A Methodology to Evaluate the Horizontal Earth Pressure Acting on Circular Shafts Based on Its Lateral Displacements
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
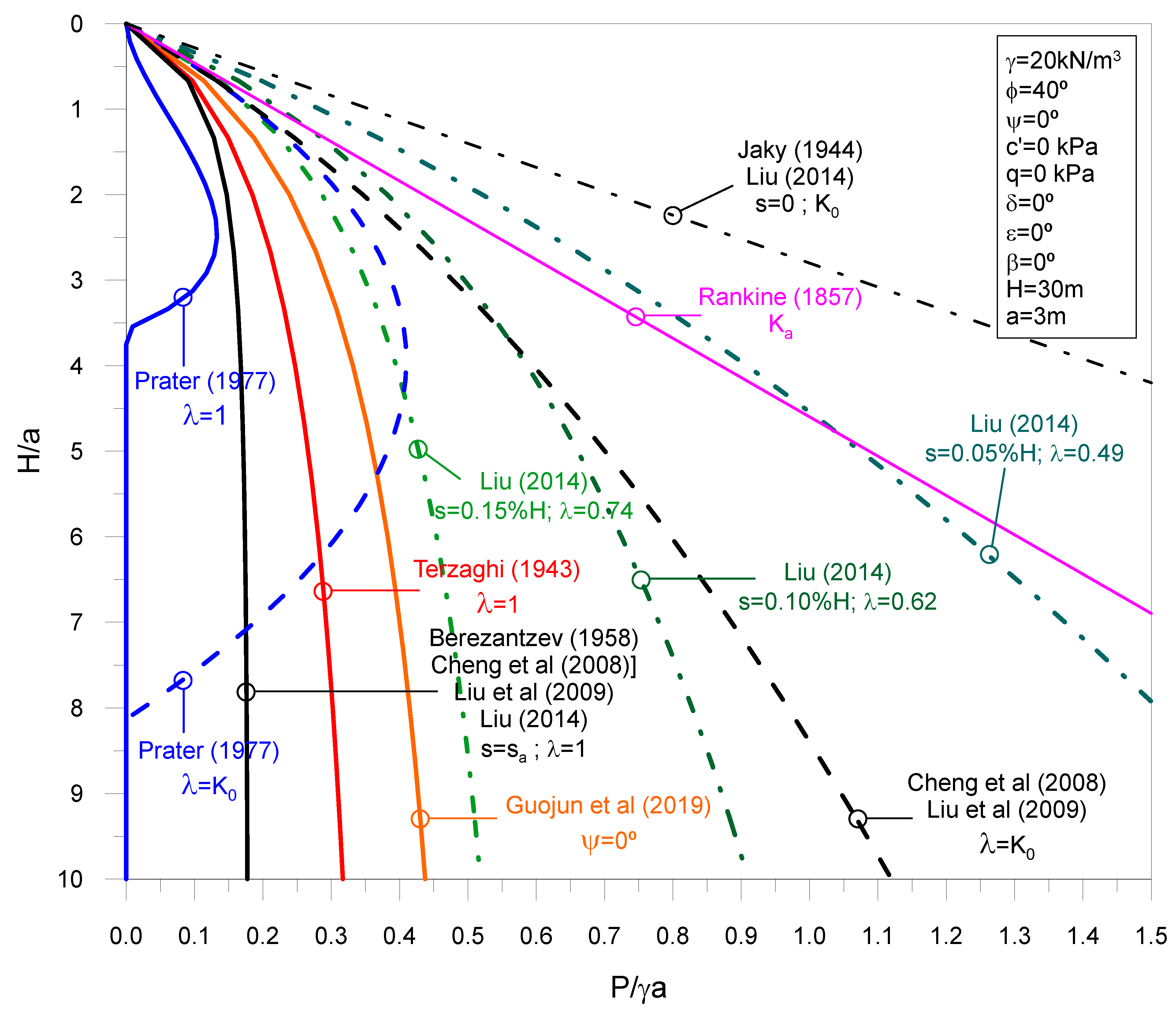
2.1. Comparison of the Analytical Methods
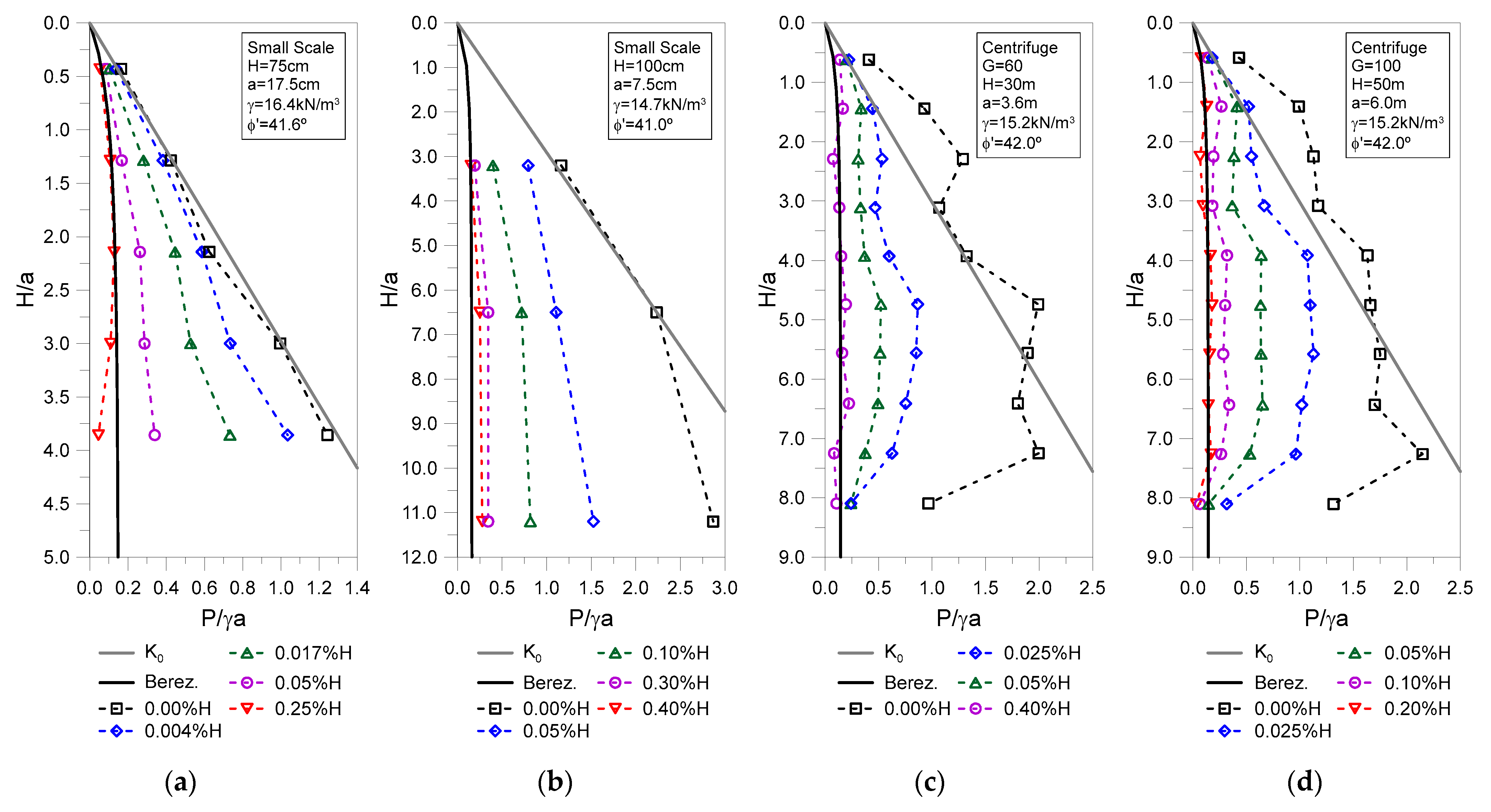
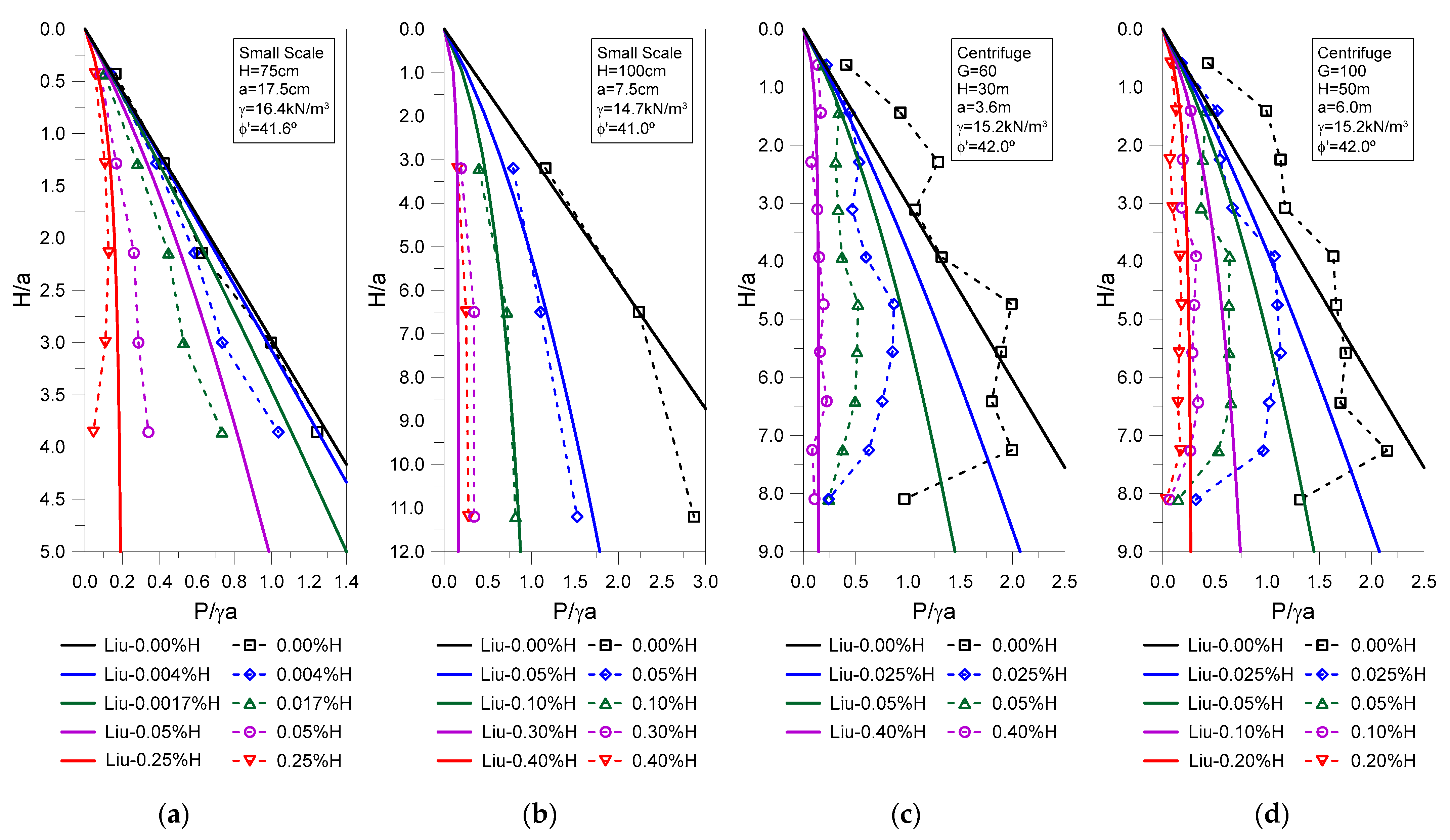
2.2. Shaft Excavation Physical Models
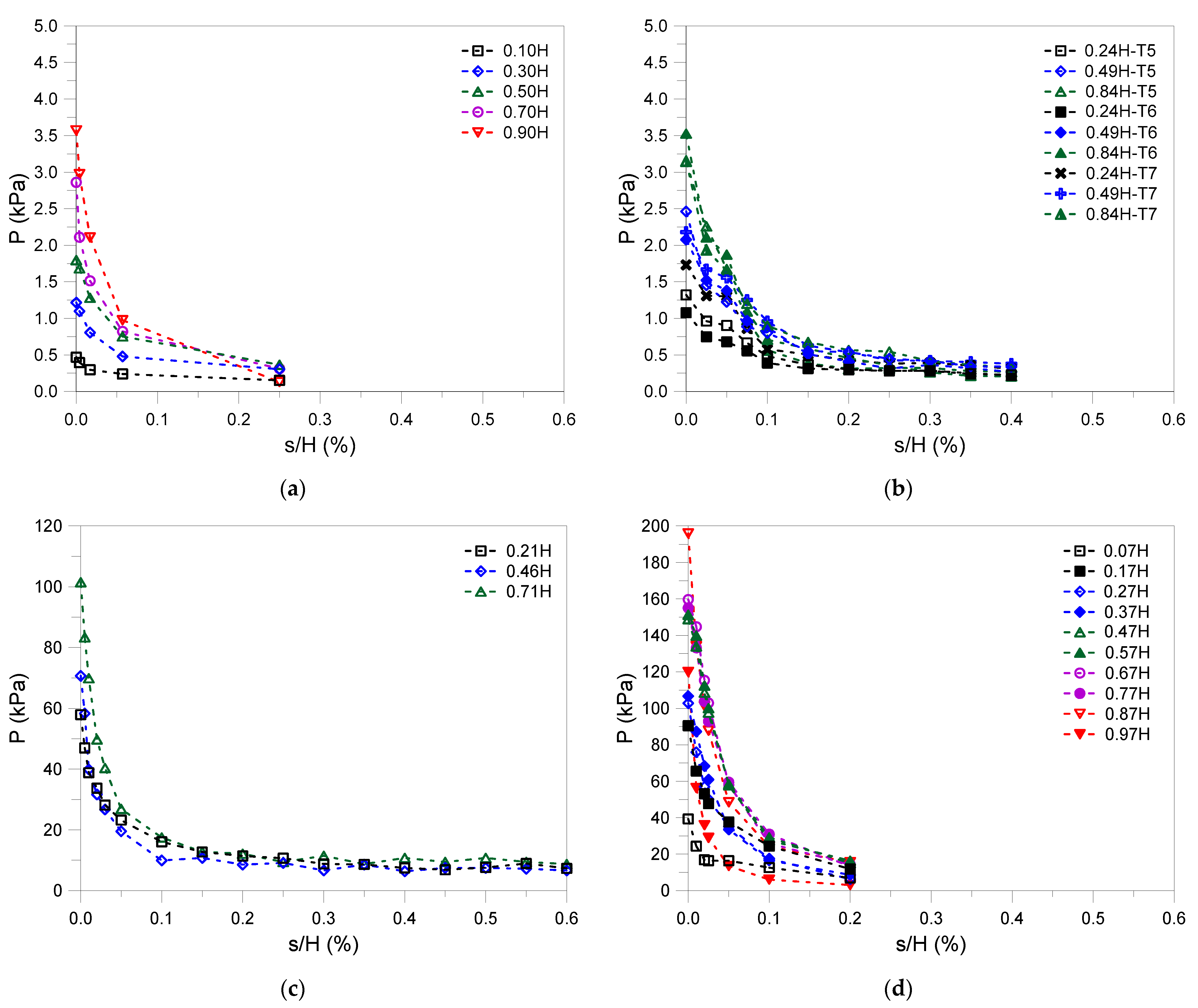
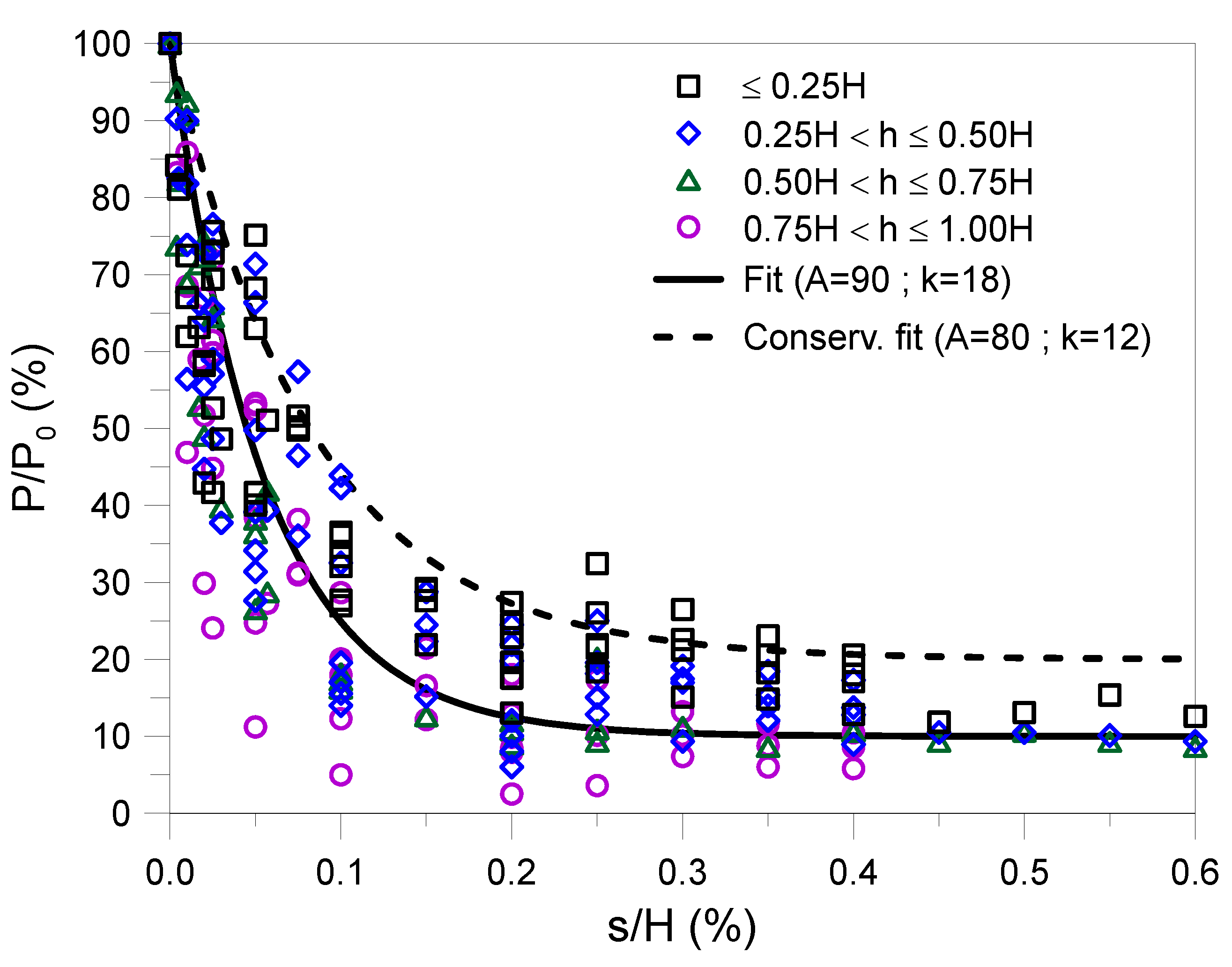
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Faustin, N.E.; Elshafie, M.Z.; Mair, R.J. Case studies of circular shaft construction in London. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng.-Ground Improv. 2018, 171, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, J.P. Deep circular excavations, remarkable projects in Mexico. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Sydney, Australia, 1–5 May 2022; p. 6. [Google Scholar]
- Kaya, A.; Tarakçi, Ü.C. Stability Investigation of a Deep Shaft Using Different Methods. Int. J. Geomech. 2021, 21, 05020009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedro, A.M.G. Geotechnical Investigation of Ivens Shaft in Lisbon. Ph.D. Thesis, Imperial College London, London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Aye, T.; Tong, M.; Yi, K.; Arunasoruban, E. Design and Construction of Large Diameter Circular Shafts. In Proceedings of the Underground Singapore (UGS), Singapore, 26 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Parashar, S.; Mitchell, R.; Hee, M.W.; Sanmugnathan, D.; Nicholson, G. Performance monitoring of deep shafts at Changi WRP project, Singapore. In 7th FMGM 2007: Field Measurements in Geomechanics; ASCE Press: Reston, VA, USA, 2007; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Pedro, A.; Zdravković, L.; Potts, D.; Almeida e Sousa, J. Numerical modelling of the Ivens shaft construction in Lisbon, Portugal. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng.-Geotech. Eng. 2019, 172, 263–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, T.G.S.; Farias, M.M.; Assis, A.P. Large diameter shafts for underground infrastructure. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2015, 45, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- França, P.; Taborda, D.M.G.; Pedro, A.M.G.; Almeida e Sousa, J.; Topa Gomes, A. Salgueiros station of the Oporto Metro—Analysis of its behaviour. In Proceedings of the XIII COBRAMSEG/III CLBG/IV SBMR, Curitiba, Brazil, 27–31 August 2006; p. 6. [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai, T.; Ariizumi, K.; Kashiwagi, A. Behaviour and analysis of a large-scale cylindrical earth retaining structure. Soils Found. 1999, 39, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janeiro, H.; Pedro, A.M.G.; Almeida e Sousa, J. Evaluation of the earth pressures acting on shafts through analytical methods. In Proceedings of the XVII National Conference in Geotechnics/X CLBG, Lisbon, Portugal, 14–17 November 2021; p. 10. [Google Scholar]
- Coulomb, C.A. Ssais sur une application des regles des maximis et minimis a quelques problems de statique relatits a l’architecture. In Proceedings of the Memoires de Mathematique de l’Academie Royale de Science 7, Sav., Paris, France, 1776. [Google Scholar]
- Rankine, W.J.M. On the stability of loose earth. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1857, 47, 9–27. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.Q.; Wang, J.H. A generalized slip line solution to the active earth pressure on circular retaining walls. Comput. Geotech. 2008, 35, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzaghi, K. Theoretical Soil Mechanics; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1943. [Google Scholar]
- Berezantzev, V.G. Earth pressure on the cylindrical retaining walls. In Proceedings of the Conference on Earth Pressure Problems, Brussels, Belgium, 1958; pp. 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Prater, E.G. Examination of some theories of earth pressure on shaft linings. Can. Geotech. J. 1977, 14, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.M.; Au, S.K.; Hu, Y.Y.; Wei, W.B. Active pressure for circular cut with Berezantzev’s and Prater’s theories, numerical modeling and field measurements. Soils Found. 2008, 48, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.Q.; Wang, J.H.; Zhang, L.L. Analytical solution of general axisymmetric active earth pressure. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 2009, 33, 551–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.Q.; Wang, J.H.; Zhang, L.L. Axi-symmetric active earth pressure obtained by the slip line method with a general tangential stress coefficient. Comput. Geotech. 2009, 36, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.Q. Lateral Earth Pressures Acting on Circular Retaining Walls. Int. J. Geomech. 2014, 14, 04014002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, G.-J.; Wang, J.-H.; Chen, J.