Potential of Salt Caverns for Hydrogen Storage in Southern Ontario, Canada
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Geological Settings
2.1. Physical and Chemical Properties of Hydrogen
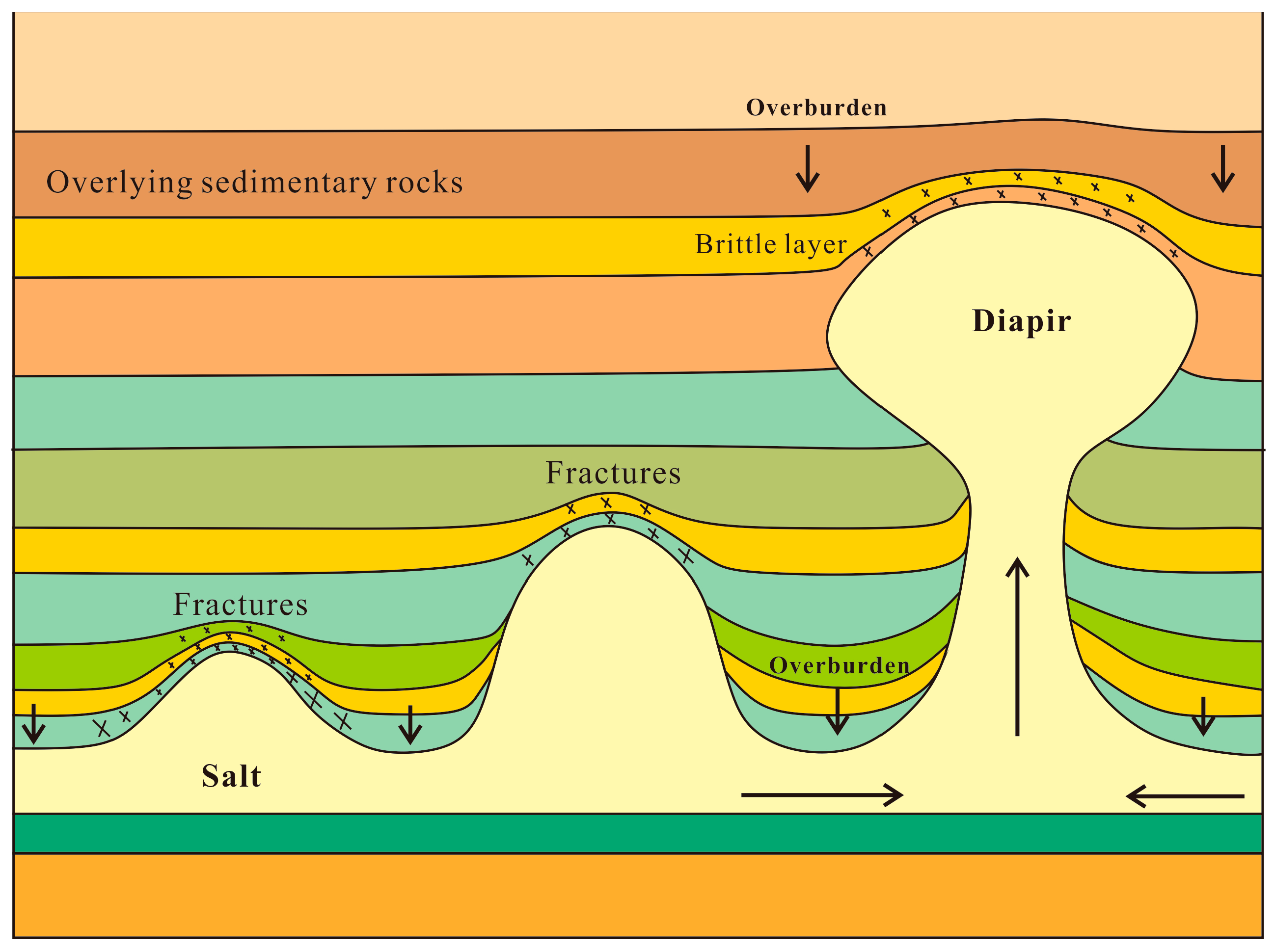
2.2. Geological Conditions of Salt Caverns
2.3. Factors Influencing Storage Potential and Stability
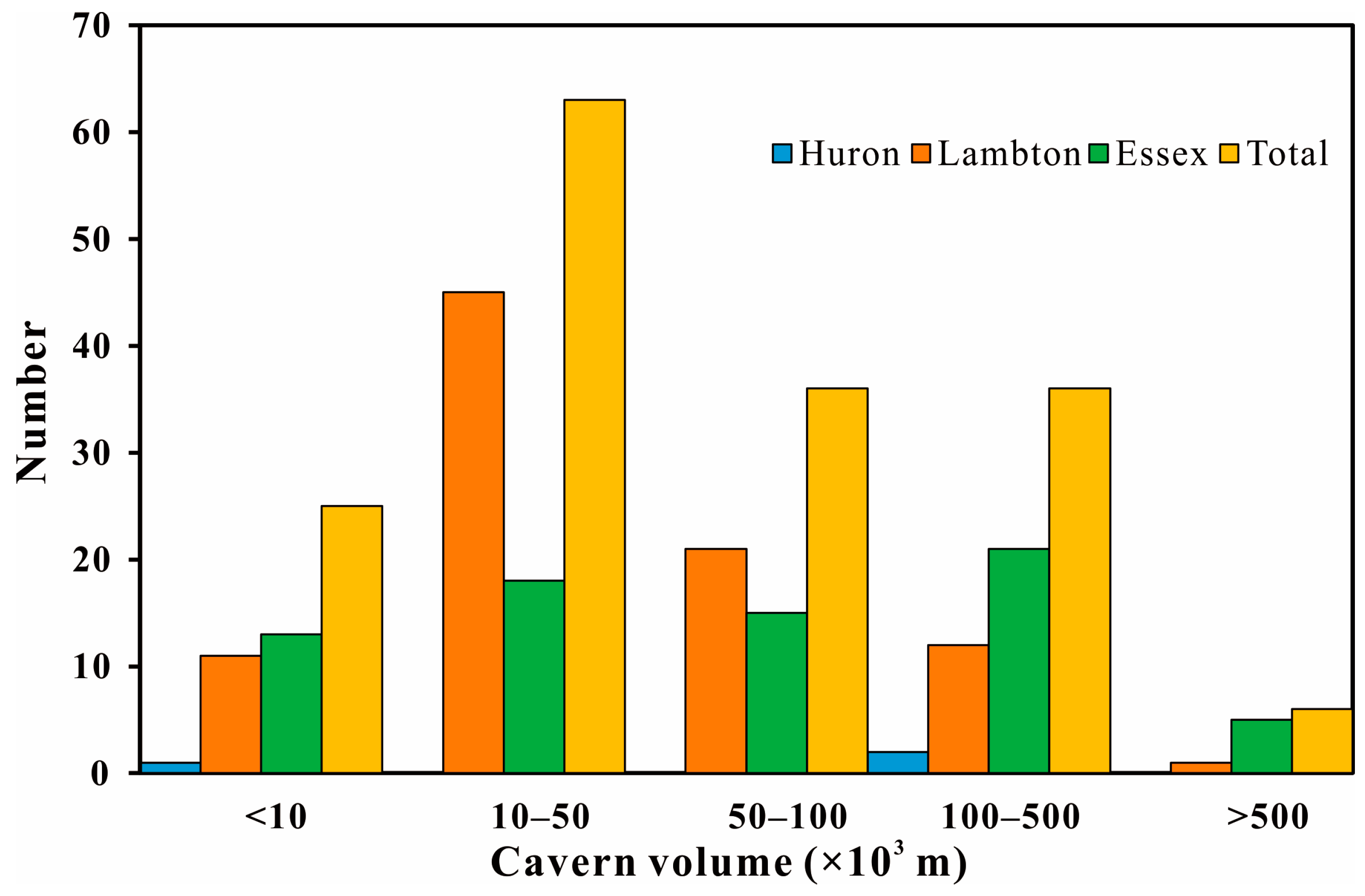
2.3.1. Scale of the Salt Cavern
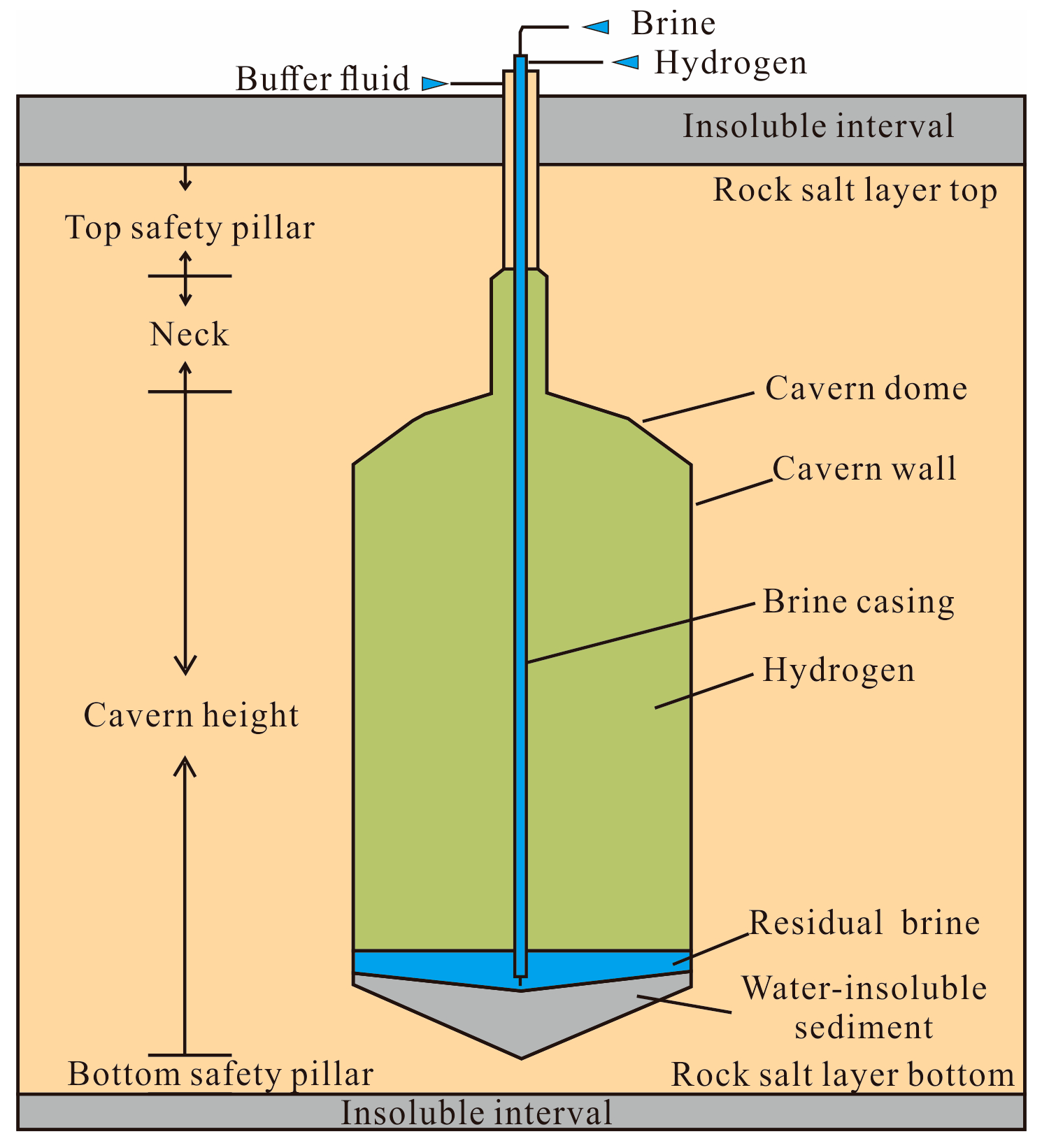
2.3.2. Cavern Height
2.3.3. Thickness of the Roof and Floor Salt Layer
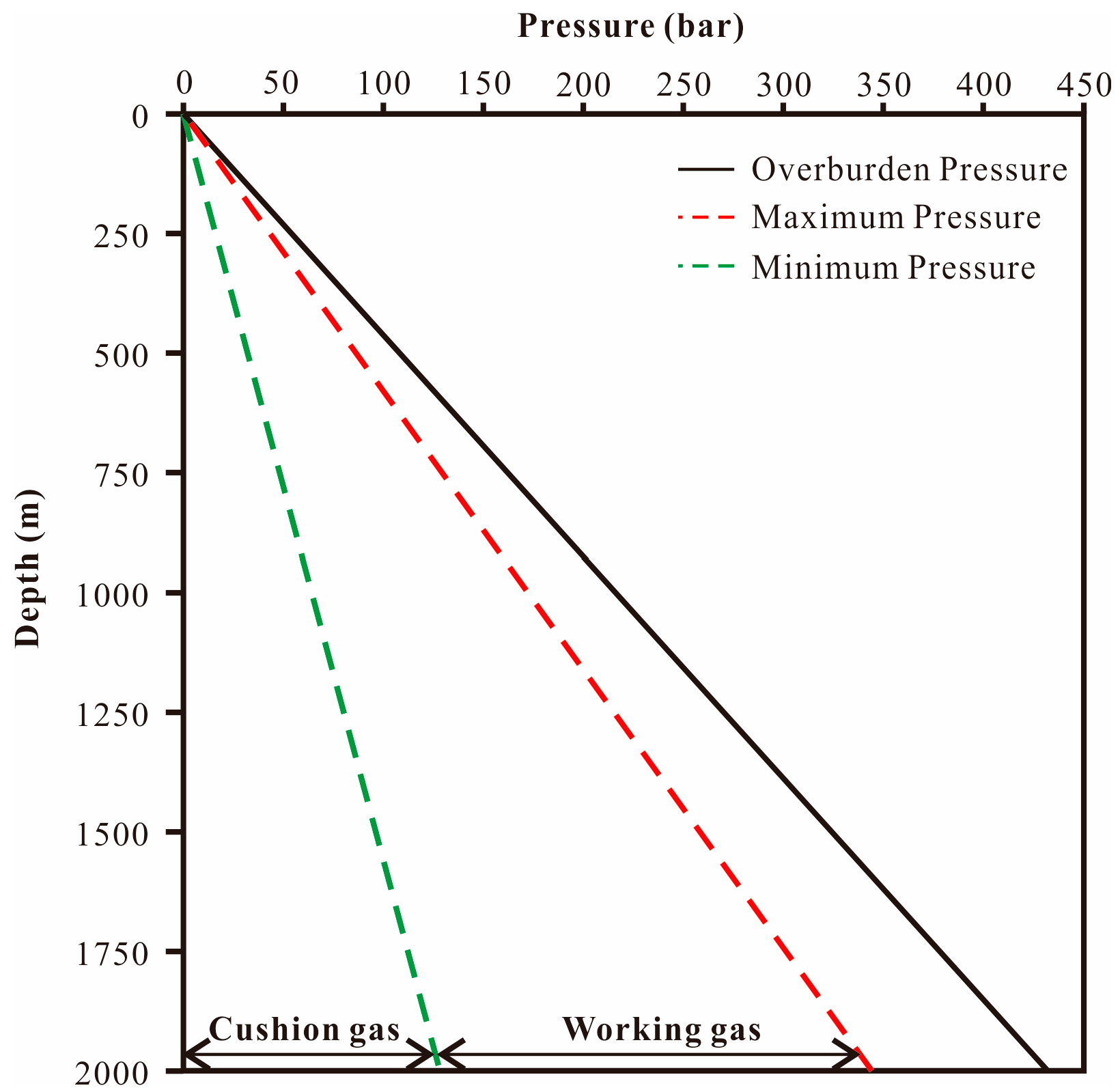
2.3.4. Internal Temperature and Pressure Conditions
3. Several Potential Problems That May Affect the Safe Storage of Hydrogen in Salt Caverns
3.1. The Determination of Pressure Difference
3.2. Salt Creep Behavior or Structure Disturbance
3.3. Engineering Safety/Humanistic Environment
4. Limitation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burke, M.J.; Stephens, J.C. Political power and renewable energy futures: A critical review. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2018, 35, 78–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawzy, S.; Osman, A.I.; Doran, J.; Rooney, D.W. Strategies for mitigation of climate change: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 2069–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, M.; Lebedev, M.; Barifcani, A.; Iglauer, S. Influence of shale-total organic content on CO2 geo-storage potential. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 8769–8775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gholami, R.; Raza, A.; Andersen, P.; Escalona, A.; Cardozo, N.; Marín, D.; Sarmadivaleh, M. Long-term integrity of shaly seals in CO2 geo-sequestration sites: An experimental study. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2021, 109, 103370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, A.; Arif, M.; Glatz, G.; Mahmoud, M.; Al Kobaisi, M.; Alafnan, S.; Iglauer, S. A holistic overview of underground hydrogen storage: Influencing factors, current understanding, and outlook. Fuel 2022, 330, 125636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambo, C.; Dudun, A.; Samuel, S.A.; Esenenjor, P.; Muhammed, N.S.; Haq, B. A review on worldwide underground hydrogen storage operating and potential fields. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 22840–22880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lankof, L.; Urbańczyk, K.; Tarkowski, R. Assessment of the potential for underground hydrogen storage in salt domes. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 160, 112309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körner, A.; Tam, C.; Bennett, S.; Gagné, J. Technology Roadmap-Hydrogen and Fuel Cells; International Energy Agency (IEA): Paris, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lankof, L.; Tarkowski, R. Assessment of the potential for underground hydrogen storage in bedded salt formation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 19479–19492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarkowski, R.; Czapowski, G. Salt domes in Poland—Potential sites for hydrogen storage in caverns. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 21414–21427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caglayan, D.G.; Weber, N.; Heinrichs, H.U.; Linßen, J.; Robinius, M.; Kukla, P.A.; Stolten, D. Technical potential of salt caverns for hydrogen storage in Europe. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 6793–6805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarkowski, R. Perspectives of using the geological subsurface for hydrogen storage in Poland. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemieux, A.; Sharp, K.; Shkarupin, A. Preliminary assessment of underground hydrogen storage sites in Ontario, Canada. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 15193–15204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crotogino, F.; Schneider, G.; Evans, D.J. Renewable energy storage in geological formations. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part A 2018, 232, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, D.K.; Carter, T.R. The Subsurface Paleozoic Stratigraphy of Southern Ontario; Ontario Geological Survey: Sudbury, ON, Canada, 2010; Volume 7, p. 301. [Google Scholar]
