AI Technology Adoption in Corporate IT Network Operations Based on the TOE Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review and Hypothesis Development
2.1. AI Technology Adoption and the TOE Model
2.2. Corporate Network Operation Productivity and Network Service Stability
2.3. Productivity, Stability, and AI Technology Adoption
3. Methods
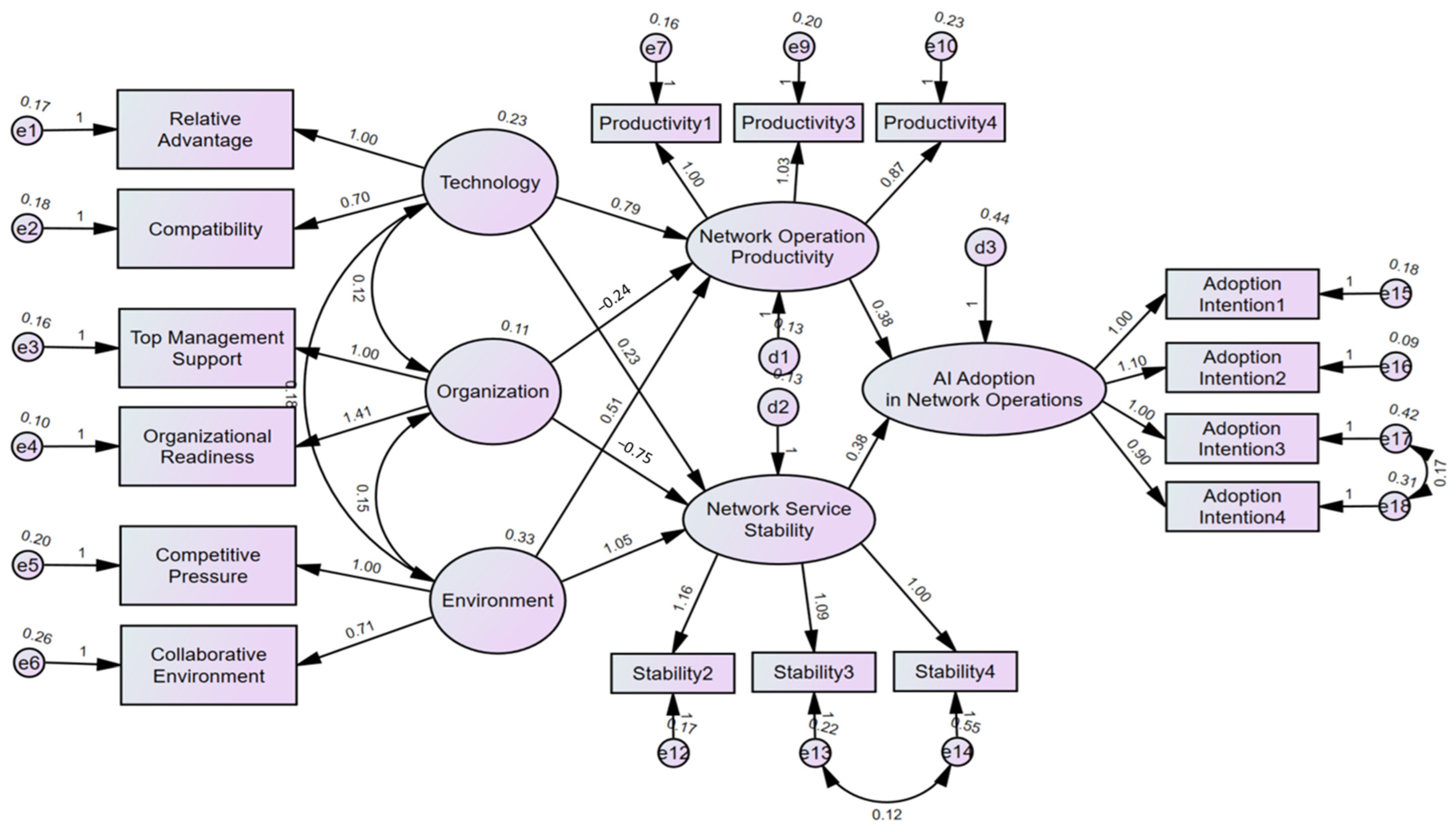
3.1. Research Model
3.2. Measurement Variable and Data Collection
3.3. Demographic Information About the Data
4. Results
4.1. Reliability and Validity Analysis Results
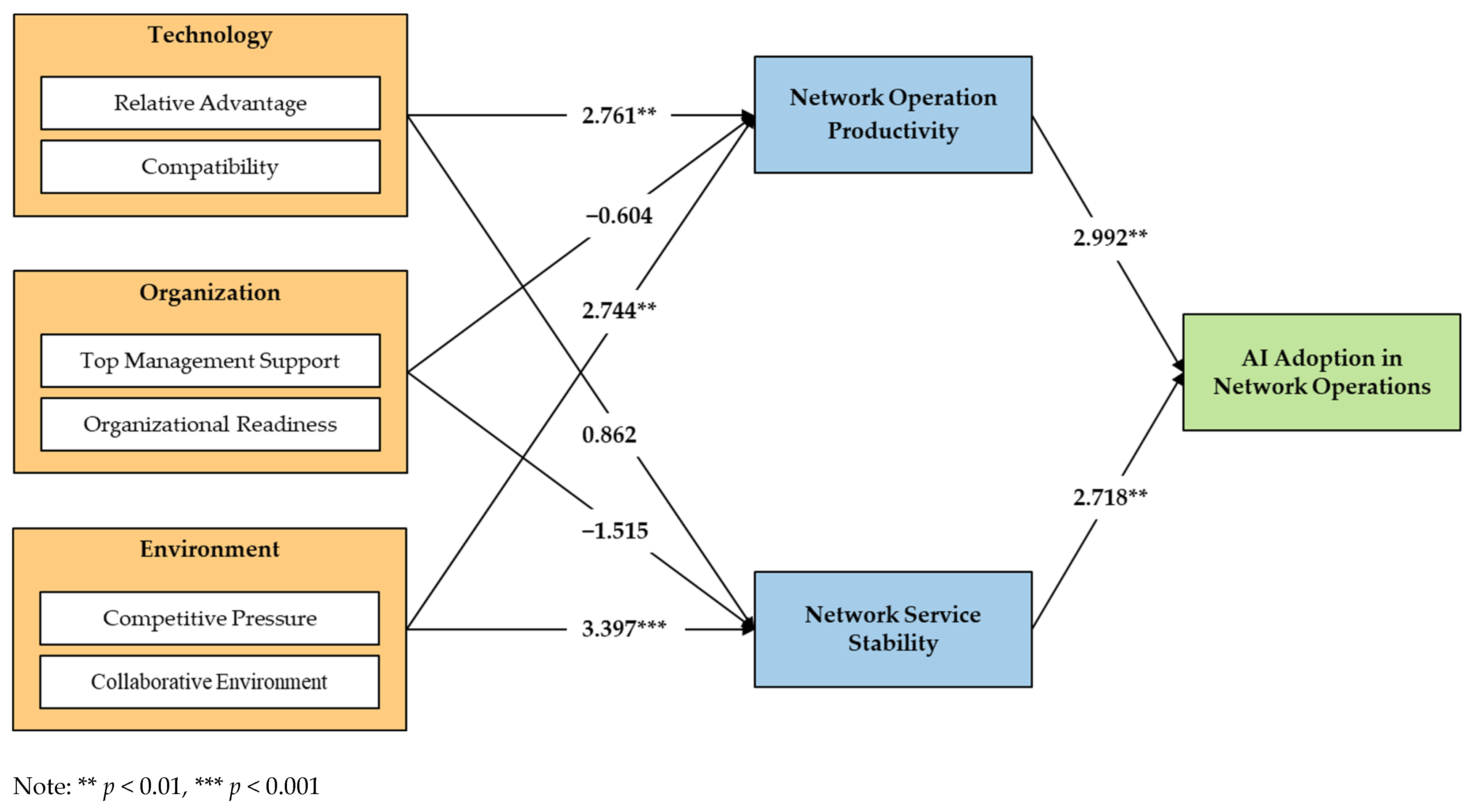
4.2. Analysis Results of the Structural Model
4.3. Mediated Effect
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
6.1. Research Implications
6.2. Research Limitations and Future Plans
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Questionnaire Sample
References
- Kibria, M.G.; Nguyen, K.; Villardi, G.P.; Zhao, O.; Ishizu, K.; Kojima, F. Big data analytics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence in next-generation wireless networks. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 32328–32338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeney, J.; van der Meer, S.; Hogan, G. A Recommender-System for Telecommunications Network Management Actions. In Proceedings of the 2013 IFIP/IEEE International Symposium on Integrated Network Management 2013, Ghent, Belgium, 27–31 May 2013; pp. 760–763. [Google Scholar]
- Oi, A.; Sato, R.; Suto, Y.; Sakata, K.; Nakajima, M.; Furukawa, T. A study on automation of network maintenance in telecom carriers for zero-touch operations. In Proceedings of the 2020 21st Asia-Pacific Network Operations and Management Symposium (APNOMS), Daegu, Republic of Korea, 22–25 September 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghili, R.; Li, H.; Khomh, F. Studying the characteristics of AIOps projects on GitHub. Empir. Softw. Eng. 2023, 28, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitsios, F.; Kamariotou, M. Artificial intelligence and business strategy towards digital transformation: A research agenda. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoef, P.C.; Broekhuizen, T.; Bart, Y.; Bhattacharya, A.; Dong, J.Q.; Fabian, N.; Haenlein, M. Digital transformation: A multidisciplinary reflection and research agenda. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 122, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, P.; Rich, C. Market Guide for AIOps Platforms. Gartner, 12 November 2018. Available online: https://www.gartner.com/en/documents/4015085 (accessed on 12 July 2023).
