Abstract
Incidental findings (IFs) are unexpected disclosures that do not fall within the aim of a test and have a potential impact on an individual’s life. In the forensic field, IFs can be considered information that is not related to the cause of death, the dynamic of the event, or the scope of the investigation. Questions regarding how forensic professionals should consider, address, and report IFs form the focus of our study. This narrative review was performing following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines with the aim of defining and summarizing evidence about IFs, analyzing their ethical and legal management, and emphasizing the importance of adequate informed consent. The current state of the art regarding IFs has revealed the need for guidelines with the purpose of making the best decisions for the parties involved since the circumstances are extremely delicate, and therefore, forensic geneticists require protection and support. For this reason, elaboration of informed consent, which considers the possibility of making accidental discoveries, could operate as an immediate solution to fill the current gaps. However, the development of clear international recommendations is the best solution to such a complex issue.
1. Introduction
In medical research and clinical practice, incidental findings (IFs) are well known as unexpected findings having potential health or reproductive implications for an individual. All the information that is not linked with the dynamic of the event, the scope of the forensic investigation, or the cause of death can be considered incidental findings (IFs) in a forensic setting. In general, when IFs occur, they may be of reproductive or health significance and may also reveal an unexpected genetic connection [1].
Technically, IFs are the same thing in clinical practice and in forensics, that is, information revealed unintentionally during a medical evaluation with a different purpose, but the context in which they appear is quite different. Following are the differences: the involvement of the interested party, such as when a deceased person is subjected to a medico-legal autopsy, and it is evident that the event was not planned by the person, but it is impossible to reconstruct their wishes [2]; the type of professionals involved, as forensic experts are required to formulate their considerations in accordance with the requirements of a judicial procedure rather than health protection; and whether judges and police are involved in the forensic context, but they are not familiar with how health-related information is communicated. The forensic practitioner will have to consider how to obtain information, how much and which information to obtain, what to report, and whether it is wise to ignore some pieces of evidence. How to manage this information raises ethical concerns [3].
However, while research on living people has always been the subject of intense ethical scrutiny, with the proposal of guidelines since the Helsinki Declaration issued by the World Medical Association in 1964 [4] or for forensic research on cadavers [5], there are no ethical standards or international guidelines involving human cadavers and remains. It is also true that, while respect for the will of the deceased person is essential, some authors nevertheless have suggested that, in a forensic context, it is not easy to obtain informed consent before death, which is, in most cases, unexpected. However, in some situations, not only the wishes but also the identity of the deceased could remain unknown [2]. In these instances, regulations such as the UK Human Tissue Act [6] or the EU Recommendation CM/Rec(2016) [7] are of little help, together with article 32 of the Declaration of Helsinki, which establishes that, in “exceptional situations where consent would be impossible or impracticable to obtain […] the research may be done only after consideration and approval of a research ethics committee” [2,4]. In a study conducted on the microbiome starting from DNA extracted for forensic purposes from deceased individuals and stored for a long time, Sguazzi et al. [8] commented that the “Provision relating to the processing of particular categories of data, pursuant to art. 21, paragraph 1, of the legislative decree 10 August 2018, n. 101”(Annex I, point 5.3) of the guarantor for the protection of personal data applies [9]. In particular, this provision establishes that, since it is not possible to obtain the consent of deceased persons, consent to the use of their samples is not required. The researcher must only ascertain, where possible, through interrogation of close family members whether the subjects declared themselves against the use of their biological material for research purposes [8]. Normally, the authorization of an ethics committee is needed for research on animal and/or human subjects worldwide according to the Declaration of Helsinki, which states in article 23 that “every protocol must be submitted for consideration, comment, guidance and approval to the concerned research ethics committee before the study begins” [4], while similar authorization for the use of human corpses and remains for scientific purposes is only mandatory in certain countries, such as Italy [10], Norway [11], and Spain [12], when the subject’s wishes are unknown and are impossible to discover [2].
For instance, during a forensic investigation, a paternity discrepancy (PD) could be discovered, and disclosing this information may result in family dissolution, yet excluding this IF from the report would result in cases having inaccurate information about their genetics [13]. An IF could even occur during a basic DNA analysis since genetic mutations leading to aggressive cancer or hereditary diseases may be discovered. It is true that comparing DNA from the same tissue, such as a bloodstain to the suspect’s blood or sperm, may be crucial in criminal cases. In this field, chimerism and partial chimerism may be problematic in forensic investigations. A chimera is an organism with cells derived from two or more distinct zygote lines, from the analysis of which false exclusions may result, and additional alleles may be wrongly interpreted as a commixt profile [14]. In these cases, when a mosaic or a chimera has potentially been discovered, the STR profile should be typed from several distinct tissues. Alternatively, the “original” alleles of the chimera and mosaic parents can be identified through genotyping [15].
