table 1, it furthermore can be deduced that the cumulative surface area of pores determined by the BJH method is higher with respect to the BET surface area. Thus, it can be concluded that all samples contain micropores. The BET surface area is expected to be higher than the surface area calculated by the BJH method. The BET surface area was calculated within the range of adsorption relative pressure of 0.05–0.3, in which the monolayer formed. The BJH is based on the Kelvin equation and it calculates the width of the defined shape pores, which means, in this method, that the shape of the pore was ideal, e.g., spherical pore, conical pore, slit pore, or others. With the BJH method, the surface area of the pores from BJH can be calculated. Normally, BET is higher than BJH because BET calculates overall surface areas, whereas BJH only calculates the surface areas of pores. However, in our samples, the agglomeration of TiNTs generated new “pores”, which will be treated as a specific new type of pores by the BJH model. Therefore, the BJH is higher than BET. Other than that, the BJH model uses different shapes for the pores which will generate a huge difference in the surface area results.
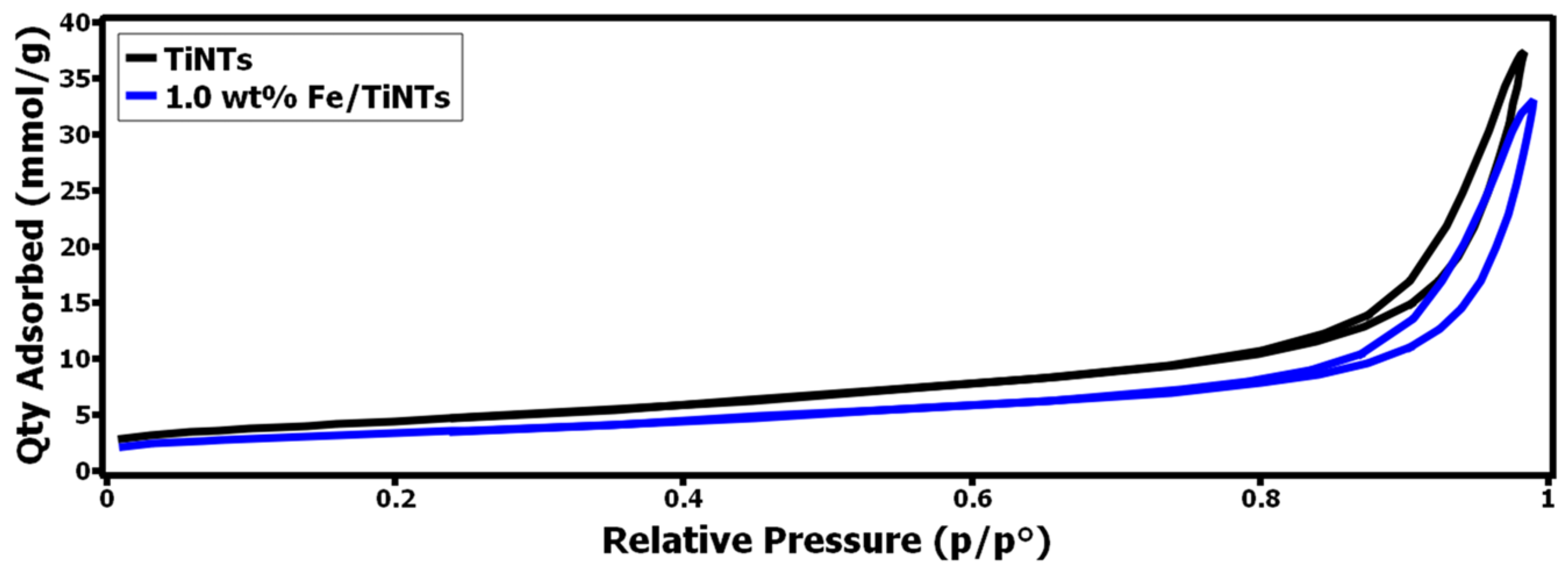
On the other hand, when we check the isotherms, in Figure 5, the Fe-doped amount is higher (1.0 w% Fe/TiNTs, the blue isotherm just drawn below the black isotherm, which means the blue one has fewer pores than the black one, which is TiNTs).
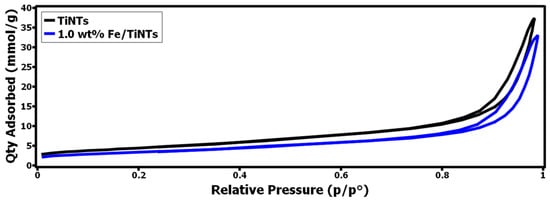
Figure 5.
Isotherm plots for 1.0 wt% F/TiNTs and TiNTs.
