Effect of KCl Addition on First Hydrogenation Kinetics of TiFe
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
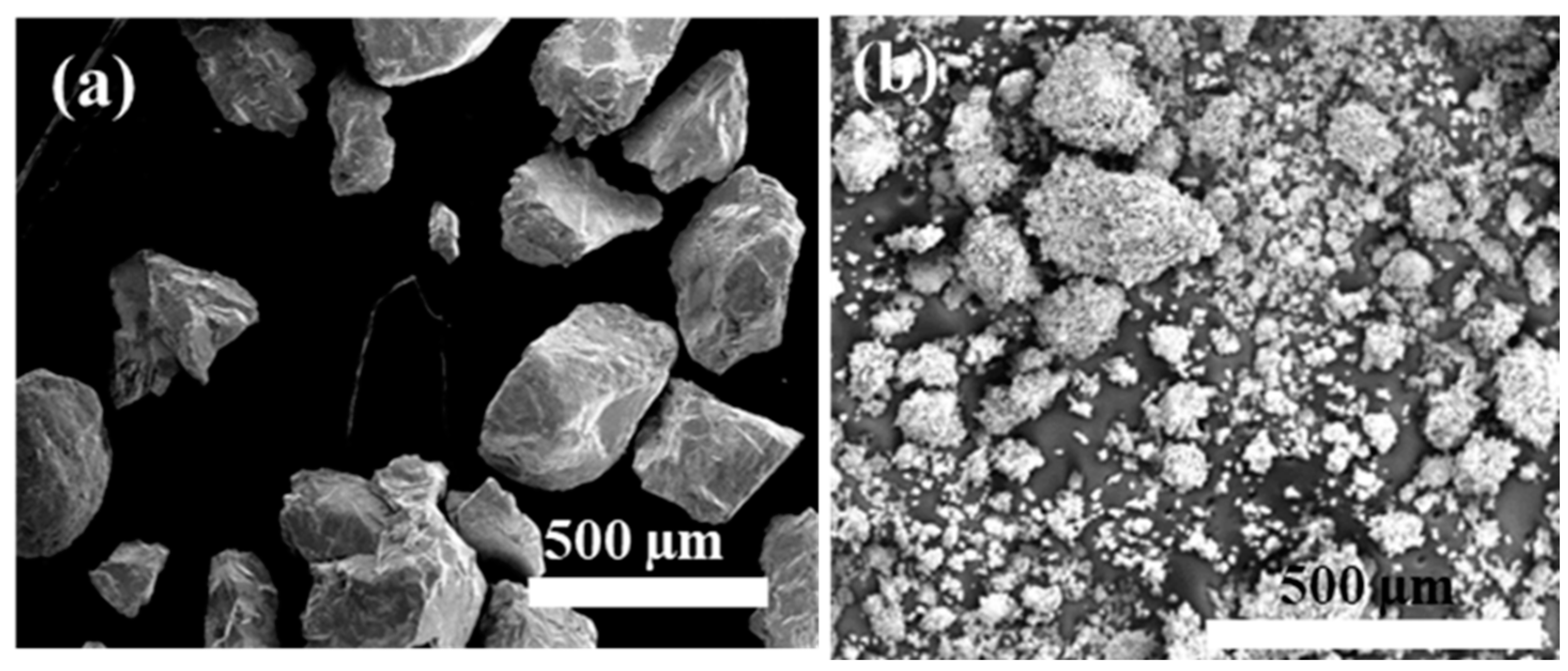
3.1. Characterization
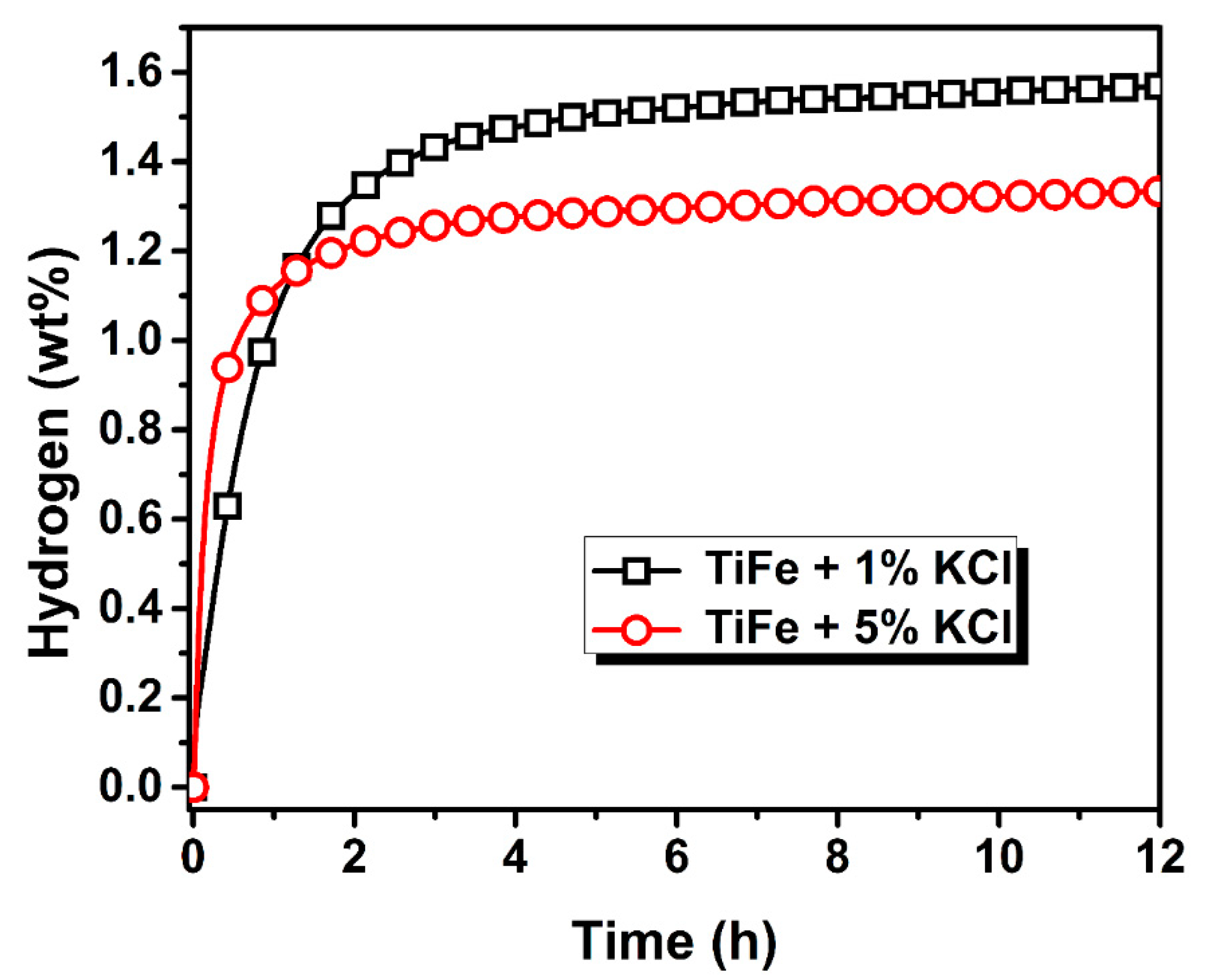
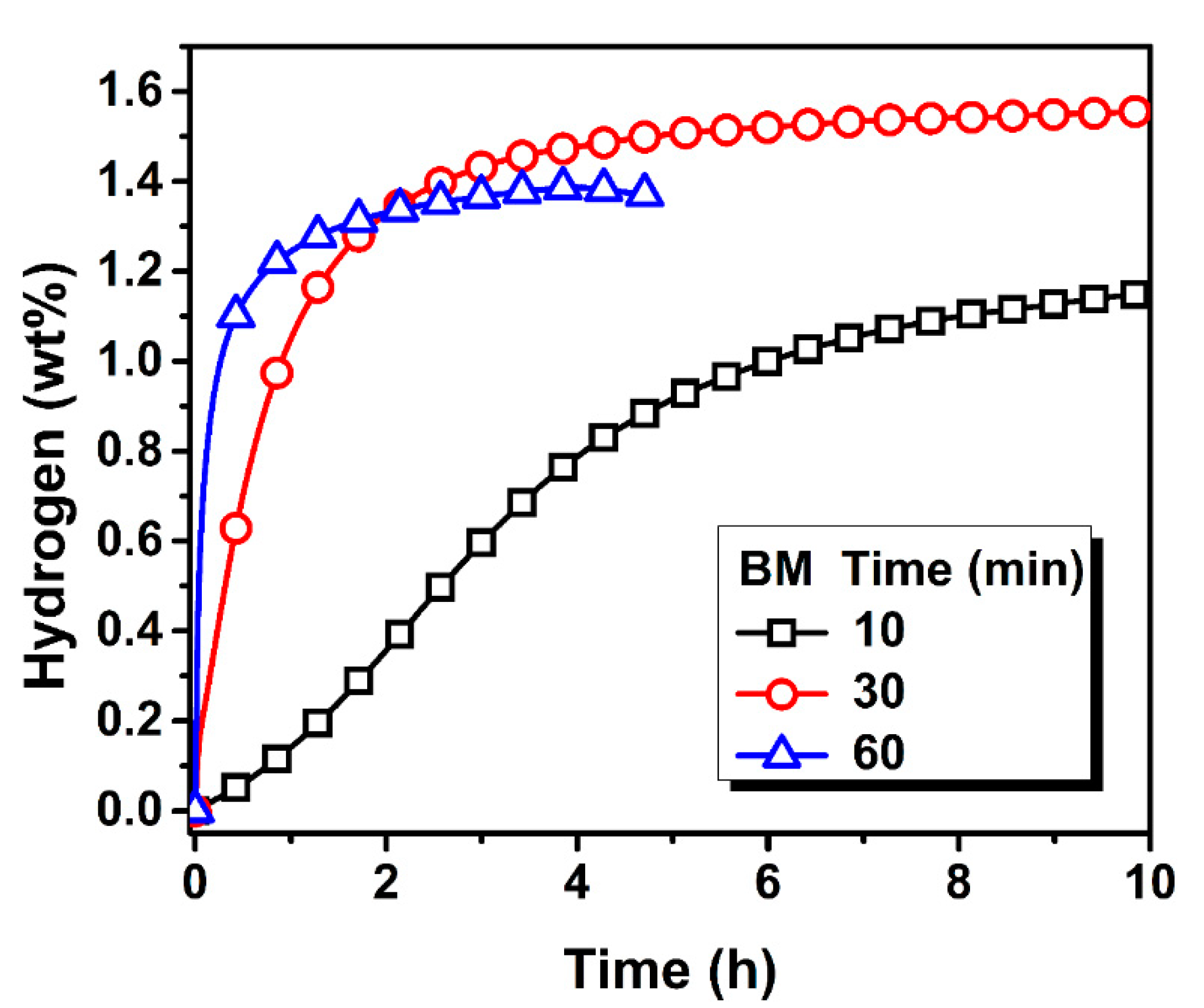
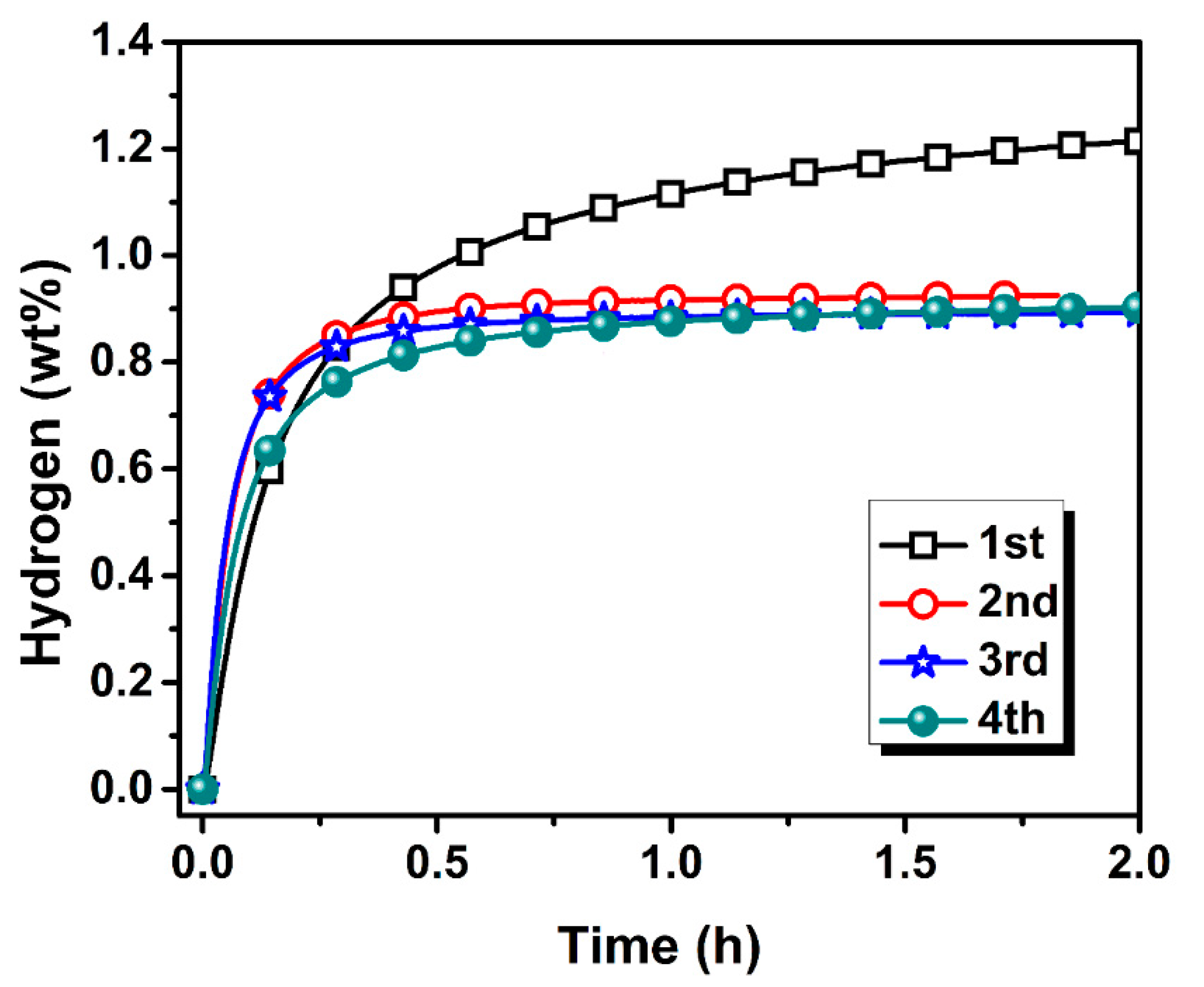
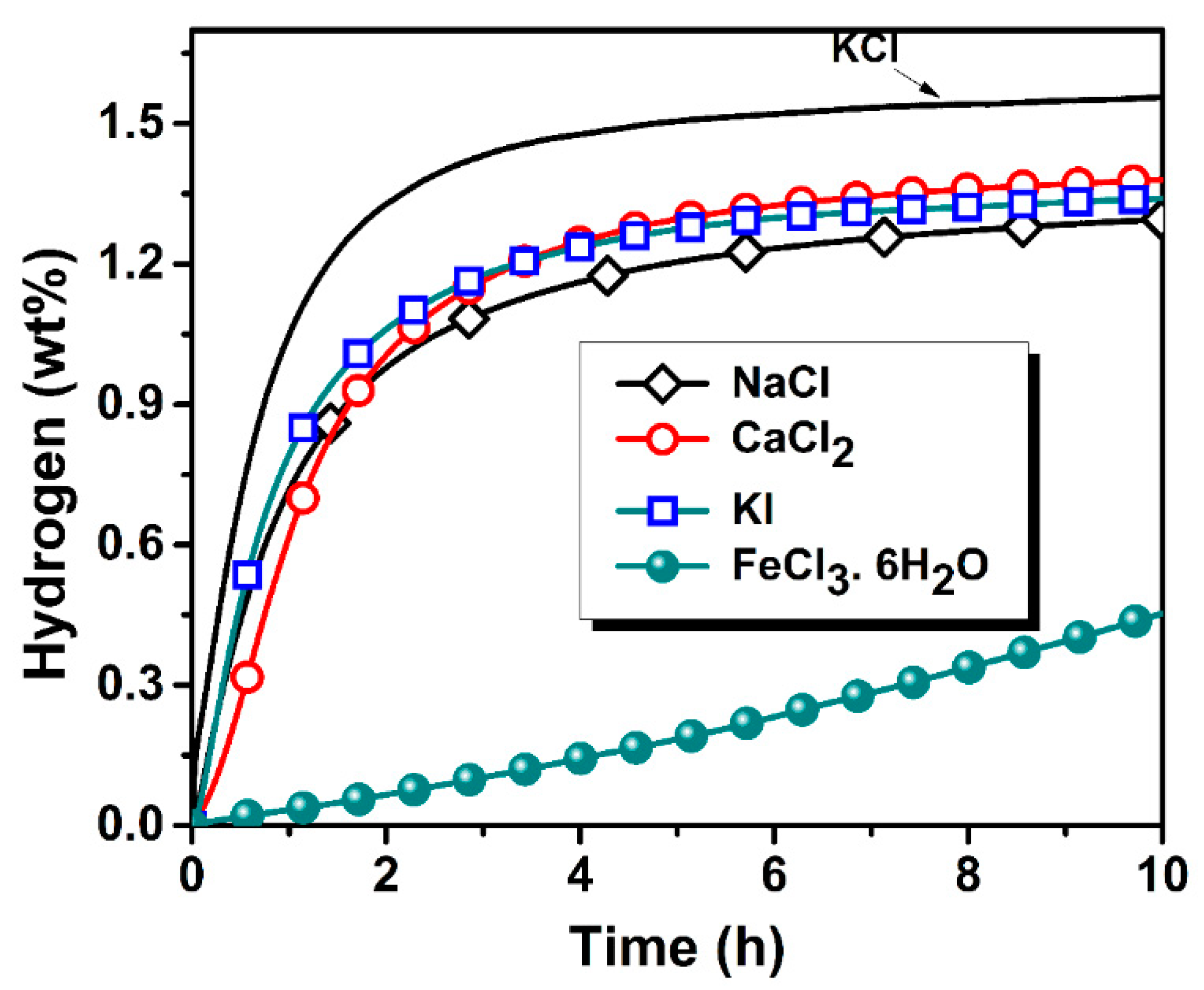
3.2. Activation Kinetics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dantzer, P. Properties of Intermetallic Compounds Suitable for Hydrogen Storage Applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2002, 329–331, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suda, T.; Ohkawa, M.; Sawada, S.; Watanabe, S.; Ohnuki, S.; Nagata, S. Effect of Surface Modification by Ion Implantation on Hydrogenation Property of TiFe Alloy. Mater. Trans. 2002, 43, 2703–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saita, I.; Sato, M.; Uesugi, H.; Akiyama, T. Hydriding Combustion Synthesis of TiFe. J. Alloys Compd. 2007, 446–447, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, P.; Huot, J. Hydrogen Storage Properties of Ti0.95FeZr0.05, TiFe0.95Zr0.05 and TiFeZr0.05 Alloys. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 22128–22133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandrock, G. A Panoramic Overview of Hydrogen Storage Alloys from a Gas Reaction Point of View. J. Alloys Compd. 1999, 293, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujan, G.K.; Pan, Z.; Li, H.; Liang, D.; Alam, N. An Overview on TiFe Intermetallic for Solid-State Hydrogen Storage: Microstructure, Hydrogenation and Fabrication Processes. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2020, 45, 410–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edalati, K.; Matsuda, J.; Iwaoka, H.; Toh, S.; Akiba, E.; Horita, Z. High-Pressure Torsion of TiFe Intermetallics for Activation of Hydrogen Storage at Room Temperature with Heterogeneous Nanostructure. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 4622–4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, J.J.; Wiswall, R.H. Formation and Properties of Iron Titanium Hydride. Inorg. Chem. 1974, 13, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, J.; Tougas, B.; Huot, J. Mechanical Activation of Air Exposed TiFe + 4 wt% Zr Alloy for Hydrogenation by Cold Rolling and Ball Milling. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 20795–20800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuziora, P.; Kunce, I.; McCain, S.; Adkins, N.J.E.; Polanski, M. The Influence of Refractory Metals on the Hydrogen Storage Characteristics of FeTi-Based Alloys Prepared by Suspended Droplet Alloying. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 21635–21645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdonosova, E.A.; Zadorozhnyy, V.Y.; Zadorozhnyy, M.Y.; Geodakian, K.V.; Zheleznyi, M.V.; Tsarkov, A.A.; Kaloshkin, S.D.; Klyamkin, S.N. Hydrogen Storage Properties of TiFe-Based Ternary Mechanical Alloys with Cobalt and Niobium. A Thermochemical Approach. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 29159–29165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, J.; Tougas, B.; Huot, J. First Hydrogenation Kinetics of Zr and Mn Doped TiFe Alloy after Air Exposure and Reactivation by Mechanical Treatment. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 11625–11631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huot, J.; Ravnsbæk, D.B.; Zhang, J.; Cuevas, F.; Latroche, M.; Jensen, T.R. Mechanochemical Synthesis of Hydrogen Storage Materials. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2013, 58, 30–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huot, J.; Tousignant, M. Effect of Cold Rolling on Metal Hydrides. Mater. Trans. 2019, 60, 1571–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, J.; Huot, J. A New Approach to the Processing of Metal Hydrides. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, L18–L22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huot, J. Nanocrystalline Metal Hydrides Obtained by Severe Plastic Deformations. Metals 2012, 2, 22–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulate-Kolitsky, E.; Tougas, B.; Neumann, B.; Schade, C.; Huot, J. First Hydrogenation of Mechanically Processed TiFe-Based Alloy Synthesized by Gas Atomization. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 7381–7389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skripnyuk, V.M.; Rabkin, E.; Estrin, Y.; Lapovok, R. Improving Hydrogen Storage Properties of Magnesium Based Alloys by Equal Channel Angular Pressing. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2009, 34, 6320–6324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiva, D.R.; Jorge, A.M.; Ishikawa, T.T.; Huot, J.; Fruchart, D.; Miraglia, S.; Kiminami, C.S.; Botta, W.J. Nanoscale Grain Refinement and H-Sorption Properties of MgH2 Processed by High-Pressure Torsion and Other Mechanical Routes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2010, 12, 786–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakintuna, B.; Lamaridarkrim, F.; Hirscher, M. Metal Hydride Materials for Solid Hydrogen Storage: A Review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2007, 32, 1121–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lototskyy, M.V.; Tolj, I.; Pickering, L.; Sita, C.; Barbir, F. The Use of Metal Hydrides in Fuel Cell Applications. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2017, 27, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.K.; Sharma, P.; Huot, J. Effect of Annealing on Microstructure and Hydrogenation Properties of TiFe + X wt% Zr (X = 4, 8). Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 6238–6243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, W.; Hao, Z.; Li, Z.; Chen, G.; Wu, Z.; Lu, X.; Li, C. Effects of Cu and Y Substitution on Hydrogen Storage Performance of TiFe0.86Mn0.1Y0.1−xCux. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 16620–16631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, W.; Li, M.; Gao, P.; Wu, C.; Li, Q.; Lu, X.; Li, C. Hydrogenation Properties of Ti-Fe-Mn Alloy with Cu and Y as Additives. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 2229–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimiya, N.; Wada, T.; Matsumoto, A.; Tsutsumi, K. Hydriding Characteristics of Zirconium-Substituted FeTi. J. Alloys Compd. 2000, 313, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamura, H.; Sakai, T.; Kuriyama, N.; Tanaka, H.; Uehara, I.; Ishikawa, H. Hydrogenation and Phase Structure of Ti-Fe-V Alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 1997, 253, 232–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, H.; Yu, Z.; Yin, J.; Li, Q.; Wu, Z.; Chou, K.C. Effects of Ce on the Hydrogen Storage Properties of TiFe0.9Mn0.1 alloy. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 23731–23736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.K.; Duguay, A.; Tougas, B.; Neumann, B.; Schade, C.; Sharma, P.; Huot, J. Study of the Microstructural and First Hydrogenation Properties of Tife Alloy with Zr, Mn and V as Additives. Processes 2021, 9, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.; Gosselin, C.; Huot, J. Effect of Zr, Ni and Zr7Ni10 Alloy on Hydrogen Storage Characteristics of TiFe Alloy. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 16921–16927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.; Gosselin, C.; Skryabina, N.; Fruchart, D.; Huot, J. Hydrogenation Properties of TiFe with Zr7Ni10 Alloy as Additive. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 636, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shwartz, A.; Shamir, N.; Froumin, N.; Zalkind, S.; Edry, I.; Haim, A.; Mintz, M.H. Initial Oxidation of TiFe1−xMnx (x = 0–0.3) by Low Dose Exposures to H2O and O2. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 610, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandrock, G.D.; Goodell, P.D. Surface Poisoning of LaNi5, FeTi and (Fe,Mn)Ti by O2, CO. J. Less-Common Met. 1980, 73, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, P.; Guzik, M.N.; Sartori, S.; Huot, J. Effect of Ball Milling and Cryomilling on the Microstructure and First Hydrogenation Propertiesof TiFe + 4 wt% Zr Alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 1828–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modi, P.; Aguey-Zinsou, K.F. Titanium-Iron-Manganese (TiFe0.85Mn0.15)Alloy for Hydrogen Storage: Reactivation upon Oxidation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 16757–16764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.; Du, J.; Pu, C.; Niu, Y.; Huang, T.; Li, Z.; Lou, Y.; Wu, Z. Effects of Co Introduction on Hydrogen Storage Properties of Ti-Fe-Mn Alloys. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 2729–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosselin, C.; Huot, J. First Hydrogenation Enhancement in TiFe Alloys for Hydrogen Storage Doped with Yttrium. Metals 2019, 9, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dematteis, E.M.; Berti, N.; Cuevas, F.; Latroche, M.; Baricco, M. Substitutional Effects in TiFe for Hydrogen Storage: A Comprehensive Review. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 2524–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcão, R.B.; Dammann, E.D.C.C.; Rocha, C.J.; Durazzo, M.; Ichikawa, R.U.; Martinez, L.G.; Botta, W.J.; Leal Neto, R.M. An Alternative Route to Produce Easily Activated Nanocrystalline TiFe Powder. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 16107–16116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadorozhnyy, V.Y.; Milovzorov, G.S.; Klyamkin, S.N.; Zadorozhnyy, M.Y.; Strugova, D.V.; Gorshenkov, M.V.; Kaloshkin, S.D. Preparation and Hydrogen Storage Properties of Nanocrystalline TiFe Synthesized by Mechanical Alloying. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2017, 27, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadorozhnyy, V.Y.; Klyamkin, S.N.; Zadorozhnyy, M.Y.; Bermesheva, O.V.; Kaloshkin, S.D. Mechanical Alloying of Nanocrystalline Intermetallic Compound TiFe Doped by Aluminum and Chromium. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 586, S56–S60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadorozhnyy, V.; Klyamkin, S.; Zadorozhnyy, M.; Bermesheva, O.; Kaloshkin, S. Hydrogen Storage Nanocrystalline TiFe Intermetallic Compound: Synthesis by Mechanical Alloying and Compacting. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 17131–17136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, I.; Tanaka, H.; Takeshita, H.; Kuriyama, N.; Sakai, T.; Uehara, I. Hydrogenation Characteristics of TiFe1−xPdx (0.05 < x < 0.30) Alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 1997, 254, 238–240. [Google Scholar]
- Bououdina, M.; Fruchart, D.; Jacquet, S.; Pontonnier, L.; Soubeyroux, J.L. Effect of Nickel Alloying by Using Ball Milling on the Hydrogen Absorption Properties of TiFe. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 1999, 24, 885–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaluski, L.; Zaluska, A.; Tessier, P.; Strom-Olsen, J.O.; Schulz, R. Effects of Relaxation on Hydrogen Absorption in FeTi Produced by Ball-Milling. J. Alloys Compd. 1995, 227, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaluski, L.; Zaluska, A.; Tessier, P.; Strom-Olsen, J.O.; Schulz, R. Hydrogen Absorption by Nanocrystalline and Amorphous Fe-Ti with Palladium Catalyst, Produced by Ball Milling. J. Mater. Sci. 1996, 31, 695–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davids, M.W.; Lototskyy, M.; Nechaev, A.; Naidoo, Q.; Williams, M.; Klochko, Y. Surface Modification of TiFe Hydrogen Storage Alloy by Metal-Organic Chemical Vapour Deposition of Palladium. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 9743–9750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.; Lototsky, M.V.; Davids, M.W.; Linkov, V.; Yartys, V.A.; Solberg, J.K. Chemical Surface Modification for the Improvement of the Hydrogenation Kinetics and Poisoning Resistance of TiFe. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, S770–S774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, E.M.B.; Vredenberg, A.M.; Boerma, D.O. H Uptake Kinetics of FeTi Films Coated with Ni. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 253, 1150–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, E.M.B.; Vredenberg, A.M.; Boerma, D.O. Hydrogen Uptake Kinetics of Pd Coated FeTi Films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 253, 771–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BRUKER AXS, TOPAS V4; General Profile and Structure Analysis Software for Powder Diffraction Data; Bruker AXS GmbH: Karlsruhe, Germany, 2008.
- Toma, O.; Dzevenko, M.; Oliynyk, A.; Lomnytska, Y.F. The Ti-Fe-P System: Phase Equilibria and Crystal Structure of Phases. Cent. Eur. J. Chem. 2013, 11, 1518–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romaka, L.; Romaka, V.V.; Stadnyk, Y.; Melnychenko, N. On the Formation of Ternary Phases in the Ti–Fe–Sn Ternary System at 773 K. Chem. Met. Alloy. 2013, 6, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, P.; Liu, Z. Effect of High Zirconium Content on Hydrogenation Properties and Anti-Poisoning Ability of Air-Exposed TiFe Alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 5972–5983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, P.; Huot, J. Hydrogenation Improvement of TiFe by Adding ZrMn2. Energy 2017, 138, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, P.; Liu, Z.; Dixit, V. Improved Hydrogen Storage Properties of TiFe Alloy by Doping (Zr + 2V) Additive and Using Mechanical Deformation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 27843–27852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, G.; Lv, P.; Huot, J. Effect of Ball Milling on the First Hydrogenation of TiFe Alloy Doped with 4 wt% (Zr + 2Mn) Additive. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 13751–13757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.K.; Duguay, A.; Tougas, B.; Schade, C.; Sharma, P.; Huot, J. Microstructure and First Hydrogenation Properties of TiFe Alloy with Zr and Mn as Additives. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 787–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami, H.; Edalati, K.; Matsuda, J.; Akiba, E.; Horita, Z. Hydrogen Storage Performance of TiFe after Processing by Ball Milling. Acta Mater. 2015, 88, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, C.H.; Chin, Z.H.; Perng, T.P. Hydrogenation of TiFe by High-Energy Ball Milling. J. Alloys Compd. 2000, 307, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyagi, H.; Aoki, K.; Masumoto, T. Effect of Ball Milling on Hydrogen Absorption Properties of FeTi, Mg2Ni and LaNi5. J. Alloys Compd. 1995, 231, 804–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubicza, J. Relationship between Microstructure and Hydrogen Storage Properties of Nanomaterials. In Defect Structure in Nanomaterials; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 301–332. [Google Scholar]
- Vega, L.E.R.; Leiva, D.R.; Leal Neto, R.M.; Silva, W.B.; Silva, R.A.; Ishikawa, T.T.; Kiminami, C.S.; Botta, W.J. Mechanical Activation of TiFe for Hydrogen Storage by Cold Rolling under Inert Atmosphere. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 2913–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraki, T.; Oishi, K.; Uchida, H.; Miyamoto, Y.; Abe, M.; Kokaji, T.; Uchida, S. Properties of Hydrogen Absorption by Nano-Structured FeTi Alloys. Int. J. Mater. Res. 2008, 99, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaluski, L.; Zaluska, A.; Strom-Olsen, J.O. Nanocrystalline metal hydrides. J. Alloys Compd. 1997, 253, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotta, H.; Abe, M.; Kuji, T.; Uchida, H. Synthesis of Ti-Fe Alloys by Mechanical Alloying. J. Alloys Compd. 2007, 439, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, M.; Kuji, T. Hydrogen Absorption of TiFe Alloy Synthesized by Ball Milling and Post-Annealing. J. Alloys Compd. 2007, 446–447, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inui, H.; Yamamoto, T.; Hirota, M.; Yamaguchi, M. Lattice Defects Introduced during Hydrogen Absorption-Desorption Cycles and Their Effects on P-C Characteristics in Some Intermetallic Compounds. J. Alloys Compd. 2002, 330, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Namba, K.; Miyaoka, H.; Jain, A.; Ichikawa, T. Hydrogen Storage Behavior of TiFe Alloy Activated by Different Methods. Mater. Lett. X 2021, 9, 100061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
