Urban Rivers Under Pressure: Human-Induced Modifications, Pollution, and Prospects for Restoration—A Case Study of the Assi River, Varanasi
Abstract
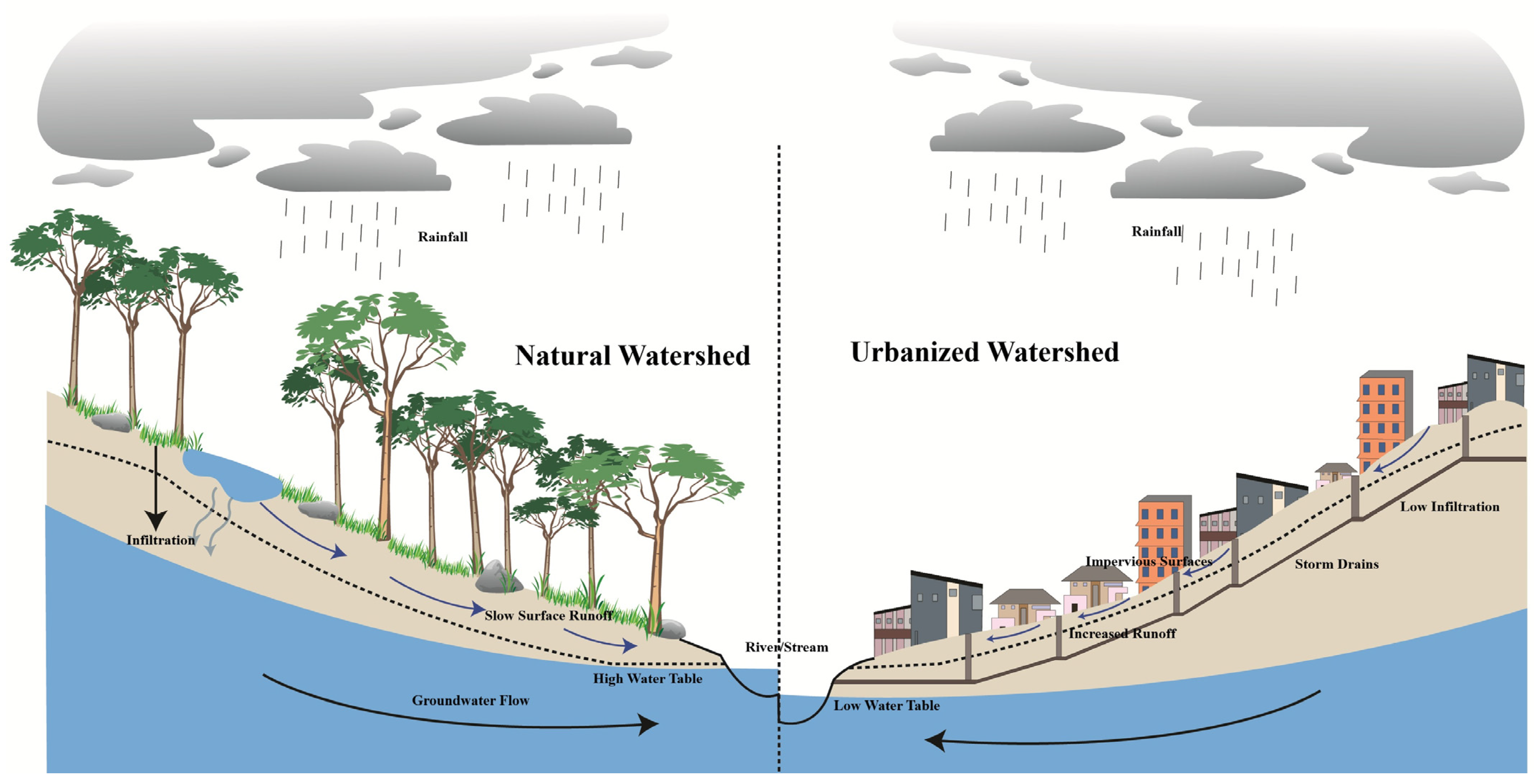
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
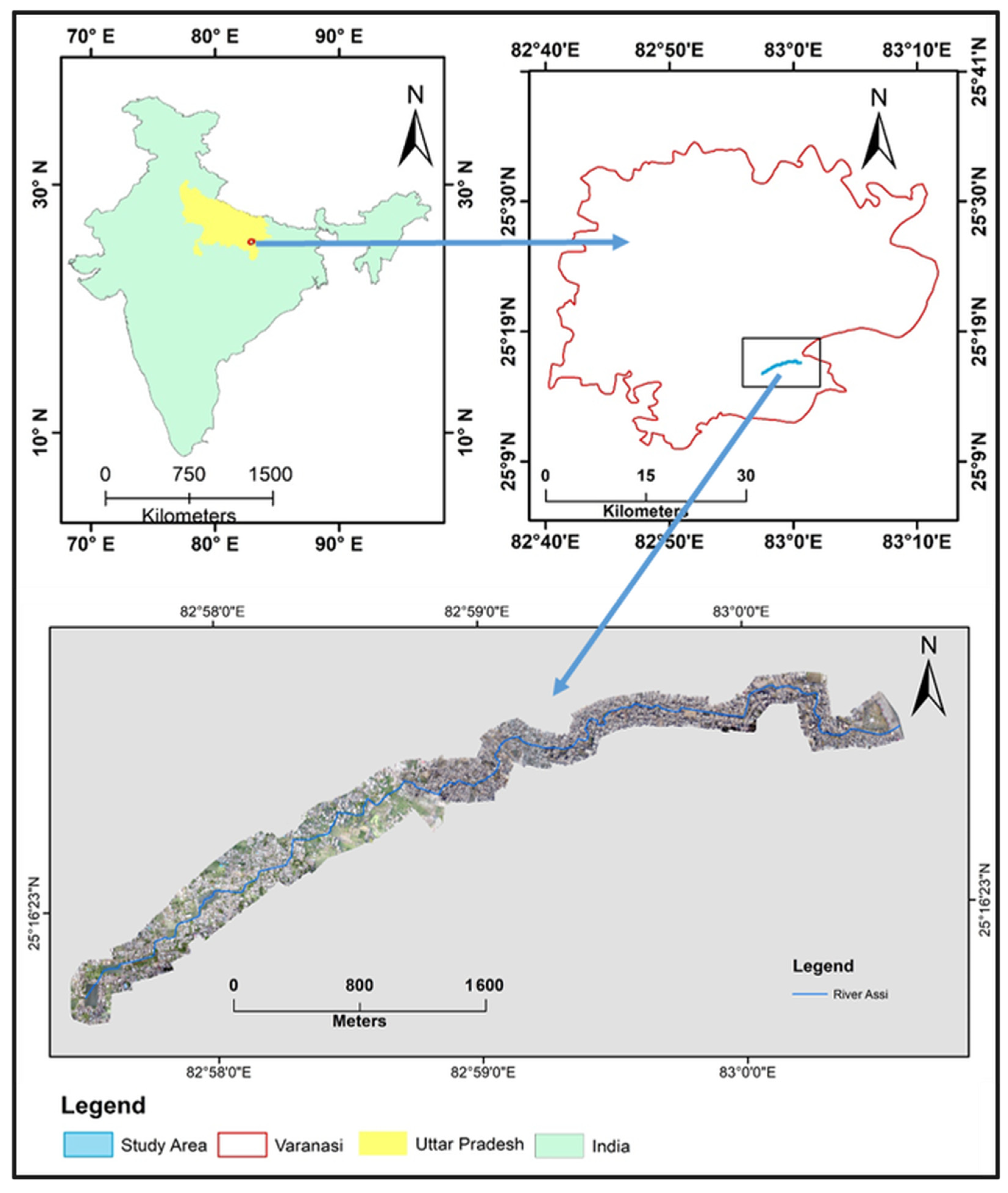
2.1. The Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
2.2.1. UAV Data Collection
2.2.2. Water Sampling and Testing
3. Results
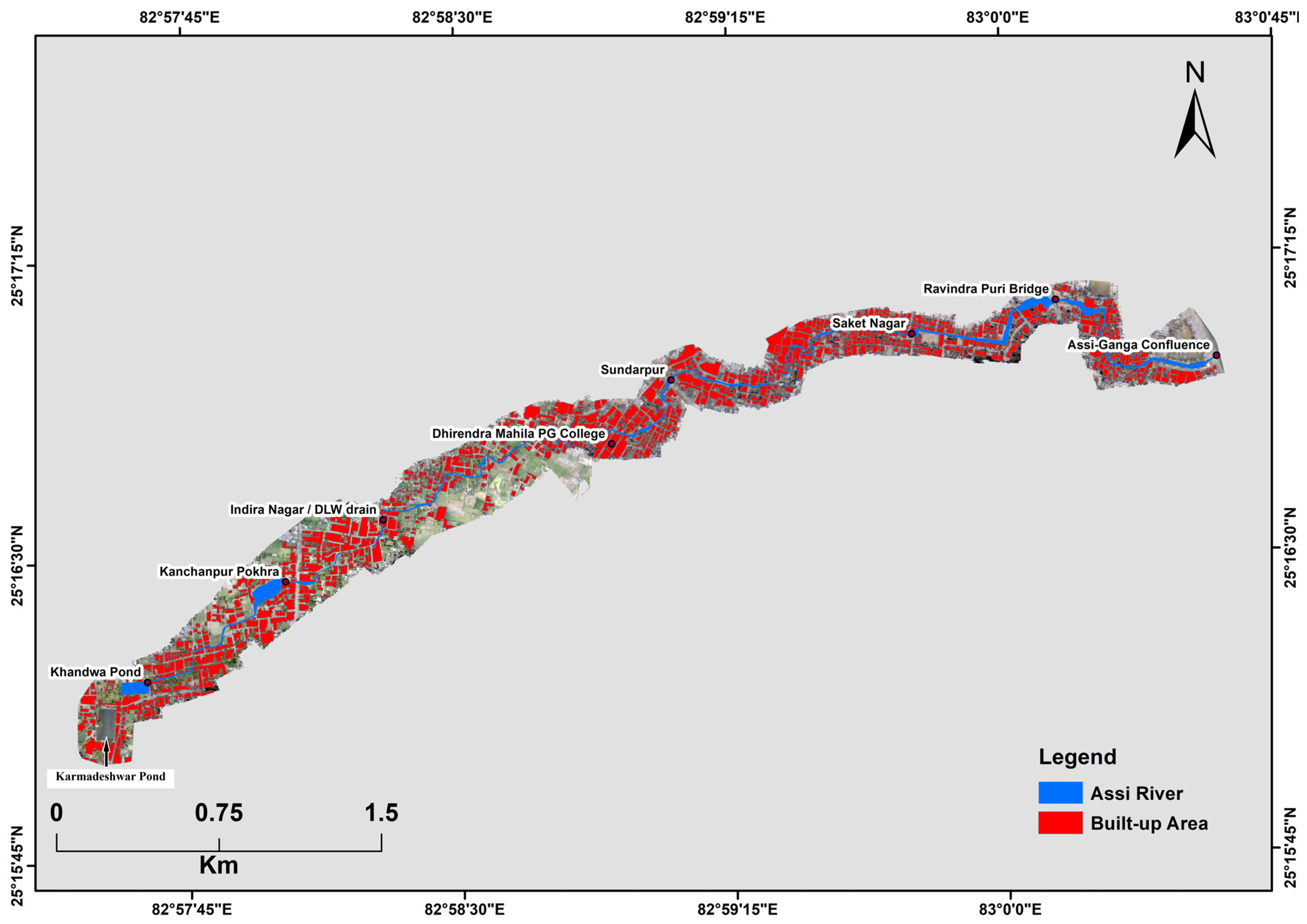
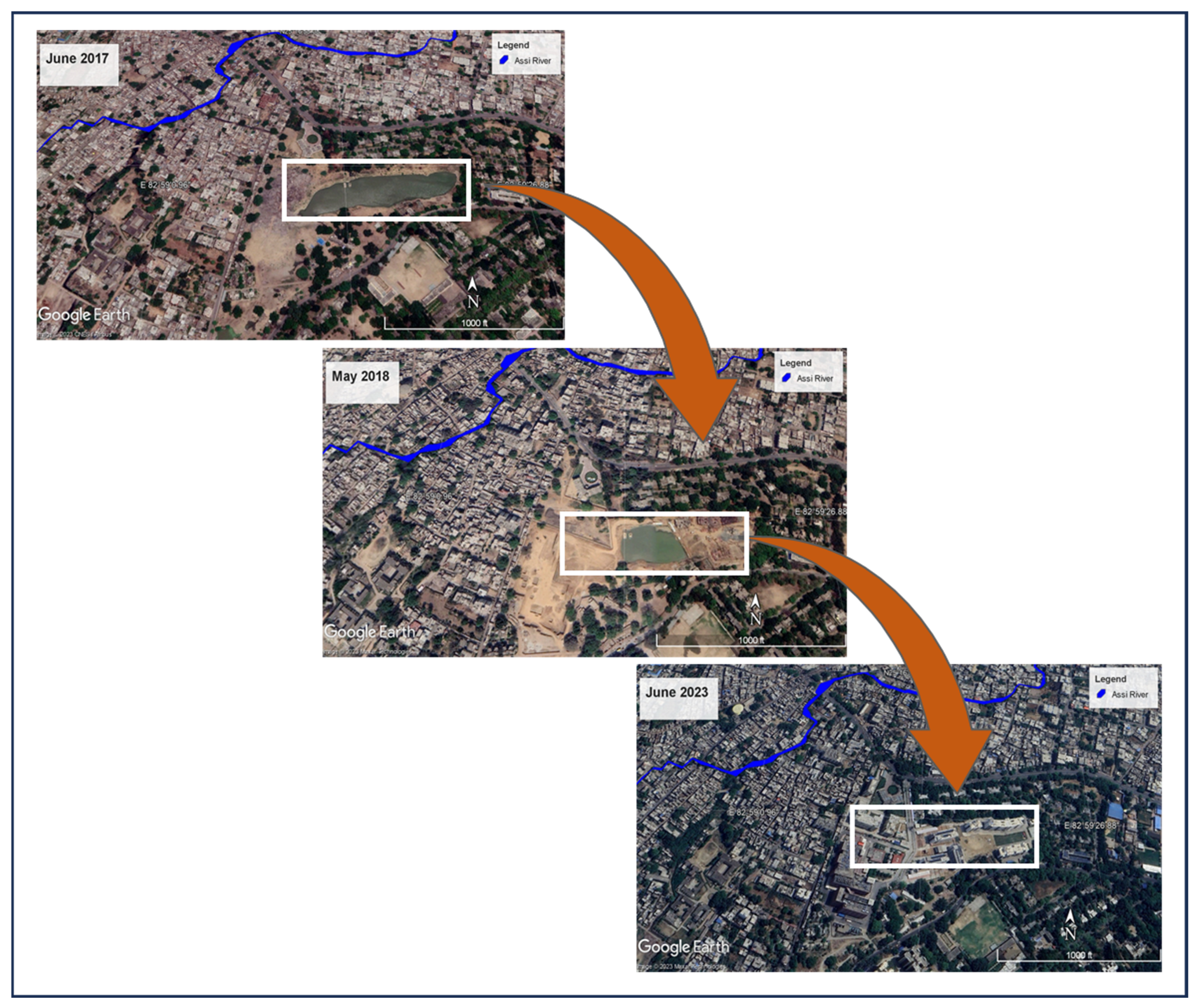
3.1. Spatial Distribution of Encroachment
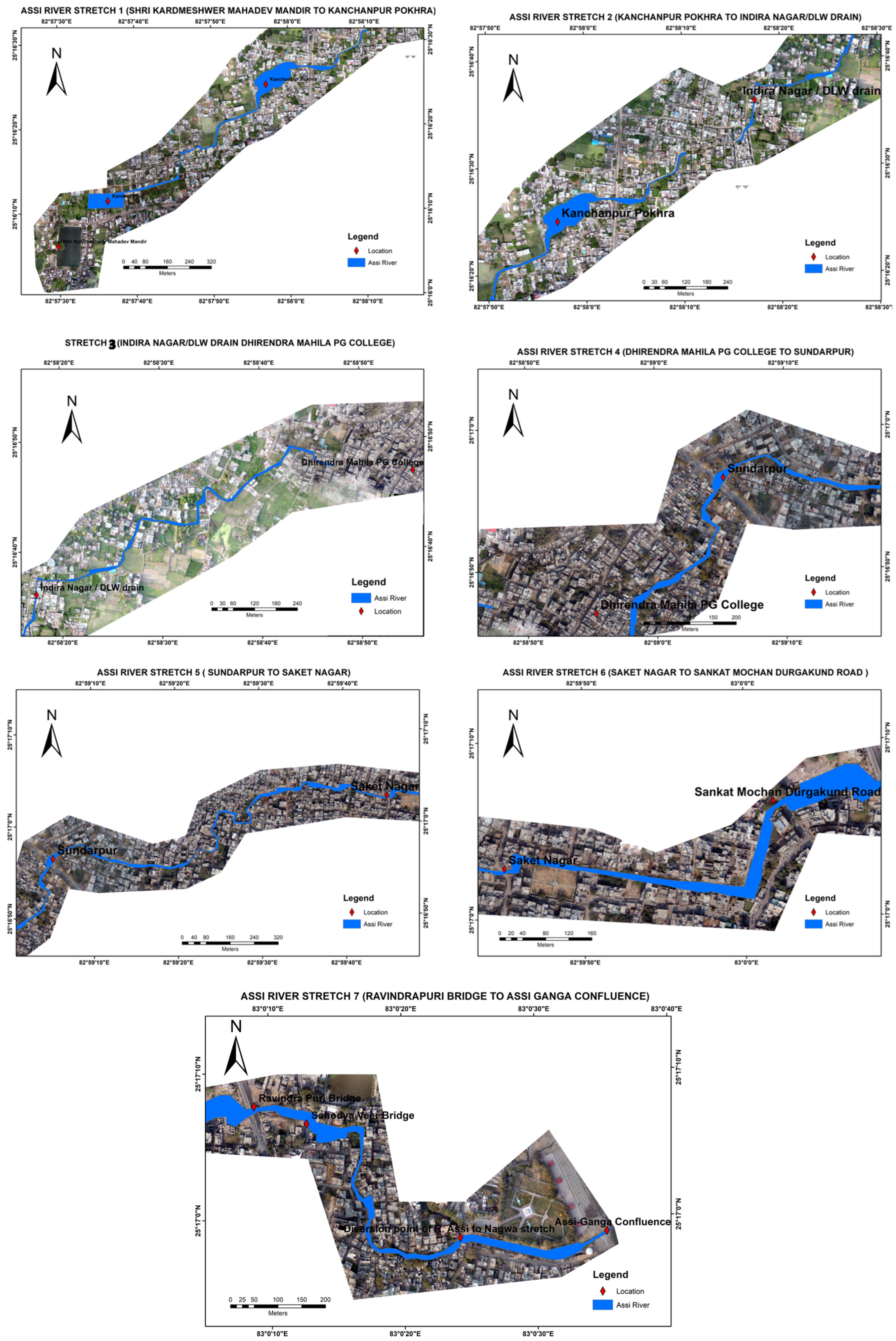
3.2. Stretch-Specific Encroachment Analysis
3.3. Physicochemical Parameters Analysis
3.4. Nutrient, Bacterial & Heavy Metal Contamination
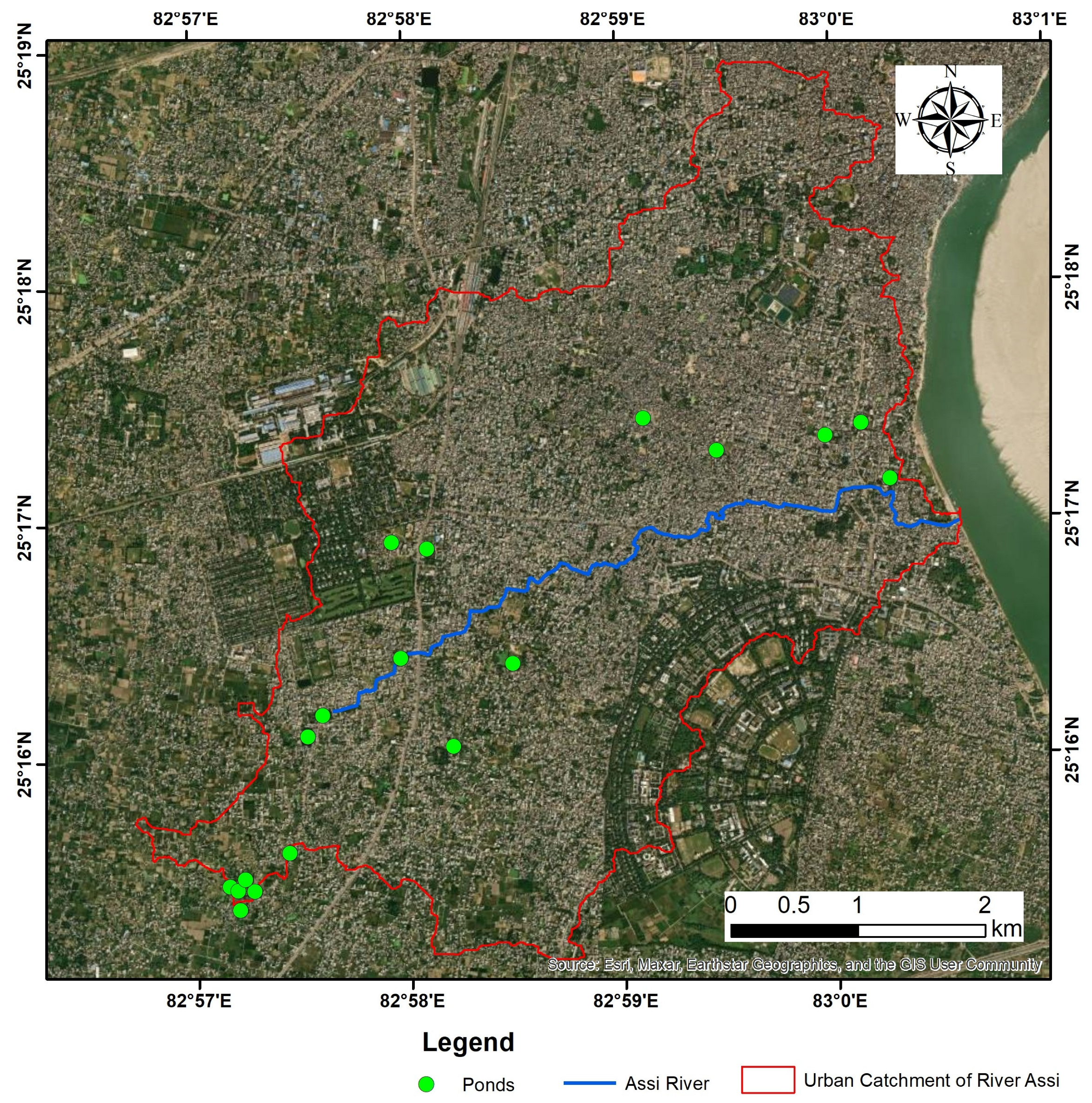
Study of Ponds in and Around the Catchment Area of the Assi River
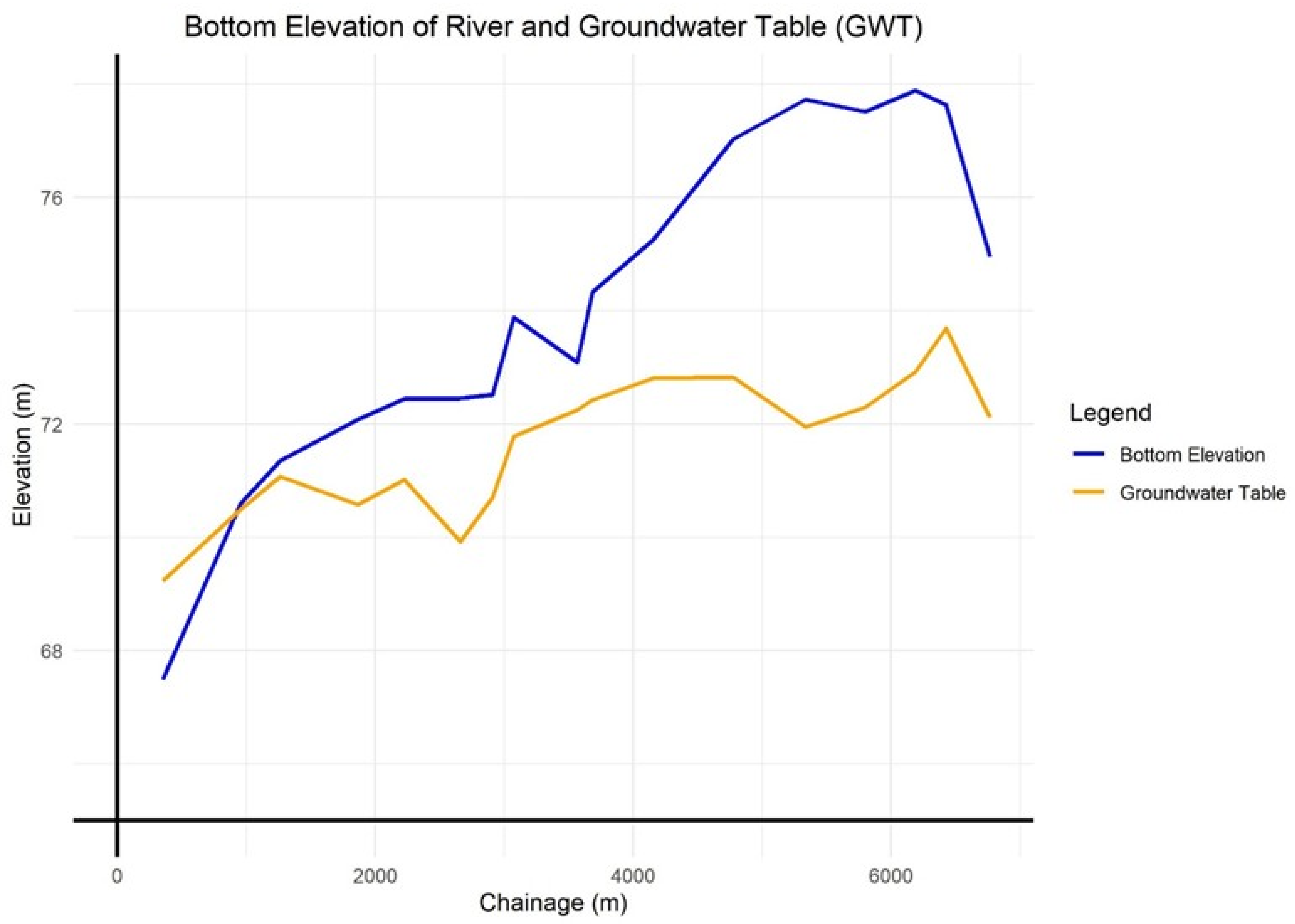
3.5. Longitudinal and Lateral Disconnection
4. Discussion
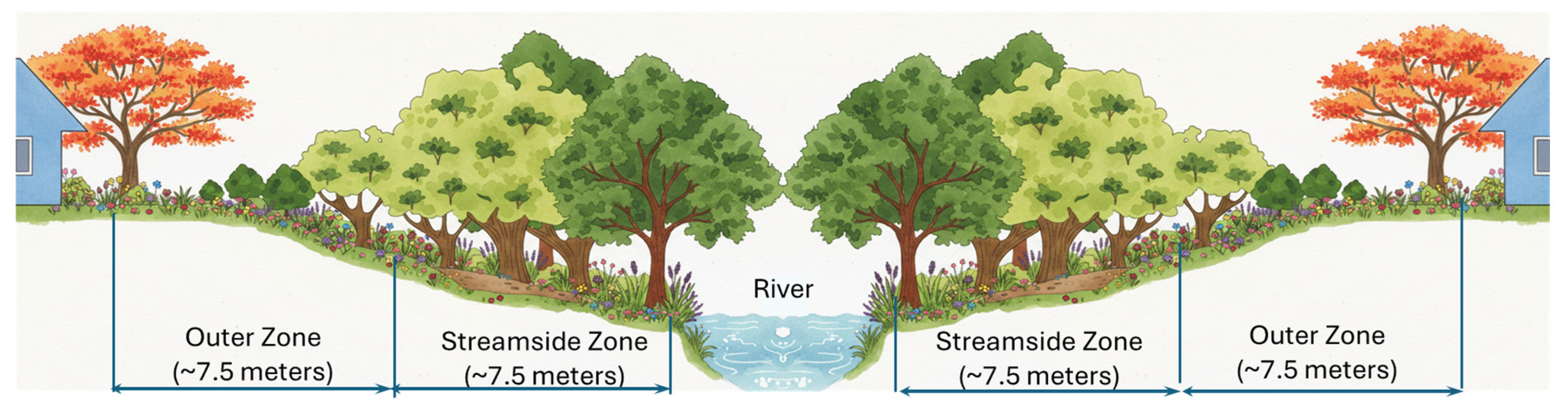
4.1. Restoration Strategies: Reconnecting the River
4.2. Policy Integration and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| APHA | American Public Health Association |
| BDL | Below Detection Limit |
| BOD | Biochemical Oxygen Demand |
| COD | Chemical Oxygen Demand |
| CP | Check Point |
| CPCB | Central Pollution Control Board |
| DGPS | Differential Global Positioning System |
| DO | Dissolved Oxygen |
| DSM | Digital Surface Model |
| EC | Electrical Conductivity |
| GCP | Ground Control Point |
| GWT | Groundwater Table |
| MPN | Most Probable Number |
| NH4-N | Ammoniacal Nitrogen |
| NMCG | National Mission for Clean Ganga |
| NO3-N | Nitrate Nitrogen |
| NTU | Nephelometric Turbidity Unit |
| pH | Potential of Hydrogen |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
| SDG | Sustainable Development Goals |
| SfM | Structure-from-Motion |
| TDS | Total Dissolved Solids |
| TP | Total Phosphorus |
| UAV | Unmanned Aerial Vehicle |