Another unexpected discovery that may occur during an investigation is a discrepancy between the genetic profile and the phenotype. This variation is due to a defect of the sexual chromosomes, which could have significant consequences. Androgen insensitivity syndrome (AIS), an X-linked recessive inherited disorder caused by a mutation in the androgen receptor gene on the X chromosome, is the most common cause of sexual differentiation disorders [16,17].
From a clinical point of view, in the structure of a clinic or hospital, there are dedicated environments and professional figures for the communication of IFs, such as psychologists. On the other hand, forensic assessments have no defined guidelines for the eventual communication of IFs because the assessment is performed in institutions of forensic medicine, and the use of the information occurs exclusively in the courtroom [3].
Considering that emerging technologies such as next-generation sequencing (NGS) and advancements in science are given the greatest amount of genetic information that can be detected, they will add new obstacles to an already complicated problem [18]. This narrative review aims to highlight the urgent need for ethical oversight and regulation, as the range of applications for forensic genetic technologies expands and diversifies.
All people who work in the criminal justice system need to be educated about the situations in which these technologies should be used, as well as the potential advantages, drawbacks, and ambiguities associated with them.
Ethical, social, and legal concerns are always raised when sensitive and identifying personal data are collected, stored, and used [19]. Along with the evaluation of informed consent, genetic privacy is an important ethical issue that needs to be addressed and revisited on a regular basis, as research and technology continue to expand our technical capabilities [20]. In fact, forensic scientists, bioethicists, law enforcement agencies, genetic genealogists, and other interested parties should collaborate in the development of international policies and guidelines for best practices [21,22].
2. Materials and Methods
This narrative review was prepared following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyzes (PRISMA) guidelines [23].
The articles identified in the present review were selected from the PubMed and Scopus databases through the single or combined use of the following keywords: (“incidental findings” OR “pitfalls”) AND (“forensic genetics” OR “DNA fingerprinting” OR “genetic identification” OR “personal identification”) AND (“critical aspects” OR “ethical reflections” OR “ethical issues” OR “informed consent” OR “psychological implications”).
The evaluation of the articles was performed individually by two reviewers (G.F. and G.S.), who met and discussed the results obtained. The search was performed by reading and synthesizing the information collected and selecting the articles with content that was supplied with greater relevance, specificity, and scientific evidence. In the case of disagreements, the consensus of the research supervisor (S.G.) was sought. The inclusion criteria were the following: the articles must have been published over the last 22 years, between 2000 and 2022; both articles and reviews were considered; they had to be written in English or Italian; and free full text had to be available. A total of 248 works were identified in the PubMed and Scopus databases. Duplicates were removed, and a total of 206 articles were screened first by title, which allowed for the elimination of 114 works. Then, a total of 92 works were screened by abstract, after which 45 articles were investigated in their full-text form for eligibility. The number of articles excluded or included was registered and reported in a PRISMA flowchart (Figure 1).
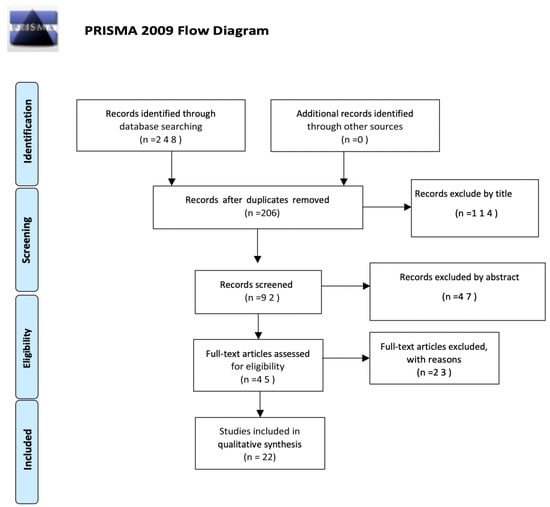
Figure 1.
Flow chart of the selection process for Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) 2009.
3. Results
To make the results obtained in the current review more comprehensible to the reader, we have summarized the selected works by grouping them into the following five categories: (a) ethical issues; (b) legal issues; (c) DNA databases; (d) informed consent; and (e) informed consent in cases of minors. Table 1 shows the breakdown by topic of the articles included in this literature review.

