Abstract
Coastal areas are highly dynamic environments, vulnerable to natural processes and human interventions. This study presents the first application of the Integrated Coastal Vulnerability Index (ICVI) in Cyprus, focusing on two major tourism-dependent beaches, Fig Tree Bay and Vrysi Beach, located along the Protaras coastline. Despite their economic significance, these coastal areas face increasing vulnerability due to intensive tourism-driven modifications and natural coastal dynamics, necessitating a structured assessment framework. This research addresses this gap by integrating the ICVI with geographical information system (GIS) and analytic hierarchy process (AHP) methodologies to evaluate the coastal risks in this tourism-dependent environment, providing a replicable approach for similar Mediterranean coastal settings. Ten key parameters were analysed, including coastal slope, rate of coastline erosion, geomorphology, elevation, tidal range, wave height, relative sea level rise, land cover, population density, and road network. The results revealed spatial variations in vulnerability, with 16% of the coastline classified as having very high vulnerability and another 16% as having high vulnerability. Fig Tree Bay, which is part of this coastline, emerged as a critical hotspot due to its geomorphological instability, low elevation, and intensive human interventions, including seasonal beach modifications and infrastructure development. This study underscores the need for sustainable coastal management practices, including dune preservation, controlled development, and the integration of the ICVI into planning frameworks to balance economic growth and environmental conservation.
1. Introduction
During the last few decades, coastlines have become some of the most critical linear features on the Earth’s surface [1]. Coastal systems are complex and dynamic [2], defined as the meeting points between land and water, including a wide range of ecosystems, communities, and activities [3,4,5,6]. They are vital due to various factors, especially for biodiversity, as they provide a habitat for many species of plants and animals and breeding and nesting sites for marine life [7]. They are also important for economically significant activities derived from human activities, including tourism, fishing, agriculture, shipping, algae farming, and urban development [8]. Despite the enormous importance of these activities, they contribute significantly to the environmental, social, and economic pressures on coastal ecosystems. Specifically, these activities lead to habitat destruction, pollution, biodiversity loss, and economic losses [9]. Moreover, coastal areas are also vulnerable to natural hazards like global climate change, hurricanes, sea level rise, tsunamis, storm surges, and coastal floods [10,11,12].
Coastal vulnerability assessment is a topic with growing interest around the world. According to the literature, numerous studies have played a critical role in coastal planning and coastal disaster risk reduction management for sustainable development [13,14]. One of the most widely used tools for coastal vulnerability assessment is the Coastal Vulnerability Index (CVI), which was initially introduced by Gornitz et al. [15] and later refined by Thieler and Hammar-Klose [16] and Pendleton et al. [17], which evaluates coastal vulnerability by considering various physical factors that contribute to coastal erosion. Due to its effectiveness, the CVI has been extensively applied worldwide, including in the assessment of coastal vulnerability in the Laguna de Terminos, the most important coastal lagoon in Mexico [8]; the Xiamen Coast in Southeast China [10]; San Francisco Bay in the US; Swansea Bay in the UK; and in Doha, Qatar [18]. These diverse applications highlight the global relevance and adaptability of the CVI in various coastal contexts.
Remote sensing plays a crucial role in coastal vulnerability monitoring by providing comprehensive, frequent, and accurate data for assessing coastal dynamics and identifying areas at risk of erosion. In addition to remote sensing, several approaches have been developed to assess the vulnerability of coastal areas [19,20,21]. Today, data collected from remote sensing technologies, including satellite imagery and UAV-based monitoring, combined with the analytical capabilities of GISs, allow for detailed assessments without the need for extensive fieldwork [22]. Recent studies emphasise that UAV-based remote sensing provides a cost-effective and high-resolution approach to coastal monitoring, enabling detailed assessments of shoreline evolution, beach morphology shifts, and infrastructure susceptibility to coastal hazards. These capabilities enhance coastal vulnerability assessments by providing frequent and spatially accurate data, allowing for improved detection of erosion patterns and human-induced modifications [23,24,25,26,27,28]. In addition to UAV applications, various techniques have been employed for monitoring coastline changes, including historical land-based imagery, coastal maps [29], GPS field measurements, and remote sensing imagery [4,30]. Specifically, launching satellites equipped with microwave and optical electromagnetic spectrum sensors has significantly enhanced the ability to map extensive shorelines and perform frequent updates for practical monitoring purposes [31]. These images have been acquired from various sources, ranging from medium spatial resolution satellites such as Sentinel [32,33] and Landsat [34,35] to high-resolution platforms including PlanetScope [35,36], WorldView [37], and LiDAR sensors [38,39,40]. By leveraging these diverse data sources, coastal vulnerability assessments can be conducted more effectively, enabling informed decision-making for sustainable coastal management and climate resilience planning.
Most studies aiming to assess the CVI utilise a multi-criteria decision analysis (MCDA) technique, with the AHP method being the most frequently applied [41,42]. The AHP method offers a structured framework for decision-making when resolving complex scenarios. First introduced by Saaty (1980) [43], this method facilitates the comparison of multiple criteria by organising the problem hierarchically and employing pairwise comparisons to derive priority weights for each criterion [44,45,46]. This approach has been widely used in coastal vulnerability assessments to integrate diverse anthropogenic or natural factors. By quantifying subjective expert judgments, the AHP method allows for the creation of consistent weighting schemes that enhance the reliability of vulnerability indices. In studies such as those conducted on the Vila Belmiro coastal stretches, Brazil [5]; Ilha Grande Bay, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil [22]; the Central Odisha coast, India [23]; Bonny Bay, Nigeria [24]; and the Vishakhapatnam coastal tract, Andhra Pradesh, India [25], the AHP method has proven to be effective in identifying high-priority areas for intervention. This provides a strong foundation for informed coastal management in response to climate change and anthropogenic pressures, especially in touristic areas [47] such as the island of Cyprus, with Protaras being a notable example [48], as elaborated next. While previous studies have successfully applied the CVI and ICVI using MCDA approaches such as the AHP method, these applications have predominantly focused on physical vulnerability assessments without explicitly incorporating the impact of tourism-driven modifications. This study tries to fill this gap by applying the ICVI in a Mediterranean high-tourism coastal setting such as Protaras, where anthropogenic pressures significantly alter coastal stability. As the first ICVI-based assessment conducted in Cyprus, it provides critical insights into the vulnerability of highly modified coastal environments. By incorporating ten key physical and socio-economic parameters, we aim to identify the spatial distribution of vulnerability, highlight the impact of human interventions, and provide insights for sustainable coastal management. This research builds on previous CVI applications by integrating a multi-criteria approach tailored to a tourism-driven Mediterranean coastline. To ensure a systematic assessment, a structured multi-criteria approach is followed. The methodology applies the AHP method to assign parameter weights, integrate vulnerability rankings, and compute an overall ICVI score. The detailed classification weight derivation and index computation are elaborated in the methodology section.
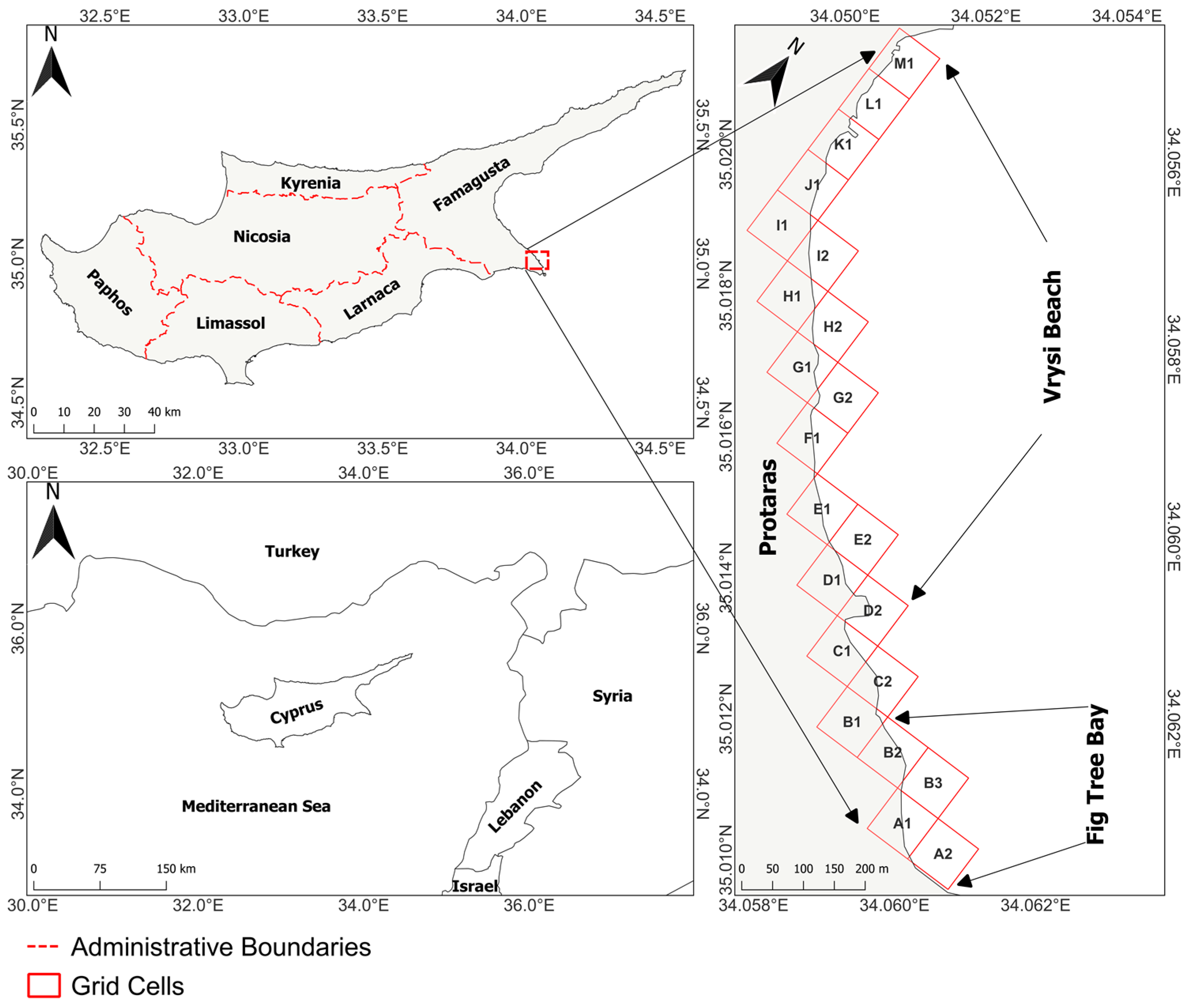
2. Study Area
Cyprus is a European island country in the Eastern Mediterranean, south of Turkey and west of Syria and Lebanon. As the third largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, Cyprus plays a significant geopolitical and economic role. The study area extends from the south side of Fig Tree Bay (Figure 1) (A2 grid cell) to the north side of Vrysi Beach (M1 grid cell) in the Protaras tourist area of the Paralimni-Deryneia municipality (Famagusta district) on the southeastern coast of Cyprus. The study area covers both beaches within a grid system with a total length of approximately 1.73 km. Protaras is a renowned and vibrant coastal resort owing mainly to its sandy beaches. Various formations define the geomorphological and textural diversity of the study area. Based on data derived from the Geological Survey Department (GSD) [49], the coastal texture of the study area predominantly consists of loam. However, this classification refers to the sedimentary composition of the broader coastal terrain rather than the active beach zone, which consists of sand and other unconsolidated sediments. The study area exhibits spatial variations in sediment texture and coastal geomorphology, transitioning from loam-based deposits inland to rocky coastal formations, particularly in grid cells I1–M1, where exposed rocky outcrops dominate. In the coastal area, there is also a diverse range of soils, classified into various soil series and types according to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) [50] World Reference Base for Soil Resources (WRB). While these soils are not directly affected by wave and current action, they influence coastal evolution indirectly by contributing to broader coastal stability. Factors such as vegetation cover, sediment retention, and the ability of soils to resist inland erosion play a role in maintaining the integrity of the coastline.
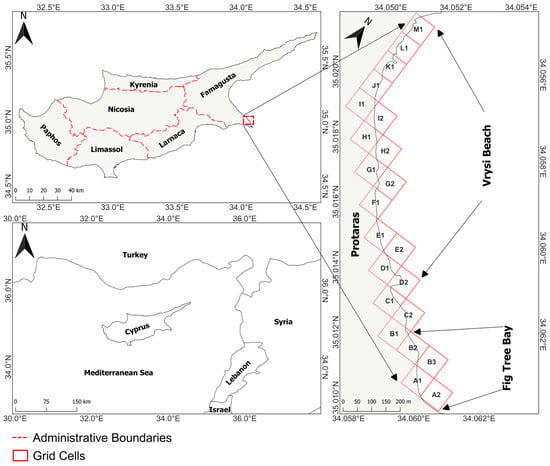
Figure 1.
The study area.
Additionally, anthropogenic modifications in these soil zones, such as land reclamation and urban expansion, can alter surface runoff, affecting sediment transport toward the beach and modifying erosion and deposition patterns. The identified soil series include Alassa (grid cells A1–C2), Vasileia (grid cells D1–F1), and Kafkalla (grid cells G1–M1), each contributing to the unique pedological profile of the region. According to the WRB classification, the soils in the study area are primarily categorised as Cambisols (grid cells A1–H2), Technosols (grid cells I1–J1), and Calcisols (grid cells K1–M1). These classifications reflect the influence of carbonate-rich materials, urbanisation impacts, and the relatively young age of some soils in the area. Beyond their environmental and geomorphological importance, these beaches play a crucial role in the local economy. The economic significance of these two beaches cannot be overlooked as they form a cornerstone of Protaras’ tourism-driven economy. Tourism has a pivotal role in the Cypriot economy, constituting approximately 21.4% in 2016 [51], 22.3% in 2018 [52], 13.5% in 2019, and 12.9% in 2023 [53] of the country’s gross domestic product (GDP). Protaras, one of Cyprus’ primary resort destinations, depends heavily on these beaches to sustain its vibrant tourism industry.
Additionally, the environmental quality of Fig Tree Bay and Vrysi Beach is central to the branding and marketing of Protaras as a Mediterranean destination of choice. Therefore, the sustainable management of these coastal assets is vital for ensuring the long-term viability of the tourism industry and the associated economic benefits. In general, the studied beaches present complex and dynamic coastal systems, which are influenced by numerous factors, as analysed in Section 3.
3. Materials and Methods
The ICVI was estimated for the two beaches mentioned earlier to assess their coastal vulnerability due to their importance to the region’s tourism-driven economy. The CVI has evolved into the ICVI to enhance traditional coastal vulnerability assessments, incorporating a weighted approach to better reflect region-specific dynamics. While the original CVI has proven to be a valuable tool, it assigns equal importance to all parameters, which can oversimplify the complexity of coastal systems [54]. To address this limitation, the CVI has evolved into a weighted CVI, tested in various studies conducted in different environmental contexts and geographical regions [55,56]. The ICVI incorporates multi-criteria decision-making techniques such as the analytic hierarchy process (AHP) [22]. The transition from the original to the weighted CVI allows the ICVI to reflect region-specific dynamics, enabling more precise identification of high-risk areas and offering a more robust framework for informed coastal management strategies [19].
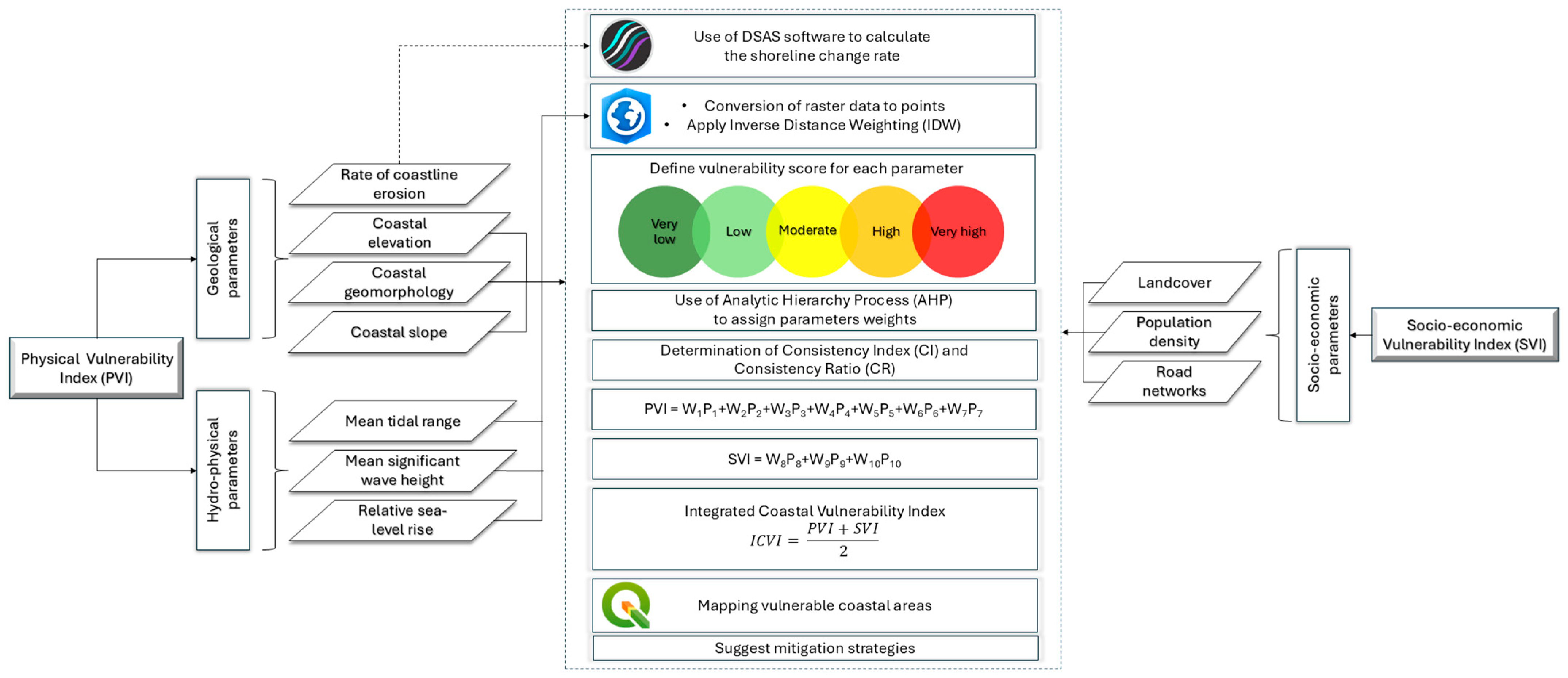
The exploited data for the calculation of the ICVI varied in resolution since they were obtained from various sources; hence, to facilitate the ICVI estimations, the authors automated the processing by creating a model in the ModelBuilder within ArcGIS Pro software (version 3.3), integrating all the required processing steps into a streamlined workflow. To fill in the gaps in marine data along the study area’s coastline, the inverse distance weighting (IDW) [57] spatial interpolation technique was applied to ensure spatial continuity by addressing low-resolution regions in the existing datasets. The raster data were then converted into points and integrated through the spatial join tool with the transects created using Digital Shoreline Analysis System (DSAS) software (version 6.0.168) [58]. To account for positional uncertainty in the shoreline change analysis, a ±5 m threshold was applied within DSAS based on the resolution of the datasets used in this study. While the dataset resolutions ranged from 0.15 m (aerial photographs) to 3 m (satellite imagery), this margin ensures consistency with the best practices in shoreline assessments and accounts for potential variations in georeferencing accuracy across different periods and data sources. In total, 22 grids with a size of 100 × 100 m were created, covering a shoreline length of 1.73 km. This is a standard procedure in coastal vulnerability assessment studies, as it facilitates the spatial analysis of coastal vulnerability by dividing the study area into manageable units for data integration and processing [19,57]. The grid cells were initially generated as a structured spatial framework, and the coastal vulnerability information for each cell was assigned using the spatial join tool in ArcGIS Pro. Specifically, the data from the transects created in DSAS, which intersected each grid cell, were transferred to the respective cell to ensure that each segment contained relevant coastal parameters for ICVI computation. This approach ensured that the grid cells retained the highest possible spatial detail while preserving a consistent analytical structure. Detailed information and the rationale for selecting each parameter are provided in the subsequent sections. Moreover, information about the data and sources for each factor used to estimate the ICVI is provided below in Table 1. The selection of the vulnerability parameters in this study followed various established coastal vulnerability assessment methodologies [30,55,59,60], ensuring consistency with prior Mediterranean coastal vulnerability assessments. Parameters were chosen based on their scientific relevance, data availability, and applicability to the study area. Figure 2 shows the methodology flowchart conducted in this study to calculate the ICVI. For more information about the processing steps for each factor, please refer to [30].

