Recent Progress in Blue Energy Harvesting Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerators
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. History and Development of Applying TENG in Blue Energy Harvesting
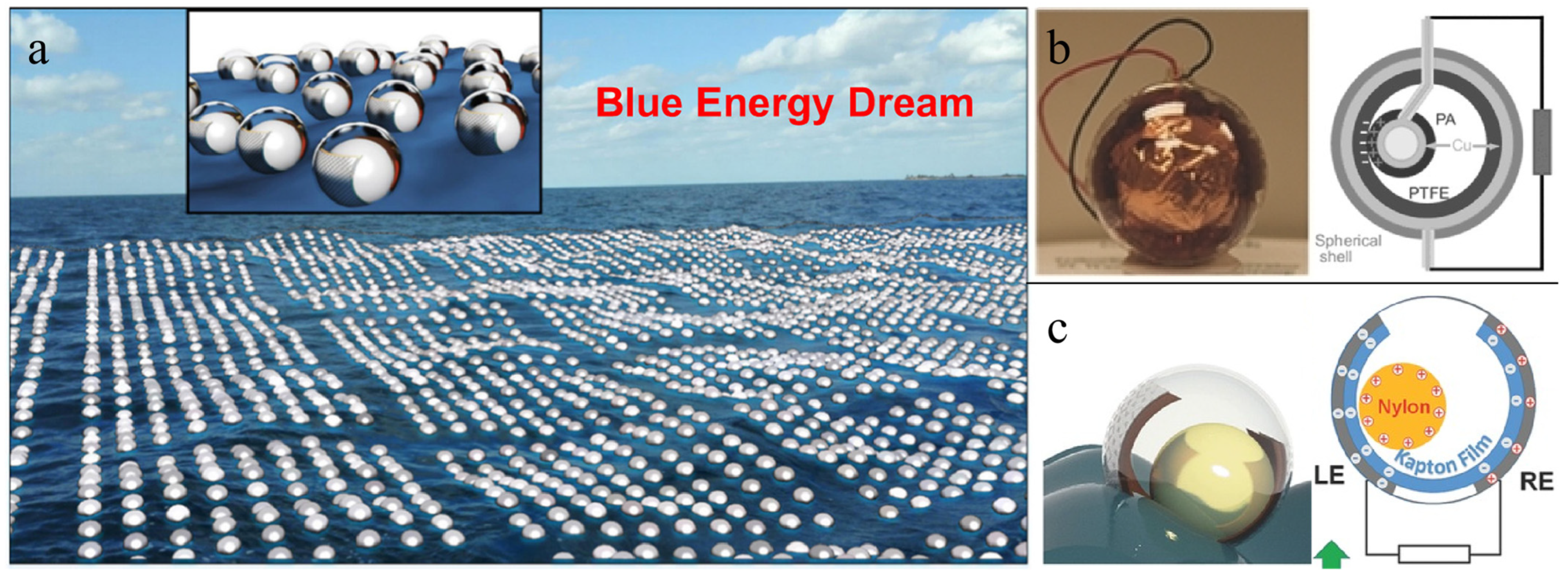
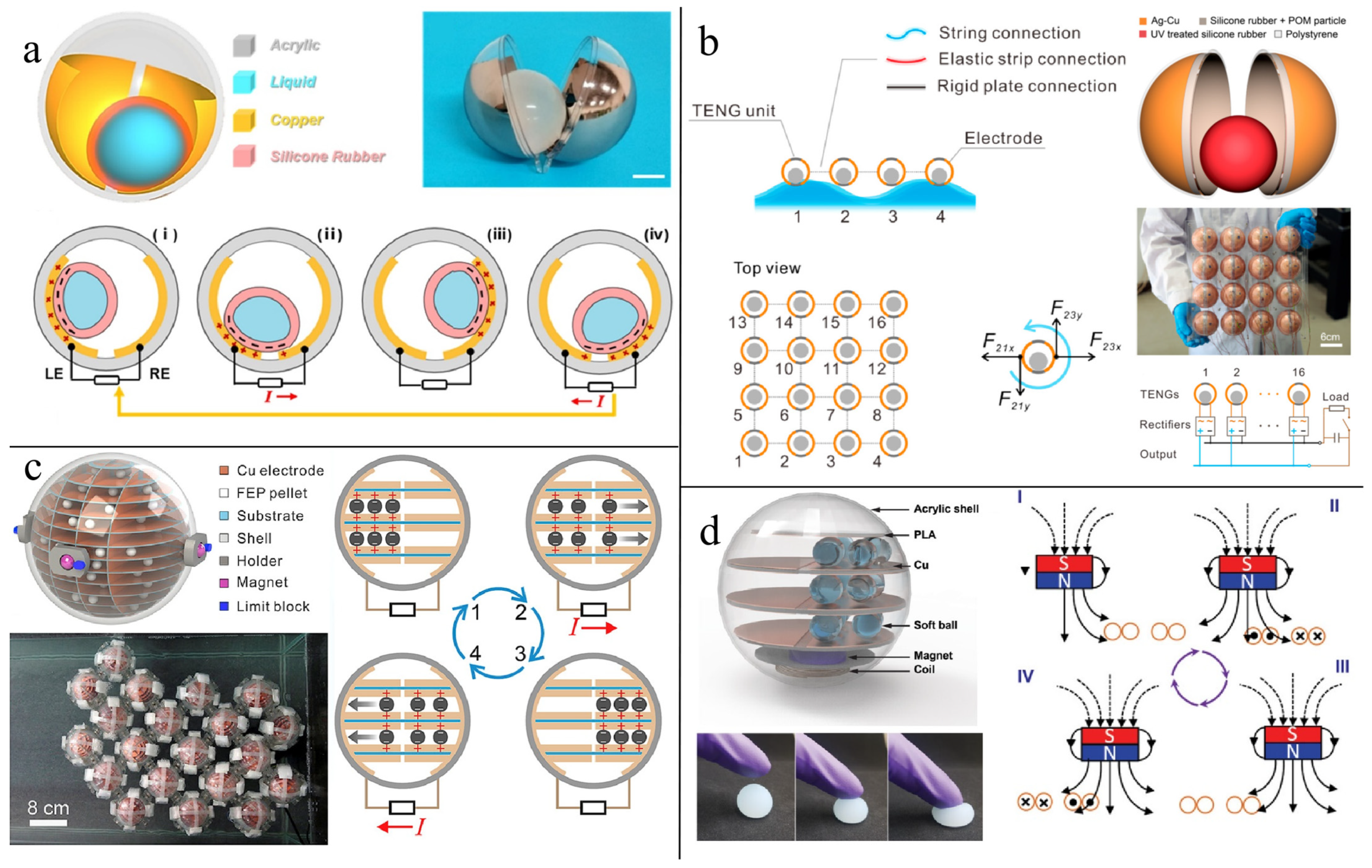
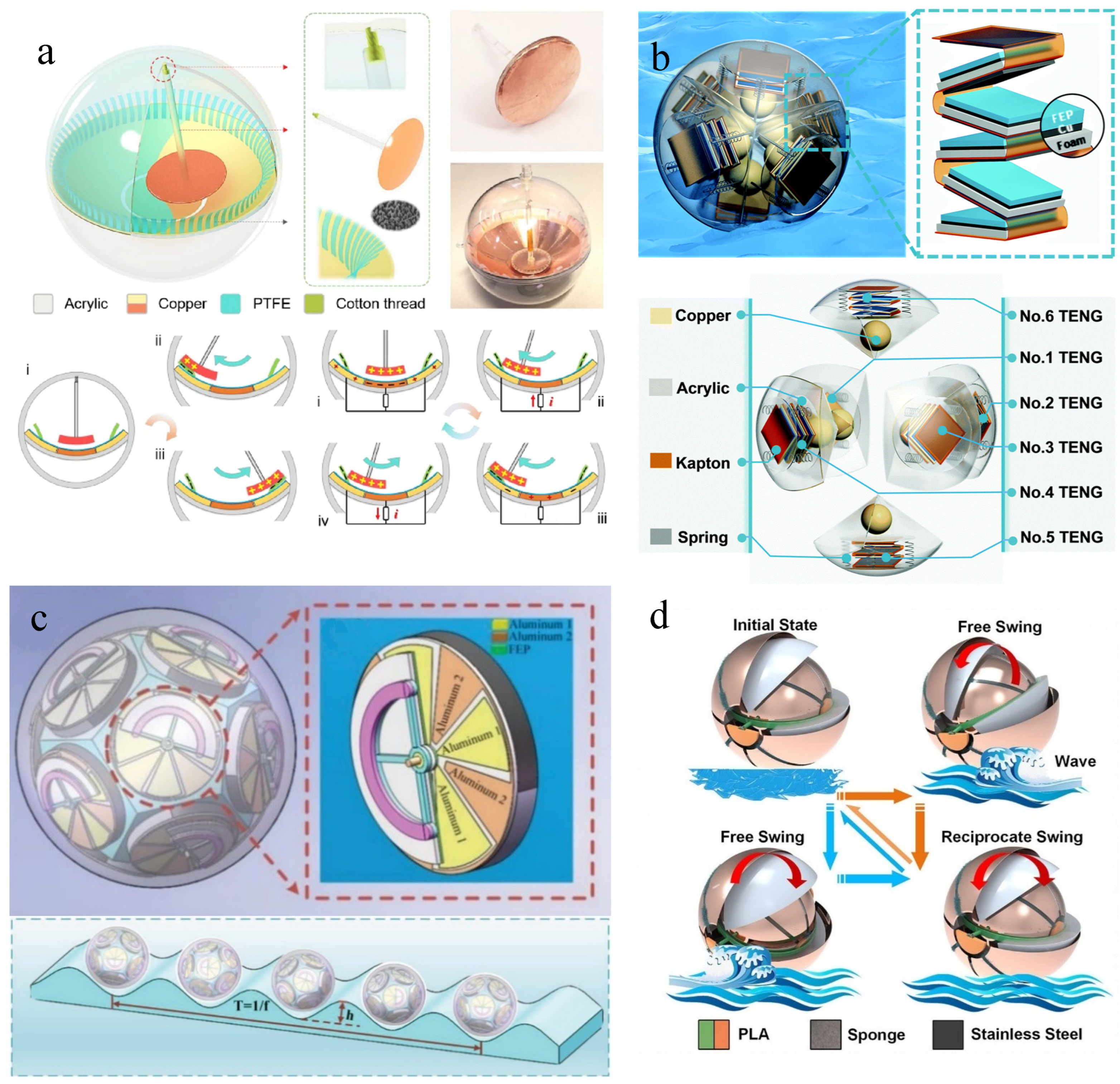
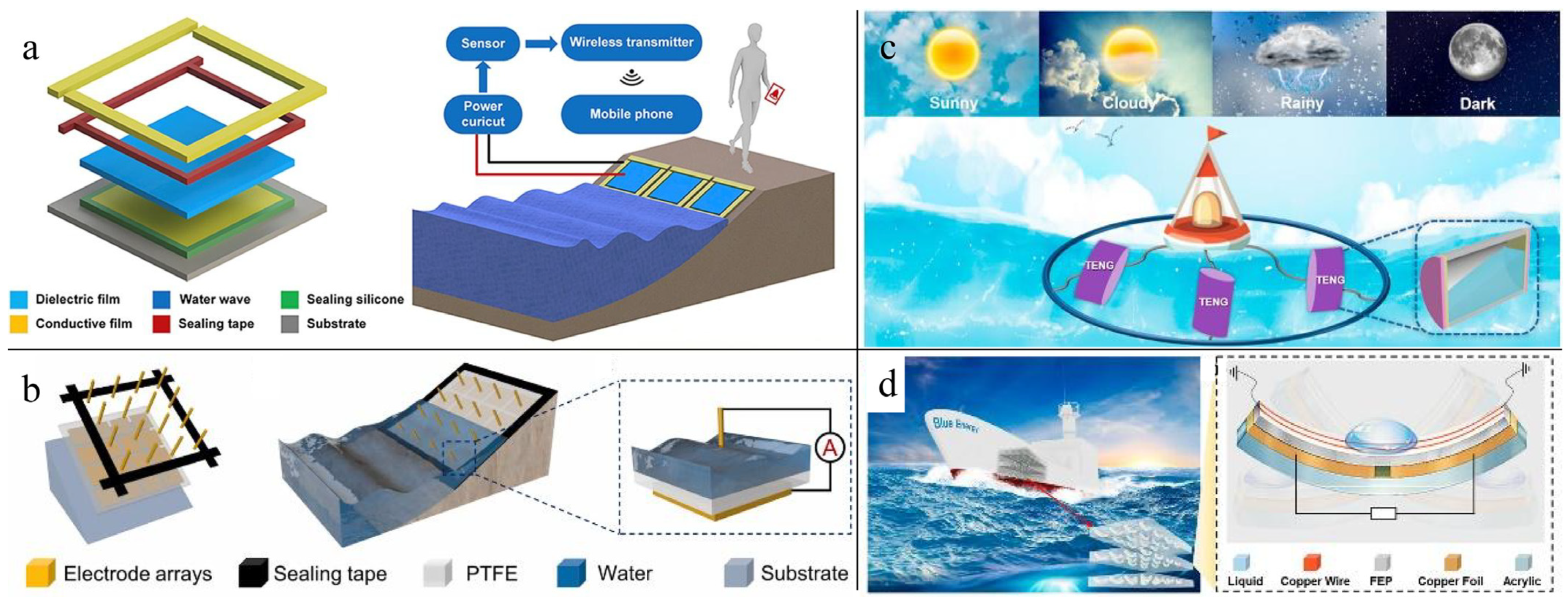
3. Buoy Structural TENG Applied in Blue Energy Harvesting
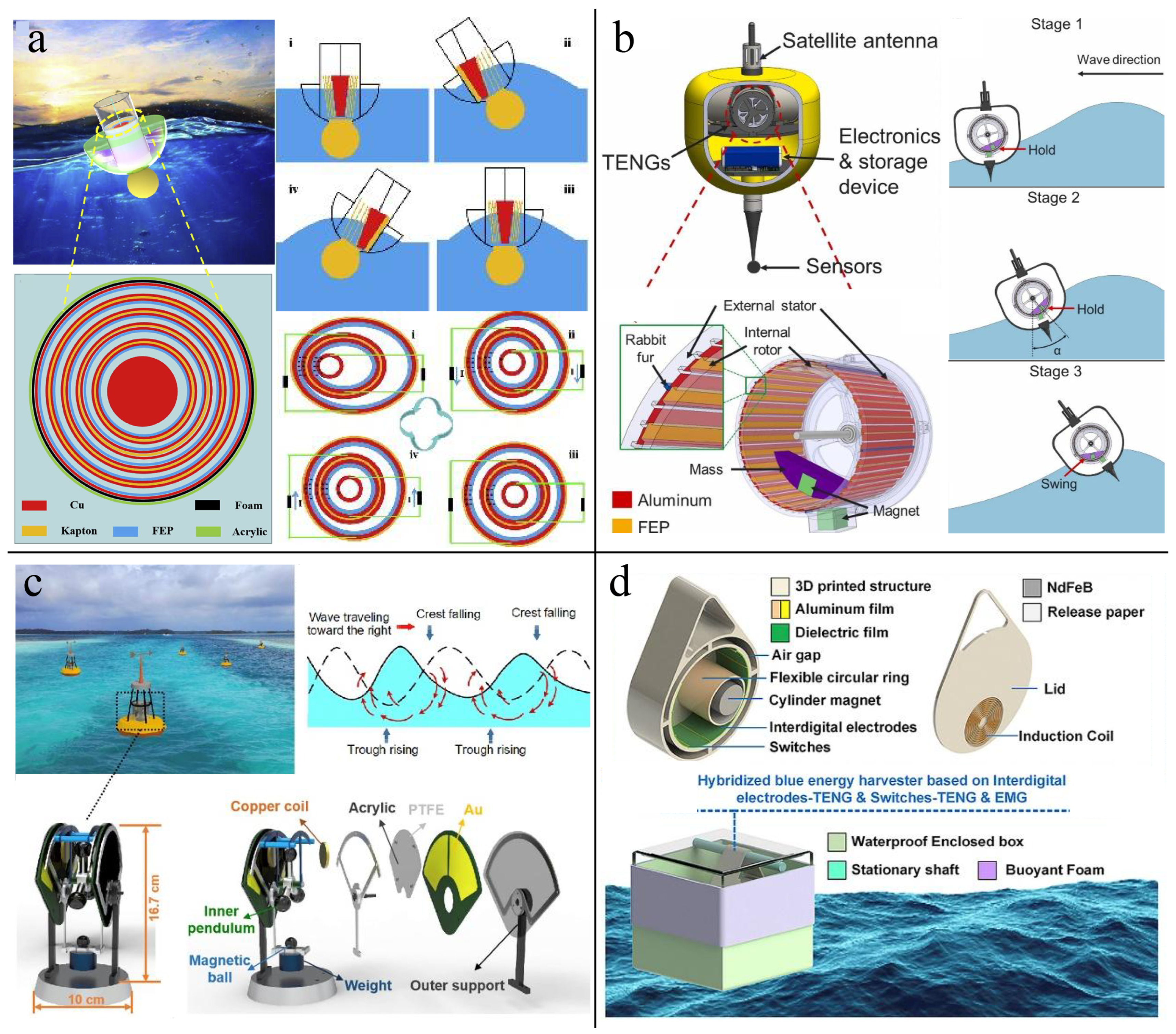
4. Liquid–Solid-Based TENG Applied in Blue Energy Harvesting
5. Performance Comparison and Power Management
6. Summary and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, N.; Kalair, A.; Abas, N.; Haider, A. Review of ocean tidal, wave and thermal energy technologies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 72, 590–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilberforce, T.; El Hassan, Z.; Durrant, A.; Thompson, J.; Soudan, B.; Olabi, A.G. Overview of ocean power technology. Energy 2019, 175, 165–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Z.A.; Khan, H.A.; Aziz, M. Harvesting Energy from Ocean: Technologies and Perspectives. Energies 2022, 15, 3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastgar, M.; Moradi, K.; Burroughs, C.; Hemmati, A.; Hoek, E.; Sadrzadeh, M. Harvesting Blue Energy Based on Salinity and Temperature Gradient: Challenges, Solutions, and Opportunities. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 10156–10205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babarit, A. Ocean Wave Energy Conversion: Resource, Technologies and Performance; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, W.; Li, J. Ocean wave energy converters: Technical principle, device realization, and performance evaluation. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 141, 110764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunn, K.; Stock-Williams, C. Quantifying the global wave power resource. Renew. Energy 2012, 44, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tollefson, J. Power from the oceans: Blue energy. Nature 2014, 508, 302–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. Entropy theory of distributed energy for internet of things. Nano Energy 2019, 58, 669–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Wang, Z.L. Toward a New Era of Sustainable Energy: Advanced Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Harvesting High Entropy Energy. Small 2022, 18, e2107034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, F.; Wang, H.; He, T.; Shi, Q.; Sun, Z.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, Z.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, T.; et al. Battery-free short-range self-powered wireless sensor network (SS-WSN) using TENG based direct sensory transmission (TDST) mechanism. Nano Energy 2020, 67, 104266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Wu, H.; Wang, H.; Wu, H.; Lee, C. Self-Powered Gyroscope Ball Using a Triboelectric Mechanism. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1701300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; Yen, S.-C.; Sheshadri, S.; Wang, J.; Lee, S.; Liu, Y.-H.; Liao, L.-D.; Thakor, N.V.; Lee, C. Progress of Flexible Electronics in Neural Interfacing – A Self-Adaptive Non-Invasive Neural Ribbon Electrode for Small Nerves Recording. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 4472–4479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, T.; Shi, Q.; Wang, H.; Wen, F.; Chen, T.; Ouyang, J.; Lee, C. Beyond energy harvesting—Multi-functional triboelectric nanosensors on a textile. Nano Energy 2019, 57, 338–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.J.; Wang, Z.L. Recent progress of triboelectric nanogenerators: From fundamental theory to practical applications. EcoMat 2020, 2, e12059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.-R.; Tian, Z.-Q.; Wang, Z.L. Flexible triboelectric generator. Nano Energy 2012, 1, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Liang, X.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Z.L. Advances in Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Blue Energy Harvesting and Marine Environmental Monitoring. Engineering 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Wang, H.; Xi, Z.; Wang, W.; Xu, M. Recent Progress on Wave Energy Marine Buoys. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zi, Y.; Guo, H.; Wen, Z.; Yeh, M.-H.; Hu, C.; Wang, Z.L. Harvesting Low-Frequency (<5 Hz) Irregular Mechanical Energy: A Possible Killer Application of Triboelectric Nanogenerator. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 4797–4805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Li, Z.J.; Guo, H.Y.; Yang, Z.B.; Wu, H.; Wang, M.; Luo, J.; Xie, S.R.; Peng, Y.; Pu, H.Y. Recent Advances towards Ocean Energy Harvesting and Self-Powered Applications Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2021, 7, 2100277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.; Lee, Y.; Lin, Z.H.; Cho, S.; Kim, M.; Ao, C.K.; Soh, S.; Sohn, C.; Jeong, C.K.; Lee, J.; et al. Recent Advances in Triboelectric Nanogenerators: From Technological Progress to Commercial Applications. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 11087–11219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matin Nazar, A.; Idala Egbe, K.-J.; Abdollahi, A.; Hariri-Ardebili, M.A. Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Energy Harvesting in Ocean: A Review on Application and Hybridization. Energies 2021, 14, 5600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. From nanogenerators to piezotronics—A decade-long study of ZnO nanostructures. MRS Bull. 2012, 37, 814–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. Nanogenerators and piezotronics: From scientific discoveries to technology breakthroughs. MRS Bull. 2023, 48, 1014–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. On the first principle theory of nanogenerators from Maxwell’s equations. Nano Energy 2020, 68, 104272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. On Maxwell’s displacement current for energy and sensors: The origin of nanogenerators. Mater. Today 2017, 20, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. On the expanded Maxwell’s equations for moving charged media system-General theory, mathematical solutions and applications in TENG. Mater. Today 2022, 52, 348–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Shao, J.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric nanogenerators. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2023, 3, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Yao, Y.; Xu, L.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, T.; Wang, Z.L. Spring-assisted triboelectric nanogenerator for efficiently harvesting water wave energy. Nano Energy 2017, 31, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, K.; Fu, J.; Xu, Z. Multiple-Frequency High-Output Triboelectric Nanogenerator Based on a Water Balloon for All-Weather Water Wave Energy Harvesting. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 2000426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Zhang, B.F.; Zhang, C.G.; Yang, O.; Liu, Y.B.; He, L.X.; Zhou, L.L.; Zhao, Z.H.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.L. Anaconda-shaped spiral multi-layered triboelectric nanogenerators with ultra-high space efficiency for wave energy harvesting. One Earth 2022, 5, 1055–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, L.; Lin, P.; Yang, X.; Wang, H.; Qin, H.; Wang, Z.L. Three-dimensional chiral networks of triboelectric nanogenerators inspired by metamaterial’s structure. Energy Environ. Sci. 2023, 16, 3040–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Yang, H.X.; Li, Z.K.; Cheng, M.F.; Zhao, Y.L.; Wan, L.Y.; Yu, A.F.; Zhai, J.Y. A columnar multi-layer sliding triboelectric nanogenerator for water wave energy harvesting independent of wave height and direction. Nano Res. 2023, 17, 3029–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.T.; Wan, L.Y.; Lin, Y.; Liu, G.L.; Qu, H.; Wen, H.G.; Ding, J.J.; Ning, H.; Yao, H.L. Synchronous nanogenerator with intermittent sliding friction self-excitation for water wave energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2022, 95, 106994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado, U.T.; Pu, S.H.; White, N.M. Wave impact energy harvesting through