Probing Contact Electrification between Gas and Solid Surface
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
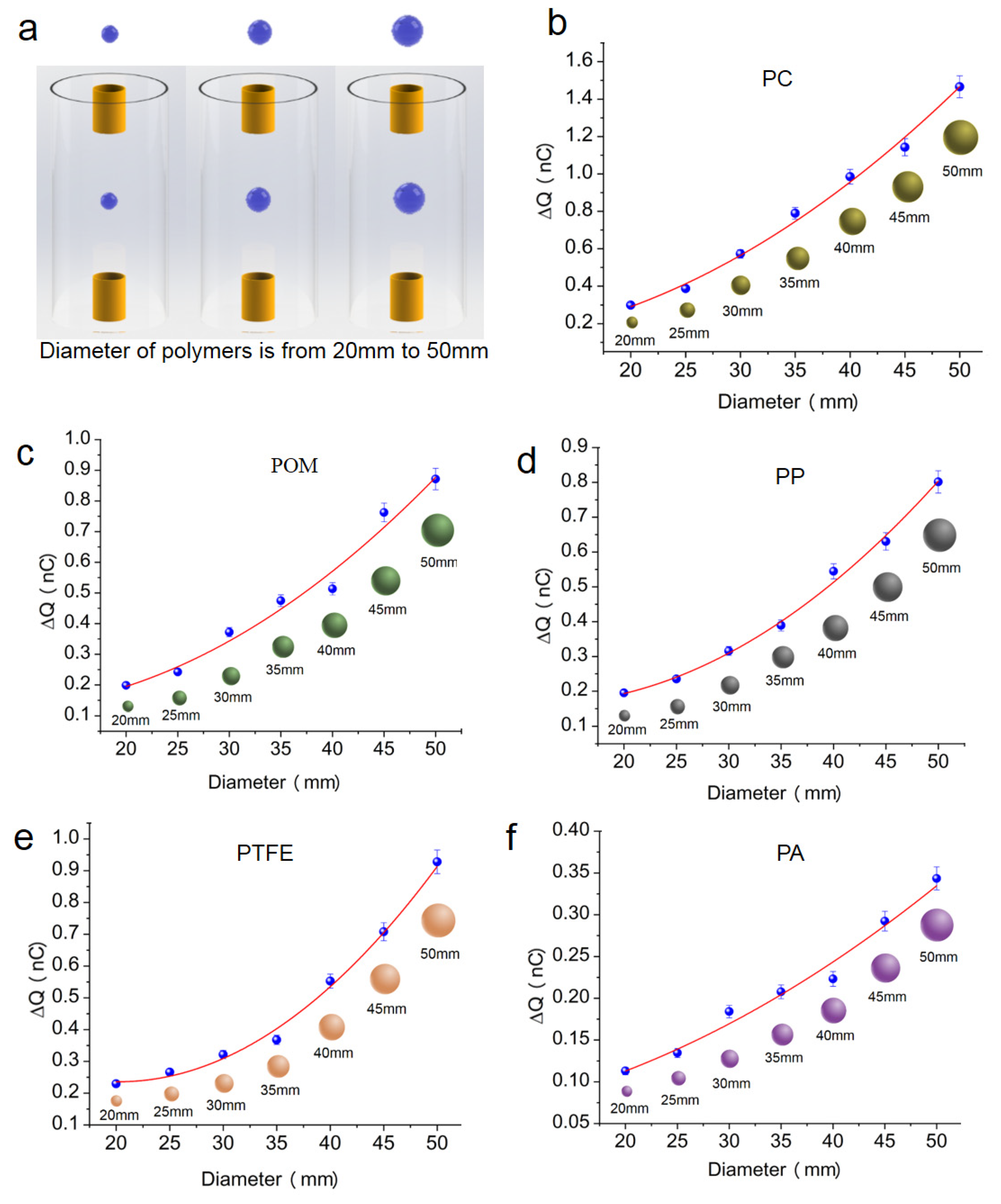
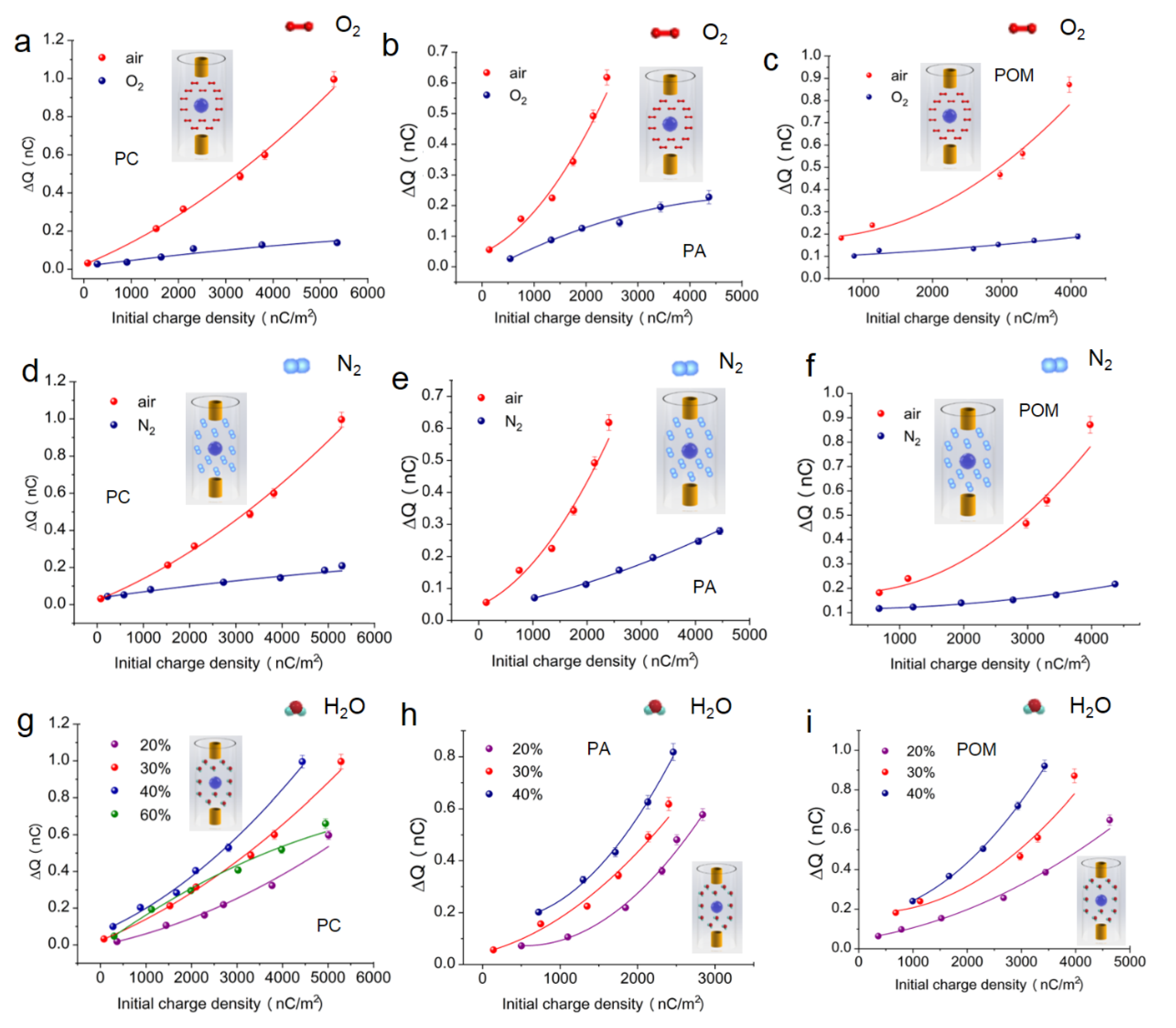
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, Z.; Xie, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhu, G.; Wang, Z.L. Enhanced Triboelectric Nanogenerators and Triboelectric Nano- sensor Using Chemically Modified TiO2 Nanomaterials. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 4554–4560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Cho, H.; Chun, J.; Kim, K.; Kim, S.; Ahn, C.; Kim, I.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.; Yang, C.; et al. Robust Nanogenerators Based on Graft Copolymers via Control of Dielectrics for Remarkable Output Power. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, 1602902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.; Bae, Y.; Moon, H.; Kim, J.; Choi, S.; Kim, Y.; Yoon, H.; Lee, M.; Nah, J. Formation of Triboelectric Series via Atomic-Level Surface Functionalization for Triboelectric Energy Harvesting. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 6131–6138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, F.R.; Tian, Z.Q.; Wang, Z.L. Flexible Triboelectric Generator! Nano Energy 2012, 1, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Bai, P.; Chen, J.; Jing, Q.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric nanogenerators as a new energy technology: From fundamentals, devices, to applications. Nano Energy 2015, 14, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric Nanogenerators as New Energy Technology for Self-Powered Systems and as Active Mechanical and Chemical Sensors. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 9533–9557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Xu, L.; Zhu, L.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.L. Electron Transfer in Nanoscale Contact Electrification: Photon Excitation Effect. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1901418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shao, T. Contact Electrification Between Polymers and Steel. J. Electrost. 2013, 71, 862–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, X.; Li, H.; Wang, F.; Hu, Y. First-Principles Investigations on the Contact Electrification Mechanism between Metal and Amorphous Polymers for Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2019, 63, 103864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, A.; Wijewardhana, K.R.; Song, J.K.J. Contact Electrification Efficiency Dependence on Surface Energy at the Water- Solid Interface. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 113, 023901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.; Lee, S.; Park, S.; Cho, H.; Hwang, W.; Kim, D. Energy Harvesting Model of Moving Water Inside a Tubular System and its Application of a Stick-Type Compact Triboelectric Nano- generator. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 2481–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Zhou, J.; Guo, W. Harvesting Energy from Water Flow over Graphene. Nano Lett. 2011, 12, 1736–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, S.; Seol, M.; Kim, D.; Park, S.; Choi, Y. Self-Powered ion Concentration Sensor with Triboelectricity from Liquid-Solid Contact Electrification. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2016, 2, 160006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, S.; Lin, S.; Lee, J.; Ryu, H.; Kim, T.; Zhong, H.; Chen, H.; Kim, S. Triboelectrification-Induced Large Electric Power Generation from a Single Moving Droplet on Graphene/Polytetra- fluoroethylene. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 7297–7302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; Hu, Z.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Du, T.; Zhang, S.L.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, T.; et al. A Triboelectric-Nanogenerator-Based Gas–Solid Two-Phase Flow Sensor for Pneumatic Conveying System Detecting. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2021, 6, 2001270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, D.; Yang, Y.; Mi, Q.; Zhang, J.; Yu, L. Multifunctional Latex/Polytetrafluoroethylene-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Self-Powered Organ-like MXene/Metal−Organic Framework-Derived CuO Nanohybrid Ammonia Sensor. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 2911–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, D.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Guo, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, W. Diversiform sensors and sensing systems driven by triboelectric and piezoelectric nanogenerators. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 427, 213597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Yang, Z.; Li, P.; Pang, M.; Xue, Q. Flexible self-powered high-performance ammonia sensor based on Audecorated MoSe2 nanoflowers driven by single layer MoS2-flake piezoelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2019, 65, 103974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Xu, Z.; Yang, Z.; Song, X. High performance flexible self-powered tin disulfide nanoflowers/reduced graphene oxide nanohybrid-based humidity sensor driven by triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2020, 67, 104251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Thangavel, G.; Wang, J.; Zhou, X.; Lee, P.S. Self-healable sticky porous elastomer for gas-solid interacted power generation. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabb4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Lin, S.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, H.; Duan, J.; Hu, B.; Zhou, J. Fiber-Based Energy Conversion Devices for Human-Body Energy Harvesting. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, e1902034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, K.; Tang, W.; Chen, J.; Luo, J.; Xu, L.; Wang, Z.L. Effects of Environmental Atmosphere on the Performance of Contact- Separation Mode TENG. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2018, 4, 1800569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Tang, W.; Lu, C.; Xu, L.; Yang, Z.; Chen, B.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Z.L. Characteristics of Triboelectrification on Dielectric Surfaces Contacted with a Liquid Metal in Different Gases. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 110, 201603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Xu, L.; Tang, W.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.L. Electron Transfer in Nano-Scale Contact Electrification: Atmosphere Effect on the Surface States of Dielectrics. Nano Energy 2019, 65, 103956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.L.; Lin, S.Q.; Tang, W.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.L. Effect of Redox Atmosphere on Contact Electrification of Polymers. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 17354–17364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schella, A.; Herminghaus, S.; Schröter, M. Influence of humidity on the tribo-electric charging and segregation in shaken granular media. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, C.; Tang, W.; Wang, Z. Probing Contact Electrification between Gas and Solid Surface. Nanoenergy Adv. 2023, 3, 1-11. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv3010001
Sun L, Wang Z, Li C, Tang W, Wang Z. Probing Contact Electrification between Gas and Solid Surface. Nanoenergy Advances. 2023; 3(1):1-11. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv3010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Linlin, Ziming Wang, Chengyu Li, Wei Tang, and Zhonglin Wang. 2023. "Probing Contact Electrification between Gas and Solid Surface" Nanoenergy Advances 3, no. 1: 1-11. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv3010001
APA StyleSun, L., Wang, Z., Li, C., Tang, W., & Wang, Z. (2023). Probing Contact Electrification between Gas and Solid Surface. Nanoenergy Advances, 3(1), 1-11. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv3010001









