Abstract
Early-age cracking during the plastic stage is unsightly and a cause of future durability problems. This paper investigates the effects of various simple curing methods used in practice to enhance early-age concrete cracking performance, including covering concrete with a plastic sheet and wet hessian fabric, surface power floating and use of cold water in the mix. The benefits offered by the use of three standard curing admixtures (Safecure Super concrete, Safecure Super 90W-10%, and superplasticizer), as well as recycled tire steel fibres at 40 kg/m3, are also examined. A digital image processing (DIP) technique is used to measure the crack widths, whilst the temperature in the concrete is measured via a thermocouple. The results show that all the concrete curing methods are successful in restraining micro and plastic shrinkage cracks, although the use of recycled tire steel fibre (RTSFC40) is most effective in eliminating micro and plastic shrinkage surface cracks. All of the examined methods are compared in terms of the speed and cost of application, quality of the surface finish and environmental credentials. This study will inform best practice on enhancing the durability and sustainability of concrete structures, particularly for slab-on-grade applications.
1. Introduction
The fast drying of concrete in its plastic stage before the final set can affect the concrete durability due to the development of micro and plastic shrinkage cracks [1]. Such early-age cracks are known to impact concrete performance (mainly in slabs and pavements), as they can lead to potential large cracks, physical and chemical deterioration of concrete as well as reinforcement corrosion [2,3]. Therefore, in practice, concrete curing is necessary not only to improve the mechanical characteristics but also to mitigate the occurrence of plastic shrinkage-induced cracks and enhance the durability of concrete [4]. ASTM C192/C192M [5] provides good practice guidance on material mixing and curing to avoid concrete durability issues.
Micro and plastic shrinkage cracks commonly occur during the first six hours whilst concrete is in the plastic state and before the final set [6]. Research confirms that the main parameters that increase the possibility of plastic shrinkage cracking are: (1) environmental conditions (temperature, wind speed, and relative humidity), (2) materials and mix proportions, and (3) construction procedures [7,8,9]. These parameters affect the evaporation rate and the rate at which concrete water bleeds to the surface [10].
1.1. Concrete Curing Methods
Many practical and proprietary methods exist to avoid plastic shrinkage cracking, including various curing methods, power floating, the use of cold water, shrinkage reducing admixtures, and fibres.
Covering concrete with plastic sheets or wet burlap is the most common practical concrete curing method. Nasir et al. [11] conducted a study on specimens made of concretes, including different cementitious materials (OPC, fly ash, very fine fly ash, silica fume, blast furnace slag and natural pozzolan concrete), and cured under a plastic sheet, and they found that plastic shrinkage cracks were reduced by up to 25% compared with non-covered specimens. Al-Amoudi et al. [12] studied the drying shrinkage of specimens made of plain concrete and concrete containing silica fume and covered with wet burlap. They found that there was no discernible improvement in the drying shrinkage performance. Nevertheless, there is no published research on the effect of wet burlap on plastic shrinkage cracks.
Power floating is also used to eliminate plastic cracks in slabs and to polish the surface. This method, which is applied once all the surface bleed water rises and starts to evaporate, involves the use of a power floating machine to polish the surface of the concrete (with or without the application of a dry shake) while also sealing any micro and plastic shrinkage cracks [13]. Combrinck et al. [1] found out that power floating can close the plastic shrinkage cracks on the surface, although deep in the concrete, the cracks may reappear, depending on the time of the power floating application. In general, power floating is not recommended earlier than two hours from casting, as if it is applied too early, the bleed water can be trapped under the sealed surface and cause subsequent delamination.
In hot environmental conditions, the use of cold water is another possible solution, as it is expected to delay the evaporation of the bleed water and reduce the temperature rise due to hydration. Surprisingly, Jacobsen et al. [14] found that ice water can propagate and enhance the damage due to micro cracks on the surface of concrete. On the contrary, Xie et al. [15] showed that replacing 50% of the water with crushed ice in ultra-high-performance concrete reduced the drying shrinkage cracking.
Proprietary shrinkage-reducing admixtures are widely used, and some are specifically designed to delay the evaporation of bleed water [16]. Shah et al. [17] conducted a study on the use of shrinkage-reducing admixtures (propylene glycol derivatives) in volumes of 1% and 2% of the total water and found a reduction in the plastic shrinkage cracks up to 32% and 45%, respectively. Pease et al. [18] examined the effects of using another shrinkage-reducing admixture (Tetraguard AS20) in a volume of 2.5% of the total water and found that the total crack area was reduced by up to 60%.
The use of superplasticizers in concrete is widespread because they increase the workability of concrete and reduce the water demand. However, increased workability may increase the bleed water and promote plastic shrinkage cracks [19]. Combrinck et al. [20] confirmed experimentally that an increase in the superplasticizer dosage resulted in larger plastic crack widths.
