Abstract
Energy harvesting from the ambient environment can be a beneficial and promising source for powering micro- and nanodevices. Triboelectric nanogenerator (TENG) technology has been proved to be a simple and cost-effective method to harness ambient mechanical energy. The performance of the TENG device mainly depends on the careful selection of the material pair. So far, metals and polymer materials have dominated TENG technology. Recently, there have been few reports on metal–organic framework (MoF)-based TENGs. MoFs are very interesting and offer excellent chemical and thermal stability, besides their unique properties, such as tunable pore size and high surface area. Herein, we report a zeolitic imidazole framework (ZIF-67)-based TENG device for self-powered device applications. We used ZIF-67 as one tribolayer, and PET and PMMA as opposite tribolayers. The output performance of the TENG device fabricated with the PMMA/ZIF-67 pair showed values of 300 V, 47.5 µA, and 593 mW/m2 of open-circuit voltage, short-circuit current, and power density, respectively. To the best of our knowledge, these are the highest reported values so far for ZIF-67-based TENG devices. The fabricated TENG device lit up 250 LEDs and was employed to explore different self-powered device applications.
1. Introduction
In recent years, new technologies that harvest energy from the ambient environment as clean and sustainable energy at a low frequency have attracted a lot of attention. The need for alternative energy sources has become extremely important with the increased usage of sensor systems, wireless networks, and IoT-based devices. In 2018, the IoT-based systems in use were estimated at 50 billion, and they are expected to reach around 200 billion by 2025 []. All these network systems use many sensors and electronic circuits for different applications, such as health monitoring, wearable sensors, and self-powered devices. The minimum required power in the range of microwatts is essential to operate these electronic items [,]. Therefore, the ideal solution for providing sustainable, green, portable self-power to these large-scale sensors is scavenging energy from the ambient surroundings with energy-harvesting technologies. Scavenging energy from the ambient environment not only reduces the use of a large number of batteries but also provides an alternative solution for the size constraints of micro- and nanoscale IoT-based devices [,]. Several mechanical energy-harvesting methods, such as piezoelectric, triboelectric, and electromagnetic nanogenerators, already exist in the literature. Among all, triboelectric nanogenerators have been proved to be a cost-effective, highly efficient, flexible, and portable technique for the cleanest and most sustainable energy source to power these devices. Z.L. Wang’s research group introduced the TENG concept in 2012 []. The TENG works with the coupled effect of contact electrification (triboelectrification) and the electrostatic induction phenomenon [,,]. In the triboelectrification process, charges are produced upon the physical contact between two dissimilar materials with opposite electron affinity []. Typical triboelectrification can only generate the accumulation of charges, but current is not generated, because there is no discharge process []. However, the TENG device uses the coupled effect of an electrostatic phenomenon with contact electrification to generate current. The triboelectric effect can be observed in a wide variety of materials, and there is no limitation on the material of choice. Therefore, researchers have been working on different suitable pairs of tribomaterials to generate maximum power efficiencies.
The search for new materials in TENG device design has recently grown considerably to improve the power density. The output performance parameters, such as voltage, short-circuit current, power density, and stability, are crucial parameters for optimizing a suitable TENG device. Currently, materials such as polymers and metals with known tribocharge density, dielectric constant, and other relevant parameters are widely used as triboelectric layers. However, these are just a small fraction of the existing materials []. The search for new materials gave surprising results, such as cellulose acetate, which was traditionally believed not to be a good tribomaterial until 2019 []. Other than cellulose, there are biopolymers [], natural materials [], bio-waste [], plant-based materials [], carbon-derived materials [], 2D-layered materials [], metal-oxide-based materials [], and metal–organic frameworks [] for exploring the energy-harvesting-based TENG devices. Among all the materials mentioned above, metal–organic framework (MoF)-based TENGs are not explored to their full potential in the literature. Recently, a large number of MoFs with zeolitic architectures have been successfully prepared as hybrid frameworks. Among them, zeolitic imidazole frameworks (ZIFs) have recently gained considerable attention due to their outstanding chemical and thermal stability. They possess a large surface area, an easily functional pore surface, adjustable pore size, and high crystallinity. ZIFs are a subclass of MoF materials with a special 3D network formed by coordination bonds between the metal ion (metal clusters) and an organic ligand. The unique properties of ZIFs have attracted numerous applications, such as gas storage, separation, liquid separation, catalysis, electrochemical sensing, storage, and battery applications [,,,,,]. Apart from direct applications, ZIFs are used as precursors and templates to derive functional and next-generation materials [,,,].
