Abstract
The admissible concentrations of toxic fumes, which appear after blasting works in open pits and underground mine excavations, are presented in this paper. Fumes were examined according to the national standard, which was designed according to European regulations. Fumes that are taken under consideration according to the European standard are carbon monoxide (CO) and nitrate oxides (NOx). The afterburning effect was not included. Analysis showed inconclusive results of possible explosive applicability in countries that are applying the general toxicity index (toxicity coefficient may vary between countries from 5 to 10) instead of the recommended European regulation. Based on the obtained results, it was concluded that the most environmentally friendly explosives are emulsion explosives. Moreover, the ammonium nitrate prill diameter has not significantly affected the fumes’ concentration; however, it significantly influences the velocity of detonation.
1. Introduction
Blasting is one of the most commonly used mining techniques due to its low cost and a large volume of excavated rock mass in a short period of time. The most commonly used explosives in terms of mining (both underground and open-pit) are ANFO, emulsion explosives, and dynamites. According to (Standard and Poor’s) S&P Global analysis, the largest consumers of explosives in industrial applications are China, the United States, the Commonwealth of Independent States, and Central and South America. Moreover, in spite of the mining industry, a significant volume of explosives is applied in civil works (construction industry) [1]. In terms of mining, coal mining is, according to S&P Global, the largest consuming sector for industrial explosives. It is responsible for ca. 40% of total explosives consumption. However, it was observed that with the energy shift towards green technology, and concerning the Paris Agreement which aims at the reduction of carbon dioxide, the coal mining output started to decrease which resulted in a smaller consumption of explosives [1]. In addition to coal mining, ore mining is responsible for ca. 33% of the world’s explosive consumption. According to S&P Global analysis, this sector of the mining industry is projected to increase during the 2019–24 forecast period [1]. Stone quarrying for the construction and production of cement is responsible for 16% of the world’s explosive consumption. Biegańska and Barański indicated that in 2020 in the Polish market, the consumption of ANFO and emulsion in open-pit mining was, respectively, ca. 7.02 million kg and ca. 17.88 million kg [2].
Oluwoye et al. estimated that the total NOx emission rate in 2017 from AN-based explosives was ca 0.05 Tg (5 × 104 t) N per year [3]. They concluded that this is a minor share in comparison to the total global annual anthropogenic NOx emissions which was evaluated as 41.3 × 106 t N per year [3]. However, Olowoye et al. have indicated that despite this fact, blasting works emit a large localized plume of fumes of a high NOx concentration (close to ca. 500 ppm) which exceeds up to 3000 times the permissible levels [3].
In terms of explosives, detonation is a type of chemical reaction, which occurs rapidly and results in a considerable volume of fumes (it is expected that around 1000 dm3 of fumes may appear from 1 kg of explosive in the assumption of optimal charge diameter). When the solid explosive is shocked, its temperature, pressure, and density rise sharply; consequently, a chemical reaction is triggered and a detonation wave is produced [4]. As a result of a chemical reaction, a large volume of high-pressure gases is obtained. The volume of fumes is proportional to the attained pressure. In addition, the composition of fumes is determined by the detonation heat. The heat directly affects the temperature resulting from product decomposition. In other words, the detonation process has the highest velocity, is strong enough to crush rocks, and provides the least amount of toxic substances [5]. On the other hand, some properties such as toxicity and melting point are also needed in the case of developing a new type of energetic material [6].
Since the 1960s, a strong emphasis has been put on the health and safety conditions of workers. Studies on the impact of toxic fumes on the human body have been carried out. Based on the findings, it has been determined that long-term exposure to a small concentration of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and carbon monoxide (CO) can lead to respiratory problems. A higher concentration of toxic fumes can cause death. Obtained results by researchers in Poland, in the 1980s, contributed to the design of general standards (PN-C-86067) for maximum concentrations of toxic fumes in underground mining [7,8]. Access to the European Union resulted in the need to adjust the applicable national regulation to the European Union directive.
Evaluation of the emission of toxic fumes, which appear after the detonation process, is widely discussed in papers across the world [9,10,11,12]. To ensure the safety of workers and the environment, several analytical methods have been developed both in risk assessment [13] as well as in the evaluation of oxide’s harmful potential in underground mines [14,15] and open-pit mining [16].
The evaluation of the volume of toxic fumes is generally provided in papers that are subjected to the blasting properties of the explosives, or packaging. Based on the volume of the CO and NOx, Biessikirski et al. investigated fumes in the case of the addition of silicon dioxide, microstructure charcoal, various assortments of ammonium nitrate(V), or the application of different types of fuel oils [17,18,19]. Oluwoye et al. focused on the next type of explosive mixtures which are obtained by the application of new types of fuels or additives [3], Araos and Onderra evaluated fumes in the new type of hydrogen peroxide-based explosives [20]. Kuterasiński et al. researched the potential addition of zeolite Y type to the ANFO. One of his evaluated factors was fumes derived from the detonation of non-ideal explosives [21]. Bhattacharyya investigated the influence of packaging on the NO2 and CO of semi-gel nitroglycerine-based explosives. They concluded that a bigger prill size of ammonium nitrate(V) results in a higher volume of fumes [22]. Torno and Toraño as well as Tiile made research based on the field detonation in the underground mines. Based on the results, they established a 4d CFD model [23,24]. Suceska evaluated fumes based on the thermodynamic calculations performed in Explo5 software as well as according to the BKW code [25]. Zawadzka-Małota has tested mining explosives concerning the content of carbon oxides and nitrogen oxides in their detonation products [26].