| URMP | Urban River Management Plan |
References
- Kumari, A.; Sarika. Riverine Biodiversity and Importance: Potential Threat and Conservational Challenges; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wohl, E. The significance of small streams. Front. Earth Sci. 2017, 11, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, D.; Barquín, J.; Álvarez-Cabria, M.; Peñas, F.J. Land-use coverage as an indicator of riparian quality. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 41, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyssen, J.; Pontzeele, J.; Billi, P. Effect of beaver dams on the hydrology of small mountain streams: Example from the Chevral in the Ourthe Orientale basin, Ardennes, Belgium. J. Hydrol. 2011, 402, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdonschot, P.F.M.; Verdonschot, R.C.M. The role of stream restoration in enhancing ecosystem services. Hydrobiologia 2023, 850, 2537–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, W.; Leitner, P.; Hanetseder, I.; Ittner, L.D.; Dossi, F.; Hauer, C. Ecological degradation of a meandering river by local channelization effects: A case study in an Austrian lowland river. Hydrobiologia 2016, 772, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.A.; Gaskell, P.; Jackiin, T.; Williams, J.E. Brown Trout Management for the 21st Century; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Škrinár, A.; Danáčová, M.; Výleta, R. Restoration OF Small River to Increase the Recreational and Tourist Potential of Rural Area. In Public Recreation and Landscape Protection—With Environment Hand in Hand…, Proceedings of the 13th Conference, Křtiny, Czech Republic, 9–10 May 2022; Mendel University in Brno: Brno, Czech Republic, 2022; pp. 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroli, B.; De Blust, G.; Van Looy, K.; Van Rooij, S. Setting targets in strategies for river restoration. Landsc. Ecol. 2002, 17, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cody, B.A.; Stern, C.V.; Carter, N.T.; Sheikh, P.A. Water Resource Issues in the 113th Congress; Congress Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lespez, L.; Germaine, M.