Table 1.
Breakdown by topic of the articles included in this narrative review.
3.1. Ethical Issues
Identifying individuals, living or dead, from their DNA can help to convict offenders or exonerate innocent people. It can confirm one’s presence at a crime scene or one’s place in a family tree. However, the sensitive nature of the genetic information locked in the coils of the DNA molecule also gives rise to ethical dilemmas. Varsha in 2006 [25] and subsequently Levitt in 2007 [19], considering that DNA can provide insights into many aspects of people and their families, including susceptibility to genetic disorders, legitimacy of birth, and fertility, emphasized that the collection, storage, and use of sensitive personal data always raise ethical, social, and legal issues. The authors concluded that these processes could increase the potential for genetic discrimination by government, society, and others. Therefore, DNA typing should be performed in a very sophisticated way, should meet all international standards, and should follow and abide by all ethical, legal, and social concerns.
More recently, Caenazzo et al. [1] emphasized that, for forensic experts, to the ethical principles and issues that have already been discussed in the literature from the fields of clinical and biomedical research has been added the complex legal management of accidental discoveries.
In this regard, it is necessary that governments seek advice on how to influence public policy based on evolving genetic knowledge, and scientists should be involved in this process, as communicated in van Heyningen and Cox (2002) [24]. Authors have also reported, as noted by Lee (2020) and Teodorović et al. (2017) [18,20], that, since the more science that evolves, the more information that is extrapolated by the genes, consequently genetic privacy, along with the ethical issues regarding it, needs to be re-examined.
Therefore, all the parties involved by scientific evolution in the forensic field should collaborate on the creation of international best practices, guidelines, and policies to keep up, as stated by Kennett (2019) [22].
The secondary use of collected biological materials from a forensic investigation should be guided by the same ethical principles that have been discussed in general regarding secondary uses in other fields (routine medical activities or research), particularly those involving vulnerable individuals. The return of results in certain investigations, such as those involving massive disasters, is a challenging aspect of secondary use of samples for research. In fact, it appears difficult to manage any IFs that reveal specific health effects for survivors. It is difficult to manage unusual circumstances in this context, such as the discovery of a false paternity during reference sample research, since the massive disaster has already had an impact on daily family life, and additional traumatic information may be upsetting. Providing guidance to researchers and research ethics boards and addressing ethical concerns regarding secondary sample use are becoming increasingly important, as also noted by Caenazzo et al. (2013) [26].
Forensic DNA phenotyping necessitates further contextualization of the operational capability within a broader privacy framework that is more ethically informed. In general, according to Scudder et al. (2018 [27], there are a number of inherent risks associated with any exploitation of the human genome, particularly if the donors have not given their informed consent. The same report concluded that whole genome sequencing significantly raises the stakes for medical information. It also mentioned the need to strike a balance between the public good and the government’s responsible stewardship, as well as the need to respect people’s dignity and privacy.
3.2. Legal Issue
DNA typing is a powerful tool in criminal investigations. The advent of DNA profiling has revolutionized the criminal justice system. Since the discovery of DNA to now, it has provided a cogent evidential base to corroborate guilt or innocence in courts of law. The report of the medical-legal team is sent to the judicial system, rather than the healthcare system, and the forensic expert is only required to refer information to the judge, who must be able to understand the scientific report and the pitfalls contained therein. On the other hand, in the case of IFs, as stated by Caenazzo et al. (2021) [3], the only way to inform someone in charge of receiving technical information about the case may be to include IFs in the forensic expert’s report to the judge since cases may result in having inaccurate genetic information if certain IFs were omitted from the report, as noted by Bellis et al. (2005) [13], but also because they could indicate health and social risks for the relatives of the person under investigation, even if not relevant to the legal aspects of the case [1,3]. However, as noted by Caenazzo et al., 2021 [3], the IFs need to be examined regarding how they might be reconciled with the judge’s obligation to maintain confidentiality.
According to Caenazzo et al., 2021 [3], with the judge’s permission, the forensic expert may be anyhow permitted to communicate with the family based on local law. When such approval is granted, practitioners of forensic science will have access to information about IFs that relatives do not know, and the victim’s relatives may or may not want to know. The investigators are unable to anticipate or mitigate the positive or negative effects of the disclosure of some IFs. To better understand the clinical significance of the IFs, a clinical multidisciplinary team or the family’s general practitioner may be helpful in these situations.
