An Exploratory Study of Relationships Between Arginine Vasopressin and Cerebral Edema: Usefulness of Postmortem Serum and Cerebrospinal Fluid
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Autopsy Samples
2.3. Biochemical Analysis
2.4. Normalization of BW Using Computed Tomography (CT) Scan Data
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Relationship of AVP Concentrations with Sex, Age, Survival, Postmortem Period, and Sampling Site
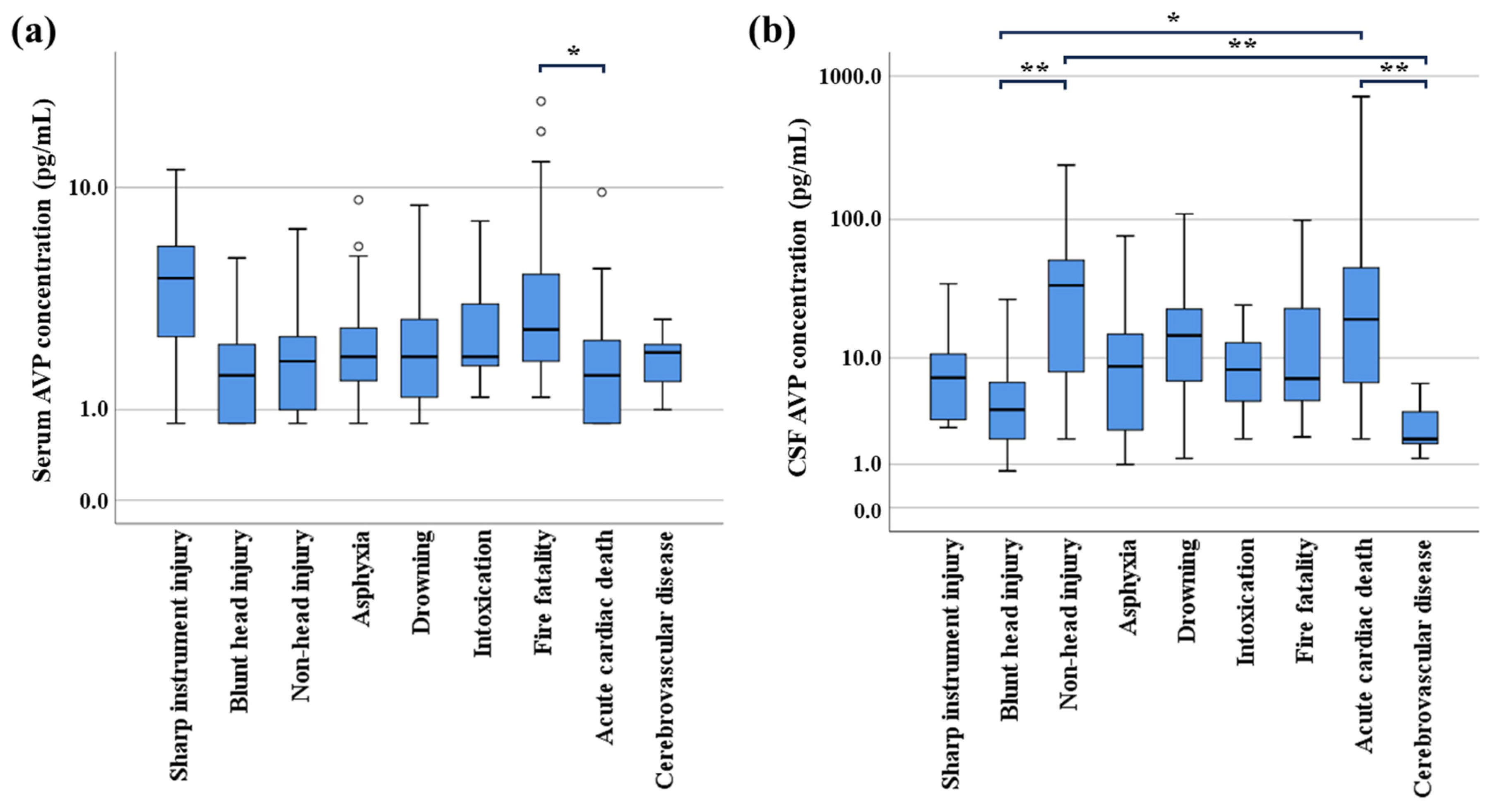
3.2. Relationship Between AVP Levels and Cause of Death
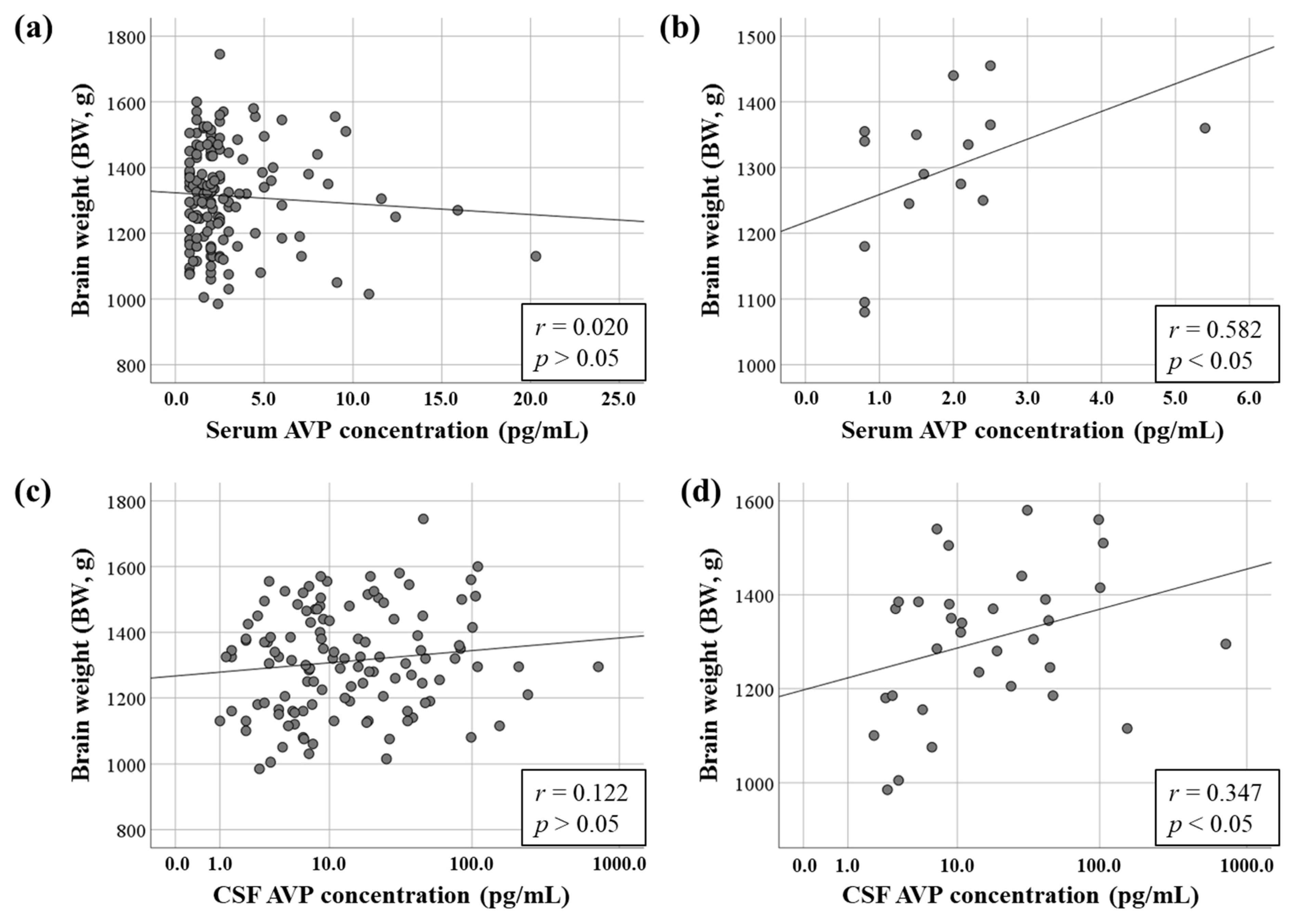
3.3. Relationship Between AVP Concentrations and BW
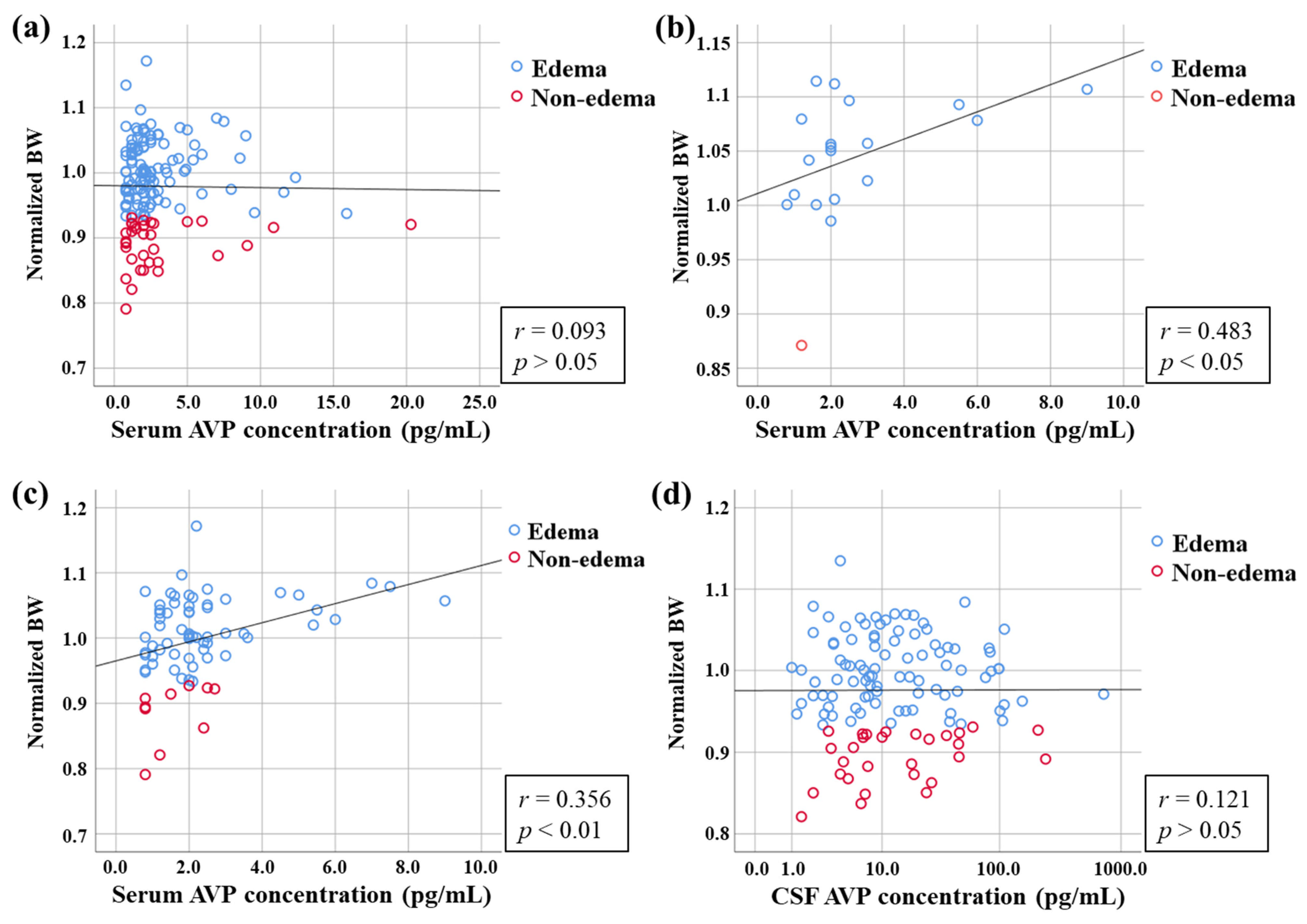
3.4. Relationship Between AVP Concentration and Normalized BW
3.5. Relationship Between AVP Concentration and Classification of Edema by Normalized BW
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marmarou, A. Pathophysiology of traumatic brain edema: Current concepts. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2003, 86, 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- Lundesgaard Eidahl, J.M.; Opdal, S.H.; Rognum, T.O.; Stray-Pedersen, A. Postmortem evaluation of brain edema: An attempt with measurements of water content and brain-weight-to-inner-skull-circumference ratio. J. Forensic Leg. Med. 2019, 64, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Xu, J.T.; Jin, H.N.; Zhao, R.; Zhao, D.; Du, S.H.; Xue, Y.; Xie, X.L.; Wang, Q. Increased cerebral expressions of MMPs, CLDN5, OCLN, ZO1 and AQPs are associated with brain edema following fatal heat stroke. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Ishikawa, T.; Michiue, T.; Zhu, B.L.; Guan, D.W.; Maeda, H. Molecular pathology of brain matrix metalloproteases, claudin5, and aquaporins in forensic autopsy cases with special regard to methamphetamine intoxication. Int. J. Legal Med. 2014, 128, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donkin, J.J.; Vink, R. Mechanisms of cerebral edema in traumatic brain injury: Therapeutic developments. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2010, 23, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, I.; Russell, J.A.; Landgraf, R. Oxytocin and vasopressin release within the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei of pregnant, parturient and lactating rats: A microdialysis study. Neuroscience 1993, 53, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmiere, C.; Augsburger, M. Copeptin as a diagnostic biomarker for sepsis-related deaths. Peptides 2014, 59, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katan, M.; Müller, B.; Christ-Crain, M. Copeptin: A new and promising diagnostic and prognostic marker. Crit. Care 2008, 12, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgenthaler, N.G.; Struck, J.; Alonso, C.; Bergmann, A. Assay for the measurement of copeptin, a stable peptide derived from the precursor of vasopressin. Clin. Chem. 2006, 52, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotondo, F.; Butz, H.; Syro, L.V.; Yousef, G.M.; Di Ieva, A.; Restrepo, L.M.; Quintanar-Stephano, A.; Berczi, I.; Kovacs, K. Arginine vasopressin (AVP): A review of its historical perspectives, current research and multifunctional role in the hypothalamo-hypophysial system. Pituitary 2016, 19, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankir, L.; Bichet, D.G.; Morgenthaler, N.G. Vasopressin: Physiology, assessment and osmosensation. J. Intern. Med. 2017, 282, 284–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, S.W.; Liu, X.Y.; Wang, S.C.; Wang, Y.F. Vasopressin Hypersecretion-Associated Brain Edema Formation in Ischemic Stroke: Underlying Mechanisms. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2016, 25, 1289–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hausmann, R.; Vogel, C.; Seidl, S.; Betz, P. Value of morphological parameters for grading of brain swelling. Int. J. Legal Med. 2006, 120, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, M.; Deigendesch, N.; Wittig, H.; Scheurer, E.; Lenz, C. Tissue sample analysis for post mortem determination of brain edema. Forensic Sci. Int. 2021, 323, 110808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radojevic, N.; Radnic, B.; Vucinic, J.; Cukic, D.; Lazovic, R.; Asanin, B.; Savic, S. Mathematical model in post-mortem estimation of brain edema