Longyearbyen Lagoon (Spitsbergen): Gravel Spits Movement Rate and Mechanisms
Abstract
1. Introduction
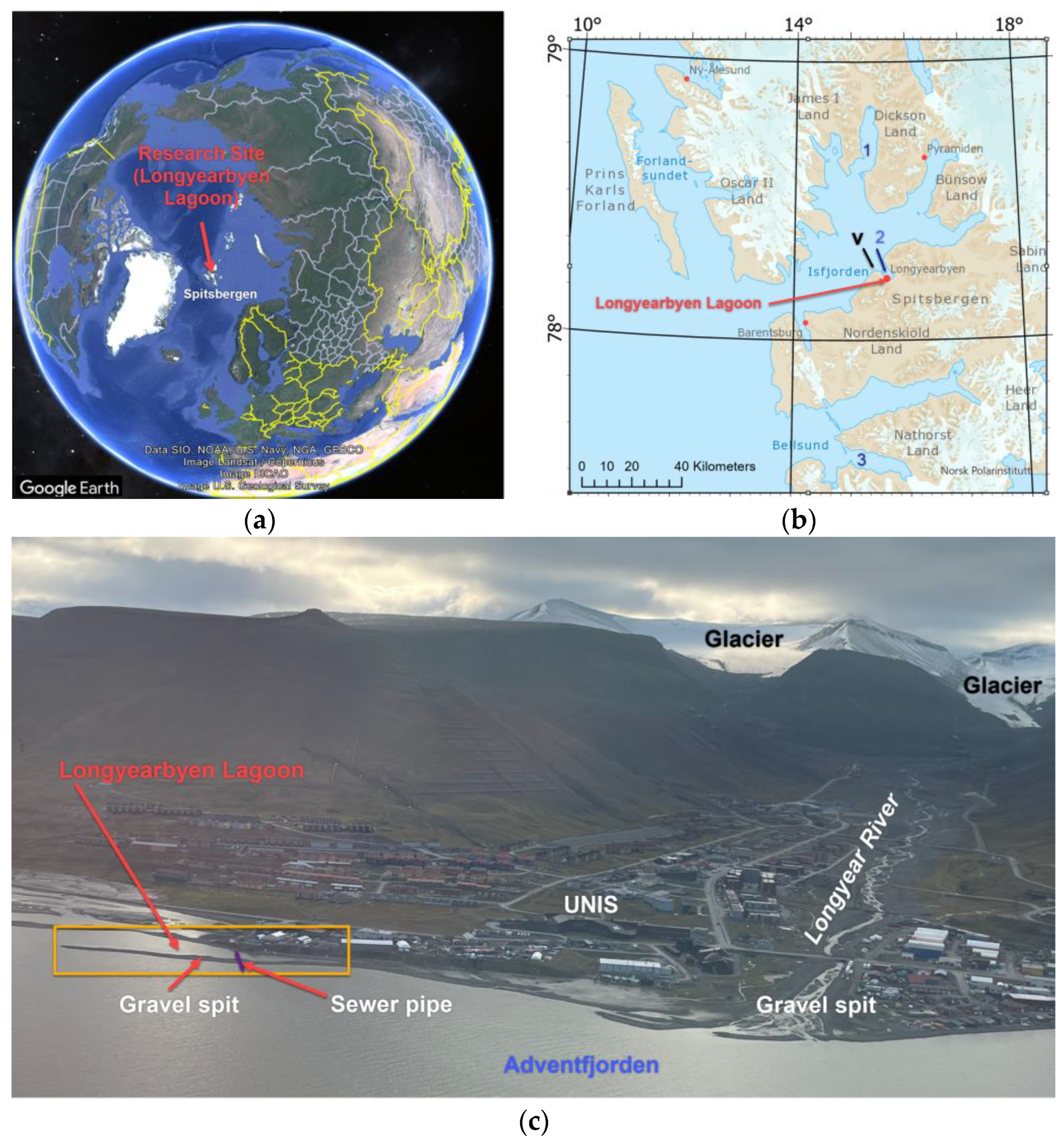
2. Geographical Framework
3. Data and Methods
3.1. Aerial Photos and Satellite Images
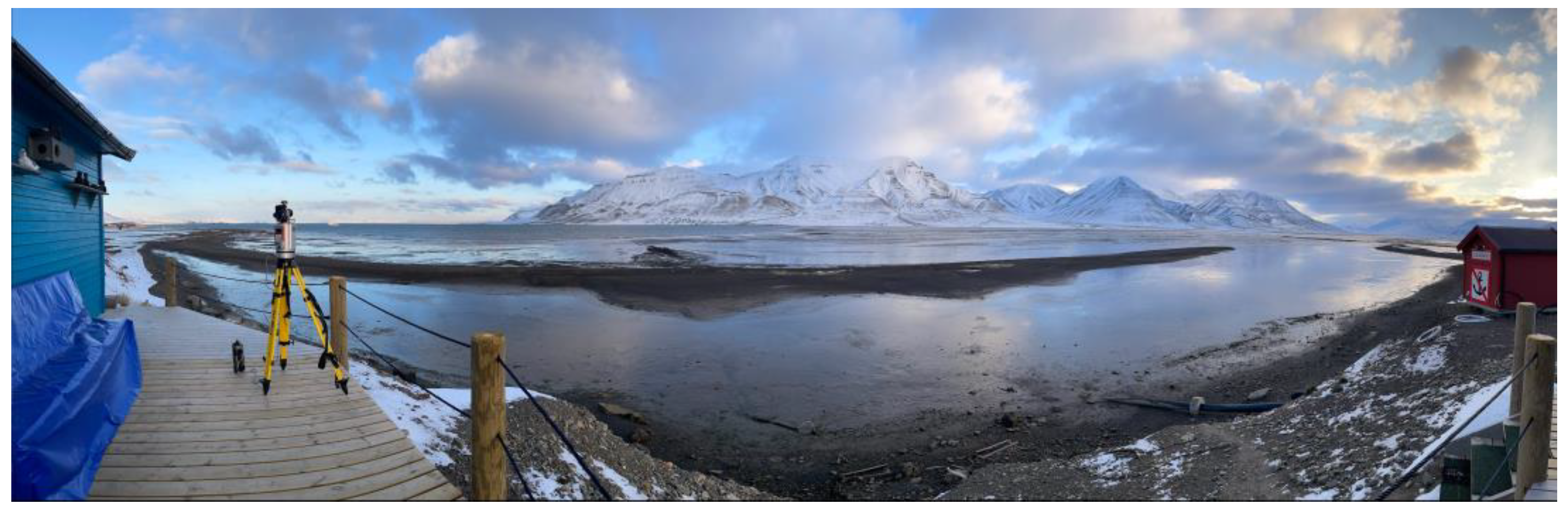
3.2. Laser Scanning
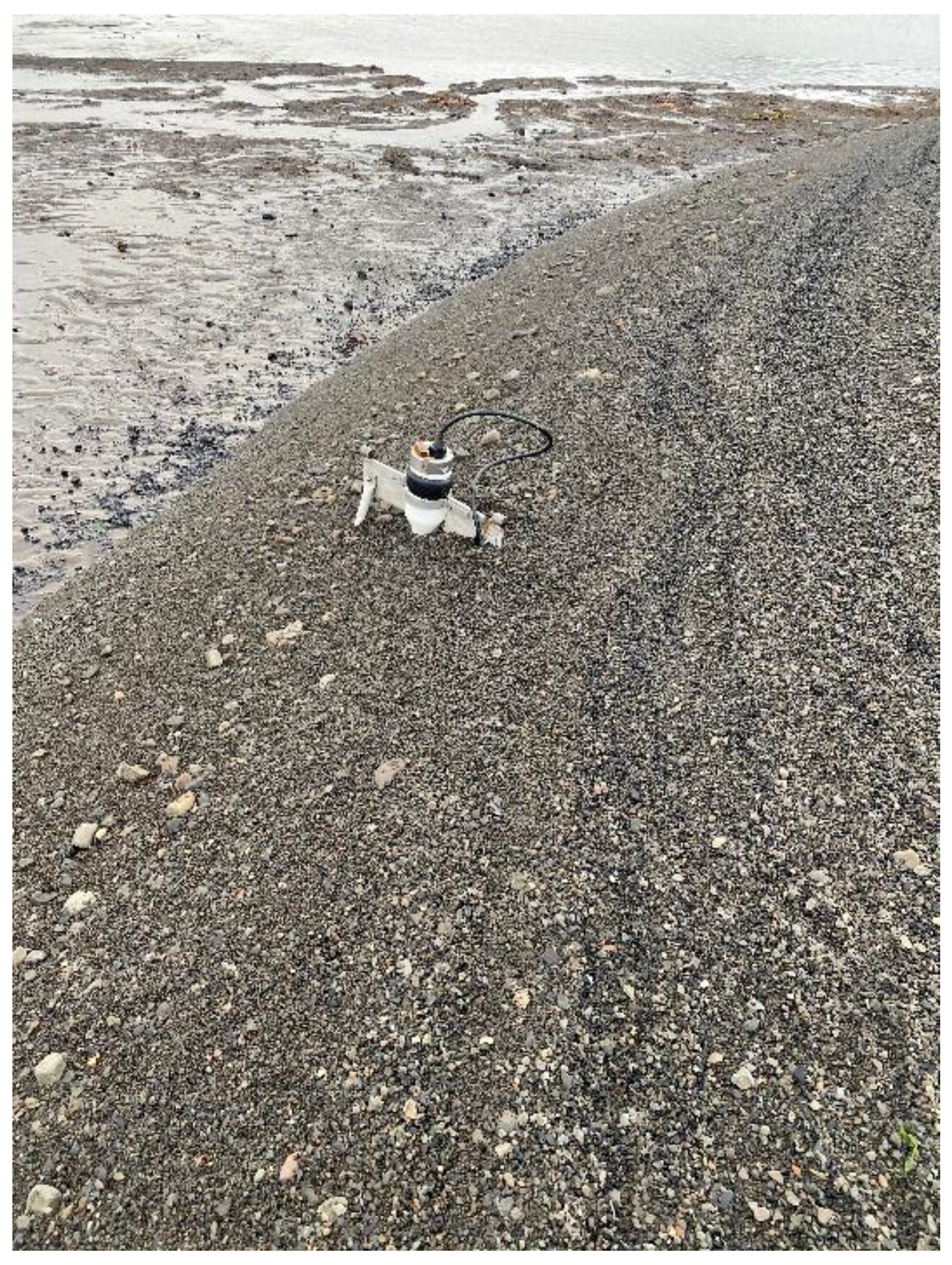
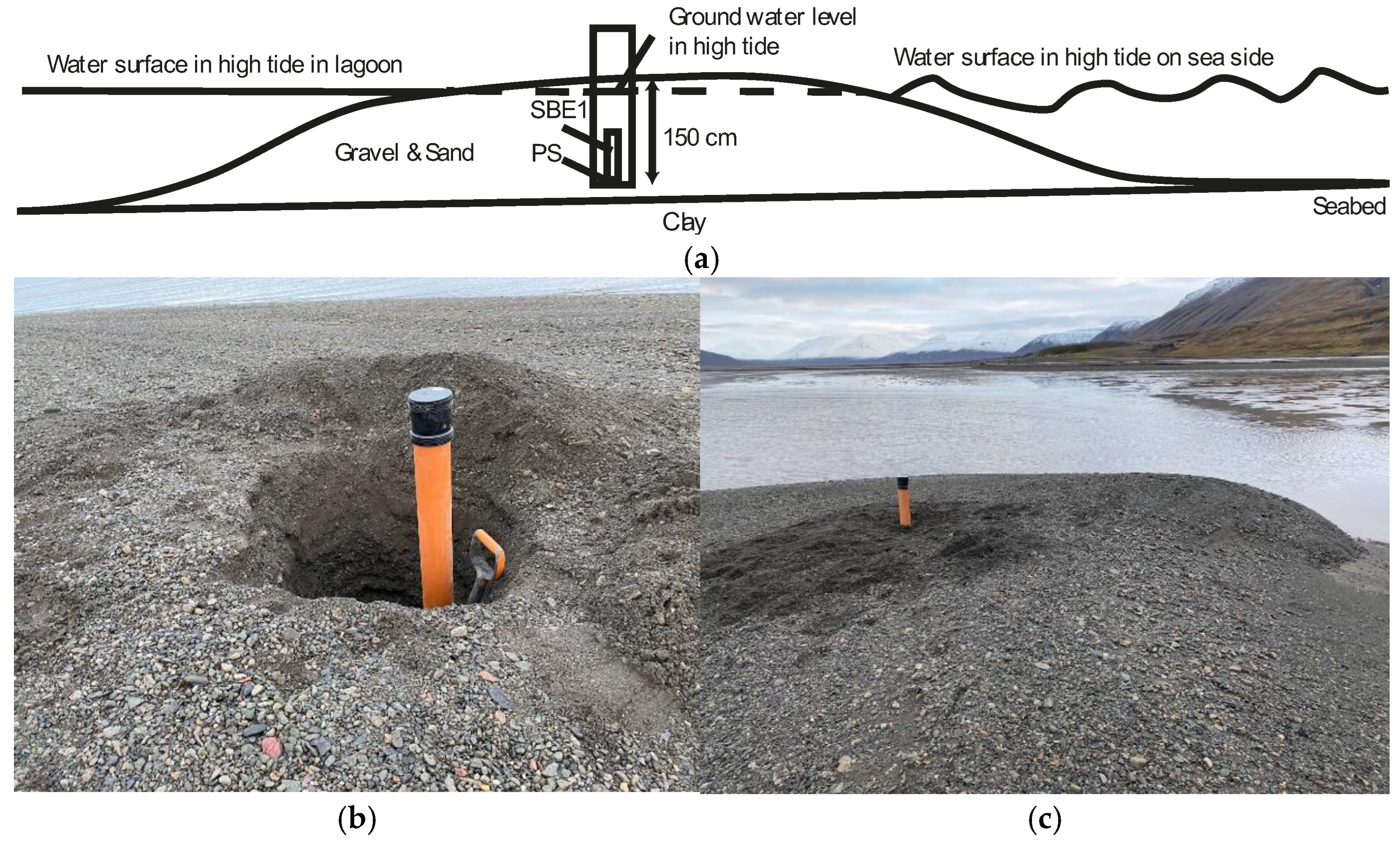
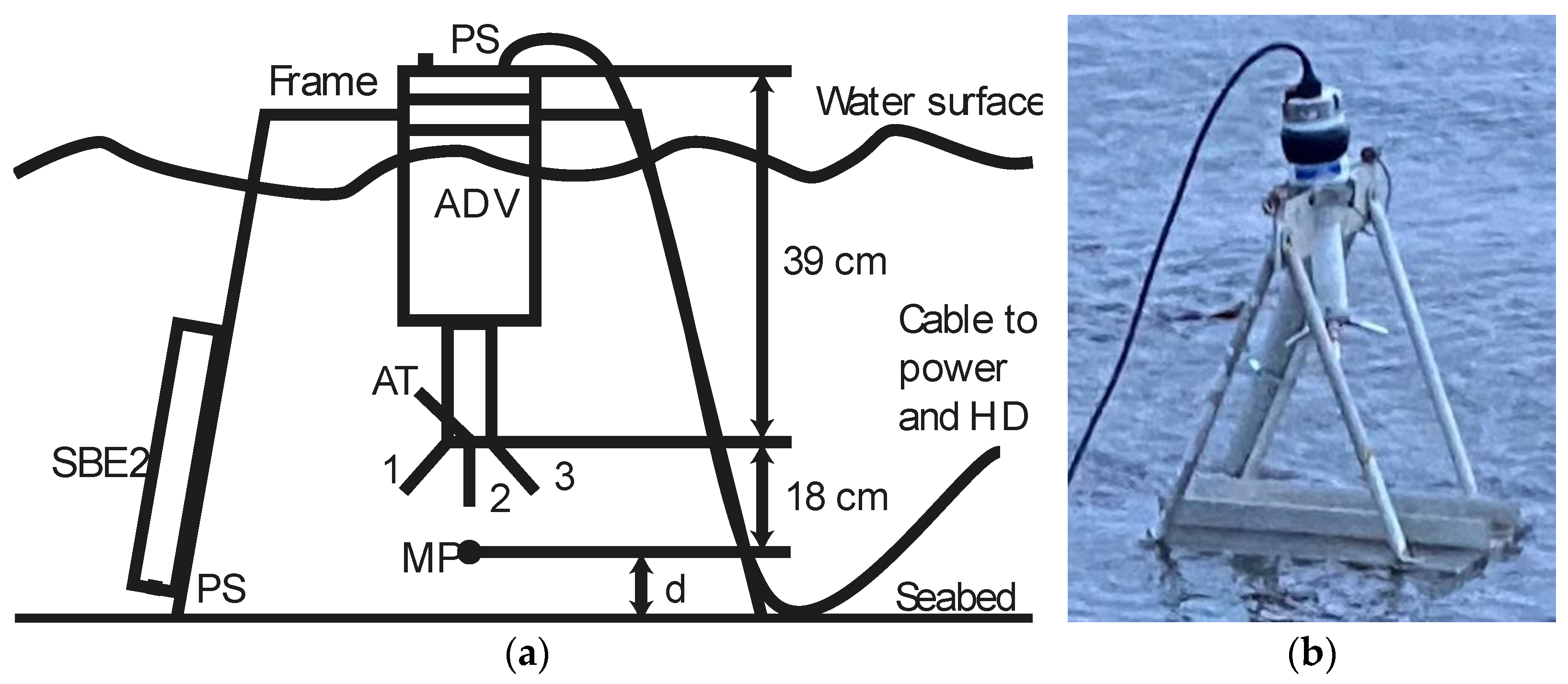
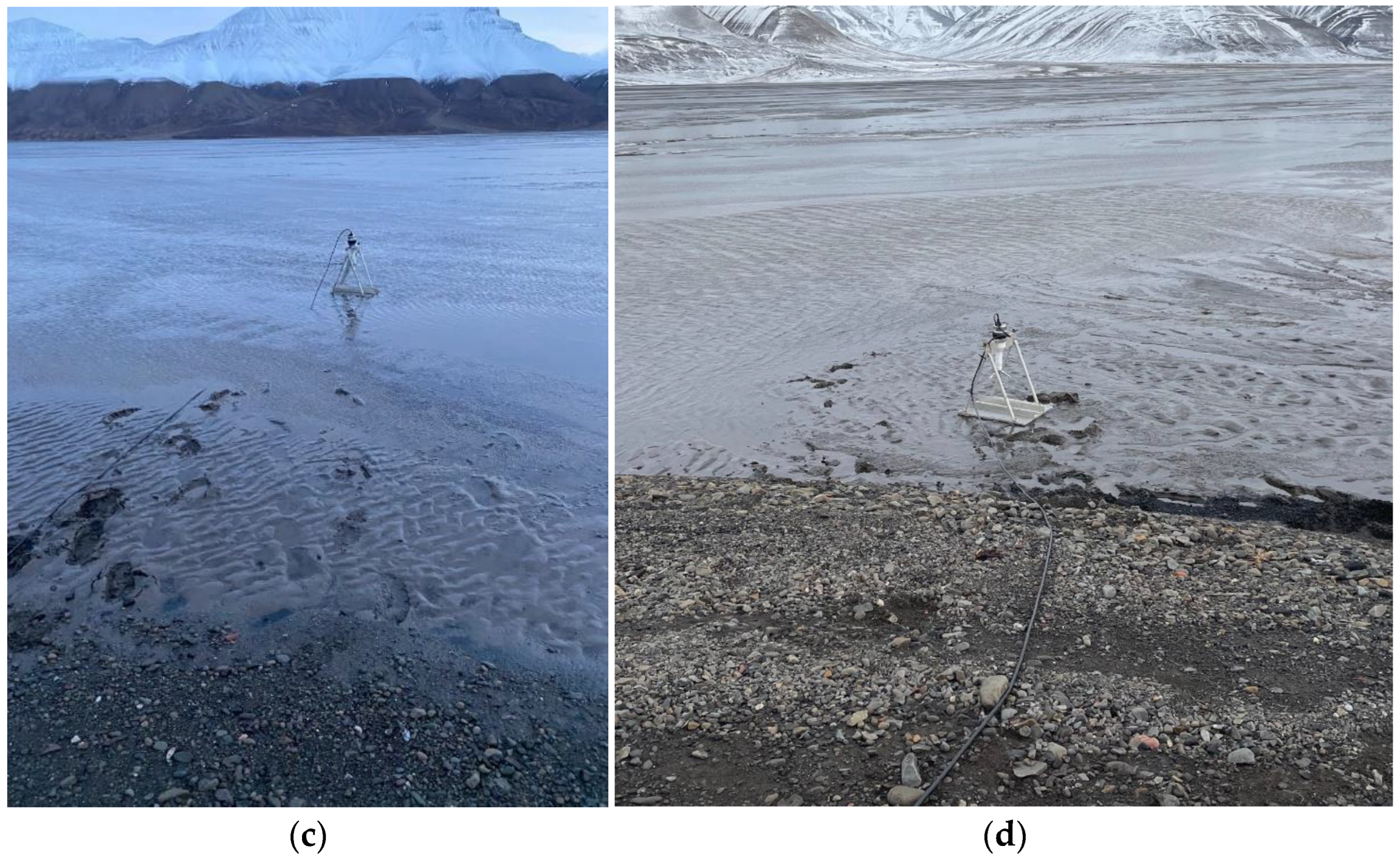
3.3. Hydrological Measurements
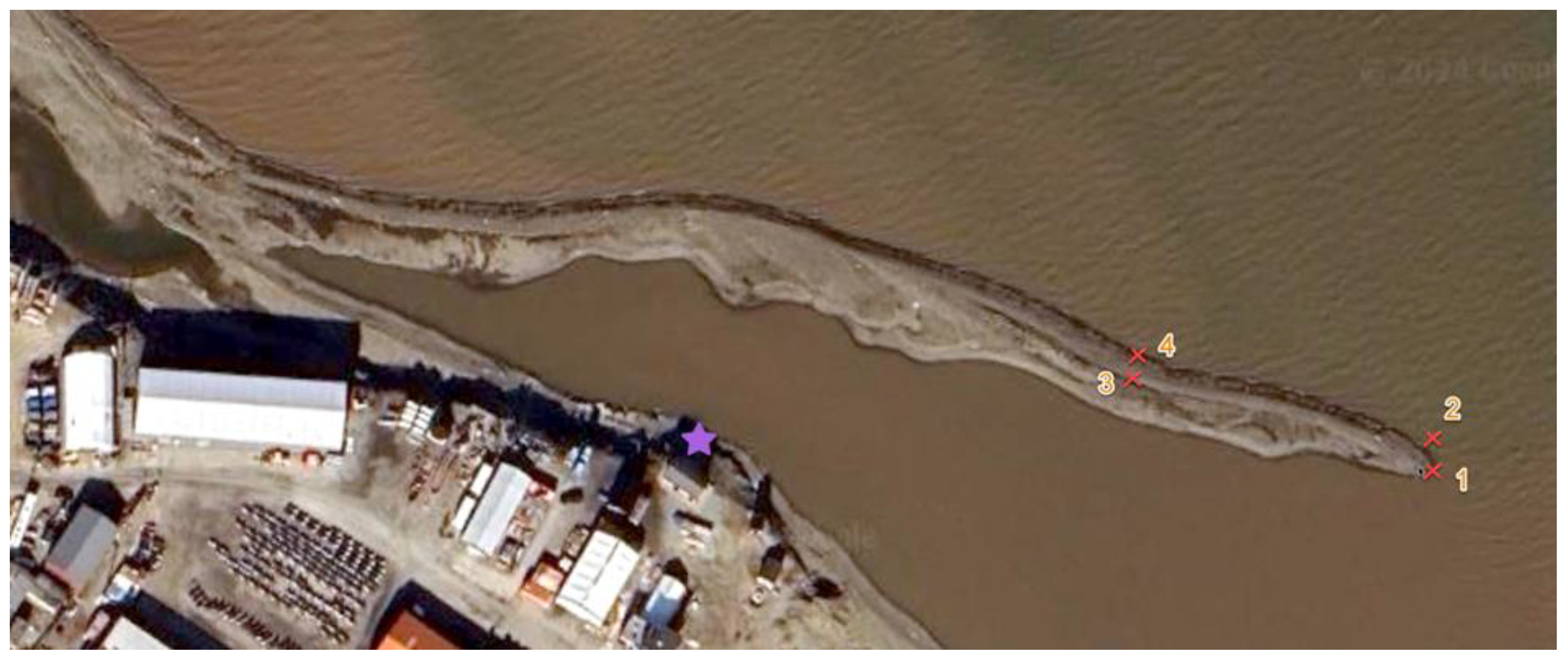
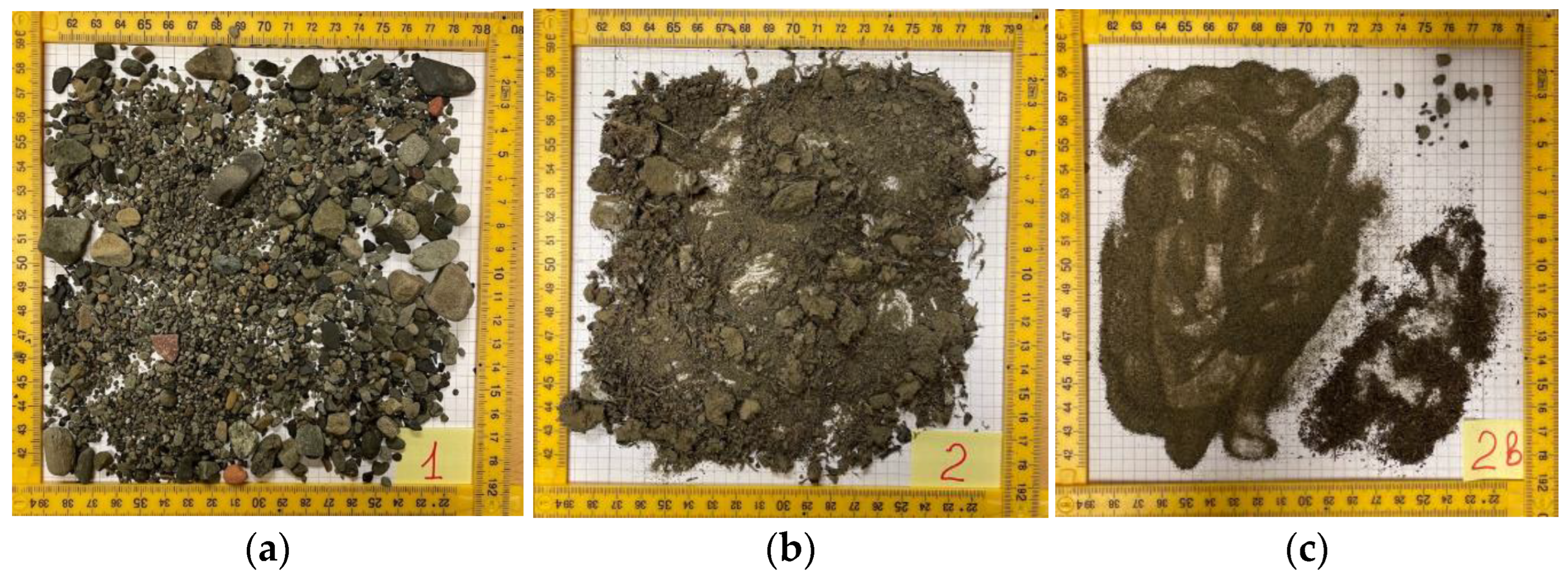
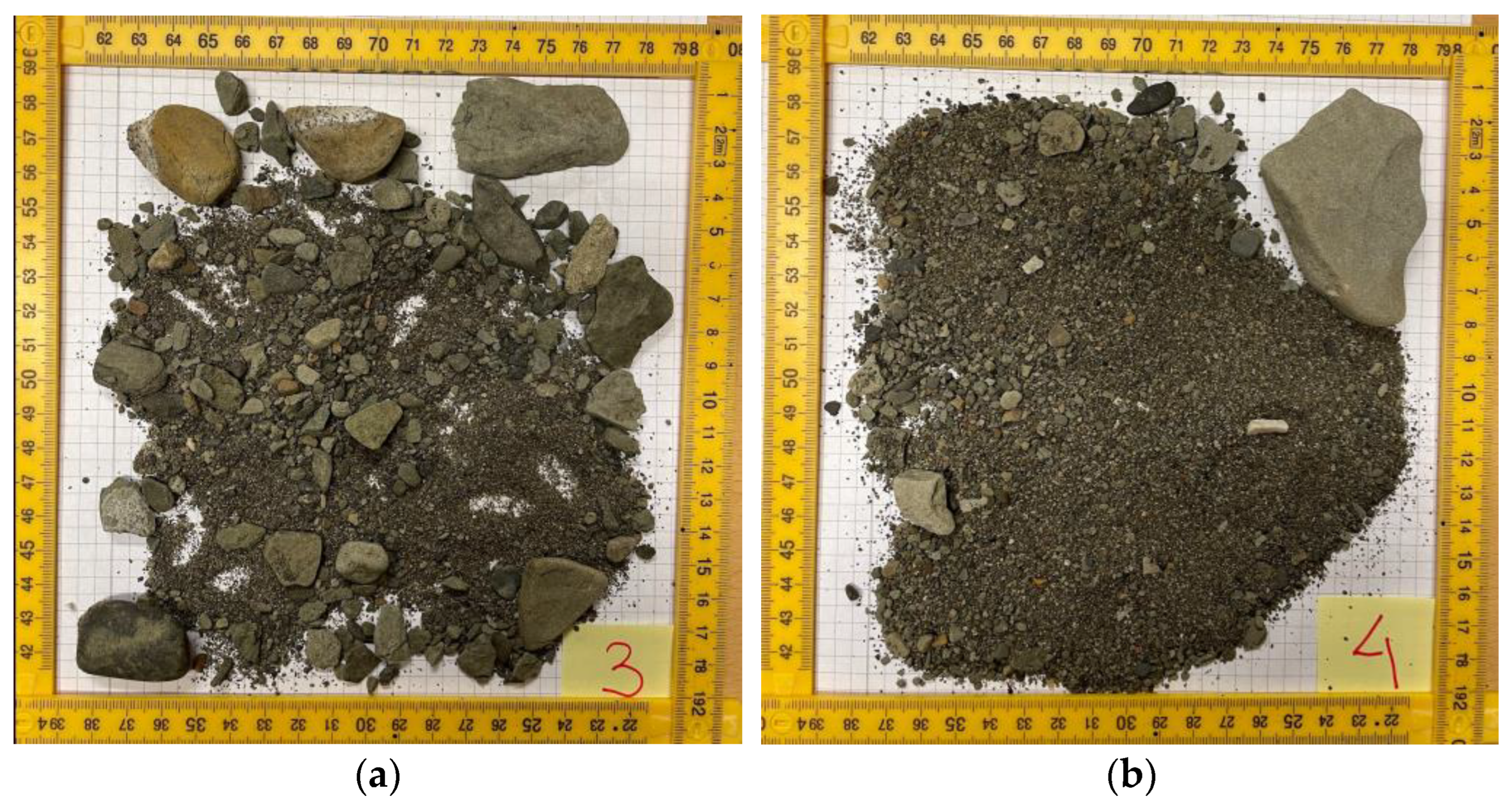
3.4. Sediment Samples and Criterion of Sediment Stability at Seabed
4. Results and Discussions
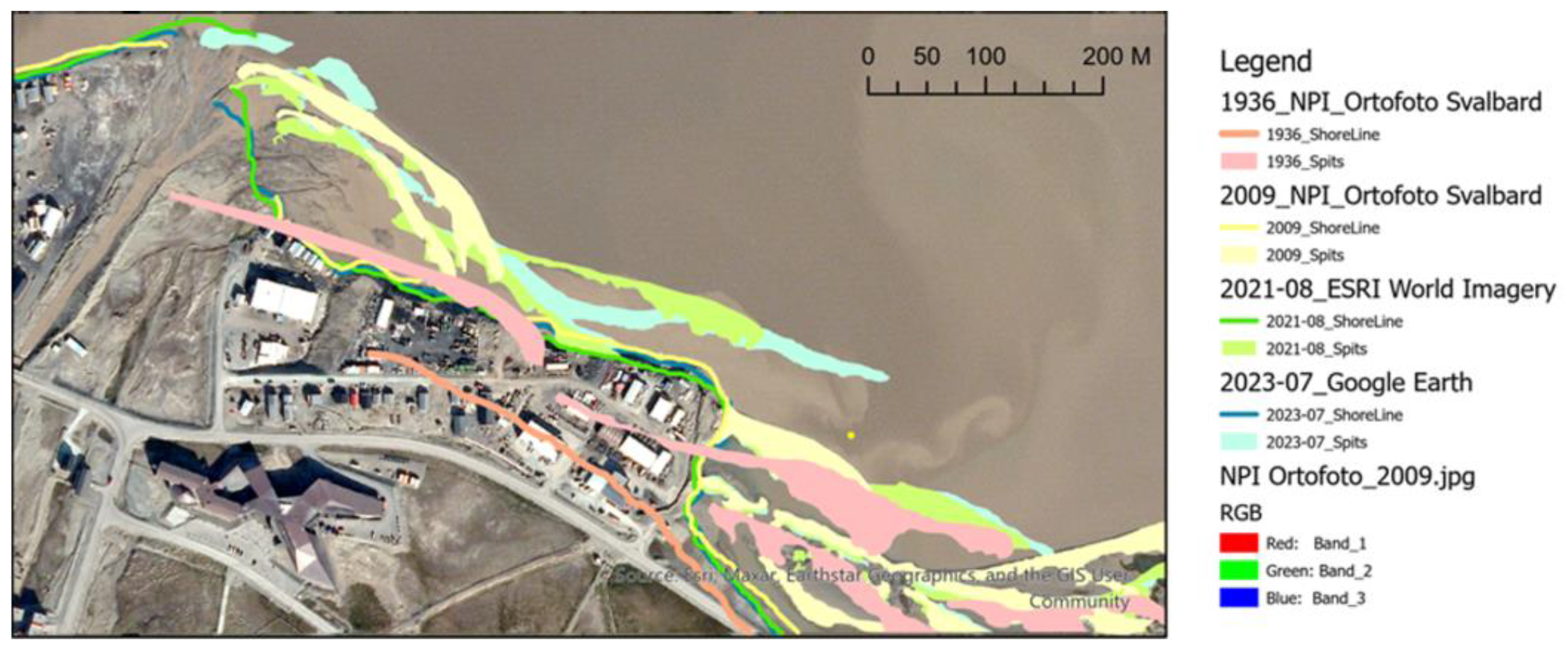
4.1. Longyearbyen Lagoon System Development 1936–2024
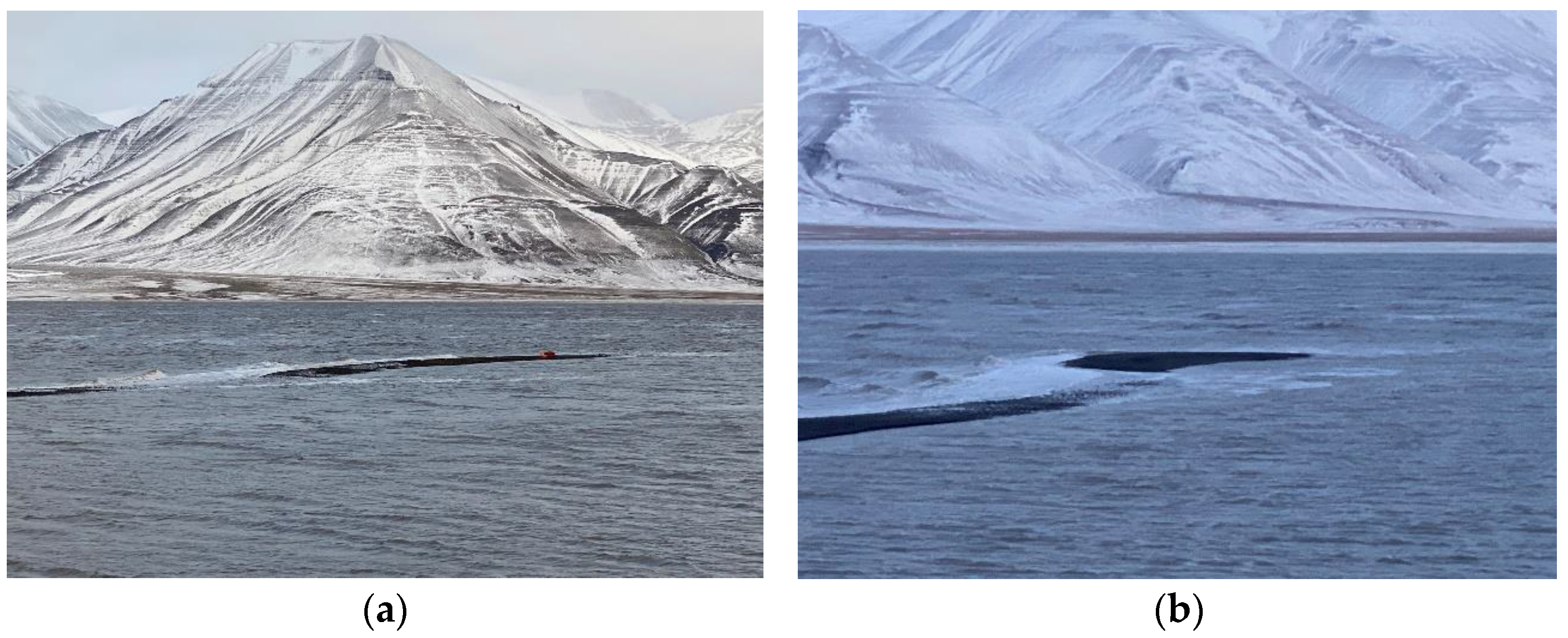
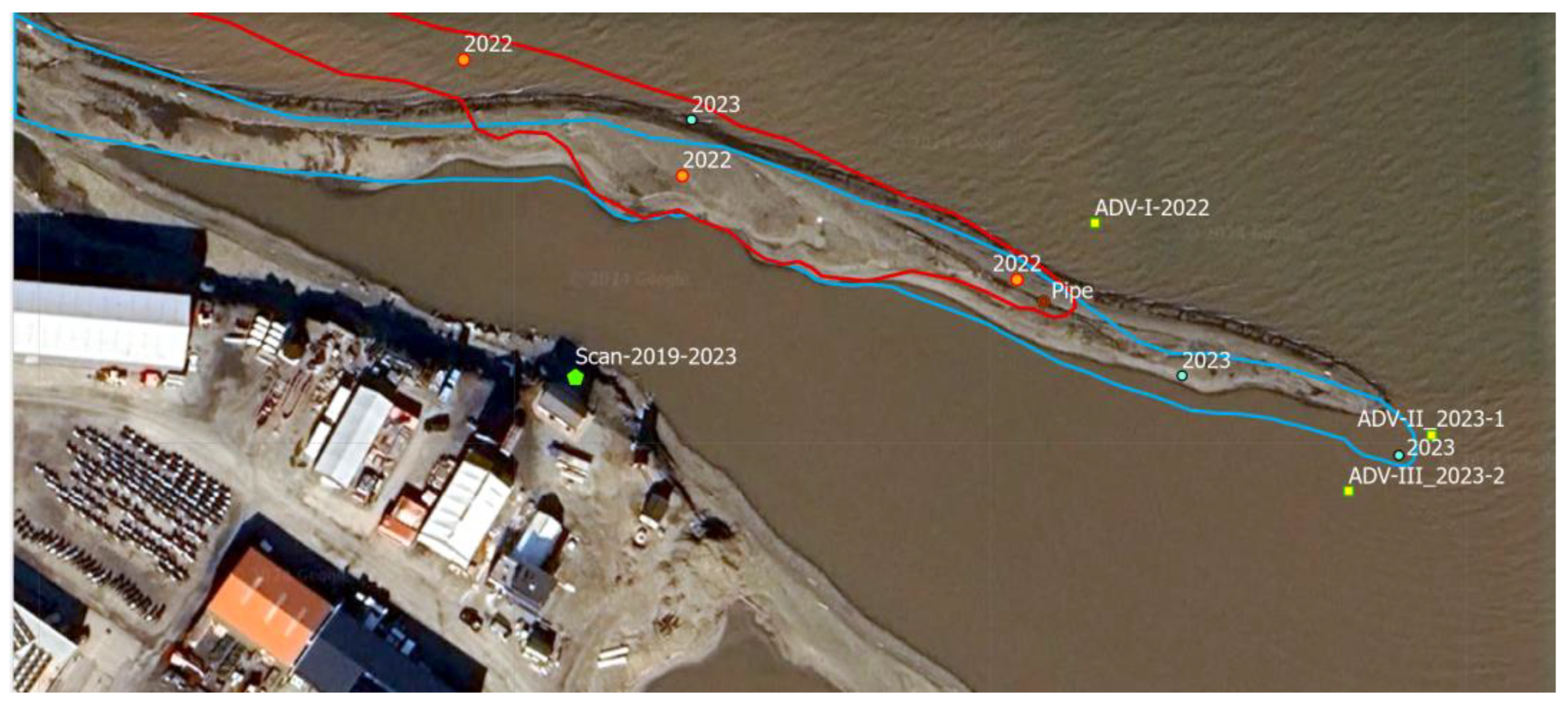
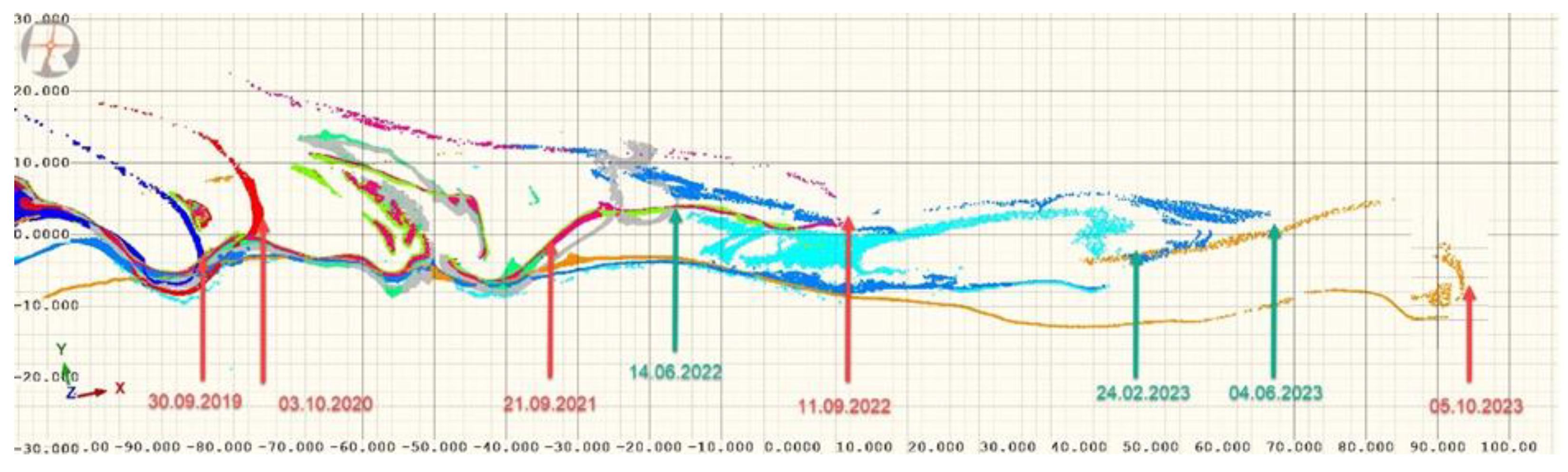
4.2. Gravel Spit Topography and Movement 2019–2023
4.3. Spit Expansion Rate 2019–2023
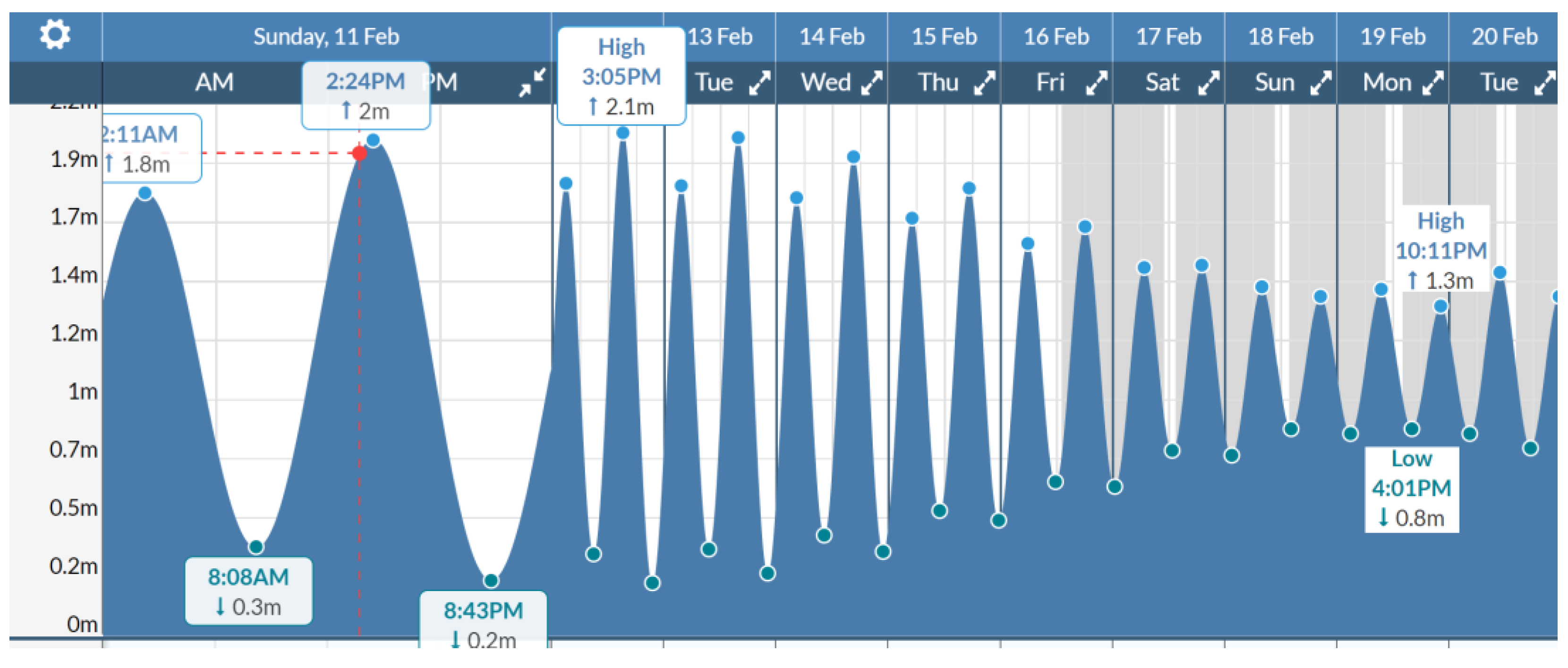
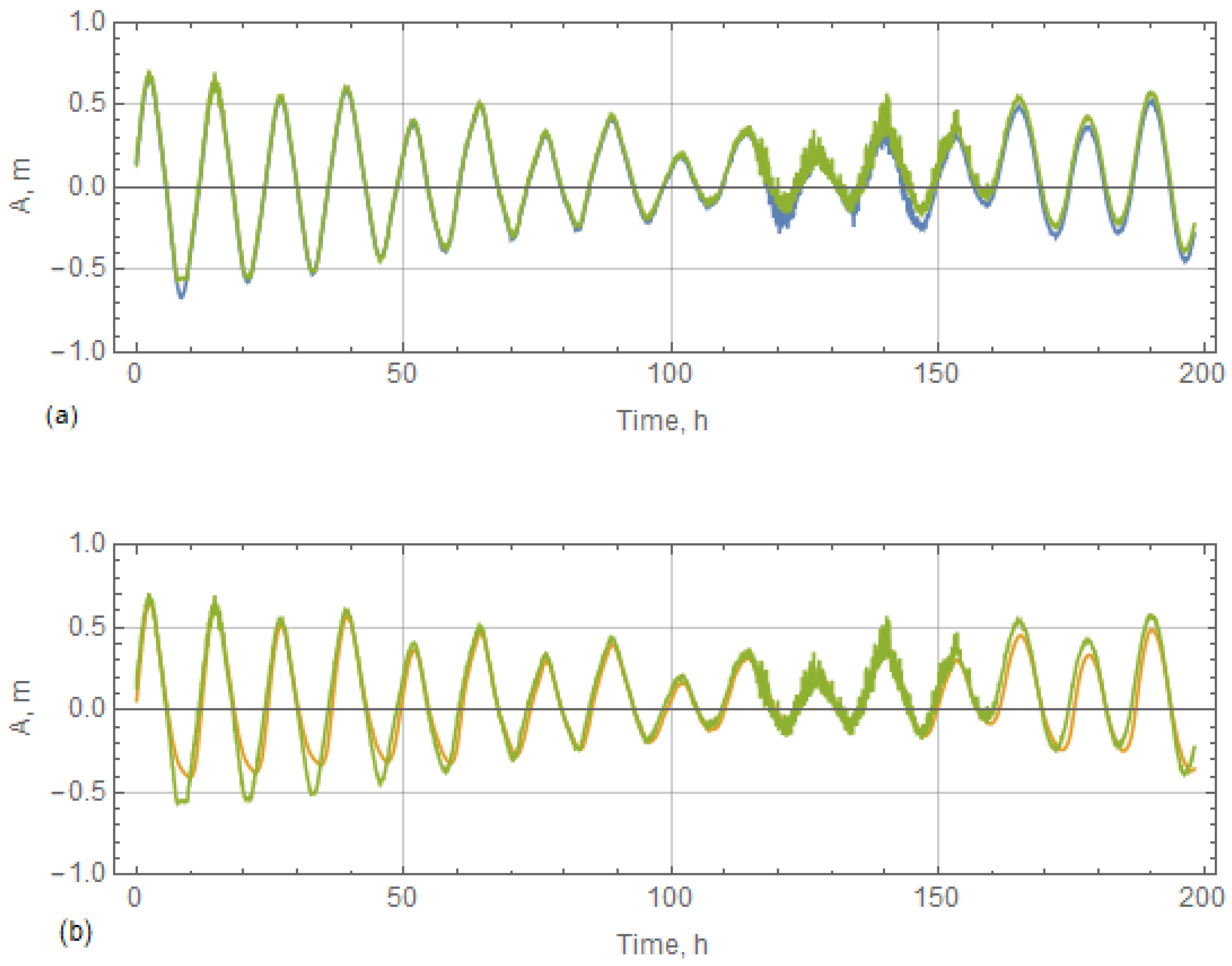
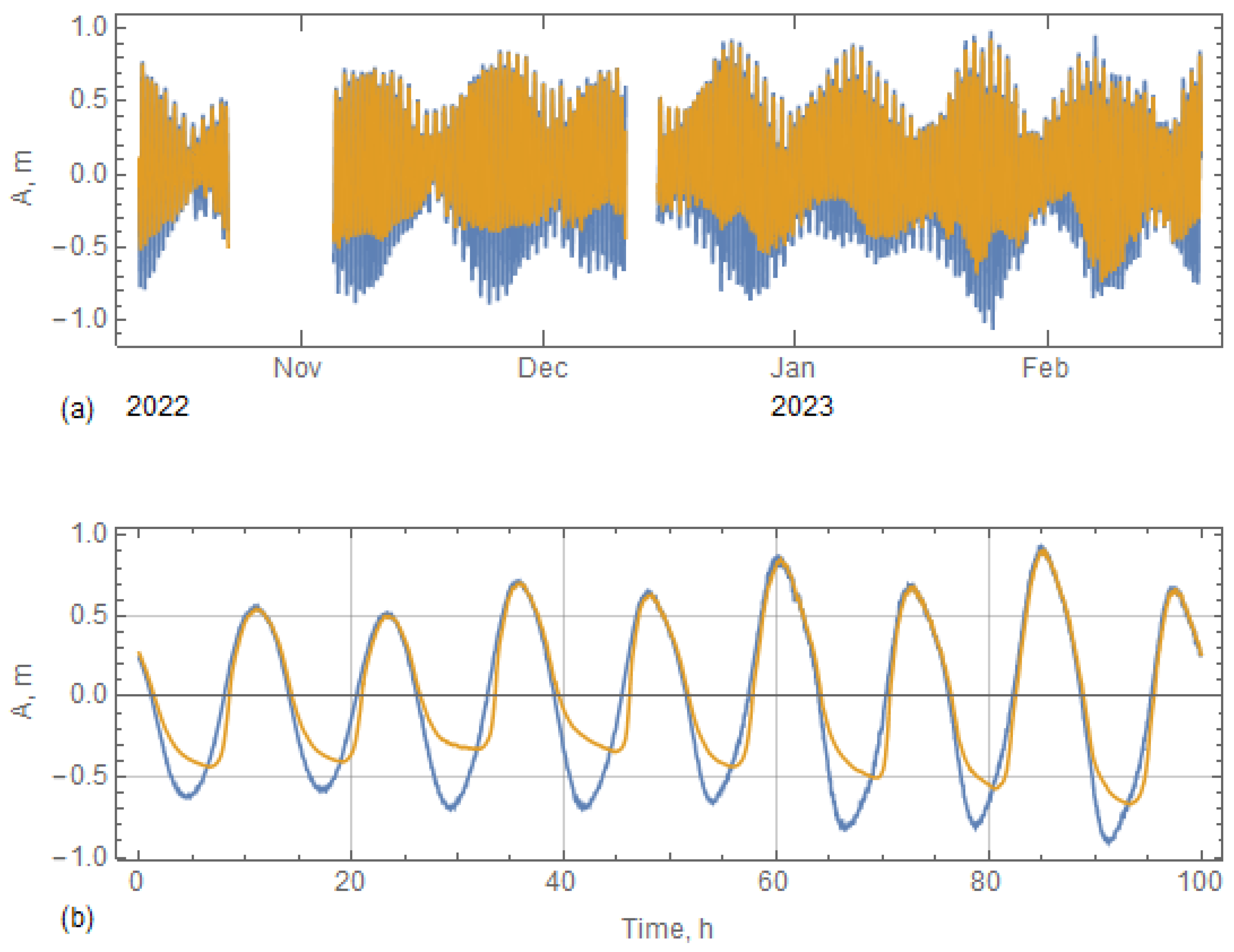
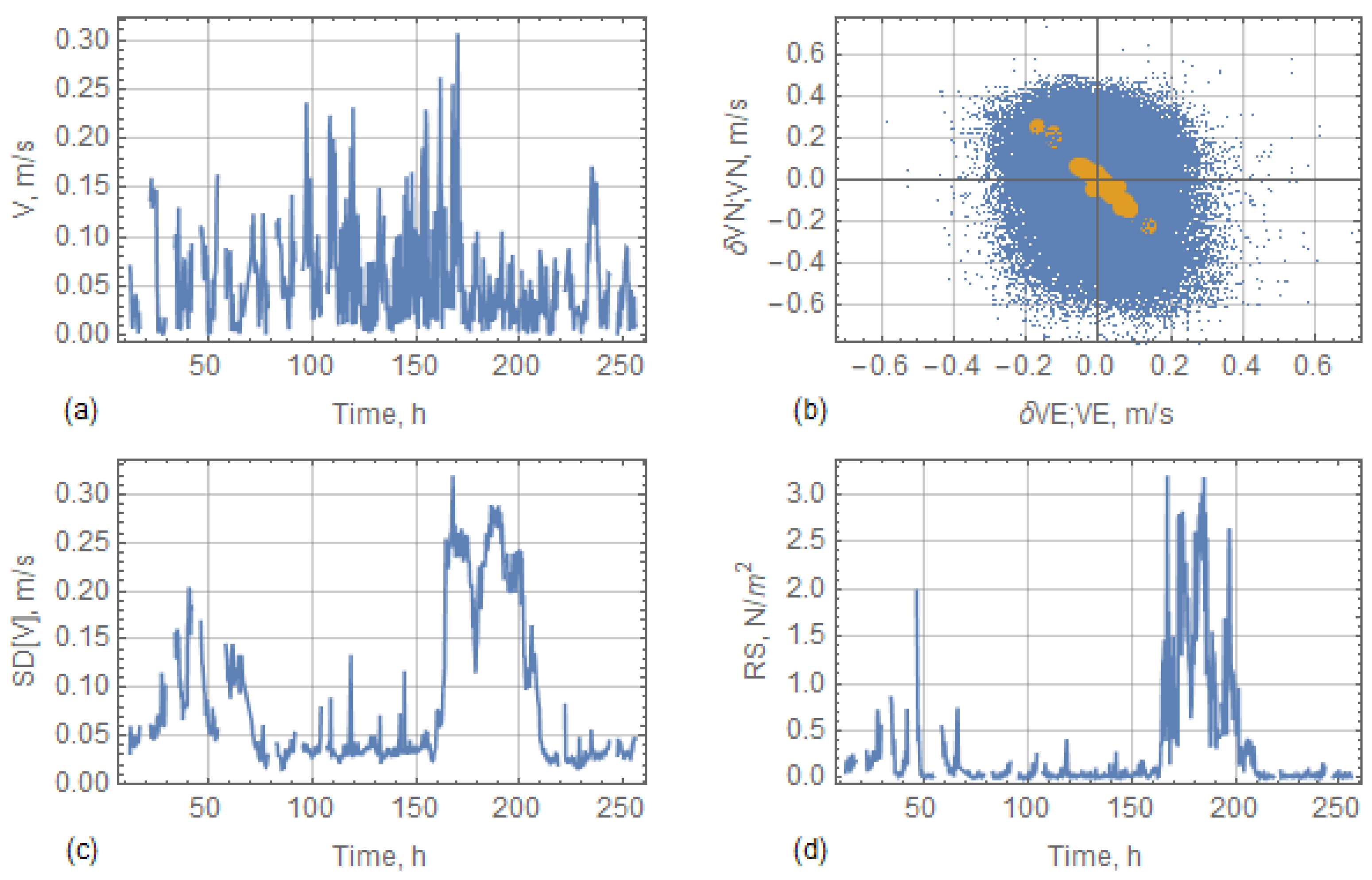
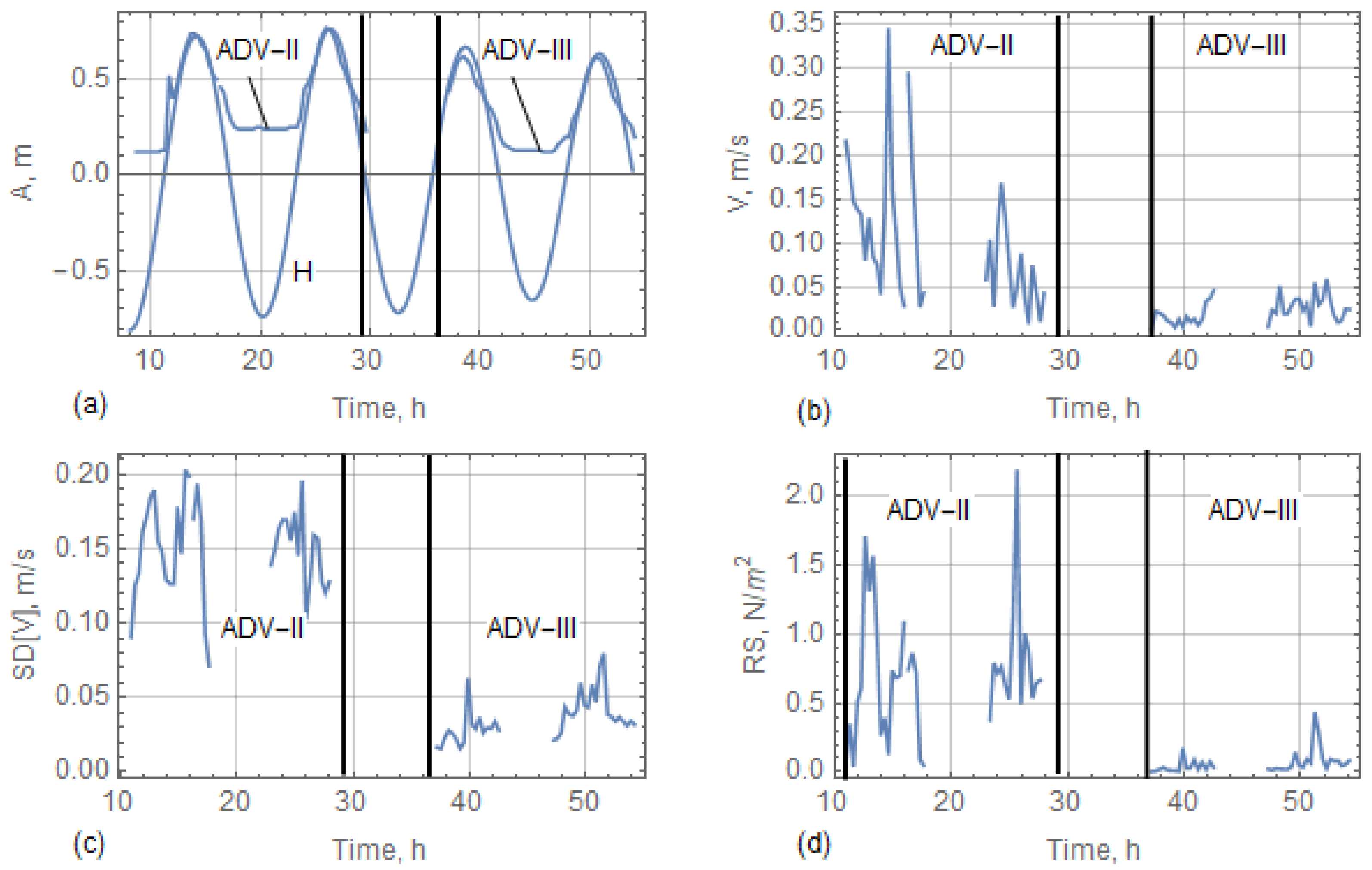
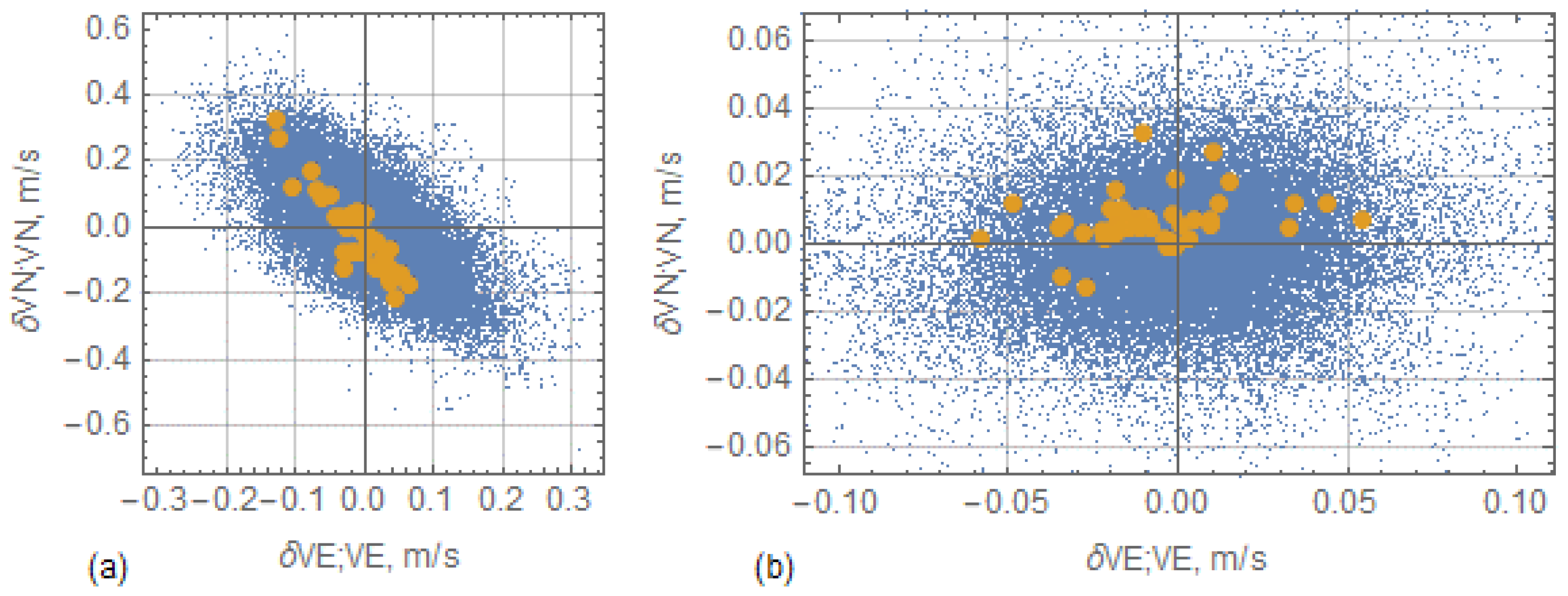
4.4. Results of Hydrological Measurements
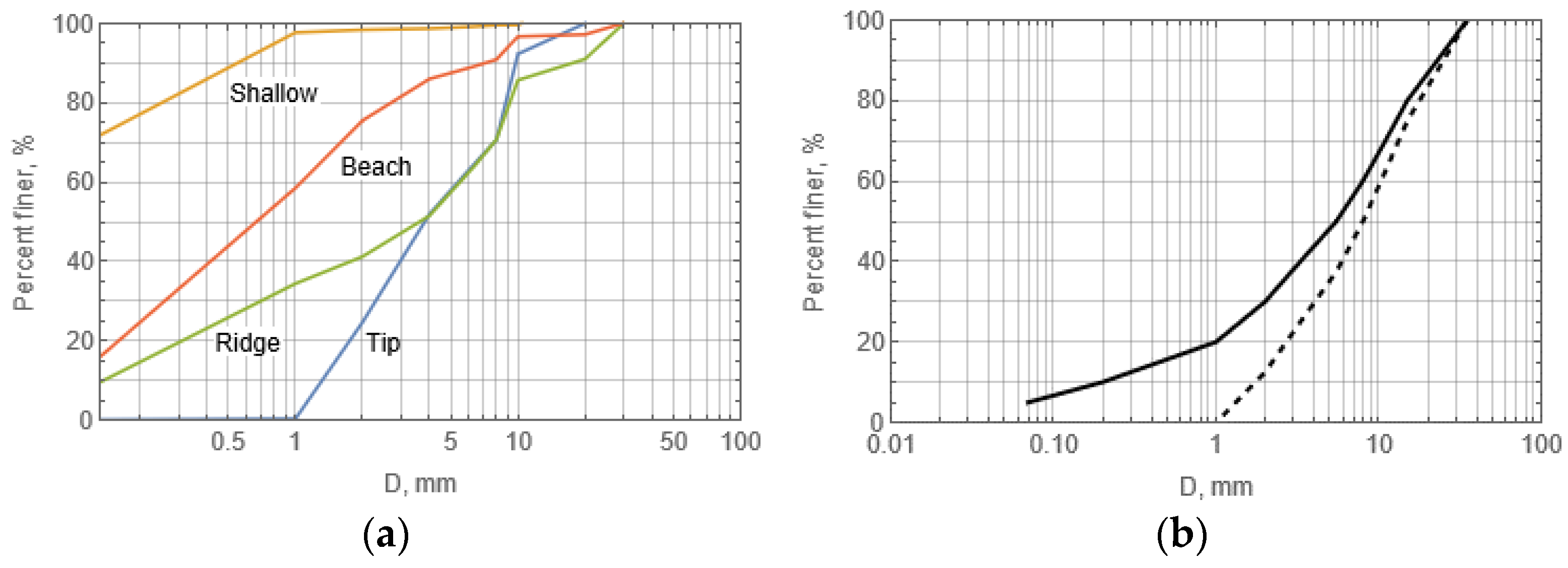
4.5. Sediment Analysis
4.6. Physical Effects Influencing Spit Movement
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GIS | Geographical Information System |
| ADV | Acoustic Doppler velocimeter |
| SBE | Sea Bird—pressure and temperature recorders by https://www.seabird.com/, accessed on 1 April 2025 |
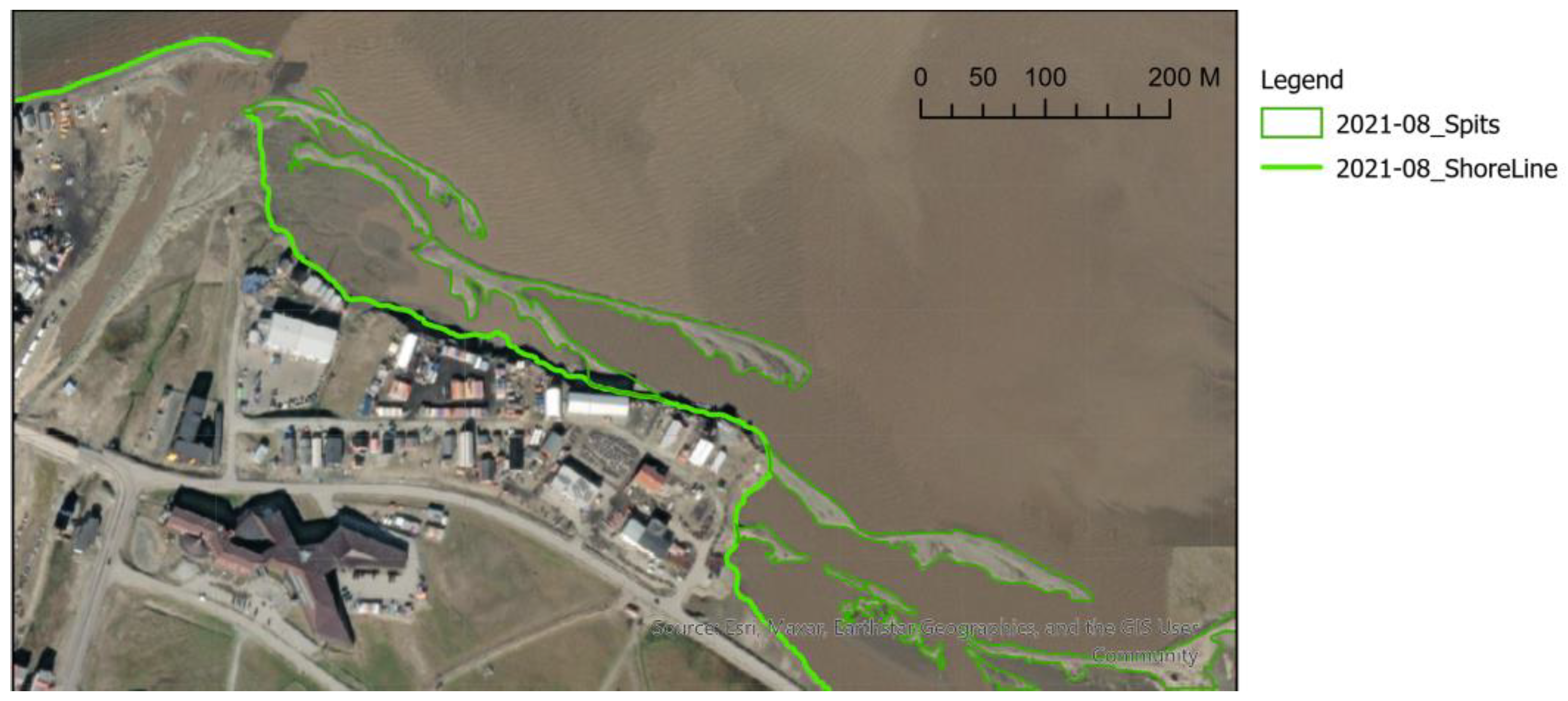
Appendix A. Longyearbyen Lagoon System Development from 1936 to 2023
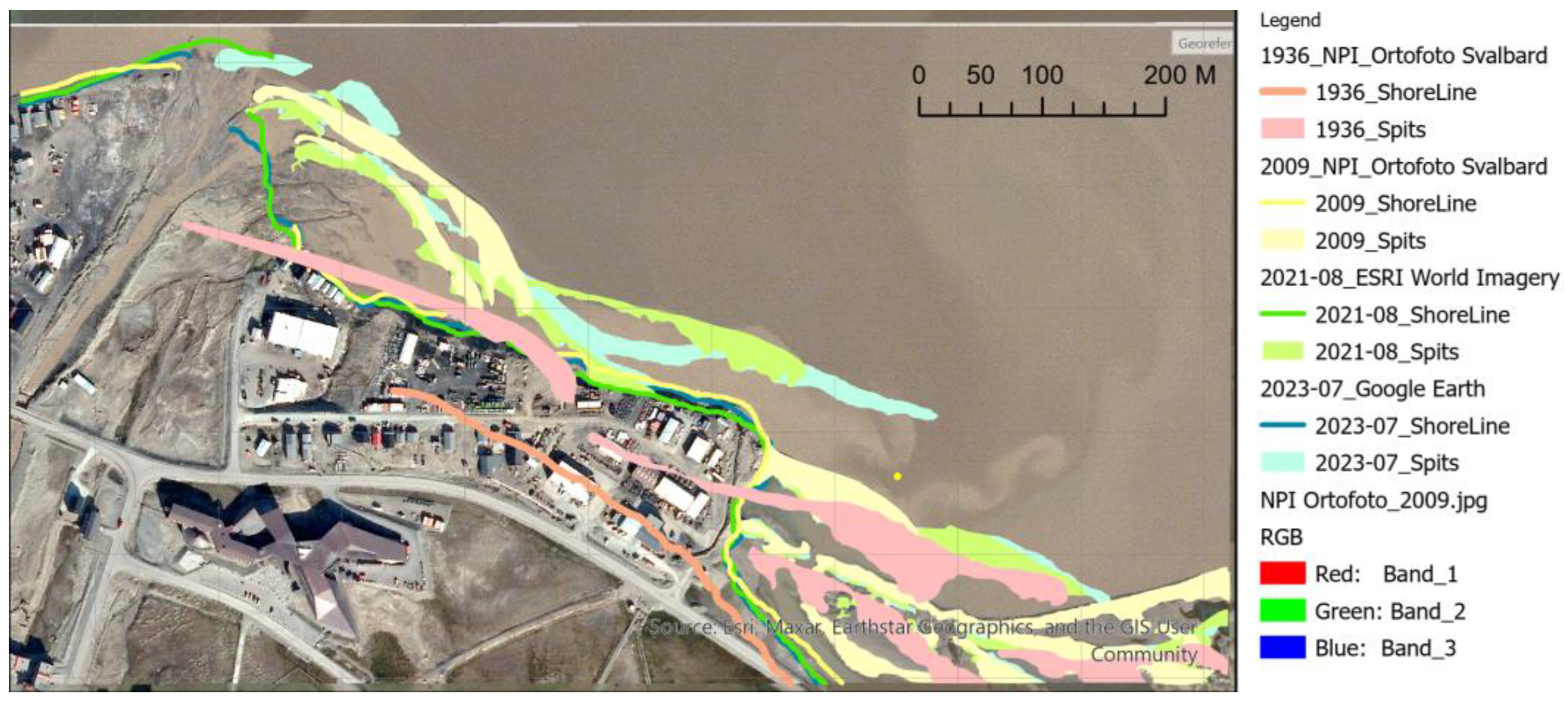
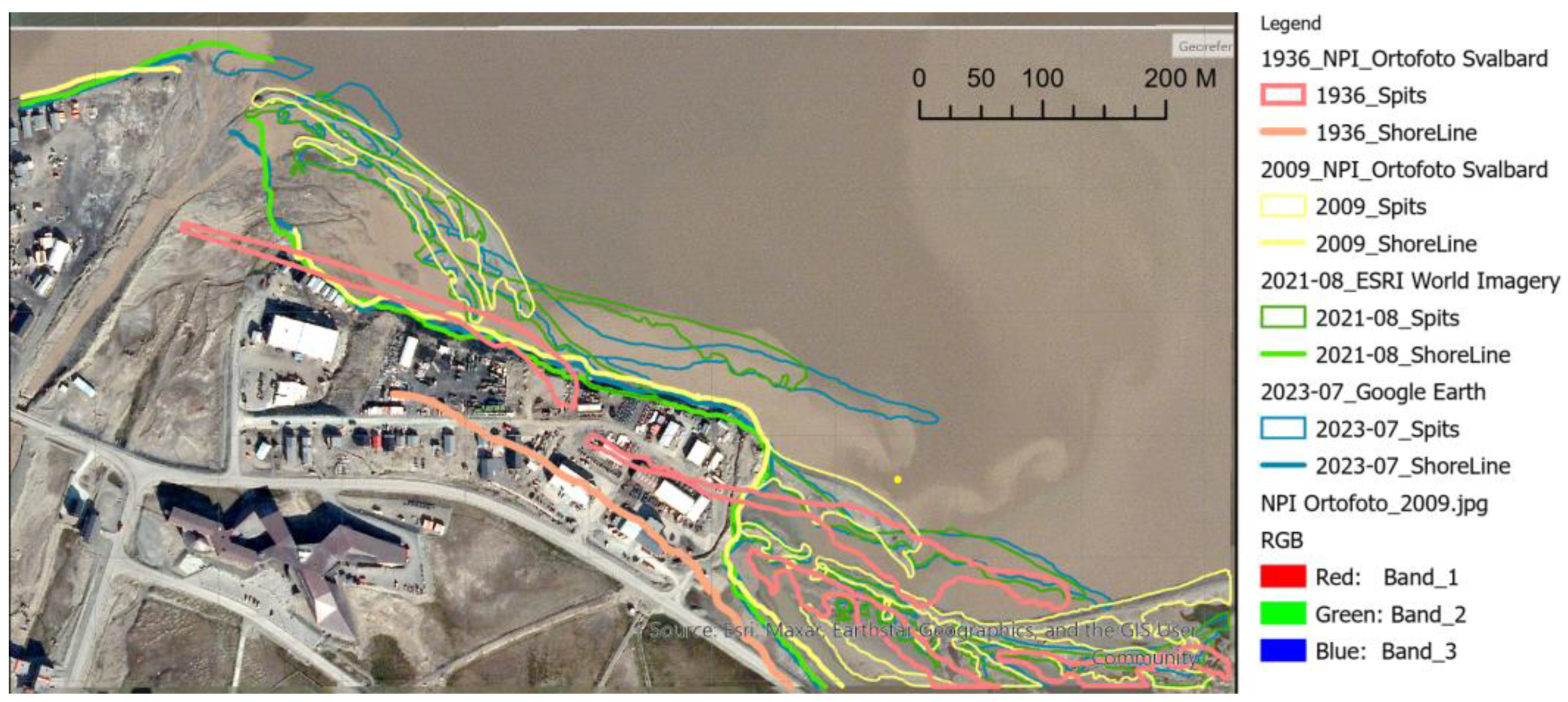
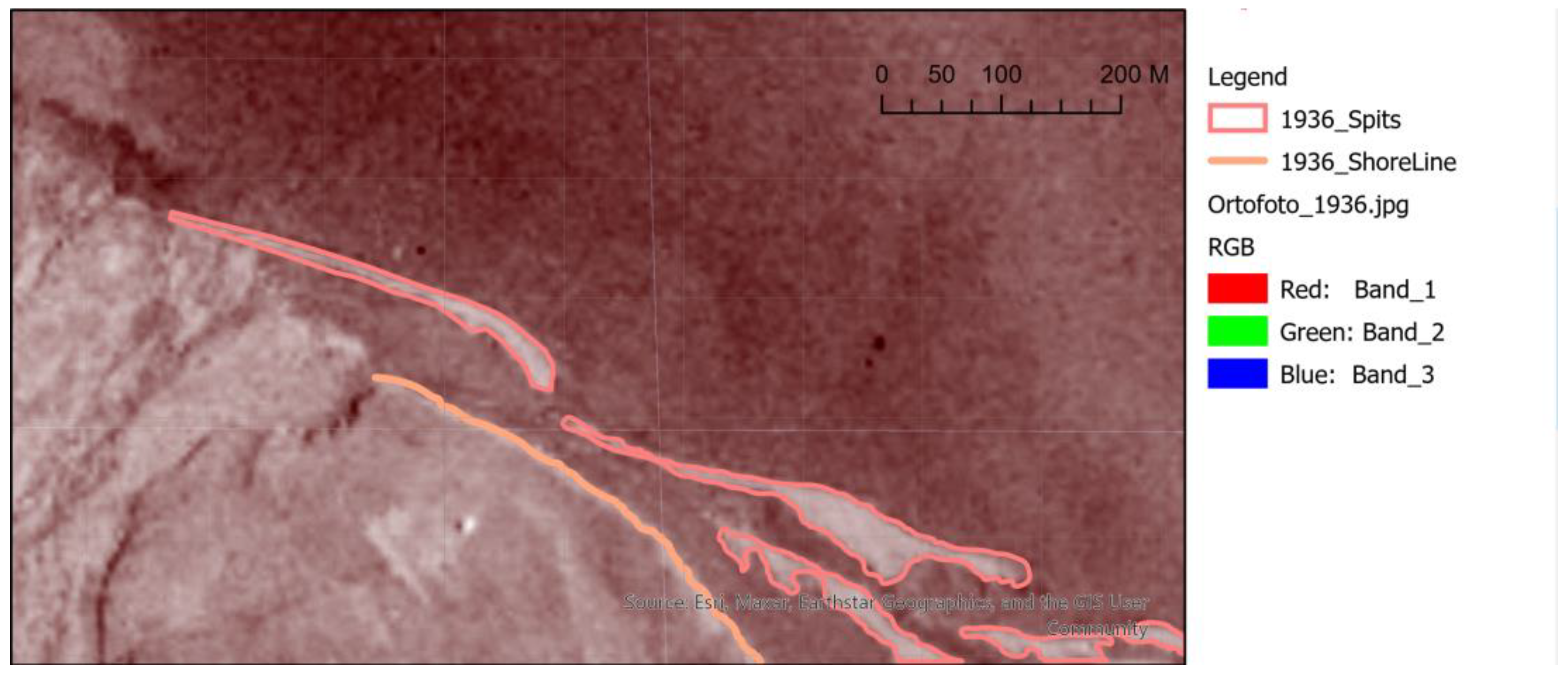
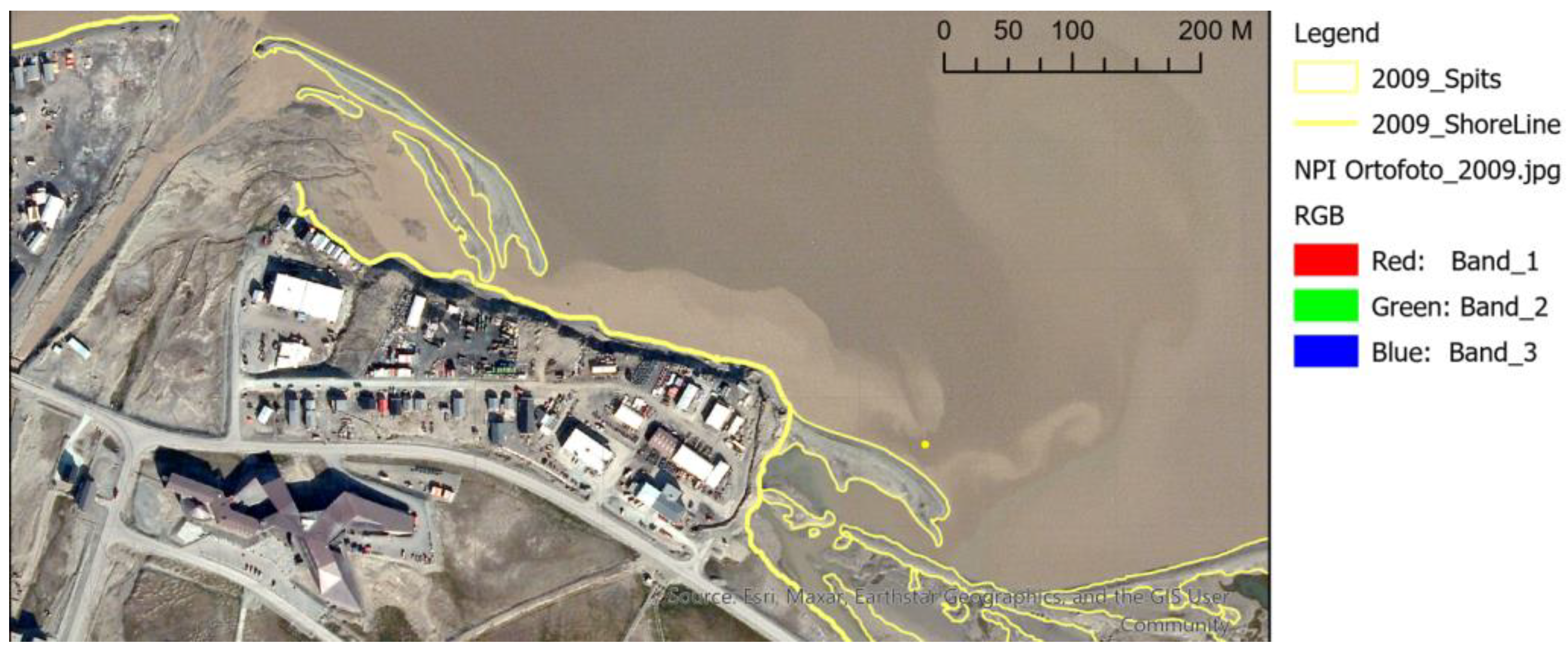

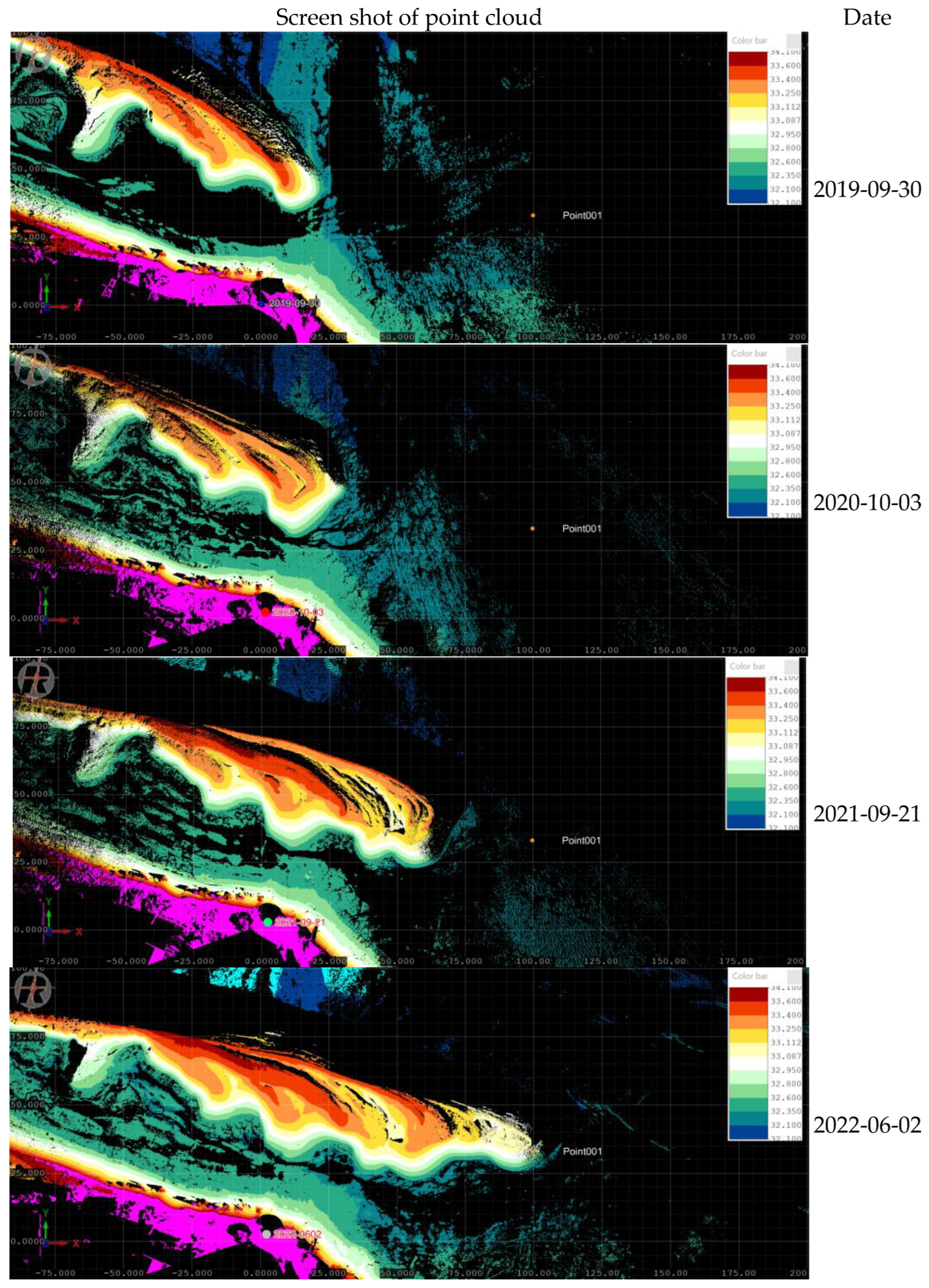
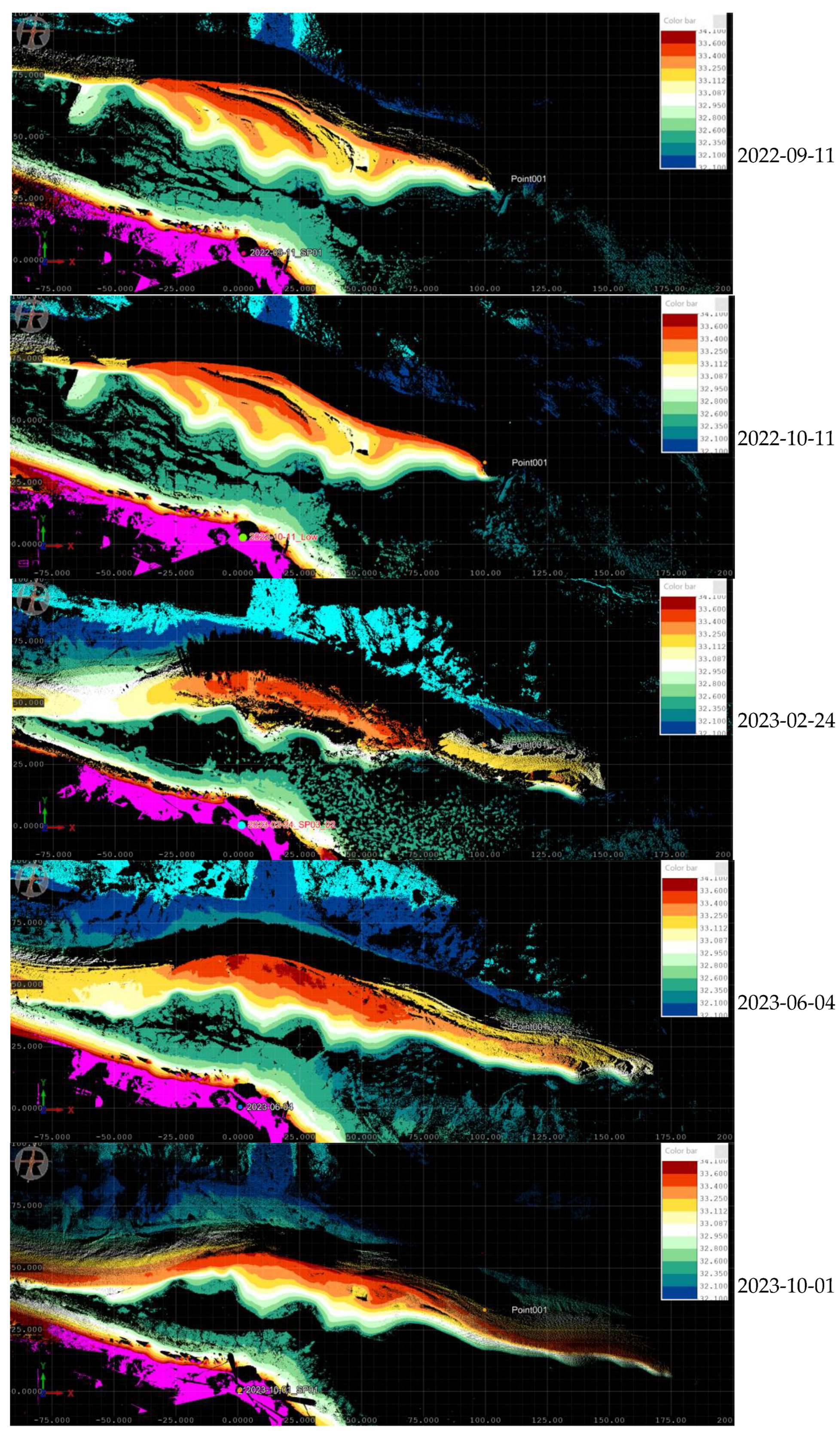
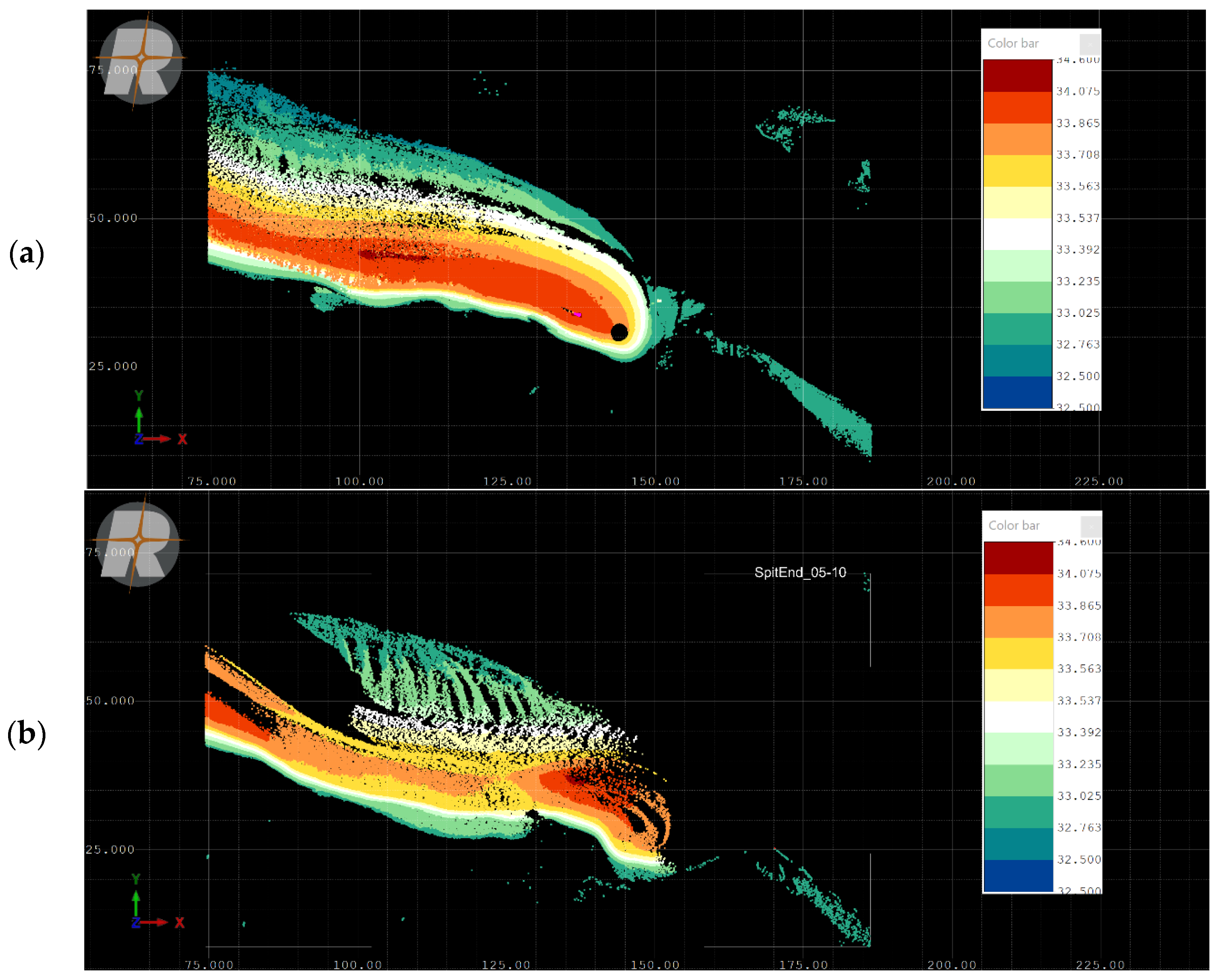