Table 1.
Data used for this study.
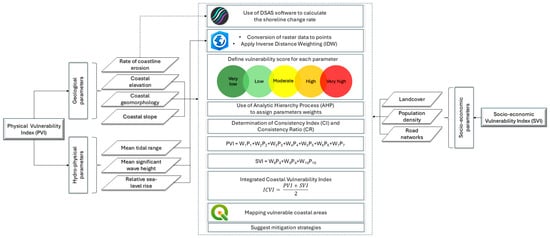
Figure 2.
Methodology flowchart of the study.
3.1. Geological and Hydro-Physical Parameters (PVI)
Geological parameters play a key role in determining the inherent vulnerability of a coastline. They include parameters describing the physical characteristics and stability of the coastal zone, which influence how it responds to natural forces such as erosion, flooding, and sea level rise [65,66]. The coastline’s geomorphology, slope, and elevation are crucial in defining resistance to physical processes, while the erosion rate quantifies the dynamic variations, highlighting areas of significant vulnerability [67]. Hydro-physical parameters represent the interaction of marine forces with the coastline. These parameters are essential for understanding the dynamic processes that drive erosion, sediment transport, and inundation [68].
Coastal slope is a critical factor in coastal vulnerability assessments as it determines how susceptible a coastline is to processes like flooding and erosion. Gentler slopes tend to dissipate wave energy more gradually, causing waves to break further offshore. This process reduces the wave energy reaching the shoreline but can lead to sediment deposition and increased inundation risk due to prolonged water contact. In contrast, steeper slopes allow waves to retain more energy as they approach the shore, resulting in higher erosive forces at the coastline [69]. Given these dynamics, gentler slopes were classified as more vulnerable, while steeper slopes were ranked as having very low vulnerability, aligning with previous Mediterranean studies [30,70,71,72]. In this study, the coastal slope was derived from a DTM provided by the DLS. The slopes were calculated as percentages utilising the slope analysis tool in ArcGIS Pro, measuring the rate of elevation change at each point across the study area. This approach ensures spatially accurate slope calculations, providing valuable insights into the vulnerability of different coastal segments.
The coastline erosion rate measures the shoreline’s dynamic changes caused by natural forces and human activities over time. It quantifies the retreat or the advance of the shoreline over time, simultaneously providing insights into the coastal stability [73]. The calculation of the erosion rates was conducted through DSAS software, evaluating eight historical shorelines in total from 1963 to 2024. The five coastline positions recorded in 1963, 1993, 2009, 2014, and 2019 were derived from historical aerial photographs captured by the DLS. The 1974, 2013, and 2024 shorelines were derived from Corona, WorldView-2, and PlanetScope satellite imagery, respectively. Each satellite provides unique resolution and historical coverage advantages, enabling a comprehensive analysis of shoreline dynamics over time. The 1974 shoreline was extracted utilising declassified satellite imagery from the Keyhole-9 (KH-9) program, also known as Project Hexagon, provided by the USGS EROS Archive [74]. The 2013 shoreline was derived from WorldView-2 satellite imagery through the ESA Third Party Mission (TPM) Programme [75], with a 0.46 m spatial resolution. The 2024 shoreline was created using PlanetScope satellite imagery with a 3 m spatial resolution, providing daily Earth imagery, making it ideal for daily monitoring of coastal changes [76]. Two key metrics were calculated using DSAS to estimate the rate of coastline erosion: the linear regression rate (LRR) and the net shoreline movement (NSM). The LRR calculates the rate of shoreline movement over time (m/year) by fitting a regression line to multiple shoreline positions, offering valuable measurements of long-term trends in erosion or accretion. On the other hand, the NSM measures the distance the shoreline has shifted between the earliest and the most recent positions, providing a cumulative assessment of change.
Coastal geomorphology in this study refers specifically to the beach and its immediate surrounding landforms, including cliffs, dunes, and rocky formations, that influence shoreline stability and vulnerability. This classification does not extend to inland terrain beyond the active coastal zone. These features are critical in determining a coastline’s resilience to natural forces, including wave action, storm surges, and rising sea levels [77]. Changes in geomorphology, driven by natural processes or human activities, can have profound implications for coastal vulnerability. For example, removing natural barriers like dunes or marshes exacerbates exposure to flooding and wave-driven erosion. Conversely, geomorphological features like ridges or cliffs reduce vulnerability by providing natural protection [78]. For this parameter, a DTM was used to create landform classes through ArcGIS Pro software, where they matched with the classes presented below in Table 2.