Researchers have started exploring energy-harvesting applications based on ZIFs. Khandelwal et al. reported ZIF-8-, ZIF-7-, ZIF-9-, ZIF-11-, ZIF-12-, and ZIF-62-based triboelectric nanogenerators [,,,]. G. Khandelwal et al. reported most of ZIF-based TENGs in the literature. In all the reports, ZIF films were created by attaching ZIF powder to the conducting glue placed on the aluminum substrate. The excess ZIF powder was removed using an argon air gun. Rayyan Ali et al. recently reported an MoF-5-based TENG device, and PTFE was used as an opposite triboelectric layer []. Chao Huang et al. reported a bimetallic Zn/Co-MoF-based TENG device with PVDF as a negative triboelectric layer []. Sugato Hajra et al. reported a ZIF-67-based TENG with different negative triboelectric layers, such as Teflon, PDMS, and paper []. They used a multi-unit S-shaped device prepared with ZIF-67 particles. The device with Teflon as another triboelectric layer showed a peak-to-peak output voltage of 118 V, a current of 1.7 μA, and a power density of about 150 mW/m2. The low output power density may have been due to the pressed ZIF-67 powder on the copper tape, and the pressed ZIF-67 film may have provided a less effective contact area during the TENG operation. Furthermore, the opposite triboelectric layer with ZIF-67 is also a crucial parameter in deciding the TENG performance.
The performances of TENG devices based on different MoFs are summarized in Table 1. In this work, we report a TENG device based on ZIF-67 as a positive triboelectric layer and PMMA as a negative triboelectric layer. To the best of our knowledge, this tribopair is reported for the first time. The novelty of the manuscript lies in the study of ZIF-67 and PMMA in TENG applications for the first time and in reporting the highest power density so far. The ZIF-67 and PMMA pair showed an outstanding power output and excellent stability. Compared with other reports, the simple ZIF-67- and PMMA-based TENG device showed an output voltage of 300 V, a current of 47.5 µA, and a power density of 593 mW/m2.

Table 1.
Comparison of ZIF-based TENG device performances reported in the literature.
The improvement in the output performance of the device may be attributed to the large surface area of the ZIF-67 thin film. We deposited ZIF-67 powder as a thin film on the aluminum substrate rather than using ZIF-67 powder directly as reported by Hazara et al. Thin-film deposition dramatically enhanced the surface characteristics and contact points for the electrification process and improved the device stability []. This manuscript adopted a cost-effective, straightforward, single-step approach for TENG fabrication compared with the existing complex and expensive 3D-printing-based ZIF-67 TENG devices reported. The obtained power density of the ZIF-67/PMMA-based TENG device is the highest so far among all ZIF-based devices.
In this work, ZIF-67-based TENGs were fabricated with a simple and cost-effective method. The fabricated TENGs were explored for self-powered device applications.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of ZIF-67 Powder
All the chemicals used for synthesizing the ZIF-67 metal–organic framework were purchased from Sigma Aldrich and used without further modification. We followed the ZIF-67 synthesis procedure reported in the literature []. To summarize, 450 mg of cobalt nitrate hexahydrate [Co(NO3)2·6H2O] was first dissolved in 3 mL of deionized water, which we labeled solution 1. Solution 2 was independently prepared by dissolving 5.5 g of 2-methylimidazole (Hmim) in 20 mL of deionized water. These two solutions were vigorously mixed for 6 h at room temperature; then, the resultant purple-colored precipitate was collected after centrifuging at 8000 rpm and washed carefully with water and methanol three times. Finally, the precipitant was vacuum-dried at 80 °C for 24 h to obtain ZIF-67 powder. The detailed procedure of ZIF-67 powder synthesis is depicted in Figure 1a.
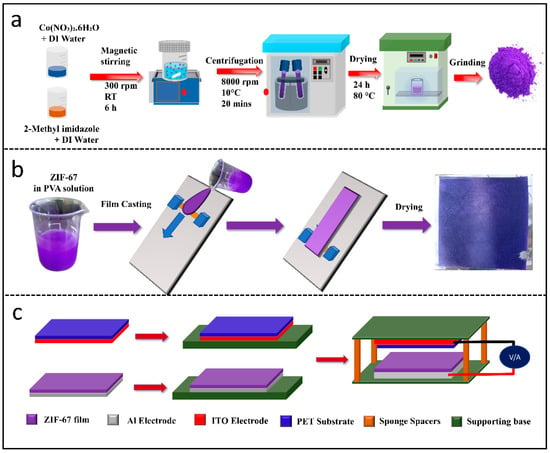
Figure 1.
(a) Synthesis steps of ZIF-67 powder, (b) ZIF-67 film preparation steps using doctor blade method, (c) TENG device fabrication steps.
2.2. Preparation of ZIF-67 Films
ZIF-67 was deposited on aluminum (Al) substrate using the doctor blade coating technique. Before the deposition of ZIF-67, the Al substrate was cleaned with acetone and deionized water in an ultrasonication bath for 5 min. The as-prepared ZIF-67 powder was mixed (0.2 g) in Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) (5 mL), and the mixture was stirred continuously for one hour to obtain a homogeneous solution. The mixed solution was initially dropped on the Al substrate, and a spreader was driven through the solution at a blade speed of 30 mm/sec to obtain ZIF-67 thin films on the Al substrate. The schematic of the film preparation, actual photographs of the ZIF-67 solution dissolved in PVA, and ZIF-67 thin film on Al substrate are shown in Figure 1b.
2.3. Characterization of ZIF-67
The obtained ZIF-67 powder was characterized using X-ray diffraction (XRD; Bruker D8), and the surface functional groups were confirmed with FTIR spectroscopy (FTIR Bruker alpha II); the morphology of ZIF-67 was studied using scanning electron microscopy (SEM, ZEISS), and the thickness of ZIF-67 was measured using an optical microscope (Olympus BX53).