The addition of fibres to concrete can improve the stability of wet concrete and reduce the bleed water, and in turn, it can stop plastic shrinkage cracking also due to the crack-bridging effect of the fibres. Many different types of fibres are currently being used to control cracking in concrete, such as polymeric fibres, natural fibres, metallic fibres (including recycled fibres [21,22]), as well as other non-metallic high-modulus fibres such as glass, carbon, and basalt [23]. Banthia et al. [24] investigated the effects of using different dosages of polypropylene fibres (0.1% to 0.3% by volume) of two different lengths to control early-age cracking. The results showed that the polypropylene fibres had a positive effect on reducing early-age concrete cracks, with the longer fibre performing best. Al-Tulaian et al. [25] examined the use of recycled plastic fibres (1.5% by volume) of different lengths and also found that the longer fibres resulted in better performance. Sivakumar et al. [26] examined the effects of different types of fibres (steel and polyester, polypropylene and glass) on plastic shrinkage cracking and found that the steel fibres were the best performing and reduced cracking by up to 99% compared with the plain concrete.
Among the various methods used to control plastic shrinkage, it is difficult to discern which are the most effective, as there is a lack of empirical evidence comparing the effects of the various methods.
1.2. Significance of the Research
This paper presents a comparative study on the effects of using different concrete curing methods and mitigation strategies on the plastic shrinkage cracking behaviour of concrete. A multi-parameter (time, cost, and quality) analysis is carried out to compare the examined methods and recommendations are made.
2. Materials and Experimental Methods
2.1. Mixture Proportioning
The mix design used in this experimental study (Table 1) was adopted from [27], as it was used in previous research work by the authors and the results from this study can provide useful complementary data on the material behaviour during the plastic stage. All the aggregates were sieved and weighted a day before casting to control the moisture content and temperature, as recommended in [6,28].

Table 1.
Concrete mix proportions.
2.2. Mixing and Placing
The concrete was mixed in a pan mixer of 60 L capacity. The dry materials were added first and mixed with some of the mixing water before starting the mixer. After starting the mixer, the rest of the mixing water was added along with the superplasticizer and mixing continued for 3 min, followed by a 3 min rest and a 2 min final mixing, as recommended by [5].
2.3. Experimental Methods
2.3.1. Plastic Shrinkage Test
A plastic shrinkage test was performed, as recommended in ASTM C1579 [6], to evaluate the restrained early-age cracking of the concrete. The plastic shrinkage test set-up is shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2. It involved a controlled environmental chamber divided into two compartments with the same environmental conditions. Two slabs, one reference slab and one using a special admixture or curing method, were placed in the two compartments and their behaviour was compared over the same amount of time from casting. Each of the slabs was equipped with a thermocouple (TC) placed at a depth of 20 mm to continuously monitor the concrete temperature during the test. Each compartment had an exposed water pan to determine the hourly evaporation rate during the test. The test duration after the slabs were placed inside the chamber was 6 h. At the end of the test, the doors of the chamber were opened for 24 h to allow the specimens to return to standard laboratory environmental conditions. During the test, the environment conditions were controlled, as recommended in ASTM C1579 [6], as follows: temperature (36 ± 3 °C), relative humidity (30 ± 10%) and wind speed greater than 4.7 m/s.
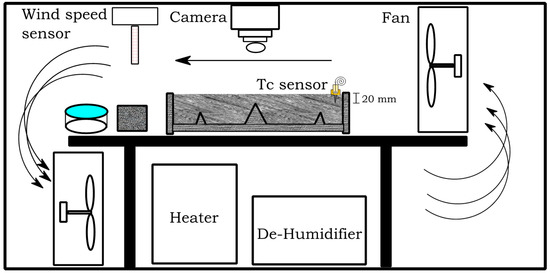
Figure 1.
Plastic shrinkage test chamber.
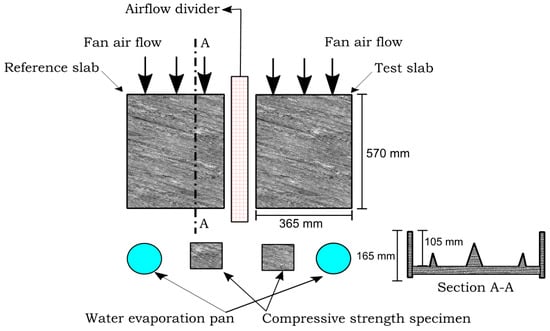
Figure 2.
Layout of the specimens inside the chamber and cross-section of the steel mould used to cast the specimens.
The measurements of the plastic shrinkage cracks (length, width, and area) were carried out using a 2D digital image processing (DIP) method, whereby a camera was placed above the samples during the test to capture images of the samples at specified times. The images were then analysed using DIP software (in MATLAB R2022b). In addition, after 24 h from the start of the test, a millimetre steel ruler was used to measure the crack width at more than 25 locations along each crack, and these measurements were compared to the results obtained from the DIP. The average plastic shrinkage crack width for each specimen was used to calculate the crack reduction ratio (CRR) using the following equation (Equation (1)), as recommended in ASTM C1579 [6]:
2.3.2. Evaporation Rate
Two different methods were used to estimate the evaporation rate, as recommended in [6,29]. Firstly, the evaporation rate at successive time intervals was estimated based on the mass loss of the two water pans (left and right) stored inside the chamber and according to ASTM C1579 [6], as shown in Equation (2).
where E is the evaporation rate (kg/m2/h), M2 − M1 is the mass loss between successive weightings, g, and T2 − T1 is the time interval between successive weightings, h.