-J. Analytical Solution for Axisymmetric Active Earth Pressure Based on the Characteristics Method considering Orthoradial Geometric Condition. Int. J. Geomech. 2019, 19, 04019099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guojun, X.; Jianhua, W. A rigorous characteristic line theory for axisymmetric problems and its application in circular excavations. Acta Geotech. 2018, 15, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, R.C.K.; Kaiser, P.K. Design and performance evaluation of vertical shafts—Rational shaft design method and verification of design method. Can. Geotech. J. 1988, 25, 320–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.M.; Hu, Y.Y.; Wei, W.B. General Axisymmetric Active Earth Pressure by Method of Characteristics-Theory and Numerical Formulation. Int. J. Geomech. 2007, 7, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobar, T.; Meguid, M.A. Comparative evaluation of methods to determine the earth pressure distribution on cylindrical shafts: A review. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2010, 25, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, S.; Muramatsu, M.; Sueoka, T. Ground movement, earth and water pressures due to shaft excavations. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Underground Construction in Soft Ground, New Delhi, India, 3 January 1994; pp. 151–154. [Google Scholar]
- Enami, A.; Morishita, H.; Ogihara, M.; Homma, M.; Tezuka, H.; Hiramatsu, Y. Earth pressure acting on a deep circular shaft wall. In Geotechnical Aspects of Underground Construction in Soft Ground; Routledge: London, UK, 1996; pp. 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- New, B.; Bowers, K. Ground movement model validation at the Heathrow Express trial tunnel. In Tunnelling ’94; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1994; pp. 301–329. [Google Scholar]
