Probabilistic Analysis of Soil Moisture Variability of Engineered Turf Cover Using High-Frequency Field Monitoring
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Construction of Test Section
2.2. Instrumentation
2.3. Soil Characteristics
2.4. Normality and Variance Testing
2.5. Gaussian Distribution Theorem
3. Results
3.1. Soil Moisture Response to Precipitation
3.2. Descriptive Statistics and Analysis
3.3. Standard Normal Distribution (SND)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EnT | Engineered Turf |
| ET | Evapotranspiration |
| CC | Compacted Clay |
| CBS | Capillary Barrier Systems |
| Q-Q | Quantile–Quantile |
| VMC | Volumetric Moisture Content |
| Probability Density Function | |
| SND | Standard Normal Distribution |
| CV | Coefficient of Variation |
| OMC | Optimum Moisture Content |
| MDD | Maximum Dry Density |
| ASTM | American Society for Testing |
| LLDPE | Linear Low-Density Polyethylene |
| USCS | Unified Soil Classification System |
| LL | Liquid Limit |
| PL | Plastic Limit |
| PI | Plasticity Index |
| GCL | Geosynthetic Clay Liner |
| RCRA | Resource Conservation and Recovery Act |
| USEPA | U.S. Environmental Protection Agency |
References
- Hauser, V.L.; Gimon, D.M. Evaluating Evapotranspiration (ET) Landfill Cover Performance Using Hydrologic Models; Air Force Center for Environmental Excellence: San Antonio, TX, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Benson, C.; Khire, M. Earthen materials in surface barriers. In Barrier Technologies for Environmental Management; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1997; pp. 79–89. [Google Scholar]
- Gross, B.; Bonaparte, R.; Giroud, J. Waste containment systems: Problems and lessons learned. In Appendix F, Assessment and Recommendations for Optimal Performance of Waste Containment Systems, EPA, USA; National Service Center for Environmental Publications (NSCEP): Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer, S.F. Construction Overview of Six Landfill Cover Designs; Technical report; Sandia National Labs.: Albuquerque, NM, USA; Livermore, CA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Albright, W.H.; Benson, C.H.; Gee, G.W.; Roesler, A.C.; Abichou, T.; Apiwantragoon, P.; Lyles, B.F.; Rock, S.A. Field Water Balance of Landfill Final Covers. J. Environ. Qual. 2004, 33, 2317–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, C.H.; Albright, W.H.; Roesler, A.C.; Abichou, T. Evaluation of final cover performance: Field data from the alternative cover assessment program (ACAP). Proc. Waste Manag. 2002, 2, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Benson, C.H.; Bareither, C.A. Designing Water Balance Covers for Sustainable Waste Containment: Transitioning State of the Art to State of the Practice; Geotechnical Special Publication: Oakland, CA, USA, 2012; pp. 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.J.B.; Hossain, M.S. Evaluation of Post-Construction Changes in Soil Hydraulic Properties through Field Instrumentation and In Situ Testing. In Proceedings of the Geo-Congress 2019 Geotechnical Materials, Modeling, and Testing, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 24–27 March 2019; pp. 722–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, C.H.; Othman, M.A. Hydraulic Conductivity of Compacted Clay Frozen and Thawed In Situ. J. Geotech. Eng. 1993, 119, 276–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khire, M.V.; Benson, C.H.; Bosscher, P.J. Water Balance Modeling of Earthen Final Covers. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 1997, 123, 744–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogorzalek, A.S.; Bohnhoff, G.L.; Shackelford, C.D.; Benson, C.H.; Apiwantragoon, P. Comparison of Field Data and Water-Balance Predictions for a Capillary Barrier Cover. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2008, 134, 470–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohnhoff, G.L.; Ogorzalek, A.S.; Benson, C.H.; Shackelford, C.D.; Apiwantragoon, P. Field Data and Water-Balance Predictions for a Monolithic Cover in a Semiarid Climate. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2009, 135, 333–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, C.E.; Stormont, J.C. Capillary Barriers and Subtitle D Covers: Estimating Equivalency. J. Environ. Eng. 1997, 123, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kämpf, M.; Montenegro, H. On the performance of capillary barriers as landfill cover. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 1997, 1, 925–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawangsuriya, A.; Jotisankansa, A. Capillary Barrier System for Resilient Slope Cover. In Geoenvironmental Engineering; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2020; pp. 169–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarfone, R. Modelling the Hydraulic Behaviour of Unsaturated Soils and Application to the Numerical and Experimental Study of Capillary Barrier Systems. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Glasgow, Glasgow, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarfone, R.; Wheeler, S.J.; Smith, C.C. Numerical modelling of the application of capillary barrier systems for prevention of rainfall-induced slope instability. Acta Geotech. 2023, 18, 355–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetri, J.K.; Reddy, K.R. Advancements in Municipal Solid Waste Landfill Cover System: A Review. J. Indian Inst. Sci. 2021, 101, 557–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Shi, Z.H.; Zhu, H.D.; Zhang, H.Y.; Ai, L.; Yin, W. Soil moisture dynamics within soil profiles and associated environmental controls. Catena 2016, 136, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gao, Z.; Wang, M.; Li, Y.; Ma, Y.; Shi, M.; Zhang, H. Study on the dynamic characteristics of groundwater in the valley plain of Lhasa City. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency; Innovation, T.; Division, F.S. Fact Sheet on Evapotranspiration Cover Systems for Waste Containment; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2003.
- Brown, D.W.; Daley, D.J.; Tully, W.P. Determination of Evapotranspiration Landfill Cover System Design Parameters Using the Simultaneous Heat and Water (SHAW) Model. Master’s Thesis, State University of New York, Syracuse, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bronstert, A.; Plate, E.J. Modelling of runoff generation and soil moisture dynamics for hillslopes and micro-catchments. J. Hydrol. 1997, 198, 177–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadek, S.; Ghanimeh, S.; El-Fadel, M. Predicted performance of clay-barrier landfill covers in arid and semi-arid environments. Waste Manag. 2007, 27, 572–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henneberger, R.; Chiri, E.; Bodelier, P.E.; Frenzel, P.; Lüke, C.; Schroth, M.H. Field-scale tracking of active methane-oxidizing communities in a landfill cover soil reveals spatial and seasonal variability. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 1721–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S. Dealing with uncertainty in environmental model predictions. Eos 2001, 82, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brum, M.; Fan, F.M.; Salla, M.R.; von Sperling, M. Analysis of a probabilistic approach for modelling and assessment of the water quality of rivers. J. Hydroinform. 2022, 24, 783–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.J.B.; Aggarwal, M.; Rahman, N. Investigation of the Effect of Geosynthetics on Climate-Induced Changes in Unsaturated Soil Behavior Using Non-Parametric Measure. In Proceedings of the Geo-Congress 2024. American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 25–28 February 2024; pp. 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, T.G.; Tabatabai, S.; Huntington, J.M.; Davies, G.E.; Fuhrmann, M. Evapotranspiration covers at uranium mill tailings sites. Vadose Zone J. 2022, 21, e20222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.J.; Schnabel, W.E. Implementation of a Pilot Scale Evapotranspiration Landfill Cover for Use in Cold Regions. In Proceedings of the World Water Congress 2005: Impacts of Global Climate Change—Proceedings of the 2005 World Water and Environmental Resources Congress, Anchorage, AK, USA, 15–19 May 2005; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, R.; Zhu, M. Sustainability aspects of geosynthetic landfill final cover systems. E3S Web Conf. 2024, 569, 06004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albright, W.H.; Benson, C.H.; Gee, G.W.; Abichou, T.; Tyler, S.W.; Rock, S.A. Field Performance of Three Compacted Clay Landfill Covers. Vadose Zone J. 2006, 5, 1157–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- METER Group Inc. Method A: Soil-Specific Calibrations for METER Soil Moisture Sensors. 2023. Available online: https://metergroup.com/resources/services/custom-calibration/ (accessed on 16 May 2023).