Secondly, the “single operation” equation (Equation (3)) (based on Menzel’s formula) was used to find the evaporation rate [29] based on the temperature in the concrete and the external environmental parameters. This method is also suitable for on-site quick checks to assess whether evaporation will affect plastic shrinkage cracking.
where E is the evaporation rate (kg/m2/h), Tc is the concrete (water surface) temperature (°C), Ta is the air temperature (°C), r is the (RH percent)/100, and V is the wind velocity (kph).
E = 5([Tc + 18]2.5 − r × [Ta + 18]2.5) (V + 4) × 10−6
2.3.3. Parameters of the Study
The concrete curing methods compared in this study are listed below. A specimen made from a plain concrete (PC) mix, with no additional admixtures and not subjected to special curing methods, was used for the direct comparisons. The PC contained a normal plasticiser (Sika ViscoCrete 30HE) at (1.5 L/m3)/(335 kg/m3).
PSC: Plastic sheet concrete. Covering concrete with a plastic sheet is common because it prevents direct water evaporation
HFC: Hessian fabric concrete. Concrete is covered with a wet hessian concrete to retain the moisture and provide additional water for curing. This is often applied in smaller structures and laboratory specimens.
PFC: Power float concrete. Power float concrete is normally applied on slabs-on-grade (SoG) or slabs for which a polished surface is required. The power floating concrete method was examined in the laboratory as well as in an on-site application. In the laboratory, due to the small dimensions, the concrete slab was hand trowelled under controlled environmental conditions. A larger-scale trial was conducted at a site in Saudi Arabia under ambient environmental conditions.
CWC: Cold water concrete. To mitigate the effects of extreme environments, the initial concrete temperature may be modified to reduce issues during the plastic stage [30]. The normal water temperature used for the PC was room temperature (around 20 °C), whilst the cold water used for the CWC was at 7 °C.
SSC: Safecure Super concrete and SS90WC: Safecure Super 90W-10% concrete. Two shrinkage-reducing admixtures were selected (Safecure Super and Safecure Super 90w-10%). Both were supplied by Adomast Manufacturing Ltd. (Barnsley, UK) and approved by the Water Regulations Approval Scheme (WRAS) and tested in [31,32]. The admixtures were applied on the specimens, as recommended in the data sheet, at 4–6 m2 per litre.
PC-S: A PC devoid of superplasticizer was used for comparison purposes.
RTSFC40: Recycled tire steel fibre 40 kg/m3 concrete: As steel fibres are commonly used in SoG, a recycled tire steel fibre (RTSF) mix was examined at 40 kg/m3. The use of 40 kg/m3 was found in an earlier study by Alshammari et al. [33] to provide the best performance in avoiding plastic shrinkage concrete cracks at the surface. The average tensile strength of the RTSF was measured from individual fibres and was found to be 2380 MPa. The full characterization of the RTSF can be found in [34].
The time of application of the concrete curing methods and strategies depended on the need for the application. For example, some of the concrete curing methods and strategies, such as adding RTSF, PC-S, and CWC, were applied during mixing. The covering concrete curing methods and strategies (PSC and HFC) were applied immediately after casting the concrete. The shrinkage-reducing admixtures (SSC and SS90WC) and PFC were applied after the concrete had hardened, as specified by the manufacturers.
3. Experimental Results and Discussion
In accordance with ASTM C1579 [6], and as shown in Figure 3, during the test timescale (6 h), the environmental conditions in the chamber were kept within the recommended limits of air temperature 36 ± 3 °C, relative humidity 30 ± 10% and a wind speed of 5 m/s. These conditions were necessary to achieve a similar evaporation environment for all the specimens.
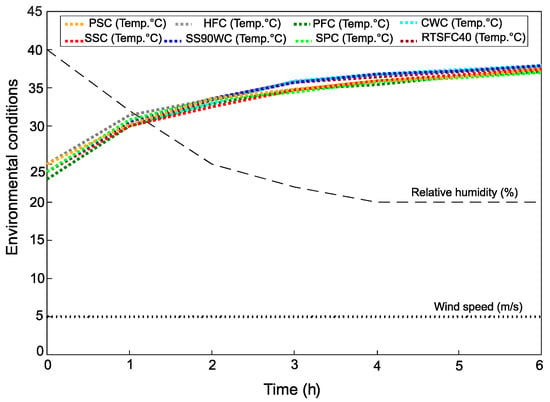
Figure 3.
Environmental conditions for all the concrete curing methods.
The temperature recorded inside the concrete is shown in Figure 4. In general, the temperature starts from room temperature and increases to about 30 °C after 6 h, mainly due to the heat of hydration. The PSC temperature increases faster than the other specimens and reaches 37 °C at the end of the test. This is as expected, as the plastic sheet provided some insulation and prevented heat loss due to water evaporation. The CWC shows the overall lower temperatures, as it starts at a lower temperature than the other specimens.