To decrease the migration of CO, Harris, and Mainiero suggested the application of negative pressure to a borehole by placing the drilling boom over an existing open hole near the blast site [27]. Silvester et al. studied particulate emissions from the open pit quarry [15].
Moreover, to determine the post-detonation properties of condensed-phase explosives some thermochemical computer codes like FORTRAN BKW, CHEETAH, EXPLO5, BARUT-X have been developed [27]. Thermochemical computer codes such as BKW, RUBY, TIGER, CHEQ, and CHEETAH, by assuming all of the chemical equations for all possible chemical compounds in the reaction fumes product and solving these with thermochemical analogs, can estimate the isentropic expansion having the equilibrium energy and gas quantities along with the Rankine–Hugoniot jump equations [6].
In 2003, Poland became part of The European Union. Following Directive 93/15/ECC, Poland, and other EU countries were obliged to design a uniform law, which included hazardous substances like toxic fumes [28]. The purpose of this law was to ensure the health and safety of the employees. This resulted in the creation of Polish Standard PN-EN 13631-16:2006, which focused on the cause of the concentration of toxic fumes, which are obtained throughout the detonation process [29]. The main aim of this paper is to present a fumes evaluation based on the most commonly used mining explosives such as Ammonium Nitrate Fuel Oil, dynamite, and emulsion. An emphasis is put on the general toxicity aspect.
2. General Toxicity
Because of the appearance of fumes, explosives materials are classified according to the corresponding countries’ requirements. In Poland, the general toxicity limits of carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides are set according to the following Equation (1).
where LCO is general toxicity, dm3·kg−1; [XCO], [YNOx] is a volume of toxic fumes, dm3·kg−1; and kNO2 is the toxicity coefficient.
LCO = [XCO] + kNO2 [YNOx]
The general toxicity expresses the sum of carbon monoxide and nitric oxide toxicity multiplied by the toxicity coefficient. The toxicity factor (k) expresses the ratio of the maximum permissible concentration of CO and maximum permissible concentrations of nitrogen dioxide.
In European Union countries that do not have either accredited measurement stations or European standards of toxic fume measurements, the controls of toxic oxides must be carried out directly at the workplace. In such cases, the toxicity factor determines the ratio of the maximum permissible concentrations (MPC) of carbon monoxide to nitrogen dioxide, which is expressed in Equation (2) [30]:
where [MPCCO] is the maximum permissible concentration of carbon monoxide, and [MDCNO2] is the maximum permissible concentration of nitrogen dioxide.
KNO2 = [MPCco]·[MPCNO2]−1
Following [31], the maximum concentration of oxides at the pit face must not exceed the value presented in Table 1 [31].

Table 1.
The maximum permissible concentration of carbon monoxide [32].
The permissible concentration of toxic oxides, which determines the allowable explosive materials in various countries in underground mining is presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
The permissible concentration of toxic fumes in underground mining in various countries [33].
In countries such as Finland, Netherlands, Romania, Sweden, United Kingdom, and Hungary, there are no strict criteria which limit the concentration of toxic fumes. The permissible concentration of oxides for underground ventilation is defined by each national legislation.
Since 2010, a tendency to move away from theoretically calculated values of general toxicity has been observed.
Based on Table 2, it can be observed that permissible concentrations of toxic fumes in Polish underground mines are, in the case of CO ,no more than 0.135% by volume, which is 27 dm3 kg−1, and for NOx, no more than 0.080% by volume, which is 16 L·kg−1.
3. The Decomposition Products
The detonation process relies on the decomposition of molecular structures. Complex molecules decompose into simpler ones or single atoms. Based on the ideal model of the detonation process, reactants decompose into carbon dioxide, water vapor, and nitrogen. Reactants may also decompose into gaseous and other products, which did not decompose but underwent secondary reactions. In such cases, the products of the detonation process are carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, water vapor, and methane. In some cases, depending on the condition of the reaction, hydrogen may appear. Sulfur dioxide and hydrogen sulfide are not present in toxic fumes. Those products can appear only if blasting works are conducted in rock masses that contain sulfur. The same process can occur with lead and mercury.