- Cabarkapa, Z.; Milligan, G.W.E.; Menkiti, C.O.; Murphy, J.; Potts, D.M. Design and performance of a large diameter shaft in Dublin Boulder Clay. In Proceedings of the BGA International Conference on Foundations: Innovations, Observations, Design and Practice, Dundee, UK, 2–5 September 2003; pp. 175–185. [Google Scholar]
- Taborda, D.M.G.; Pedro, A.M.G.; Xia, H.; Hardy, S. A methodology for improved predictions of surface ground movements around shafts. Geotech. Eng. 2024. under peer-review. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, J.; Lim, H.; Jeong, S.; Kim, K. Analysis of lateral earth pressure on a vertical circular shaft considering the 3D arching effect. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2015, 48, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaky, J. The coefficient of earth pressure at rest. J. Soc. Hung. Archit. Eng. 1944; 8, 355–358. [Google Scholar]
- Walz, B. Left bracket apparatus for measuring the three-dimensional active soil pressure on a round model caisson right bracket. Baumasch. Bautech. 1973, 20, 339–344. [Google Scholar]
- Chun, B.; Shin, Y. Active Earth Pressure Acting on the Cylindrical Retaining Wall of a Shaft. South Korea Ground Environ. Eng. J. 2006, 7, 15–24. [Google Scholar]