- Incorporation of Fe3+ ions into the crystal structure of TiNTs
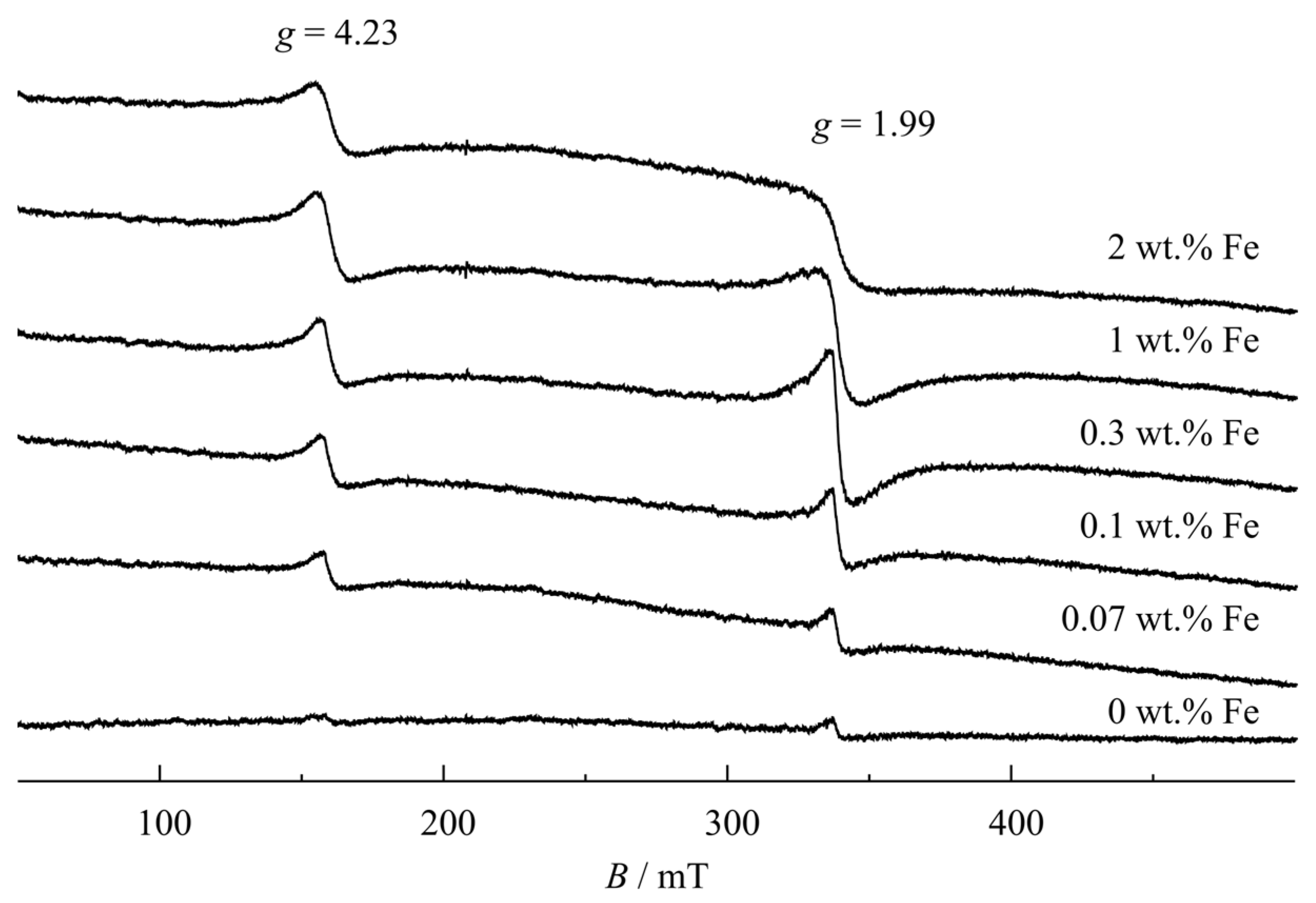
ESR was used to study the doping of Fe3+ into TiNTs. It is a sensitive spectroscopic technique for examining paramagnetic species, and can detect small quantities down to 0.01 wt% Fe3+ dopant level and give information about the environment of the paramagnetic Fe3+- dopant ions within Fe/TiNTs [6]. Thus, continuous-wave ESR spectra of Fe/TiNTs with various Fe3+ concentrations were measured at room temperature (Figure 6).
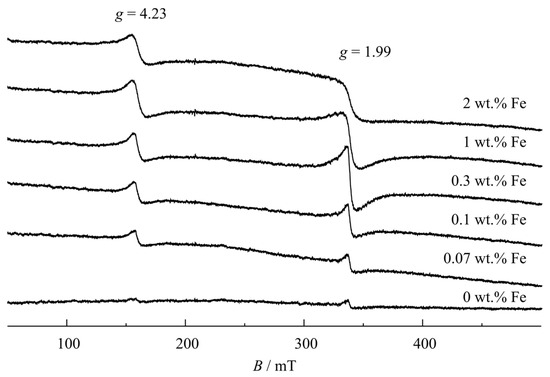
Figure 6.
ESR spectra of pure and Fe-doped TiNTs with different concentrations.
All of the ESR spectra for Fe/TiNTs samples contain two broad single-line resonances. One resonance occurs at g = 1.99 with a symmetric line shape and the other at g = 4.23 with a very slightly asymmetric line shape, the former being more than twice bigger than the latter and the peak-to-peak widths approx. 8.5 and 9 mT for 0.3% Fe3+ loading, respectively. Both of these resonances are also present with very small intensity in the pure TiNTs sample. The high-field resonance (g = 1.99) is assigned to a substitutional high-spin (S = 5/2) at the only octahedral Ti site in anatase, and the low-field (g = 4.23) to a Ti site next to a charge-compensated O vacancy [44,45,46]. No additional resonance is resolved for the rutile side phase in the high Fe3+-containing samples because its incorporation into rutile is reported to require higher than 400 °C heat treatment [47].
Therefore, the ESR results are in agreement with the incorporation of Fe3+ ions into the crystal structure of anatase TiNTs.
