Dissipation of Energy and Generation of Pore Pressure in Load-Controlled and Displacement-Controlled Cyclic Tests
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background
2.1. Cyclic Laboratory Tests
2.1.1. Cyclic Triaxial Tests
2.1.2. Cyclic Direct Simple Shear Tests
2.2. Pore Pressure Generation in Cyclic Laboratory Tests
2.3. Energy Dissipation and Pore Pressure Generation
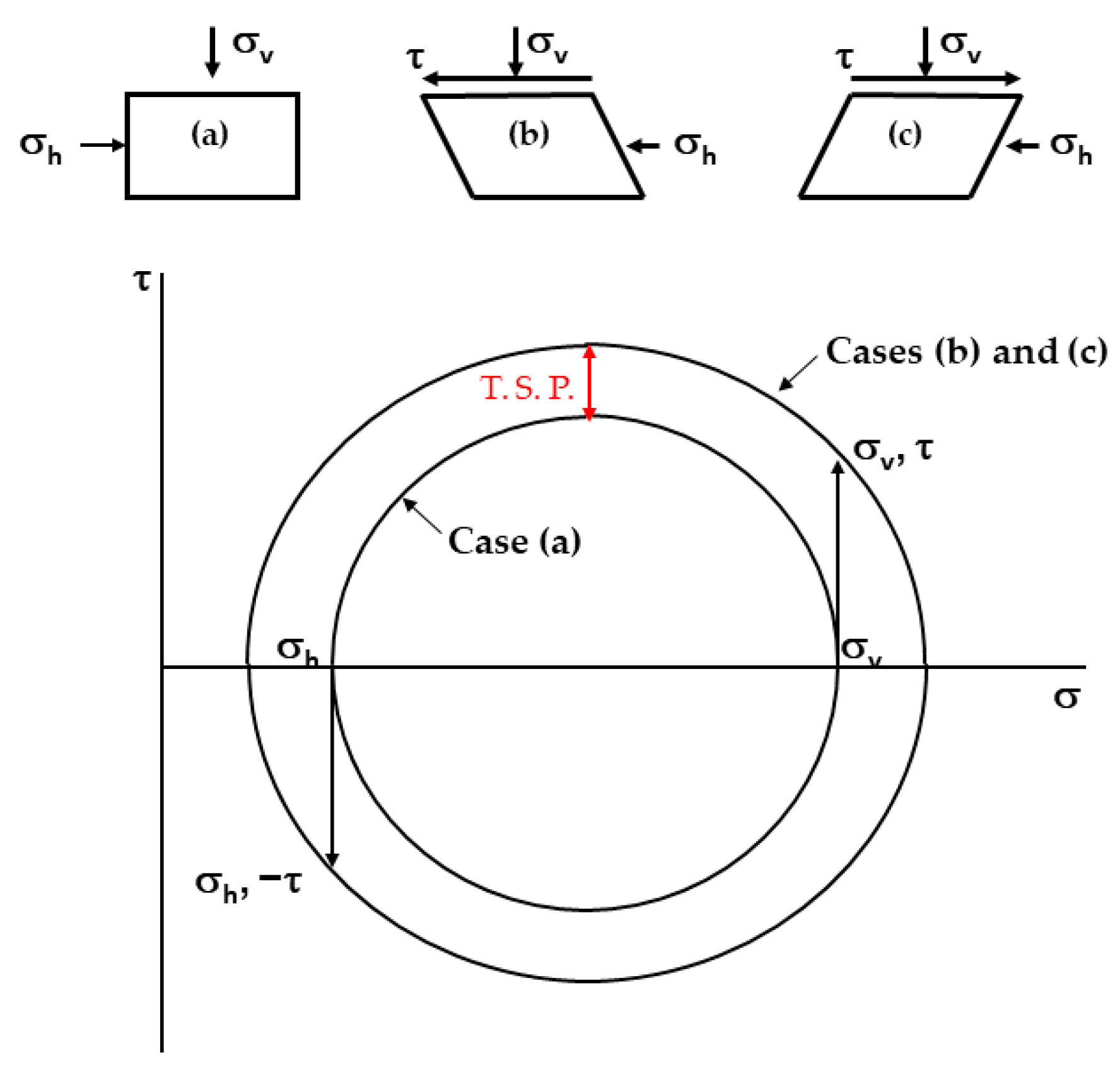
2.4. Terminology
2.5. Previous Studies
3. The Laboratory Testing Program
4. Results of Laboratory Testing
5. Analysis of Test Results
5.1. Visual Evaluation of Laboratory Test Data
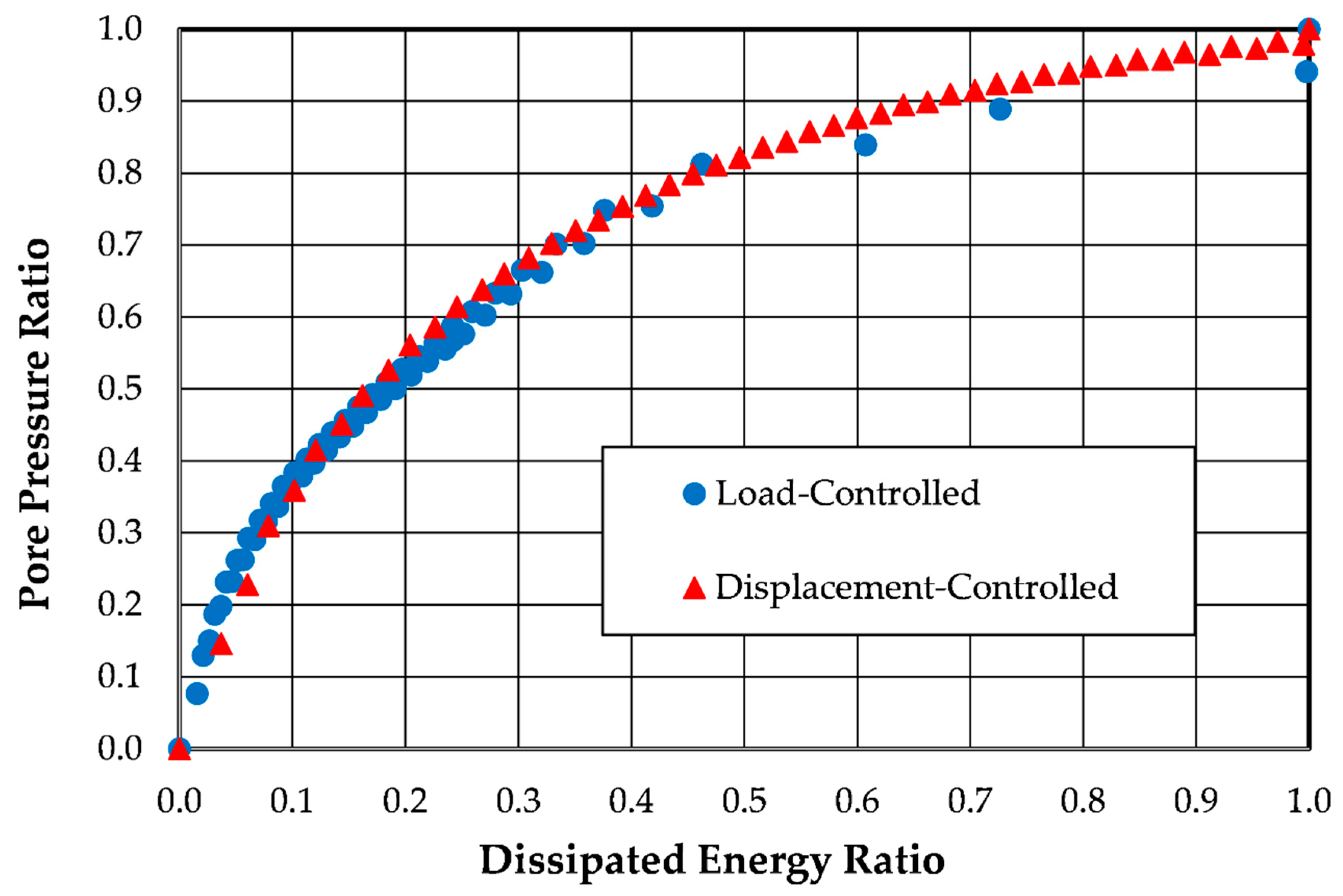
5.2. Evaluation of Pore Pressure Generation
6. Discussion of Test Results
6.1. Discussion of Pore Pressure Generation Patterns Observed
6.2. Implications of This Study’s Findings
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Umar, M.; Chiaro, G.; Kiyota, T.; Ullah, N. Deformation and cyclic resistance of sand in large-strain undrained torsional shear tests with initial static shear stress. Soils Found. 2021, 61, 765–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.Z.; Chen, Y.M.; Li, W.W.; Liu, H.L. Monotonic and cyclic behaviors of loose anisotropically consolidated calcareous sand in torsional shear tests. Mar. Georesources Geotechnol. 2019, 37, 438–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahnazari, H.; Rezvani, R.; Tutunchian, M.A. Post-cyclic volumetric strain of calcareous sand using hollow cylindrical torsional shear tests. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2019, 124, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, R.R.; Ueda, K.; Uemura, K. Influence of the relative density and K0 effects in the cyclic response of Ottawa F-65 sand-cyclic Torsional Hollow-Cylinder shear tests for LEAP-ASIA-2019. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2020, 133, 106111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaro, G.; De Silva, L.I.N.; Koseki, J. Modeling the effects of static shear on the undrained cyclic torsional simple shear behavior of liquefiable sand. Geotech. Eng. J. 2017, 48, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Salam, S.; Xiao, M. Evaluation of the effects of shaking history on liquefaction and cone penetration resistance using shake table tests. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2020, 131, 106025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, R.E.S.; Honnette, T.R.; Jacobs, J.S. Large-scale liquefaction and postliquefaction shake table testing. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2020, 146, 04020138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, Y.Y.; Chen, C.H. On the variation of mechanical properties of saturated sand during liquefaction observed in shaking table tests. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2020, 129, 105946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahed Orang, M.; Motamed, R.; Prabhakaran, A.; Elgamal, A. Large-scale shake table tests on a shallow foundation in liquefiable soils. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2021, 147, 04020152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, D.; Montgomery, J.; Stuedlein, A.W. Observations and challenges in simulating post-liquefaction settlements from centrifuge and shake table tests. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2022, 153, 107089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, B.; Xie, X.; Zhao, T.; Song, S.; Ma, Z.; Feng, X.; Wang, H. Centrifuge tests of macroscopic and mesoscopic investigation into effects of seismic histories on sand liquefaction resistance. J. Earthq. Eng. 2022, 26, 4302–4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, B.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Lu, P.; Ren, F. Centrifuge model testing on reliquefaction characteristics of sand. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2019, 17, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darby, K.M.; Boulanger, R.W.; DeJong, J.T.; Bronner, J.D. Progressive changes in liquefaction and cone penetration resistance across multiple shaking events in centrifuge tests. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2019, 145, 04018112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Wu, D.; Zuo, K.; Tessari, A. Centrifuge shake table tests on the liquefaction resistance of sand with clayey fines. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2022, 148, 04021180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, T.; Chiaradonna, A.; Love, N.; Wilson, D.; Ziotopoulou, K.; Martinez, A.; DeJong, J. Effect of soil gradation on embankment response during liquefaction: A centrifuge testing program. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2022, 157, 107221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seed, H.B.; Lee, K.L. Liquefaction Of Saturated Sands During Cyclic Loading. J. Soil Mech. Found. Div. 1966, 92, 105–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seed, H.B.; Idriss, I.M. Ground Motions and Soil Liquefaction during Earthquakes; Earthquake Engineering Research Institute: Oakland, CA, USA, 1982; p. 134. [Google Scholar]
- Finn, W.; Vaid, Y.; Bhatia, S.K. Constant Volume Cyclic Simple Shear Testing. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Microzonation for Safer Construction: Research and Applications, San Francisco, CA, USA, 26 November–1 December 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Finn, W.D.L. Aspects of constant volume cyclic simple shear. In Proceedings of the Advances in the Art of Testing of Soils Under Cyclic Conditions, Detroit, MI, USA, 24 October 1985; American Society of Civil Engineers: New York, NY, USA; 1985; pp. 74–98. [Google Scholar]
- Franke, E.; Kiekbusch, M.; Schuppener, B. A new direct simple shear device. Geotech. Test. J. 1979, 2, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentini, V.; Castelli, F. Liquefaction resistance of sandy soils from undrained cyclic triaxial tests. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2019, 37, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhang, F.; Peng, Q.; Dupla, J.C.; Canou, J.; Cumunel, G.; Foerster, E. Effect of the loading frequency on the sand liquefaction behaviour in cyclic triaxial tests. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2021, 147, 106779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, B.; Han, J.T.; Kim, J.; Kwak, T.Y. Liquefaction characteristic of Pohang sand based on cyclic triaxial test. J. Korean Geotech. Soc. 2020, 36, 21–32. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J. Influence of fines contents on soil liquefaction resistance in cyclic triaxial test. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2020, 38, 4735–4751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Mittal, S.; Shukla, S.K. Liquefaction proneness of stratified sand-silt layers based on cyclic triaxial tests. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2023, 15, 1826–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polito, C.P.; Martin, J.R., II. Effects of nonplastic fines on the liquefaction resistance of sands. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2001, 127, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polito, C.; Green, R.A.; Dillon, E.; Sohn, C. Effect of load shape on relationship between dissipated energy and residual excess pore pressure generation in cyclic triaxial tests. Can. Geotech. J. 2013, 50, 1118–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokusho, T.; Tanimoto, S. Energy capacity versus liquefaction strength investigated by cyclic triaxial tests on intact soils. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2021, 147.4, 04021006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nong, Z.Z.; Park, S.S.; Lee, D.E. Comparison of sand liquefaction in cyclic triaxial and simple shear tests. Soils Found. 2021, 61, 1071–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mele, L.; Lirer, S.; Flora, A. The effect of confinement in liquefaction tests carried out in a cyclic simple shear apparatus. E3S Web Conf. 2019, 92, 08002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Guo, L. Effect of phase difference on the liquefaction behavior of sand in multidirectional simple shear tests. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2021, 147, 06021015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcino, D.D.; Triantafyllidis, T.; Wichtmann, T.; Tomasello, G. Application of critical state approach to liquefaction resistance of sand–silt mixtures under cyclic simple shear loading. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2021, 147, 04020177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasello, G.; Porcino, D.D. Influence of sloping ground conditions on cyclic liquefaction behavior of sand under simple shear loading. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2022, 163, 107516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappellaro, C.; Cubrinovski, M.; Bray, J.D.; Chiaro, G.; Riemer, M.F.; Stringer, M.E. Liquefaction resistance of Christchurch sandy soils from direct simple shear tests. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2021, 141, 106489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.S.; Nong, Z.Z.; Lee, D.E. Effect of vertical effective and initial static shear stresses on the liquefaction resistance of sands in cyclic direct simple shear tests. Soils Found. 2020, 60, 1588–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Chen, J.F.; Peng, M.; Zhu, Y. Liquefaction behavior of fiber-reinforced calcareous sands in unidirectional and multidirectional simple shear tests. Geotext. Geomembr. 2022, 50, 794–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijic, Z.; Bray, J.D.; Riemer, M.F.; Rees, S.D.; Cubrinovski, M. Cyclic and monotonic simple shear testing of native Christchurch silty soil. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2021, 148, 106834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booker, J.R.; Rahman, M.S.; Seed, H.B. GADFLEA—A Computer Program for the Analysis of Pore Pressure Generation and Dissipation During Cyclic or Earthquake Loading; EERC 76-24; University of California: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Dobry, R.; Ladd, R.; Yokel, F.; Chung, R.; Powell, D. Prediction of Pore Water Pressure Buildup and Liquefaction of Sands during Earthquakes by the Cyclic Strain Method; NBS Building Science Series 138; National Bureau of Standards, US Department of Commerce: Washington, DC, USA, 1982.