Table 2.
Coastal vulnerability score of used parameters.
Coastal elevation is a fundamental parameter for examining vulnerability to sea level rise and storm surges. Generally, low-lying areas are more prone to flooding and inundation, especially during extreme weather events and high tides. On the contrary, higher elevations provide natural protection against rising water levels [79]. As with the aforementioned parameters, the DTM was also used for this parameter, enabling precise elevation mapping along the study area and ensuring accurate identification of areas most at risk.
The mean tidal range (MTR) represents the vertical distance between the average high-tide and low-tide levels, affecting sediment movement shoreline stability while playing a critical role in shaping coastal dynamics and features such as beaches and estuaries [80]. MTR data were sourced from the global ecological classification of Coastal Segment Units (CSUs), a dataset that provides a standardised framework for understanding coastal processes and dynamics on a global scale [61]. CSUs are distinct coastal divisions characterised by shared ecological, geomorphological, and oceanographic properties, enabling detailed assessment of coastal variability and vulnerability. The tidal range significantly affects coastal processes, where more extensive tidal ranges contribute to dynamic environments, influencing tidal flooding, accelerating erosion rates, and increasing saltwater intrusion into freshwater systems [81]. However, there is an ongoing debate among researchers regarding how tidal ranges should be ranked in vulnerability assessments [67]. For this study, it was assumed that sensitivity decreases as the tidal range increases. This assumption is supported by the notion that extreme water levels, such as those caused by storms, often exceed the highest tidal levels, thus minimising the relative impact of the tidal range in macro-tidal environments. For example, a storm surge of two meters might not exceed the tidal elevation in areas with a tidal range of five meters, reducing its potential impact [82]. In contrast, the influence of CVI areas with low tidal ranges is considered more vulnerable. More specifically, these regions lack the natural defences provided by larger tidal ranges, making them more susceptible to coastal flooding and storm surges.
The mean significant wave height (SWH) represents the average height of the highest one-third of waves over a given period, serving as a key indicator of wave energy impacting the coastline. The Copernicus Marine Service (CMS) was used to acquire wave height data covering the period of 1993–2023. The SWH parameter plays a central role in coastal dynamics, impacting erosion rates, sediment transport, and shoreline morphology. High wave energy can accelerate erosion and reshape coastal features, particularly in areas with limited natural defences, such as low-elevation or gentle slopes [83,84].
Relative sea level rise (RSLR) is a key long-term factor influencing coastal vulnerability, representing the combined effect of global sea level rise and local vertical land movement, such as subsidence or uplift [85]. However, its impact varies by region and is often compounded by other physical and socio-economic drivers of coastal change. Additionally, this parameter is pivotal in increasing the frequency and intensity of coastal flooding, accelerating erosion, and threatening natural habitats and human infrastructure. In this study, RSLR data were obtained from the CMS. More specifically, the Global Ocean Mean Sea Level trend map from Observations Reprocessing was obtained, covering the period from 1993 to 2023. This dataset is highly accurate and reliable as it is derived from satellite altimetry measurements. These measurements provide precise, globally consistent sea level observations, offering a clear advantage over traditional tide gauge data, which are limited in spatial coverage and may be influenced by local environmental factors. Furthermore, satellite altimetry undergoes validation and reprocessing, ensuring the data’s robustness for long-term studies. RSLR is particularly important in regions with low-lying coasts and extensive human activity, as even small increases in sea level can exacerbate the risks of inundation and erosion [86].
3.2. Socio-Economic Parameters (SVI)
Socio-economic factors are essential for assessing the CVI as they capture the human dimension of coastal risk, especially in areas heavily reliant on tourism, such as Protaras.
Land cover is a socio-economic parameter that presents the extent of urbanisation, vegetation, and other land uses along the coastline. Urbanised areas like built-up zones are typically more vulnerable due to their reduced capacity to provide a buffer against natural hazards like storm surges and coastal flooding. On the other hand, vegetated areas provide essential ecosystem services, including sediment stabilisation and wave energy dissipation, helping to reduce vulnerability [87]. Land cover data were acquired from the ESA WorldCover (Version 2), which provides global land cover classifications with a spatial resolution of 10 m.
Population density directly influences the risk exposure level and the potential impact on natural hazards. Densely populated areas are more vulnerable to coastal hazards such as flooding, erosion, and storm surges due to the presence of increased people and infrastructure; hence, these areas may require more resources for disaster response and recovery, increasing their socio-economic vulnerability [88]. In regions where tourism drives the economy, such as the Mediterranean, the population density peaks seasonally due to the influx of tourists. This amplifies the stress on coastal ecosystems and infrastructure, exacerbating vulnerability [60]. Higher population densities in coastal regions often correlate with increased land-use changes, overdevelopment, and habitat loss, all of which reduce natural resilience to coastal hazards [59]. The population density dataset was sourced from the WorldPop Population Density Dataset covering the period of 2000–2020, accessed via the ArcGIS Living Atlas of the World, providing annual estimates of population density at a resolution of 1 km [64].
The road network is a vital socio-economic parameter in coastal vulnerability assessments, reflecting the accessibility, economic value, and potential disruption risk of critical infrastructure in coastal areas. Roads near the coastline have a dual role. On the one hand, they provide connectivity for tourism and commerce. On the other hand, they are also highly vulnerable to hazards such as flooding, erosion, and storm surges [89,90]. Roads closer to the beach are more susceptible to damage from coastal hazards, as they are directly exposed to wave action, saltwater intrusion, and rising sea levels. The road network was derived through the HCMGIS plugin (v. 25.1.9) in QGIS software (v. 3.22.16-Białowieża), collecting road network information by Geofabrik.
3.3. Calculation of ICVI with AHP Method
Integrating the parameters mentioned above, the ICVI was used to address the limitations of the traditional CVI, and 152 perpendicular transects were created at approximately 10-m intervals along the 1.73 km study area, with each transect extending 100 m inland. While the theoretical distance covered by 152 transects at strict 10-m intervals would be around 1.52 km, minor variations arose due to coastline curvature and methodological constraints in transect placement within DSAS. These variations do not affect the accuracy of the analysis but ensure optimal spatial representation of the study area. Incorporating a multi-criteria decision-making technique (AHP), the ICVI allows for more accurate assessments by assigning weights to parameters based on their relative importance. This approach ensures that the index reflects site-specific coastal dynamics and allows for a more precise coastal vulnerability assessment, particularly in areas with unique geomorphological and hydrodynamic conditions. More specifically, to develop the ICVI, the first step involved creating a ranking table to evaluate the relative vulnerability of each parameter. Each parameter was assigned a vulnerability ranking from 1 (very low vulnerability) to 5 (very high vulnerability). These rankings were based on a combination of quantitative and qualitative data specific to the characteristics of the study area, ensuring a tailored assessment. This study utilised ranking criteria for all the parameters based on studies conducted in areas with similar coastal and climate characteristics [55,60,83] (Table 2). This ranking table was the first step to integrate all the different parameters into a composite index, providing a standardised framework for assessing vulnerability. The AHP method was employed as the next step for the ICVI calculation, assigning weights to the parameters and reflecting their relative importance in contributing to coastal vulnerability. A numerical scale was utilised to assign values during pairwise comparisons, ranging from 1 (equal importance) to 9 (extreme importance), with intermediate values for cases where differences in importance were less pronounced (Table 3).

Table 3.
Importance scale utilised in AHP.
Pairwise comparisons were recorded in two comparison matrices: one for the physical parameters (Table 4) and one for the socio-economic parameters (Table 5), where each parameter was evaluated against every other parameter to quantify its relative importance. These matrices are the foundation for deriving the parameter weights, ensuring consistency and alignment with expert judgment and regional priorities [46]. The weighting process was guided by expert evaluation, which was informed by prior similar studies and local coastal vulnerability considerations. The pairwise comparisons used in the AHP method enabled a structured ranking of the parameters based on their relative influence on coastal vulnerability. After constructing the comparison matrices, two normalised matrices were created by dividing each cell by the sum of its respective columns separately for the two comparison matrices. The weights for each parameter were then calculated as the average of the normalised values in each row, as presented in Table 6 (physical parameters) and Table 7 (socio-economic parameters). To ensure the consistency and reliability of the comparisons, consistency ratios (CRs) were calculated, since Saaty’s method [91] defines the matrix as being consistent. Generally, if the CR is below <0.10, the matrix is consistent. In contrast, if the CR is higher than >0.10, then re-evaluation of the pairwise comparisons is needed, followed by testing the consistency again using AHP. The CR is an essential measure in AHP, indicating the degree of consistency within the pairwise comparisons, calculated utilising the formula below.
where CI (Consistency Index) is calculated as follows:
where λmax represents the principal eigenvalue of the matrix, and n is the size (order) of the comparison matrix.