- Absorption shift from UV light to visible light and determination of band gap
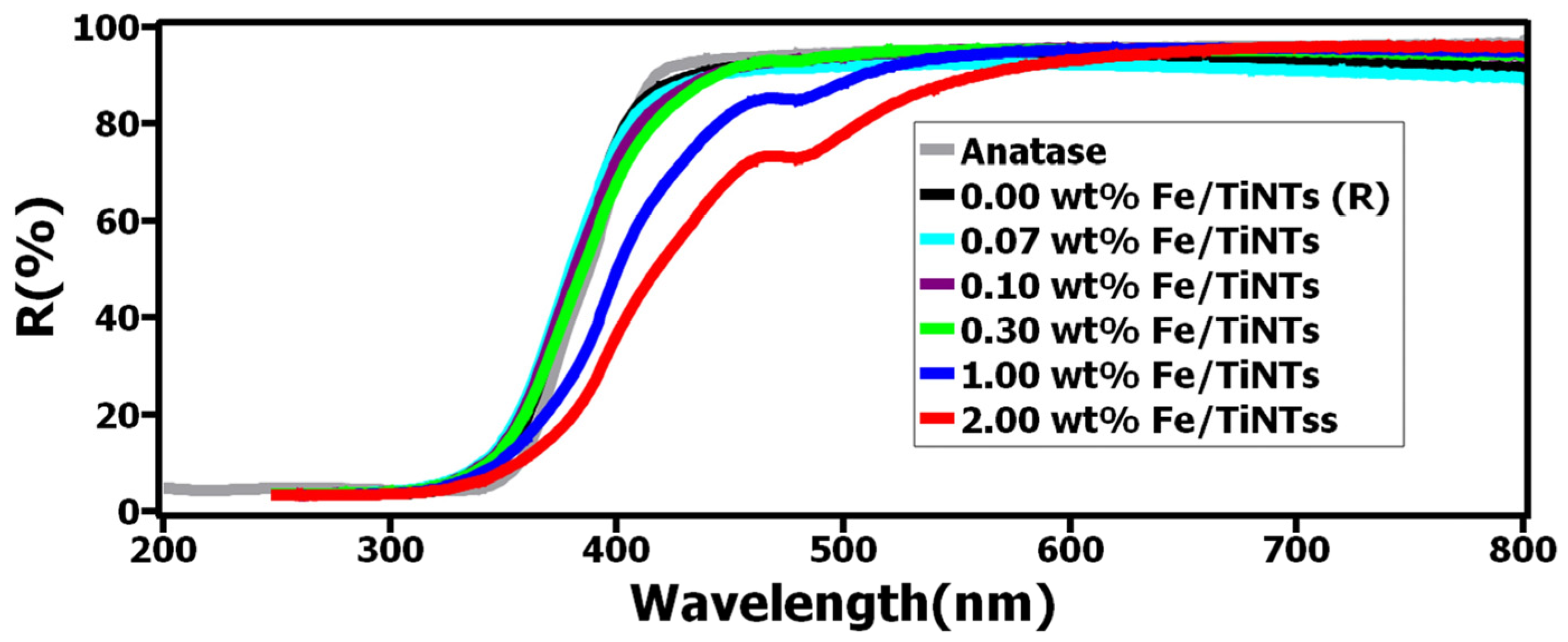
To study the light absorption behavior of Fe/TiNTs, UV–Vis diffuse reflectance (DRS) of the TiNTs with different amounts of Fe doping was measured. Spectra of TiNTs and Fe/TiNTs are shown in Figure 7. It is observed that TiNTs only absorb in the UV region (>400 nm), while Fe/TiNTs show considerable absorption in the visible region.
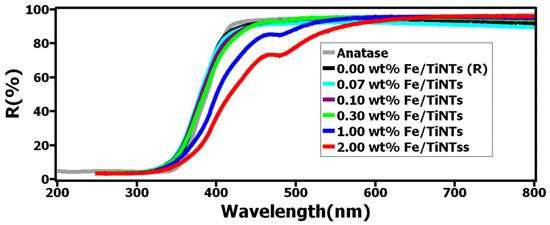
Figure 7.
UV–Vis diffuse reflectance spectra of TiNTs and Fe/TiNTs.
This enhancement is observed in the range of 400 to 600 nm, particularly with the higher concentration of dopant, where the absorption edge becomes more apparent and shifts further into the visible light region.
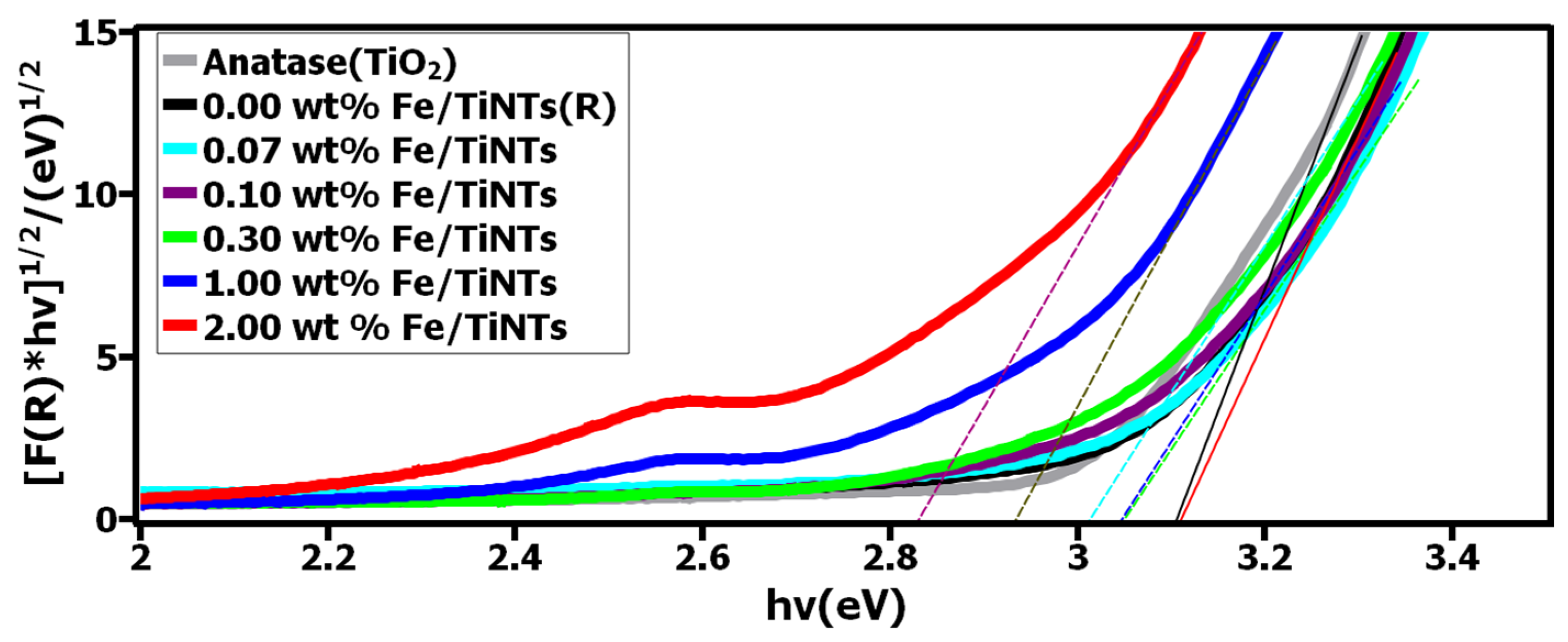
The Kubelka–Munk function was used to analyze diffuse reflectance data, from which the optical band gap was estimated via a Tauc plot, according to the following equation:
F(R) = (1 − R)2/2R
By plotting [F(R)*hv]1/2 vs. hv and extrapolating the linear part of the curve to [F(R)*hv]1/2 = 0, the indirect band gap was determined for all samples [48]. R describes the absolute value of reflectance, h the Plank constant, and v the light frequency. Figure 8 shows the measured band gap for Fe/TiNTs, TiNTs, and anatase nanoparticles as a second reference. It is clearly observed that the band gap for Fe/TiNTs was narrowed compared to the references (TiNTs and anatase NP). The band gap for the anatase NP was found to be 3.15 eV and 3.14 eV for TiNTs. A trend of the narrowing of the band gap is observed (3.15, 3.14, 3.10, 3.07, 2.95, 2.84 eV) as the amount of dopant in Fe/TiNTs is increased (0.0, 0.07, 0.1, 0.3, 1.0, 2.0 wt%). These results are in good agreement with the literature [15,16,34,49]. The shifting of absorption from UV to the visible region and narrowing of the band gap for Fe/TiNTs is ascribed to doping transition metal into TiNTs, more precisely to an electronic transition from the valence band of the dopant (Fe3+/Fe4+) to the conduction band of TiO2 [3]. As a consequence, the doping, in turn, should considerably enhance the photocatalytic properties of TiO2 under visible light illumination.
