Sedum yongkangense (Crassulaceae), a New Species from Zhejiang, East China †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Work and Sampling
2.2. DNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.3. Data Analysis
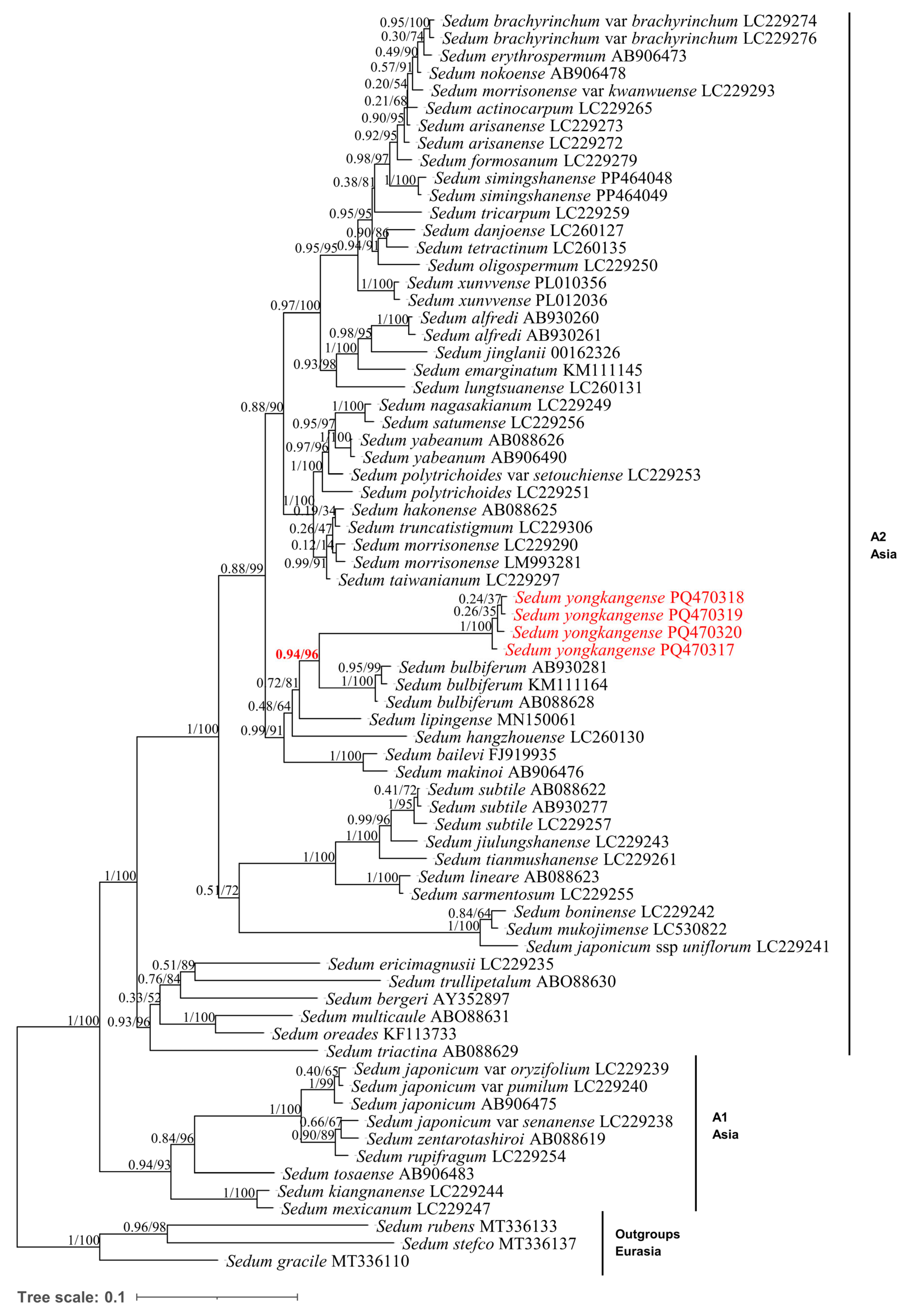
3. Results
3.1. Morphological Analysis
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Taxonomic Treatment
- 1.
- Leaf blade flat ........................................................................................................................2
- +
- Leaf blade terete.....................................................................................................................3
- 2.
- Bulbils in leaf axils; fertile stem congested; sepals unequal; anthers deepyellow..................................................................................................................S. bulbiferum
- +
- No bulbils in leaf axils; fertile stem solitary; sepals equal; anthers red................................................................................................................................................S. mukojimense
- 3.
- Biennial; leaf blade sparse; inflorescences with many flowers; sepals unequal;follicles horizontal spreading....................................................................S. yongkangense
- +
- Perennial; leaf blade densely; inflorescences with solitary or 1–12 flowers; sepalsequal; follicles spreading......................................................................................................4
- 4.