Appendix B. Lagoon Spit Point Clouds 2019–2023
References
- Barnes, R.S.K. Lagoons. In Encyclopedia of Ocean Sciences; Steele, J.H., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2001; pp. 1427–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraley, K.; Jones, T.; Robards, M.; Smith, B.; Tibbles, M.; Whiting, A. The Forgotten Coast: A Synthesis of Current Knowledge of Southern Chukchi Sea Lagoon Ecosystems. Arctic 2022, 75, 291–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogorodov, S.A. Atlas of Abrasion and Ice-Exaration Hazards of the Coastal-Shelf Zone of the Russian Arctic. 2020, p. 69. Available online: https://rus.arcticcoast.ru/atlas/ (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Haug, F.D.; Myhre, P.I. Naturtyper på Svalbard: Laguner og pollers betydning, med katalog over lokaliteter. In Kortrapport; Norsk Polarinstitutt: Tromsø, Norway, 2016; p. 174. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, C.A.; Bonsell, C.; McTigue, N.D.; Kelley, A.L. The seasonal phases of an Arctic lagoon reveal the discontinuities of pH variability and CO2 flux at the air–sea interface. Biogeosciences 2021, 18, 1203–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrazas, M.N.; Cardenas, M.B.; Demir, C.; Watson, J.A.; Connolly, C.T.; McClelland, J.W. Absence of ice-bonded permafrost beneath an Arctic lagoon revealed by electrical geophysics. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabb5083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, K.W.; Ambrose, W.G.; Reynolds, M.J.; Johnson, B.J.; Whiting, A.; Clough, L.M. Arctic lagoon and nearshore food webs: Relative contributions of terrestrial organic matter, phytoplankton, and phytobenthos vary with consumer foraging dynamics. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 257, 107388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenrich, M.; Angelopoulos, M.; Grosse, G.; Overduin, P.P.; Schirrmeister, L.; Nitze, I.; Biskaborn, B.K.; Liebner, S.; Grigoriev, M.; Murray, A.; et al. Thermokarst Lagoons: A Core-Based Assessment of Depositional Characteristics and an Estimate of Carbon Pools on the Bykovsky Peninsula. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 637899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PSMSL; Valkarvai. Permanent Service for Mean Sea Level 2022. Available online: https://www.psmsl.org/data/obtaining/stations/792.php (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Marchenko, A.V.; Morozov, E.G. Asymmetric tide in Lake Vallunden (Spitsbergen). Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 2013, 20, 935–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozov, E.G.; Marchenko, A.V.; Filchuk, K.V.; Kowalik, Z.; Marchenko, N.A.; Ryzhov, I.V. Sea ice evolution and internal wave generation due to a tidal jet in a frozen sea. Appl. Ocean Res. 2019, 87, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, D.M.; Pieper, P.; Barkhordarian, A.; Overduin, P.; Ilyina, T.; Brovkin, V.; Baehr, J.; Dobrynin, M. Increase in Arctic coastal erosion and its sensitivity to warming in the twenty-first century. Nat. Clim. Change 2022, 12, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogorodov, S.; Aleksyutina, D.; Baranskaya, A.; Shabanova, N.; Shilova, O. Coastal Erosion of the Russian Arctic: An Overview. J. Coast. Res. 2020, 95, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanguy, R.; Bartsch, A.; Nitze, I.; Irrgang, A.; Petzold, P.; Widhalm, B.; von Baeckmann, C.; Boike, J.; Martin, J.; Efimova, A.; et al. Pan-Arctic Assessment of Coastal Settlements and Infrastructure Vulnerable to Coastal Erosion, Sea-Level Rise, and Permafrost Thaw. Earth’s Future 2024, 12, e2024EF005013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Jo, J.; Nam, S.-I.; Choi, K. Morphodynamic evolution of paraglacial spit complexes on a tide-influenced Arctic fjord delta (Dicksonfjorden, Svalbard). Mar. Geol. 2022, 447, 106800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strzelecki, M.C.; Long, A.J.; Lloyd, J.M. Post-Little Ice Age Development of a High Arctic Paraglacial Beach Complex. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2017, 28, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strzelecki, M.C.; Long, A.J.; Lloyd, J.M.; Małecki, J.; Zagórski, P.; Pawłowski, Ł.; Jaskólski, M.W. The role of rapid glacier retreat and landscape transformation in controlling the post-Little Ice Age evolution of paraglacial coasts in central Spitsbergen (Billefjorden, Svalbard). Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 1962–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaskólski, M.W.; Pawłowski, Ł.; Strzelecki, M.C. High Arctic coasts at risk—The case study of coastal zone development and degradation associated with climate changes and multidirectional human impacts in Longyearbyen (Adventfjorden, Svalbard). Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 2514–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourriquen, M.; Baltzer, A.; Mercier, D.; Fournier, J.; Pérez, L.; Haquin, S.; Bernard, E.; Jensen, M. Coastal evolution and sedimentary mobility of Brøgger Peninsula, northwest Spitsbergen. Polar Biol. 2016, 39, 1689–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lønne, I.; Nemec, W. High-arctic fan delta recording deglaciation and environment disequilibrium. Sedimentology 2004, 51, 553–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagórski, P. Shoreline dynamics of Calypsostranda (NW Wedel Jarlsberg Land, Svalbard) during the last century. Pol. Polar Res. 2011, 32, 67–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weslawski, J.; Gluchowska, M.; Kotwicki, L.; Szczuciński, W.; Tatarek, A.; Wiktor, J.; Wlodarska-Kowalczuk, M.; Zajączkowski, M. Adventfjorden: Arctic Sea in the Backyard; Institute of Oceanology PAS: Sopot, Poland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Instanes, A. Incorporating climate warming scenarios in coastal permafrost engineering design—Case studies from Svalbard and northwest Russia. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2016, 131, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCCS. Climate in Svalbard 2100—A Knowledge Base for Climate Adaptation; Hanssen-Bauer, E.J.F.I., Hisdal, H., Mayer, S., Sandø, A.B., Sorteberg, A., Eds.; The Norwegian Centre for Climate Services: Oslo, Norway, 2019; p. 105. [Google Scholar]