Products of the detonation process that result from primary and secondary decomposition reactions can be explained by dividing the process of explosive detonation into two stages. During the first stage, a large increase in pressure results in a large volume of highly heated gases. This stage lasts until the rock mass, which surrounds the blasthole, starts to crack. In the second stage, rapid expansion occurs. Products from the first stage mix with air, which leads to cooling and secondary reactions. The main factor which results in the formation of toxic fumes is the oxygen balance. The excess or deficiency of oxygen may cause the formation of NOx and carbon monoxide CO. It should be noted that these oxides may be formed in both stages of the reaction. In the primary reaction, during the explosion, and the secondary reactions. The secondary reaction and oxygen deficiency contribute to the formation of carbon monoxide. Based on the Kistiakovsky–Wilson rule, it can be seen that oxygen deficiency prevents the decomposition of carbon monoxide into carbon dioxide. This incomplete oxidation causes an additional emission of CO. Certain quantities of carbon can react with water or carbon dioxide, according to Equation (3) [34]:
H2O + C ↔ CO + H2
If the detonation process is completed, a reduction in carbon dioxide with hydrogen may occur, Equation (4):
CO2 + H2 ↔ CO + H2O
Therefore, following Le Chatelier’s Braun rule, an endothermic reaction results in an increasing amount of CO with increasing temperature and a decreasing amount of CO with increasing pressure.
After the detonation process, free carbon or carbon monoxide may react with the oxygen in the air according to Equation (5):
C + 0.5O2 ↔ CO
Another source of carbon monoxide formation is the ability of carbon to react with small amounts of carbon dioxide. This is a typical reaction for explosives which are characterized by oxygen deficiency. The reaction scheme is represented in Equation (6):
CO2 + C ↔ CO
Often, methane is a byproduct of secondary reactions, as in Equations (7)–(9).
C+ 2H2 ↔ CH4
CO + 3H2 ↔ CH4 + H2O
2CO + 2H2 ↔ CH4 +CO2
Nitrogen oxides are formed mainly from the incomplete decomposition of ammonium nitrate, as in Equation (10):
3NH4NO3 ↔ 3NO +1.5N2 + 6H2O
As a result of the incomplete decomposition of ammonium nitrate, obtained nitrous oxide undergoes a further violent explosive reaction. The reaction occurs at the time of detonation or after the decomposition. This results in a minimum concentration of nitrous oxide in toxic fumes. The reaction takes place according to Equation (11):
N2O + H2 → N2 + H2O
NOx is formed during the incomplete decomposition of ammonium nitrate. Of all nitrogen oxides, the one produced in the largest quantities during the detonation process is nitric oxide. However, when it comes into contact with oxygen, nitric oxide oxidizes and converts to NO2. This reaction is presented in Equation (12):
2NO + 0.5O2 ↔ 2NO2
At a temperature of around 150 °C, nitrogen dioxide has a high tendency to associate, as demonstrated by Equation (13):
2NO2 ↔ N2O4
During the cooling process, the equilibrium of the reaction shifts to the right side (in the direction of dinitrogen tetroxide). This results in the presence of oxide in toxic fumes.
Fumes may include N2O3 and N2O5. However, due to their low toxicity and negligible concentrations, the reactions of their formation will not be discussed.
In addition to the primary and secondary reactions, the detonation of explosives can be followed by the afterburning effect. This means that in the case of the negative oxygen balance, the additional content of carbon monoxide, and soot which may be present in the composition of the post-blast fumes may interact with products of the decomposition reaction and lead to further increased detonation pressure [34]. In the research of Salzano and Basco, it was shown that the afterburning effect of the black powder decomposition products enables energy that is equal to the afterburning energy of TNT [35]. Moreover, the results of the afterburning effect were presented by [36].
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
Blasting tests were made for the explosives which were used in underground and open-pit mining.
In all tests, ANFO, emulsion, and dynamite charge in the form of a booster were researched.
In the case of ANFO, samples were produced by blending prilled ammonium nitrate(V) with fuel oil in a ratio 94:6. ANFO was placed in the glass tube. The diameter of the tube was 46 mm. The length of the tube was 750 mm. An exemplary charge is presented in Figure 1.

Figure 1.
ANFO charge.
Ammonium nitrate(V) used in this research was of different prill sizes and absorption ratios. The absorption ratio was between 12 and 14%. Prill sizes were in the range of 7–8 mm. Prills of smaller diameter (higher absorption ratio) were used in ANFO samples: 4, 7, and 8.
In the case of emulsion explosives, the emulsion was placed in the polyethylene cartridge. The charge diameter was ca. 46 mm.
The general chemical composition of dynamite samples is presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Chemical compositions of researched dynamites.
The chemical composition of dynamite sample 3 was not available.
Four types of emulsion bulk explosives were tested. An approximated chemical composition of emulsion bulk explosives is presented in Table 4.

Table 4.
Chemical composition of tested emulsion explosives.
Emulsion sample 1, emulsion sample 2, and emulsion sample 4 were low-water composition (LWC) explosives.