- Hubler, J.; Athanasopoulos-Zekkos, A.; Zekkos, D. Monotonic and cyclic simple shear response of gravel-sand mixtures. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2018, 115, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, R.A.; Mitchell, J.K.; Polito, C.P. An energy-based pore pressure generation model for cohesionless soils. In Proceedings of the John Booker Memorial Symposium—Developments in Theoretical Geomechanics, Balkema, Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 16–17 November 2000; pp. 383–390. [Google Scholar]
- Seed, H.B.; Idriss, I.M. Simplified Procedure For Evaluation Soil Liquefaction Potential. J. Soil Mech. Found. Div. 1971, 97, 1249–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemat-Nasser, S.; Shokooh, A. A Unified Approach to Densification and Liquefaction of Cohesionless Sand in Cyclic Shearing. Can. Geotech. J. 1979, 16, 659–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrill, J.B.; Davis, R.O. Energy Dissipation and Seismic Liquefaction of Sands: Revised Model. Soils Found. 1985, 25, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasello, G.; Porcino, D.D. Energy-Based Pore The prediction of pore pressure build-up by an energy-based model calibrated from the results of in-situ tests. In Proceedings of the Conference on Performance-based Design in Earthquake. Geotechnical Engineering, Beijing, China, 15–17 July 2022; pp. 1622–1629. [Google Scholar]
- Green, R.A. Energy-Based Evaluation and Remediation of Liquefiable Soils. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Civil Engineering, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Blacksburg, VA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Karakan, E.; Tanrinian, N.; Sezer, A. Cyclic undrained behavior and post liquefaction settlement of a nonplastic silt. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2019, 120, 214–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polito, C.; Martin, J.R. Dissipated Energy and Pore-pressure-generation patterns in Sands and Non-Plastic Silts Subjected to Cyclic Loadings. Geotechnics 2024, 4, 264–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polito, C.; Sibley, E. Threshold Fines Content and the Behavior of