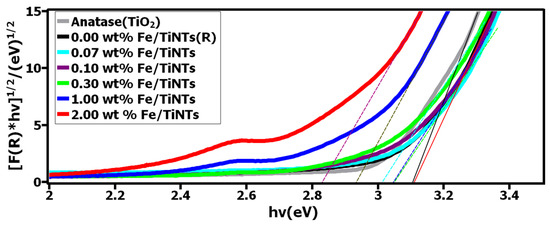
Figure 8.
Plots of [F(R)*hv]1/2 vs. hv of the TiNTs and Fe/TiNTs.
3.2. The Course of Hydration Reaction
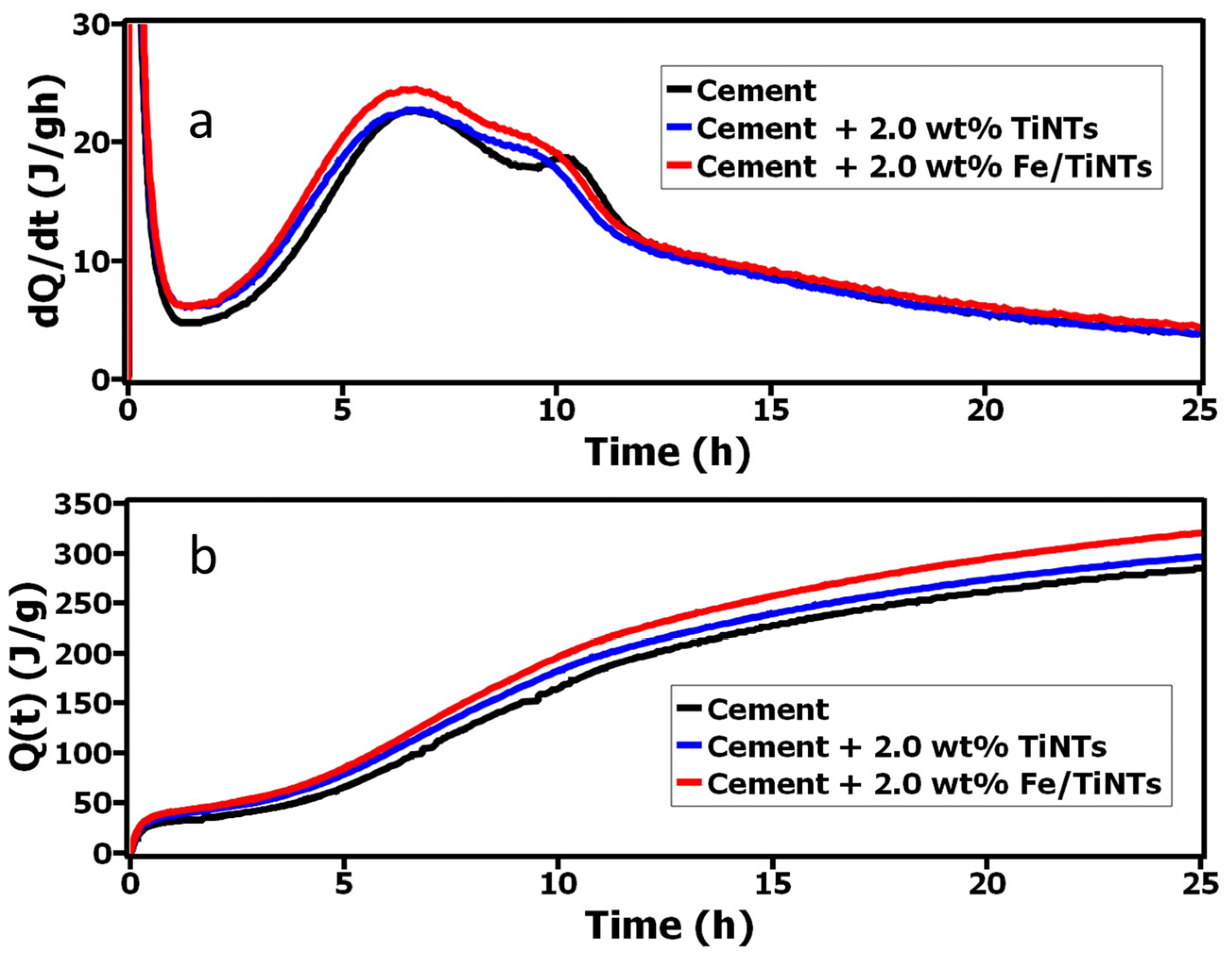
The heat evolution of Portland cement hydration was studied by isothermal calorimetry. The heat evolution (dQ/dt (J/gh)) and cumulative heat (J/g) during 24 h hydration of cement in the presence and absence of both TiNTs and Fe/TiNTs with 2.00 wt% in cement are shown in Figure 9. As is observed, the induction period of hydrated cement in the presence of both types of nanotubes was shortened compared to the pure cement. Also, the cumulative heat of hydration of cement was increased for both samples with respect to the reference. The increase in the cumulative heat evolution and a higher rate of heat evolution indicate improvement in the hydration reactions of cement. The impact of shortening the induction period and increasing cumulative heat development is seen more efficiently in the presence of Fe/TiNTs compared to references. As observed from Figure 9, both the rate evolution and cumulative curves stayed higher with 2.0 wt% Fe/TiNTs during 24 h hydration.