- Carter, T. Bedded salt in Ontario: Geology, Solution mining and Cavern Storage. In Proceedings of the Ontario Petroleum Institute’s 48, Sarnia, ON, Canada, 10–12 November 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Oil, Salt, and Gas Resource Library. Ontario Cavern Storage-Members-Report. 2021. Available online: https://s3.amazonaws.com/members.ogsrlibrary.com/downloads/OGSR+Library+-+Cavern+Storage+(Members+Report).pdf (accessed on 6 July 2023).
- Heinemann, N.; Scafidi, J.; Pickup, G.; Thaysen, E.M.; Hassanpouryouzband, A.; Wilkinson, M.; Satterley, A.K.; Booth, M.G.; Edlmann, K.; Haszeldine, R.S. Hydrogen storage in saline aquifers: The role of cushion gas for injection and production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 39284–39296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammed, N.S.; Haq, B.; Al Shehri, D.; Al-Ahmed, A.; Rahman, M.M.; Zaman, E. A review on underground hydrogen storage: Insight into geological sites, influencing factors and future outlook. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 461–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemme, C. Storage of Gases in Deep Geological Structures Spatial and Temporal Hydrogeochemical Processes Evaluated and Predicted by the Development and Application of Numerical Modeling. Ph.D. Thesis, Clausthal University of Technology, Clausthal-Zellerfeld, Germany, 26 February 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Engineering ToolBox. Air—Diffusion Coefficients of Gases in Excess of Air. 2018. Available online: https://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/air-diffusion-coefficient-gas-mixture-temperature-d_2010.html (accessed on 6 July 2023).
