Subadult Age Estimation Using the Mixed Cumulative Probit and a Contemporary United States Population
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Observer Error and Reliability of the Variables
2.4. Methodology
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
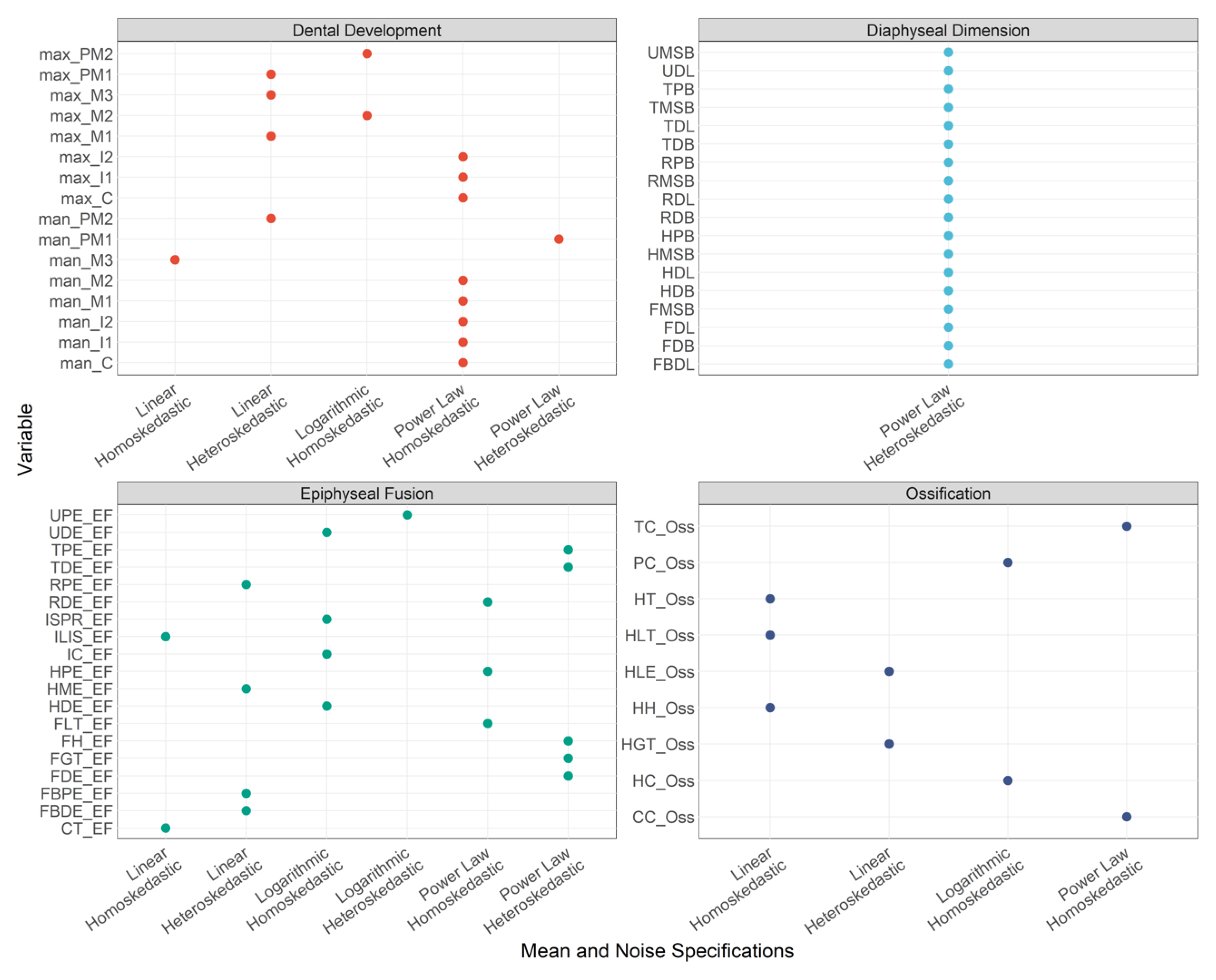
3.1. Mean and Noise Specifications
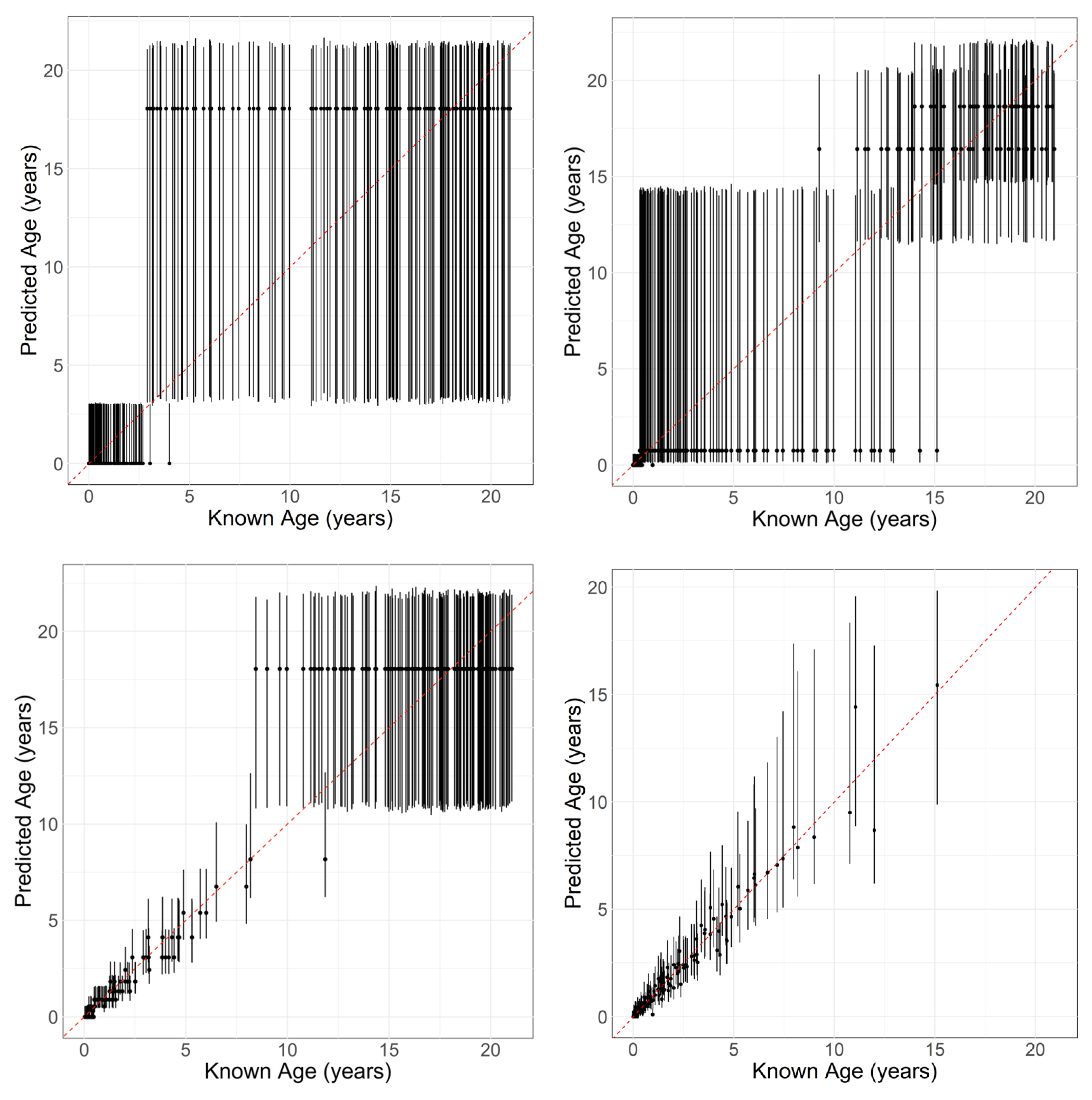
3.2. Performance: Univariate Models
3.3. Performance: Multivariate and Mixed Models
3.4. K-L Statistic
4. Discussion
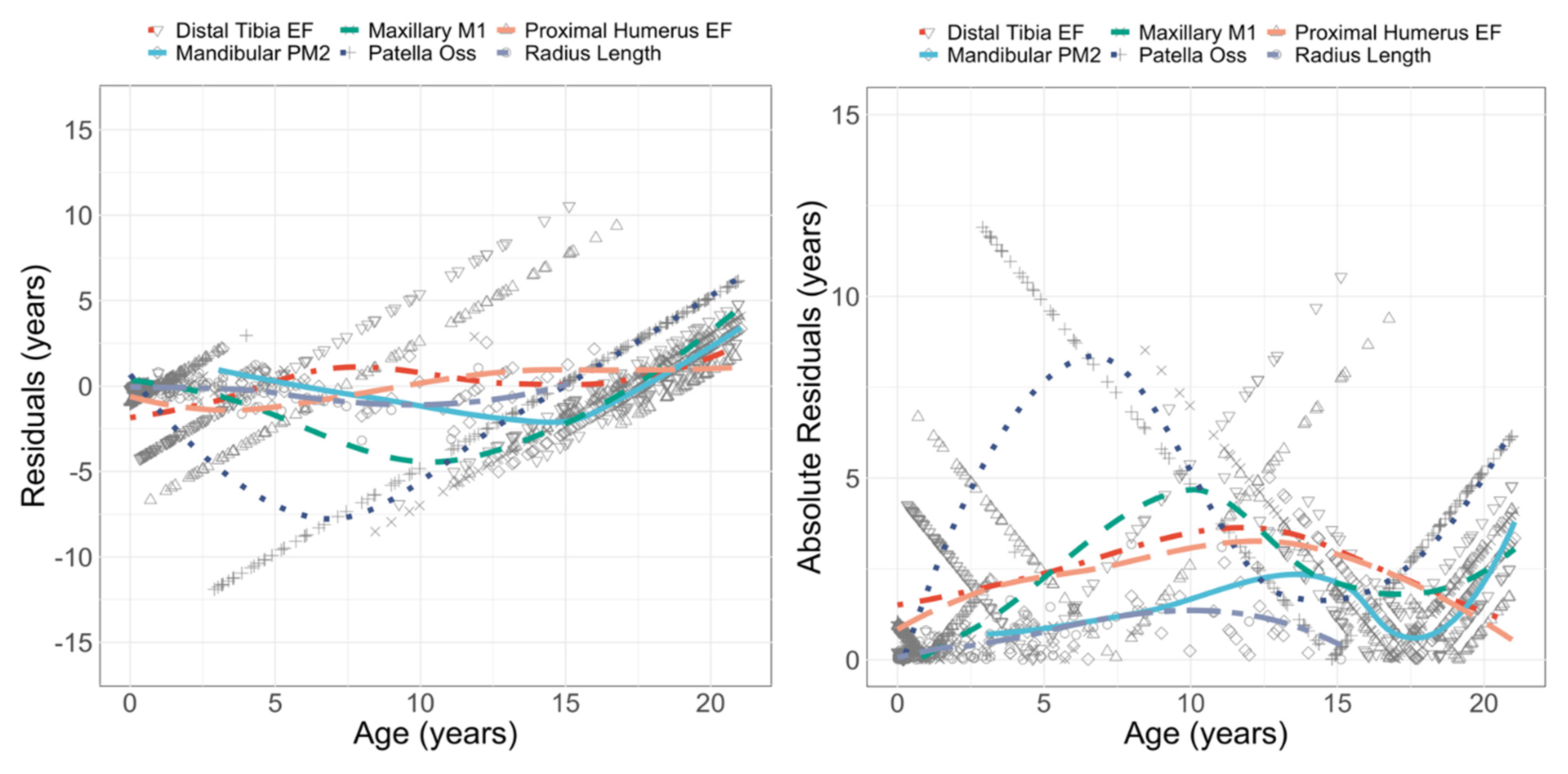
4.1. Evaluating the Performance
4.2. Achieving High Accuracy and the Variability around 95%
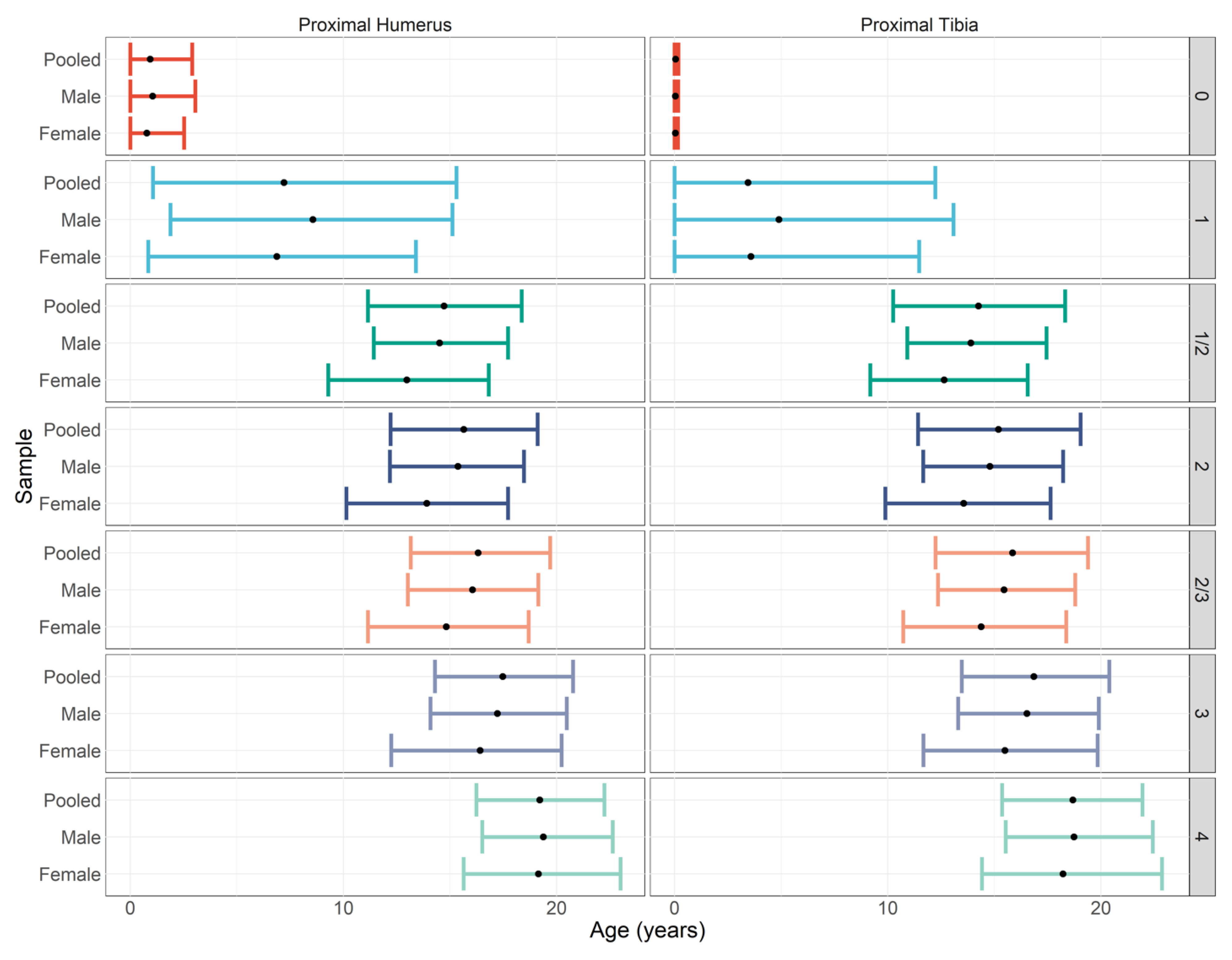
4.3. Sex Differences and their Impact on Age Estimation
4.4. Accessibility and Usability
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Tobel, J.; Fieuws, S.; Hillewig, E.; Phlypo, I.; van Wijk, M.; de Haas, M.B.; Politis, C.; Verstraete, K.L.; Thevissen, P.W. Multi-Factorial Age Estimation: A Bayesian Approach Combining Dental and Skeletal Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Forensic Sci. Int. 2020, 306, 110054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumagai, A.; Willems, G.; Franco, A.; Thevissen, P. Age Estimation Combining Radiographic Information of Two Dental and Four Skeletal Predictors in Children and Subadults. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2018, 132, 1769–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coqueugniot, H.; Weaver, T.; Houët, F. Brief Communication: A Probabilistic Approach to Age Estimation from Infracranial Sequences of Maturation. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 2010, 142, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sgheiza, V. Conditional Independence Assumption and Appropriate Number of Stages in Dental Developmental Age Estimation. Forensic Sci. Int. 2022, 330, 111135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duangto, P.; Janhom, A.; Prasitwattanaseree, S.; Iamaroon, A. New Equations for Age Estimation Using Four Permanent Mandibular Teeth in Thai Children and Adolescents. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2018, 132, 1743–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esan, T.A.; Schepartz, L.A. The Timing of Permanent Tooth Development in a Black Southern African Population Using the Demirjian Method. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2019, 133, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubelaker, D.H.; Khosrowshahi, H. Estimation of Age in Forensic Anthropology: Historical Perspective and Recent Methodological Advances. Forensic Sci. Res. 2019, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konigsberg, L.W.; Frankenberg, S.R.; Sgheiza, V.; Liversidge, H.M. Prior Probabilities and the Age Threshold Problem: First and Second Molar Development. Hum. Biol. 2022, 93, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sironi, E.; Vuille, J.; Morling, N.; Taroni, F. On the Bayesian Approach to Forensic Age Estimation of Living Individuals. Forensic Sci. Int. 2017, 281, e24–e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, S.D.; Edgar, H.J. Announcement: The New Mexico Decedent Image Database. Forensic Imaging 2021, 24, 200436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stull, K.E.; Corron, L.K. The Subadult Virtual Anthropology Database (SVAD): An Accessible Repository of Contemporary Subadult Reference Data. Forensic Sci. 2022, 2, 20–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, H.; Berry, D. NMDID: A New Research Resource for Biological Anthropology. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. Suppl. 2019, 168, 166. [Google Scholar]
- Stull, K.E.; L’Abbé, E.N.; Ousley, S.D. Using Multivariate Adaptive Regression Splines to Estimate Subadult Age from Diaphyseal Dimensions. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 2014, 154, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stull, K.; Corron, L.; Price, M. Subadult Age Estimation Variables: Exploring Their Varying Roles across Ontogeny. In Remodeling Forensic Skeletal Age; Algee-Hewit, B., Kim, J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 49–73. [Google Scholar]
- Corron, L.; Marchal, F.; Condemi, S.; Telmon, S. Integrating Growth Variability of the Ilium, Fifth Lumbar Vertebra, and Clavicle with Multivariate Adaptive Regression Splines Models for Subadult Age Estimation. J. Forensic Sci. 2019, 64, 34–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, H.F.V.; Abrantes, J.; Humphrey, L.T. Age Estimation of Immature Human Skeletal Remains from the Diaphyseal Length of the Long Bones in the Postnatal Period. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2014, 128, 809–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, E.; Baccino, E.; Martrille, L.; Ramsthaler, F.; Prieto, J.; Schuliar, Y.; Lynnerup, N.; Cattaneo, C. The Problem of Aging Human Remains and Living Individuals: A Review. Forensic Sci. Int. 2009, 193, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council (U.S.) (Ed.) Strengthening Forensic Science in the United States: A Path Forward; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2009; ISBN 978-0-309-13135-3. [Google Scholar]