Sands with Non-Plastic Silt. Can. Geotech. J. 2020, 57, 462–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, T.; Laue, J.; Mattson, H.; Jia, Q. Excess pore water pressure generation in fine granular materials under undrained cyclic triaxial loading. Int. J. Geo-Eng. 2023, 14, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polito, C.; Grossman, J. The Effect off Height to Diameter Ratio on Cyclic Triaxial Tests. In Proceedings of the GeoSaskatoon 2023, Saskatoon, SK, Canada, 1–4 October 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Khashila, M.; Hussien, M.N.; Karray, M.; Chekired, M. Liquefaction resistance from cyclic simple and triaxial shearing: A comparative study. Acta Geotech. 2021, 16, 1735–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D5311/D5311M-13; Standard Test Method for Load-Controlled Cyclic Triaxial Strength of Soil. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013.
- Ladd, R.S. Preparing Test Specimens Using Undercompaction. Geotech. Test. J. 1978, 1, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D8296-19; Standard Test Method for Consolidated Undrained Cyclic Direct Simple Shear Test under Constant Volume with Load Control or Displacement Control. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013.












| Soil Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Specific Gravity, Gs | 2.65 |
| Median Grain Size, D50 (mm) | 0.39 |
| Coefficient of Uniformity, Cu | 1.91 |
| Coefficient of Curvature, Cc | 0.95 |
| Maximum Index Void Ratio, emax | 0.688 |
| Minimum Index Void Ratio, emin | 0.436 |
| Test Type | Method of Test Control | CSR or Applied Shear Strain | Cycles to Cause Liquefaction NL | NDEPUV Ws,L | Proposed Behavior | Measured Behavior |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
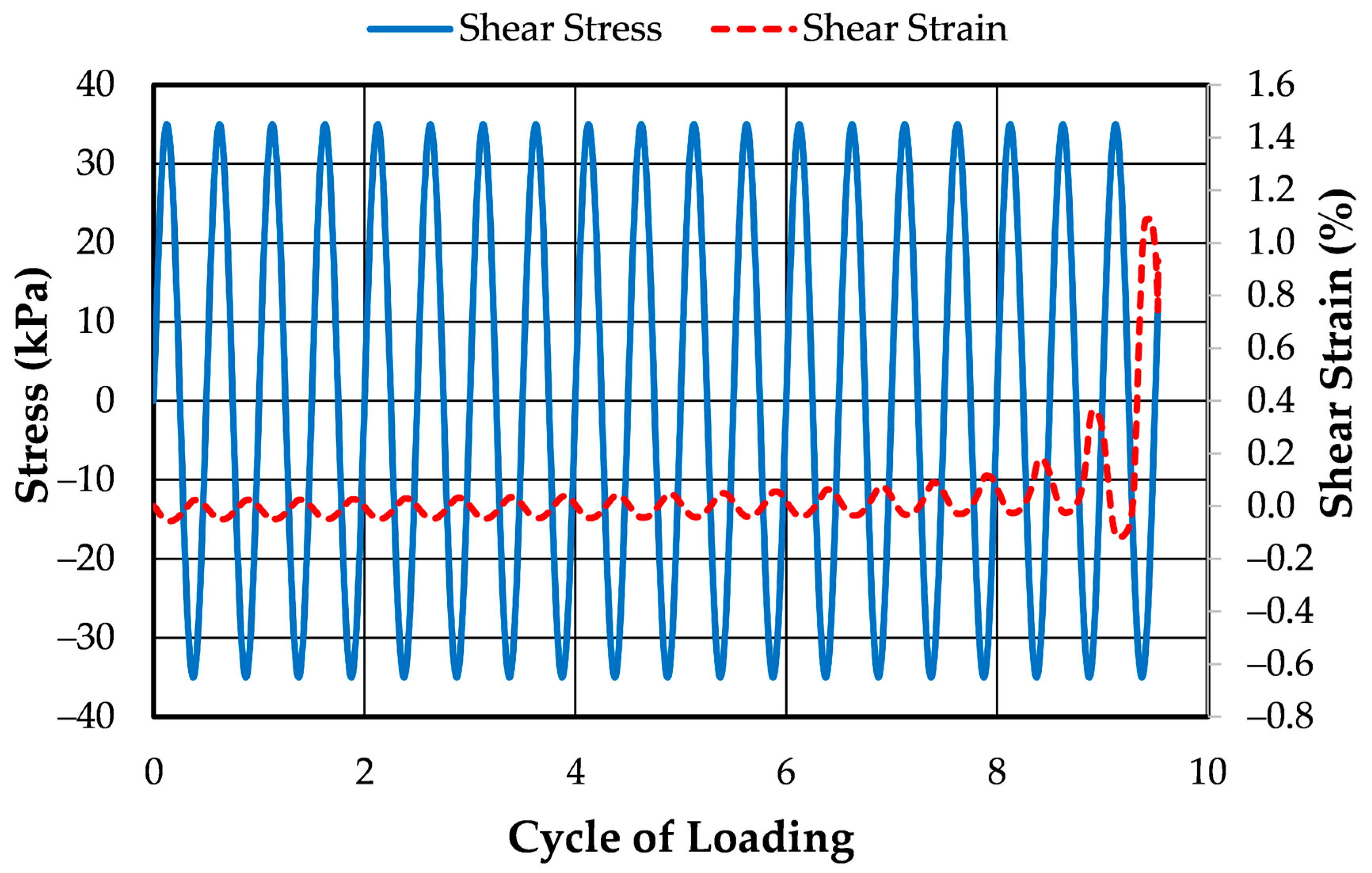
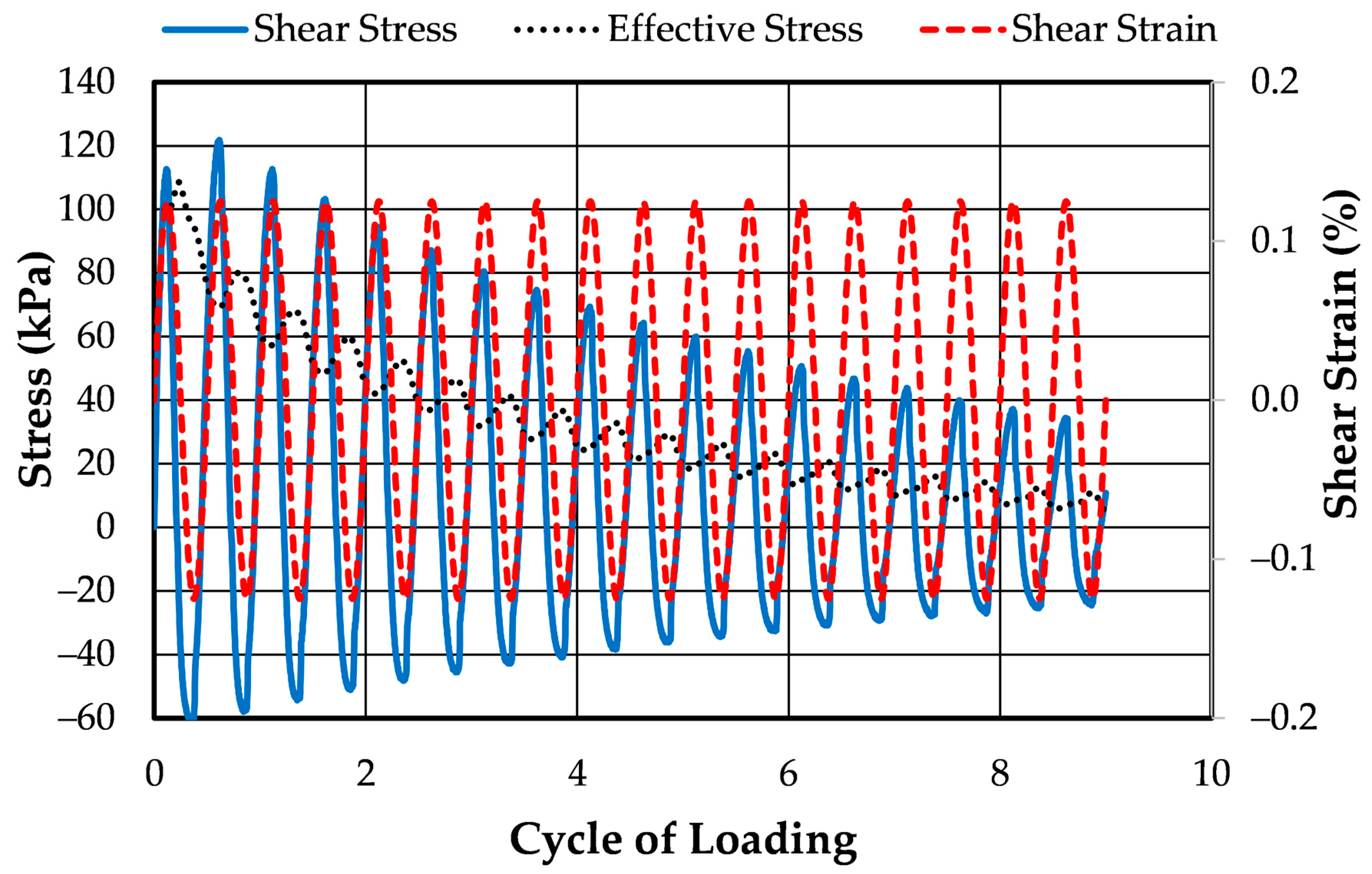
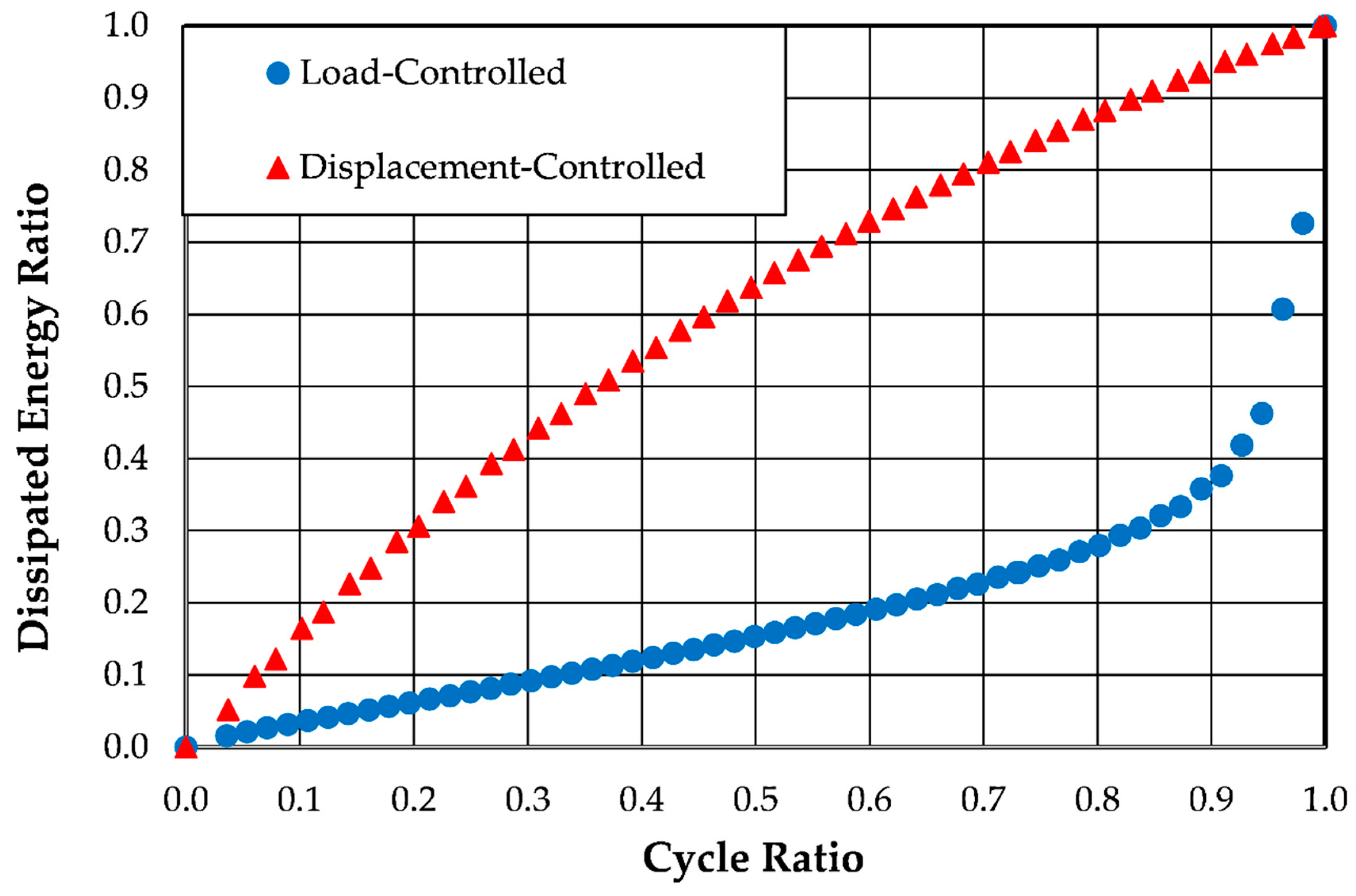
| CTX | stress | 0.22 | 28.1 | 0.01758 | Figure 3 | Figure 9 |
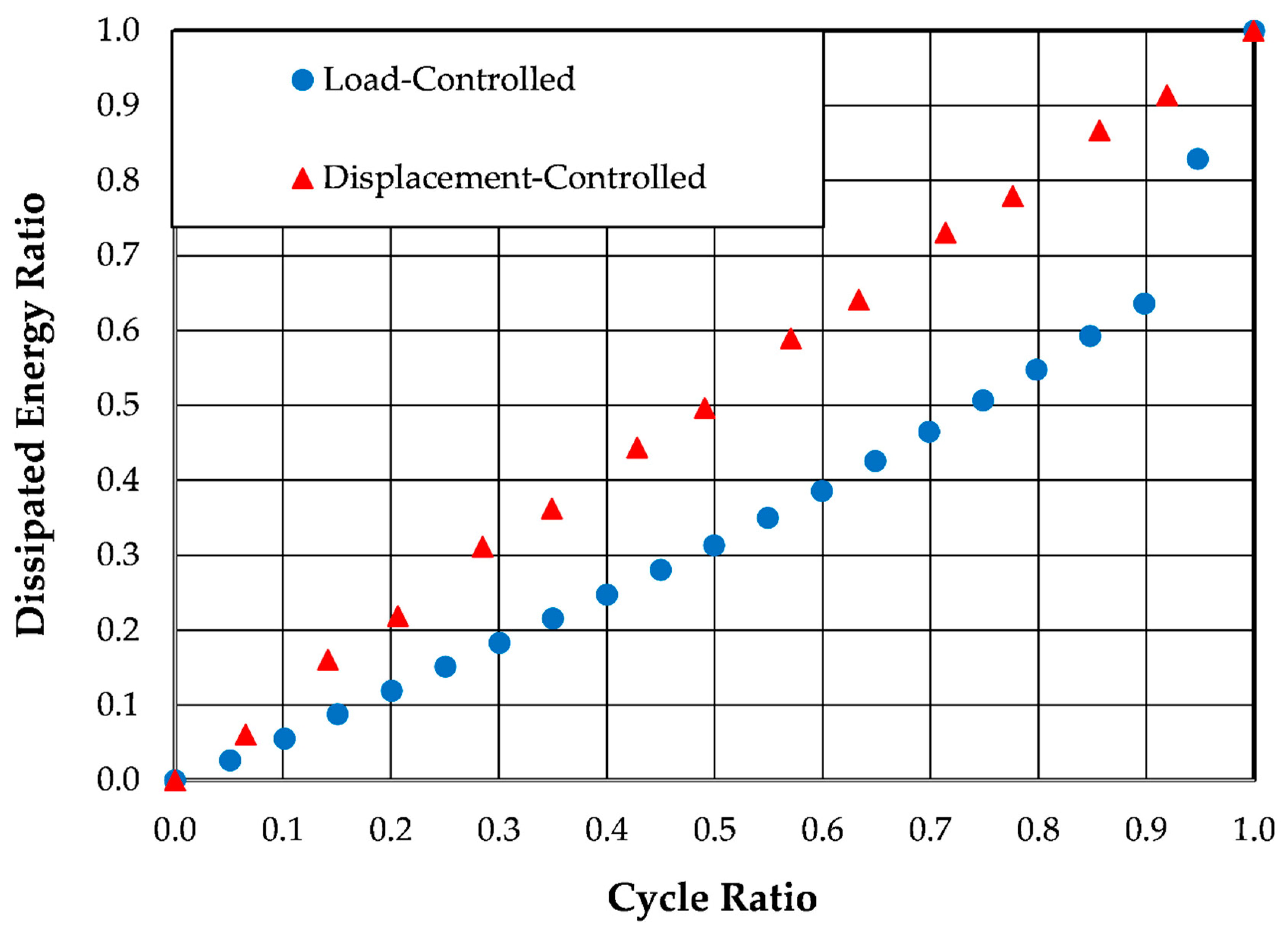
| strain | 0.10% | 24.0 | 0.01767 | Figure 5 | Figure 11 | |
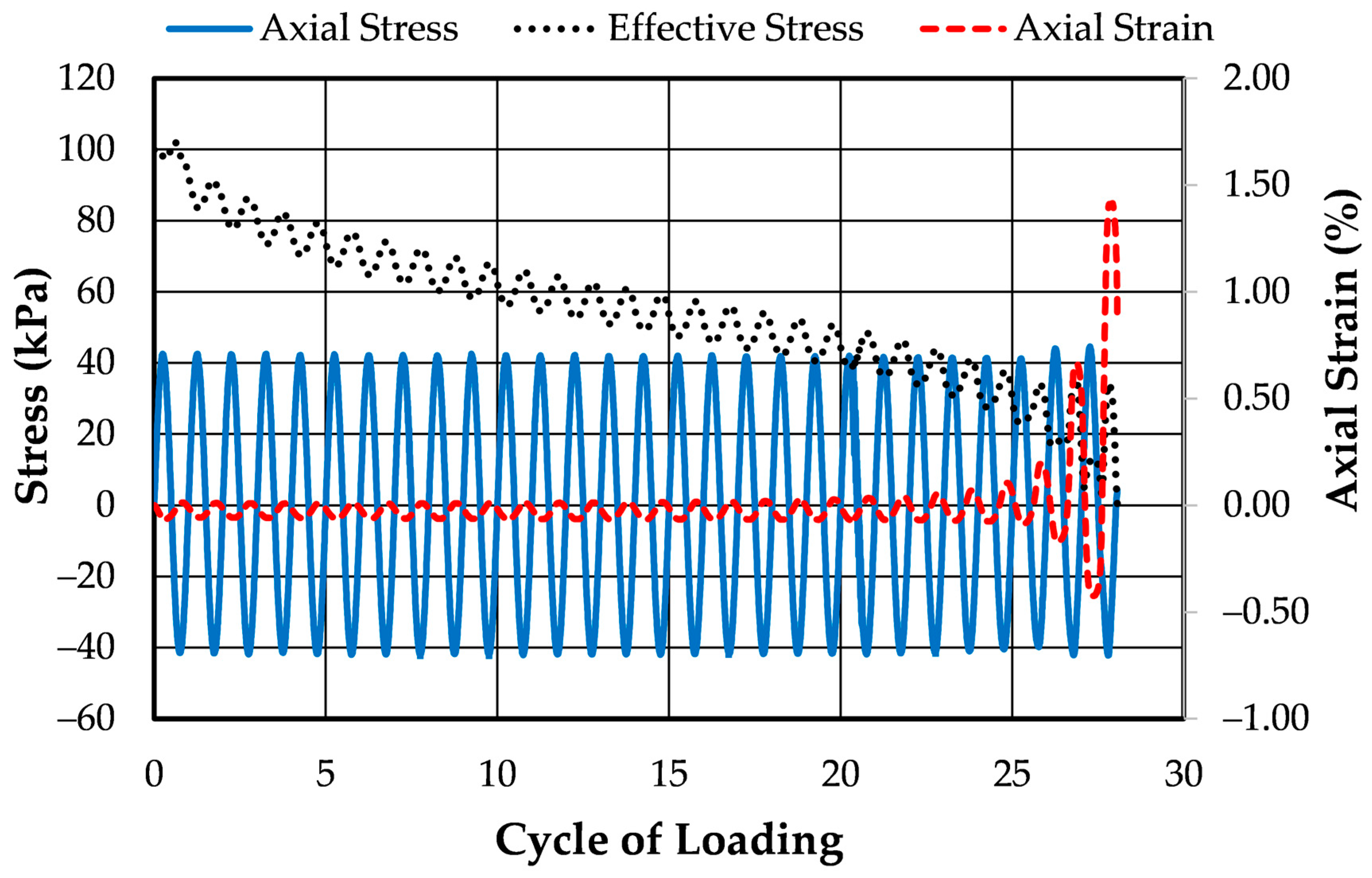
| CDSS | stress | 0.07 | 10.0 | 0.0016 | Figure 4 | Figure 10 |
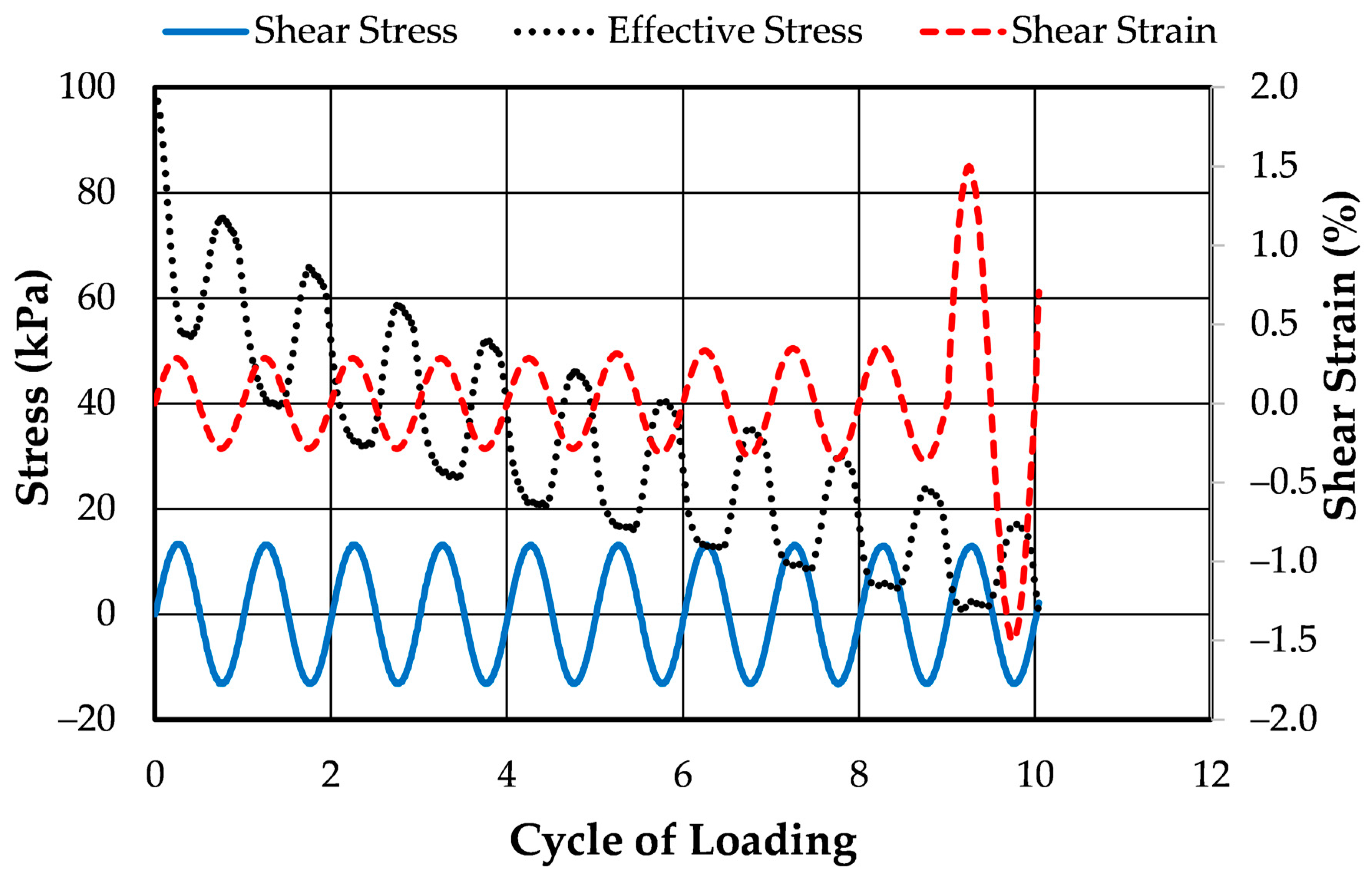