4.2. Methods
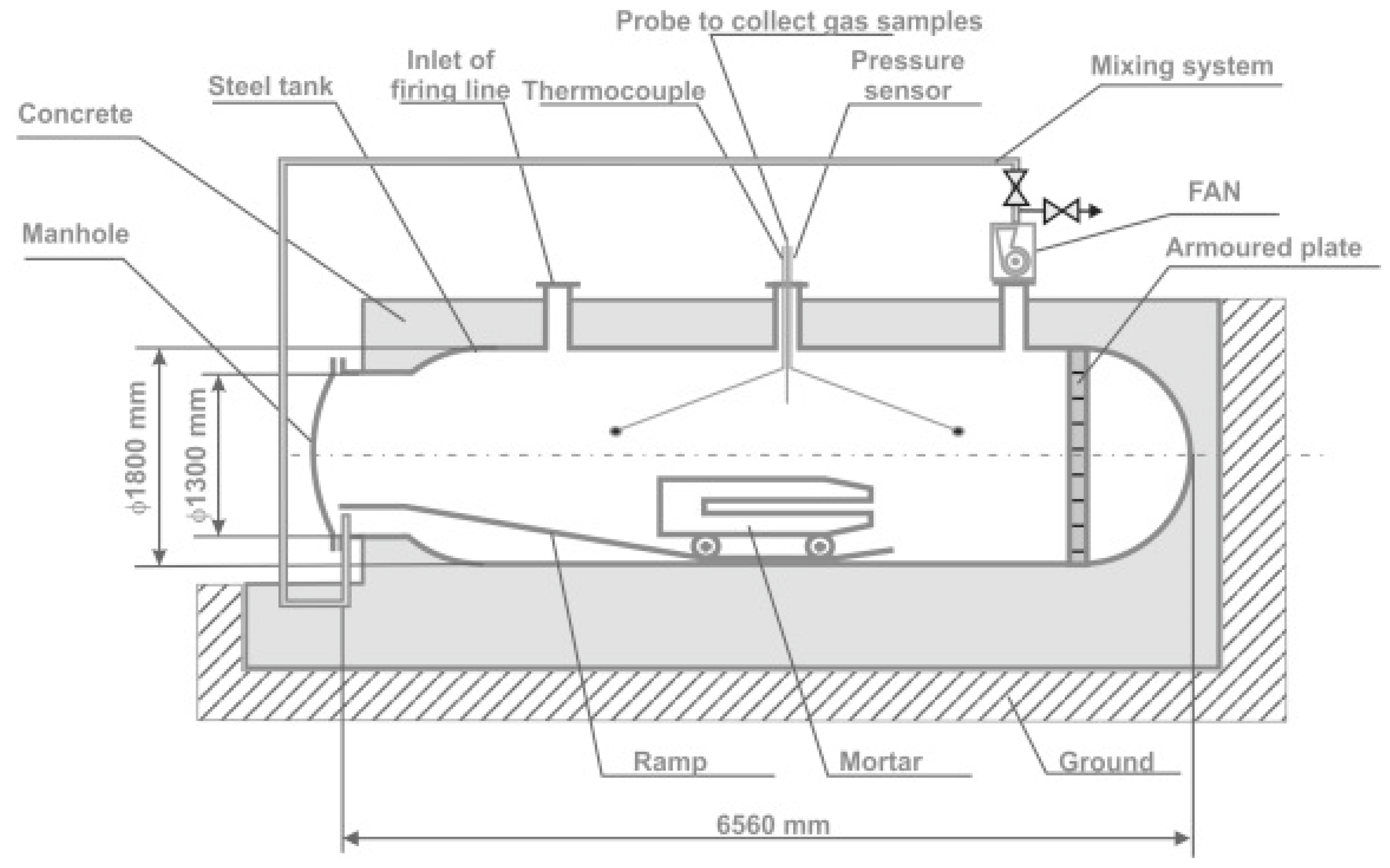
The measurement of the volume of toxic fumes was obtained by the detonation of Polish explosives. Measurements were made according to [37]. Tests were carried out in the blasting chamber made of steel, Figure 2.
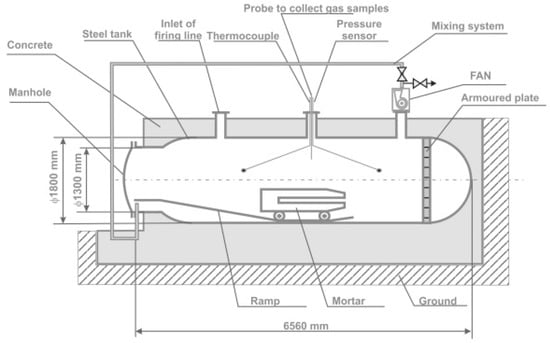
Figure 2.
Blasting chamber [36].
The blasting chamber volume was 15 m3. The explosive booster was placed centrally in the mortar. The diameter of the borehole in the mortar was ca. 48 mm. Each explosive charge was initiated by the primer (cap-sensitive explosive in the form of the booster with a detonator). The RDX booster was armed with a single instantaneous electric detonator 0.2 A. After the decomposition, a 20 min measurement period begins. The blasting chamber is equipped with a mixing system combined with a fan system. The fan allows fume homogenization. The gas samples were collected automatically by the probe. From the probe, toxic fumes were transported along the cooling gas line to the analyzers. NOx was measured by the TOPAZE 32M chemiluminescent analyzer. CO was evaluated based on the results obtained from MIR 25e, an infrared spectroscopy analyzer [37].