- Boldsen, J.; Milner, G.; Konigsberg, L.; Wood, J. Transition Analysis: A New Method for Estimating Age from Skeletons. In Paleodemography: Age Distributions from Skeletal Samples; Hoppa, R., Vaupel, J., Eds.; Cambrige University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2002; pp. 73–106. [Google Scholar]
- DiGangi, E.; Bethard, J.; Kimmerle, E.; Konigsberg, L. A New Method for Estimating Age-At-Death From the First Rib. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 2009, 138, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fojas, C.L.; Kim, J.; Minsky-Rowland, J.D.; Algee-Hewitt, B.F.B. Testing Inter-Observer Reliability of the Transition Analysis Aging Method on the William M. Bass Forensic Skeletal Collection. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 2018, 165, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getz, S.M. The Use of Transition Analysis in Skeletal Age Estimation. WIREs Forensic Sci. 2020, 2, e1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godde, K.; Hens, S.M. Modeling Senescence Changes of the Pubic Symphysis in Historic Italian Populations: A Comparison of the Rostock and Forensic Approaches to Aging Using Transition Analysis. Am. J. Phys. Anthr. 2015, 156, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hens, S.M.; Godde, K. New Approaches to Age Estimation Using Palatal Suture Fusion. J. Forensic Sci. 2020, 65, 1406–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jooste, N.; L’Abbé, E.N.; Pretorius, S.; Steyn, M. Validation of Transition Analysis as a Method of Adult Age Estimation in a Modern South African Sample. Forensic Sci. Int. 2016, 266, 580.e1–580.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sironi, E.; Taroni, F. Bayesian Networks for the Age Classification of Living Individuals: A Study on Transition Analysis. J. Forensic Sci. Med. 2015, 1, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangmose, S.; Thevissen, P.; Lynnerup, N.; Willems, G.; Boldsen, J. Age Estimation in the Living: Transition Analysis on Developing Third Molars. Forensic Sci. Int. 2015, 257, 512.e1–512.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konigsberg, L.; Herrmann, N.; Wescott, D.; Kimmerle, E. Estimation and Evidence in Forensic Anthropology: Age-at-Death. J. Forensic Sci. 2008, 53, 541–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konigsberg, L.W.; Frankenberg, S.R. Estimation of Age Structure in Anthropological Demography. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 1992, 89, 235–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milner, G.R.; Boldsen, J.L. Transition Analysis: A Validation Study with Known-Age Modern American Skeletons. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 2012, 148, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikita, E.; Nikitas, P. Skeletal Age-at-Death Estimation: Bayesian versus Regression Methods. Forensic Sci. Int. 2019, 297, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konigsberg, L.W. Multivariate Cumulative Probit for Age Estimation Using Ordinal Categorical Data. Ann. Hum. Biol. 2015, 42, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fieuws, S.; Willems, G.; Larsen-Tangmose, S.; Lynnerup, N.; Boldsen, J.; Thevissen, P. Obtaining Appropriate Interval Estimates for Age When Multiple Indicators Are Used: Evaluation of an Ad-Hoc Procedure. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2015, 130, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stull, K.; Chu, E.; Corron, L.; Price, M. Mixed Cumulative Probit: A Multivariate Generalization of Transition Analysis That Accommodates Variation in the Shape, Spread, and Structure of Data. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2022. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Allison, P.A.; Bottjer, D.J. Taphonomy: Bias and Process Through Time. In Taphonomy: Process and Bias Through Time; Allison, P.A., Bottjer, D.J., Eds.; Aims & Scope Topics in Geobiology Book Series; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 1–17. ISBN 978-90-481-8643-3. [Google Scholar]
- Stodder, A.L.W. Taphonomy and the Nature of Archaeological Assemblages. In Biological Anthropology of the Human Skeleton; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 73–115. ISBN 978-1-119-15164-7. [Google Scholar]
- Berry, S.D.; Edgar, H.J.H. Extracting and Standardizing Medical Examiner Data to Improve Health. AMIA Jt. Summits Transl. Sci. Proc. 2020, 2020, 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- Edgar, H.; Daneshvari Berry, S.; Moes, E.; Adolphi, N.; Bridges, P.; Nolte, K. New Mexico Decedent Image Database (NMDID); Office of the Medical Investigator, University of New Mexico: Albuquerque, NM, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ousley, S. A Radiographic Database for Estimating Biological Parameters in Modern Subadults; Final Technical Report, National Institute of Justice Award Number 2008-DN-BX-K152; Mercyhurst University: Erie, PA, USA, 2013. Available online: https://ncjrs.gov/pdffiles1/nij/grants/242697.pdf (accessed on 7 November 2022).