- Chen, L.; Shapiro, S.S. An alternative test for normality based on normalized spacings. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 1995, 53, 269–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.P.; Eckersley, R.J. Inferential Statistics IV: Choosing a Hypothesis Test. In Statistics for Biomedical Engineers and Scientists; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 147–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razali, N.M.; Wah, Y.B. Power comparisons of shapiro-wilk, kolmogorov-smirnov, lilliefors and anderson-darling tests. J. Stat. Model. Anal. 2011, 2, 21–33. [Google Scholar]
- Engmann, S.; Cousineau, D. Comparing distributions: The two-sample anderson-darling test as an alternative to the kolmogorov-smirnoff test. J. Appl. Quant. Methods 2011, 6, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Mason, D.M.; Schuenemeyer, J.H. A Modified Kolmogorov-Smirnov Test Sensitive to Tail Alternatives. Ann. Statist. 1983, 11, 933–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, D.; Kolassa, J. Power considerations for Kolmogorov–Smirnov and Anderson–Darling two-sample tests. Commun. Stat.-Simul. Comput. 2023, 52, 3137–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, D.M. The distribution of the Anderson Darling statistic. In Communications in Statistics—Simulation and Computation; Taylor & Francis: Oxfordshire, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastwirth, J.L.; Gel, Y.R.; Miao, W. The Impact of Levene’s Test of Equality of Variances on Statistical Theory and Practice. Statist. Sci. 2009, 24, 343–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, R.J.; Schneider, H. A note on levene’s tests for equality of variances. Stat. Probab. Lett. 1985, 3, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doob, J.L. The Development of Rigor in Mathematical Probability (1900–1950). Am. Math. Mon. 1996, 103, 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellison, B.E. Two Theorems for Inferences about the Normal Distribution with Applications in Acceptance Sampling. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1964, 59, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, L. Measurable functions on Hilbert space. Trans. Am. Math. Soc. 1962, 105, 372–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, D.T. A