- ITV News. Svalbard: The Remote Arctic Island Warming Seven Times Faster than the Global Average. 2023. Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KXTPduyDamE (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Google. Google Earth Pro Image. 2023. Available online: https://earth.google.com/web (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Norwegian Polar Institute. TopoSvalbard. 2024. Available online: http://toposvalbard.npolar.no/ (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Piepjohn, K.; Stange, R.; Jochmann, M.; Hübner, C. The Geology of Longyearbyen; LoFF: Longyearbyen, Svalbard and Jan Mayen, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kowalik, Z.; Marchenko, A.; Brazhnikov, D.; Marchenko, N. Tidal currents in the western Svalbard Fjords. Oceanologia 2015, 57, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tide Times and Tide Charts for the World. Tide Times for Longyearbyen, Spitsbergen. 2024. Available online: https://www.tide-forecast.com/locations/Longyearbyen-Spitsbergen/tides/latest (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Marchenko, N.; Brazhnikov, D.; Marchenko, A.; Finseth, J. Monitoring of sea currents and waves in Spitsbergen fjords. In Geophysical Research Abstracts; 2014; Available online: http://meetingorganizer.copernicus.org/EGU2014/EGU2014-12294.pdf (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Marchenko, N.; Marchenko, A. Ice formation, Growth and Dynamics in Arctic Lagoon (Spitsbergen). In IAHR International Symposium on Ice; IAHR: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Marchenko, N. Coastal Ice Rubbles in Isfjorden (Spitsbergen). In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Port and Ocean Engineering under Arctic Conditions (POAC-23), Glasgow, UK, 12–16 June 2023; p. 11. [Google Scholar]