- Yuan, D.; Luo, Y.; Zhuang, X.; Rodrigues, G.R.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jain, P.U.; Stumm, M. Simple testing can prevent most critical failures: An analysis of production failures in distributed da-ta-intensive systems. In Proceedings of the 11th USENIX Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation (OSDI 14), Broomfield, CO, USA, 6–8 October 2014; pp. 249–265. [Google Scholar]
- Agostini, L.; Filippini, R. Organizational and managerial challenges in the path toward Industry 4.0. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2019, 22, 406–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brock, J.K.; Von Wangenheim, F. Demystifying AI: What digital transformation leaders can teach you about realistic artificial intelligence. Calif. Manag. Rev. 2019, 61, 110–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ransbotham, S.; Kiron, S.D.; Gerbert, P.; Reeves, M. Reshaping business with artificial intelligence: Closing the gap between ambition and action. MIT Sloan Manag. Rev. 2017, 59. Available online: https://sloanreview.mit.edu/projects/reshaping-business-with-artificial-intelligence/ (accessed on 12 May 2024).
- Gartner, Aiops (Artificial Intelligence for It Operations). Available online: https://www.gartner.com/en/information-technology/glossary/aiops-artificial-intelligence-operations (accessed on 15 October 2023).
- Duan, Q.; Wang, S.; Ansari, N. Convergence of networking and cloud/edge computing: Status, challenges, and opportunities. IEEE Netw. 2020, 34, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, Y.R.; Raj, Y.; Ben-Menahem, S.M.; Krogh, G.V. Organizational decision-making structures in the age of artificial intelligence. Calif. Manag. Rev. 2019, 61, 66–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.Y.; Ko, N.; Yang, S.; Kim, S.M. Trends in network and AI technologies. Electron. Telecommun. Trends 2020, 35, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, P.D.; Hage, J.; Hull, F.M. Organizational and technological predictors of change in automaticity. Acad. Manag. J. 1988, 31, 512–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, E.M. Diffusion of Innovations; Simon and Schuster: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, J. The technology–organization–environment framework. Inf. Syst. Theory 2012, 1, 231–245. [Google Scholar]
- Phuoc, N.V. The critical factors impacting artificial intelligence applications adoption in Vietnam: A structural equation modeling analysis. Economies 2022, 10, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DePietro, R.; Wiarda, E.; Fleischer, M. The context for change: Organization, technology and environment. Process. Technol. Innov. 1990, 199, 151–175. [Google Scholar]
- Tornatzky, L.G.; Fleischer, M.; Chakrabarti, A.K. Processes of Technological Innovation; Lexington Books: Lexington, KY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Kankanhalli, A. Innovation in Government Services: The Case of Open Data. In Proceedings of the Grand Successes and Failures in IT. Public and Private Sectors: IFIP WG 8.6 International Working Conference on Transfer and Diffusion of IT, Bangalore, India, 27–29 June 2013; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 644–651. [Google Scholar]
- El Khatib, M.M.; Al-Nakeeb, A.; Ahmed, G. Integration of cloud computing with artificial intelligence and its impact on telecom sector: A case study. iBusiness 2019, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Plessis, G.; Smuts, H. The Diffusion of Innovation Experience: Leveraging the Human Factor to Improve Technological Adoption Within an Organisation. In Proceedings of theResponsible AI and Analytics for an Ethical and Inclusive Digitized Society: 20th IFIP WG 6.11 Conference on e-Business, e-Services and e-Society, Galway, Ireland, 1–3 September 2021; pp. 318–329. [Google Scholar]
- Solaimani, S.; Swaak, L. Critical success factors in a multi-stage adoption of artificial intelligence: A necessary condition analysis. J. Eng. Technol. Manag. 2023, 69, 101760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Hou, B.; Yu, W.; Lu, X.; Yang, C. Applications of artificial intelligence in intelligent manufacturing: A review. Front. Inf. Technol. Electron. Eng. 2017, 18, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hradecky, D.; Kennell, J.; Cai, W.; Davidson, R. Organizational readiness to adopt artificial intelligence in the exhibition sector in Western Europe. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2022, 65, 102497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tushman, M.; Nadler, D. Organizing for innovation. Calif. Manag. Rev. 1986, 28, 74–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbanna, A. Top management support in multiple-project environments: An in-practice view. Eur. J. Inf. Syst. 2013, 22, 278–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobakhloo, M.; Ching, N.T. Adoption of digital technologies of smart manufacturing in SMEs. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2019, 16, 100107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.T.; Kim, B.Y. Decision-making model for reinforcing digital transformation strategies based on artificial intelligence technology. Information 2022, 13, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.J.; Jang, W.Y. Determinants of the adoption of enterprise resource planning within the technology-organization-environment framework: Taiwan’s communications industry. J. Comput. Inf. Syst. 2008, 48, 94–102. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.F. Understanding the determinants of electronic supply chain management system adoption: Using the technology–organization–environment framework. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2014, 86, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, S.; Heo, S.; Han, S.; Shin, Y.; Roh, Y. Acceptance model of artificial intelligence (AI)-based technologies in construction firms: Applying the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) in combination with the Technology–Organisation–Environment (TOE) framework. Buildings 2022, 12, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, T.; Martins, M.F. A Comparison of Web Site Adoption in Small and Large Portuguese Firms. Int. Conf. E-Bus. 2008, 2, 370–377. [Google Scholar]
- Assael, H. Consumer Behavior and Marketing Action; Kent Pub. Co.: Boston, MA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Johnsen, T.E. Supplier involvement in new product development and innovation: Taking stock and looking to the future. J. Purch. Supply Manag. 2009, 15, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laut, P.; Dumbach, P.; Eskofier, B.M. Integration of artificial intelligence in the organizational adoption: A configurational perspective. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Systems (ICIS) 2021 in University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ, USA, 12 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bharadiya, J.P. Machine learning and AI in business intelligence: Trends and opportunities. Int. J. Comput. 2003, 48, 123–134. [Google Scholar]
- Mughal, A.A. Artificial intelligence in information security: Exploring the advantages, challenges, and future directions. J. Artif. Intell. Mach. Learn. Manag. 2018, 2, 22–34. [Google Scholar]
- Banica, L.; Polychronidou, P.; Stefan, C.; Hagiu, A. Empowering IT Operations Through Artificial Intelligence–A New Business Perspective; KnE Social Sciences: Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 2020; pp. 412–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Skeete, J.P.; Owusu, G. Understanding the implications of artificial intelligence on field service operations: A case study of BT. Prod. Plan. Control 2022, 33, 1591–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastane, D.O. The impact of technology adoption on organizational productivity. J. Ind. Distrib. Bus. 2020, 11, 7–18. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Kang, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Xu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, L.; Sun, J.; Xu, Z.; et al. Towards Intelligent Incident Management: Why We Need It and How We Make It. In Proceedings of the 28th ACM Joint Meeting on European Software Engineering Conference and Symposium on the Foundations of Software Engineering, Virtual, 8–13 November 2020; pp. 1487–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, A.; Hashmi, A. AIOps: Predictive analytics & machine learning in operations. Cogn. Comput. Recipes 2019, 359–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijal, L.; Colomo-Palacios, R.; Sánchez-Gordón, M. Aiops: A multivocal literature review. In Artificial Intelligence for Cloud and Edge Computing; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 31–50. [Google Scholar]
- Mughal, A.A. The art of cybersecurity: Defense in depth strategy for robust protection. Int. J. Intell. Autom. Comput. 2018, 1, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Belgaum, M.R.; Alansari, Z.; Musa, S.; Alam, M.M.; Mazliham, M.S. Impact of artificial intelligence-enabled software-defined networks in infrastructure and operations: Trends and challenges. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zohuri, B.; Rahmani, F.M. Artificial intelligence driven resiliency with machine learning and deep learning components. Int. J. Nanotechnol. Nanomed. 2019, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosch, W.D.; Maher, A.; Sasscer, B. The intelligent network. In The Intelligent Network: A Joint Study by Bell Atlantic, IBM and Siemens; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1989; pp. 5–21. [Google Scholar]