theorem for physicists in the theory of random variables. Am. J. Phys. 1983, 51, 520–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phoon, K.K. Reliability-Based Design in Geotechnical Engineering: Computations and Applications, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; pp. 1–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, J.M. Factors of Safety and Reliability in Geotechnical Engineering. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2000, 126, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, D. Probabilistic approaches for geotechnical site characterization and slope stability analysis. In Probabilistic Approaches for Geotechnical Site Characterization and Slope Stability Analysis; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 1–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Choudhary, S.S.; Burman, A.; Singh, R.K.; Bardhan, A.; Asteris, P.G. Probabilistic Slope Stability Analysis of Mount St. Helens Using Scoops3D and a Hybrid Intelligence Paradigm. Mathematics 2023, 11, 3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantarangsi, W.; Liu, W.; Bretz, F.; Kiatsupaibul, S.; Hayter, A.J.; Wan, F. Normal probability plots with confidence. Biom. J. 2015, 57, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sürücü, B.; Koç, E. Assessing the validity of a statistical distribution: Some illustrative examples from dermatological research. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2008, 33, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
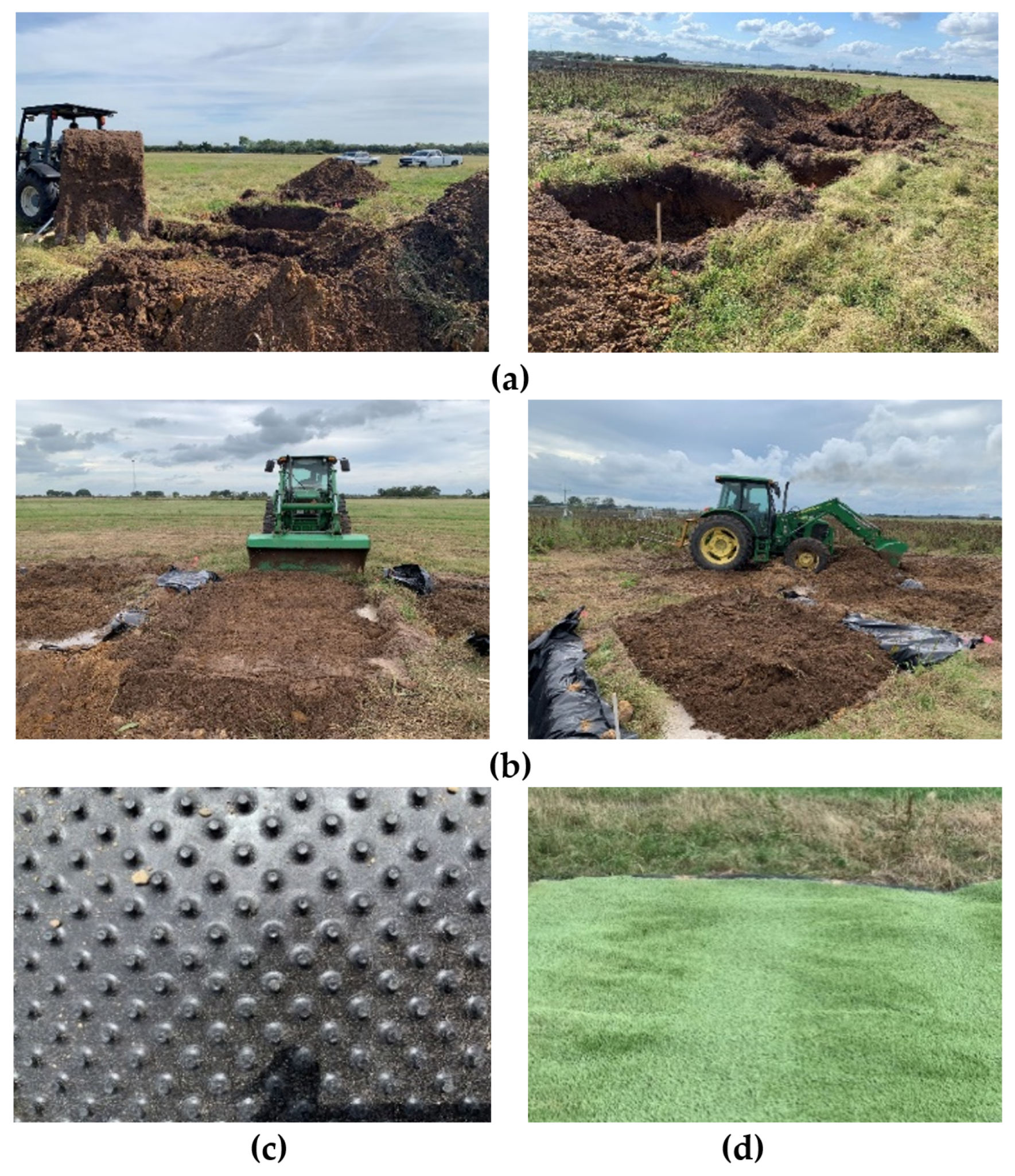


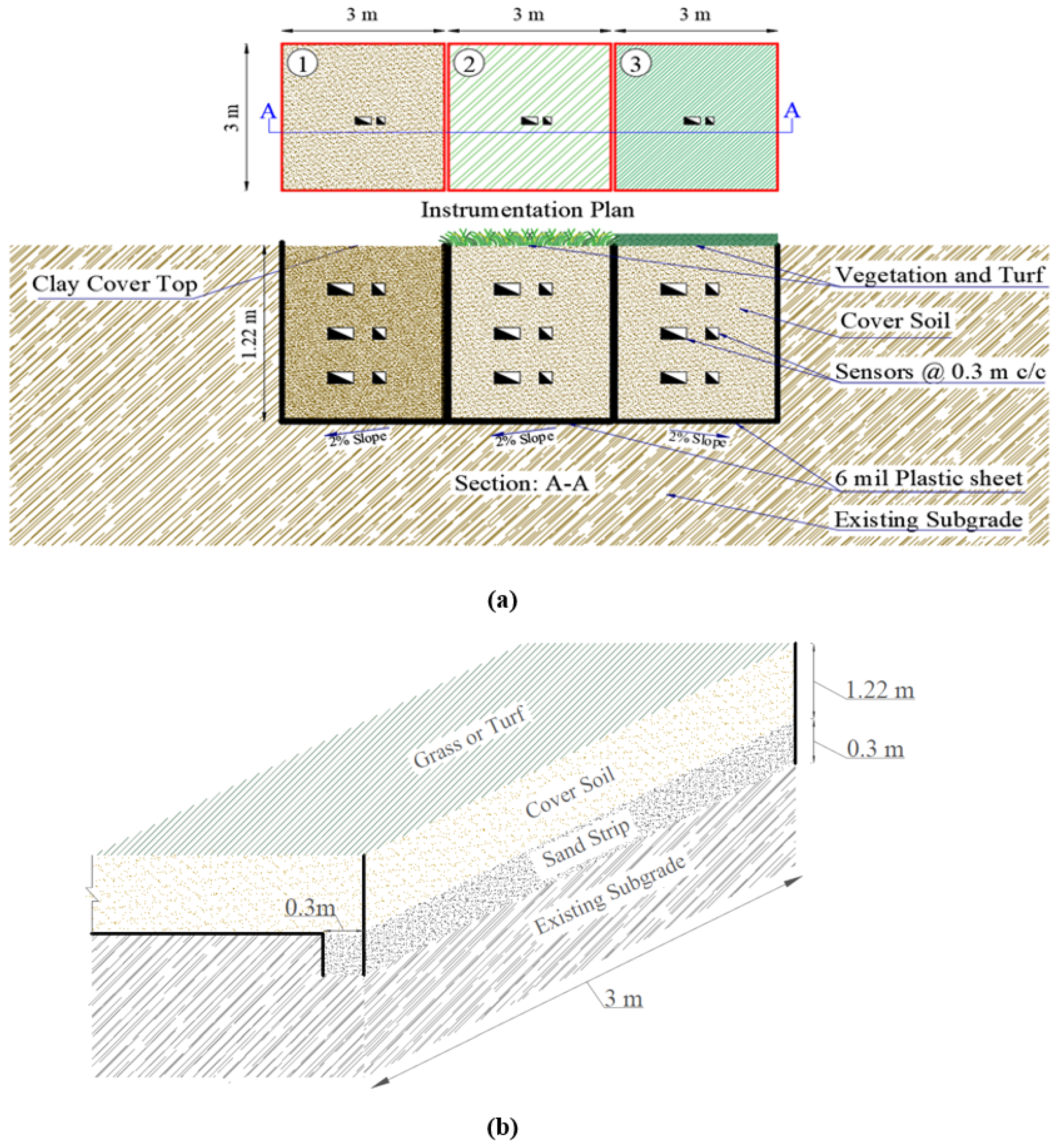

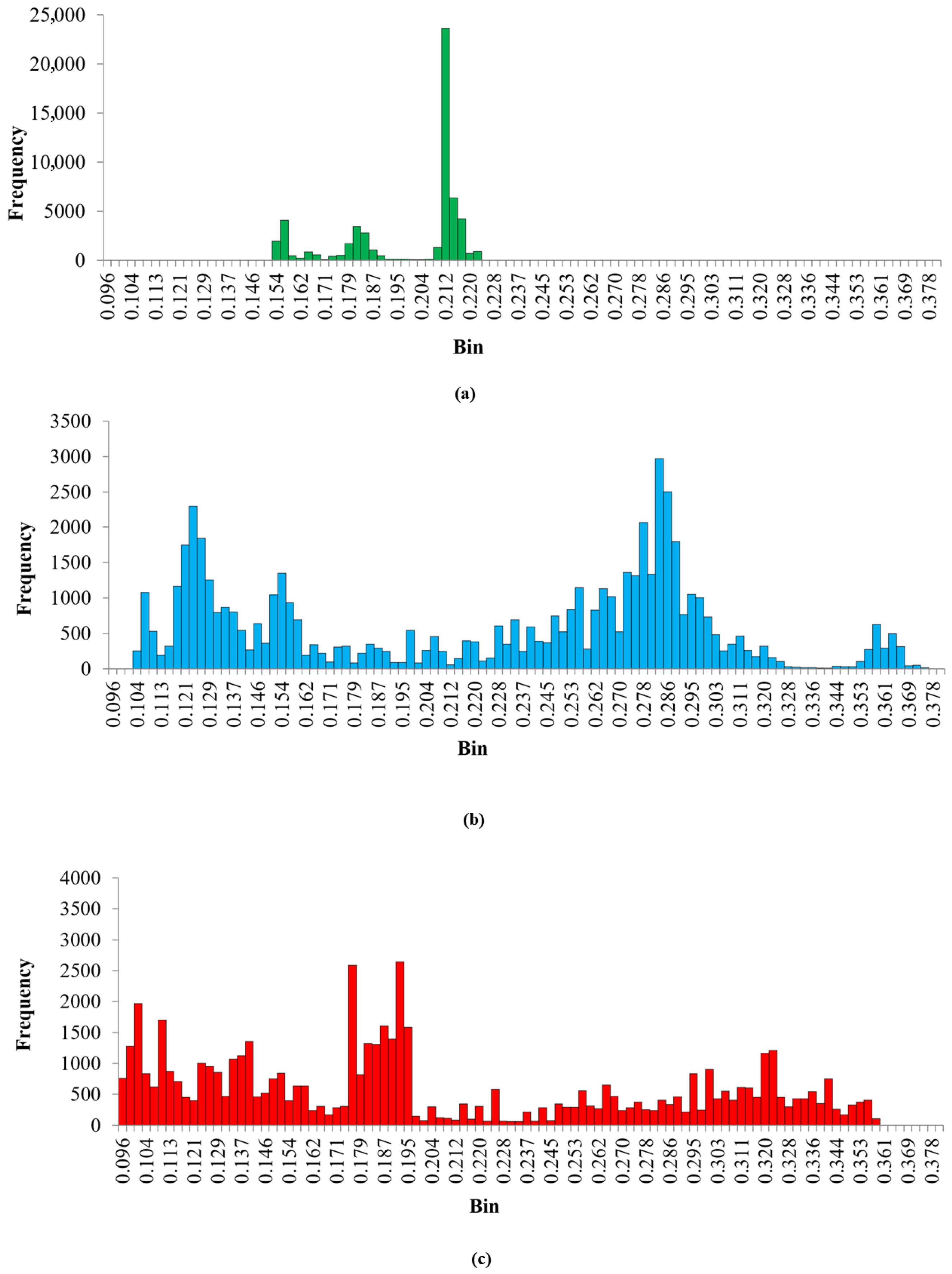
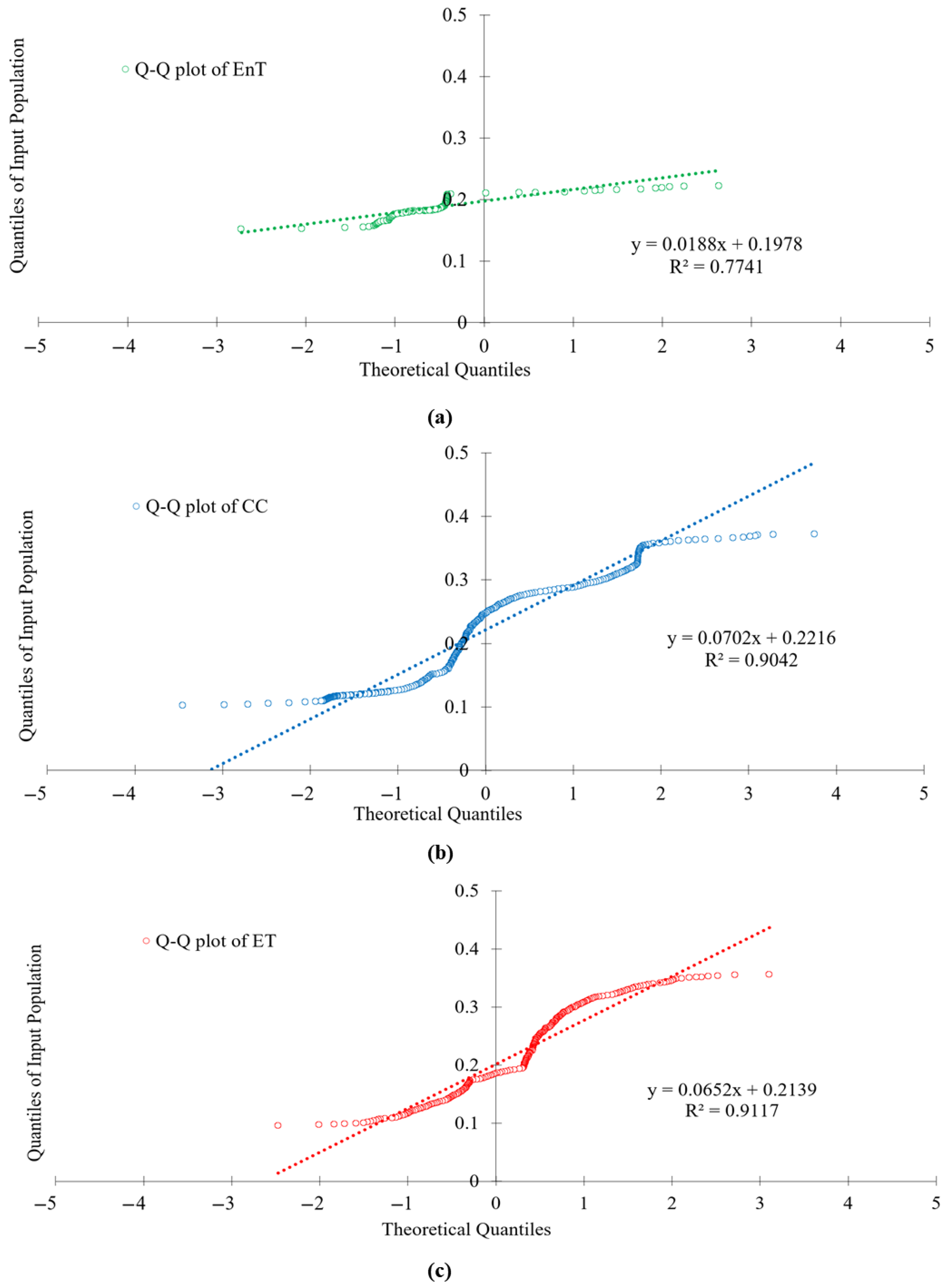
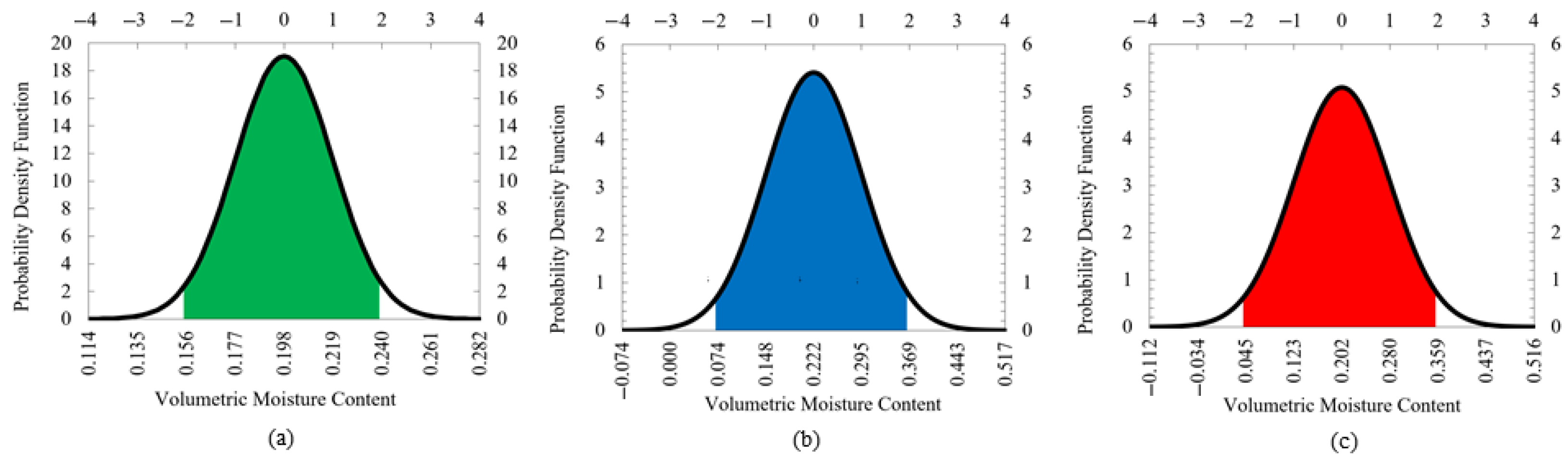
| Cover Type | Surface | Compaction | Depth (m) | Sensor Placement |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EnT | Engineered Turf | 95% of MDD | 1.2 | TEROS11 at 0.3 m |
| CC | Bare Soil | 95% of MDD | 1.2 | TEROS11 at 0.3 m |
| ET | Bermuda Grass | 80% of MDD | 1.2 | TEROS11 at 0.3 m |
| Descriptive Statistics | EnT | CC | ET |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean () | 0.198 | 0.222 | 0.202 |
| Standard Error | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Median | 0.210 | 0.247 | 0.185 |
| Mode | 0.210 | 0.281 | 0.193 |