| strain | 0.10% | 9.0 | 0.0017 | Figure 6 | Figure 12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Polito, C.P.; Zhang, Z.; Moldenhauer, H.H.M. Dissipation of Energy and Generation of Pore Pressure in Load-Controlled and Displacement-Controlled Cyclic Tests. Geotechnics 2024, 4, 1026-1047. https://doi.org/10.3390/geotechnics4040052
Polito CP, Zhang Z, Moldenhauer HHM. Dissipation of Energy and Generation of Pore Pressure in Load-Controlled and Displacement-Controlled Cyclic Tests. Geotechnics. 2024; 4(4):1026-1047. https://doi.org/10.3390/geotechnics4040052
Chicago/Turabian StylePolito, Carmine P., Zhuoyue Zhang, and Henry H. M. Moldenhauer. 2024. "Dissipation of Energy and Generation of Pore Pressure in Load-Controlled and Displacement-Controlled Cyclic Tests" Geotechnics 4, no. 4: 1026-1047. https://doi.org/10.3390/geotechnics4040052
APA StylePolito, C. P., Zhang, Z., & Moldenhauer, H. H. M. (2024). Dissipation of Energy and Generation of Pore Pressure in Load-Controlled and Displacement-Controlled Cyclic Tests. Geotechnics, 4(4), 1026-1047. https://doi.org/10.3390/geotechnics4040052