using morphometric parameters. J. Forensic Leg. Med. 2017, 4, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, M.; Gerlach, K.; Scheurer, E.; Lenz, C. Analysis of different post mortem assessment methods for cerebral edema. Forensic Sci. Int. 2020, 308, 110164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutlu, E.; Çil, N.; Avci, E.; Bir, F.; Kiliç, İ.D.; Dereli, A.K.; Acar, K. Significance of postmortem biomarkers and multimarker strategy in sudden cardiac death. Leg. Med. 2023, 61, 102212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michiue, T.; Hishmat, A.M.; Oritani, S.; Miyamoto, K.; Amin, M.F.; Ishikawa, T.; Maeda, H. Virtual computed tomography morphometry of the patella for estimation of sex using postmortem Japanese adult data in forensic identification. Forensic Sci. Int. 2018, 285, 206.e1–206.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, G.; Dingman, J.F. Distribution, blood transport, and degradation of antidiuretic hormone in man. J. Clin. Investig. 1976, 57, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, M.; Catford, S.R.; Kumareswaran, K.; Hamblin, P.S.; Topliss, D.J. Persistent syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion following traumatic brain injury. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. Case Rep. 2015, 2015, 150070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjizacharia, P.; Beale, E.O.; Inaba, K.; Chan, L.S.; Demetriades, D. Acute diabetes insipidus in severe head injury: A prospective study. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2008, 207, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dóczi, T.; László, F.A.; Szerdahelyi, P.; Joó, F. Involvement of vasopressin in brain edema formation: Further evidence obtained from the Brattleboro diabetes insipidus rat with experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 1984, 14, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, J.S.; Mather, H.M.; Ang, V. Vasopressin in human cerebrospinal fluid. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1980, 50, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, M.; Berger, C.; Gerlach, K.; Scheurer, E.; Lenz, C. Post mortem evaluation of brain edema using quantitative MRI. Forensic Sci. Int. 2022, 337, 111376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Song, Y.; Rocha, M.; Shi, Y. Ischemic brain edema: Emerging cellular mechanisms and therapeutic approaches. Neurobiol. Dis. 2023, 178, 106029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmiere, C.; Tettamanti, C.; Bonsignore, A.; De Stefano, F.; Vanhaebost, J.; Rousseau, G.; Scarpelli, M.P.; Bardy, D. Cardiac troponins and NT-proBNP in the forensic setting: Overview of sampling site, postmortem interval, cardiopulmonary resuscitation, and review of the literature. Forensic Sci. Int. 2018, 282, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Zhao, M.; Xu, C.; Zhang, T.; Jia, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhu, B. Evaluation of agonal cardiac function for sudden cardiac death in forensic medicine with postmortem brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) and NT-proBNP: A meta-analysis. J. Forensic Sci. 2020, 65, 686–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Cause of Death | n | Male/Female | Age (Years) | Postmortem Time (h) | Survival Time (n) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range (Median) | Range (Median) | Acute (<0.5 h) | Subacute (0.5–12 h) | |||
| Sharp instrument injury | 8 | 7/1 | 47–86 (73.5) | 20–41 (32) | 2 | 6 |
| Blunt head injury | 15 | 13/2 | 38–92 (64) | 12–83 (35) | 5 | 10 |
| Non-head injury | 18 | 16/2 | 31–93 (70) | 13–88 (30) | 7 | 11 |
| Asphyxia | 19 | 15/4 | 21–79 (58) | 14–85 (34) | 19 | - |
| Drowning * | 14 | 10/4 | 29–85 (62) | 17–88 (37) | 14 | - |
| Intoxication ** | 13 | 7/6 | 21–69 (47) | 28–85 (35) | 3 | 10 |
| Fire fatality | 24 | 14/10 | 44–92 (73) | 8–82 (25.5) | 24 | - |
| Acute cardiac death | 25 | 24/1 | 25–93 (73) | 10–77 (26) | 25 | - |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 7 | 4/3 | 24–77 (47) | 19–83 (47) | 5 | 2 |
| Total | 143 | 110/33 | 21–93 (66) | 8–88 (33) | 104 | 39 |
| Cause of Death | n | Serum AVP Concentration (pg/mL) | Cerebrospinal Fluid AVP Concentration (pg/mL) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Edema | Non-Edema | Edema (Median) | Non-Edema (Median) | Edema (Median) | Non-Edema (Median) | |