Assuming a gas-tight chamber, the concentrations of CO and CO2, reach a constant value after the initial mixing period. The baseline concentration of NOx oxides is obtained by extrapolating the dependence on concentration changes with time [37]. Each blasting was repeated 10 times per explosive type. Initially, obtained concentration values were averaged [37].
The construction of the chamber allows for multiple explosive detonations of an explosive mass of 450 ÷ 750 g (30 ÷ 50 g of explosive per 1 m3 of the chamber).
The velocity of detonation (VOD) was researched according to the standard in [38]. In terms of ANFO, the 600 g samples of non-ideal explosive charge were placed in a glass pipe. The pipe’s inner diameter was 46 mm. Emulsion explosives and dynamite charges were in the form of boosters. In each test, a separate explosive charge was primed with 14 g RDX charge initiated by the electric detonator 0.2 A. VOD was measured by placing two short-circuit probes close to the top and bottom of the tube. The distance between the probes was 150 mm. The VOD was established by the division of the time difference which was derived by the progressing detonation with a distance between probes.
In terms of fumes and VOD tests, such an explosive sample was primed by the 14 g RDX-based booster armed with an instantaneous electric detonator.
5. Results and Discussion
Average concentrations of toxic oxides, VOD, and density ANFO samples are presented, respectively, in Table 5 and Table 6. All calculations of general toxicity were made according to Equation (1).

Table 5.
VOD and density of ANFO samples.

Table 6.
Average fumes volume and general toxicity of various ANFO.
Based on Table 5, it can be observed that all tested ANFO samples had a VOD over 1000 m/s, which indicates that all samples detonated and further interpretation of fume results is relevant.
Based on Table 6, it can be concluded that the average concentration of NOx is around 10.61 dm3∙kg−1 and CO is around 11.63 dm3∙kg−1. By taking into consideration Polish permissible levels of toxic fumes which are, respectively, 27 dm3 and 16 dm3 for CO and NOx it can be stated that all tested samples did not exceed the permissible limit. Moreover, all examined explosives did not exceed the permissible limits of toxic fumes in other countries. However, if potential explosives applicability would be evaluated based on the permissible concentration which includes the general toxicity limits, the decision of potential explosive applicability in various countries can be different. Table 2 indicates that depending on the toxicity coefficient (k index in the range of 5–10) by taking into consideration Equation (1) and Table 2, the difference in results depending on the k factor is ca. 50–65 dm3∙kg−1. For example, the biggest difference is in the case of sample 10 which is 65.50 dm3∙kg−1. This shows the potential ambiguity of the potential applicability in various markets.
Based on Table 6, it can be observed that the lowest volume of CO was calculated for samples 4, 7, and 8 (respectively 7.80, 15.00, and 4.01 dm3∙kg−1). Moreover, the same samples indicate the lowest NOx volume, respectively, for sample 4: 10.20 dm3∙kg−1, for sample 5: 12.40 dm3∙kg−1, for sample 8: 7.64 dm3∙kg−1. This indicates that samples 4, 7, and 8 are close to the zero-oxygen balance. Furthermore, by taking into account that ANFO samples 4, 7, and 8 were based on the smaller prill size, it can be concluded that the surface of contact between the combustion agent and oxidant part is high, which influences the detonation process, especially by the possibility of the formation of the highest number of hot spots in comparison with the ANFO obtained based on the higher grade AN.
By comparison, fume volume (Table 6) derived from the detonation explosives that were produced between 2000 and 2010 (samples 1–5) compared with contemporary explosives (samples 6–8) showed no significant difference. The difference is strongly visible with the VOD. One of the factors which affects the VOD is the density of the explosive. It is well known that in a limited manner, the VOD rises with the density of the explosives. Based on Table 5, the linear relation is visible. However, it should be taken into account that ANFO is considered a non-ideal explosive. This means that VOD results that are obtained close to the ANFO’s critical diameter can vary significantly from the VOD obtained for the optimal explosive diameter.
Further tests were performed for a variety of the most commonly used water-in-oil (W/O) emulsion bulk explosives. In the W/O type of emulsion, a discontinuous water phase of inorganic oxidizer is dispersed in a continuous organic fuel phase. Droplets in the discontinuous phase are held in place by a proper W/O emulsifier [39]. The size of droplets is a key issue in emulsion properties, especially in the case of a highly concentrated emulsion [40]. In Table 7 and Table 8, the basic emulsion explosives parameters such as density and VOD as well as average concentrations of emulsion bulk explosives are provided. All calculations of general toxicity were made according to Equation (1).

Table 7.
VOD and density of emulsion samples.

Table 8.