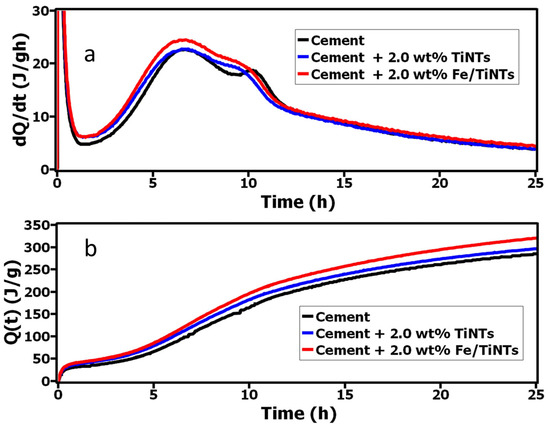
Figure 9.
Heat evolution (a) and cumulative heat evolution (b) of OPC in the presence and absence of TiNTs and Fe/TiNTs during the 24 h hydration.
As we declared in our previous work [38], the reason for this acceleration could be due to the high specific surface area of TiO2 tubes which in turn produce further nucleation sites for the hydration reaction. As is observed, the effect of improvement on hydration was notable for the Fe/TiNTs sample and this is feasibly due to the created active sites by replaced iron with titanium in the crystal structure of TiO2 nanotubes. The replaced iron dopant with titanium in the crystal lattice of TiO2 nanotubes generated a spatial environment for TiNTs, and as a consequence of that, the charge difference was increased within the surface of TiO2 nanotubes. This increased charge difference facilitates more nucleation sites for the formation of portlandite [50].
- Evaluation of Photocatalytic Activity
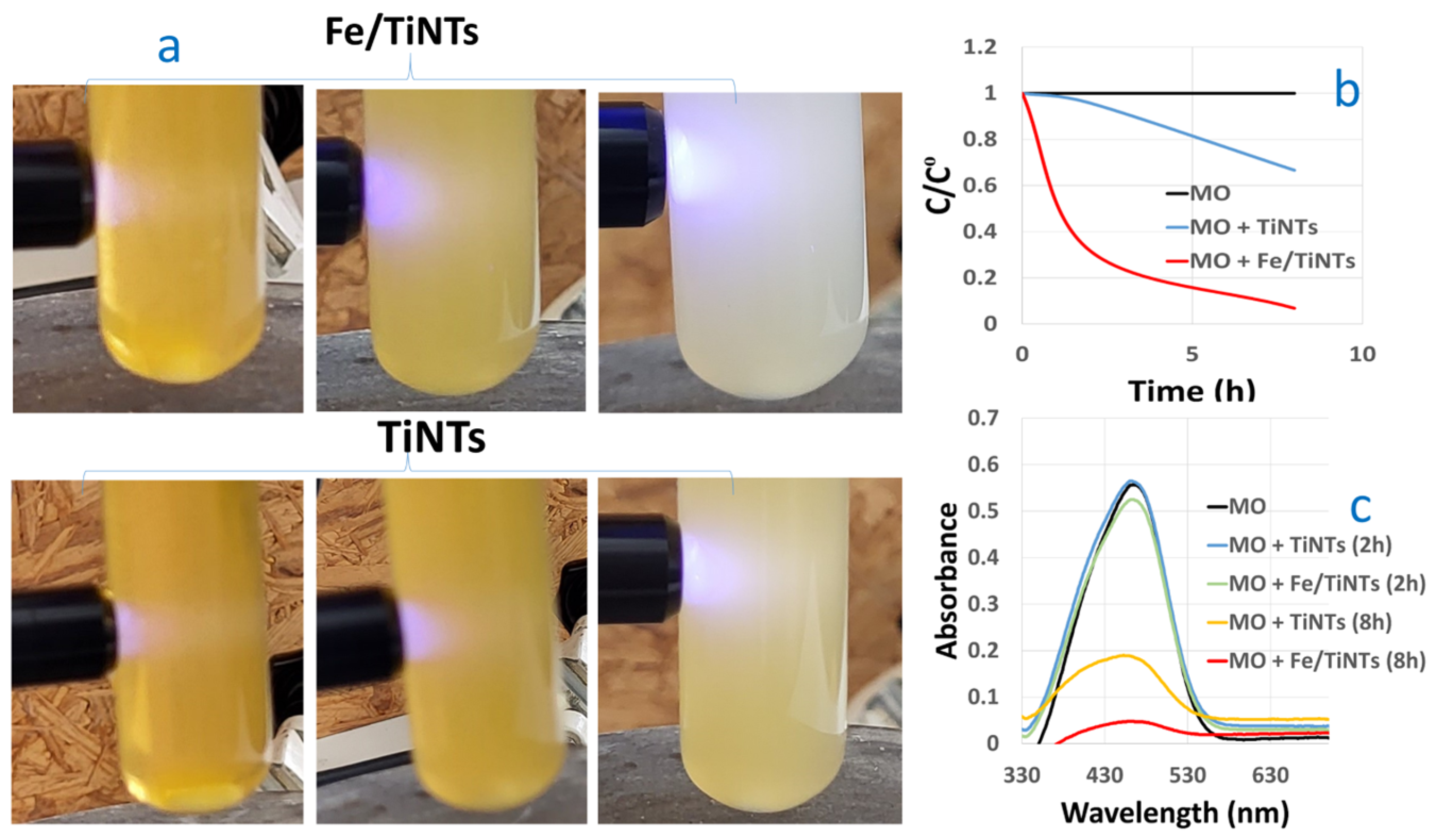
The photocatalytic activity of the Fe/TiNTs was evaluated by the degradation of methyl orange (MO), a model compound for photocatalytic wastewater treatment. A doping concentration of 2.0 wt% was chosen for these experiments based on the evaluation of the light-absorption properties of doped materials. Figure 10 shows the photocatalytic degradation process of MO in the presence of Fe/TiNTs and undoped TiNTs. The photocatalytic activities of Fe/TiNTs were evaluated by monitoring the degradation of MO under light irradiation at 365 nm. Figure 10a optically shows the degradation of MO in the presence of both Fe/TiNTs and TiNTs after the first minute, 2 h, and 8 h. As expected, the efficiency of degradation increases with time. The solution containing Fe/TiNTs was almost decolored after 8 h illumination, while TiNTs still showed an orange color. Similar observations are inferred from Figure 10b, showing the concentration profile of MO under illumination, without or with TiNTs or Fe/TiNTs. Totals of 10% and 93% of MB were degraded after 2 h and 8 h illumination in the presence of Fe/TiNTs, while only 4% and 68% of MO were degraded with the addition of TiNTs. Figure 10c shows the absorbance of the MO solution with respect to the wavelength dependence of the photocatalytic degradation. A superior decrease in the absorbance maximum of MO was observed in the presence of Fe/TiNTs compared to TiNTs and pure MO solution. Potential explanations for these observations are that either doped Fe3+ ions act as a charge carrier trap and inhibit the hole–electron recombination, and/or the induced transformation of anatase TiNTs to mixed anatase/rutile TiNTs during doping facilitates an efficient separation of photogenerated electron–hole pairs (due to band alignment between these phases).