water-dielectric triboelectrification with single-electrode triboelectric nanogenerators for battery-less systems. Nano Energy 2020, 78, 105204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Wang, S.; Zhang, S.L.; Ding, W.; Kien, P.T.; Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Pan, X.; Wang, Z.L. A highly-sensitive wave sensor based on liquid-solid interfacing triboelectric nanogenerator for smart marine equipment. Nano Energy 2019, 57, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhao, T.; Wang, C.; Zhang, S.L.; Li, Z.; Pan, X.; Wang, Z.L. High Power Density Tower-like Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Harvesting Arbitrary Directional Water Wave Energy. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 1932–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, C.; Yuan, W.; Wu, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.L. All-Weather Droplet-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Wave Energy Harvesting. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 13200–13208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, S.; Zhang, Z. Fundamental theories and basic principles of triboelectric effect: A review. Friction 2018, 7, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, L.; Wang, P.; He, X.; Dai, G.; Zheng, H.; Chen, C.; Wang, A.C.; Xu, C.; et al. Quantifying the triboelectric series. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, D.; Jang, S.; Cho, S.; Choi, D.; Kim, D.S. A Liquid Triboelectric Series. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, e2300699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.Y.; Olin, H. Material choices for triboelectric nanogenerators: A critical review. EcoMat 2020, 2, e12062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Guan, D.; Fu, J.; Li, X.; Li, A.; Ding, W.; Zi, Y. Density of Surface States: Another Key Contributing Factor in Triboelectric Charge Generation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 5355–5362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.L.; Jiang, T.; Xu, L. Toward the blue energy dream by triboelectric nanogenerator networks. Nano Energy 2017, 39, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.L.; Liu, R.Y.; Wen, X.N.; Hou, T.C.; Wang, Z.L. Fully Enclosed Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Applications in Water and Harsh Environments. Adv. Energy Mater. 2013, 3, 1563–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.F.; Niu, S.M.; Yin, Y.J.; Yi, F.; You, Z.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric Nanogenerator Based on Fully Enclosed Rolling Spherical Structure for Harvesting Low-Frequency Water Wave Energy. Adv. Energy Mater. 2015, 5, 1501467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. Catch wave power in floating nets. Nature 2017, 542, 159–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Han, J.; Xu, M.; Liang, X.; Jiang, T.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.L. Blue Energy for Green Hydrogen Fuel: A Self-Powered Electrochemical Conversion System Driven by Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 12, 2103143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Fan, Z.Q.; Zhao, T.C.; Dong, J.L.; Wang, S.Y.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, X.; Liu, C.X.; Pan, X.X.; Zhao, Y.P.; et al. Sandwich-like triboelectric nanogenerators integrated self-powered buoy for navigation safety. Nano Energy 2021, 84, 105920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.L.; Mo, J.L.; Wu, W.H.; Song, H.N.; Nie, S.X. Triboelectric pulsed direct-current enhanced radical generation for efficient degradation of organic pollutants in wastewater. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2022, 312, 121422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.; Guo, H.; Wen, Z.; Zhang, C.; Yin, X.; Li, X.; Liu, D.; Song, W.; Sun, X.; Wang, J.; et al. Largely enhanced triboelectric nanogenerator for efficient harvesting of water wave energy by soft contacted structure. Nano Energy 2019, 57, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Jiang, T.; Lin, P.; Shao, J.J.; He, C.; Zhong, W.; Chen, X.Y.; Wang, Z.L. Coupled Triboelectric Nanogenerator Networks for Efficient Water Wave Energy Harvesting. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 1849–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Xu, L.; Lin, P.; Zhong, W.; Bai, Y.; Luo, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.L. Macroscopic self-assembly network of encapsulated high-performance triboelectric nanogenerators for water wave energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2019, 60, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.K.; Fang, Y.H.; Su, J.J.; Wang, H.G.; Tan, Y.Q.; Cao, C.Y. Soft Ball-Based Triboelectric-Electromagnetic Hybrid Nanogenerators for Wave Energy Harvesting. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2023, 8, 2201246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.Q.; Wang, C.F.; Xi, J.G.; Han, X.; Li, J.; Han, S.T.; Gao, W.C.; Pan, C.F. Spherical Triboelectric Nanogenerator with Dense Point Contacts for Harvesting Multidirectional Water Wave and Vibration Energy. ACS Energy Lett. 2021, 6, 2809–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.K.; Chen, S.E.; Chu, Y.H.; Wang, Z.L.; Cao, C.Y. Matryoshka-inspired hierarchically structured triboelectric nanogenerators for wave energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2019, 66, 104131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Guo, H.; Ding, W.; Wang, Y.C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.L. A Hybridized Triboelectric-Electromagnetic Water Wave Energy Harvester Based on a Magnetic Sphere. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 2349–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Zhang, B.; Guo, H.; Wu, Z.; Zou, H.; Yang, J.; Wang, Z.L. Super-robust and frequency-multiplied triboelectric nanogenerator for efficient harvesting water and wind energy. Nano Energy 2019, 64, 103908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Jiang, T.; Liu, G.X.; Feng, Y.W.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.L. Spherical triboelectric nanogenerator integrated with power management module for harvesting multidirectional water wave energy. Energy Environ. Sci. 2020, 13, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.G.; Huang, M.K.; Chen, C.X.; An, Y.; Liu, H.Z.; Zhang, Q.P.; Wang, X.P.; Liu, Y.; Yin, W.L.; Li, X.F. Spherical Triboelectric Nanogenerator Based on Eccentric Structure for Omnidirectional Low Frequency Water Wave Energy Harvesting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2202048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Xu, Y.; Yu, X.; Jing, Z.; Cheng, T.; Wang, Z.L. Gyroscope-Structured Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Harvesting Multidirectional Ocean Wave Energy. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 6781–6788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.Y.; Sun, Y.G.; Wei, X.L.; Chen, J.H.; Yuan, Z.H.; Jin, X.; Tao, L.; Wu, Z.Y. A hybridized water wave energy harvester with a swing magnetic structure toward intelligent fishing ground. Nano Energy 2021, 90, 106631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, K.; Yi, H.; Yang, Y.; Chang, H.; Wu, J.; Tang, L.; Yang, Z.; Wang, N.; Hu, L.; Fu, Y.; et al. Origami-inspired electret-based triboelectric generator for biomechanical and ocean wave energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2020, 67, 104197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Liu, Z.R.; Feng, Y.W.; Han, J.J.; Li, L.L.; An, J.; Chen, P.F.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Z.L. Spherical triboelectric nanogenerator based on spring-assisted swing structure for effective water wave energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2021, 83, 105836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Liu, S.J.; Ren, Z.W.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Z.L. Self-Powered Intelligent Buoy Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Water Level Alarming. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2205313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Yang, P.; Liu, G.; Xu, S.; Yao, H.; Li, W.; Qu, H.; Ding, J.; Li, J.; Wan, L. Flower-like triboelectric nanogenerator for blue energy harvesting with six degrees of freedom. Nano Energy 2022, 93, 106796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.M.; Xu, L.; Bai, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Pumping up the charge density of a triboelectric nanogenerator by charge-shuttling. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Guo, H.; Xu, S.; Hu, C.; Wang, Z.L. Oblate Spheroidal Triboelectric Nanogenerator for All-Weather Blue Energy Harvesting. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1900801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.M.; Yang, Q.X.; Ji, P.Y.; Wu, Z.F.; Li, Q.Y.; Yang, H.K.; Li, X.C.; Zheng, G.C.; Xi, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Modeling of liquid-solid hydrodynamic water wave energy harvesting system based on triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2022, 99, 107362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gao, Q.; Zhu, M.; Wang, J.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Z.L.; Cheng, T. Bioinspired butterfly wings triboelectric nanogenerator with drag amplification for multidirectional underwater-wave energy harvesting. Appl. Energy 2022, 323, 119648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, Q.; Ren, D.; Yang, H.; Li, X.; Li, Q.; Liu, H.; Hu, C.; He, X.; Xi, Y. Omnidirectional water wave-driven triboelectric net-zero power smart ocean network: An advanced hardware solution to long-distance target detection. Nano Energy 2023, 114, 108614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Ma, X.; Tang, T.Y.; Zha, F.S.; Chen, Z.H.; Liu, H.C.; Sun, L.N. High-efficient built-in wave energy harvesting technology: From laboratory to open ocean test. Appl. Energy 2022, 322, 119498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aderinto, T.; Li, H. Review on Power Performance and Efficiency of Wave Energy Converters. Energies 2019, 12, 4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamed, R.; McKee, K.; Howard, I. Advancements of wave energy converters based on power take off (PTO) systems: A review. Ocean Eng. 2020, 204, 107248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.; Friedman, B.; Hwang, W.; Copping, A.; Branch, R.; Deng, Z.D. Self-powered arctic satellite communication system by harvesting wave energy using a triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2023, 114, 108633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Gao, L.X.; Chen, J.F.; Lu, S.; Zhou, H.; Wang, T.T.; Wang, A.B.; Zhang, Z.F.; Guo, S.F.; Mu, X.J.; et al. A chaotic pendulum triboelectric-electromagnetic hybridized nanogenerator for wave energy scavenging and self-powered wireless sensing system. Nano Energy 2020, 69, 104440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Shi, Q.; Lee, C. A novel hybridized blue energy harvester aiming at all-weather IoT applications. Nano Energy 2020, 76, 105052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Liu, J.H.; Wang, S.Y.; Zheng, J.X.; Guan, T.Z.; Liu, X.Y.; Wang, T.Y.; Chen, T.Y.; Wang, H.; Xie, G.M.; et al. A Self-powered Triboelectric Coral-like Sensor Integrated Buoy for Irregular and Ultra-Low Frequency Ocean Wave Monitoring. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2022, 7, 2101098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.Y.J.; Ouro-Koura, H.; Salalila, A.; Salalila, M.; Deng, Z.D. Frequency-multiplied cylindrical triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting low frequency wave energy to power ocean observation system. Nano Energy 2022, 99, 107365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.W.; Liang, X.; An, J.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Z.L. Soft-contact cylindrical triboelectric-electromagnetic hybrid nanogenerator based on swing structure for ultra-low frequency water wave energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2021, 81, 105625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.; Kim, J.S.; Jeong, Y.; Hwang, S.; Yoo, H.; Jeong, Y.; Gu, J.; Mahato, M.; Ko, J.; Jeon, S.; et al. All-Recyclable Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Sustainable Ocean Monitoring Systems. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2201341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.P.; Fan, Z.Q.; Bi, C.W.; Wang, H.; Mi, J.C.; Xu, M.Y. On hydrodynamic and electrical characteristics of a self-powered triboelectric nanogenerator based buoy under water ripples. Appl. Energy 2022, 308, 118323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Wu, M.; Liu, C.; Xiang, C.; Xu, R.; Yang, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Xu, P.; Xing, F.; et al. Highly Integrated Triboelectric-Electromagnetic Wave Energy Harvester toward Self-Powered Marine Buoy. Adv. Energy Mater. 2023, 13, 2301665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Xi, Y.; Shi, Y. Toward wear-resistive, highly durable and high performance triboelectric nanogenerator through interface liquid lubrication. Nano Energy 2020, 72, 104659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Zhang, B.; Zou, H.; Wu, Z.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, Z.L. Rationally designed rotation triboelectric nanogenerators with much extended lifetime and durability. Nano Energy 2020, 68, 104378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Wang, N.N.; Yang, D.; Wang, J.; Lu, W.L.; Wang, D.A. Robust Solid-Liquid Triboelectric Nanogenerators: Mechanisms, Strategies and Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2300764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.J.; Kuang, S.Y.; Wang, Z.L.; Zhu, G. Highly Adaptive Solid–Liquid Interfacing Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Harvesting Diverse Water Wave Energy. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 4280–4285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Shi, Q.; Ho, J.S.; Lee, C. Study of thin film blue energy harvester based on triboelectric nanogenerator and seashore IoT applications. Nano Energy 2019, 66, 104167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.J.; Zhang, N.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Ye, S.M.; Wang, W.J.; Xu, W.H.; Zheng, H.X.; Song, Y.X.; Jiao, J.W.; Wang, Z.A.K.; et al. A bulk effect liquid-solid generator with 3D electrodes for wave energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2021, 87, 106218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.X.; Zheng, Y.B.; Li, T.H.; Feng, M.; Cui, S.W.; Liu, Y.P.; Chen, S.G.; Wang, D.A. Liquid-solid triboelectric nanogenerators array and its applications for wave energy harvesting and self-powered cathodic protection. Energy 2021, 217, 119388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.X.; He, M.; Pan, X.X.; Huang, D.D.; Long, H.H.; Jia, M.S.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Zhang, C.; Xu, M.Y.; Li, S.S. High performance liquid-solid tubular triboelectric nanogenerator for scavenging water wave energy. Nano Energy 2022, 103, 107810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, Z.K.; Zi, Y.L. Multi-Mode Water-Tube-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator Designed for Low-Frequency Energy Harvesting with Ultrahigh Volumetric Charge Density. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2100038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tao, J.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; Pan, C.; Wang, Z.L. Networks of High Performance Triboelectric Nanogenerators Based on Liquid–Solid Interface Contact Electrification for Harvesting Low-Frequency Blue Energy. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1800705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Liu, S.J.; Lin, S.Q.; Yang, H.B.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Z.L. Liquid-Solid Triboelectric Nanogenerator Arrays Based on Dynamic Electric-Double-Layer for Harvesting Water Wave Energy. Adv. Energy Mater. 2023, 13, 2300571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Guo, W.; Dong, S.; Liu, A.; Cao, Y.; Xu, Z.; Lin, C.; Zhang, J. A hybrid triboelectric nanogenerator for enhancing corrosion prevention of metal in marine environment. NPJ Mater. Degrad. 2022, 6, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.M.; Han, C.B.; Jiang, T.; Zhou, T.; Li, X.H.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.L. Multilayer wavy-structured robust triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting water wave energy. Nano Energy 2016, 22, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yang, J.; Li, Z.; Fan, X.; Zi, Y.; Jing, Q.; Guo, H.; Wen, Z.; Pradel, K.C.; Niu, S.; et al. Networks of Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Harvesting Water Wave Energy: A Potential Approach toward Blue Energy. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 3324–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Su, Y.; Bai, P.; Chen, J.; Jing, Q.; Yang, W.; Wang, Z.L. Harvesting Water Wave Energy by Asymmetric Screening of Electrostatic Charges on a Nanostructured Hydrophobic Thin-Film Surface. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 6031–6037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.X.; Liang, X.; Jiang, T.; Xu, L.; Shao, J.J.; Nie, J.H.; Bai, Y.; Zhong, W.; Wang, Z.L. Spherical Triboelectric Nanogenerators Based on Spring-Assisted Multilayered Structure for Efficient Water Wave Energy Harvesting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1802634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Jiang, T.; Liu, G.; Xiao, T.; Xu, L.; Li, W.; Xi, F.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric Nanogenerator Networks Integrated with Power Management Module for Water Wave Energy Harvesting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1807241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, M.; Ma, Z.; Ouyang, H.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, S.L.; Niu, H.; Pan, X.; Xu, M.; Li, Z.; et al. Self-Powered Distributed Water Level Sensors Based on Liquid–Solid Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Ship Draft Detecting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1900327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Jiang, T.; Feng, Y.W.; Lu, P.J.; An, J.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric Nanogenerator Network Integrated with Charge Excitation Circuit for Effective Water Wave Energy Harvesting. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 2002123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Shang, C.J.; Ma, H.X.; Li, C.Z.; Xue, L.; Xu, Q.Y.; Wei, Z.H.; Li, W.L.; Yalikun, Y.; Lai, Y.C.; et al. A tube-shaped solid-liquid-interfaced triboelectric-electromagnetic hybrid nanogenerator for efficient ocean wave energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2022, 100, 107540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Zhou, H.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, E.; Xu, S.; Li, W.; Yao, H.; Wan, L.; Liu, G. 0.5 m Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Efficient Blue Energy Harvesting of All-Sea Areas. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, e2204407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.Y.; Shang, C.J.; Ma, H.X.; Hong, Q.; Li, C.Z.; Ding, S.; Xue, L.; Sun, X.; Pan, Y.C.; Sugahara, T.; et al. A guided-liquid-based hybrid triboelectric nanogenerator for omnidirectional and high-performance ocean wave energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2023, 109, 108240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Pang, H.; An, J.; Lu, P.; Feng, Y.; Liang, X.; Zhong, W.; Wang, Z.L. Robust Swing-Structured Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Efficient Blue Energy Harvesting. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 2000064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Wang, S.; Lin, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.S.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Theoretical study of contact-mode triboelectric nanogenerators as an effective power source. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 3576–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Tong, T.; Bu, T.; Cao, Y.; Xu, S.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, C. Overview of power management for triboelectric nanogenerators. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2020, 2, 1900129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Wu, H.; Yao, G.; Chen, L.; Yang, X.; Chen, B.; Huang, X.; Zhong, W.; Chen, X.; Yin, Z. Giant voltage enhancement via triboelectric charge supplement channel for self-powered electroadhesion. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 10262–10271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; Chen, J.; Zhang, T.; Jing, Q.; Wang, Z.L. Radial-arrayed rotary electrification for high performance triboelectric generator. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, F.; Pang, Y.; Liu, G.; Wang, S.; Li, W.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.L. Self-powered intelligent buoy system by water wave energy for sustainable and autonomous wireless sensing and data transmission. Nano Energy 2019, 61, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Cheng, G.; Zi, Y.; Gu, G.; Zhang, B.; Shang, W.; Yang, F.; Yang, J.; Du, Z.; Wang, Z.L. High Energy Storage Efficiency Triboelectric Nanogenerators with Unidirectional Switches and Passive Power Management Circuits. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1805216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, Y.; Du, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, S.; Fan, D.; Xiao, X.; Mutsuda, H.; Jiao, P. Self-powered and self-sensing blue carbon ecosystems by hybrid fur triboelectric nanogenerators (F-TENG). Nano Energy 2024, 119, 109091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Device | Structures | Efficiency | Typical Output | Size | Materials | Durability | Year | Ref. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental Setup | Peak Power | Peak Power Density | Load | ||||||||
| SS-TENG | Spherical Structures | - | linear motor (5 Hz) | 10 mW | - | 100 MΩ | 7 cm in diameter | Ecoflex/Cu | 70,000 cycles | 2019 | [51] |
| P-TENG | - | linear motor (1 Hz) | 18.6 μW | - | 90 MΩ | 120 mm in diameter | PTFE/Cu | 1,000,000 cycles | 2019 | [58] | |
| GS-TENG | - | linear motor | 0.6 mW | 0.28 W/m3 | 200 MΩ | 180 mm in diameter | PTFE/Fur/Cu | 30 days | 2022 | [61] | |
| TEHG | - | wave tank | - | 10.1 W m−3 | - | 12 cm in diameter | Ecoflex/PTFE/Cu | 5 days | 2023 | [54] | |
| CS-TENG | Derivative spherical Structures | - | wave tank | 126.67 mW | 30.24 W m−3 | 300 kΩ | 120 mm × 100 mm | PTFE/PP/ Zn-Al | - | 2020 | [67] |
| IPM-TENG | 14.5% | linear motor (2 Hz) | 20.1 mW | - | 5 MΩ | 10 cm in diameter | PTFE/Al | - | 2022 | [69] | |
| BBW-TENG | - | wave tank (1 Hz) | 0.69 mW | - | 200 MΩ | 80 mm in diameter | PTFE/Cu | 45 days | 2022 | [70] | |
| TENG/EMG | Buoy Structures | - | linear motor (2.5 Hz) | 15.21 μW/ 1.23 mW | - | 400 MΩ/ 400 Ω | 100 mm in diameter, 167 mm in height | PTFE/Au | 2 months | 2020 | [76] |
| SS-TENG | 28.2% | linear motor (7.5 m s−2) | 4.56 mW | 1.29 W m−3 | 300 MΩ | 14 cm in diameter, 18 cm in height | PTFE/Cu | 400,000 cycles | 2020 | [106] | |
| Arctic-TENG | - | wave simulator, (0.2 Hz) chest freezer, (−40 °C) | - | 21.4 W/m3 | 20 MΩ | 112.7 mm (outer diameter, rotor), 114.1 mm (inner diameter, stator) | FEP/Fur/Al | 170 days | 2023 | [75] | |
| U-TENG/ B-TENG | Liquid–solid contact Structures | - | wave pump | 1.51 mW/ 30 mW | - | 53 MΩ/ 100 kΩ | 22 cm × 22 cm | Kapton/FEP/ PVC/Al | 5000 cycles | 2019 | [88] |
| DB-TENG | - | linear motor | 23.3 μW | - | 500 MΩ | 250 mm in diameter, 120 mm in height | FEP/Cu | - | 2021 | [38] | |
| LS-TENG | - | wave tank, linear motor (0.8 Hz) | 18.36 mW | 11.7 W/m2 | 51 kΩ | 10 cm × 10 cm | PTFE/Al | - | 2021 | [89] | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, L.; Hu, T.; Zhao, X.; Lee, C. Recent Progress in Blue Energy Harvesting Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Nanoenergy Adv. 2024, 4, 156-173. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv4020010
Liu L, Hu T, Zhao X, Lee C. Recent Progress in Blue Energy Harvesting Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Nanoenergy Advances. 2024; 4(2):156-173. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv4020010
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Long, Tong Hu, Xinmao Zhao, and Chengkuo Lee. 2024. "Recent Progress in Blue Energy Harvesting Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerators" Nanoenergy Advances 4, no. 2: 156-173. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv4020010
APA StyleLiu, L., Hu, T., Zhao, X., & Lee, C. (2024). Recent Progress in Blue Energy Harvesting Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Nanoenergy Advances, 4(2), 156-173. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv4020010