2.4. Fabrication of TENG Device
The schematic of TENG device fabrication is shown in Figure 1c. The aluminum and ITO substrates were used for the top and bottom electrodes. The ZIF-67 film on the Al substrate and the PET surface of ITO/PET substrate were used as two frictional layers and attached to a cardboard/acrylic base, as shown in Figure 1c. Four sponge spacers were placed between the supporting bases to maintain the distance of ~ 1cm between the frictional layers. The overall structure of the TENG device was Al/ZIF-67/PET/ITO. The output voltage of the TENG device was recorded using a digital oscilloscope (Tektronix TBS1102) with the aid of interface software (Tekvisa) using a computer. The short-circuit current of the TENG was measured using a low-noise current amplifier (Stanford Research SR570). The TENG device was tested at a hand-tapping frequency of ~3–4 Hz. Furthermore, we investigated the effect of hand-tapping frequency, different dimensions of the device, and different frictional layers while keeping ZIF-67 constant on the TENG performance. Finally, the stability and durability of the TENG devices were tested over a long period and with a large number of test cycles.
3. Results and Discussion
The crystalline and structural properties of as-prepared ZIF-67 film were characterized with XRD studies, and the corresponding XRD spectrum is shown in Figure 2a. The sharp and highly intense peaks suggest the highly crystalline nature of the synthesized ZIF-67. The experimental data were fitted with the Rietveld refinement method using Full-Prof software by assuming the cubic crystal structure to have a space group of I3 m. The refined lattice and Rietveld parameters are given in Table S1 (see Supplementary Information (SI), S1). The observed crystal structure was in single-phase formation, and no impurity phases were detected. The obtained ZIF-67 film XRD pattern was consistent with those in the previously reported literature [,,].
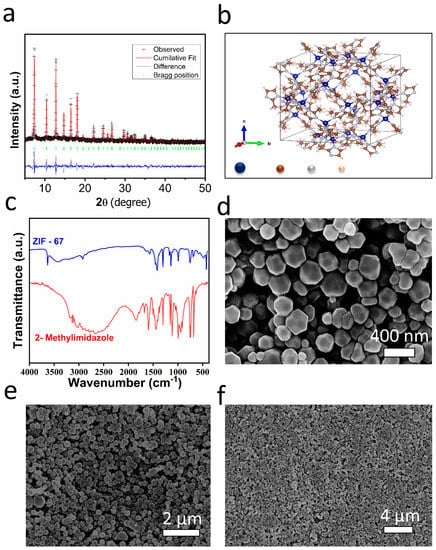
Figure 2.
(a) XRD studies of ZIF-67 and Rietveld refinement analysis, (b) simulated ZIF-67 structure, (c) FTIR spectrum of ZIF-67 crystal, and (d–f) SEM images of synthesized ZIF-67 at high and low magnifications.
The as-synthesized ZIF-67 and organic linker 2-methyl imidazole (MIM) were characterized with FTIR to determine the material’s chemical composition and bonding information and are presented in Figure 2b. The peak observed in the MIM spectrum at 1842 cm−1 was due to the -N-H group; the same was absent in the ZIF-67 spectra, strongly suggesting the successful coordination of Co and the -N-H group of MIM []. Moreover, a broad peak ranging from 3400 cm−1 to 2200 cm−1 centered at 2600 cm−1 was attributed to the presence of the N-H-N hydrogen bond. The FTIR spectrum of ZIF-67 showed the absence of the broad hump, also confirming ZIF-67 structure formation and the completely deprotonated MIM linkers []. The intense bands ranging from 1300 cm−1 to 1500 cm−1 were attributed to the characteristic imidazole ring stretching. The peaks appearing at 1596 cm−1 and 757 cm−1 were attributed to the C = N stretching vibrations and out-of-plane bending modes, respectively []. The new absorption peak arising at 426 cm−1 attributed to the Co-N stretching vibration of ZIF-67 was consistent with the previously reported literature results []. Figure 2d–f show the surface morphology of as-synthesized ZIF-67 film at high and low magnifications. The sphere-shaped ZIF-67 particles were observed uniformly all over the substrate. The observed morphology of ZIF-67 particles was similar to the reported literature results [,].