- Stull, K.E.; Wolfe, C.A.; Corron, L.K.; Heim, K.; Hulse, C.N.; Pilloud, M.A. A Comparison of Subadult Skeletal and Dental Development Based on Living and Deceased Samples. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 2021, 175, 36–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spake, L.; Hoppa, R.D.; Blau, S.; Cardoso, H.F.V. Lack of Biological Mortality Bias in the Timing of Dental Formation in Contemporary Children: Implications for the Study of Past Populations. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 2021, 174, 646–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spake, L.; Hoppa, R.D.; Blau, S.; Cardoso, H.F.V. Biological Mortality Bias in Diaphyseal Growth of Contemporary Children: Implications for Paleoauxology. Am. J. Biol. Anthropol. 2022, 178, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stull, K.; Corron, L.K. Subadult Virtual Anthropology Database (SVAD) Data Collection Protocol: Epiphyseal Fusion, Diaphyseal Dimensions, Dental Development Stages, Vertebral Neural Canal Dimensions. Zenodo 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corron, L.K.; Stock, M.K.; Cole, S.J.; Hulse, C.N.; Garvin, H.M.; Klales, A.R.; Stull, K.E. Standardizing Ordinal Subadult Age Indicators: Testing for Observer Agreement and Consistency across Modalities. Forensic Sci. Int. 2021, 320, 110687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stull, K.; Corron, L. SVAD_US (1.0.0) [Data Set]. Zenodo 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlQahtani, S.J.; Hector, M.P.; Liversidge, H.M. Brief Communication: The London Atlas of Human Tooth Development and Eruption. Am. J. Phys. Anthr. 2010, 142, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corron, L.K.; Broehl, K.A.; Chu, E.Y.; Vlemincq-Mendieta, T.; Wolfe, C.A.; Pilloud, M.A.; Scott, G.R.; Spradley, M.K.; Stull, K.E. Agreement and Error Rates Associated with Standardized Data Collection Protocols for Skeletal and Dental Data on 3D Virtual Subadult Crania. Forensic Sci. Int. 2022, 334, 111272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colman, K.L.; de Boer, H.H.; Dobbe, J.G.G.; Liberton, N.P.T.J.; Stull, K.E.; van Eijnatten, M.; Streekstra, G.J.; Oostra, R.-J.; van Rijn, R.R.; van der Merwe, A.E. Virtual Forensic Anthropology: The Accuracy of Osteometric Analysis of 3D Bone Models Derived from Clinical Computed Tomography (CT) Scans. Forensic Sci. Int. 2019, 304, 109963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colman, K.L.; Dobbe, J.G.G.; Stull, K.E.; Ruijter, J.M. The Geometrical Precision of Virtual Bone Models Derived from Clinical Computed Tomography Data for Forensic Anthropology. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2017, 131, 1155–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garvin, H.M.; Stock, M.K. The Utility of Advanced Imaging in Forensic Anthropology. Acad. Forensic Pathol. 2016, 6, 499–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stock, M.K.; Garvin, H.M.; Corron, L.K.; Hulse, C.N.; Cirillo, L.E.; Klales, A.R.; Colman, K.L.; Stull, K.E. The Importance of Processing Procedures and Threshold Values in CT Scan Segmentation of Skeletal Elements: An Example Using the Immature Os Coxa. Forensic Sci. Int. 2020, 309, 110232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, M. Caret: Classification and Regression Training; Astrophysics Source Code Library, 2015. 1505.003. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/caret%3A-Classification-and-Regression-Training-Kuhn/258c7e3242b91e02e092e77e058f6275ba52b12d (accessed on 31 October 2022).
- Valsecchi, A.; Irurita Olivares, J.; Mesejo, P. Age Estimation in Forensic Anthropology: Methodological Considerations about the Validation Studies of Prediction Models. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2019, 133, 1915–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelman, A.; Hwang, J.; Vehtari, A. Understanding Predictive Information Criteria for Bayesian Models. Stat. Comput. 2014, 24, 997–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gneiting, T. Making and Evaluating Point Forecasts. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2011, 106, 746–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corron, L. Juvenile Age Estimation in Physical Anthropology: A Critical Review of Existing Methods and the Application of Two Standardised Methodological Approaches. Ph.D. Thesis, Aix-Marseille University, Marseille, France, 2016; 870p. [Google Scholar]