In the forensics field, according to Caenazzo et al. (2020) [1], if the incidental finding is related to a deceased subject, the moral obligation to have the permission of the interested party to reveal the information ceases, but the legal and formal obligation for this disclosure to be authorized by the judge remains. In the clinical context, permission to contact family members must be granted by the patient. The individuals to whom the information refers cannot express their decisions regarding whether or not to share the IFs with members of their family in this setting.
3.3. DNA Databases
A DNA database is a collection of DNA profiles and/or DNA samples (also known as a DNA databank) that can be used by law enforcement agencies to identify suspects of crimes; in contrast, biobanking is a way of collecting samples of bodily fluid or tissue for research purposes to help understand how health and diseases work.
A person’s DNA profile, once entered in the database, according to Mateen et al. (2021) [29], raises serious concerns because it may affect the person’s family and friends. In addition, it may violate a person’s human rights to “not know” what happens to his or her DNA profile in the database and how it affects his or her family. As a result, a person’s DNA profile in the DNA database has several implications for his or her fundamental rights.
Privacy ought to be a top priority today. The careless transfer of DNA compromises both the privacy of genetically related individuals who have not explicitly consented to be included in a database and the collective ability to safeguard personal privacy, as mentioned by Moran (2018) [28]. People may be asked for permission to include their DNA analyses in a DNA database. By restricting the scope of consent, extensive use of genetic material may be avoided or permitted. A person who voluntarily provides genetic material in a DNA dragnet, for instance, may expressly consent to have his/her DNA used in that investigation, but he or she may refuse to be included in a DNA database after the current investigation is concluded. Citizens can only use their consent effectively if they understand that they can consent to all, some, or none of the use of their genetic material, as stated by Fernandez (2005) [30].
Samuel et al. (2018) [21] called attention to DNA from those convicted of crimes, which should be the primary focus of forensic databases. There are very few situations in which forensic use of DNA without the subject’s full and informed consent can be justified, such as to solve a very serious crime, in addition to non-forensic DNA databases not typically being accessible for forensic purposes.
Levitt (2007) and Tozzo et al. (2017) [19,31] explained how the donation of biological samples for research purposes ought to be recognized, further motivated, and implemented to improve public trust in research biobanks. The person in charge of collecting, storing, and using personal data must be trusted. Therefore, it seems more appropriate than ever to implement a system of involvement, education, and information provision to the population about the aims of research biobanks. In addition, it is appropriate to consider the actual level of population awareness of DNA database applications for forensic purposes to improve interactions between policymakers and citizens and increase their awareness of the need to strike a balance between individual rights and society’s security.
3.4. The Importance of the Informed Consent
In general, there are several dangers associated with any use of the human genome, particularly when it is undertaken without the donor’s informed consent. In human research, obtaining the subject’s informed and free consent is required by pursuing the subject’s autonomy in its manifestation, as reported by both Katsanis et al. (2018) and Scudder et al. (2018) [27,32].
What informed consent must include was properly explained by Machado and Silva (2015) and Nijhawan et al. (2013) [33,34] and summarized in the following points: (a) a description of any potential discomforts or risks that the subject might experience, an estimate of how likely they are, and eventual measures that will be taken to avoid or minimize them; (b) a description of any anticipated benefits for the subject or for others; (c) a statement outlining who may have access to the records and the extent to which they will be kept secret; (d) the right of data subjects to be informed about the known and unknown risks associated with DNA sample collection and DNA profiling, including the content of the samples, their possible and inadmissible uses, and their storage time and availability and (e) the protection of individuals in relation to the processing of personal data and the free movement of such data, indicating the procedures linked with the recovery of samples and data and the terms under which samples and data can be accessed.
Before the collection and procedures are performed, as stated by Machado and Silva (2015) and Nijhawan et al. (2013) [33,34], informed consent must be obtained by the individual of interest, and both the subject/legally acceptable representative and the individual obtaining consent must personally sign and date the form. The informed consent document’s signature by the prospective subject or legally acceptable representative indicates that the document’s content has been adequately discussed and that the subject or legally acceptable representative has freely given informed consent. In addition, to ensure that a copy of the signed consent form is kept at the site, source documents must indicate that consent was obtained prior to the start of the study’s treatments and procedures.
No physician, laboratory, or other entity should be able to sequence, store, or test identifiable DNA unless the person being tested has given written informed consent or conditions for exceptions for people who are incompetent to consent, as recorded in Robertson (2003) [35]. This process should be required by public policy, as well as ethical guidelines. To safeguard individuals and instill confidence that personal rights in one’s own DNA and its information are protected, such a policy will be absolutely necessary. To sequence an identifiable whole genome or any part of it, access it for later testing, or disclose the results of any testing that has occurred, an individual’s informed consent would be required under such a policy.