- Bulbs form underground after flowering; sterile stem absent; leaf blade 5–16 cmlong; inflorescences with usually 1–3 flowers..................................................S. boninense
- +
- No bulbs; sterile stem present; leaf blade 3–6 cm long; inflorescences with solitaryflower....................................................................................................................S. ryukyuense
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thiede, J.; Eggli, U. Crassulaceae. In The Families and Genera of Vascular Plants; Kubitzki, K., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; Volume 9, pp. 83–118. [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson, R. Sedum. Cultivated Stonecrops; Timber Press: Portland, OR, USA, 1994; 355p. [Google Scholar]
- Nikulin, V.Y.; Gontcharova, S.B.; Stephenson, R.; Gontcharov, A.A. Phylogenetic relationships between Sedum L. and related genera (Crassulaceae) based on ITS rDNA sequence comparisons. Flora 2016, 224, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo-Reyes, P.; Sosa, V.; Mort, M.E. Molecular phylogeny of the Acre clade (Crassulaceae): Dealing with the lack of definitions for Echeveria and Sedum. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2009, 53, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, K.T.; Ohba, H. Crassulaceae. In Flora of China 8; Editorial Committee of Flora of China, Ed.; Missouri Botanical Garden Press: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2001; pp. 202–268. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.S.; Meng, K.K.; Sun, Y.Y.; Chen, Z.X.; Fan, Q. A new species of Sedum (Crassulaceae) from Mount Danxia in Guangdong, China. PhytoKeys 2023, 221, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohba, H. Crassulaceae. In Flora of Japan 2b; Iwatsuki, K., Boufford, D.E., Ohba, H., Eds.; Kodansha: Tokyo, Japan, 2001; pp. 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, T.; Yu, C.C.; Yokota, M.; Kokubugata, G. Sedum formosanum subsp. miyakojimense (Crassulaceae), a new subspecies from Miyako-jima Island of the Ryukyu Islands, Japan. PhytoKeys 2020, 148, 51–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuyama, T. Plantæ Boninenses Novæ vel Criticæ. VII. Shokubutsugaku Zasshi 1936, 50, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blattner, F.R. Direct amplification of the entire ITS region from poorly preserved plant material using recombinant PCR. BioTechniques 1999, 27, 1180–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J. Amplification and Direct Sequencing of Fungal Ribosomal RNA Genes for Phylogenetics. In PCR Protocols; Innis, M.A., Gelfand, D.H., Sninsky, J.J., White, T.J., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1990; pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messerschmid, T.F.E.; Klein, J.T.; Kadereit, G.; Kadereit, J.W. Linnaeus’s folly—Phylogeny, evolution and classification of Sedum (Crassulaceae) and Crassulaceae subfamily Sempervivoideae. Taxon 2020, 69, 892–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, M.L.; Wu, Y.M.; Zhang, Y.; Pu, J.B.; Chen, B.I.N.; Xu, Y.L.; Li, P.A.N. Sedum xunvense, a new species from Southeast China. Phytotaxa 2024, 644, 258–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burland, T.G. DNASTAR’s Lasergene sequence analysis software. Methods Mol. Biol. 2000, 132, 71–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capella-Gutiérrez, S.; Silla-Martínez, J.M.; Gabaldón, T. trimAl: A tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1972–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; van der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Hohna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, T.; Yu, C.C.; Nakamura, K.; Chung, K.F.; Yang, Q.E.; Fu, C.X.; Qi, Z.C.; Kokubugata, G. Unique parallel radiations of high-mountainous species of the genus Sedum (Crassulaceae) on the continental island of Taiwan. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2017, 113, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Chen, R.; Yang, Q.-E.; Saito, Y.; Yokota, M.; Kokubugata, G. Taxonomic reexamination of Sedum formosanum (Crassulaceae) in Japan, Taiwan, and the Philippines based on molecular data. J. Phytogeogr. Taxon. 