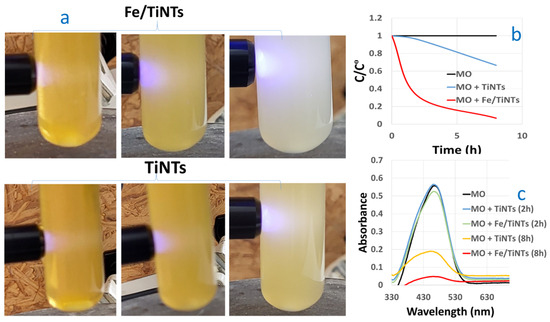
Figure 10.
Photocatalytic degradation process of MO in the presence of the Fe/TiNTs in comparison with TiNTs, after 2 h and 8 h irradiation. Here, (a) shows degradation images under LED (365 nm) light illumination; (b,c) show the degradation concentration and absorbance spectra of MO under UV–visible light in the presence and absence of both of Fe/TiNTs and TiNTs, respectively.
Concerning our finding, previous researchers like Sina et al. [51] reported 47% MB degradation in the presence of 2.0% of Fe-doped TiO2 nanoparticles after 3 h. Also, Mishra et al. [52] found 80% degradation of MB after 2 h for 1.0 wt% Fe-doped TiO2 nanoparticle sample.
4. Conclusions
In this work, both Fe/TiNTs and TiNTs were synthesized by a modified hydrothermal method. Without using an autoclave, in one step, Fe/TiNTs were obtained, which means that facile, cheap, and large amounts of Fe/TiNTs can be synthesized. The products were characterized by using SEM, TEM, XRD, ESR, UV–Vis, and gas adsorption studies and the following results were achieved:
- TiNTs were successfully doped with iron and the initial wt% of iron with respect to anatase for the synthesis of Fe/TiNTs were 0.0, 0.07, 0.1, 0.3, 1.0, and 2.00 wt%.
- SEM and TEM confirmed the formation of both types of nanotubes, TiNTs and Fe/TiNTs.
- TEM confirmed that the nanotubes were hollow and with a tubular structure. They consist of multilayers with an average outer diameter of 23–48 nm and length of 10–15 µm, respectively.
- XRD proved the doping process of TiNTs with Fe3+- ions, via altering on the XRD pattern. The FWHM of the (101) anatase plane increased from ~1° in the undoped TiNT to ~1.4° in the Fe/TiNT sample with 2.00 wt% Fe. Such an observation is expected to be a direct effect of doping of anatase TiNTs with Fe3+ ions. Furthermore, rutile formation within the anatase structure was observed upon doping higher levels of Fe3+, which is expected to enhance charge separation within the TiNTs and, consequently, enhance the photocatalytic efficiency of the material.
- ESR is in agreement with the interpretation that Fe3+ ions were incorporated into the crystal structure of anatase TiNTs occupying an octahedral site and another site next to an O vacancy .
- DRS showed an enhancement of light absorption in the visible region in the range of 400–600 nm. Particularly with the higher concentration of dopant, the absorption edge becomes more apparent and shifts further into the visible light region.
- A decrease in the optical band gap of Fe/TiNTs samples was revealed by DRS proportionally to the dopant concentration.
- The highest BET-specific surface area for the nanotubes was obtained for the pure TiNTs with 356 m2/g. As the wt% of iron in the samples increased, a decline in the values of BET-specific surface area of Fe/TiNTs was observed. Even though the doped samples showed lower surface areas than their undoped counterparts, their catalytic activity significantly surpassed the TiNTs, which highlights the beneficial nature of Fe3+ doping.
- An improvement in the hydration of Portland cement was observed in the presence of 2.0 wt% Fe/TiNTs compared to the references. The induction period was decreased and an acceleration was observed.
Finally, the photocatalytic activity of the samples was evaluated by degrading methyl orange in the presence of Fe/TiNTs and TiNTs. The samples were illuminated by a light-emitting diode (LED), and then the degradation was followed via UV–Vis spectroscopy. Fe/TiNTs (2.0 wt%) showed the highest efficiency to degrade MO up to 93% after 8 h illumination.
On the basis of the abovementioned results, it can be concluded that the doping of TiNTs with Fe3+ was successful and more effective when the dopant wt% was higher. The synthesized Fe/TiNTs can be utilized in various fields depending on their desired aspect as a photocatalyst.
We believe that our product has the potential to be used as a component of future concrete. Our product has a wonderful feature, which is enhanced photocatalytic activity at higher wavelengths. This remarkable property will give self-cleaning property to concrete not only outdoors but even in indoor environments, such as kitchens, where the intensity of UV radiation is limited. Smaller percentages (1–2 wt% or even lower) are sufficient for application in concrete. We only need a small amount of our product to use on the top layer of concrete, where it is needed. Furthermore, it has a high specific surface area which can contribute to the reinforcement of UHPC concrete.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.M.Y.Q.; methodology, S.M.Y.Q.; investigation, S.M.Y.Q., J.N., C.P., T.K. and S.M.F.K.M.; resources, M.S.K. and R.H.F.T.; data curation, S.M.Y.Q. and J.N.; writing—original draft, S.M.Y.Q.; writing—review and editing, C.P., T.K., Y.S., S.M.F.K.M., J.N., J.S.a.d.G., C.W., R.H.F.T. and M.S.K.; visualization, S.M.Y.Q. and J.N.; project administration, S.M.Y.Q., M.S.K. and R.H.F.T.; funding acquisition, S.M.Y.Q. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors would like to thank the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation’s Philipp Schwartz Initiative and DAAD (Ref.n. 91563809) for financially supporting this research project.