- Norwegian Polar Institute. Ortofoto Svalbard 1936. Svalbardkartet 2024. Available online: https://geokart.npolar.no/Html5Viewer/index.html?viewer=Svalbardkartet (accessed on 14 February 2024).
- ESRI.; MAXAR. World Imagery. 2023. Available online: https://www.arcgis.com/apps/mapviewer/index.html?webmap=c03a526d94704bfb839445e80de95495 (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Riegl. Terrestrial Laser Scanning. 2024. Available online: http://www.riegl.com/nc/products/terrestrial-scanning/ (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Riegl. RiSCAN PRO. Operating and Processing Software for RIEGL 3D Laser Scanners. 2021. Available online: http://www.riegl.com/products/software-packages/riscan-pro/ (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Sea-Bird Scientific. SBE 39plus Temperature (Depth) Recorder. 2025. Available online: https://www.seabird.com/moored/sbe-39plus-temperature-depth-recorder/family?productCategoryId=54627473774 (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Geoengineer. Step-by-Step Guide for Grain Size Analysis. 2024. Available online: https://www.geoengineer.org/education/laboratory-testing/step-by-step-guide-for-grain-size-analysis (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Magilligan, F.J.; Roberts, M.O.; Marti, M.; Renshaw, C.E. The impact of run-of-river dams on sediment longitudinal connectivity and downstream channel equilibrium. Geomorphology 2021, 376, 107568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rijn, L.C. Principles of Sediment Transport in Rivers, Estuaries and Coastal Seas; Aquapublications: Blokzijl, The Netherlands, 2006; 1200p. [Google Scholar]
- Wentworth, C.K. A scale of grade and class terms for clastic sediments. J. Geol. 1922, 30, 377–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordli, Ø.; Wyszyński, P.; Gjelten, H.M.; Isaksen, K.; Łupikasza, E.; Niedźwiedź, T.; Przybylak, R. Revisiting the extended Svalbard Airport monthly temperature series, and the compiled corresponding daily series 1898–2018. Polar Res. 2020, 39, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esau, I.; Miles, V. A local climate perspective on possible development pathways for Longyearbyen, Svalbard. Polar Rec. 2024, 60, e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapointe, F.; Karmalkar, A.V.; Bradley, R.S.; Retelle, M.J.; Wang, F. Climate extremes in Svalbard over the last two millennia are linked to atmospheric blocking. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogen, J.; Bønsnes, T.E. Erosion and sediment transport in High Arctic rivers, Svalbard. Polar Res. 2003, 22, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallesen, L.M. Sediment source-to-sink in a warming Arctic; thawing moraines, slope processes and river erosion in Longyeardalen, Svalbard. In Institutt for Geovitenskap og Petroleum; NTNU: Trondheim, Norway, 2022; p. 114. [Google Scholar]
- Winther, S.; Gudmestad, O. Impact of and solutions to effects of climate changes for Longyearbyen, Svalbard, Norway. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2023, 1294, 012036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygård Jakobsen, A. Omfattende planer for å sikre Longyearbyen mot naturkatastrofer (Comprehensive plans to secure Longyearbyen against natural disasters). In NRK Web; NRK: Oslo, Norway, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ottem, M.J.D. The Longyearelva River-to-Ocean System; Monitoring an anthropogenic arctic fluvial system in changing climate over short and long timescales. In Institutt for Geovitenskap og Petroleum; NTNU: Trondheim, Norway, 2022; p. 119. [Google Scholar]
- Longyearbyen Lokalstyre. Flomsikringstiltak Longyearelva (Flood Protection Measures at Longyear River). 2016. Available online: https://www.lokalstyre.no/flomsikringstiltak-longyearelva.5920630-209814.html (accessed on 13 November 2016).