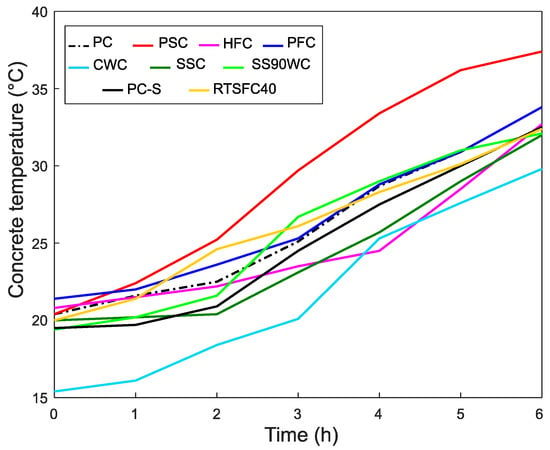
Figure 4.
Concrete temperature for all the concrete curing methods.
3.1. Evaporation Rate
The evaporation rate was determined using two methods, as described earlier: (a) ASTM C1579 [6] and (b) Menzel’s formula [29]. As shown in Figure 5a–h, the evaporation rates obtained using the water pan evaporation rate method are almost identical, with a very small deviation from the average evaporation rate calculated across all the specimens (ASTM Ave). This is as expected, as the specimens themselves cannot change the local environment by much. The initial water pan temperatures were about 15 ± 3 °C. However, there is a significant difference in the predicted evaporation rates determined using Menzel’s formula and the water pan method due to differences in the concrete temperatures developed as a result of the curing methods applied.
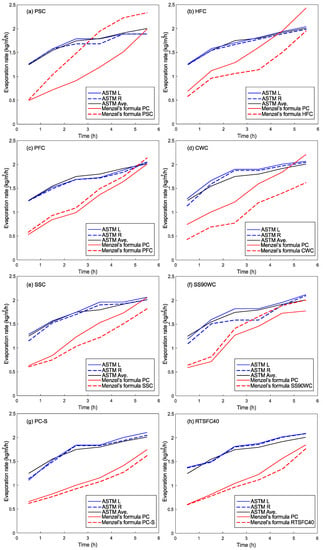
Figure 5.
Evaporation rates for the various curing methods compared to the PC.
In the PSC, Menzel’s formula predicts a higher evaporation rate (see Figure 5a). This is a natural consequence of the higher concrete temperature recorded. Nonetheless, as the surface is shielded from the wind, the actual concrete surface evaporation rate is not correct according to either method, as the bleed water cannot evaporate freely.
The HFC evaporation rate is shown in Figure 5b. The hessian seems to keep the temperature of the concrete slightly lower than that of the PC specimen; hence, the Menzel’s formula predicted evaporation rate is lower than for the PC. The hessian fabric was weighed before wetting (97 g), after wetting (364 g), and at the end of the test (at 24 h, 109 g). As the hessian was not completely dry, it shows that the hessian retained some moisture and kept the concrete wet by delaying the evaporation of the bleed water. Hence, the HFC provides a barrier to water evaporation without trapping the heat of hydration. Other studies, such as McCarter and Ben-Saleh [35], found similar results. Maslehuddin et al. [36] also examined curing compounds (acrylic, bitumen-based and coal tar epoxy) on plain and silica fume concrete and found that wetted hessian fabric gave the best results in terms of the shrinkage and corrosion resistance of concrete.
The PFC evaporation rate is shown in Figure 5c. The rates found by both methods are similar for both specimens (PC and PFC) due to the similar temperature rises, as also found by others [6,29].
In the case of the cold water concrete curing method, the temperature of the water in both pans before the test started was 15 °C. The pan evaporation rate is similar to the other tests, as it is only influenced by the external environmental conditions (see Figure 5d). At the beginning of the test, the CWC temperature was 15.4 °C, while for the PC it was 20.4 °C, a difference of 5 °C. This difference remained more or less the same throughout the test, with the specimens ending at 34.4 °C for the CWC and 29.8 °C for the PC As the initial concrete temperatures are affected by the temperature of the water, Menzel’s formula predicts a lower evaporation rate for the CWC, and in this case, this evaporation rate is likely to be more accurate than the pan method. Shen et al. [37] also found that cooling concrete in hot environmental conditions improves concrete hydration and delays the evaporation of bleed water.
The evaporation rates of the two shrinkage-reducing admixtures are similar, as shown in Figure 5e,f. As they affect the concrete temperature slightly differently, slightly different evaporation rates are predicted using Menzel’s formula. The Safecure Super admixture appeared to create a thin membrane on the surface of the concrete, which should have retarded the evaporation and also resulted in a slightly lower concrete temperature. The Safecure Super 90W-10% admixture is a wax emulsion that also formed a thin layer on the surface of the concrete. However, this thin layer seems to have increased slightly the concrete temperature by acting a bit like a plastic sheet. Hence, it appears that different admixtures have different effects on evaporation and temperature.