Average fumes volume and general toxicity of various compositions of emulsion bulk explosives.
The obtained results of general toxicity show a similar conclusion as in the case of ANFO. Based on Table 8, it can be observed that the average concentration of NOx is around 4.9 dm3∙kg−1 and CO is around 12.23 dm3∙kg−1. By taking into consideration Polish permissible levels as well as other nationally permissible levels, it can be stated that tested emulsion explosives samples did not exceed the permissible limits. In the case of general toxicity, the maximum difference between the samples was ca. 27.0 dm3∙kg−1 in emulsion samples 1 and 4. The difference is much lower in comparison with ANFO. This can be explained by the low differences in NOx volume between emulsion samples. The low volume of NOx fumes amplifies the fact that emulsion explosives are the most ecologically friendly type of explosives in the mining industry.
Based on Table 8, the highest volume of CO was observed for emulsion sample 3 (19.80 dm3∙kg−1). This can be explained by the chemical composition of explosive material. Emulsion explosive sample 3 had the highest content of organic components up to c.a. 6.0% in comparison with other emulsion samples (fuel component in the range of 4.2 ÷ 5.5%). By taking into consideration the modified Kistiakowski–Willson rule or Springall–Roberts rule, the first phase of decomposition is the oxidation of carbon atoms to carbon monoxide. Moreover, emulsion explosives samples 1, 2, and 4 were low-water-composition explosives that were characterized by a water content of up to 7%. In terms of regular emulsion explosives, water content is on average 15%. The higher content of water influences the heat of detonation and VOD. Usually, LWC explosives have a higher heat of detonation and VOD values. Based on Table 7, it can be observed that low-water-composition emulsions (samples 1, 2, and 4) had a higher VOD in comparison to emulsion explosive sample 3, respectively, 3710, 3900, 4080 m/s to 3700 m/s. The high VOD in terms of sample 3 and sample 4 can also be explained by the addition of aluminum powder (respectively, 4 and 5%), which increased the heat of the explosion.
Besides ANFO and emulsion bulk explosives, one of the most popular explosive types that is applied in the mining industry is dynamite. The results of density, general toxicity, and toxic fumes are presented in Table 9 and Table 10. All calculations of general toxicity were made according to Equation (1).

Table 9.
VOD and density of dynamite samples.

Table 10.
Average fume volume and general toxicity of various compositions of dynamite explosives.
Based on Table 10, it can be observed that dynamite sample 4 has the highest volume of CO ca. 23.93 dm3/kg. This can be explained by the chemical composition of the explosive sample. In the case of sample 4, the combustible components (fuels, modifiers, an TNT) consist of the larger part of the dynamite chemical composition (ca. 9.2%). It can be assumed that dynamite sample 3 has a similar chemical composition to dynamite sample 4. In the case of dynamite sample 1 and sample 2, the combustible components consist, respectively, of ca. 7.01% and 7.5%. This results in a similar volume of CO. In terms of NOx, it can be observed that dynamite sample 1 has the highest volume of nitrous fumes. This partially corresponds with the oxygen balance (6.64%, Table 9). Normally, with higher positive values (oxygen balance), more NOx appears. By taking into consideration Table 9, the highest oxygen balance can be observed with dynamite sample 2 which corresponds with the lowest volume of NOx. However, based on the chemical composition of the explosives, it can be observed that despite the oxidizing agents consisting of similar parts of the explosive, the main difference stems from sodium nitrate. Dynamite sample 2 consists of the highest content of this oxidizing agent ca. 10%. Other samples have a lower content of sodium nitrate(V) which causes there to be additional nitrogen atoms in the chemical composition which influences decomposition products (NOx and N2).
Based on the general toxicity, it can be concluded that all tested samples meet Polish and other national standards. However, if we take into consideration different toxicity coefficients, it can be observed that the difference between general toxicity values reaches up to ca. 76.0 dm3/kg (dynamite sample 1). The large variance between results leaves room for inaccurate interpretation.
An average volume of toxic fumes of all types of explosives is presented in Table 11.

Table 11.
Average fumes volume and general toxicity of tested ANFO, emulsion explosives, and dynamites.
Based on Table 11, it is noted that the explosives which were tested meet the standards for civilian use. ANFO has a low concentration of nitrogen oxides. The concentration of NOx is comparable in value with the concentration of carbon monoxide produced by the ANFO detonation. This is due to the chemical composition of the explosive. The dominant component is highly porous ammonium nitrate. Oxygen balance and ammonium nitrate are responsible for the formation of NOx. Carbon oxides are the product of the decomposition of the organic part, which comprises only a small percentage of the total weight of the product. This is the reason why the concentration of carbon monoxide is low.
Furthermore, it must be noted that emulsion bulk explosives are the most environmentally friendly.
6. Conclusions
Based on the obtained results, it can be concluded that an evaluation methodology simulates typical conditions of blasting works and allows for research of various types of explosives. However, the mortar diameter is close to the critical diameter of non-ideal explosives, which can have a significant influence on results. In the future, the construction of the mortar could be improved.