- Tobar, T.; Meguid, M.A. Experimental Study of the Earth Pressure Distribution on Cylindrical Shafts. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2011, 137, 1121–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, V.D.H.; Meguid, M.A.; Chouinard, L.E. Discrete Element and Experimental Investigations of the Earth Pressure Distribution on Cylindrical Shafts. Int. J. Geomech. 2014, 14, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagiwara, T.; Imamura, S.; Fujii, T.; Nomoto, T.; Kusakabe, O. Earth pressure acting on a deep circular shaft and associated ground deformation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Centrifuge, Tokyo, Japan, 23–25 September 1998; pp. 643–648. [Google Scholar]
- Imamura, S.; Nomoto, T.; Fujii, T.; Hagiwara, T. Earth pressures acting on a deep shaft and the movements of adjacent ground in sand. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Geotechnical Aspects of Underground Construction in Soft Ground, IS-Tokyo ’99, Tokyo, Japan, 19-21 July 1999; pp. 647–652. [Google Scholar]
- Lade, P.V.; Jessberger, H.L.; Makowski, E.; Jordan, P. Modeling of deep shafts in centrifuge test. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering, Stockholm, Sweden, 15–19 June 1981; pp. 683–691. [Google Scholar]
- Fujii, T.; Hagiwara, T.; Ueno, K.; Taguchi, A. Experiment and analysis of earth pressure on an axisymmetric shaft in sand. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Centrifuge, Singapore, 31 August–2 September 1994; pp. 791–796. [Google Scholar]
- Ueno, K.; Yokoyama, Y.; Ohi, A.; Fujii, T. Earth pressures acting on flexible circular shafts in sand. In Proceedings of the Geotechnical Aspects of Underground Construction in Soft Ground, London, UK, 15–17 April 1996; pp. 237–242. [Google Scholar]