Table 4.
Pairwise comparison matrix of geological and hydro-physical parameters.

Table 5.
Pairwise comparison matrix of socio-economic parameters.

Table 6.
Normalised matrix of geological and hydro-physical parameters.

Table 7.
Normalised matrix of socio-economic parameters.
RI (Random Index) is a predefined value based on the matrix size derived from statistical simulations of random pairwise comparison matrices [92], as presented in Table 8.

Table 8.
Values of RI, with n order of the matrix.
Based on the calculations, the CRs for the physical and socio-economic matrices are 4.4% and 0.4%, respectively, as shown in Table 9. Since the CR values are below the acceptable threshold of 10%, the comparisons are considered consistent, and the derived weights are reliable; hence, no further re-evaluation is needed. The final weights of the parameters derived from the AHP process are summarised below in Table 10, reflecting their relative influence on coastal vulnerability.

Table 9.
Consistency ratio estimation variables.

Table 10.
Final weights for parameters.
Continuing further into the methodology, to calculate the ICVI, the derived weights utilising AHP were exploited for the computation of the Physical Vulnerability Index (PVI) (Equation (3)) and the Socio-economic Vulnerability Index (SVI) (Equation (4)):
where Wi is the weight value for each parameter derived from AHP, and Pi is used for each parameter in this study. Finally, both the PVI and SVI were combined to calculate the ICVI (Equation (5)), expressed as follows:
Using this formula, it was ensured that physical and socio-economic factors were considered equally to assess coastal vulnerability. By incorporating both types of factors, this approach provides a comprehensive evaluation of vulnerability that considers the environmental and geological conditions and socio-economic dynamics that influence coastal areas’ resilience and adaptive capacity.
4. Results
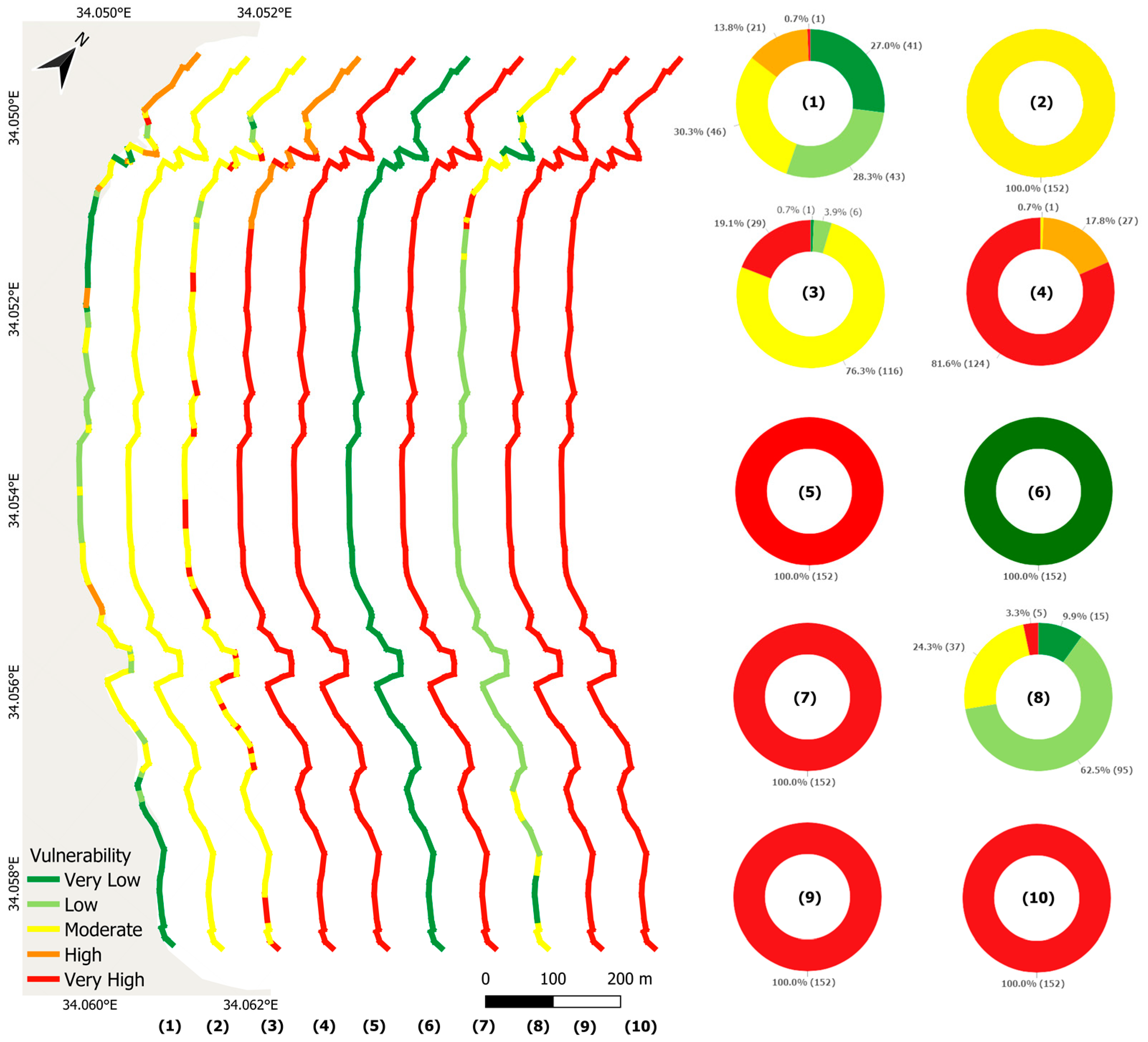
As mentioned earlier, this study identified and utilised ten parameters to assess the coastal vulnerability in Protaras, as illustrated in Figure 3.