The predicted evaporation rates of the PC-S and PC were almost equal according to both methods, as shown in Figure 5g. During the experiment, it was noticed that the bleeding rate was lower than that of plain concrete due to the low flowability of the concrete. This was also reported by Combrinck et al. [20] when examining different doses of superplasticizer. The superplasticizer also seems to have slowed down the temperature rise, probably by retarding the hydration reaction.
The addition of 40 kg/m3 of recycled tire steel fibre (RTSF) does not seem to have affected the evaporation rates, as shown in Figure 5h.
3.2. Crack Width
The surface crack width development over time is shown in Figure 6a–h for all the tests. The graphs also show the concrete surface temperature and identify the temperature at the initiation of the first crack. All the PC specimens cracked at around 2 h, when the surface temperature was around 24 °C, and reached a width of just over 1 mm after 6 h. This consistency shows that the environmental chamber controlled the environment very well and that the concrete PC mixes were consistent with each other, enabling fair comparisons.
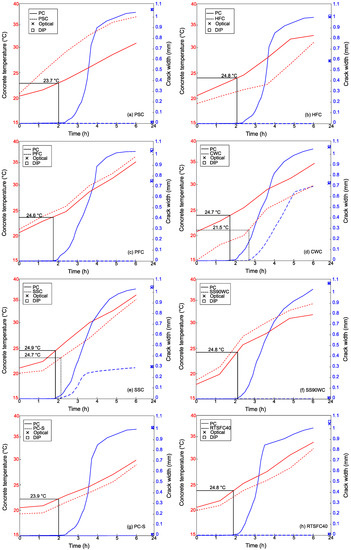
Figure 6.
Temperature (red curves) and crack width (blue curves) evolution for all the curing methods compared to their PC counterpart.
In the PSC, no plastic cracks were recorded, as shown in Figure 6a; hence, the crack reduction ratio was 100% (see Figure 7). This was also found by other authors. For example, Nabil et al. [38] examined concrete in hot environmental conditions by covering concrete with plastic sheets and curing membrane and by adding ice to the concrete and polypropylene fibres. The results showed that the curing compound, followed by the plastic sheet covering, was most efficient in controlling micro and plastic shrinkage cracks on the surface of the concrete.
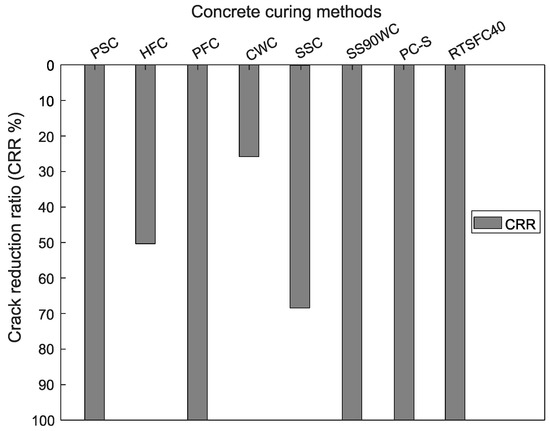
Figure 7.
Crack reduction ratio for all the concrete curing methods.
During the wet hessian test, the crack development could not be observed directly, as the surface was covered. When the hessian was removed after 24 h, although a crack of around 0.6 mm was found (Figure 6b), this was still approximately 50% lower than that observed in the plain concrete (see Figure 7). Nassif et al. [39], who studied silica fume and fly ash cement replacements, also found that none of the applied concrete curing methods (air-dry curing, wet-burlap, and moist curing) totally controlled early-age cracks, despite the early-age strength enhancement.
The crack development for the power float concrete is shown in Figure 6c. The PFC cracked at the edges only. As the floating was done by hand, it is possible that the cracks developed at edges that could not be floated properly. Therefore, the CRR of the PFC at the canter was a 100% reduction in the crack width compared to the PC, as shown in Figure 7. Similarly, for the in situ application where half the slab was power floated, no cracks appeared in the PFC, whilst cracks appeared on the boundary of the PC half of the slab (see Figure 8). Kori et al. [40] also studied power float concrete and found an improvement in durability and a reduction in the total crack area at the surface of the concrete.

Figure 8.
Concrete surface finish after the power floating of in situ large-scale slabs: (a) inner area, and (b) edge of slab.
The CWC delayed the crack initiation by about one hour compared to the PC, as shown in Figure 6d. The concrete also appeared to crack at the lower temperature of 21.5 °C compared to 24 °C for all the other specimens that cracked. The crack reduction ratio of the CWC (see Figure 7) was 25%.
The SS90WC was found to offer the best crack control width of the three admixtures used, with a crack reduction of 100% (Figure 7). The SSC also helped, offering a 70% crack reduction. Saliba et al. [41] also reported that shrinkage-reducing admixtures (SRA) can control early-age cracking in normal laboratory environmental conditions. The study reported that the SRA reduced the micro and plastic shrinkage cracking by up to 25% compared to plain concrete. Leemann et al. [42] investigated self-compacting concrete with an organic hydroxyl compound as SRA in environmental conditions of T = (30 ± 1) °C, RH = (60 ± 5) %, and a wind speed of (7 ± 0.5) m/s. The results showed that with increasing doses of SRA, the crack width was reduced but cracks were still seen at the surface of the concrete.