| Method | Shaft Geometry | Soil | Soil–Wall Friction | Surcharge | Backfill Inclination | Circumferential Stress Ratio—σθ/σv | Shaft Lateral Displacement | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Height | Radius | Inclination | Weight | Cohesion | Friction Angle | Dilation | ||||||
| Terzaghi [15] | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | – | ||||
| Berezantzev [16] | – | – | – | – | 1 | – | ||||||
| Prater [17] | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | |||||
| Cheng et al. [18] | – | – | – | – | – | |||||||
| Liu et al. [19] | – | 1 | – | |||||||||
| Liu et al. [20] | – | – | – | – | – | |||||||
| Liu [21] | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | |||||
| Xiong et al. [22] | – | 2 | 3 | – | – | – | – | |||||
| Reference | Chun and Shin [35] | Tobar and Meguid [36] | Hagiwara et al. [38] | Imamura et al. [39] | |
| Type of test | Small-scale | Small-scale | Centrifuge | Centrifuge | |
| Soil | Sand | Dense | Dense | Dense | Dense |
| γ (kN/m3) | 16.4 | 14.7 | 15.2 | 15.2 | |
| ϕ’ (°) | 41.6 | 41.0 | 42.0 | 42.0 | |
| Acceleration | (g) | – | – | 60 | 100 |
| Model/Prototype | (m) | 0.75 | 1.00 | 30.00 | 50.00 |
| a (m) | 0.175 | 0.750 | 3.600 | 6.000 | |
| Maximum shaft displacement | |||||
| Reference | Chun and Shin [35] | Tobar and Meguid [36] | Hagiwara et al. [38] | Imamura et al. [39] | ||||||||||||
| s/H (%) | 0.004 | 0.017 | 0.05 | 0.25 | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.025 | 0.05 | 0.4 | 0.025 | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.2 | |
| Proposed | 93.8 | 76.3 | 46.6.1 | 11.0 | 46.6 | 24.9 | 10.4 | 10.1 | 67.4 | 46.6 | 10.1 | 67.4 | 46.6 | 24.9 | 12.5 | |