3.5. How to Act with a Minor: Informed Consent and Consequences
Before non-routine screening procedures are performed, informed consent must be obtained. If the research involves children younger than 18, parental consent or permission must be obtained, as noted by Nijhawan et al. (2013) [33]. Because they are unable to give informed consent for their participation, children are a research population that is particularly at risk. The decision of the minor must be considered, in addition to the consent of the parent(s) or legal guardian, particularly for older children whose objections must be considered, as stated by Tozzo et al. (2010) [36].
The possibility that the identification of a genetic predisposition could result in stigma, particularly for genetic risks related to psychiatric issues or undesirable behaviors, is one of the concerns that is frequently expressed regarding genetic information, as published and illustrated with an example by Burke and Diekema (2006) [37]. A gene variant in the catechol-O-methyl transferase gene may increase the likelihood of adolescent cannabis use being followed by adult psychosis, according to some studies. This case is an illustration of a possible IF that may occur when screening a child’s DNA, in which parents may experience distress and become overprotective or hypervigilant of their children. Even though such vigilance might be necessary in some situations, it could also cause a disruption in the child’s life, give the child the impression that he/she is “different” from other children, and hinder the child’s growth in other ways. When genetic testing results are only moderately predictive or when specific preventative measures are unavailable, it is important to consider whether the added information outweighs the potential for increased familial anxiety.
4. Discussion
As we reported in the current narrative review, there have been substantial improvements in forensic genetics since the day it was introduced. In addition, with the evolution of science and DNA technologies, the need for specific guidelines to keep up with the times have become more important.
In practices regarding, for example, STRs and DNA fingerprinting, the need for guidelines for complex samples have been satisfied, even if only partially, by several organizations. They have provided a series of documents and recommendations to help forensic experts move toward possible complex situations and to perform with correct analyses, especially considering the delicate and life-changing contests into which forensic investigations are inserted most of the time.
Incidental findings can easily arise during forensic investigations and cannot be predicted in any way; therefore, we think it should be mandatory to have a series of directions, for the purpose of making the best decisions for the parties involved. In order to cover every contest, the guidelines should be international and written by genetics, judges, forensic investigators, and any other experts who might be involved.
It is common knowledge that the circumstances surrounding forensic investigations are frequently extremely delicate and stressful for everyone involved: the parties under investigation, their families, and even the experts, who bear a significant amount of responsibility for the lives of the interested parties. For example, with a paternity discrepancy discovery, we have to consider that, in some countries, adultery is punished with the death penalty. During this waiting period, until there is an official international direction, it remains true the professionals may find themselves in the position of deciding whether or not to communicate an IF.
The Declaration of Helsinki in article 26 governs the importance of proper and detailed information about the aims, methods, and risks of a study and the discomforts that it may entail, post-study provisions, and any other relevant aspects, emphasizing that the subject has the right to withdraw consent at any time [4]. In Italy, on 31 January 2018, Law n.219/2017 [38] came into force, containing “Rules on informed consent and advance provisions on processing”. Article 1 of this Act states that “no medical treatment may be commenced or preceded without the free and informed consent of the person concerned, except in cases expressly provided for by law”, in compliance with the principles of the Constitution (articles 2, 13 and 32) [39] and the Charter of Fundamental Rights of the European Union [40]. The same article affirms the right of every person “to know his or her state of health and to be informed in a complete, updated and understandable way [...]”. For these reasons, every piece of information, result, and sample must be treated and kept in compliance with the law and according to the information given to the subject before the test; all of these factors are also governed by the Criminal Code (art. 622) [41], the Code of Criminal Procedure (art. 200) [42], and the Code of Medical Ethics (Chapter III) [43] for the maintenance of professional secrecy.
In this context, a possible partial solution would be to take advantage of the opportunity to inform the interested party about the incidental finding and hear his/her opinion about it, as filling out the informed consent form and understanding every part of it are a necessary step before undergoing a DNA test.
To achieve this goal, we elaborated the information reported in the Supplementary Materials (Document S1) to add to the informed consent forms currently in use. Doing so would discharge the expert from the responsibility of deciding whether or not it is necessary to communicate the accidental discovery to the individual involved through the following note:
“I give the authorization to communicate to me any eventual incidental findings discovered. If any incidental findings are discovered, I give the authorization to communicate it to me only in case my health or the health of my relatives is threatened.”