- Krader, T.; Franck, E.U. The Ternary Systems H20–CH4–NaCl and H20–CH4–CaC12 to 800 K; Berichte der Bunsengesellschaft für Physikalische Chemie; Deutsche Bunsen-Gesellschaft: Frankfurt, Germany, 1987; pp. 627–634. [Google Scholar]
- Simbeck, D.R. CO2 capture and storage-the essential bridge to the hydrogen economy. In Proceedings of the Greenhouse Gas Control Technologies—6th International Conference, Kyoto, Japan, 1–4 October 2002; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, J.D.O.; Williamson, J.P.; Parkes, D.; Evans, D.J.; Kirk, K.L.; Sunny, N.; Hough, E.; Vosper, H.; Akhurst, M.C. Does the United Kingdom have sufficient geological storage capacity to support a hydrogen economy? Estimating the salt cavern storage potential of bedded halite formations. J. Energy Storage 2022, 53, 105109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaledi, K.; Mahmoudi, E.; Datcheva, M.; Schanz, T. Stability and serviceability of underground energy storage caverns in rock salt subjected to mechanical cyclic loading. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2016, 86, 115–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, M. Gas storage in the Cheshire salt deposits, In Proceedings of the SMI Conference Gas Storage, Copthorne Tara Hotel, London, UK, 25–26 September 2012.