- Milner, G.; Boldsen, J. Skeletal Age Estimation: Where Are We and Where Should We Go? In A Companion to Forensic Anthropology; Dirkmaat, D., Ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Malden, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Corron, L.; Marchal, F.; Condemi, S.; Adalian, P. A Critical Review of Sub-Adult Age Estimation in Biological Anthropology: Do Methods Comply with Published Recommendations? Forensic Sci. Int. 2018, 288, 328.e1–328.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmeling, A.; Garamendi González, P.; Prieto, J.; Landa, M. Forensic Age Estimation in Unaccompanied Minors and Young Living Adults. In Forensic Medicine from Old Problems to New Challenges; Vieira, D.N., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2011; ISBN 978-953-307-262-3. [Google Scholar]
- Stull, K.; Armelli, K. Combining Variables to Improve Subadult Age Estimation. Forensic Anthropol. 2020, 3, 203–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štern, D.; Payer, C.; Giuliani, N.; Urschler, M. Automatic Age Estimation and Majority Age Classification From Multi-Factorial MRI Data. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2019, 23, 1392–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, H.F.V.; Vandergugten, J.M.; Humphrey, L.T. Age Estimation of Immature Human Skeletal Remains from the Metaphyseal and Epiphyseal Widths of the Long Bones in the Post-Natal Period. Am. J. Phys. Anthr. 2017, 162, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, C.; Chu, E.; Corron, L.; Price, M.; Stull, K. Advances in Subadult Age Estimation: Using Information Theory to Explore the Relationship Between Growth Indicators and Age. In Proceedings of the 91st Annual Meeting, Denver, CO, USA, 23–26 March 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Stull, K.; Cole, S.; Cirillo, L.; Hulse, C. Subadult Sex Estimation. In Sex Estimation of the Human Skeleton: History, Methods, and Emerging Techniques; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; p. 424. [Google Scholar]
- ANSI/ASB Standard 0090; Standard for Sex Estimation in Forensic Anthropology. Academy Standards Board: Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 2019.
- Badyaev, A.V. Growing Apart: An Ontogenetic Perspective on the Evolution of Sexual Size Dimorphism. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2002, 17, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogin, B. Patterns of Human Growth, 3rd ed.; Cambridge Studies in Biological and Evolutionary Anthropology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2020; ISBN 978-1-108-43448-5. [Google Scholar]
- Hauspie, R.; Roelants, M. Adolescent Growth. In Human Growth and Development; Cameron, N., Bogin, B., Eds.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 57–79. [Google Scholar]
- Krüger, G.; L’Abbe, E.; Stull, K. Sex Estimation from the Long Bones of Modern South Africans. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2017, 131, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stull, K.; L’Abbe, E.; Ousley, S. Subadult Sex Estimation from Diaphyseal Dimensions. Am. J. Phys. Anthr. 2017, 163, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spradley, M.; Jantz, R. Sex Estimation in Forensic Anthropology: Skull versus Postcranial Elements. J. Forensic Sci. 2011, 56, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheuer, L.; Black, S. Developmental Juvenile Osteology; Elsevier Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Liversidge, H.M.; Peariasamy, K.; Folayan, M.O.; Adeniyi, A.O.; Ngom, P.I.; Mikami, Y.; Shimada, Y.; Kuroe, K.; Tvete, I.F.; Kvaal, S.I. A Radiographic Study of the Mandibular Third Molar Root Development in Different Ethnic Groups. J. Forensic Odontostomatol. 2017, 35, 97–108. [Google Scholar]