-A.; Gob, F.; Tales, E.; Thommeret, N.; de Milleville, L.; Archaimbault, V.; Letourneur, M. A new tool to characterise the socio-environmental dimensions of urban rivers: Urban river socio-environmental index. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2025, 261, 105388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, C.; Brittain, J.E. Remedial strategies in regulated rivers: Introductory remarks. Regul. Rivers Res. Manag. 1996, 12, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffagni, A.; Tenchini, R.; Cazzola, M.; Erba, S.; Balestrini, R.; Belfiore, C.; Pagnotta, R. Detecting the impact of bank and channel modification on invertebrate communities in Mediterranean temporary streams (Sardinia, SW Italy). Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 1138–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, D.; Hughes, S.J.; Varandas, S.; Cortes, R.M.V. Conservation benefits of riparian buffers in urban areas: The case of the rio corgo (North Portugal). Fundam. Appl. Limnol. 2014, 185, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattacini, L. Urban design and rivers: A critical review of theories devising planning and design concepts to define riverside urbanity. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohde, S.; Hostmann, M.; Peter, A.; Ewald, K.C. Room for rivers: An integrative search strategy for floodplain restoration. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2006, 78, 50–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, M.; Soloviev, M. The urban river syndrome: Achieving sustainability against a backdrop of accelerating change. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Pang, X.; Wang, Z.J.; Yuan, X.Z.; Zhang, Y.G. Advances in research on the influence of urbanization on stream benthic macroinvertebrate communities. Shengtai Xuebao 2017, 37, 6275–6288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohl, E. Connectivity in rivers. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2017, 41, 345–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Qin, G.; Gu, X.; Liu, Y.; An, S.; Liu, R.; Leng, X.; Wan, Y. Effects of seasonal hydrological regulation of cascade dams on the functional diversity of zooplankton: Implications for the management of massive reservoirs and dams. J. Hydrol. 2022, 610, 127825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Jiang, Y.; Li, X.; Su, J. Evaluation of river connectivity using a composite index method and its impact on nutrients dynamics in large rivers. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 155, 110961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grill, G.; Lehner, B.; Thieme, M.; Geenen, B.; Tickner, D.; Antonelli, F.; Babu, S.; Borrelli, P.; Cheng, L.; Crochetiere, H.; et al. Mapping the world’s free-flowing rivers. Nature 2019, 569, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dui, Z.; Huang, Y.; Wang, M.; Jin, J.; Gu, Q. Segmentation and Connectivity Reconstruction of Urban Rivers from Sentinel-2 Multi-Spectral Imagery by the WaterSCNet Deep Learning Model. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, B.S.; Bhandari, M.; Bandini, F.; Pizarro, A.; Perks, M.; Joshi, D.R.; Wang, S.; Dogwiler, T.; Ray, R.L.; Kharel, G.; et al. Unmanned Aerial Vehicles in Hydrology and Water Management: Applications, Challenges, and Perspectives. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2021WR029925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, D.; Sinha, R. Integrating UAV-Based Topographic and Geomorphic Analysis for the Development of River Rehabilitation Plans in Semi-Urban Settings. River Res. Appl. 2025, 41, 