Figure 3.
Coastal vulnerability of the physical (1–7) and socio-economic (8–10) variables. (1) Coastal slope, (2) rate of coastline erosion, (3) coastal geomorphology, (4) coastal elevation, (5) mean tidal range, (6) mean significant wave height, (7) relative sea level rise, (8) land cover, (9) population density, and (10) road network. The pie charts show the proportion of each classification of coastal vulnerability, and the parentheses represent the number of the created perpendicular transects.
4.1. Physical Parameters
The analysis of the coastal slope revealed very low vulnerability for 0.46 km (27%) of the coastline, corresponding to slopes steeper than 12%, which provide significant resistance to wave energy. A further 28.3% (0.49 km) of the coastline was classified as having low vulnerability, with slopes ranging from 8 to 12%, and 30.3% (0.52 km) was categorised as moderately vulnerable, with slopes between 4 and 8%. The remaining sections demonstrated higher risk, with 14.5% (0.24 km) classified as highly vulnerable (2–4% slopes) and 0.7% (0.12 km) as very highly vulnerable (slopes below 2%) (Figure 3(1)).
In terms of the rate of coastline erosion (LRR), the results showed that the entire coastline was ranked as moderately vulnerable (Figure 3(2)). This corresponds to erosion rates ranging from −1 to +1.0 m/year from 1963 to 2024. Although categorised as moderate, these rates reflect the cumulative impact of long-term shoreline changes, which can result in significant land loss and heightened exposure to coastal hazards over decades.
Regarding the coastal geomorphology, most of the coastline was ranked as moderately vulnerable, primarily comprising features like low cliffs and alluvial plains, accounting for 76.3% (1.32 km). Another 19.1% (0.33 km) was ranked as very highly vulnerable. The remaining proportion of the coastline was categorised as having low vulnerability, covering 3.9% (0.06 km), and very low vulnerability, representing only 0.7% of the total length (Figure 3(3)).
Coastal elevation analysis revealed that 81.6% (1.41 km) of the coastline was classified as very highly vulnerable, with elevations ranging from 0 to 2 m, indicating significant exposure to inundation risks. An additional 17.8% (0.3 km) was ranked as highly vulnerable (2–5 m elevations), while 0.7% exhibited moderate vulnerability (5–10 m elevations). No sections of the coastline were categorised as having low or very low vulnerability, underscoring the overall susceptibility of the study area to elevation-related risks (Figure 3(4)).
The mean tidal range parameter analysis indicated that the entire coastline was categorised as very highly vulnerable, reflecting the area’s micro-tidal characteristics. No sections of the coastline fell into the other vulnerability categories, emphasising the uniform vulnerability profile for this parameter (Figure 3(5)).
Analysing the mean significant wave height parameter showed that the entire extent of the study area was classified as having very low vulnerability. According to the ranking table, this corresponds to regions with a mean significant wave height of less than 0.55 m, typical for sheltered coastal environments or areas with limited wave exposure. No other vulnerability categories indicated the area’s minimal exposure to high wave energy (Figure 3(6)).
The relative sea level rise parameter indicated a consistent high-vulnerability classification across the study area, corresponding to sea level rise rates between 3.0 and 3.4 mm/year (Figure 3(7)). This trend reflects climate change’s global and regional impacts, where rising sea levels amplify coastal flooding, erosion, and salinisation risks.
4.2. Socio-Economic Parameters
The land cover analysis revealed that 3.3% (0.057 km) of the coastline was highly vulnerable, highlighting areas dominated by built-up land uses lacking natural defences. Moderate vulnerability was observed along 24.3% of the coastline (0.42 km), primarily in regions with grassland coverage. The majority of the coastline (62.5%—1.08 km) exhibited low vulnerability, characterised by shrubland and bare soil. Lastly, 9.9% (0.17 km) of the coastline was classified as having very low vulnerability, corresponding to areas with tree coverage providing natural protection against coastal hazards (Figure 3(8)).
The population density analysis showed a high concentration of people, with densities of 634 and 655 people/km2 in the two 1 × 1 km grid cells. Both values exceed the 600 people/km2 threshold defined in the ranking table for very high vulnerability. These high population densities highlight the intense human activity in the area, which is further amplified by its status as a central tourism hub, placing significant socio-economic and environmental pressures on the area, particularly during peak touristic seasons, increasing the overall vulnerability (Figure 3(9)).
The road network parameter, specifically the presence of roads in terms of distance from the shoreline, was classified as very highly vulnerable according to Table 2, as roads are located at a distance of less than 0.5 km. This proximity exposes infrastructure to heightened risks from coastal hazards. Moreover, the presence of roads near the beach intensifies human activity and pressures on the coastal environment, further amplifying the area’s overall vulnerability (Figure 3(10)).
4.3. Integrated Coastal Vulnerability Index (ICVI)
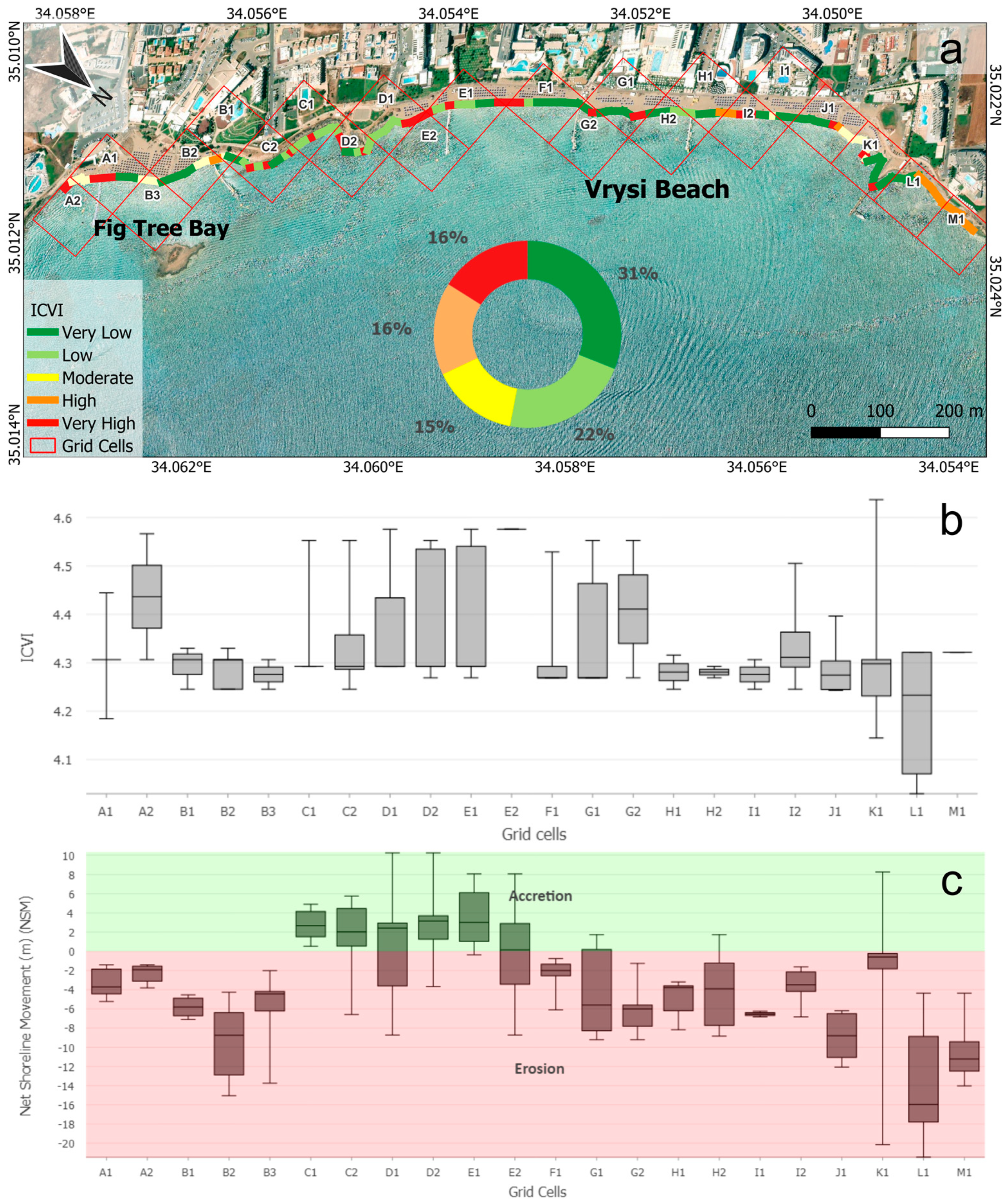
The estimated ICVI results for Protaras revealed spatial variations in vulnerability scores along the 1.73 km of the shoreline. Specifically, it was divided into five vulnerability categories based on quartile ranges, with the ICVI values varying between 4.029 and 4.637. Very high vulnerability accounted for 16% (0.27 km), while another 16% (0.27%) was classified as highly vulnerable. Moderate vulnerability covered 15% (0.26 km) of the shoreline. Low vulnerability was observed in 23% (0.39 km), and the largest proportion, 31% (0.53 km), was categorised as having very low vulnerability (Figure 4a). According to the data, the highest ICVI values were located in K1 (4.637), D1–2 (4.576–4.555), E1–2 (4.576), C1–2 (4.552), and G1–2 (4.552). Based on the box plot in Figure 4b, grid cell E1 demonstrated the highest ICVI value, followed closely by grid cells A2 and G2, indicating very high vulnerability due to a combination of physical and socio-economic factors. On the other hand, the lowest average values were located in grid cell L1, indicating that it experiences the least overall vulnerability among the assessed grid cells. Delving further into the analysis, according to the box plots for the NSM (Figure 4c), grid cells L1 and K1 exhibited the highest levels of erosion, with mean NSM values of −16.65 m and −10.89 m, respectively. These extreme negative values indicate a significant landward retreat of the shoreline. Moreover, grid cell M1 with a mean NSM value of −10.78 highlights the vulnerability in the northeastern part of the study area. On the other hand, grid cells C1–C2 and D1–D2 exhibited positive NSM values, with averages ranging from +2 m to +6 m, indicating accretion. In addition, grid cells E1 and E2 demonstrated significant accretion, mainly in grid cell E1, with a mean NSM of +6.95 m. It is evident that an erosional pattern emerges, where erosion dominates the southern and northern ends of the coastline, while accretion occurs more centrally.
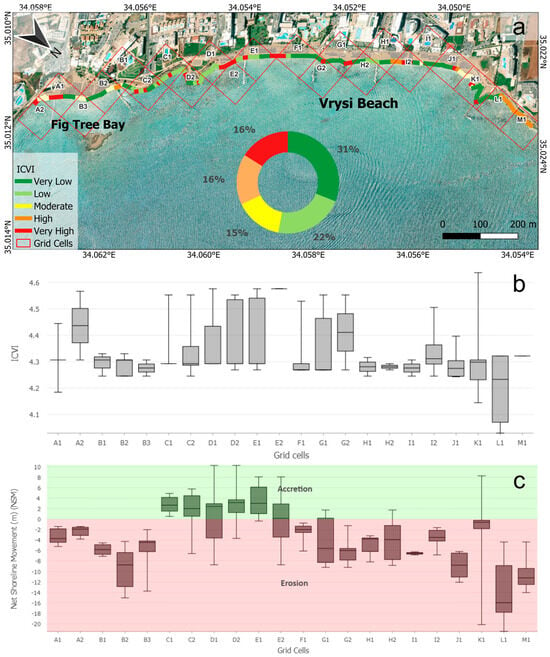
Figure 4.
(a) The ICVI map of the study area. (b) Box plot chart of ICVI values per grid cell. (c) Box plot chart of NSM values per grid cell (the horizontal black lines inside the box plots represent the median value).
5. Discussion
The ICVI was calculated by estimating the PVI and SVI through ten key parameters influencing coastal vulnerability. The analysis of the results provides valuable insights into the spatial variation of coastal vulnerability along Fig Tree Bay and Vrysi Beach (both located in Protaras in Cyprus), revealing complexity in the interaction between physical and socio-economic factors. The classification of the ICVI values highlighted critical zones where interventions are needed. Specifically, 16% of the coastline was classified as having very high vulnerability, and another 16% exhibited high vulnerability, predominantly in areas with geomorphological instability, low elevation, and human activity. In contrast, 31% of the coastline exhibited very low vulnerability, attributed to natural geomorphological features such as rocky formations. The findings of this study align with studies conducted in similar Mediterranean coastal environments. For instance, studies in areas like Limassol, Cyprus [30]; Calabria and Apulian, Italy [55,93]; Peloponnese, Greece [59]; Tetouan, Morocco [88]; and Rachgoun, Algeria [60], have highlighted the significant impact of a low elevation and high population density on coastal vulnerability. The use of the CVI and ICVI in these studies has consistently shown that areas with intense human activity and development are more prone to erosion and flooding. This study further validates these findings by demonstrating similar patterns in Protaras in Cyprus. The socio-economic parameters played a decisive role in increasing the vulnerability scores in the study area. The high tourism footprint in Protaras, especially around Fig Tree Bay, intensifies the pressure on coastal systems. Hotels, parking facilities, and infrastructure close to the beach have altered the natural drainage patterns, leading to preferential surface flow pathways (Figure A1). As a result, enhanced erosion phenomena occur during relatively high precipitation events, often leading to beach trenches covered by sand (Figure A2 and Figure A3). Moreover, the dense road network within 0.5 km of the shoreline further exacerbates the vulnerability by restricting natural processes and increasing sediment transport disruptions. While the ICVI methodology delivers a comprehensive coastal vulnerability assessment, certain limitations should be noted. The weighting parameters utilising AHP, while consistent and widely used, involve a degree of subjectivity that could influence the results. The assignment of weights is based on expert judgment, which, although informed, can vary between experts and contexts. This subjectivity may introduce biases affecting final vulnerability scores [94].
Human interventions, particularly in Fig Tree Bay, pose additional challenges to accurately assessing coastal vulnerability. Seasonal activities, such as using heavy machines (e.g., beach cleaners) to flatten beaches, significantly alter the natural coastal dynamics (Figure A4). Although these types of machines utilise a screening system to sift through the sand, which helps maintain a clean and aesthetically pleasing beach environment, they can negatively impact the beach ecosystem. Removing sand dunes and organic material is one of the disturbances that can have an impact, which is essential to maintaining the beach’s stability. Furthermore, beach cleaners can inadvertently remove tiny organisms living in the sand, such as crabs, insects, and other invertebrates, which play a crucial role in the beach ecosystem [95,96].
Furthermore, the operation of heavy machinery on the beach can lead to sand compaction, which can affect the natural drainage and aeration of the sand, potentially impacting plant growth and the habitat of burrowing animals. These beach cleaning activities are generally carried out mainly during the off-season (January–March) when most hotels and coastal infrastructures are closed, aiming to repair damage or alterations to the beach (Figure A4); however, this activity is also occasionally performed during the summer months. Small streams of previously natural drainage outlets have now been replaced by parking lots and concrete infrastructure, leading to a redistribution of artificial sediments. A notable example is the reappearance of stormwater drainage infrastructures and pipes exposed on the beach surface during the rainy season (Figure A5, Figure A6 and Figure A7), frequently covered with sand. Moreover, sand dunes, which act as natural barriers and reduce the erosive effect on the coastline [97], are frequently levelled annually to create a flat beach profile. However, this repeated intervention prevents the sand dunes from fully forming, thus erasing these essential natural features and increasing the beach’s susceptibility to erosion and the loss of resilience to extreme weather events.
Alongside the aforementioned negative factors, additional interventions, such as rock removal [98] and the construction of a jetty in 2012 [99], have further contributed to significant alterations in the coastal dynamics of the study area. Although the jetty construction and rock removal have altered the coastal dynamics, these interventions were not included as a standalone technical parameter in the ICVI assessment. Instead, their impacts are reflected in other measured parameters, such as shoreline erosion rates and slope variations, which indirectly capture the effects of these structures on coastal vulnerability. This structure, built without proper environmental assessments, has triggered noticeable erosion in adjacent areas, as confirmed by the results of this study. The erosion patterns align with the ICVI and NSM findings, defining the area as a high-risk zone and highlighting that poorly planned interventions amplify risks rather than mitigate them. While the ICVI is a valuable tool for identifying areas of high vulnerability, it is crucial to consider the dynamic nature of coastal systems when planning interventions. “Hard” engineering solutions, such as seawalls and groynes, can disrupt natural sediment transport processes, increasing erosion in downdrift areas. Moreover, Randazzo et al. (2020) [100] highlighted the importance of soft engineering and nature-based solutions that enhance coastal resilience while maintaining sediment continuity. Recent studies have further demonstrated nature-based solutions’ effectiveness in reducing coastal vulnerability, emphasising their role in coastal engineering and adaptation strategies [27,28]. Implementing measures like dune and seagrass meadow restoration, beach nourishment, and removal of obsolete structures can mitigate erosion without adverse downdrift effects. It is also essential to consider the potential impact of interventions on bordering cells within the ICVI framework. Coastal adaptation measures, particularly those involving sediment management (e.g., nourishment, breakwaters), can influence adjacent shoreline segments by altering sediment transport and hydrodynamic conditions. Additionally, developing a local or regional plan against coastal erosion, as proposed by Randazzo, reinforces the need for integrated management strategies that involve continuous monitoring and stakeholder engagement to adapt to evolving coastal dynamics. It is important to note that the ICVI assessment provides site-specific insights for targeted adaptation. Expanding to a regional scale would require additional datasets, but this methodology can be adapted for broader applications in future research.
6. Conclusions
This study highlights critical coastal vulnerabilities in Protaras, emphasising the urgent need for sustainable management strategies in tourism-driven coastal zones. Policymakers should prioritise implementing sustainable tourist practices, including stricter regulations on coastal infrastructure expansions, beach modifications, and illegal constructions. Strategies such as dune preservation, minimising concentrated surface runoff flow during extreme weather events, managed retreat, and controlled development in high-vulnerability zones could mitigate the impacts of both natural and anthropogenic hazards. Incorporating ICVI-based assessments into local development plans can provide a robust framework for balancing economic growth with environmental conservation. Additionally, adopting more dense and frequent beach monitoring is better to understand the local coastal dynamics and erosion patterns. Enhancing stormwater drainage systems and promoting nature-based solutions, such as sand dune restoration, may improve the area’s resilience.
Additionally, UAV-based remote sensing has proven to be a valuable tool for coastal monitoring. Integrating UAV data could refine ICVI assessments by providing detailed observations of coastal slope variations and sediment transport, enhancing future coastal management strategies. Moreover, proactive measures to mitigate the impacts of unregulated activities, such as jetty construction and sand levelling, are crucial for preserving natural coastal barriers. This study has demonstrated how a regionally adapted ICVI framework can inform targeted interventions in Mediterranean coastal areas, emphasising the need for data-driven coastal management decisions. The AHP weighting process was crucial in refining the ICVI assessment, ensuring that the vulnerability rankings accurately reflected the relative importance of the physical and socio-economic parameters within the study area. The high weight assigned to factors such as RSLR and population density underscores the combined impact of long-term environmental changes and tourism-driven pressures in Protaras. These insights provide a more nuanced understanding of risk distribution, offering a structured basis for prioritising coastal adaptation measures. Beyond its application to Protaras, this study contributes a regionally adapted ICVI framework tailored to Mediterranean coastal environments, marking Cyprus’ first ICVI-based vulnerability assessment. Moreover, expanding the ICVI framework by incorporating additional parameters such as groundwater dynamics, sediment supply, bathymetry, storm surge potential, precipitation trends, and wind speed and direction could provide a more holistic understanding of the coastal vulnerability in Protaras.
Future assessments could integrate more localised geomorphological parameters, including wave exposure, beach slope variations, shoreline exposure, and sediment granulometry, to further refine the spatial differentiation of vulnerability across smaller coastal regions. While wave exposure can be assessed using remote sensing and numerical modelling approaches, other factors such as sediment granulometry (grain size, composition, colour) and beach slope variation typically require on-site field sampling and elevation surveys. Given that this study employed a GIS and remote sensing-based methodology, direct field data collection was not feasible within its scope. These measures will preserve coastal ecosystems while supporting the tourism-driven economy of Protaras and other coastal regions facing similar challenges.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, C.T. and K.N.; methodology, C.T.; software, C.T.; validation, C.T. and K.N.; formal analysis, C.T. and K.N.; investigation, C.T., M.P., M.D. and E.K.; resources, K.N.; data curation, C.T.; writing—original draft preparation, C.T., M.P. and M.D.; writing—review and editing, C.T., K.N., M.E. and C.K.; visualisation, C.T.; supervision, D.H.; project administration, M.E.; funding acquisition, D.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded through the EXCELSIOR Teaming project (Grant Agreement No. 857510, www.excelsior2020.eu, accessed on 22 January 2025), which has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme, and from the Government of the Republic of Cyprus through the Directorate General for the European Programmes, Coordination and Development, as well as the Cyprus University of Technology.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the ‘EXCELSIOR’: ERATOSTHENES: Excellence Research Centre for Earth Surveillance and Space-Based Monitoring of the Environment H2020 Widespread Teaming project (www.excelsior2020.eu). The ‘EXCELSIOR’ project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under Grant Agreement No 857510, from the Government of the Republic of Cyprus through the Directorate General for the European Programmes, Coordination and Development and the Cyprus University of Technology. Also, the authors acknowledge the “coaSTal Erosion in cyPrus from Space” (STEPS) project, which is funded under the 8th European Space Agency (ESA) Plan for European Cooperating States (PECS) with Contract No. 4000142840/23/NL/MH/nh.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A