- Wang, T.; Yang, C.; Ma, H.; Daemen, J.J.K.; Wu, H. Safety evaluation of gas storage caverns located close to a tectonic fault. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2015, 23, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitt, D. Salt in Ontario; Industrial Mineral Report; Ontario Geological Survey: Sudbury, ON, Canada, 1962; Volume 6, p. 38. [Google Scholar]
- Karen, R.C. Thermal History of Michigan Basin. AAPG Bull. 1984, 68, 130–136. [Google Scholar]
- Crotogino, F.; Donadei, S.; Bunger, U.; Landinger, H. Large-scale hydrogen underground storage for securing future energy supplies. In Proceedings of the 18th World Hydrogen Energy Conference (WHEC2010), Essen, Germany, 16–21 May 2010; pp. 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- Valle-Falcones, L.M.; Grima-Olmedo, C.; Mazadiego-Martínez, L.F.; Hurtado-Bezos, A.; Eguilior-Díaz, S.; Rodríguez-Pons, R. Green Hydrogen Storage in an Underground Cavern: A Case Study in Salt Diapir of Spain. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozarslan, A. Large-scale hydrogen energy storage in salt caverns. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 14265–14277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crotogino, F.; Huebner, S. Energy storage in salt caverns/developments and concrete projects for adiabatic compressed air and for hydrogen storage. In Proceedings of the Solution Mining Research Institute SMRI Spring 2008 Technical Conference, Porto, Portugal, 27–30 April 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Klusman, R.W. Faults as windows to monitor gas seepage: Application to CO2 sequestration and CO2-EOR. Geosciences 2018, 8, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elodie, L.; Lafortune, S.; Donato, D.P.; Gombert, P.; Adelise, F. Development of monitoring tools in aquifer for underground H2 storage through an in-situ leakage experiment Communication. In Proceedings of the Virtual EGU General Assembly, Online, 4–8 May 2020; Available online: https://presentations.copernicus.org/EGU2020/EGU2020-17949_presentation.pdf (accessed on 6 July 2023).
- Carter, N.L.; Hansen, F.D.; Senseny, P.E. Stress magnitudes in natural rock salt. J. Geophys. Res. 1982, 87, 9289–9300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Li, Y.; Feng, C.; Shi, X.; Qu, D. Advances in researches of the mechanical behaviors of bedded salt rocks. Adv. Mech. 2008, 38, 484–494. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, G. Experimental investigations of the creep–damage–rupture behaviour of rock salt. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2014, 66, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennis-King, J.; Michael, K.; Strand, J.; Sander, R.; Green, C. Underground Storage of Hydrogen: Mapping Out Options for Australia; Future Fuel CRC: Windang, Australia, 2021. [Google Scholar]


| Average Volume (×105 m3) | Standard Deviation (×105 m3) | Total Volume (×105 m3) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Huron | 1.96 | 1.38 | 5.88 |
| Lambton | 0.76 | 1.73 | 69.38 |
| Essex | 1.38 | 2.20 | 99.02 |
| Overall | 1.05 | 1.97 | 174.27 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hui, S.; Yin, S.; Pang, X.; Chen, Z.; Shi, K. Potential of Salt Caverns for Hydrogen Storage in Southern Ontario, Canada. Mining 2023, 3, 399-408. https://doi.org/10.3390/mining3030024
Hui S, Yin S, Pang X, Chen Z, Shi K. Potential of Salt Caverns for Hydrogen Storage in Southern Ontario, Canada. Mining. 2023; 3(3):399-408. https://doi.org/10.3390/mining3030024
Chicago/Turabian StyleHui, Shasha, Shunde Yin, Xiongqi Pang, Zhuoheng Chen, and Kanyuan Shi. 2023. "Potential of Salt Caverns for Hydrogen Storage in Southern Ontario, Canada" Mining 3, no. 3: 399-408. https://doi.org/10.3390/mining3030024
APA StyleHui, S., Yin, S., Pang, X., Chen, Z., & Shi, K. (2023). Potential of Salt Caverns for Hydrogen Storage in Southern Ontario, Canada. Mining, 3(3), 399-408. https://doi.org/10.3390/mining3030024