314–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, A.D.; Gardner, K.H.; Greenwood, S.; Still, B. UAV and Structure-From-Motion Photogrammetry Enhance River Restoration Monitoring: A Dam Removal Study. Drones 2022, 6, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djenontin, I.N.S.; Fischer, H.W.; Yin, J.; Chi, G. Unveiling global narratives of restoration policy: Big data insights into competing framings and implications. Geoforum 2025, 161, 104241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, C.; Schneider, M.; Mutz, M.; Haustein, M.; Halle, M.; Seidel, M.; Sieker, H.; Wolter, C.; Hinkelmann, R. Model-based design for restoration of a small urban river. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2015, 9, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, C.; Tetzlaff, D.; Hinkelmann, R.; Soulsby, C. Effects of 66 years of water management and hydroclimatic change on the urban hydrology and water quality of the Panke catchment, Berlin, Germany. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 900, 165764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singare, P.U.; Mishra, R.M.; Trivedi, M.P. Heavy Metal Pollution in Mithi River of Mumbai. Front. Sci. 2012, 2, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, M.; Mohanty, M.P.; Kishore, P.; Karmakar, S. Performance evaluation of potential inland flood management options through a three-way linked hydrodynamic modelling framework for a coastal urban watershed. Hydrol. Res. 2021, 52, 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhamodharan, A.; Abinandan, S.; Aravind, U.; Ganapathy, G.P.; Shanthakumar, S. Distribution of Metal Contamination and Risk Indices Assessment of Surface Sediments from Cooum River, Chennai, India. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2019, 13, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Mizunoya, T. Sustainability Assessment Model of the Buriganga River Restoration Project in Bangladesh: A System Dynamics and Inclusive Wealth Study. Sustainability 2022, 14, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, K. Public attitudes toward restoration of impaired river ecosystems: Does residents’ attachment to place matter? Urban Ecosyst. 2011, 14, 635–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Ahmad, S.A.; Islam, R. Water quality perceptions and willingness to pay: Valuing river water quality using contingent valuation method. J. Adv. Res. Dyn. Control Syst. 2019, 11, 1011–1022. [Google Scholar]
- Thapa, V. A Dying Holy River An Examination of Urban Contamination in the Bagmati River Basin. Master’s Thesis, Dartmouth College, Hanover, HN, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Shakya, L.; Tiwari, S.R. Impact of Landuse Changes on Bagmati River. Proc. IOE Grad. Conf. 2014, 250–255. Available online: https://conference.ioe.edu.np/publications/ioegc2014/IOE-CONF-2014-32.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2024).
- Mishra, B.K.; Regmi, R.K.; Masago, Y.; Fukushi, K.; Kumar, P.; Saraswat, C. Assessment of Bagmati river pollution in Kathmandu Valley: Scenario-based modeling and analysis for sustainable urban development. Sustain. Water Qual. Ecol. 2017, 9–10, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Agnihotri, A.K.; Pipil, S.; Gaur, S.; Ohri, A. Chapter 4—Surveying techniques for urban areas. In Earth Observation; Kumar, A., Srivastava, P.K., Saikia, P., Mall, R.K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 69–91. [Google Scholar]
- URMP Urban River Management Plan (URMP). A Strategic Framework for Managing Urban River Stretches in the Ganga River Basin; Components and Guidance note; National Mission for Clean Ganga: New Dehli, India; National Institute of Urban Affairs (NIUA): New Dehli, India, 2020; Available online: https://niua.in/waterandenvironment/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/URMP-Framework-pdf.pdf (accessed on 25 August 2024).