On the other hand, the PC cracked faster than the PC-S, which had no visible cracks on the surface of the concrete (see Figure 6g). The reason for the PC-S having no cracks was because of the low workability of the concrete, which failed to reach the target of the slump test of 100 ± 10 mm. Combrinck et al. [43] also found that super-plasticized concrete (PC) results in larger micro and plastic shrinkage cracks compared to concrete devoid of admixtures (PC-S).
The RTSFC40 eliminated completely concrete cracks on the surface of the concrete, as shown in Figure 6h. Eren et al. [44] also found that steel fibres (hooked end) of different lengths and aspect ratios can reduce cracks by up to 70% when using high fibre volumes (1.5%) and longer fibre lengths (80 mm).
3.3. Comparison of the Concrete Curing Methods
All the concrete curing methods are compared in terms of the cost, time of application, sustainability, quality, crack initiation and temperature in Table 2 and Figure 9.

Table 2.
Comparison of the concrete curing methods (in brackets, the efficiency index used in Figure 9).
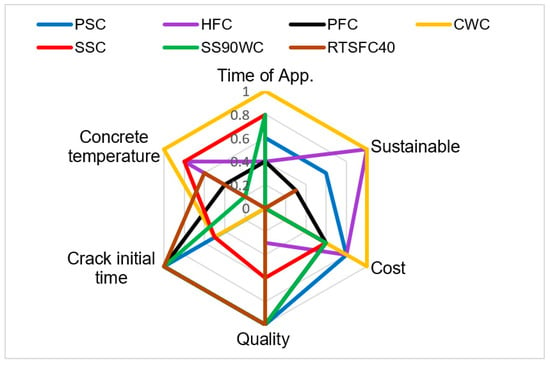
Figure 9.
Comparison between the concrete curing methods.
Equation (4) was used to find the total cost of power floating a slab with a surface area of 360 m2 in Saudi Arabia, which was used as a reference site.
The time of application was determined from the start to finish of the curing method as if it had been applied on the reference slab. The minimum efficiency index is given for the application that took the longest.
The sustainability index was based on whether the material was recycled, reusable, and eco-friendly. That is, if the used material is recycled and can be reused in the next concrete curing, then the material has advantages in improving the sustainability of the concrete. In addition, when the material has low CO2 emissions during production and application, it is considered an eco-friendly material.
The quality index is proportional to the CRR%. The crack initiation index is one for the methods that did not crack, and the worse score is attributed to the slabs that cracked between 2 and 3 h. The concrete temperature index is linear between 20 and 30 °C.
where CM is the materials cost (£/m2) and CL is the labourer cost per hour (£/m2).
Total cost = CM + CL
In the PSC, the plastic sheets can be reused many times, up to five times, and the method is cheap and fast, taking only 13 s/m2 to prepare and apply. The PSC avoided early-age cracking during the test, although it increased the concrete temperature, which could result in drying shrinkage cracks in the future.
In the HFC, the hessian fabric can also be reused up to 10 times, although the cost, drying and storing are probably a bit more of an issue than the plastic sheets, though with less environmental impact. The preparation and speed of application of the HFC was around 20 s/m2. The HFC delayed the crack initiation and reduced the overall crack width without increasing the concrete temperature.
The PFC was applied directly on site and accurate values were available. Power floating machines can be used hundreds of times but need fuel to run. Hence, they produce some gas emissions that can affect air quality and are also noisy. The large-scale application of the PFC was found to increase the concrete surface temperature in the outdoor environmental conditions slab, possibly due to the work done by the machine. The cost of PFC depends on the area of the concrete, although it still higher compared to the other concrete curing methods used in this study. The PFC can help control surface cracks, although it is time consuming and possibly only viable when a polished surface is required.
The need for cold mixing water in relation to the CWC adds only a small amount of time to the construction process. The cost of cold water or ice depends on the total volume of the concrete, but in general, it is low compared to other curing methods. In this study, only the direct refrigeration costs were considered. The CWC can delay and reduce plastic shrinkage cracks and can also have longer-term benefits due to the reduced temperature of the concrete at the early age.
The shrinkage-reducing admixtures used are both non-toxic and non-flammable. The cost of the SSC and SS90WC was 0.33 £/m2, which is higher compared to most curing methods used in this study. Applying them is relatively easy by spraying the concrete surface and it takes just 5 s/m2, but it should be applied to the concrete surface when all the bleeding water has evaporated. The SS90WC eliminated cracking completely, although it led to a slight increase in temperature, whilst the SSC helped delay and reduce the plastic shrinkage cracks.
The PC-S is not acceptable as a concrete curing method because it results in low workability concrete; hence, it is not evaluated for efficiency.
The RTSFC40 eliminated the cracks completely and it is relatively time-consuming to apply at 30 s/m2. However, it can also help with long-term cracks, and it is often used as structural reinforcement. Its relative cost was found to be higher compared to the other curing methods; hence, it may not be the ideal solution if only needed for plastic shrinkage.