The mechanical energy conversion of the fabricated TENG (10 × 10 cm2) was tested against hand tapping. The TENG device size was 10 × 10 cm2; the spacing between the two triboelectric layers was maintained at 1 cm, and the tapping frequency was maintained at ~3–4 Hz. Figure 3a,b show the open-circuit output voltage and short-circuit current of a ZIF-67-based TENG device in the switching polarity test. In the switching polarity test, the TENG device connections were interchanged at the input of the measuring instrument to confirm whether the response came from the device or instrument noise [,]. It is clear from Figure 3a,b that the electrical output came from the TENG device. The TENG device generated the average voltage and current of ~100 V and ~35 μA, respectively, in both forward and reversed connections. The working mechanism of the ZIF-67-based TENG in vertical contact separation mode is presented in Supplementary Information S2. The TENG device electrical output was recorded for different load resistance values to find out the maximum power density. The behaviors of the TENG output voltage and current are presented in Figure 3c. The output voltage increased with the increase in load resistance and saturated after 60 MΩ. This behavior was consistent with the other reported literature results [,,]. At the same time, the current decreased with the increase in the external load due to ohmic losses. Furthermore, the instantaneous power density was calculated from Figure 3c and presented in Figure 3d. The instantaneous power density was calculated using the P = (VI/A) formula, where I = current, V = voltage, and A = active area of the device [,,]. Initially, the instantaneous power density increased with load resistance and reached the maximum value of ~81.9 mW/m2 at a 4 MΩ load resistance and then decreased at greater load resistances. The observed maximum instantaneous power density at 4 MΩ load resistance can be understood with the maximum power transfer theorem [,]. When the TENG device’s internal resistance matched the load resistance, it exhibited the maximum power density. The stability of the TENG device was tested for 15,000 cycles using a linear motor at a tapping frequency of ~4 Hz. The stability of the device was tested continuously for 60 min with the linear motor (1 min, ~240 cycles). The response of the TENG device was recorded every 10th min for 1 h, and the results are presented in Figure 4a (see Supplementary Video, S1). The TENG output voltage exhibited a stable response for 15,000 cycles, showing the device’s exceptional durability and mechanical stability.
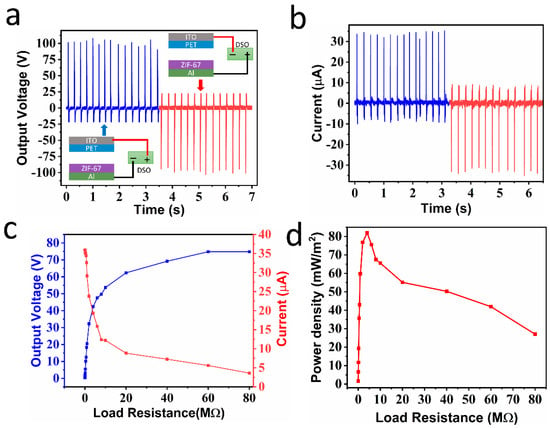
Figure 3.
(a) Forward and reverse current, (b) forward and reverse voltage, (c) voltage and current response at different external loads, and (d) power density vs. load resistance of the TENG device (all the measurements were recorded considering a device area of 10 × 10 cm2).
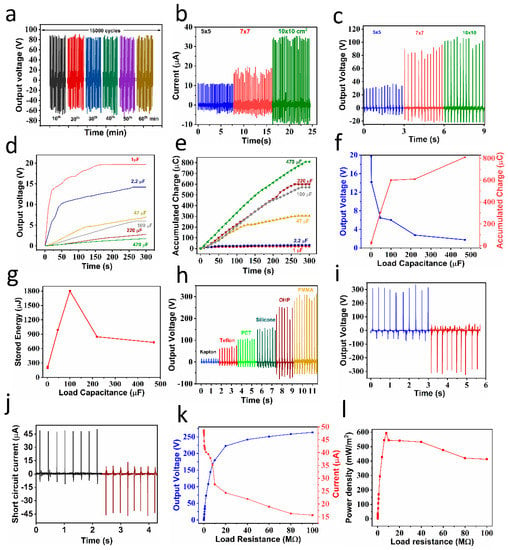
Figure 4.
Stability of the TENG device (10 × 10 cm2): (a) TENG electrical characteristics with different sizes of the frictional layer, (b) short-circuit current, (c) open-circuit voltage, (d) charging curves for different capacitors, (e) stored charge curves of different load capacitors as a function of time, (f) output voltage and stored charges behavior as a function of the load capacitance, (g) the maximum stored energy as a function of the load capacitance, (h) output voltage response of TENG device with different top triboelectric layers and ZIF-67 as the bottom triboelectric layer (Al/ZIF-67/PMMA/Al TENG device), (i) output voltage response, (j) output current response, (k) voltage and current response with load resistant variation, and (l) power density variation with different load resistance (all the measurements were recorded considering a device area of 10 × 10 cm2).
The device’s effective size (size of frictional layers) plays a vital role in the output performance of a TENG device. We chose three sizes for the TENG device: 5 × 5, 7 × 7, and 10 × 10 cm2 (effective area). The short-circuit current and open-circuit output voltages increased with the device size, as shown in Figure 4b,c. The current value increased from ~10.5 μA to ~35 μA, and the voltage increased from 35 V to 100 V. The increase in the current and voltage was attributed to the enhanced contact area. The increase in the contact area produced a greater triboelectrification of charges, which resulted in greater current and voltage. The behavior of TENGs with the different active areas is well supported by the reported literature [,,]. It is necessary to convert the AC output of a TENG to the DC output to store in a capacitor. We used an IC DB 107 full-wave rectifier to convert the AC output into the DC output and charged different load capacitors with the continuous operation of the TENG for 5 min. Figure 4d illustrates the charging voltage curves of different load capacitors (CL) of 1 µF, 2.2 µF, 47 µF, 100 µF, 220 µF, and 470 µF. We investigated the stored voltage, charge, and energy as a function of different load capacitors. As shown in Figure 4d, the 1 μF capacitor showed excellent charging capability, and it charged up to 13.4 V within 20 s and then increased slowly to the saturated voltage of 19.7 V in 220 sec, a behavior which is in agreement with earlier reports [,,]. With a smaller CL, the charging pace was faster, and the time until the voltage reached saturation was shorter. The charge stored on these varied capacitors was estimated by multiplying the charged voltage (V) by the capacitance (CL), and the results are presented in Figure 4e. In Figure 4f, the values of charged voltage and stored charge are illustrated as functions of various load capacitance values. With respect to the load capacitor, the behavior of charged voltage and stored charge was opposite in nature. Furthermore, we calculated the energy stored in the capacitors as follows: The variation in the maximum stored energy as a function of CL is shown in Figure 4g. At an optimum load capacitance (CL) of 100 µF, the maximum stored energy was found to be around 1800 µJ.