| Sharp instrument injury | 5 | 3 | 0.8–11.6 (4.0) | 2.5–6.0 (5.0) | 2.6–35 (7.0) | 3.0–10.8 (3.2) |
| Blunt head injury | 11 | 4 | 0.8–5.4 (2.0) | 0.8–2.4 (1.15) | 1.8–27 (4.2) | 0.8–19.8 (2.9) |
| Non-head injury | 13 | 5 | 0.8–7.0 (1.8) | 0.8–2.7 (2.0) | 2.0–109.6 (22.5) | 19.8–240 (46.4) |
| Asphyxia | 18 | 1 | 0.8–9.0 (2.0) | 1.2 | 1.0–76.6 (9.1) | 1.4 |
| Drowning | 11 | 3 | 0.8–8.6 (2.0) | 1.2–7.1 (2.0) | 1.2–109.2 (16.8) | 6.6–19.1 (10) |
| Intoxication | 13 | 0 | 1.2–7.5 (2.0) | - | 2.0–24.6 (8.1) | - |
| Fire fatality | 13 | 11 | 1.8–15.9 (2.7) | 1.2–20.3 (2.7) | 2.1–98.7 (6.3) | 4.0–60 (7.2) |
| Acute cardiac death | 19 | 6 | 0.8–9.6 (1.6) | 0.8–2.0 (1.5) | 2.7–720 (29) | 2.0–45.6 (12.3) |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 7 | 0 | 1.2–2.4 (2.1) | - | 1.2–6.3 (2.0) | - |
| Total | 110 | 33 | 0.8–15.9 (2.0) | 0.8–20.3 (2.0) | 1.0–720 (8.6) | 0.8–240 (7.4) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tani, N.; Miyamoto, K.; Ishikawa, T. An Exploratory Study of Relationships Between Arginine Vasopressin and Cerebral Edema: Usefulness of Postmortem Serum and Cerebrospinal Fluid. Forensic Sci. 2025, 5, 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/forensicsci5040058
Tani N, Miyamoto K, Ishikawa T. An Exploratory Study of Relationships Between Arginine Vasopressin and Cerebral Edema: Usefulness of Postmortem Serum and Cerebrospinal Fluid. Forensic Sciences. 2025; 5(4):58. https://doi.org/10.3390/forensicsci5040058
Chicago/Turabian StyleTani, Naoto, Kazunori Miyamoto, and Takaki Ishikawa. 2025. "An Exploratory Study of Relationships Between Arginine Vasopressin and Cerebral Edema: Usefulness of Postmortem Serum and Cerebrospinal Fluid" Forensic Sciences 5, no. 4: 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/forensicsci5040058
APA StyleTani, N., Miyamoto, K., & Ishikawa, T. (2025). An Exploratory Study of Relationships Between Arginine Vasopressin and Cerebral Edema: Usefulness of Postmortem Serum and Cerebrospinal Fluid. Forensic Sciences, 5(4), 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/forensicsci5040058