- Liversidge, H.M. Controversies in Age Estimation from Developing Teeth. Ann. Hum. Biol. 2015, 42, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.; Cheng, J.; Allaire, J.; Sievert, C.; Schloerke, B.; Xie, Y.; Allen, J.; McPherson, J.; Dipert, A.; Borges, B. Shiny: Web Application Framework for R. 2021. Available online: https://shiny.rstudio.com/ (accessed on 7 November 2022).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Heuze, Y.; Cardoso, F. Testing the Quality of Nonadult Bayesian Dental Age Assessment Methods to Juvenile Skeletal Remains: The Lisbon Collection Children and Secular Trend Effects. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 2007, 135, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

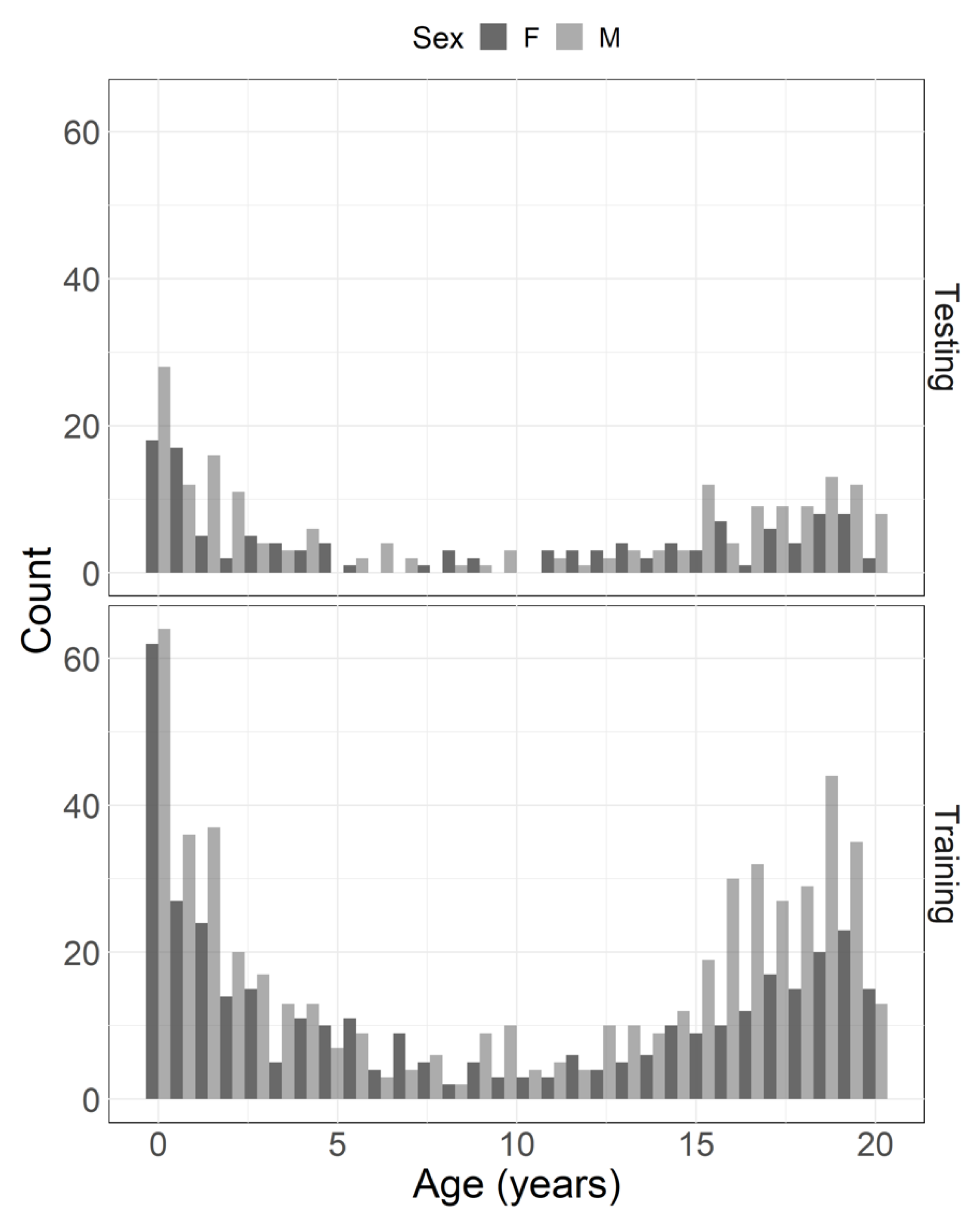
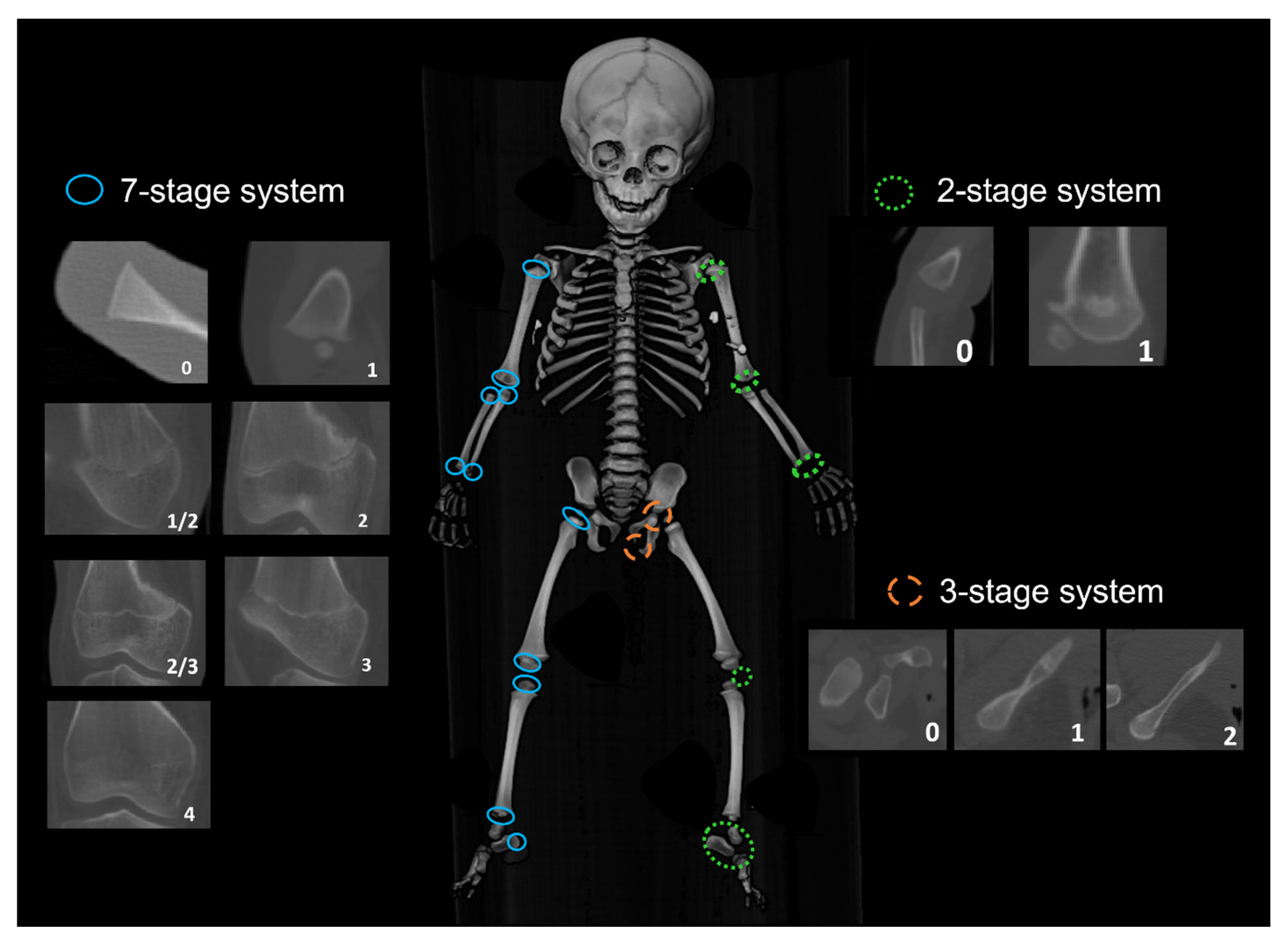
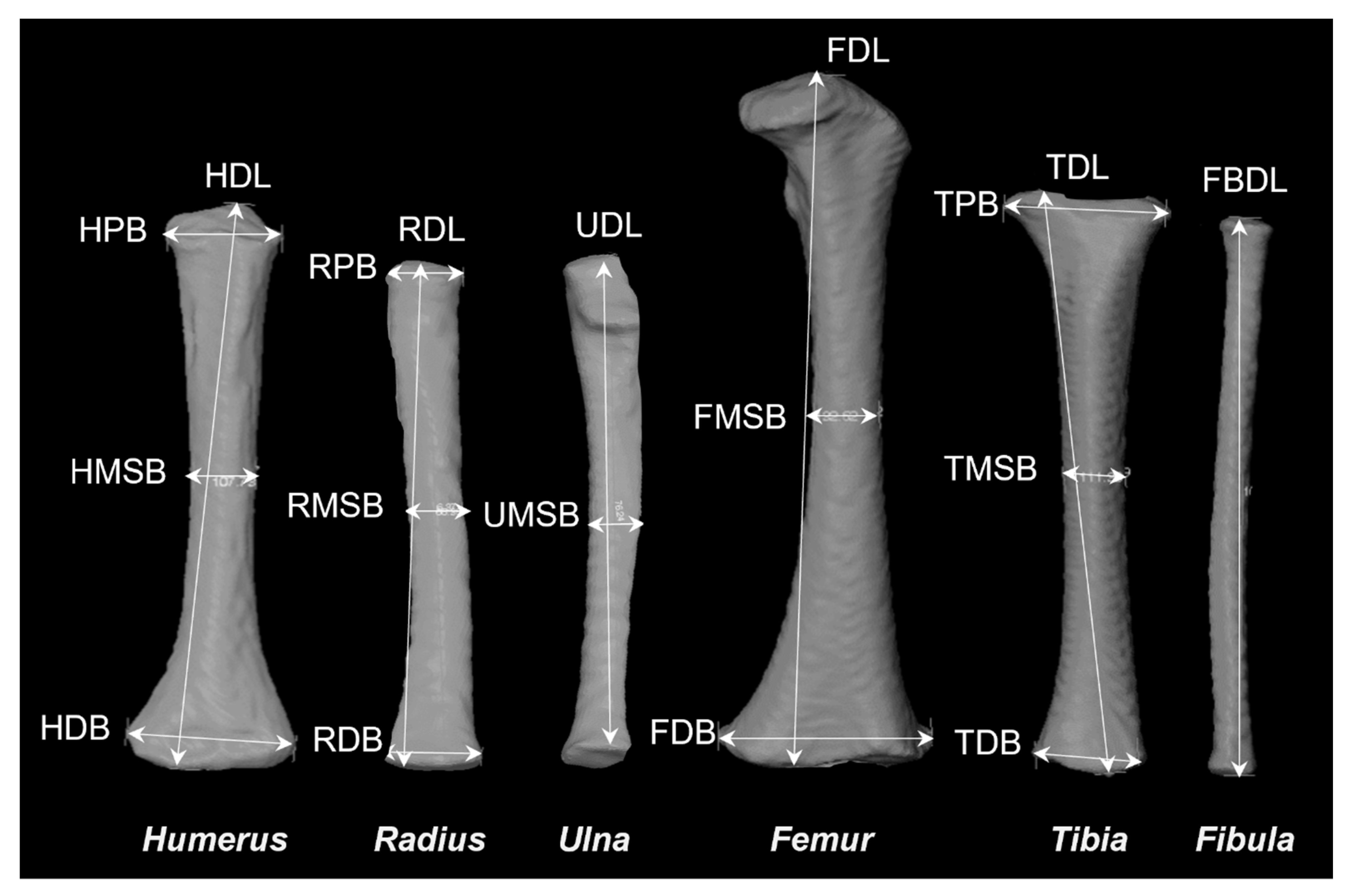
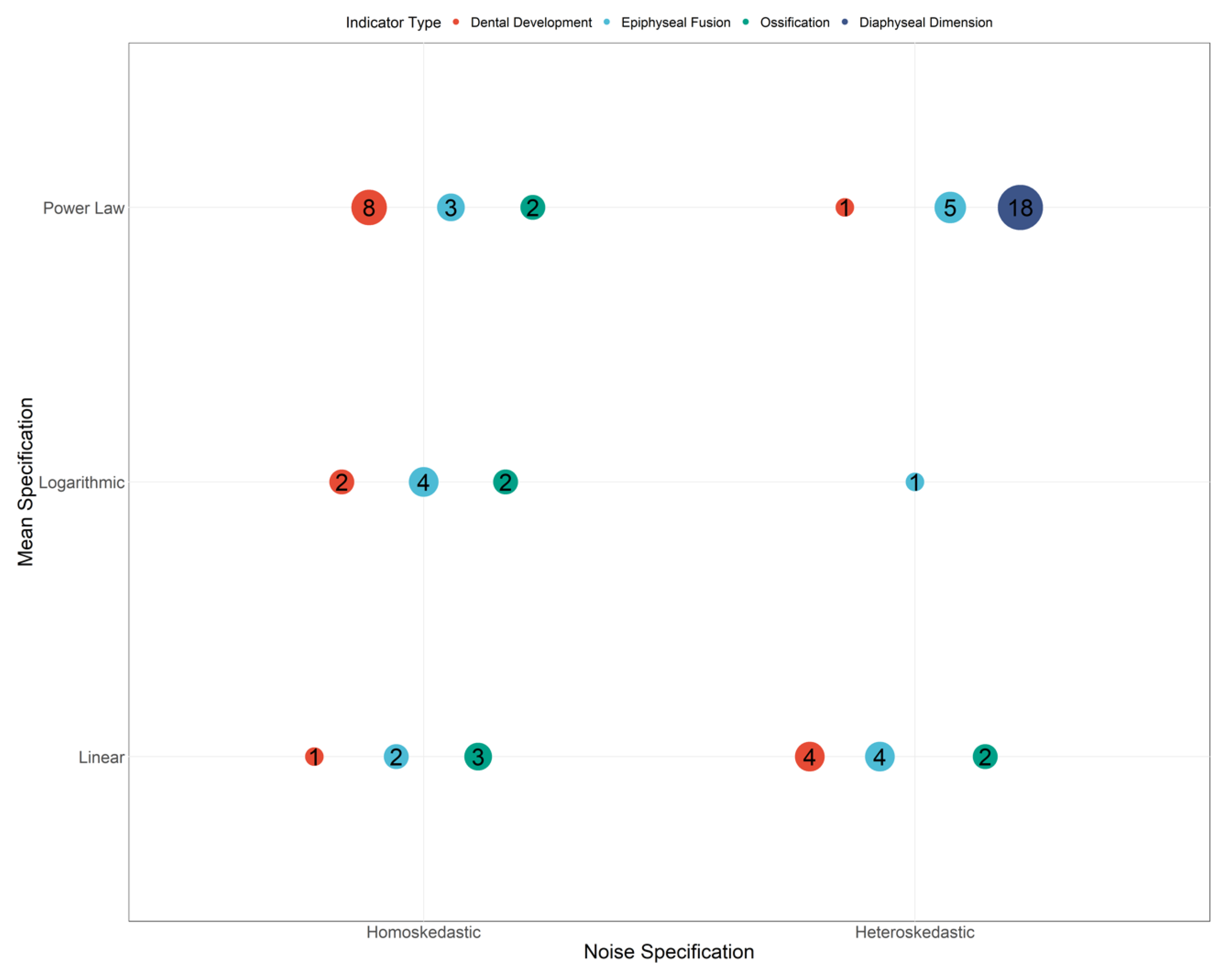

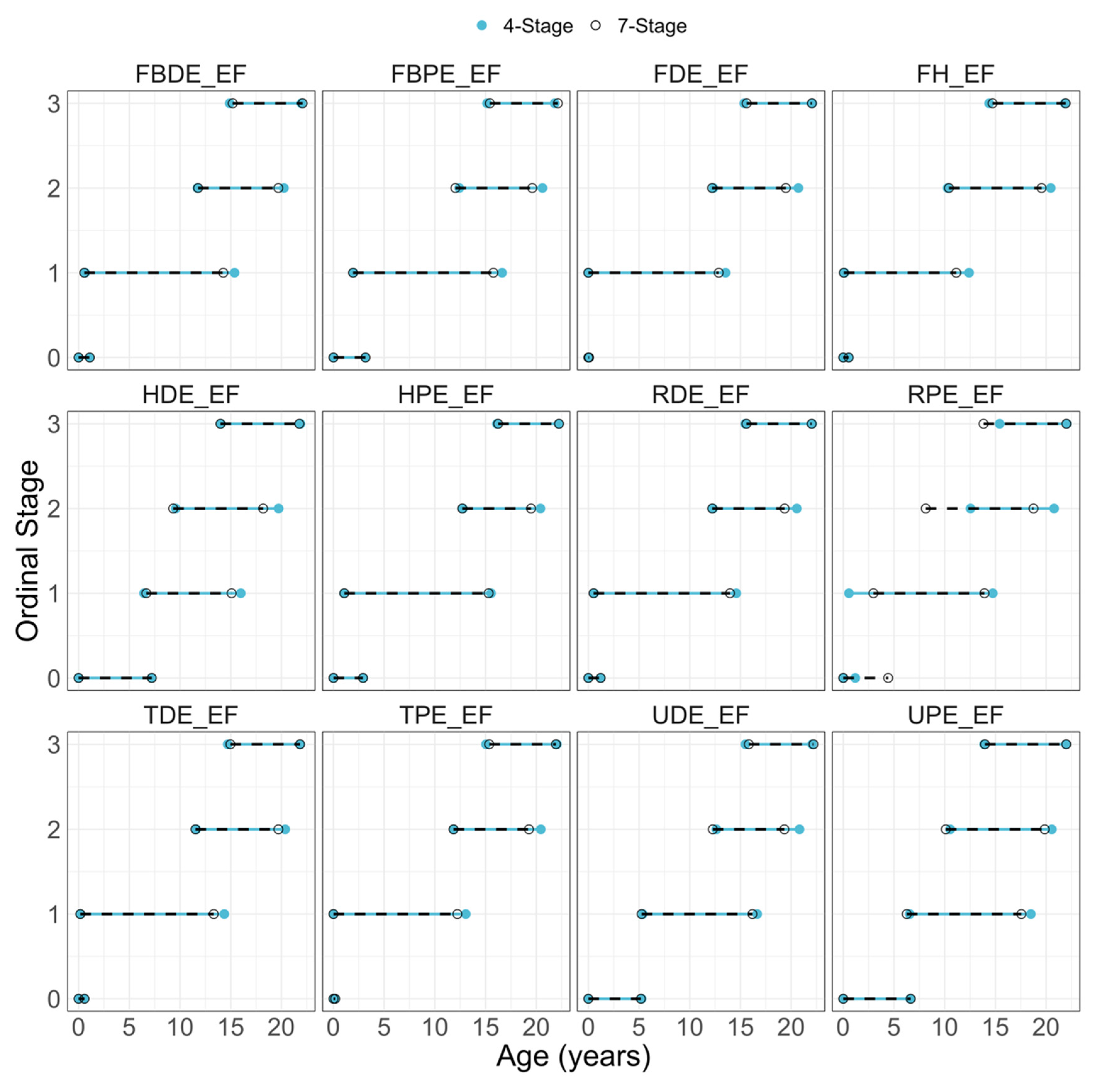
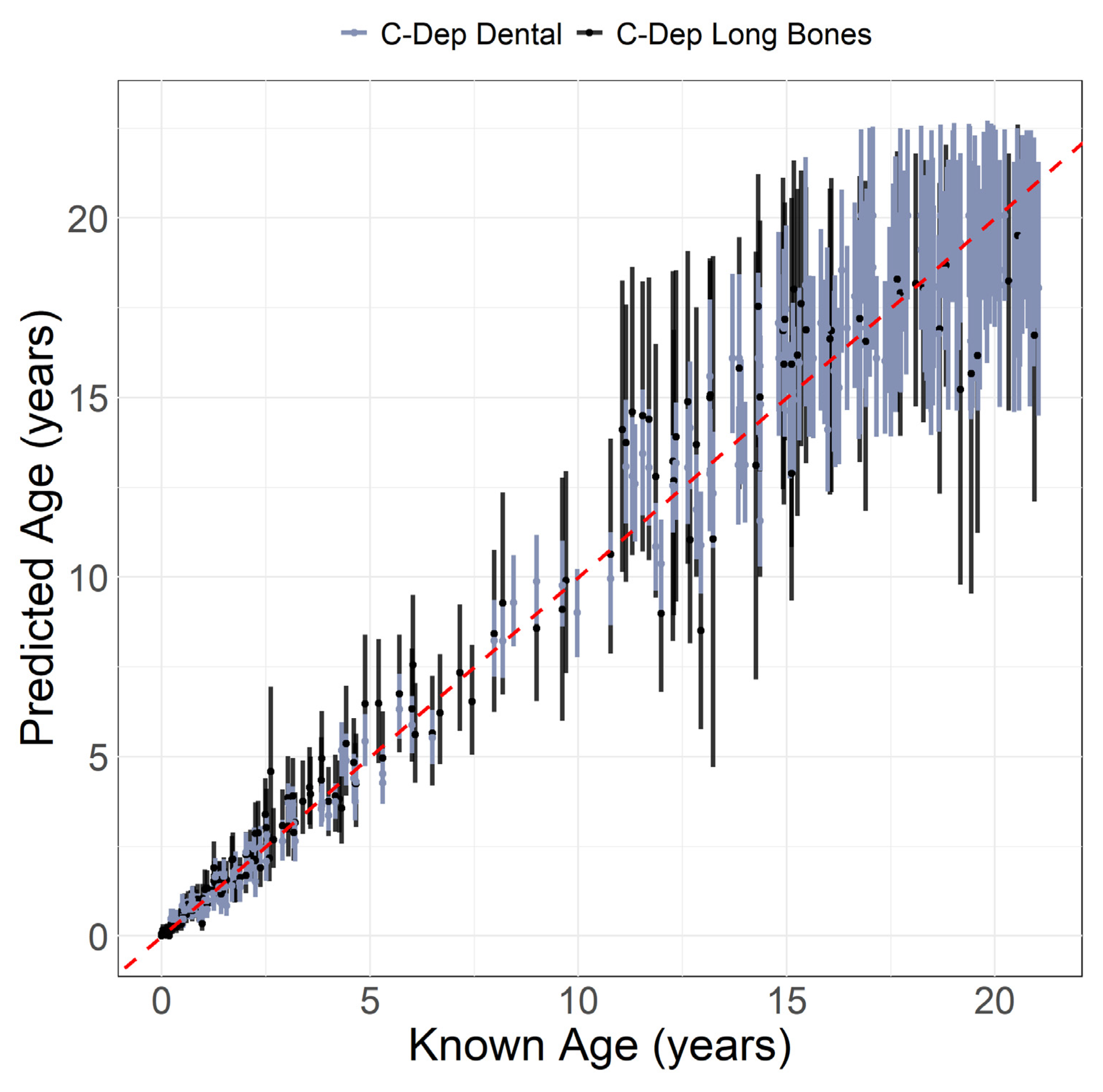
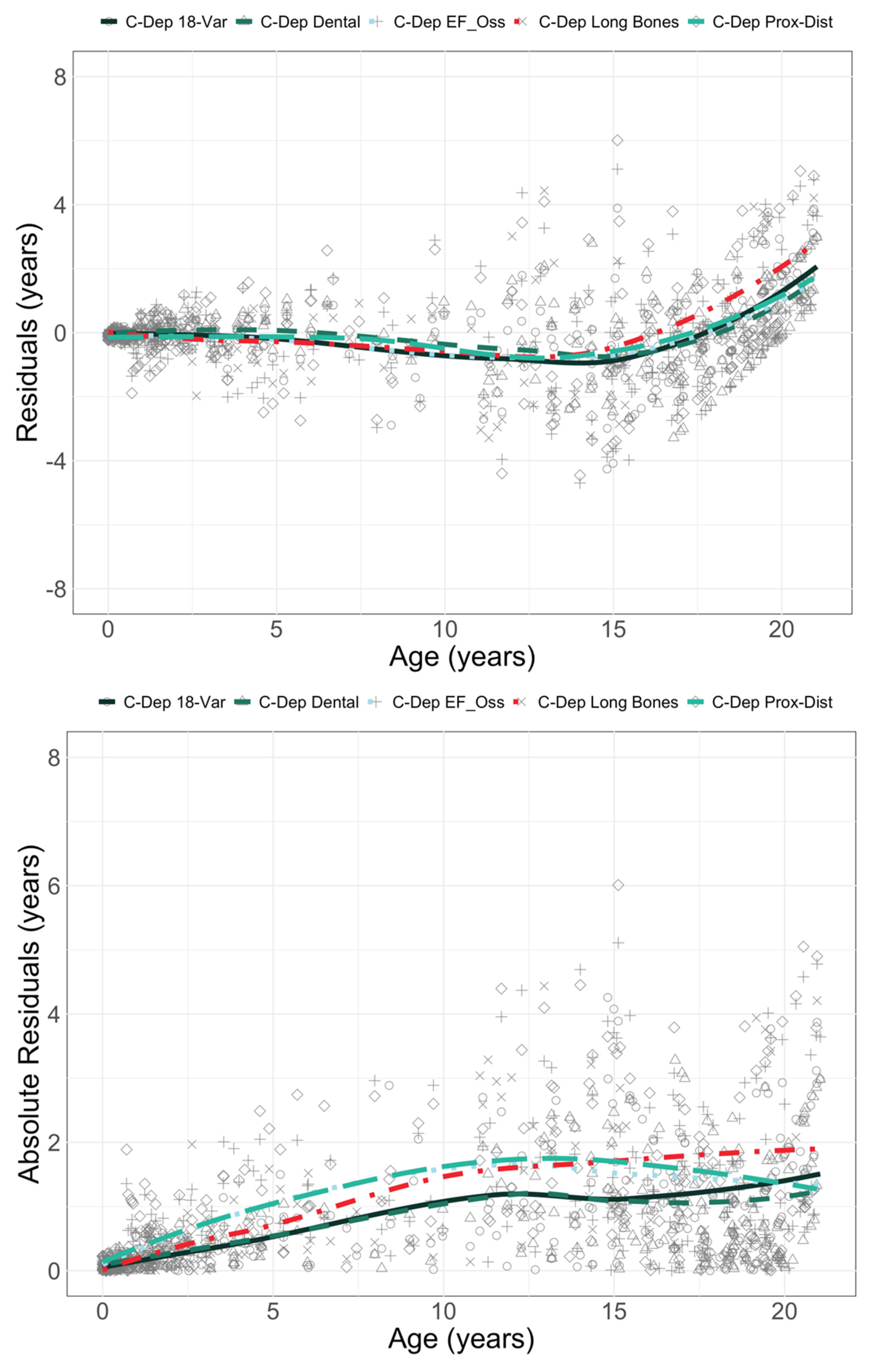
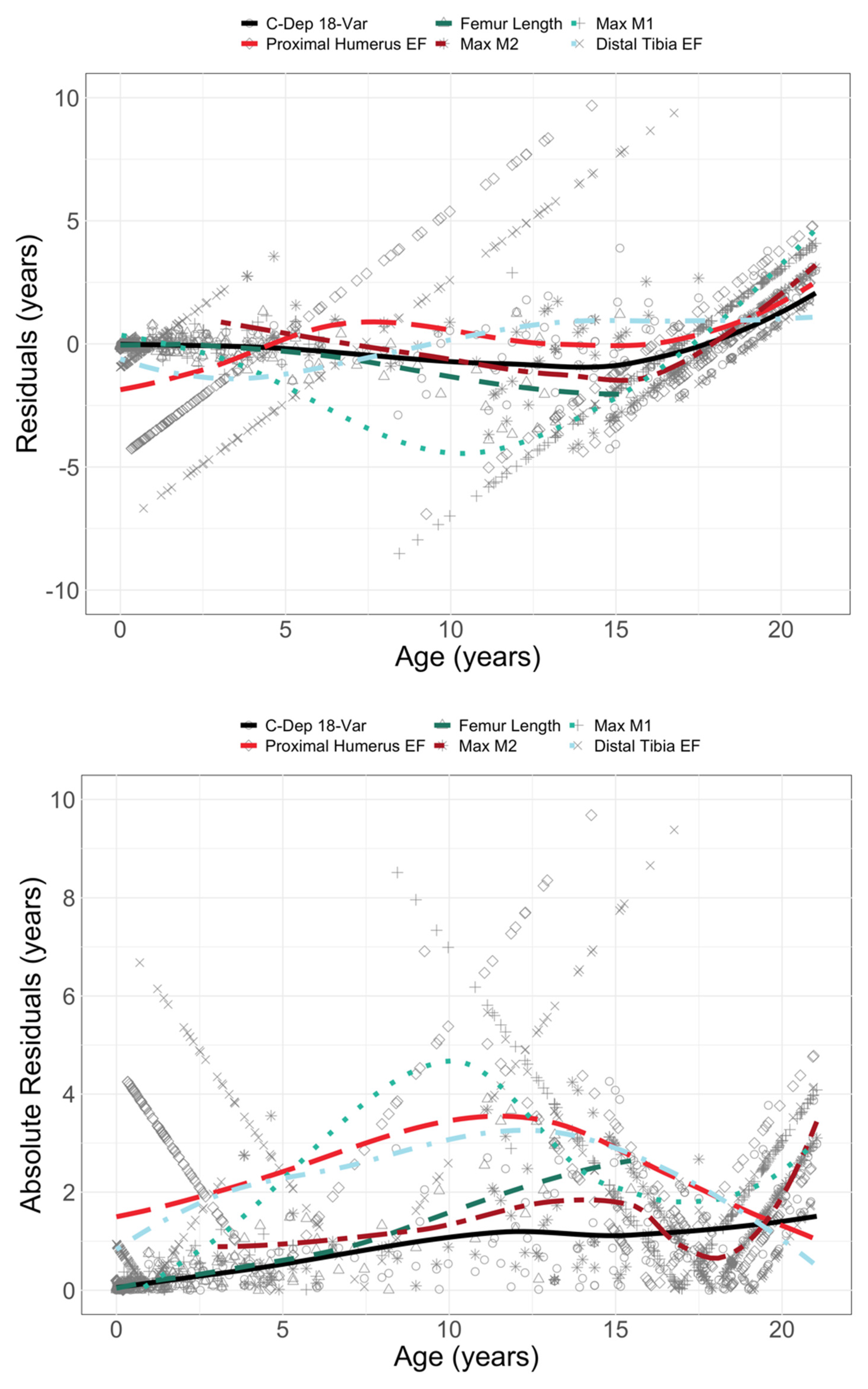

| Age (years) | Sex | Count | Age (years) | Sex | Count |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | F | 123 | 11 | F | 14 |
| M | 139 | M | 10 | ||
| 1 | F | 38 | 12 | F | 9 |
| M | 65 | M | 19 | ||
| 2 | F | 25 | 13 | F | 13 |
| M | 39 | M | 17 | ||
| 3 | F | 18 | 14 | F | 19 |
| M | 23 | M | 21 | ||
| 4 | F | 20 | 15 | F | 18 |
| M | 20 | M | 45 | ||
| 5 | F | 19 | 16 | F | 25 |
| M | 12 | M | 66 | ||
| 6 | F | 7 | 17 | F | 28 |
| M | 8 | M | 53 | ||
| 7 | F | 11 | 18 | F | 39 |
| M | 10 | M | 70 | ||
| 8 | F | 6 | 19 | F | 47 |
| M | 9 | M | 66 | ||
| 9 | F | 8 | 20 | F | 45 |
| M | 17 | M | 65 | ||
| 10 | F | 4 | 21 | F | 1 |
| M | 6 | M | 0 |
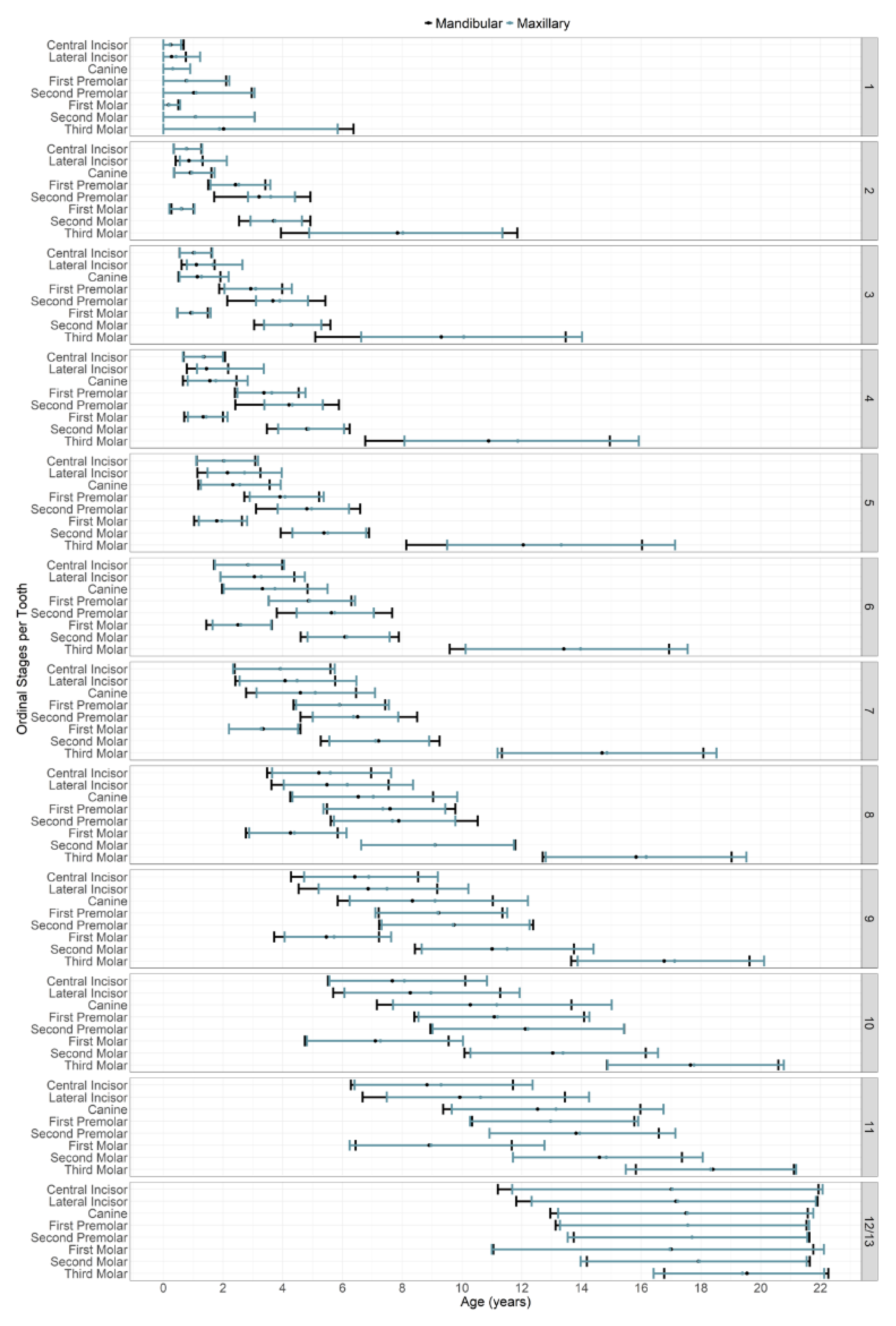
| Stage | Description | Original Abbreviation |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Initial cusp formation | ci |
| 2 | Coalescence of cusps | Cco |
| 3 | Cusp outline complete | Coc |
| 4 | Crown half completed with dentine formation | Cr ½ |
| 5 | Crown three quarters completed | Cr ¾ |
| 6 | Crown completed with defined pulp roof | Crc |
| 7 | Initial root formation with diverge edges | Ri |
| 8 | Root length less than crown length | R ¼ |
| 9 | Root length equals crown length | R ½ |
| 10 | Three quarters of root length developed with diverge ends | R ¾ |
| 11 | Root length completed with parallel ends | Rc |
| 12 | Apex closed (root ends converge) with wide periodontal ligament | A ½ |
| 13 | Apex closed with normal periodontal ligament width * | Ac |
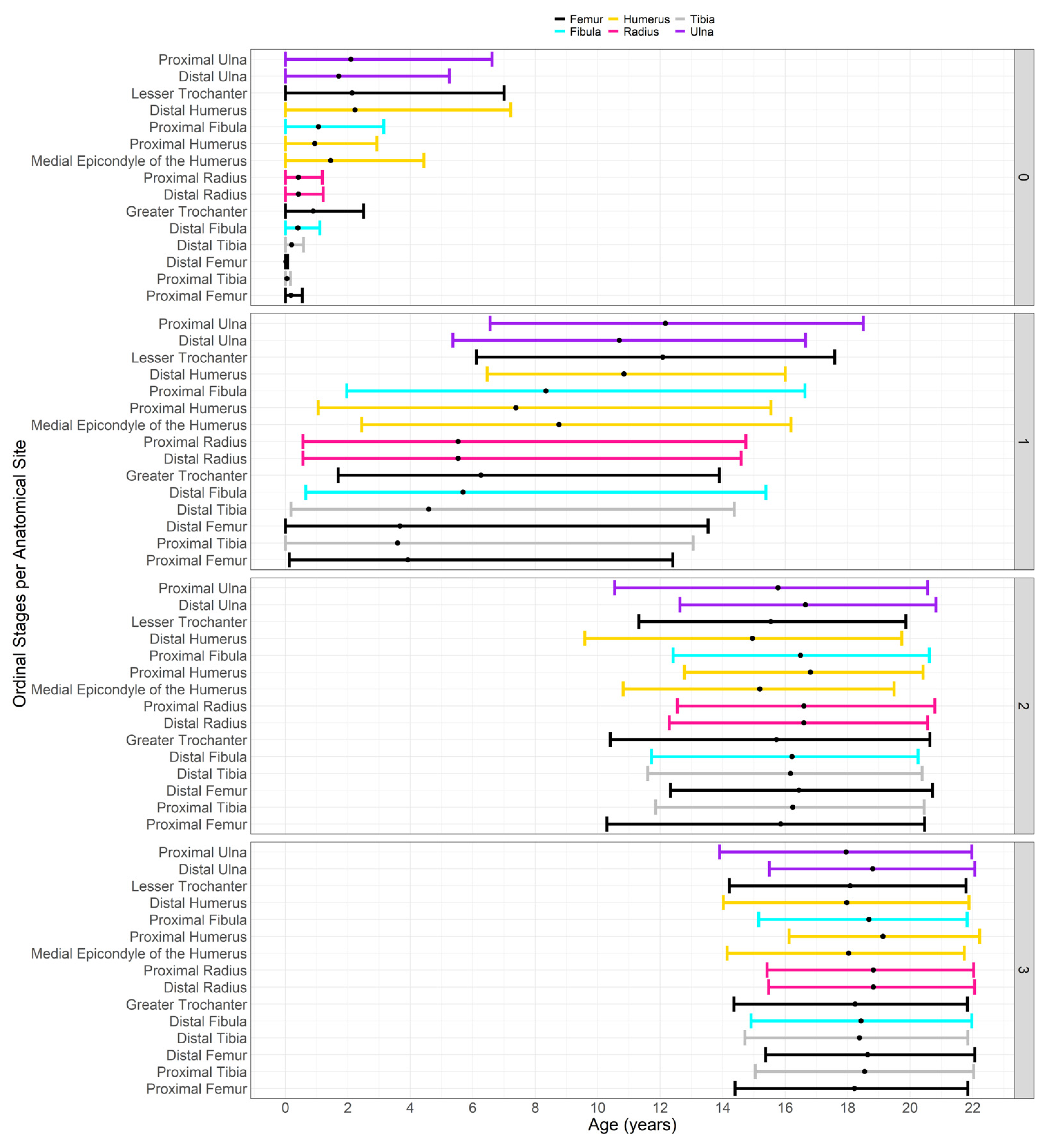
| Bone | Epiphyses | Abbreviation | Scoring System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Humerus | Humeral Head Ossification | HH_Oss | 2-stage scoring system |
| Greater Tubercle Ossification | HGT_Oss | ||
| Lesser Tubercle Ossification | HLT_Oss | ||
| Proximal Epiphysis Epiphyseal (PE) Fusion (PE = fused HH, GT and LT) If PE not fused, score 0 If PE fused but unfused to diaphysis, score 1 | HPE_EF = fused HH + HGT + HLT | 7-stage scoring system | |
| Capitulum Ossification | HC_Oss | 2-stage scoring system | |
| Trochlea Ossification | HT_Oss | ||
| Lateral Epicondyle Ossification | HLE_Oss | ||
| Distal Epiphysis Epiphyseal Fusion (fusion to the diaphysis) | HDE_EF | 7-stage scoring system | |
| Medial Epicondyle Epiphyseal Fusion | HME_EF | 7-stage scoring system | |
| Radius | Proximal Epiphysis Epiphyseal Fusion | RPE_EF | 7-stage scoring system |
| Distal Epiphysis Epiphyseal Fusion | RDE_EF | ||
| Ulna | Proximal Epiphysis Epiphyseal Fusion | UPE_EF | 7-stage scoring system |
| Distal Epiphysis Epiphyseal Fusion | UDE_EF | ||
| Femur | Femoral Head Epiphyseal Fusion | FH_EF | 7-stage scoring system |
| Greater Trochanter Epiphyseal Fusion | FGT_EF | ||
| Lesser Trochanter Epiphyseal Fusion | FLT_EF | ||
| Distal Epiphysis Epiphyseal Fusion | FDE_EF | ||