However, this statement is not sufficient because it does not cover every possibility. Even if the person whose DNA was tested signs an informed consent stating that he/she does not wish to know an inadvertent IF, the professional should be able to determine whether the accidental discovery should be communicated to the relative involved if the IF is an inherit mutation that could pose a threat to the health of family members or involves genetic information about another relative. There is no doubt that this situation could conflict with the obligation for professional secrecy.
Article 10 of the Code of Medical Ethics stipulates that physicians must keep a secret of everything that is confided to them or become aware of in the exercise of the profession (professional secrecy) [43]. The death of the patient does not exempt the physician from the obligation of secrecy; a revelation is admitted only when motivated by a just cause, (i.e., complaint and report to a judicial authority, health complaints, notifications of infectious diseases, mandatory certifications). In 2021, the Italian Society of Forensic Geneticists (Ge.F.I) [44] approved a code of conduct for forensic geneticists aligned with article 3 of the Code of Medical Ethics in matters of professional secrecy [43].
Informed consent in the case of a minor is another point that we should emphasize. The legal guardian makes the decision about the will, and it is important to consider whether the children can be contacted and told about the decisions during the treatment of only once they become adults. Article 3 of the Italian law 219/2017 [38] indicates the need to involve the minors in considering their will in relation to their age and their maturity. Given that this is situation is personal, we believe it should be addressed to provide the party with the maximal level of protection. It is possible that the parents have agreed to a settlement that does not conform to the interested person’s will.
Along with the ethical and legal issues analyzed in the results, we highlighted the DNA database and biobank matters. We concur with the authors who took the time to underscore the issues associated with people’s lack of trust in these data collection tools and their continued significance to scientific advancement and research. Accordingly, we inserted into the new composition previously reported a comment to be provided by the subject whose DNA is tested, in which the possibility is broached of tissue being deposited in a biobank and contributing to research while maintaining his/her full privacy and anonymity. It is extremely important to sensitize people regarding questions that are important for progress and to dispel preconceptions.
In forensic investigations, the forensic expert and the judge are the only people who seem to be able to reveal IFs, while in clinical practice, these reports can be supported by a psychologist. Since contests regarding forensic examinations are already unusually fragile, we believe that the inclusion of a professional figure, such as a psychologist, as an expert in sustaining psychologically distressed people should be mandatory and considered.
5. Conclusions
The progress in forensic DNA techniques and emerging technologies have aggravated an already complicated problem since the more that science advances, the more IFs that will be discovered. Therefore, the need to provide guidance to experts managing unexpected IFs in fragile situations can no longer be ignored, especially considering the context in which they occurred.
We hope that the investigation of and reflection on the ethical, legal, and psychological issues and the importance of informed consent will provide the incentive to propose a solution.
We believe that our proposal for informed consent (Supplementary Materials—Document S1), with an additional note that includes the possibility of accidental discoveries, could work as an immediate solution for the simplest circumstances or when the incidental findings have no relevance to the investigation. The situation is different when the accidental discovery could have a relationship with the facts, representing a potential motive of the offense, as reported in the case report (Supplementary Materials—Document S2). Our view in these circumstances is that the information obtained should be forwarded to the judicial authority, which will be responsible for using it purely for investigative purposes during the investigation.
Nevertheless, we strongly recommend the development of clear international recommendations and guidelines, as was undertaken for STRs and DNA fingerprinting, as the finest and most permanent solution to an extremely complex topic.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/forensicsci3020026/s1: Document S1: Information regarding the possibility of incidental findings; and Document S2: Case report.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.S. and S.G.; methodology, G.F. and G.S.; formal analysis, G.F.; investigation, G.F. and G.S.; data curation, G.F. and G.S.; writing—original draft preparation, G.F.; writing—review and editing; G.S. and S.G.; supervision, S.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
This review is the result of a study conducted within the framework of the International PhD in Global Health, Humanitarian Aid, and Disaster Medicine organized by Università del Piemonte Orientale (UPO).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Caenazzo, L.; Tozzo, P.; Dierickx, K. New Frontiers and Old Challenges: How to Manage Incidental Findings When Forensic Diagnosis Goes Beyond. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarpulla, V.; Amadasi, A.; Pelotti, S.; Ingravallo, F. Applicability and usefulness of the Declaration of Helsinki for forensic research with human cadavers and remains. Forensic Sci. Med. Pathol. 2022, 19, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caenazzo, L.; Tozzo, P.; Dierickx, K. Incidental findings in forensics: Are we sure that it is a question easy to deal with? Int. J. Leg. Med. 2021, 135, 591–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The World Medical Association Inc. Available online: https://www.wma.net/policies-post/wma-declaration-of-helsinki-ethical-principles-for-medical-research-involving-human-subjects/ (accessed on 7 March 2019).