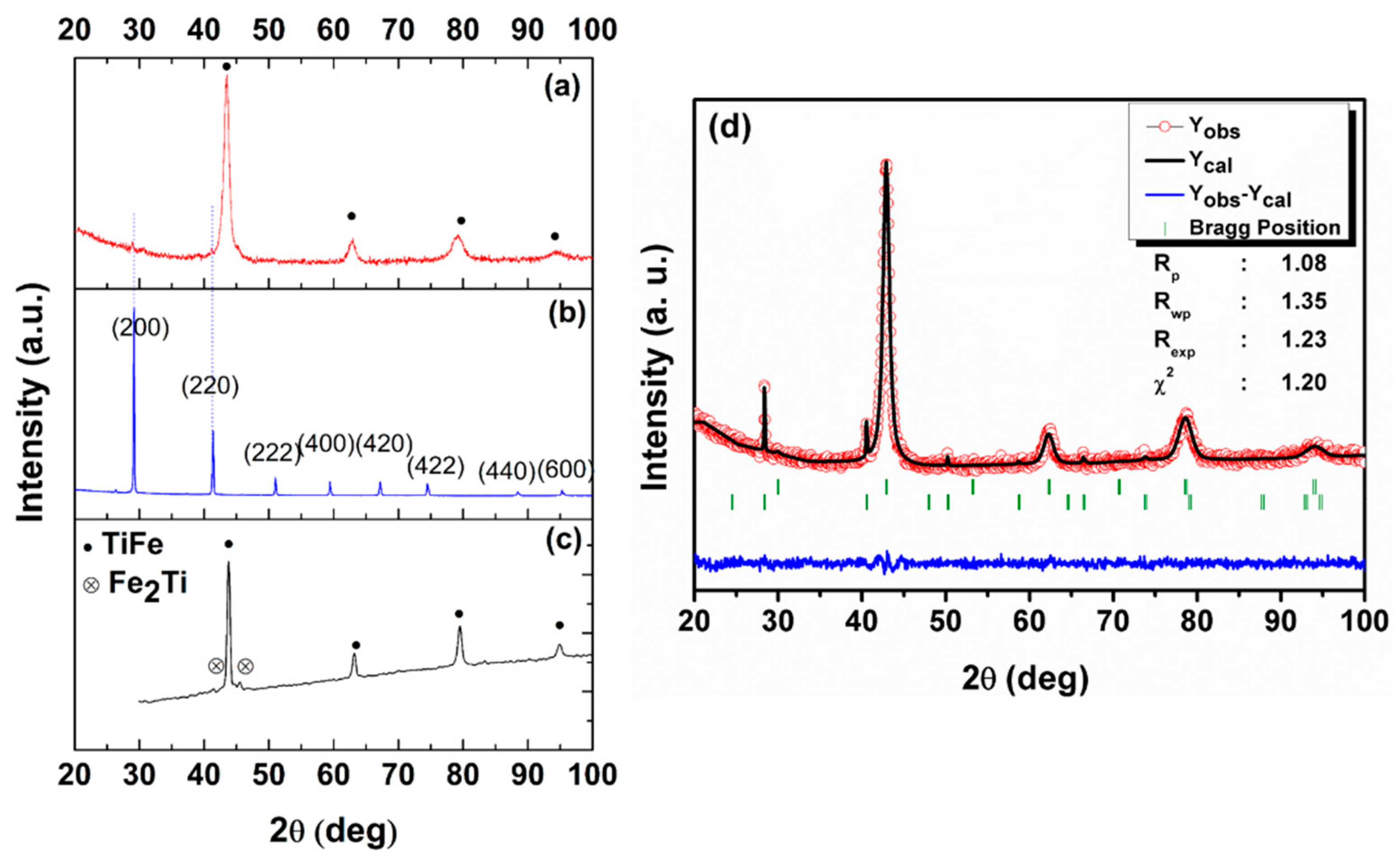

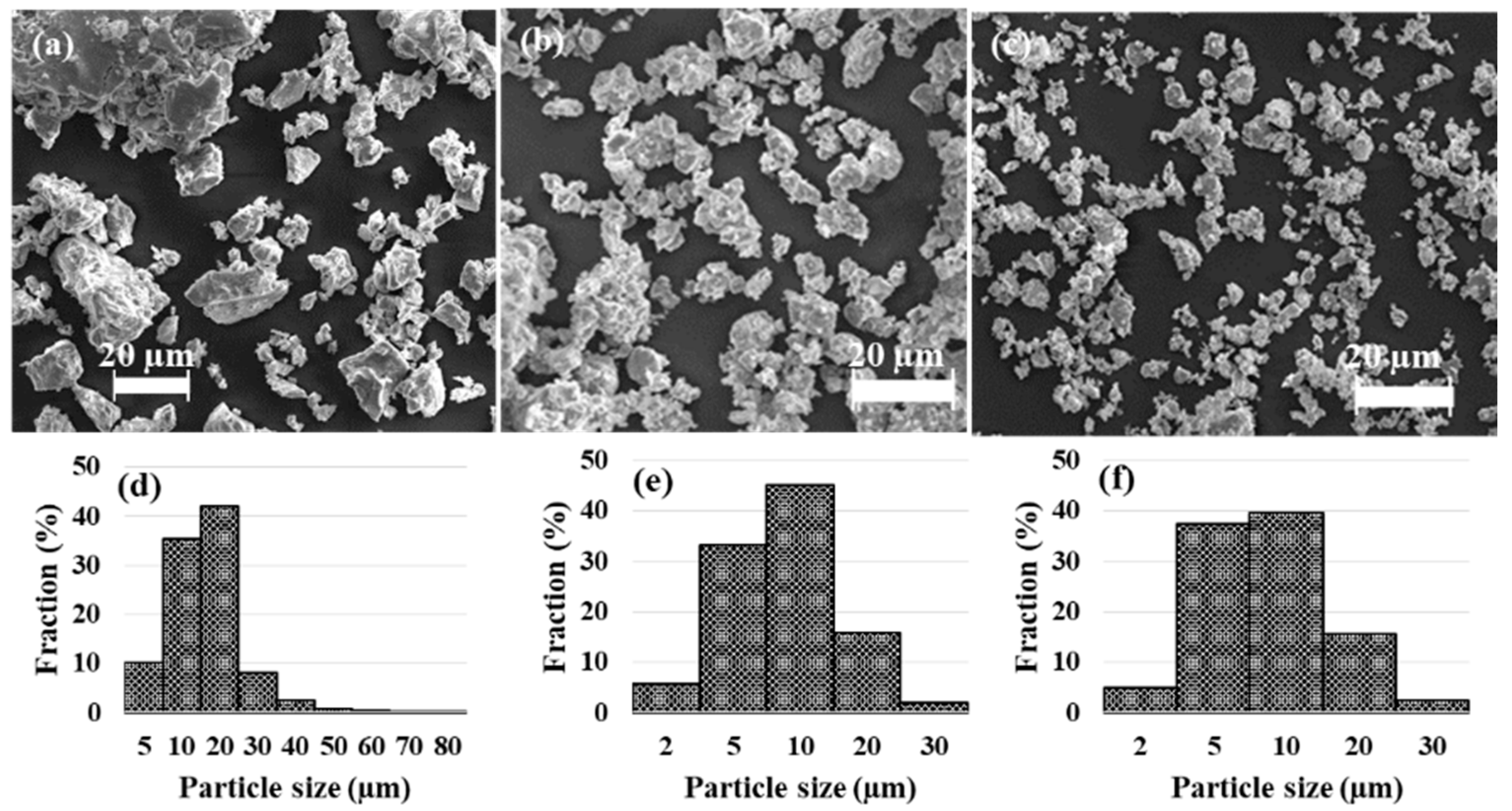
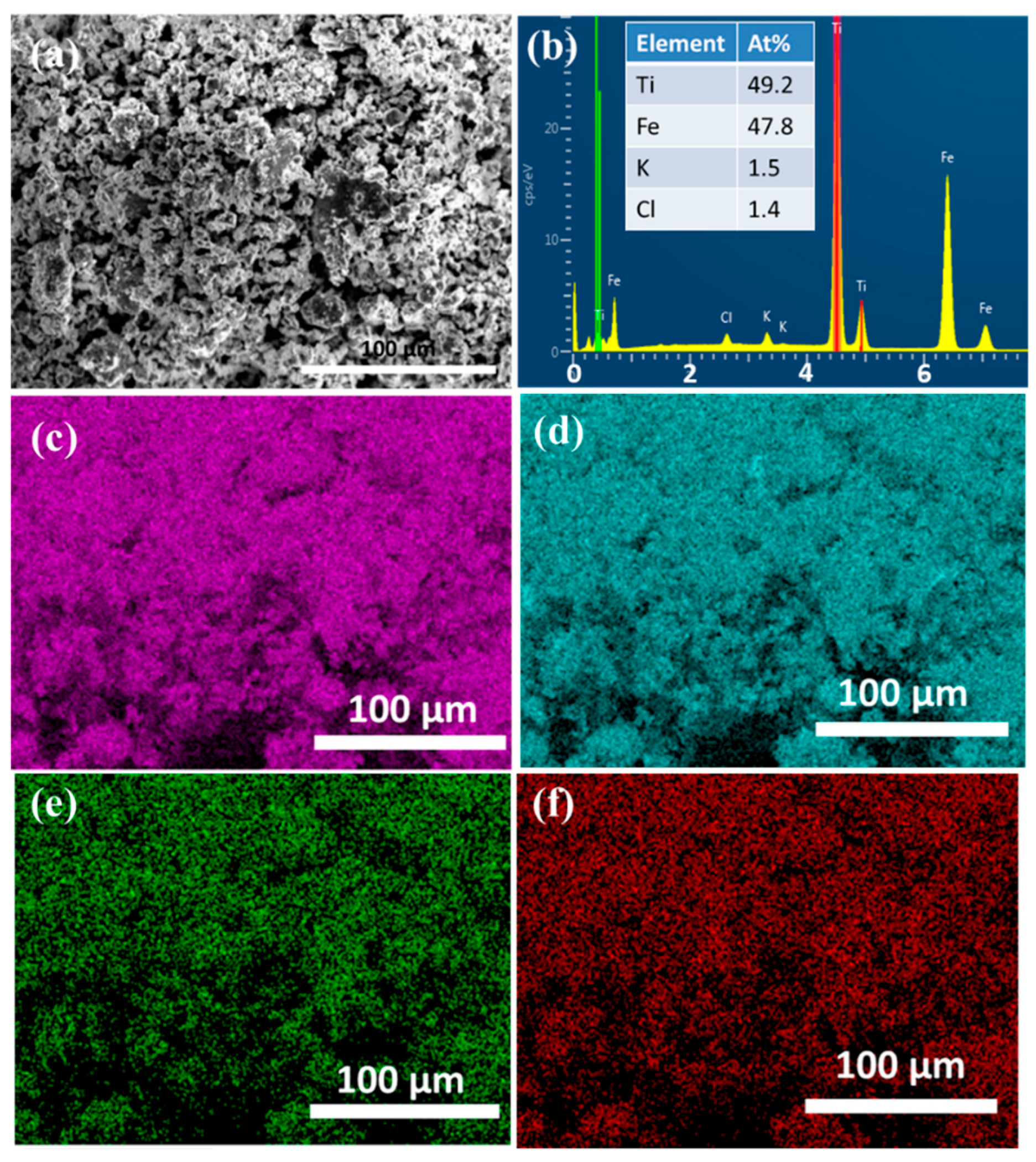
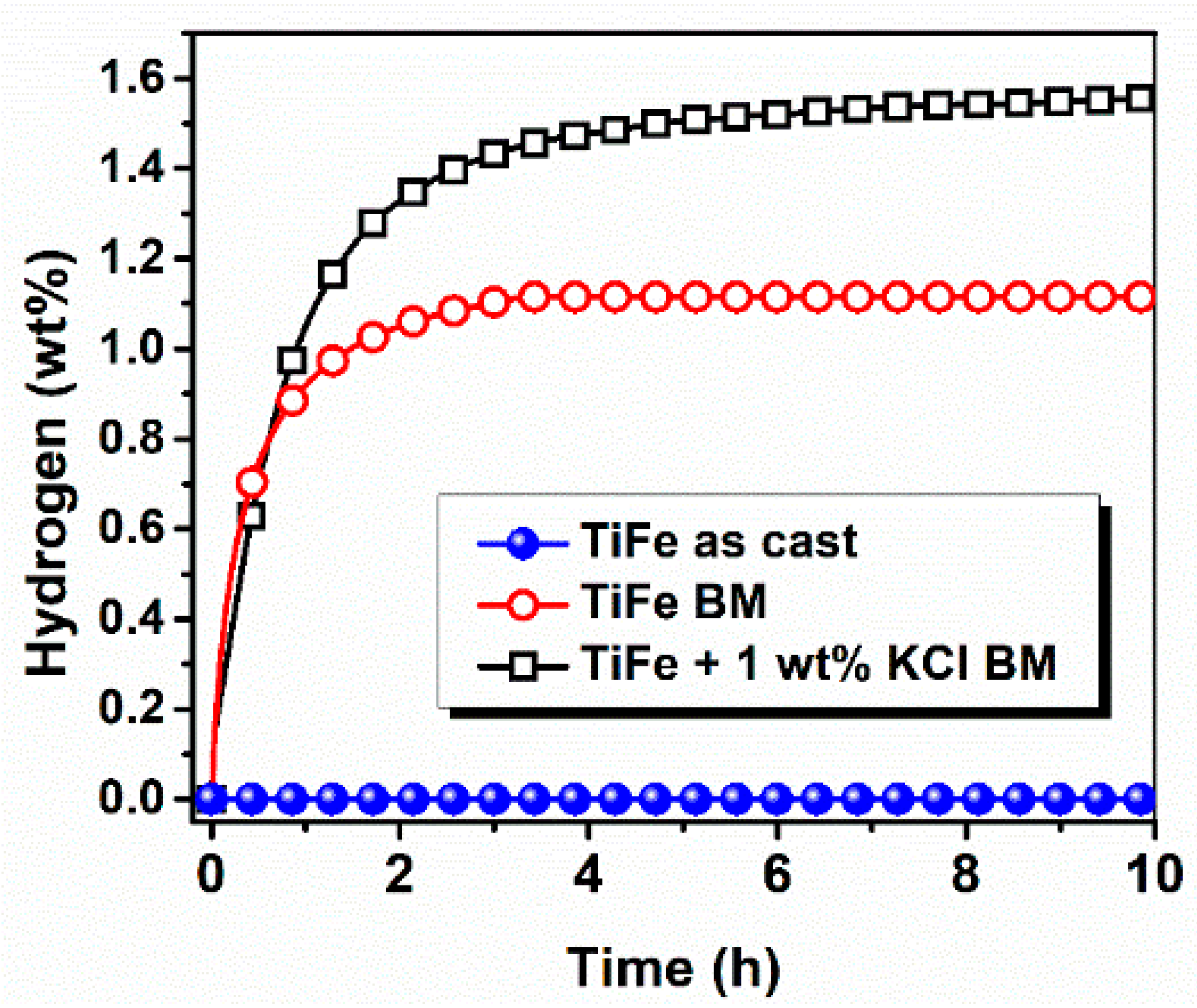
| Sample | Phase | Composition (wt.%) | Lattice Parameter (Å) | Crystallite Size (nm) | Microstrain (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As-cast TiFe | TiFe | 95(1) | 2.9808(3) | 23.8(7) | 0.092(4) |
| Fe2Ti | 5(1) | a = 4.840(4), c = 8.11(1) | 32(12) | -- | |
| TiFe + 1 wt.% KCl | TiFe | 98.6(3) | 2.9815(6) | 8.5(2) | 0.269(7) |
| KCl | 1.4(3) | 6.2849 | 50(20) | -- | |
| TiFe + 5 wt.% KCl | TiFe | 95.4(3) | 2.9806(2) | 9.1(2) | 0.264(7) |
| KCl | 4.6(3) | 6.2849 | 89(13) | -- |
| Sample | Synthesis Process | Air Exposure | Treatment | H2 Adsorbed | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical | Thermal | |||||
| TiFe | Induction melting | As-cast | Ball milling | No | 1.1 wt.% (20 bars, 20 °C) | [12] |
| TiFe | Mechanical alloying | - | - | 5 cycles of vacuum and 150 bar H2 pressure at 300 °C | 1.3 wt.% | [65] |
| TiFe | Purchased | - | Ball milling | Annealing (1000 °C) | 1.3–1.5 wt.% (100 bar, 30 °C) | [58] |
| TiFe | Purchased | Ball milled with ethanol | - | 1.2 wt.% (RT) | [68] | |
| TiFe | Arc melting | Ball milling with 1% KCl | - | 1.5 wt.% (RT, 20 bars) | This study | |
| TiFe0.85Mn0.15 | Arc-melting | 2 h | Ball milling | 300 °C under 3 MPa H2 pressure, 3 times | <1 wt.% (30 bars, 30 °C) | [34] |
| TiFe + 2 wt.% Mn + 4 wt.% Zr | Gas atomization | 60 days | Cold rolling | No | 2.1 wt.% (20 bars, RT) | [17] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Manna, J.; Huot, J. Effect of KCl Addition on First Hydrogenation Kinetics of TiFe. Compounds 2022, 2, 240-251. https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds2040020
Manna J, Huot J. Effect of KCl Addition on First Hydrogenation Kinetics of TiFe. Compounds. 2022; 2(4):240-251. https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds2040020
Chicago/Turabian StyleManna, Joydev, and Jacques Huot. 2022. "Effect of KCl Addition on First Hydrogenation Kinetics of TiFe" Compounds 2, no. 4: 240-251. https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds2040020
APA StyleManna, J., & Huot, J. (2022). Effect of KCl Addition on First Hydrogenation Kinetics of TiFe. Compounds, 2(4), 240-251. https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds2040020