Furthermore, different TENG devices were prepared by keeping ZIF-67 as one constant triboelectric layer, and other triboelectric layers such as Kapton, Teflon, Silicone, and overhead projector (OHP) PET, and PMMA sheets were selected. Figure 4h shows the output voltages of the fabricated TENG devices with different triboelectric layers in combination with ZIF-67. It was observed that PMMA showed the highest output voltage (~300 V) with ZIF-67 as a triboelectric pair. Furthermore, we studied the electrical characteristics of the best TENG device (ZIF-67-PMMA) and explored its different applications. The open-circuit output voltage and short-circuit current of Al/ZIF-67/PMMA/Al was tested by switching the polarity of the geometry, and we found the same response as shown in Figure 4i,j, respectively. Furthermore, the TENG load characteristics and instantaneous power density are presented in Figure 4k,l. The highest power density of 593 mW/m2 at 8 MΩ was observed, and it is the highest reported value so far for a metal–organic-framework-based TENG device to the best of our knowledge (Table 1). The highest power density may have been due to the triboelectric pair of ZIF-67 and PMMA. The power density of the TENG strongly depended on the triboelectric pair selection, which is evidenced in Figure 4h. Triboelectric films with a large work function difference can be expected to have a higher power density [,]. In addition to the above, the effective contact area between triboelectric films plays a significant role in deciding the TENG performance [,,].
4. Applications of the TENG (ZIF-67-PMMA)
Self-powered electronic device applications were explored with the TENG (ZIF-67/PMMA). Figure 5a,b show the photographs of portable electronic devices (calculator, digital watch, and digital thermometer), a series connected 250 LEDs, an electroluminescence (EL) device, and a commercial hygrometer connected to the TENG in the OFF and ON conditions, respectively. The electroluminescence (EL) device was fabricated with the help of two conducting tin-doped indium oxide electrodes used for contact, and luminescent active materials (ZnS-Cu, Al) were sandwiched between two ITO electrodes. The output of the TENG was sufficient to turn on the calculator, the digital watch, the digital thermometer, the connected series of 250 LEDs, and the EL device (see Supplementary Information Videos S2–S4). However, the hygrometer was not turned on with the TENG output due to the high power required by a large LCD. We stored energy provided by the TENG in a capacitor, which was used to switch on the hygrometer (see Supplementary Information Video S6).
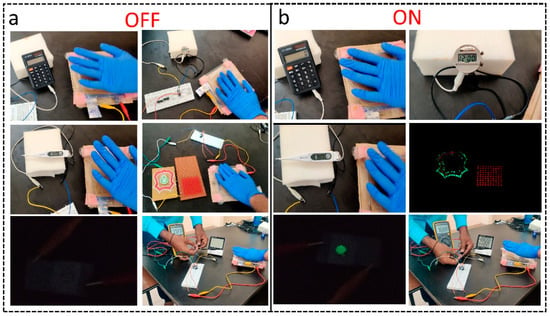
Figure 5.
Photographs of the various portable devices, EL device, and hygrometer powered with the ZIF-67-based TENG: (a) OFF state and (b) ON state.
5. Conclusions
This work presents high-performance ZIF-67-based TENGs and their application in self-powered devices. The best TENG device consisted of ZIF-67 and PMMA as triboelectric layers, and it exhibited an output voltage of ~300 V and a 47.5 μA short-circuit current. The highest power density of 593 mW/m2 was reported in this manuscript, which is the highest among the ZIF-based TENGs reported so far. The fabricated device could switch on different portable electronic devices without any storage element. The power density of the TENG could be further enhanced with the help of different surface modification methods. The present work involves a simple, cost-effective design that can easily be scaled to large areas.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/nanoenergyadv2040015/s1, Table S1: The Rietveld refined lattice parameters of ZIF-67 and Rp, Rwp, and the goodness-of-fit (χ2) values of the fitting, Video S1: Operation of a calculator with the output power of the ZIF-67-based TENG device, Video S2: Operation of a digital watch with the output power of the ZIF-67-based TENG device, Video S3: Operation of a thermometer with the output power of the ZIF-67-based TENG device, Video S4: Lighting of 250 LEDs with the output power of the ZIF-67-based TENG device, Video S5: Operation of an electroluminescence device with the output power of the ZIF-67-based TENG device, Video S6: Operation of a digital hygrometer with the output power of the ZIF-67-based TENG device. Figure S1: Schematic illustration of the working mechanism of TENG.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, U.K.K. and R.K.R.; methodology, S.B., A.B., S.P., N.M., U.K.K., and R.K.R.; validation, N.M., S.M., R.N., and T.C.; formal analysis, S.B., A.B., S.P., S.M., and N.M.; investigation, S.B., A.B., S.P., S.M., and N.M.; resources, R.N., T.C., H.D., and P.K.; data curation, A.B., S.P., N.M., and S.M.; writing—original draft preparation, S.B., A.B., S.P., and R.N.; writing—review and editing, U.K.K., R.K.R., P.K., and H.D.; visualization, S.M., R.N., T.C., and P.K.; supervision, U.K.K., R.K.R., and H.D.; project administration, U.K.K. and R.K.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research study received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article and Supplementary Materials.