Data Availability Statement
Measured data are available in this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Fujishima, A.; Honda, K. Electrochemical Photolysis of Water at a Semiconductor Electrode. Nature 1972, 238, 37–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, F.; Anpo, M.; He, D. Preparation, Photocatalytic Activity, and Mechanism of Nano-TiO2 Co-Doped with Nitrogen and Iron (III). J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 10618–10623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.; Swati, I.K. Fe3+-Doped Anatase TiO2 with d-d Transition, Oxygen Vacancies and Ti3+ Centers: Synthesis, Characterization, UV-Vis Photocatalytic and Mechanistic Studies. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 6619–6633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; He, H.; Liu, F. Effect of Fe on the Photocatalytic Removal of NOx over Visible Light Responsive Fe/TiO2 Catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 179, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Liu, B.; Zhao, X.; Nakata, K.; Murakami, T.; Fujishima, A. Synthesis, Characterization, and Photocatalysis of Fe-Doped TiO2: A Combined Experimental and Theoretical Study. Int. J. Photoenergy 2012, 2012, 368750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elghniji, K.; Atyaoui, A.; Livraghi, S.; Bousselmi, L.; Giamello, E.; Ksibi, M. Synthesis and Characterization of Fe3+ Doped TiO2 Nanoparticles and Films and Their Performance for Photocurrent Response under UV Illumination. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 541, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, N.; Sohn, Y.; Leung, K.T.; Pradhan, D. Engineered Electronic States of Transition Metal Doped TiO2 Nanocrystals for Low Overpotential Oxygen Evolution Reaction. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 29499–29506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shwetharani, R.; Fernando, C.A.N.; Balakrishna, G.R. Excellent Hydrogen Evolution by a Multi Approach via Structure-Property Tailoring of Titania. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 39122–39130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eadi, S.B.; Kim, S.; Jeong, S.W.; Jeon, H.W. Novel Preparation of Fe Doped TiO2 Nanoparticles and Their Application for Gas Sensor and Photocatalytic Degradation. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 2017, 2191659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Li, T.; Zhou, Q. Impact of Titanium Dioxide (TiO2) Modification on Its Application to Pollution Treatment—A Review. Catalysts 2020, 10, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellouzi, I.; El hajjaji, S.; Harir, M.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P.; Laânab, L. Coprecipitation Synthesis of Fe-Doped TiO2 from Various Commercial TiO2 for Photocatalytic Reaction. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2020, 14, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Yang, S.; Jeon, E.H.; Baik, J.; Kim, N.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, H. Enhancement of Photo-Oxidation Activities Depending on Structural Distortion of Fe-Doped TiO2 Nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anatase, K.; Tio, I.; Method, M.S.; Activity, P. ARTICLE ORIGINAL Iron-Doped TiO2 Catalysts with Photocatalytic Activity. J. Water Environ. Nanotechnol. 2019, 4, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Luo, X.; Zhang, J.D.; Long, Y.F.; Xue, X.; Xu, B.J. Kinetic Study on the Crystal Transformation of Fe-Doped TiO2 via In Situ High-Temperature X-Ray Diffraction and Transmission Electron Microscopy. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancuso, A.; Sacco, O.; Vaiano, V.; Bonelli, B.; Esposito, S.; Freyria, F.S.; Blangetti, N.; Sannino, D. Fe-Doped TiO2 Prepared by a Three-Block Copolymer Templating Approach. Materials 2021, 14, 3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matias, M.L.; Pimentel, A.; Reis-Machado, A.S.; Rodrigues, J.; Deuermeier, J.; Fortunato, E.; Martins, R.; Nunes, D. Enhanced Fe-TiO2 Solar Photocatalysts on Porous Platforms for Water Purification. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Bu, Q.; Zhao, R.; Xu, W.; Jia, N.; Yang, L.; Tang, J. A Novel Preparation of Trace Iron-Doped 3D Urchin-like TiO2 for Efficient Degradation and Mineralization of Trimethoprim under Simulated Sunlight. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 11138–11149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mragui, A.; Aadnan, I.; Zegaoui, O.; Esteves da Silva, J.C.G. Physico-Chemical Characterization and Photocatalytic Activity Assessment under UV-A and Visible-Light Irradiation of Iron-Doped TiO2 Nanoparticles. Arab. J. Chem. 2023, 16, 105331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soundarya, T.L.; Harini, R.; Manjunath, K.; Udayabhanu; Nirmala, B.; Nagaraju, G. Pt-Doped TiO2 Nanotubes as Photocatalysts and Electrocatalysts for Enhanced Photocatalytic H2 Generation, Electrochemical Sensing, and Supercapacitor Applications. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 31855–31874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eroğlu, Ö.; Kizil, H. The Effect of the Iron Doping on Anatase TiO2 Anode for Electrochemical Performance of Sodium-Ion Batteries. Solid State Ionics 2023, 393, 116168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.W.; Juan, J.C.; Ko, W.B.; Bee Abd Hamid, S. An Overview: Recent Development of Titanium Oxide Nanotubes as Photocatalyst for Dye Degradation. Int. J. Photoenergy 2014, 2014, 524135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozio, A. Effect of Tantalum Doping on TiO2 Nanotube Arrays for Water-Splitting. Mod. Res. Catal. 2015, 4, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wu, J.; Lu, D.; Yang, J. Enhanced Visible Light Photocatalytic Activity for TiO2 Nanotube Array Films by Codoping with Tungsten and Nitrogen. Int. J. Photoenergy 2013, 2013, 471674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, N.; Quan, X.; Li, J.Y.; Chen, S.; Yu, H.T.; Chen, G. Fabrication of Boron-Doped TiO2 Nanotube Array Electrode and Investigation of Its Photoelectrochemical Capability. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 11836–11842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreekantan, S.; Zaki, S.M.; Lai, C.W.; Tzu, T.W. Copper-Incorporated Titania Nanotubes for Effective Lead Ion Removal. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2014, 26, 620–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syamsul, S.; Harun, Z.; Norhayati, W.; Salleh, W.; Nur, M.; Abd, H.; Sazali, N.; Hussin, R.; Basri, H. The Influence of Fe Doped TiO2 as Inorganic Additive on the Properties of Polysulfone Ultrafitration Membrane. Malaysian J. Anal. Sci. 2019, 15, 725–730. [Google Scholar]