| Standard Deviation () | 0.021 | 0.074 | 0.078 |
| Coefficient of Variation (CV) | 10.6% | 33.3% | 38.6% |
| Excess Kurtosis | −0.368 | −1.325 | −1.138 |
| Skewness | −1.056 | −0.149 | 0.431 |
| Range | 0.070 | 0.270 | 0.260 |
| Minimum | 0.152 | 0.102 | 0.096 |
| Maximum | 0.222 | 0.372 | 0.356 |
| Count | 56578 | 56578 | 56578 |
| Confidence Level (95.0%) | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| Cover/Comparison | Test | Test Statistic | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cover | Normality Test | W-Statistic | p-Value | Interpretation |
| EnT | 0.7512 | <0.001 | Not normal | |
| CC | Shapiro–Wilk | 0.9036 | <0.001 | Not normal |
| ET | 0.9151 | <0.001 | Not normal | |
| Cover | Normality Test | A2-Statistic | p-value | Interpretation |
| EnT | 6309.94 | <0.001 | Not normal | |
| CC | Anderson–Darling | 2302.51 | <0.001 | Not normal |
| ET | 1631.67 | <0.001 | Not normal | |
| Comparison | Homogeneity Test | F-Statistic | p-value | Interpretation |
| EnT vs. CC | 63026.38 | <0.001 | Unequal variances | |
| EnT vs. ET | Levene’s Test | 53891.15 | <0.001 | Unequal variances |