- Rice, E.W.; Baird, R.B.; Eaton, A.D. (Eds.) Standard Methods for Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA; American Water Works Association: Washington, DC, USA; Water Environment Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, D.D.; Thind, P.S.; Sharma, M.; Sahoo, S.; John, S. Environmentally sensitive elements in groundwater of an industrial town in India: Spatial distribution and human health risk. Water 2019, 11, 2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borthakur, A.; Singh, P. India’s lost rivers and rivulets. Energy Ecol. Environ. 2016, 1, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.L. Study of physico-chemical characteristics of water samples from Assi River, Varanasi, U.P. India. Pollut. Res. 2011, 30, 209–212. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, S.; Agnihotri, A.K. Assessment of Water Quality of River Assi by using WQI, Varanasi, India. Int. J. Environ. Sustain. 2018, 114–121. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, M.; Raju, K.N.P.; Raju, P.V. Palaeo and present channel of Assi river, Uttar Pradesh, India. Curr. Sci. 2020, 118, 630–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapworth, D.J.; Dochartaigh, B.Ó.; Nair, T.; O’Keeffe, J.; Krishan, G.; MacDonald, A.M.; Khan, M.; Kelkar, N.; Choudhary, S.; Krishnaswamy, J.; et al. Characterising groundwater-surface water connectivity in the lower Gandak catchment, a barrage regulated biodiversity hotspot in the mid-Gangetic basin. J. Hydrol. 2021, 594, 125923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Rojas, R.; Gonzalez, D. Trends in Groundwater Levels in Alluvial Aquifers of the Murray–Darling Basin and Their Attributions. Water 2022, 14, 1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.K.; Singh, V.P.; Mishra, V.B. Design and Testing of a Flow Measurement System for an Urban Sewage Drain. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2012, 138, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainstone, C.P.; Dils, R.M.; Withers, P.J.A. Controlling sediment and phosphorus transfer to receiving waters—A strategic management perspective for England and Wales. J. Hydrol. 2008, 350, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granger, S.J.; Harris, P.; Upadhayay, H.R.; Sint, H.; Pulley, S.; Stone, M.; Krishnappan, B.G.; Collins, A.L. Novel approaches to investigating spatial variability in channel bank total phosphorus at the catchment scale. Catena 2021, 202, 105223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahel, F.J.; McLaughlin, R.L. Selective fragmentation and the management of fish movement across anthropogenic barriers. Ecol. Appl. 2018, 28, 2066–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Do, Y. Macroinvertebrate conservation in river ecosystems: Challenges, restoration strategies, and integrated management approaches. Entomol. Res. 2023, 53, 271–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnie-Gauvin, K.; Nielsen, J.; Frandsen, S.B.; Olsen, H.M.; Aarestrup, K. Catchment-scale effects of river fragmentation: A case study on restoring connectivity. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 264, 110408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paillex, A.; Schuwirth, N.; Lorenz, A.W.; Januschke, K.; Peter, A.; Reichert, P. Integrating and extending ecological river assessment: Concept and test with two restoration projects. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 72, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Décamps, H.; Pinay, G.; Naiman, R.J.; Petts, G.E.; McClain, M.E.; Hillbricht-Ilkowska, A.; Hanley, T.A.; Holmes, R.M.; Quinn, J.; Gibert, J.; et al. Riparian zones: Where biogeochemistry meets biodiversity in management practice. Polish J. Ecol. 2004, 52, 3–18. [Google Scholar]
- Glenn, E.P.; Nagler, P.L.; Shafroth, P.B.; Jarchow, C.J. Effectiveness of environmental flows for riparian restoration in arid regions: A tale of four rivers. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 106, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondolf, G.M. Setting Goals in River Restoration: When; Where Can the River “Heal Itself”? American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; Volume 194. [Google Scholar]
- Langendoen, E.J.; Lowrance, R.R.; Simon, A. Assessing the impact of riparian processes on streambank stability. Ecohydrology 2009, 2, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayawardana, J.M.C.K. Thoughts for stream restoration: Link between riparian, instream vegetation and macroinvertebrates. Environ. Res. J. 2010, 4, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, R.-J. Achieving successful river restoration in dense urban areas: Lessons from Taiwan. Sustainability 2016, 8, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Kim, H.; Hong, Y. Revealed preference and effectiveness of public investment in ecological river restoration projects: An application of the count data model. Sustainability 2016, 8, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westwood, C.G.; Teeuw, R.M.; Wade, P.M.; Holmes, N.T.H.; Guyard, P. Influences of environmental conditions on macrophyte communities in drought-affected headwater streams. River Res. Appl. 2006, 22, 703–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Land-Use Type | Area in Buffer Width on Both Sides of the River (in m2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 m | 10 m | 20 m | 30 m | |
| Agriculture Land | 306 | 1988 | 4381 | 8197 |
| Built Up | 5566 | 25,240 | 82,303 | 137,580 |
| Vacant Plot | 5161 | 17,136 | 38,454 | 53,990 |
| Stretch | Length (m) | Encroached Area (m2/100 m) Length in Buffer Width on both Sides of the River | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 m | 5 m | 10 m | 15 m | 20 m | 30 m | ||
| a | 1049.00 | 6.01 | 31.46 | 188.66 | 474.55 | 813.54 | 1542.14 |
| b | 816.00 | 2.21 | 11.40 | 185.05 | 514.83 | 870.22 | 1670.22 |
| c | 1459.00 | 23.24 | 121.93 | 533.04 | 1061.27 | 1631.87 | 2733.17 |
| d | 411.00 | 1.70 | 44.77 | 345.01 | 766.67 | 1226.52 | 2349.64 |
| e | 1518.00 | 17.79 | 76.61 | 318.91 | 611.53 | 892.42 | 1489.99 |
| f | 666.00 | 71.02 | 174.77 | 621.62 | 1205.41 | 1739.34 | 2866.82 |
| g | 1014.00 | 15.48 | 84.12 | 352.56 | 954.34 | 1251.18 | 1630.08 |