Results of fume analysis performed according to the standard in [34] are extremely important in terms of the application of explosives in underground mines. The preliminary results indicate the potential influence of fumes on the miners’ working conditions and influence work safety.
Based on the results it can be stated that all tested explosives comply with the standards for different permissible levels of toxic oxides. The lowest concentration of fumes (NOx) occurs in emulsion explosives. It is caused by a very large surface of contact between the oxidant and organic phase. Also, an oxygen balance that is close to 0 is highly recommended. However, the significant amount of CO in emulsion explosives can be explained by the polyethylene cartridge which also takes a part in the decomposition reaction.
Explosive materials, which have an oxygen balance from 0 to 5% are characterized by the least amount of toxic gases and the greatest strength of detonation. This is the reason why manufacturers strive towards these types of materials.
The formula for general toxicity has different characteristics in different EU countries or in the U.S. Due to the possible toxicity coefficient (k) in the range of 5 to 10, or the maximal permissible volume of fumes, it is noted that—assuming different values—the same explosive material can obtain varying compartment results. From this, it follows that the same explosive material, in some countries, can have a general toxicity value over the permissible level. It is possible to notice a slow trend of neglecting the general toxicity coefficient in EU standards. However, coefficient unification should be recommended. Future work should focus on the design of unified permissible levels of fumes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: A.B.; methodology, A.B.; validation, A.B., M.D. and M.T.; formal analysis, A.B., investigation, A.B., resources, A.B., M.T. and M.D.; writing—original draft preparation, A.B., M.T. and M.D.; writing—review and editing, A.B., M.T. and M.D.; visualization, A.B., M.T. and M.D.; supervision, A.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors wish to thank you for your financial research support no. 16.16.100.215 of The Faculty of Civil Engineering and Resource Management at the AGH University of Krakow.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author (A.B.).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the contribution of Iwona Zawadzka-Małota, from Conformity Assessment Body, Central Mining Institute in Poland who made part of the research available.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors wish to confirm that there are no known conflicts of interest associated with this publication, and there has been no significant financial support for this work that could have influenced its outcome.
References
- Standard and Poor’s (S&P) Global Commodity Insights. Available online: https://www.spglobal.com/commodityinsights/en/ci/products/explosives-and-blasting-chemical-economics-handbook.html (accessed on 3 October 2023).
- Biegańska, J.; Barański, K. Environmental aspects of the use of biomass to produce high-energy. In Proceedings of the International Conference Energy Fuels Environment, Kraków, Poland, 20–23 September 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Oluwoye, I.; Dlugogorski, B.Z.; Gore, J.; Oskierski, H.C.; Altarawneh, M. Atmospheric emission of NOx from mining explosives: A critical review. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 167, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulazeem, M.S. Shock and detonation properties of solid explosives with gaseous products. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onderka, Z. Inżynieria Strzelnicza Część I (Blasting Technique Part I); Skrypt AGH Kraków: Kraków, Polska, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Keshavarz, M.H.; Poretedal, H.R. Simple determination of performance of explosives without using any experimental data. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 119, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cybulski, W. Badania nad ilościowym składem gazów odstrzałowych. (Research on quantitive composition of fumes). Przegląd Górniczy 1966, 1, 114–121. [Google Scholar]
- Cybulska, R. Badania nad Możliwością Zatruć Gazami Odstrzałowymi w Robotach Kamiennych i Węglowych (Research on the possibility of Poisoning by Fumes Derived from Blasting Works in Open-Pits and Coal Mines). Ph.D. Thesis, Wydział Górniczy Politechniki Śląskiej, Gliwice, Poland, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Turcotte, R.; Yang, R.; Lee, M.; Short, B.; Shomaker, R. Factors affecting fume production in surface coal blasting operations. In Proceedings of the 28th Conference on Explosives and Blasting Technique, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 10–13 February 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Volk, F. Detonation gases and residues of composite explosives. J. Energetic Mater. 1986, 41, 93–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk, F. Energy output of insensitive high explosives by measuring the detonation products. J. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Phys. Eng. Sci. 1992, 339, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onderra, I.; Bailey, V.; Cavanough, G.; Torrance, A. Understanding main causes of nitrogen oxide fumes in surface blasting. J. Min. Technol. 2012, 121, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaren, D. A comparative global assessment of potential negative emissions technologies. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2012, 90, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukuczka, M. A new method for determining explosibility of complex gas mixtures. Mech. Autom. Gor. 1982, 164, 36–39. [Google Scholar]