Figure A1.
Hotels, parking facilities, and infrastructure near Fig Tree Bay, Protaras, Cyprus. Image by dronepicr, licensed under CC BY 2.0. accessed on 4 February 2025.
Figure A1.
Hotels, parking facilities, and infrastructure near Fig Tree Bay, Protaras, Cyprus. Image by dronepicr, licensed under CC BY 2.0. accessed on 4 February 2025.


Figure A2.
Formation of trenches after heavy rainfall events in grid cell J1. The image was captured on 8 December 2025 at 08:06 a.m.
Figure A2.
Formation of trenches after heavy rainfall events in grid cell J1. The image was captured on 8 December 2025 at 08:06 a.m.


Figure A3.
Evidence of surface runoff pathways caused by heavy precipitation leading to the shoreline in grid cell J1. The image was captured on 25 January 2025 at 09:20 a.m.
Figure A3.
Evidence of surface runoff pathways caused by heavy precipitation leading to the shoreline in grid cell J1. The image was captured on 25 January 2025 at 09:20 a.m.


Figure A4.
A beach cleaner machine operated between grid cells A1 and B2 at Fig Tree Bay, Protaras. The image was captured on 8 January 2025 at 08:27 a.m.
Figure A4.
A beach cleaner machine operated between grid cells A1 and B2 at Fig Tree Bay, Protaras. The image was captured on 8 January 2025 at 08:27 a.m.
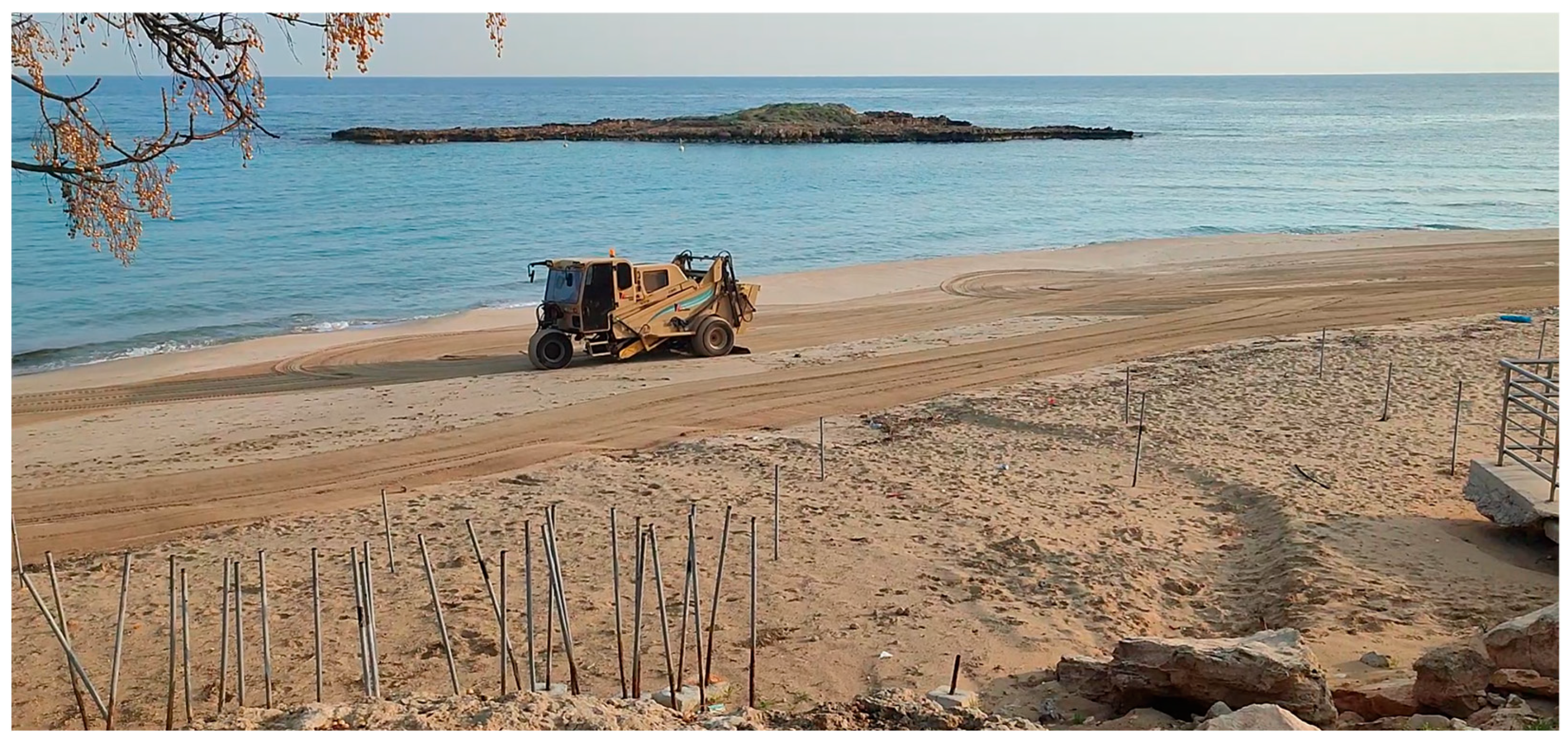


Figure A5.
Exposed stormwater drainage infrastructure in grid cell G1. The image was captured on 25 January 2025 at 09:26 a.m.
Figure A5.
Exposed stormwater drainage infrastructure in grid cell G1. The image was captured on 25 January 2025 at 09:26 a.m.


Figure A6.
Exposed stormwater drainage infrastructure in grid cell I2. The image was captured on 25 January 2025 at 09:23 a.m.
Figure A6.
Exposed stormwater drainage infrastructure in grid cell I2. The image was captured on 25 January 2025 at 09:23 a.m.