The overall relative score shows that the CWC was the best concrete curing method, even though it did not eliminate plastic shrinkage cracking completely. Therefore, combining two concrete curing methods may be necessary to obtain the best performance of concrete curing methods, such as CWC with PSC or RTSFC40.
4. Conclusions
This paper presents an experimental work on various concrete curing methods to restrain micro and plastic shrinkage cracking, and it compares them in terms of the cost, time of application, sustainability, quality, crack initiation and temperature. Plastic shrinkage is determined according to ASTM C1579 under controlled environmental conditions. From the findings, the following conclusions can be drawn:
- The ASTM evaporation rates are similar for all the specimens and are affected by the initial water pan temperature, while the Menzel’s formula evaporation rates increase with an increase in the concrete temperature.
- All the concrete curing methods are successful to some extent in restraining plastic shrinkage cracking.
- Covering concrete with plastic sheets (PSC) prevents the evaporation of the bleed water and eliminates plastic shrinkage cracks, albeit at the expense of increased temperatures, while covering concrete with wet hessian fabric (HFC) decreases micro and plastic shrinkage cracks and keeps the concrete temperature down.
- The power floating concrete curing method (PFC) reduces or eliminates cracks, although it takes time to apply and increases the concrete temperature.
- Cold water concrete (CWC) gives the best overall relative efficiency score but does not eliminate cracking, so it is recommended as a supplementary method in hot climates.
- Both shrinkage-reducing admixtures (SSC and SS90WC) used in this study prevent and reduce plastic shrinkage cracks but affect the concrete temperature negatively.
- Recycled tire steel fibres (RTSFC40) eliminate plastic shrinkage cracking, but due to their cost, they are not recommended just for plastic shrinkage control.
The use of CWC shows a reduction in the concrete temperature but does not prevent plastic shrinkage cracks. On the other hand, PSC and RTSFC40 eliminate completely concrete cracks on the surface of the concrete, although they increase the concrete temperature. Therefore, combining two concrete curing methods may be necessary to obtain the best performance of the concrete curing methods, for example, CWC with PSC or RTSFC40.
Future work on real-scale applications could provide more representative data in terms of the cost, quality and time of application. The synergistic effect of two or more curing methods should be explored to optimize the structural performance and environmental impact.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, software, data curation, investigation and writing—original draft, T.O.A.; methodology, writing—review and editing, supervision K.P. and M.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The first author would like to thank Jouf University and the Ministry of Education in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia for sponsoring his PhD studies.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Combrinck, R.; Steyl, L.; Boshoff, W.P. Influence of concrete depth and surface finishing on the cracking of plastic concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 175, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matalkah, F.; Jaradat, Y.; Soroushian, P. Plastic shrinkage cracking and bleeding of concrete prepared with alkali activated cement. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaikh, F.U.A. Effect of Cracking on Corrosion of Steel in Concrete. Int. J. Concr. Struct. Mater. 2018, 12, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, M.; Gazder, U.; Maslehuddin, M.; Al-Amoudi, O.S.B.; Syed, I.A. Prediction of Properties of Concrete Cured Under Hot Weather Using Multivariate Regression and ANN Models. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2020, 45, 4111–4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C192/C192M; Standard Practice for Making and Curing Concrete Test Specimens in the Laboratory. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2016; pp. 1–8. [CrossRef]
- ASTM C1579; Standard Test Method for Evaluating Plastic Shrinkage Cracking of Restrained Fiber Reinforced Concrete. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2006; pp. 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Safiuddin, M.; Kaish, A.B.M.A.; Woon, C.O.; Raman, S.N. Early-Age Cracking in Concrete: Causes, Consequences, Remedial Measures, and Recommendations. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Schutter, G.; Taerwe, L. Specific heat and thermal diffusivity of hardening concrete. Mag. Concr. Res. 1995, 47, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moelich, G.M.; van Zyl, J.; Rabie, N.; Combrinck, R. The influence of solar radiation on plastic shrinkage cracking in concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 123, 104182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naaman, A.E.; Wongtanakitcharoen, T.; Hauser, G. Influence of different fibers on plastic shrinkage cracking of concrete. ACI Mater. J. 2005, 102, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, M.; Al-Amoudi, O.S.B.; Maslehuddin, M. Effect of placement temperature and curing method on plastic shrinkage of plain and pozzolanic cement concretes under hot weather. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 152, 943–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Amoudi, O.S.B.; Maslehuddin, M.; Shameem, M.; Ibrahim, M. Shrinkage of plain and silica fume cement concrete under hot weather. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2007, 29, 690–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ACI 224R-01; Control of Cracking in Concrete Structures Reported by ACI Committee 224. ACI Committee: Farmington Hills, MI, USA, 2001; pp. 1–46.