| Tibia | Proximal Epiphysis Epiphyseal Fusion | TPE_EF | 7-stage scoring system |
| Distal Epiphysis Epiphyseal Fusion | TDE_EF | ||
| Fibula | Proximal Epiphysis Epiphyseal Fusion | FBPE_EF | 7-stage scoring system |
| Distal Epiphysis Epiphyseal Fusion | FBDE_EF | ||
| Os Coxa | Ischio-Pubic Ramus Union | ISPR_EF | 3-stage scoring system |
| Ilio-ischial Union | ILIS_EF | ||
| Iliac Crest Epiphyseal Fusion | IC_EF | 73-stage scoring system | |
| Calcaneus | Calcaneal Tuberosity Epiphyseal Fusion | CT_EF | 7-stage scoring system |
| Patella | Patella Ossification | PC_Oss | 2-stage scoring system |
| Carpals | Number of carpals present | CC_Oss | 0–8 |
| Tarsals | Number of tarsals present | TC_Oss | 0–7 |
| Bone | Diaphyseal Length | Proximal Breadth | Midshaft Breadth | Distal Breadth |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Humerus | HDL | HPB | HMSB | HDB |
| Radius | RDL | RPB | RMSB | RDB |
| Ulna | UDL | - | UMSB | - |
| Femur | FDL | - | FMSB | FDB |
| Tibia | TDL | TPB | TMSB | TDB |
| Fibula | FBDL | - | - | - |
| Variable Subset (Model) | Number of Variables | Variables | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dental (Dent) | 16 | max_M1 max_M2 max_M3 max_PM1 | max_PM2 max_C max_I1 max_I2 | man_M1 man_M2 man_M3 man_PM1 | man_PM2 man_C man_I1 man_I2 |
| Epiphyseal Fusion (EF_Oss) | 28 | FH_EF FGT_EF FLT_EF FDE_EF TPE_EF TDE_EF FBPE_EF | FBDE_EF HH_Oss HGT_Oss HLT_Oss HPE_EF HC_Oss HT_Oss | HLE_Oss HDE_EF HME_EF RPE_EF RDE_EF UPE_EF UDE_EF | CT_EF CC_Oss TC_Oss ISPR_EF ILIS_EF PC_Oss IC_EF |
| Epiphyseal Fusion (Prox-Dist) | 13 | FH_EF FDE_EF TPE_EF TDE_EF | FBPE_EF FBDE_EF HH_Oss | HPE_EF HDE_EF RPE_EF | RDE_EF UPE_EF UDE_EF |
| Long Bone Dimensions (LBs) | 18 | FDL FMSB FDB TDL TPB | TMSB TDB FBDL HDL HPB | HMSB HDB RDL RPB | RMSB RDB UDL UMSB |
| 18-Variable Mixed Model (18 Vars) | 18 | max_M1 max_M2 max_PM2 man_M1 man_M2 | man_PM1 man_C FGT_EF HME_EF RPE_EF | UDE_EF CC_Oss ISPR_EF ILIS_EF | FDL TPB HDL HPB |
| Variable | Mean Specifications | Noise Specification | Indicator Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| max_M1 | Linear | Heteroskedasticity | Dental Development |
| max_M2 | Logarithmic | Homoskedasticity | Dental Development |
| max_M3 | Linear | Heteroskedasticity | Dental Development |
| max_PM1 | Linear | Heteroskedasticity | Dental Development |
| max_PM2 | Logarithmic | Homoskedasticity | Dental Development |
| max_C | Power Law | Homoskedasticity | Dental Development |
| max_I1 | Power Law | Homoskedasticity | Dental Development |
| max_I2 | Power Law | Homoskedasticity | Dental Development |
| man_M1 | Power Law | Homoskedasticity | Dental Development |
| man_M2 | Power Law | Homoskedasticity | Dental Development |
| man_M3 | Linear | Homoskedasticity | Dental Development |
| man_PM1 | Power Law | Heteroskedasticity | Dental Development |
| man_PM2 | Linear | Heteroskedasticity | Dental Development |
| man_C | Power Law | Homoskedasticity | Dental Development |
| man_I1 | Power Law | Homoskedasticity | Dental Development |
| man_I2 | Power Law | Homoskedasticity | Dental Development |
| FH_EF | Power Law | Heteroskedasticity | Epiphyseal Fusion |
| FGT_EF | Power Law | Heteroskedasticity | Epiphyseal Fusion |
| FLT_EF | Power Law | Homoskedasticity | Epiphyseal Fusion |
| FDE_EF | Power Law | Heteroskedasticity | Epiphyseal Fusion |
| TPE_EF | Power Law | Heteroskedasticity | Epiphyseal Fusion |
| TDE_EF | Power Law | Heteroskedasticity | Epiphyseal Fusion |
| FBPE_EF | Linear | Heteroskedasticity | Epiphyseal Fusion |
| FBDE_EF | Linear | Heteroskedasticity | Epiphyseal Fusion |
| HH_Oss | Linear | Homoskedasticity | Ossification |
| HGT_Oss | Linear | Heteroskedasticity | Ossification |
| HLT_Oss | Linear | Homoskedasticity | Ossification |
| HPE_EF | Power Law | Homoskedasticity | Epiphyseal Fusion |
| HC_Oss | Logarithmic | Homoskedasticity | Ossification |
| HT_Oss | Linear | Homoskedasticity | Ossification |
| HLE_Oss | Linear | Heteroskedasticity | Ossification |