Figure A7.
The appearance of a storm drain outlet at the beach surface, as a result of concentrated flow, during the rainy season in grid cell G1 (towards the side of grid cell H2). The image was captured on 8 December 2025 at 03:20 p.m.
Figure A7.
The appearance of a storm drain outlet at the beach surface, as a result of concentrated flow, during the rainy season in grid cell G1 (towards the side of grid cell H2). The image was captured on 8 December 2025 at 03:20 p.m.

References
- Winarso, G.; Judijanto; Budhiman, S. The Potential Application Remote Sensing Data for Coastal Study. 2001. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Gathot-Winarso/publication/237787781_THE_POTENTIAL_APPLICATION_REMOTE_SENSING_DATA_FOR_COASTAL_STUDY/links/5562d55d08ae8c0cab3339c6/THE-POTENTIAL-APPLICATION-REMOTE-SENSING-DATA-FOR-COASTAL-STUDY.pdf (accessed on 3 February 2025).
- Šimac, Z.; Lončar, N.; Faivre, S. Overview of Coastal Vulnerability Indices with Reference to Physical Characteristics of the Croatian Coast of Istria. Hydrology 2023, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.-L.; Li, X.-Y. Coastline Change of the Yellow River Estuary and Its Response to the Sediment and Runoff (1976–2005). Geomorphology 2011, 127, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossen, M.F.; Sultana, N. Shoreline Change Detection Using DSAS Technique: Case of Saint Martin Island, Bangladesh. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2023, 30, 100943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethuraman, S.; Alshahrani, H.M.; Tamizhselvi, A.; Sujaatha, A. Assessment of Coastal Vulnerability Using AHP and Machine Learning Techniques. J. South Am. Earth Sci. 2024, 147, 105107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boak, E.H.; Turner, I.L. Shoreline Definition and Detection: A Review. J. Coast. Res. 2005, 214, 688–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arun Kumar, A.; Kunte, P.D. Coastal Vulnerability Assessment for Chennai, East Coast of India Using Geospatial Techniques. Nat. Hazards 2012, 64, 853–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canul Turriza, R.A.; Fernández-Díaz, V.Z.; Cárdenas Rojas, D.M.; Tzuc, Ó.M. Coastal Vulnerability Assessment with a Hierarchical Coastal Segments Approach. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2024, 249, 106989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahendra, R.S.; Mohanty, P.C.; Bisoyi, H.; Kumar, T.S.; Nayak, S. Assessment and Management of Coastal Multi-Hazard Vulnerability along the Cuddalore–Villupuram, East Coast of India Using Geospatial Techniques. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2011, 54, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.-T.; Cai, F.; Chen, S.-L.; Gu, D.-Q.; Feng, A.-P.; Cao, C.; Qi, H.-S.; Lei, G. Coastal Vulnerability to Erosion Using a Multi-Criteria Index: A Case Study of the Xiamen Coast. Sustainability 2018, 11, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balica, S.F.; Popescu, I.; Beevers, L.; Wright, N.G. Parametric and Physically Based Modelling Techniques for Flood Risk and Vulnerability Assessment: A Comparison. Environ. Model. Softw. 2013, 41, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velegrakis, A.F.; Chatzistratis, D.; Chalazas, T.; Armaroli, C.; Schiavon, E.; Alves, B.; Grigoriadis, D.; Hasiotis, T.; Ieronymidi, E. Earth Observation Technologies, Policies and Legislation for the Coastal Flood Risk Assessment and Management: A European Perspective. Anthr. Coasts 2024, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, D.; Uddin, M.M.; Mahbub-E-Kibria, A.S.M.; Kumar Das, M.; Hasan, M. Coastal Vulnerability Assessment to Multi Hazards in the Exposed Coast of Southeastern Coastal Region of Bangladesh. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2024, 73, 103484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantamaneni, K.; Xing, L.; Gupta, V.; Campos, L.C. Vulnerability Assessment of English and Welsh Coastal Areas. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 27467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gornitz, V.; White, T.W.; Cushman, R.M. Vulnerability of the US to Future Sea Level Rise; Oak Ridge National Lab.: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Thieler, E.R.; Hammar-Klose, E.S. National Assessment of Coastal Vulnerability to Sea-Level Rise: Preliminary Results for the U.S. Atlantic Coast; United States Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Pendleton, E.A.; Thieler, E.R.; Williams, S.J.; Beavers, R.L. Coastal Vulnerability Assessment of Padre Island National Seashore (PAIS) to Sea-Level Rise; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Gerrity, B.; Phillips, M. Comparative Analysis of Coastal Vulnerability Indexes in Different Geographic Settings. J. Coast. Res. 2025, 113, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Ramírez, C.J.; Chávez, V.; Silva, R.; Muñoz-Perez, J.J.; Rivera-Arriaga, E. Coastal Management: A Review of Key Elements for Vulnerability Assessment. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukvic, A.; Rohat, G.; Apotsos, A.; de Sherbinin, A. A Systematic Review of Coastal Vulnerability Mapping. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roukounis, C.N.; Tsihrintzis, V.A. Indices of Coastal Vulnerability to Climate Change: A Review. Environ. Process. 2022, 9, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arda, T.; Bayrak, O.C.; Uzar, M. Analyzing Coastal Vulnerability Using Analytic Hierarchy Process and Best–Worst Method: A Case Study of the Marmara Gulf Region. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2025, 50, 1851–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapapría, V.E.; Peris, J.S.; González-Escrivá, J.A. Coastal Monitoring Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) for the Management of the Spanish Mediterranean Coast: The Case of Almenara-Sagunto. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jessin, J.; Heinzlef, C.; Long, N.; Serre, D. A Systematic Review of UAVs for Island Coastal Environment and Risk Monitoring: Towards a Resilience Assessment. Drones 2023, 7, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paola, G.; Minervino Amodio, A.; Dilauro, G.; Rodriguez, G.; Rosskopf, C.M. Shoreline Evolution and Erosion Vulnerability Assessment along the Central Adriatic Coast with the Contribution of UAV Beach Monitoring. Geosciences 2022, 12, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minervino Amodio, A.; Di Paola, G.; Rosskopf, C.M. Monitoring Coastal Vulnerability by Using DEMs Based on UAV Spatial Data. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2022, 11, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, M.; Nasca, S.; Alkharoubi, A.I.; Cavallaro, L.; Foti, E.; Musumeci, R.E. Efficacy of Nature-Based Solutions for Coastal Protection under a Changing Climate: A Modelling Approach. Coast. Eng. 2025, 198, 104700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unguendoli, S.; Biolchi, L.G.; Aguzzi, M.; Pillai, U.P.A.; Alessandri, J.; Valentini, A. A Modeling Application of Integrated Nature Based Solutions (NBS) for Coastal Erosion and Flooding Mitigation in the Emilia-Romagna Coastline (Northeast Italy). Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 867, 161357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasiotis, T.; Andreadis, O.; Chatzipavlis, A.; Mettas, C.; Evagorou, E.; Kountouri, J.; Hadjimitsis, D.; Christofi, D.; Loizidou, M.; Chrysostomou, G. A Holistic High-Resolution Monitoring Approach in Studying Coastal Erosion of a Highly Touristic Beach, Coral Bay, Cyprus. In Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Remote Sensing and Geoinformation of the Environment (RSCy2023), SPIE, Ayia Napa, Cyprus, 3–5 April 2023; Volume 12786, pp. 376–385. [Google Scholar]
- Theocharidis, C.; Doukanari, M.; Kalogirou, E.; Christofi, D.; Mettas, C.; Kontoes, C.; Hadjimitsis, D.; Argyriou, A.V.; Eliades, M. Coastal Vulnerability Index (CVI) Assessment: Evaluating Risks Associated with Human-Made Activities along the Limassol Coastline, Cyprus. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengoufa, S.; Niculescu, S.; Mihoubi, M.K.; Belkessa, R.; Rami, A.; Rabehi, W.; Abbad, K. Machine Learning and Shoreline Monitoring Using Optical Satellite Images: Case Study of the Mostaganem Shoreline, Algeria. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2021, 15, 026509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, L.H.; Le, T.G.; Tran, X.B.; Tran, Q.V.; Le, V.P.; To, T.P. Monitoring of Coastline Change Using Sentinel-2 MSI Data. A Case Study in Thanh Hoa Province, Vietnam. Bull. Geogr. Phys. Geogr. Ser. 2024, 26, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şenol, H.İ.; Kaya, Y.; Yiğit, A.Y.; Yakar, M. Extraction and Geospatial Analysis of the Hersek Lagoon Shoreline with Sentinel-2 Satellite Data. Surv. Rev. 2024, 56, 367–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazeer, M.; Waqas, M.; Shahzad, M.I.; Zia, I.; Wu, W. Coastline Vulnerability Assessment through Landsat and Cubesats in a Coastal Mega City. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassidy, G.; Wiseman, M.; Lange, K.; Eilers, C.; Bradley, A. Seasonal Coastal Erosion Rates Calculated from PlanetScope Imagery in Arctic Alaska. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collin, A.; James, D.; Feunteun, E. Towards Better Coastal Mapping Using Fusion Of High Temporal Sentinel-2 And Planetscope-2 Imageries: 12 Bands At 3 M Through Neural Network Modelling. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2022, XLIII-B3-2022, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domazetović, F.; Šiljeg, A.; Marić, I.; Faričić, J.; Vassilakis, E.; Panđa, L. Automated Coastline Extraction Using the Very High Resolution WorldView (WV) Satellite Imagery and Developed Coastline Extraction Tool (CET). Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, H.M.; Chen, Q.; Fletcher, C.H.; Barbee, M.M. Assessing Vulnerability Due to Sea-Level Rise in Maui, Hawai‘i Using LiDAR Remote Sensing and GIS. Clim. Change 2013, 116, 547–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Ruan, C.; Guo, J.; Li, J.; Lian, X.; Yin, Z.; Fu, D.; Zhong, S. Storm Surge Hazard Assessment of the Levee of a Rapidly Developing City-Based on LiDAR and Numerical Models. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, H.M.; Fletcher, C.H.; Chen, Q.; Barbee, M.M. Sea-Level Rise Vulnerability Mapping for Adaptation Decisions Using LiDAR DEMs. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2013, 37, 745–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boumpoulis, V.; Depountis, N.; Dimas, A.; Papatheodorou, G. Presentation and Analysis of the Geotechnical Coastal Vulnerability Index and Validation of Its Application to Coastal Erosion Problems. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzouk, M.; Azab, S. Modeling Climate Change Adaptation for Sustainable Coastal Zones Using GIS and AHP. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L. The Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP). J. Oper. Res. Soc. 1980, 41, 1073–1076. [Google Scholar]
- Araujo, J.C.; Dias, F.F. Multicriterial Method of AHP Analysis for the Identification of Coastal Vulnerability Regarding the Rise of Sea Level: Case Study in Ilha Grande Bay, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Nat. Hazards 2021, 107, 53–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnasri, H.; Nunes, A.; Sahnoun, H.; Abdelkarim, B.; Mahmoudi, S. Assessment of Soil Erosion in Southern Tunisia Using AHP-GIS Modeling. Euro-Mediterr. J. Environ. Integr. 2024, 9, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Cozannet, G.; Garcin, M.; Bulteau, T.; Mirgon, C.; Yates, M.L.; Méndez, M.; Baills, A.; Idier, D.; Oliveros, C. An AHP-Derived Method for Mapping the Physical Vulnerability of Coastal Areas at Regional Scales. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 13, 1209–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, M.L.; Silva, R.; Pérez-Maqueo, O.; Chávez, V.; Mendoza-González, G.; Maximiliano-Cordova, C. The Dilemma of Coastal Management: Exploitation or Conservation? Camb. Prism. Coast. Futur. 2024, 2, e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andolina, C.; Signa, G.; Tomasello, A.; Mazzola, A.; Vizzini, S. Environmental Effects of Tourism and Its Seasonality on Mediterranean Islands: The Contribution of the Interreg MED BLUEISLANDS Project to Build up an Approach towards Sustainable Tourism. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 8601–8612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geological Survey Department. Available online: https://www.moa.gov.cy/moa/gsd/gsd.nsf/dmlIndex_en/dmlIndex_en?opendocument (accessed on 7 January 2025).