| Liu [21] | 0.35 | 0.38 | 0.48 | 0.92 | 0.48 | 0.61 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.40 | 0.47 | 1.00 | 0.40 | 0.47 | 0.60 | 0.83 | |
| 30.0 | 30.7 | 32.3 | 40.2 | 31.7 | 34.1 | 41.0 | 41.0 | 31.4 | 32.7 | 42.0 | 31.4 | 32.7 | 35.0 | 39.0 | ||
| Reference | Chun and Shin [35] | Tobar and Meguid [36] | Hagiwara et al. [38] | Imamura et al. [39] | |||||||||||
| s/H (%) | 0.004 | 0.017 | 0.05 | 0.25 | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.025 | 0.05 | 0.4 | 0.025 | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| Proposed | 0.25 | 0.12 | 0.04 | 0.14 | 0.69 | 0.50 | 0.17 | 0.09 | 18.8 | 7.7 | 2.7 | 33.2 | 20.6 | 9.9 | 4.2 |
| Liu [21] | 0.44 | 0.72 | 0.87 | 0.21 | 0.19 | 0.07 | 0.17 | 0.09 | 40.0 | 31.1 | 2.7 | 54.1 | 46.6 | 28.8 | 10.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pedro, A.M.G. A Methodology to Evaluate the Horizontal Earth Pressure Acting on Circular Shafts Based on Its Lateral Displacements. Geotechnics 2024, 4, 952-965. https://doi.org/10.3390/geotechnics4030048
Pedro AMG. A Methodology to Evaluate the Horizontal Earth Pressure Acting on Circular Shafts Based on Its Lateral Displacements. Geotechnics. 2024; 4(3):952-965. https://doi.org/10.3390/geotechnics4030048
Chicago/Turabian StylePedro, António M. G. 2024. "A Methodology to Evaluate the Horizontal Earth Pressure Acting on Circular Shafts Based on Its Lateral Displacements" Geotechnics 4, no. 3: 952-965. https://doi.org/10.3390/geotechnics4030048
APA StylePedro, A. M. G. (2024). A Methodology to Evaluate the Horizontal Earth Pressure Acting on Circular Shafts Based on Its Lateral Displacements. Geotechnics, 4(3), 952-965. https://doi.org/10.3390/geotechnics4030048