Acknowledgments
In this section, the authors are thankful to T. Venkatappa Rao for offering the use of a facility to use the automatic film coater.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Burhan, M.; Rehman, R.A.; Khan, B.; Kim, B.S.; Elements, I. Layered Architectures and Security Issues: A Comprehensive Survey. Sensors 2018, 18, 2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Jie, Y.; Wang, N.; Wang, Z.L.; Cao, X.; Jie, Y.; Wang, N.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric Nanogenerators Driven Self-Powered Electrochemical Processes for Energy and Environmental Science. Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 6, 1600665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Shen, M.; Cui, X.; Shao, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y. Triboelectric nanogenerator based self-powered sensor for artificial intelligence. Nano Energy 2021, 84, 105887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Wu, F.; Shi, Q.; Lee, C.; Yuce, M.R. Yuce, Sensors and Control Interface Methods Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerator in IoT Applications. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 92745–92757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Hassan, I.; El-Kady, M.F.; Radhi, A.; Jeong, C.K.; Selvaganapathy, P.R.; Zu, J.; Ren, S.; Wang, Q.; Kaner, R.B. Integrated Triboelectric Nanogenerators in the Era of the Internet of Things. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1802230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, F.R.; Tian, Z.Q.; Wang, Z.L. Flexible triboelectric generator. Nano Energy 2012, 1, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willatzen, M.; Wang, Z.L. Theory of contact electrification: Optical transitions in two-level systems. Nano Energy 2018, 52, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Wang, A.C. On the origin of contact-electrification. Mater. Today 2019, 30, 34–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Zi, Y.; Wang, A.C.; Zou, H.; Dai, Y.; He, X.; Wang, P.; Wang, Y.C.; Feng, P.; Li, D.; et al. On the Electron-Transfer Mechanism in the Contact-Electrification Effect. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1706790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowell, J.; Rose-Innes, A.C. Advances in Physics Contact electrification Contact electrification. Adv. Phys. 1980, 296, 947–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Olin, H. Material choices for triboelectric nanogenerators: A critical review. EcoMat 2020, 2, e12062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Dahlström, C.; Zou, H.; Jonzon, J.; Hummelgård, M.; Örtegren, J.; Blomquist, N.; Yang, Y.; Andersson, H.; Olsen, M.; et al. Cellulose-Based Fully Green Triboelectric Nanogenerators with Output Power Density of 300 W m−2. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2002824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Fan, F.R.; Xi, Y.; Wu, W. Bio-Derived Natural Materials Based Triboelectric Devices for Self-Powered Ubiquitous Wearable and Implantable Intelligent Devices. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2020, 4, 2000108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slabov, V.; Kopyl, S.; Santos, M.P.S.d.; Kholkin, A.L. Natural and Eco-Friendly Materials for Triboelectric Energy Harvesting. Nano-Micro Lett. 2020, 12, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaukat, R.A.; Saqib, Q.M.; Khan, M.U.; Chougale, M.Y.; Bae, J. Bio-waste sunflower husks powder based recycled triboelectric nanogenerator for energy harvesting. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, A.; Rakesh, D.; Supraja, P.; Mishra, S.; Kumar, K.U.; Kumar, R.R.; Haranath, D.; Mamidala, E.; Nagapuri, R. Plant-based triboelectric nanogenerator for biomechanical energy harvesting. Results Surfaces Interfaces 2022, 8, 100075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabris, M.A.; Ping, J. Carbon nanomaterial-based nanogenerators for harvesting energy from environment. Nano Energy 2021, 90, 106494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seol, M.; Kim, S.; Cho, Y.; Byun, K.E.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, S.W.; Shin, H.J.; Park, S. Triboelectric Series of 2D Layered Materials. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1801210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Lee, J.; Park, S.; Park, C.; Park, C.; Choi, H.J. Effect of the relative permittivity of oxides on the performance of triboelectric nanogenerators. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 49368–49373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandelwal, G.; Chandrasekhar, A.; Raj, N.P.M.J.; Kim, S.J. Metal–Organic Framework: A Novel Material for Triboelectric Nanogenerator–Based Self-Powered Sensors and Systems. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1970043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, A.E.; Burns, D.A.; Liu, B.; Thoi, V.S. Metal-organic framework functionalization and design strategies for advanced electrochemical energy storage devices. Commun. Chem. 2019, 2, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leus, K.; Muylaert, I.; van Speybroeck, V.; Marin, G.B.; van der Voort, P. A coordinative saturated vanadium containing metal organic framework that shows a remarkable catalytic activity. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 2010, 175, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Zhou, S.; Guo, L.; Xin, X.; Zeng, S.; Qu, K.; Wang, N.; Zhang, X. Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework 67-Derived Ce-Doped CoP@N-Doped Carbon Hollow Polyhedron as High-Performance Anodes for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Crystals 2022, 12, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Bie, S.; Zhang, J.; Ke, X.; Wang, X.; Liang, J.; Wu, N.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, C.; Jia, Y. In Situ Construction of ZIF-67-Derived Hybrid Tricobalt Tetraoxide@Carbon for Supercapacitor. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H. Sensitive and Stable Electrochemical Sensor for Folic Acid Determination Using a ZIF-67/AgNWs Nanocomposite. Biosensors 2022, 12, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, G.; Ji, M.; Li, Z.; Yang, Z.; Qiu, X.; Zhao, Y. Electrospinning of ZIF-67 Derived Co-C-N Composite Efficiently Activating Peroxymonosulfate to Degrade Dimethyl Phthalate. Water 2022, 14, 2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, H.T.; Tran, L.T.; Le, G.H.; Nguyen, Q.K.; Vu, T.M.; Vu, T.A. Synthesis and application of novel Fe-MIL-53/GO nanocomposite for photocatalytic degradation of reactive dye from aqueous solution. Vietnam J. Chem. 2019, 57, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, F.; Hu, X.; Li, Z.; Qie, L.; Hu, C.; Zeng, R.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, Y. MOF-derived porous ZnO/ZnFe2O4/C octahedra with hollow interiors for high-rate lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 6622–6628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.Y.; Dai, S.; Jaroniec, M.; Qiao, S.Z. Metal-organic framework derived hybrid Co3O4-carbon porous nanowire arrays as reversible oxygen evolution electrodes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 13925–13931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Tan, C.; Sindoro, M.; Zhang, H. Hybrid micro-/nano-structures derived from metal–organic frameworks: Preparation and applications in energy storage and conversion. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 2660–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandelwal, G.; Raj, N.P.M.J.; Kim, S.J. Zeolitic Imidazole Framework: Metal–Organic Framework Subfamily Members for Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandelwal, G.; Raj, N.P.M.J.; Vivekananthan, V.; Kim, S.J. Biodegradable metal-organic framework MIL-88A for triboelectric nanogenerator. iScience 2021, 24, 102064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khandelwal, G.; Raj, N.P.M.J.; Kim, S.J. ZIF-62: A mixed linker metal-organic framework for triboelectric nanogenerators. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 17817–17825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaukat, R.A.; Saqib, Q.M.; Kim, J.; Song, H.; Khan, M.U.; Chougale, M.Y.; Bae, J.; Choi, M.J. Ultra-robust tribo- and piezo-electric nanogenerator based on metal organic frameworks (MOF-5) with high environmental stability. Nano Energy 2022, 96, 107128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Shao, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Xue, X.; Song, H.; Wu, Z.; Cui, S.; Zhang, L.; Huang, C.; Mi, L.; et al. Metal-Ion Coupling in Metal–Organic Framework Materials Regulating the Output Performance of a Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Inorg. Chem. 2022, 61, 2490–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajra, S.; Sahu, M.; Padhan, A.M.; Swain, J.; Panigrahi, B.K.; Kim, H.G.; Bang, S.W.; Park, S.; Sahu, R.; Kim, H.J. A new insight into the ZIF-67 based triboelectric nanogenerator for self-powered robot object recognition. J. Mater. Chem. C Mater. 2021, 9, 17319–17330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.K.; Jeong, U. Material aspects of triboelectric energy generation and sensors. NPG Asia Mater. 2020, 12, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajra, S.; Sahu, M.; Sahu, R.; Padhan, A.M.; Alagarsamy, P.; Kim, H.-G.; Lee, H.; Oh, S.; Yamauchi, Y.; Kim, H.J. Significant effect of synthesis methodologies of metal-organic frameworks upon the additively manufactured dual-mode triboelectric nanogenerator towards self-powered applications. Nano Energy 2022, 98, 107253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajra, S.; Sahu, M.; Padhan, A.M.; Lee, I.S.; Yi, D.K.; Alagarsamy, P.; Nanda, S.S.; Kim, H.J. A Green Metal–Organic Framework-Cyclodextrin MOF: A Novel Multifunctional Material Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Highly Efficient Mechanical Energy Harvesting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2101829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Sun, F.; Qin, L. Hydrothermal synthesis of zeolitic imidazolate framework-67 (ZIF-67) nanocrystals. Mater. Lett. 2012, 82, 220–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Xiong, Z.; Chen, X. Selective and Competitive Adsorption of Azo Dyes on the Metal–Organic Framework ZIF-67. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Carreon, M.A. Kinetics of transformation on ZIF-67 crystals. J. Cryst. Growth. 2015, 418, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, H.N. Zeolitic imidazolate frameworks (ZIF-8, ZIF-67, and ZIF-L) for hydrogen production. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2021, 35, e6319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Liu, J.; Guo, C.; Gao, X.; Gong, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, B.; Li, X.; Gurzadyan, G.G.; Sun, L. Metal–organic frameworks (ZIF-67) as efficient cocatalysts for photocatalytic reduction of CO2: The role of the morphology effect. J. Mater. Chem. A Mater. 2018, 6, 4768–4775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, U.P.N.; Le, K.K.A.; Phan, N.T.S. Expanding applications of metal-organic frameworks: Zeolite imidazolate framework zif-8 as an efficient heterogeneous catalyst for the knoevenagel reaction. ACS Catal. 