| CC vs. ET | 0.2347 | 0.628 | Equal variances | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mozumder, R.S.; Aggarwal, M.; Alam, M.J.B.; Rahman, N. Probabilistic Analysis of Soil Moisture Variability of Engineered Turf Cover Using High-Frequency Field Monitoring. Geotechnics 2025, 5, 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/geotechnics5030064
Mozumder RS, Aggarwal M, Alam MJB, Rahman N. Probabilistic Analysis of Soil Moisture Variability of Engineered Turf Cover Using High-Frequency Field Monitoring. Geotechnics. 2025; 5(3):64. https://doi.org/10.3390/geotechnics5030064
Chicago/Turabian StyleMozumder, Robi Sonkor, Maalvika Aggarwal, Md Jobair Bin Alam, and Naima Rahman. 2025. "Probabilistic Analysis of Soil Moisture Variability of Engineered Turf Cover Using High-Frequency Field Monitoring" Geotechnics 5, no. 3: 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/geotechnics5030064
APA StyleMozumder, R. S., Aggarwal, M., Alam, M. J. B., & Rahman, N. (2025). Probabilistic Analysis of Soil Moisture Variability of Engineered Turf Cover Using High-Frequency Field Monitoring. Geotechnics, 5(3), 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/geotechnics5030064