2014, 62, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayuzumi, S.; Ohba, H. The phylogenetic position of eastern Asian Sedoideae (Crassulaceae) inferred from chloroplast and nuclear DNA sequences. Syst. Bot. 2004, 29, 587–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.M.; Peng, D.Y.; Fang, C.W.; Qin, M.J.; Wang, D.Q.; Huang, L.Q. Sedum spiralifolium (Crassulaceae): A new species from Anhui Province, China. Phytotaxa 2014, 183, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Nakamura, K.; Park, C.; Song, G.; Maeda, A.; Watanabe, Y.; Kokubugata, G. Nuclear and plastid DNA data confirm that Sedum tosaense (Crassulaceae) has a disjunct distribution between Pacific mainland Japan and Jeju Island, Korea. Phytotaxa 2014, 177, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Nakanishi, H.; Chichibu, Y.; Minoda, K.; Kokubugata, G. Sedum danjoense (Crassulaceae), a new species of succulent plants from the Danjo Islands in Japan. Phytotaxa 2017, 309, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.B.; Deng, T.; Dou, Q.L.; He, L.; Lv, X.Y.; Jiang, H. Sedum lipingense (Crassulaceae) identifying a new stonecrop species in SE Guizhou, China, based on morphological and molecular evidence. PhytoKeys 2019, 134, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Q.; Meng, S.Y.; Wen, J.; Rao, G.Y. Phylogenetic Relationships and Character Evolution of Rhodiola (Crassulaceae) based on Nuclear Ribosomal ITS and Plastid trnL-F and psbA-trnH Sequences. Syst. Bot. 2014, 39, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Characteristics | S. yongkangense # | S. ryukyuense $ | S. mukojimense * | S. boninense $,^ | S. bulbiferum &,$ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Life cycle | biennial | perennial | perennial | perennial | perennial |
| Bulbils | no | no | bulbs form underground after flowering | bulbs form underground after flowering | bulbils in leaf axils |
| Sterile stem | absent | present, 2–4 cm tall | absent | absent | absent |
| Fertile stem | solitary, herbaceous, erect, ca. 11 cm tall, Ф1–2 mm, branched near base | erect, 4–10 cm tall, branched near base | solitary, fleshy, 7–20 cm tall, base Ф3 mm, erect, sometimes branched | solitary, erect, 5–20 cm tall, branched upward | congested, 7–22 cm tall |
| Leaf blade | sparse, linear, terete, slightly flattened | densely, narrowly oblong or linear-spatulate, terete | densely, spatulate to obovate, flat | densely, narrowly elliptic or oblanceolate, terete | proximal stem leaves opposite; leaf blade ovate-spatulate. Distal stem leaves alternate; leaf blade spatulate-oblanceolate, flat |
| Leaf size | 4–12 × 1–2.8 mm | 3–6 × 1.5–2.5 mm | 6–14 × 2–5 mm | 5–16 × 1.5–4 mm | 10–15 × 2–4 mm |
| Inflorescences | once trifurcate, secondary bifurcate, many flowers | solitary on branches | usually 1–12 flowers | usually 1–3 flowers | once trifurcate, secondary bifurcate, many flowers |
| Pedicel | sessile | sessile | sessile | short pedicellate | sessile |
| Sepals | unequal, fleshy, terete, linear, 4–6.5 × 1.1–1.3 mm, ascending at flowering | equal, fleshy, elliptic-lanceolate, ca. 2.5 mm long | equal, fleshy, narrowly elliptic or oblanceolate, 2–4 × 0.8–1.2 mm | equal, fleshy, narrowly elliptic or oblanceolate, ca. 3 mm long, ascending at flowering | unequal, lanceolate to oblanceolate, 3 – 4 × ca. 1 mm |
| Anthers | orange-red | orange-red | red | bright yellow | deep yellow |
| Ovules | 8–14 | unknown | unknown | 4–6 | 10–16 |
| Follicles | horizontal spreading | spreading | spreading | spreading | spreading |
| Seed surface | minutely pits in pale | unknown | unknown | unknown | minutely tuberculate |
| Seed size | 0.68–0.76 × 0.37–0.43 mm | unknown | unknown | unknown | 0.6 × 0.23 mm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
She, S.-Q.; Li, J.-P.; Xie, W.-Y.; Yao, S.-H.; Chen, Z.-H.; Zhou, X.; Xu, Y.-L. Sedum yongkangense (Crassulaceae), a New Species from Zhejiang, East China. Taxonomy 2025, 5, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/taxonomy5010015
She S-Q, Li J-P, Xie W-Y, Yao S-H, Chen Z-H, Zhou X, Xu Y-L. Sedum yongkangense (Crassulaceae), a New Species from Zhejiang, East China. Taxonomy. 2025; 5(1):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/taxonomy5010015
Chicago/Turabian StyleShe, Shi-Qi, Jun-Ping Li, Wen-Yuan Xie, Shen-Hao Yao, Zheng-Hai Chen, Xin Zhou, and Yue-Liang Xu. 2025. "Sedum yongkangense (Crassulaceae), a New Species from Zhejiang, East China" Taxonomy 5, no. 1: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/taxonomy5010015
APA StyleShe, S.-Q., Li, J.-P., Xie, W.-Y., Yao, S.-H., Chen, Z.-H., Zhou, X., & Xu, Y.-L. (2025). Sedum yongkangense (Crassulaceae), a New Species from Zhejiang, East China. Taxonomy, 5(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/taxonomy5010015