| Stretch No. | Stretch Name | Average Width (m) |
|---|---|---|
| Stretch 1 | Karmadeshwar Temple to Kanchanpur Pokhra | 3–27 |
| Stretch 2 | Kanchanpur Pokhra to Indira Nagar Drain | 1–18 |
| Stretch 3 | Indira Nagar Drain to Dhirendra Mahila College | 1–13 |
| Stretch 4 | Dhirendra Mahila College to Sunderpur | 4–21 |
| Stretch 5 | Sunderpur to Saket Nagar | 5–21 |
| Stretch 6 | Saket Nagar to Sankat Mochan Bridge | 6–42 |
| Stretch 7 | Sankat Mochan Bridge to Confluence of Assi-Ganga | 7–25 |
| Parameter | Units | Kardmeshwer Pond | Khandwa Pond (Stretch 1) | Kanchanpur Pokhra (Stretch 2) | Indira Nagar (Stretch 3) | Sunderpur (Stretch 4) | Saket Nagar (Stretch 5) | Sankat Mochan Bridge (Stretch 6) | Confluence of Assi-Ganga (Stretch 7) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature | °C | 28.3 ± 2.8 | 32.5 ±3.8 | 32.7 ±4.3 | 33.1 ± 5.3 | 31.5 ± 4.5 | 31.2 ±4.6 | 31.5 ±3.9 | 32.6 ±4.1 |
| DO | mg/L | 4.9± 0.8 | 1.0 ± 0.5 | 0.35 ± 0.15 | 0.75 ± 0.05 | 0.6 ± 0.1 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.1 |
| Conductivity | µS/cm | 635± 45 | 940 ± 185 | 938 ± 153 | 1063 ± 187 | 960 ± 159 | 934 ± 122 | 1090 ± 173 | 1117 ± 241 |
| TDS | mg/L | 443 ± 58 | 618 ± 67 | 632 ± 89 | 657 ± 63 | 729 ± 123 | 623 ± 133 | 719 ± 153 | 738 ± 95 |
| pH | - | 7.8 ± 0.5 | 7.1 ± 0.2 | 7.3 ± 0.3 | 7.1 ± 0.1 | 7.1 ± 0.2 | 7.2 ± 0.4 | 7.2 ± 0.3 | 7.2 ± 0.4 |
| NH4-N | mg/L | 0.65 ± 0.3 | 6.3 ± 2.2 | 8.0 ± 1.4 | 7.8 ± 1.6 | 10.8 ± 4.4 | 14.1 ± 3.5 | 6.4 ± 2.7 | 11.9 ± 3.3 |
| NO3-N | mg/L | 24.3 ± 6.3 | 34.3 ± 4.5 | 48.5 ± 6.3 | 44.6 ± 2.5 | 50.4 ± 2.0 | 42.5 ± 1.8 | 59 ± 2.8 | 63 ± 6.7 |
| Turbidity | NTU | 9.2 ± 1.6 | 58.5 ± 15.5 | 36.5 ± 15.5 | 39.5 ± 11.6 | 55.5 ± 10.5 | 54.5 ± 22.5 | 64.0 ± 16.3 | 71.5 ± 20.5 |
| BOD | mg/L | 21± 5.6 | 57 ± 5.5 | 48 ± 11.3 | 56 ± 8.7 | 104 ± 15.6 | 92 ± 9.1 | 97 ± 16.7 | 126 ± 27 |
| COD | mg/L | 89± 22 | 144 ± 15 | 192 ± 35 | 228 ± 24 | 397 ± 57 | 322 ± 76 | 307 ± 84 | 344 ± 60 |
| Total Coliform | MPN/ 100 mL | (3.0 ± 1.2) × 103 | (2.2 ± 1.1) × 107 | (4.7 ± 2.3) × 107 | (3.4 ± 0.3) × 108 | (2.3 ± 1.1) × 108 | (1.7± 0.4) × 108 | (1.9 ± 0.6) × 108 | (3.6 ± 0.6) × 108 |
| Faecal Coliform | MPN/ 100 mL | (1.1 ± 0.5) × 103 | (3.5 ± 1.6) × 106 | (1.1 ± 0.7) × 107 | (2.1 ± 1.3) × 107 | (5.3 ± 1.7) × 107 | (4.6 ± 2.1) × 107 | (3.1 ± 1.5) × 107 | (2.1 ± 1.4) × 108 |
| Total phosphorus | mg/L | 0.5 ± 0.2 | 2.43 ± 1.2 | 2.2 ± 0.7 | 2.4 ± 0.9 | 2.5 ± 1.1 | 6.1 ± 2.5 | 3.4 ± 1.5 | 2.5 ± 0.8 |
| Cadmium | mg/L | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL |
| Mercury | mg/L | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL |
| Nickel | mg/L | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL |
| Chromium | mg/L | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL |
| Lead | mg/L | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL |
| Arsenic | mg/L | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL |
| S.N. | Latitude | Longitude | Location | Top Elevation of Pond (m) | Bottom Elevation of the Pond (m) | Avg. Depth (m) | Area (m2) | Volume (m3) | Ground Water Table (GWT) (m) | Difference in GWT and Pond Bottom Elevation (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p1 | 25.25615 | 82.953264 | Amara Pond 1 | 79.59 | 74.12 | 3.4 | 3763 | 12,794 | 73.21 | 0.91 |
| p2 | 25.25781 | 82.952468 | Amara Pond 2 | 77.60 | 76.58 | 0.9 | 561 | 505 | 75.42 | 1.16 |
| p3 | 25.2575 | 82.953098 | Amara Pond 3 | 77.66 | 75.42 | 1.3 | 3186 | 4141 | 73.56 | 1.86 |
| p4 | 25.25747 | 82.954421 | Amara Pond 4 | 78.04 | 75.63 | 0.9 | 5616 | 5054 | 74.37 | 1.26 |
| p5 | 25.25829 | 82.953692 | Amara Pond 5 | 78.55 | 75.64 | 1.1 | 9019 | 9921 | 73.46 | 2.18 |
| p6 | 25.26014 | 82.957186 | Awaleshwar Mahadev Mandir Pond | 79.42 | 75.56 | 2.3 | 2838 | 6528 | 73.52 | 2.04 |
| p7 | 25.26831 | 82.958699 | Kardhmeshwar Pond | 79.72 | 73.22 | 1.4 | 13,828 | 19,359 | 73.76 | −0.54 |
| p8 | 25.26981 | 82.959887 | Kandwa Pond | 78.10 | 75.66 | 1.5 | 7500 | 11,250 | 73.76 | 1.9 |
| p9 | 25.27377 | 82.966059 | Kanchanpur | 77.90 | 74.11 | 2.7 | 9011 | 24,331 | 72.13 | 1.98 |
| p11 | 25.28193 | 82.965439 | Bhikharipur Pond 1 | 77.13 | 74.65 | 1.6 | 6216 | 10,154 | 76.09 | −1.44 |
| p12 | 25.28143 | 82.968213 | Bhikharipur Pond 1 | 78.86 | 73.89 | 3.3 | 3450 | 11,314 | 77.26 | −3.5 |
| p13 | 25.26749 | 82.970084 | Pongalpur Village Pond | 78.28 | 75.78 | 1.7 | 11,288 | 18,626 | 71.22 | 3.62 |
| p14 | 25.27329 | 82.974808 | Newada Pond 1 | 79.95 | 75.45 | 2.9 | 4631 | 13,753 | 71.44 | 3.43 |
| p15 | 25.29046 | 82.985239 | Nagawa Pond 2 | 77.82 | 75.76 | 1.4 | 4878 | 6638 | 75.47 | −2.06 |
| p16 | 25.2881 | 82.990932 | Nagawa Pond 3 | 76.39 | 73.89 | 1.6 | 13,466 | 22,218 | 76.37 | −2.13 |
| p17 | 25.28908 | 82.999411 | Durga Kund | 75.25 | 69.01 | 4.1 | 4946 | 20,351 | 72.39 | −4.96 |
| p18 | 25.28992 | 83.002225 | Kurukshetra Pond | 74.45 | 67.62 | 4.5 | 8028 | 36,155 | 70.49 | −2.87 |
| p19 | 25.28599 | 83.004469 | Pushkar Talab | 76.41 | 64.13 | 4.9 | 9691 | 47,601 | 68.86 | −4.73 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mishra, A.; Ohri, A.; Singh, P.K.; Singh, N.; Calay, R.K. Urban Rivers Under Pressure: Human-Induced Modifications, Pollution, and Prospects for Restoration—A Case Study of the Assi River, Varanasi. Geographies 2025, 5, 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/geographies5040069
Mishra A, Ohri A, Singh PK, Singh N, Calay RK. Urban Rivers Under Pressure: Human-Induced Modifications, Pollution, and Prospects for Restoration—A Case Study of the Assi River, Varanasi. Geographies. 2025; 5(4):69. https://doi.org/10.3390/geographies5040069
Chicago/Turabian StyleMishra, Anurag, Anurag Ohri, Prabhat Kumar Singh, Nikhilesh Singh, and Rajnish Kaur Calay. 2025. "Urban Rivers Under Pressure: Human-Induced Modifications, Pollution, and Prospects for Restoration—A Case Study of the Assi River, Varanasi" Geographies 5, no. 4: 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/geographies5040069
APA StyleMishra, A., Ohri, A., Singh, P. K., Singh, N., & Calay, R. K. (2025). Urban Rivers Under Pressure: Human-Induced Modifications, Pollution, and Prospects for Restoration—A Case Study of the Assi River, Varanasi. Geographies, 5(4), 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/geographies5040069