| HDE_EF | Logarithmic | Homoskedasticity | Epiphyseal Fusion |
| HME_EF | Linear | Heteroskedasticity | Epiphyseal Fusion |
| RPE_EF | Linear | Heteroskedasticity | Epiphyseal Fusion |
| RDE_EF | Power Law | Homoskedasticity | Epiphyseal Fusion |
| UPE_EF | Logarithmic | Heteroskedasticity | Epiphyseal Fusion |
| UDE_EF | Logarithmic | Homoskedasticity | Epiphyseal Fusion |
| CT_EF | Linear | Homoskedasticity | Epiphyseal Fusion |
| CC_Oss | Power Law | Homoskedasticity | Ossification |
| TC_Oss | Power Law | Homoskedasticity | Ossification |
| ISPR_EF | Logarithmic | Homoskedasticity | Epiphyseal Fusion |
| ILIS_EF | Linear | Homoskedasticity | Epiphyseal Fusion |
| PC_Oss | Logarithmic | Homoskedasticity | Ossification |
| IC_EF | Logarithmic | Homoskedasticity | Epiphyseal Fusion |
| FDL | Power Law | Heteroskedasticity | Diaphyseal Dimension |
| FMSB | Power Law | Heteroskedasticity | Diaphyseal Dimension |
| FDB | Power Law | Heteroskedasticity | Diaphyseal Dimension |
| TDL | Power Law | Heteroskedasticity | Diaphyseal Dimension |
| TPB | Power Law | Heteroskedasticity | Diaphyseal Dimension |
| TMSB | Power Law | Heteroskedasticity | Diaphyseal Dimension |
| TDB | Power Law | Heteroskedasticity | Diaphyseal Dimension |
| FBDL | Power Law | Heteroskedasticity | Diaphyseal Dimension |
| HDL | Power Law | Heteroskedasticity | Diaphyseal Dimension |
| HPB | Power Law | Heteroskedasticity | Diaphyseal Dimension |
| HMSB | Power Law | Heteroskedasticity | Diaphyseal Dimension |
| HDB | Power Law | Heteroskedasticity | Diaphyseal Dimension |
| RDL | Power Law | Heteroskedasticity | Diaphyseal Dimension |
| RPB | Power Law | Heteroskedasticity | Diaphyseal Dimension |
| RMSB | Power Law | Heteroskedasticity | Diaphyseal Dimension |
| RDB | Power Law | Heteroskedasticity | Diaphyseal Dimension |
| UDL | Power Law | Heteroskedasticity | Diaphyseal Dimension |
| UMSB | Power Law | Heteroskedasticity | Diaphyseal Dimension |
| Model | N | TMNLP | % Accuracy | RMSE | Model | N | TMNLP | % Accuracy | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDL | 138 | −0.077 | 0.96 | 0.688 | UDE_EF_c | 262 | 1.7934 | 0.93 | 2.066 |
| FDL | 155 | 0.0895 | 0.97 | 0.939 | max_I1 | 212 | 1.7983 | 0.95 | 2.312 |
| RDL | 143 | 0.1071 | 0.98 | 0.624 | RPE_EF | 262 | 1.7994 | 0.94 | 2.153 |
| UDL | 148 | 0.2488 | 0.96 | 0.996 | CT_EF_c | 255 | 1.8019 | 0.95 | 2.089 |
| TDL | 159 | 0.2497 | 0.96 | 1.076 | FH_EF_c | 262 | 1.8039 | 0.94 | 2.839 |
| FBDL | 160 | 0.3034 | 0.96 | 1.205 | RPE_EF_c | 262 | 1.8081 | 0.94 | 2.209 |
| Long Bones (C-Dep LBs) | 193 | 0.5173 | 0.93 | 1.44 | man_I1 | 211 | 1.8092 | 0.94 | 2.315 |
| TPB | 181 | 0.8479 | 0.96 | 1.714 | man_I2 | 210 | 1.833 | 0.92 | 2.171 |
| FMSB | 157 | 0.8853 | 0.96 | 2.261 | FLT_EF_c | 261 | 1.837 | 0.96 | 2.141 |
| FDB | 184 | 0.8994 | 0.96 | 1.881 | max_C | 202 | 1.844 | 0.93 | 1.889 |
| HPB | 187 | 0.9079 | 0.97 | 1.508 | TC_Oss_c | 255 | 1.8712 | 0.96 | 4.453 |
| Mixed (C-Dep 18-Var) | 323 | 0.9216 | 0.91 | 1.164 | UPE_EF | 261 | 1.8779 | 0.93 | 2.258 |
| Mixed (C-Dep 18-Var, Collapsed) | 323 | 0.9434 | 0.9 | 1.167 | man_C | 204 | 1.8799 | 0.92 | 1.849 |
| HDB | 166 | 0.9469 | 0.9 | 2.295 | UPE_EF_c | 261 | 1.8943 | 0.95 | 2.316 |
| TMSB | 160 | 1.0193 | 0.94 | 2.454 | TPE_EF | 253 | 1.8945 | 0.93 | 2.977 |
| RPB | 168 | 1.028 | 0.95 | 2.15 | max_PM2 | 161 | 1.9077 | 0.96 | 1.797 |
| TDB | 180 | 1.0807 | 0.95 | 1.982 | HDE_EF | 260 | 1.9122 | 0.93 | 2.473 |
| HMSB | 160 | 1.1064 | 0.92 | 2.932 | max_M2 | 162 | 1.9192 | 0.95 | 1.679 |
| RDB | 178 | 1.1598 | 0.96 | 2.151 | HDE_EF_c | 260 | 1.92 | 0.95 | 2.496 |
| Mixed (C-Indep 18-Var, Collapsed) | 323 | 1.1965 | 0.82 | 1.203 | max_PM1 | 174 | 1.9205 | 0.96 | 1.917 |
| RMSB | 161 | 1.2049 | 0.93 | 2.639 | man_M3 | 117 | 1.9313 | 0.95 | 1.81 |
| Mixed (C-Indep 18-Var) | 323 | 1.2188 | 0.83 | 1.202 | max_M3 | 116 | 1.9447 | 0.96 | 1.883 |
| Proximal and Distal Epiphyses (C-Dep Prox-Dist, Collapsed) | 263 | 1.3428 | 0.87 | 1.548 | man_M2 | 161 | 1.9529 | 0.94 | 1.756 |