- Transactions, E.C.S.; Society, T.E. Investigations on the Fe-Doped TiO2 Nanotube Arrays as a Photoanode for Cathodic Protection of Stainless Steel. Society 2008, 3, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Eder, D.; Motta, M.; Windle, A.H. Iron-Doped Pt-TiO2 Nanotubes for Photo-Catalytic Water Splitting. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 055602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szirmai, P.; Horváth, E.; Náfrádi, B.; Micković, Z.; Smajda, R.; Djokić, D.M.; Schenk, K.; Forró, L.; Magrez, A. Synthesis of Homogeneous Manganese-Doped Titanium Oxide Nanotubes from Titanate Precursors. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ghicov, A.; Schmidt, B.; Kunze, J.; Schmuki, P. Photoresponse in the Visible Range from Cr Doped TiO2 Nanotubes. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2007, 433, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Wang, S.; Liu, D.; Zhu, B.; Huang, W.; Wu, S.; Zhang, S. Synthesis, Characterization of Fe-Doped TiO2 Nanotubes with High Photocatalytic Activity. Catal. Lett. 2009, 129, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyankson, E.; Agyei-Tuffour, B.; Adjasoo, J.; Ebenezer, A.; Dodoo-Arhin, D.; Yaya, A.; Mensah, B.; Efavi, J.K. Synthesis and Application of Fe-Doped TiO2-Halloysite Nanotubes Composite and Their Potential Application in Water Treatment. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 2019, 4270310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, H.; Xu, S.; Sun, D.; Zhang, Y. Preparation of Fe-Doped TiO2 Nanotubes and Their Photocatalytic Activities under Visible Light. Int. J. Photoenergy 2013, 2013, 981753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, W.; Cui, X.; Yao, W.; Duan, T. One-Step Hydrothermal Synthesis of Iron and Nitrogen Co-Doped TiO2 Nanotubes with Enhanced Visible-Light Photocatalytic Activity. CrystEngComm 2015, 17, 8368–8376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.C.; Wang, K.W.; Perng, T.P. Electron Field Emission from Fe-Doped TiO2 Nanotubes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 143102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.T.; Siddiqa, A. Iron and Chromium Doped Titanium Dioxide Nanotubes for the Degradation of Environmental and Industrial Pollutants. Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2011, 8, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.L.; Lim, S.; Yap, H.C.; Abdullah, A.Z. Sonocatalytic Degradation of Rhodamine B in the Presence of Iron-Doped TiO2 Nanotubes: Characterizations and Reaction Kinetic Studies. AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1828, 020010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qattali, S.M.Y.; Pritzel, C.; Kowald, T.; Moni, S.M.F.K.; Killian, M.S.; Trettin, R. Effect of Iron-Doped TiO2 Nanotubes on the Hydration of Tricalcium Silicate. Constr. Mater. 2023, 3, 259–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.J.; Park, J.J.; Yoo, D.Y. Benefits of TiO2 Photocatalyst on Mechanical Properties and Nitrogen Oxide Removal of Ultra-High-Performance Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 285, 122921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Mei, M.; Li, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, X. Study on Photocatalytic and Mechanical Properties of TiO2 Modified Pervious Concrete. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 17, e01606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Shi, C.; He, T. SiO2/TiO2 and PDMS Modified Self-Cleaning Coating and Its Application in Decorative UHPC Surface. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 6194–6206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machala, L.; Zboril, R.; Gedanken, A. Amorphous Iron(III) Oxide—A Review. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 4003–4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scanlon, D.O.; Dunnill, C.W.; Buckeridge, J.; Shevlin, S.A.; Logsdail, A.J.; Woodley, S.M.; Catlow, C.R.A.; Powell, M.J.; Palgrave, R.G.; Parkin, I.P.; et al. Band Alignment of Rutile and Anatase TiO2. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 798–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, M.; Schwerdtfeger, C.F. Reinterpretation and Temperature Dependence of EPR in TiO2: Fe3+ (Anatase). Solid State Commun. 1970, 8, 1741–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, M.; Schwerdtfeger, C.F. EPR of Substitutional and Charge Compensated Fe3+ in Anatase (TiO2). J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1971, 32, 2529–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, J.; Grätzel, M.; Gallay, R. Inhibition of Electron-Hole Recombination in Substitutionally Doped Colloidal Semiconductor Crystallites. Helv. Chim. Acta 1987, 70, 1596–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorelli, A.; Evans, J.C.; Rowlands, C.C.; Egerton, T.A. An Electron Spin Resonance Study of Rutile and Anatase Titanium Dioxide Polycrystalline Powders Treated with Transition-Metal Ions. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1 Phys. Chem. Condens. Phases 1987, 83, 3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makuła, P.; Pacia, M.; Macyk, W. How To Correctly Determine the Band Gap Energy of Modified Semiconductor Photocatalysts Based on UV-Vis Spectra. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 6814–6817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Chen, G.; Zeng, G.; Chen, A.; He, K.; Huang, Z.; Hu, L.; Zeng, J.; Wu, J.; Liu, W. Hydrothermal Synthesis of Graphene Wrapped Fe-Doped TiO2 Nanospheres with High Photocatalysis Performance. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 7473–7480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Nicolás, M.; Navarro-Blasco, Í.; Fernández, J.M.; Alvarez, J.I. The Effect of TiO2 Doped Photocatalytic Nano-Additives on the Hydration and Microstructure of Portland and High Alumina Cements. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moalej, N.S.; Ahadi, S.; Sheibani, S. Photocatalytic Degradation of Methylene Blue by 2 Wt.% Fe Doped TiO2 Nanopowder under Visible Light Irradiation. J. Ultrafine Grained Nanostructured Mater. 2019, 52, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Chakinala, N.; Chakinala, A.G.; Surolia, P.K. Photocatalytic Degradation of Methylene Blue Using Monometallic and Bimetallic Bi-Fe Doped TiO2. Catal. Commun. 2022, 171, 106518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).