- Attalla, M.I.; Day, S.J.; Lange, T.; Lilley, W.; Morgan, S. NOx emissions from blasting operations in open-cut coal mining. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 7874–7883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveter, S.A.; Lowndes, L.S.; Gargreaves, D.M. A computational study of particulate emissions from an open pit quarry under neutral atmospheric conditions. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 6415–6424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biessikirski, A.; Barań, K.; Pytlik, M.; Kuterasiński, Ł.; Biegańska, J.; Słowiński, K. Application of Silicon Dioxide as the Inert Component or Oxide Component Enhancer in ANFO. Energies 2021, 14, 2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biessikirski, A.; Gotovac Atlagić, S.; Pytlik, M.; Kuterasiński, Ł.; Dworzak, M.; Twardosz, M.; Nowak-Senderowska, D.; Napruszewska, B.D. The Influence of Microstructured Charcoal Additive on ANFO’s Properties. Energies 2021, 14, 4354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biessikirski, A.; Czerwonka, D.; Biegańska, J.; Kuterasiński, Ł.; Ziąbka, M.; Dworzak, M.; Twardosz, M. Research on the Possible Application of Polyolefin Waste-Derived Pyrolysis Oils for ANFO Manufacturing. Energies 2021, 14, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araos, M.; Onderra, I. Detonation Characteristics of a NOx-Free Mining Explosive Based on Sensitised Mixtures of Low Concentration Hydrogen Peroxide and Fuel. Cent. Eur. J. Energ. Mater. 2017, 14, 759–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuterasiński, Ł.; Wojtkiewicz, A.M.; Sadowska, M.; Żeliszewska, P.; Napruszewska, B.D.; Zimowska, M.; Pytlik, M.; Biessikirski, A. Variously Prepared Zeolite Y as a Modifier of ANFO. Materials 2022, 15, 5855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, M.M.; Singh, P.K.; Ram, P.; Paul, R.K. Some Factors Influencing Toxic Fume Generation by NG-based Semigel Explosives in Laboratory Studies. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2001, 26, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torno, S.; Toraño, J. On the prediction of toxic fumes from underground blasting operations and dilution ventilation. Conv. Numer. Models Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2020, 96, 103194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiile, R.N. Investigating Blast Fume Propagation, Concentration and Clearance in Underground Mines Using Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD). Doctoral Dissertation, Missouri University of Science and Technology, St. Rolla, MO, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Suceska, M.; Tumara, B.S.; Skrlec, V.; Stankovic, S. Prediction of concentration of toxic gases produced by detonation of commercial explosives by thermochemical equilibrium calculations. Def. Technol. 2022, 18, 2181–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawadzka-Małota, I. Testing of mining explosives with regard to the content of carbon oxides and nitrogen oxides in their detonation products. J. Sustain. Min. 2015, 14, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, M.L.; Mainiero, J.R. Monitoring and removal of CO in blasting operations. Saf. Sci. 2008, 46, 1393–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cengiz, F.; Ulas, A. Numerical prediction of steady—State detonation properties of condensed—Phase explosives. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 172, 1646–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 13631-16:2004; Explosives for Civil Uses. iTeh Standards: Newark, DE, USA, 2015.
- Sobala, J.; Zawadzka-Małota, I. Amendment of regulations relating to explosives admitting to applying in the underground mining in the reference to the in-vestigations after—Detonation gases according to the Directive 93/15 EEC and European Standard. WUG Bezpieczeństwo Pr. Ochr. Sr. W Górnictwie 2007, 9, 116–120. [Google Scholar]
- Zawadzka-Małota, I. Wpływ struktury i składu górniczych materiałów wybuchowych na zawartość toksycznych składników w gazach postrzałowych (Influence of structure and composition of mining explosive materials on contentof toxic components in post-shot gases). Pr. Nauk. GiG 2009, 3, 113–129. [Google Scholar]
- The Decree of The Minister of Labor and Social Policy of 15.10.2005. Polish Ministry of Economy and Labor 2015, 1769.
- L’institut National de l’Environnement Industriel et des Risques, 2012. Unpublished work.
- Akhavan, J. The Chemistry of Explosives; The Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Salzano, E.; Basco, A. Comparision of the explosion thermodynamics of TNT and black powder using Le Chatelier diagrams. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2012, 37, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biessikirski, A.; Pytlik, M.; Kuterasiński, Ł.; Dworzak, M.; Twardosz, M.; Napruszewska, B.D. Influence of the Ammonium Nitrate(V) Porous Prill Assortments and Absorption Index on Ammonium Nitrate Fuel Oil Blasting Properties. Energies 2020, 13, 3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PN-EN 13631-16:2006; Polish Standard. Materiały Wybuchowe do Użytku Cywilnego. Materiały Wybuchowe Kruszące. Część 16: Wykrywanie i Oznaczanie Gazów Toksycznych. PKN: Warszawa, Poland, 2006.
- EN 13631-14:2003; European Commission. Explosives for Civil Uses. High Explosives. Part 14: Determination of Velocity of Detonation. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2003.
- Ni, O.; Zhang, K.; Yu, Z.; Tang, S. Powder Emulsion Explosives. A new Excellent Industrial Explosive. J. Energ. Mater. 2012, 30, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakhoub, H.A.; Maslava, I.; Haldenwang, R. Highly concentrated emulsions: Role of droplet size. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2010, 198, 147–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).