2011, 1, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gao, X.; Ai, L.; Jiang, J. Mechanistic insight into the interaction and adsorption of Cr(VI) with zeolitic imidazolate framework-67 microcrystals from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 274, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, A.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, M.; Yang, H.; Hou, Y. Surface modification of core–shell structured ZIF-67@Cobalt coordination compound to improve the fire safety of biomass aerogel insulation materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 430, 132809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Li, J.; Ma, R.; He, J.; Song, X.; Yu, Y.; Quan, Y.; Wang, G. The methodologically obtained derivative of ZIF-67 metal–organic frameworks present impressive supercapacitor performance. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 7230–7241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Xing, T.; Lou, Y.; Chen, J. Controlling ZIF-67 crystals formation through various cobalt sources in aqueous solution. J. Solid State Chem. 2016, 235, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivekananthan, V.; Chandrasekhar, A.; Alluri, N.R.; Purusothaman, Y.; Kim, S.J. A highly reliable, impervious and sustainable triboelectric nanogenerator as a zero-power consuming active pressure sensor. Nanoscale Adv. 2020, 2, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supraja, P.; Kumar, R.R.; Mishra, S.; Haranath, D.; Sankar, P.R.; Prakash, K.; Jayarambabu, N.; Rao, T.V.; Kumar, K.U. A simple and low-cost triboelectric nanogenerator based on two dimensional ZnO nanosheets and its application in portable electronics. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2022, 335, 113368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Liu, T.; Wu, J.; Xu, T.; Wang, X.; Han, X.; Cui, H.; Xu, X.; Pan, C.; Li, X. Energy Conversion Analysis of Multilayered Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Synergistic Rain and Solar Energy Harvesting. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2202238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric nanogenerators as flexible power sources. Npj Flex. Electron. 2017, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.T.; Vo, C.P.; Nguyen, T.H.; Ahn, K.K. A Direct-Current Triboelectric Nanogenerator Energy Harvesting System Based on Water Electrification for Self-Powered Electronics. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.W.; Huynh, N.D.; Kim, W.; Hwang, H.J.; Hong, H.; Choi, K.H.; Song, A.; Chung, K.B.; Choi, D. Effects of embedded TiO2-x nanoparticles on triboelectric nanogenerator performance. Micromachines 2018, 9, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Shi, Q.; Li, K.; Yang, Z.; Liu, H.; Sun, L.; Dziuban, J.A.; Lee, C. Investigation of position sensing and energy harvesting of a flexible triboelectric touch pad. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Lyu, Z.; Kim, D.H.; Kang, D.J. Enhancing the output power density of polydimethylsiloxane-based flexible triboelectric nanogenerators with ultrathin nickel telluride nanobelts as a co-triboelectric layer. Nano Energy 2021, 90, 106536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wu, W.; Song, G. Theoretical System of Contact-Mode Triboelectric Nanogenerators for High Energy Conversion Efficiency. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, S.; Wang, Z.L. Theoretical systems of triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2015, 14, 161–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamilya, T.; Sarkar, P.K.; Acharya, S. Unveiling Peritoneum Membrane for a Robust Triboelectric Nanogenerator. ACS Omega. 2019, 4, 17684–17690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, M.; Li, W.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhai, Y. Size effect on the output of a miniaturized triboelectric nanogenerator based on superimposed electrode layers. Nano Energy 2017, 41, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Han, W.; Jiang, Y.; Ding, Q.; Li, X.; Zhao, X.; Li, Z. Punching pores on cellulose fiber paper as the spacer of triboelectric nanogenerator for monitoring human motion. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 2851–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Guo, L.; Xue, H.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, P.; He, X.; Dai, G.; Jiang, P.; et al. Quantifying and understanding the triboelectric series of inorganic non-metallic materials. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, L.; Wang, P.; He, X.; Dai, G.; Zheng, H.; Chen, C.; Wang, A.C.; Xu, C.; et al. Quantifying the triboelectric series. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seung, W.; Gupta, M.K.; Lee, K.Y.; Shin, K.S.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, T.Y.; Kim, S.; Lin, J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.W. Nanopatterned textile-based wearable triboelectric nanogenerator. ACS Nano. 2015, 9, 3501–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.K.; Ke, K.H. High contact surface area enhanced Al/PDMS triboelectric nanogenerator using novel overlapped microneedle arrays and its application to lighting and self-powered devices. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 508, 145310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tcho, I.W.; Kim, W.G.; Jeon, S.B.; Park, S.J.; Lee, B.J.; Bae, H.K.; Kim, D.; Choi, Y.K. Surface structural analysis of a friction layer for a triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2017, 42, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).