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Available online: https://www.fao.org/home/en (accessed on 7 January 2025).
- Antonaras, A. The Cyprus Tourism Sector and the Sustainability Agenda 2030. Cyprus Rev. 2018, 30, 123–140. [Google Scholar]
- Georgiou, A. The Cyprus Tourism Sector and Its Investment Environment. Econ. Sci. 2018, 7, 202–207. [Google Scholar]
- Statista Research Department. Travel and Tourism: Share of GDP in the EU, by Country. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1228395/travel-and-tourism-share-of-gdp-in-the-eu-by-country/ (accessed on 29 January 2025).
- Hamid, A.I.A.; Din, A.H.M.; Yusof, N.; Abdullah, N.M.; Omar, A.H.; Abdul Khanan, M.F. Coastal Vulnerability Index Development: A Review. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, XLII-4/W16, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Serio, F.; Armenio, E.; Mossa, M.; Petrillo, A.F. How to Define Priorities in Coastal Vulnerability Assessment. Geosciences 2018, 8, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, M.R.I.; Shahfahad; Ahmad, I.A.; Tayyab, M.; Asgher, M.S.; Rahman, A. Coastal Vulnerability Mapping by Integrating Geospatial Techniques and Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP) along the Vishakhapatnam Coastal Tract, Andhra Pradesh, India. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2021, 49, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.Y.; Wong, D.W. An Adaptive Inverse-Distance Weighting Spatial Interpolation Technique. Comput. Geosci. 2008, 34, 1044–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himmelstoss, E.; Henderson, R.E.; Farris, A.; Kratzmann, M.; Bartlett, M.K.; Ergul, A.; McAndrews, J.; Cibaj, R.; Zichichi, J.; Thieler, R. Digital Shoreline Analysis System (Version 6); United States Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Tragaki, A.; Gallousi, C.; Karymbalis, E. Coastal Hazard Vulnerability Assessment Based on Geomorphic, Oceanographic and Demographic Parameters: The Case of the Peloponnese (Southern Greece). Land 2018, 7, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahia Meddah, R.; Ghodbani, T.; Senouci, R.; Rabehi, W.; Duarte, L.; Teodoro, A.C. Estimation of the Coastal Vulnerability Index Using Multi-Criteria Decision Making: The Coastal Social–Ecological System of Rachgoun, Western Algeria. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayre, R.; Butler, K.; Van Graafeiland, K.; Breyer, S.; Wright, D. Ecological Coastal Units–Standardized Global Shoreline Characteristics. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2022, Hampton Roads, VA, USA, 17–20 October 2022; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Korres, G.; Ravdas, M.; Zacharioudaki, A.; Denaxa, D.; Sotiropoulou, M. Mediterranean Sea Waves Reanalysis (CMEMS Med-Waves, MedWAM3 System) (Version 1) 2021. Available online: https://documentation.marine.copernicus.eu/QUID/CMEMS-MED-QUID-006-012.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- Guérou, A.; Meyssignac, B.; Prandi, P.; Ablain, M.; Ribes, A.; Bignalet-Cazalet, F. Current Observed Global Mean Sea Level Rise and Acceleration Estimated from Satellite Altimetry and the Associated Measurement Uncertainty. Ocean Sci. 2023, 19, 431–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondarenko, M. Individual Countries 1 km Population Density (2000–2020); University of Southampton: Southampton, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Anfuso, G.; Postacchini, M.; Di Luccio, D.; Benassai, G. Coastal Sensitivity/Vulnerability Characterization and Adaptation Strategies: A Review. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendleton, E.A.; Thieler, E.R.; Williams, S.J. Importance of Coastal Change Variables in Determining Vulnerability to Sea- and Lake-Level Change. J. Coast. Res. 2010, 261, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saengsupavanich, C. Flaws in Coastal Erosion Vulnerability Assessment: Physical and Geomorphological Parameters. Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dronkers, J. Dynamics of Coastal Systems; World Scientific: Singapore, 2005; Volume 25, ISBN 9814480746. [Google Scholar]
- Webb, P. Introduction to Oceanography; Roger Williams University: Bristol, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Gaki-Papanastassiou, K.; Karymbalis, E.; Poulos, S.; Seni, A.; Zouva, C. Coastal Vulnerability Assessment to Sea-Level Rise Bαsed on Geomorphological and Oceanographical Parameters: The Case of Argolikos Gulf, Peloponnese, Greece. Hell. J. Geosci. 2010, 45, 109–122. [Google Scholar]
- Karymbalis, E.; Chalkias, C.; Chalkias, G.; Grigoropoulou, E.; Manthos, G.; Ferentinou, M. Assessment of the Sensitivity of the Southern Coast of the Gulf of Corinth (Peloponnese, Greece) to Sea-Level Rise. Open Geosci. 2012, 4, 561–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manno, G.; Azzara, G.; Lo Re, C.; Martinello, C.; Basile, M.; Rotigliano, E.; Ciraolo, G. An Approach for the Validation of a Coastal Erosion Vulnerability Index: An Application in Sicily. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 11, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitzner, H. Coastal Processes and Causes of Shoreline Erosion and Accretion; New York Sea Grant: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- United States Geological Survey (USGS). EROS Archive: Declassified Satellite Imagery; United States Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hoersch, B. ESA Third Party Missions Programme. In Proceedings of the 2004 Envisat & ERS Symposium, Salzburg, Austria, 6–10 September 2004; Volume 572. [Google Scholar]
- Planet Team. Planet Application Program Interface: In Space for Life on Earth. San Francisco, CA, USA, 2017. Available online: https://api.planet.com/ (accessed on 8 January 2025).
- Davis, R.A., Jr.; FitzGerald, D.M. Beaches and Coasts; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; ISBN 1444311220. [Google Scholar]
- Pranzini, E.; Williams, A.T. Coastal Erosion and Protection in Europe; Routledge: London, UK, 2013; ISBN 1849713391. [Google Scholar]
- Schumann, A.H. (Ed.) Flood Risk Assessment and Management; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 6143, ISBN 978-90-481-9916-7. [Google Scholar]
- Pethick, J. Coastal Management and Sea-Level Rise. Catena 2001, 42, 307–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubauer, S.C.; Franklin, R.B.; Berrier, D.J. Saltwater Intrusion into Tidal Freshwater Marshes Alters the Biogeochemical Processing of Organic Carbon. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 8171–8183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuodha, P.A.O.; Woodroffe, C.D. Assessing Vulnerability to Sea-Level Rise Using a Coastal Sensitivity Index: A Case Study from Southeast Australia. J. Coast. Conserv. 2010, 14, 189–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkan, C.; Perez, K.; Mayo, T. The Impacts of Wave Energy Conversion on Coastal Morphodynamics. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 712, 136424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cao, Y.; Deng, X.; Liu, H.; Dong, C. Significant Wave Height Forecasts Integrating Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition with Sequence-to-Sequence Model. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2023, 42, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, R.J.; Lincke, D.; Hinkel, J.; Brown, S.; Vafeidis, A.T.; Meyssignac, B.; Hanson, S.E.; Merkens, J.-L.; Fang, J. A Global Analysis of Subsidence, Relative Sea-Level Change and Coastal Flood Exposure. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2021, 11, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.-L.; Cazenave, A. Satellite Altimetry and Earth Sciences: A Handbook of Techniques and Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000; ISBN 0080516580. [Google Scholar]
- Nourdi, N.F.; Raphael, O.; Achab, M.; Loudi, Y.; Rudant, J.-P.; Minette, T.E.; Kambia, P.; Claude, N.J.; Romaric, N. Integrated Assessment of Coastal Vulnerability in the Bonny Bay: A Combination of Traditional Methods (Simple and AHP) and Machine Learning Approach. Estuaries Coasts 2024, 47, 2670–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacManus, K.; Balk, D.; Engin, H.; McGranahan, G.; Inman, R. Estimating Population and Urban Areas at Risk of Coastal Hazards, 1990–2015: How Data Choices Matter. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 5747–5801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocchi, L.; Rizzo, A.G.; Paolotti, L.; Boggia, A.; Attard, M. Assessing Climate Change Vulnerability of Coastal Roads. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Chang. 2024, 29, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, D.; Dodge, S. Disaster Vulnerability in Road Networks: A Data-Driven Approach through Analyzing Network Topology and Movement Activity. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2024, 38, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L. A Scaling Method for Priorities in Hierarchical Structures. J. Math. Psychol. 1977, 15, 234–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L.; Vargas, L.G. Prediction, Projection and Forecasting: Applications of the Analytic Hierarchy Process in Economics, Finance, Politics, Games and Sports; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Pantusa, D.; D’Alessandro, F.; Frega, F.; Francone, A.; Tomasicchio, G.R. Improvement of a Coastal Vulnerability Index and Its Application along the Calabria Coastline, Italy. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munier, N.; Hontoria, E. Uses and Limitations of the AHP Method; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; ISBN 3030603911. [Google Scholar]
- Zielinski, S.; Botero, C.M.; Yanes, A. To Clean or Not to Clean? A Critical Review of Beach Cleaning Methods and Impacts. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 139, 390–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malm, T.; Råberg, S.; Fell, S.; Carlsson, P. Effects of Beach Cast Cleaning on Beach Quality, Microbial Food Web, and Littoral Macrofaunal Biodiversity. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2004, 60, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoni, D.; Sarti, G.; Alquini, F.; Ciccarelli, D. Implementing a Coastal Dune Vulnerability Index (CDVI) to Support Coastal Management in Different Settings (Brazil and Italy). Ocean Coast. Manag. 2019, 180, 104916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dialogos New Complaint about Illegal Interventions on a Protaras Beach (Greek). Dialogos. 2021. Available online: https://dialogos.com.cy/nea-kataggelia-paranomes-epemvaseis-se-paralia-protara/ (accessed on 21 January 2025).
- Tothemaonline Illegal Installation of Jetty at Fig Tree Bay in Protaras (Greek). To Thema Online. 2015. Available online: https://www.tothemaonline.com/article/31497/paranomh-h-egkatastash-limenobrahiwna-sto-fig-tree-bay-ston-prwtara (accessed on 7 January 2025).
- Randazzo, G.; Barreca, G.; Cascio, M.; Crupi, A.; Fontana, M.; Gregorio, F.; Lanza, S.; Muzirafuti, A. Analysis of Very High Spatial Resolution Images for Automatic Shoreline Extraction and Satellite-Derived Bathymetry Mapping. Geosciences 2020, 10, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).