| UMSB | 159 | 1.3488 | 0.91 | 3.647 | TPE_EF_c | 253 | 1.954 | 0.96 | 3.075 |
| Proximal and Distal Epiphyses (C-Dep Prox-Dist) | 263 | 1.3521 | 0.86 | 1.47 | man_PM1 | 174 | 1.9557 | 0.95 | 1.917 |
| Dental (C-Dep Dental) | 211 | 1.4132 | 0.84 | 1.161 | man_PM2 | 161 | 1.9596 | 0.97 | 1.863 |
| Epiphyseal Fusion and Ossification (C-Dep EF_Oss, Collapsed) | 303 | 1.4995 | 0.79 | 1.533 | ILIS_EF_c | 261 | 1.9623 | 0.94 | 2.738 |
| CC_Oss_c | 263 | 1.5881 | 0.97 | 2.305 | max_I2 | 194 | 1.9832 | 0.94 | 2.182 |
| HPE_EF_US_all | 266 | 1.6614 | 0.96 | 2.532 | FDE_EF | 256 | 1.9875 | 0.93 | 3.417 |
| FBDE_EF_US_all | 257 | 1.6654 | 0.94 | 2.793 | HLE_Oss | 260 | 2.0142 | 0.95 | 2.786 |
| man_M1 | 228 | 1.6694 | 0.95 | 2.275 | PC_Oss | 257 | 2.0179 | 0.98 | 4.175 |
| TDE_EF | 257 | 1.67 | 0.96 | 2.751 | ISPR_EF_c | 261 | 2.0228 | 0.93 | 3.045 |
| FBPE_EF | 257 | 1.6719 | 0.95 | 2.189 | FDE_EF_c | 256 | 2.0394 | 0.93 | 3.494 |
| max_M1 | 225 | 1.6919 | 0.97 | 2.336 | Dental (C-Indep Dental) | 211 | 2.0458 | 0.71 | 1.142 |
| FGT_EF_c | 257 | 1.6978 | 0.95 | 2.125 | HT_Oss | 261 | 2.0582 | 0.95 | 3.203 |
| FBDE_EF_c | 257 | 1.7045 | 0.96 | 2.862 | IC_EF_c | 112 | 2.0601 | 0.87 | 3.056 |
| TDE_EF_c | 257 | 1.7112 | 0.95 | 2.842 | HLT_Oss | 266 | 2.1379 | 0.96 | 4.988 |
| FBPE_EF_c | 257 | 1.7176 | 0.95 | 2.268 | HGT_Oss | 265 | 2.2141 | 0.94 | 5.907 |
| FH_EF | 262 | 1.7362 | 0.93 | 2.632 | HC_Oss | 262 | 2.275 | 0.95 | 6.574 |
| RDE_EF | 262 | 1.7365 | 0.91 | 2.971 | Epiphyseal Fusion and Ossification (C-Indep Prox-Dist, Collapsed) | 263 | 2.4014 | 0.7 | 1.841 |
| HPE_EF_c | 266 | 1.7381 | 0.96 | 2.639 | HH_Oss | 267 | 2.4992 | 0.96 | 7.299 |
| UDE_EF | 262 | 1.7674 | 0.93 | 1.998 | Proximal and Distal Epiphyses (C-Indep Prox-Dist) | 263 | 2.5076 | 0.71 | 1.712 |
| RDE_EF_c | 262 | 1.7714 | 0.92 | 3.021 | Epiphyseal Fusion and Ossification (C-Indep EF_Oss, Collapsed) | 303 | 2.6683 | 0.64 | 1.717 |
| HME_EF_c | 261 | 1.788 | 0.95 | 2.139 | Long Bones (C-Indep LBs) | 193 | 3.4524 | 0.56 | 1.217 |
| Models | Model Specifications | K-L bits |
|---|---|---|
| Mixed/18-Vars (c-dep, collapsed) | C-dep, collapsed | 5.26 |
| Mixed/18-Vars (c-indep, collapsed) | C-indep, collapsed | 5.98 |
| Mixed/18-Vars (c-dep) | C-dep | 5.18 |
| Mixed/18-Vars (c-indep) | C-indep | 5.98 |
| Long bones (c-dep) | C-dep | 3.96 |
| Long bones (c-indep) | C-indep | 5.5 |
| Epiphyseal fusion (c-dep, collapsed) | C-dep, collapsed | 4.39 |
| Epiphyseal fusion (c-indep, collapsed) | C-indep, collapsed | 4.74 |
| Dental development (c-dep) | C-dep | 5.24 |
| Dental development (c-indep) | C-indep | 6.24 |
| RDL (homoskedastic) | Homoskedasticity | 4.39 |
| RDL (heteroskedastic) | Heteroskedasticity | 2.87 |
| FDL (homoskedastic) | Homoskedasticity | 4.63 |
| FDL (heteroskedastic) | Heteroskedasticity | 3.97 |
| Man_PM2 (homoskedastic) | Homoskedasticity | 4.08 |
| Man_PM2 (heteroskedastic) | Heteroskedasticity | 4.11 |
| PC_Oss (homoskedastic) | Homoskedasticity | 0.52 |
| PC_Oss (heteroskedastic) | Heteroskedasticity | 0.52 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stull, K.E.; Chu, E.Y.; Corron, L.K.; Price, M.H. Subadult Age Estimation Using the Mixed Cumulative Probit and a Contemporary United States Population. Forensic Sci. 2022, 2, 741-779. https://doi.org/10.3390/forensicsci2040055
Stull KE, Chu EY, Corron LK, Price MH. Subadult Age Estimation Using the Mixed Cumulative Probit and a Contemporary United States Population. Forensic Sciences. 2022; 2(4):741-779. https://doi.org/10.3390/forensicsci2040055
Chicago/Turabian StyleStull, Kyra E., Elaine Y. Chu, Louise K. Corron, and Michael H. Price. 2022. "Subadult Age Estimation Using the Mixed Cumulative Probit and a Contemporary United States Population" Forensic Sciences 2, no. 4: 741-779. https://doi.org/10.3390/forensicsci2040055
APA StyleStull, K. E., Chu, E. Y., Corron, L. K., & Price, M. H. (2022). Subadult Age Estimation Using the Mixed Cumulative Probit and a Contemporary United States Population. Forensic Sciences, 2(4), 741-779. https://doi.org/10.3390/forensicsci2040055