- O’Grady, J.; Babanin, A.; McInnes, K. Downscaling Future Longshore Sediment Transport in South Eastern Australia. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Barry, D.A. Wave-induced beach groundwater flow. Adv. Water Resour. 2000, 23, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchenko, A.V.; Instanes, A.; Finset, J.; Onishchenko, D.A. Monitoring of thermodynamic state of soil near Arctic pipeline landfall. Vesti Gazov. Nauk. 2013, 3, 202–211. [Google Scholar]
- Fomin, Y.V.; Zhmur, V.V.; Marchenko, A. Transient seawater inflow into seacoast aquifers. Water Resour. 2017, 44, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Barry, D.A.; Pattiaratchi, C.B.; Masselink, G. BeachWin: Modelling groundwater effects on swash sediment transport and beach profile changes. Environ. Model. Softw. 2002, 17, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, D.P. Beach groundwater dynamics. Geomorphology 2002, 48, 121–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Device | Measurement Start | Measurement End |
|---|---|---|
| SBE1 | 12 October 2022 | 6 August 2023 |
| SBE2 | 12 October 2022 | 23 October 2022 |
| SBE3 | 12 October 2023 | 17 June 2023 |
| ADV-I | 12 October 2022 | 23 October 2022 |
| ADV-II | 2 October 2023 | 3 October 2023 |
| ADV-III | 3 October 2023 | 4 October 2023 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marchenko, N.; Marchenko, A. Longyearbyen Lagoon (Spitsbergen): Gravel Spits Movement Rate and Mechanisms. Geographies 2025, 5, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/geographies5020018
Marchenko N, Marchenko A. Longyearbyen Lagoon (Spitsbergen): Gravel Spits Movement Rate and Mechanisms. Geographies. 2025; 5(2):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/geographies5020018
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarchenko, Nataliya, and Aleksey Marchenko. 2025. "Longyearbyen Lagoon (Spitsbergen): Gravel Spits Movement Rate and Mechanisms" Geographies 5, no. 2: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/geographies5020018
APA StyleMarchenko, N., & Marchenko, A. (2025). Longyearbyen Lagoon (Spitsbergen): Gravel Spits Movement Rate and Mechanisms. Geographies, 5(2), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/geographies5020018