- Pentz, R.D.; Cohen, C.B.; Wicclair, M.; DeVita, M.A.; Flamm, A.L.; Youngner, S.J.; Hamric, A.B.; McCabe, M.S.; Glover, J.J.; Kittiko, W.J.; et al. Arap, Ethics guidelines for research with the recently dead. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 1145–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuels, A. Human Tissue Act 2004: The Removal and Retention of Human Organs and Tissue. Med.-Leg. J. 2004, 72, 148–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recommendation CM/Rec (2016) 4 of the Committee of Ministers to Member States on the Protection of Journalism and Safety of Journalists and Other Media Actors—Freedom of Expression, (n.d.). Available online: https://www.coe.int/en/web/freedom-expression/committee-of-ministers-adopted-texts/-/asset_publisher/aDXmrol0vvsU/content/recommendation-cm-rec-2016-4-of-the-committee-of-ministers-to-member-states-on-the-protection-of-journalism-and-safety-of-journalists (accessed on 25 April 2023).
- Sguazzi, G.; Mickleburgh, H.L.; Ghignone, S.; Voyron, S.; Renò, F.; Migliario, M.; Sellitto, F.; Lovisolo, F.; Camurani, G.; Ogbanga, N.; et al. Microbial DNA in human nucleic acid extracts: Recoverability of the microbiome in DNA extracts stored frozen long-term and its potential and ethical implications for forensic investigation. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2022, 59, 102686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzetta Ufficiale. Decreto Legislativo 10 Agosto 2018, n. 101. Available online: https://www.gazzettaufficiale.it/eli/id/2018/09/04/18G00129/sg (accessed on 2 December 2019).
- Presidente, I.L.; Repubblica, D. Legge 10 febbraio 2020, n. 10. Norme in materia di disposizione del proprio corpo e dei tessuti post mortem a fini di studio, di formazione e di ricerca scientifica. BIOETICA 2020, 2020, 590–602. [Google Scholar]
- Fossheim, H. More Than Just Bones: Research and Human Remains; The National Research Ethic Cimmittees of Norway: Oslo, Norway, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sugano, K.; Tack, J.; Kuipers, E.J.; Graham, D.Y.; El-Omar, E.M.; Miura, S.; Haruma, K.; Asaka, M.; Uemura, N.; Malfertheiner, P.; et al. Kyoto global consensus report on Helicobacter pylorigastritis. Gut 2015, 64, 1353–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellis, M.A.; Hughes, K.; Hughes, S.; Ashton, J.R. Measuring paternal discrepancy and its public health consequences. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2005, 59, 749–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miozzo, C.; Maxzud, K.; Altuna, E.; Belaus, A.; Lavezzo, A.; Modesti, N. A case of chimerism in a paternity study. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. Suppl. Ser. 2009, 2, 228–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castella, V.; Lesta, M.D.M.; Mangin, P. One person with two DNA profiles: A(nother) case of mosaicism or chimerism. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2009, 123, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottlieb, B.; Trifiro, M.A. Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome. In GeneReviews® [Internet]; Updated 11 May 2017; Adam, M.P., Mirzaa, G.M., Pago, N.R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J.H., Gripp, K.W., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Batista, R.L.; Costa, E.M.F.; Rodrigues, A.d.S.; Gomes, N.L.; Faria, J.A., Jr.; Nishi, M.Y.; Arnhold, I.J.P.; Domenice, S.; de Mendonca, B.B. Androgen insensitivity syndrome: A review. Arq. Bras. Endocrinol. Metabol. 2018, 62, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teodorović, S.; Mijović, D.; Nenadić, U.R.; Savić, M. Attitudes regarding the national forensic DNA database: Survey data from the general public, prison inmates and prosecutors’ offices in the Republic of Serbia. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2017, 28, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levitt, M. Forensic databases: Benefits and ethical and social costs. Br. Med. Bull. 2007, 83, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, T.J.; Lee, S.B. Forensic Genetics, Ethics, Privacy, and Public Policy. In Silent Witness: Forensic DNA Evidence in Criminal Investigations and Humanitarian Disasters; Erlich, H., Stover, E., White, T.J., Eds.; Oxford Academic: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, G.; Howard, H.C.; Cornel, M.; van El, C.; Hall, A.; Forzano, F.; Prainsack, B. A response to the forensic genetics policy initiative’s report “Establishing Best Practice for Forensic DNA Databases”. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2018, 36, e19–e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennett, D. Using genetic genealogy databases in missing persons cases and to develop suspect leads in violent crimes. Forensic Sci. Int. 2019, 301, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: Explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Heyningen, V.; Cox, D.R. Advice to governments: Scientific give and take. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2002, 3, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varsha DNA Fingerprinting in the Criminal Justice System: An Overview. DNA Cell Biol. 2006, 25, 181–188. [CrossRef]