- Jacobsen, S.; Scherer, G.W.; Schulson, E.M. Concrete–ice abrasion mechanics. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 73, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Fang, C.; Ali, M.M.S.; Visintin, P. Characterizations of autogenous and drying shrinkage of ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC): An experimental study. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 91, 156–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, P.M.; He, Z.H. Application of shrinkage reducing admixture in concrete: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 201, 676–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.P.; Marikunte, S.; Yang, W.; Aldea, C. Control of Cracking with Shrinkage-Reducing Admixtures. Transp. Res. Rec. 1997, 1574, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pease, B.; Shah, H.; Weiss, J. Shrinkage Behavior and Residual Stress Development in Mortar Containing Shrinkage Reducing Admixtures (SRAs). Am. Concr. Inst. ACI Spec. Publ. SP. 2005, 227, 285–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, J.G.; Cusens, A.R.; Brookes-Wang, Y. Effect of superplasticizers on the plastic shrinkage of concrete. Mag. Concr. Res. 1992, 44, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combrinck, R.; Kayondo, M.; le Roux, B.D.; de Villiers, W.I.; Boshoff, W.P. Effect of various liquid admixtures on cracking of plastic concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 202, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshammari, T.O.; Pilakoutas, K.; Guadagnini, M. Performance of Manufactured and Recycled Steel Fibres in Restraining Concrete Plastic Shrinkage Cracks. Materials 2023, 16, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banthia, N.; Yan, C. Shrinkage cracking in polyolefin fiber-reinforced concrete. Mater. J. 2000, 97, 432–437. [Google Scholar]
- Bertelsen, I.M.G.; Ottosen, L.M.; Fischer, G. Influence of fibre characteristics on plastic shrinkage cracking in cement-based materials: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 230, 116769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banthia, N.; Gupta, R. Influence of polypropylene fiber geometry on plastic shrinkage cracking in concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2006, 36, 1263–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tulaian, B.S.; Al-Shannag, M.J.; Al-Hozaimy, A.R. Recycled plastic waste fibers for reinforcing Portland cement mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 127, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, A.; Santhanam, M. A quantitative study on the plastic shrinkage cracking in high strength hybrid fibre reinforced concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2007, 29, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Papastergiou, P.; Angelakopoulos, H.; Guadagnini, M.; Pilakoutas, K. Mechanical properties of SFRC using blended Recycled Tyre Steel Cords (RTSC) and Recycled Tyre Steel Fibres (RTSF). Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 187, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C136-01; Standard Test Method for Sieve Analysis of Fine and Coarse Aggregates. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2005; Volume 13, pp. 85–86.
- Uno, P.J. Plastic shrinkage cracking and evaporation formulas. ACI Mater. J. 1998, 95, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhu, C.; Qi, C.; Wang, M.; Huan, C.; Zhang, B.; Song, K.I.I.L. Effects of curing time and ice-to-water ratio on performance of cemented paste backfill containing ice slag. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 228, 116639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C 309; Standard Specification for Liquid Membrane-Forming Compounds for Curing Concrete 1. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015; pp. 8–10.
- BS 7542; Method of Test for Curing Compounds for Concrete. BSI Group: London, UK, 1992.
- Alshammari, T.O.; Guadagnini, M.; Pilakoutas, K. The Effect of Harsh Environmental Conditions on Concrete Plastic Shrinkage Cracks: Case Study Saudi Arabia. Materials 2022, 15, 8622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isa, M.N.; Pilakoutas, K.; Guadagnini, M. Determination of tensile characteristics and design of eco-efficient UHPC. Structures 2021, 32, 2174–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarter, W.J.; Ben-Saleh, A.M. Influence of practical curing methods on evaporation of water from freshly placed concrete in hot climates. Build. Environ. 2001, 36, 919–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslehuddin, M.; Ibrahim, M.; Shameem, M.; Ali, M.R.; Al-Mehthel, M.H. Effect of curing methods on shrinkage and corrosion resistance of concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 41, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Lv, Y.; Yang, H.; Ma, W.; Zhang, L.; Pan, J. Effect of different ice contents on heat transfer and mechanical properties of concrete. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2022, 199, 103570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabil, B.; Aissa, A.; Aguida, B.I. Use of a New Approach (Design of Experiments Method) to Study Different Procedures to Avoid Plastic Shrinkage Cracking of Concrete in Hot Climates. J. Adv. Concr. Technol. 2011, 9, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassif, H.; Suksawang, N.; Mohammed, M. Effect of Curing Methods on Early-Age and Drying Shrinkage of High-Performance Concrete. Transp. Res. Rec. 2003, 1834, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kori, K.; Goliya, S.S. Use of Discrete fiber in road pavement. Mater. Today: Proc. 2022, 65, 1856–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliba, J.; Rozière, E.; Grondin, F.; Loukili, A. Influence of shrinkage-reducing admixtures on plastic and long-term shrinkage. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2011, 33, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leemann, A.; Nygaard, P.; Lura, P. Impact of admixtures on the plastic shrinkage cracking of self-compacting concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2014, 46, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combrinck, R.; Boshoff, W.P. Typical plastic shrinkage cracking behaviour of concrete. Mag. Concr. Res. 2013, 65, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eren, O.; Marar, K. Effect of steel fibers on plastic shrinkage cracking of normal and high strength concretes. Mater. Res. 2010, 13, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).