- Caenazzo, L.; Tozzo, P.; Rodriguez, D. Ethical Issues in DNA Identification of Human Biological Material from Mass Disasters. Prehospital Disaster Med. 2013, 28, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scudder, N.; McNevin, D.; Kelty, S.F.; Walsh, S.J.; Robertson, J. Forensic DNA phenotyping: Developing a model privacy impact assessment. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2018, 34, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, K.S. Damned by DNA—Balancing personal privacy with public safety. Forensic Sci. Int. 2018, 292, e3–e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateen, R.M.; Sabar, M.F.; Hussain, S.; Parveen, R.; Hussain, M. Familial DNA analysis and criminal investigation: Usage, downsides and privacy concerns. Forensic Sci. Int. 2021, 318, 110576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, H.K. Genetic Privacy, Abandonment, and DNA Dragnets: Is Fourth Amendment Jurisprudence Adequate? Häst. Cent. Rep. 2005, 35, 21–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozzo, P.; Fassina, A.; Caenazzo, L. Young people’s awareness on biobanking and DNA profiling: Results of a questionnaire administered to Italian university students. Life Sci. Soc. Policy 2017, 13, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsanis, S.H.; Snyder, L.; Arnholt, K.; Mundorff, A.Z. Consent process for US-based family reference DNA samples. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2018, 32, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musmade, P.B.; Nijhawan, L.P.; Udupa, N.; Bairy, K.; Bhat, K.; Janodia, M.D.; Muddukrishna, B. Informed consent: Issues and challenges. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2013, 4, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, H.; Silva, S. Public participation in genetic databases: Crossing the boundaries between biobanks and forensic DNA databases through the principle of solidarity. J. Med. Ethics 2015, 41, 820–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J. The $1000 genome: Ethical and legal hurdles. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2003, 4, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozzo, P.; Pegoraro, R.; Caenazzo, L. Biobanks for non-clinical purposes and the new law on forensic biobanks: Does the Italian context protect the rights of minors? J. Med. Ethics 2010, 36, 775–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, W.; Diekema, D.S. Ethical issues arising from the participation of children in genetic research. J. Pediatr. 2006, 149, S34–S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazzetta Ufficiale della Repubblica Italiana, LEGGE 22 Dicembre 2017, n. 219, (n.d.). Available online: https://www.gazzettaufficiale.it/eli/id/2018/1/16/18G00006/sg (accessed on 25 April 2023).
- La Costituzione | Senato della Repubblica, (n.d.). Available online: https://www.senato.it/istituzione/la-costituzione (accessed on 25 April 2023).
- Charter of Fundamental Rights of the European Union. 2000. Available online: https://www.europarl.europa.eu/charter/pdf/text_en.pdf (accessed on 25 April 2023).
- Codice Penale. Articolo 622—Legirel, (n.d.). Available online: https://www.legirel.cnrs.fr/spip.php?article239&lang=fr (accessed on 25 April 2023).
- Gazzetta Ufficiale della Repubblica Italiana, Codice di Procedura Penale Decreto del Presidente della Repubblica 22 Settembre 1988, n. 447, (n.d.). Available online: https://www.gazzettaufficiale.it/sommario/codici/codiceProceduraPenale (accessed on 25 April 2023).
- Federazione Nazionale degli Ordini dei Medici Chirurghi e degli Odontoiatri, Codice deontologico, 1998. Available online: https://portale.fnomceo.it/codice-deontologico/ (accessed on 25 April 2023).
- Genetisti Forensi Italiani, Codice di Comportamento del Genetista Forense, 2021. Available online: https://www.gefi-isfg.org/temp/Codice%20Comportamento%20GeFI.pdf (accessed on 25 April 2023).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).