- Yeruva, A.R. Providing a personalized healthcare service to the patients using AIOPs monitoring. Eduvest-J. Univers. Stud. 2023, 3, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemm, A.; Zhani, M.F.; Boutaba, R. Network management 2030: Operations and control of network 2030 services. J. Netw. Syst. Manag. 2020, 28, 721–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Yuan, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Yang, F. Artificial intelligence powered mobile networks: From cognition to decision. IEEE Netw. 2022, 36, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronado, E.; Behravesh, R.; Subramanya, T.; Fernàndez, A.; Siddiqui, M.S.; Costa-Pérez, X.; Riggio, R. Zero touch management: A survey of network automation solutions for 5G and 6G networks. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2022, 24, 2535–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.A.; Mehmood, A.; Ravera, J.J.D.; Muhammad, A.; Abbas, K.; Song, W.C. Intent-based orchestration of network slices and resource assurance using machine learning. In Proceedings of the NOMS 2020-2020 IEEE/IFIP Network Operations and Management Symposium, Budapest, Hungary, 20–24 April 2020; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Velasco, L.; Castro, A.; King, D.; Gerstel, O.; Casellas, R.; Lopez, V. In-operation network planning. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2014, 52, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, J.; Ge, Z. Artificial intelligence for network operations. In Artificial Intelligence for Autonomous Networks; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 189–230. [Google Scholar]
- Zeb, S.; Rathore, M.A.; Hassan, S.A.; Raza, S.; Dev, K.; Fortino, G. Toward AI-enabled nextG networks with edge intelligence-assisted microservice orchestration. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2023, 30, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hashimi, M.; Mohammed Jameel, S.; Husham Almukhtar, F.; Abdul Zahra, M.M.; Adnan Jaleel, R. Optimised Internet of Thing framework based hybrid meta-heuristic algorithms for E-healthcare monitoring. IET Netw. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andenmatten, M. AIOps–artificial intelligence for IT operations: Todays challenges of new technologies and new methodologies in IT operations. HMD Prax. Der Wirtsch. 2019, 56, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Y.; Lin, Q.; Huang, P. Aiops: Real-world challenges and research innovations. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/ACM 41st International Conference on Software Engineering: Companion Proceedings, Montreal, QC, Canada, 25–31 May 2019; pp. 4–5. [Google Scholar]
- Altamimi, S.; Altamimi, B.; Shirmohammadi, S.; Cote, D. Automating Network Operation Centers with Superhuman Performance, Authorea Preprints. 2023. Available online: https://www.techrxiv.org/doi/full/10.36227/techrxiv.15176175.v1 (accessed on 12 April 2024).
- Duan, Y.; Edwards, J.S.; Dwivedi, Y.K. Artificial intelligence for decision making in the era of Big Data–evolution, challenges and research agenda. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2019, 48, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, J.; Dwivedi, Y.K. Role of cognitive absorption in building user trust and experience. Psychol. Mark. 2021, 38, 643–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeruva, A.R. Monitoring data center site infrastructure using AIOPS architecture. J. Univers. Stud. 2023, 3, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, S.A.; Côté, D.; Shirmohammadi, S. A machine-learning-based action recommender for network operation centers. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2021, 18, 2702–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raisch, S.; Krakowski, S. Artificial intelligence and management: The automation augmentation paradox. Acad. Manag. Rev. 2021, 46, 192–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helo, P.; Hao, Y. Artificial intelligence in operations management and supply chain management: An exploratory case study. Prod. Plan. Control 2022, 33, 1573–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, L.; Chen, Y. Explore success factors that impact artificial intelligence adoption on telecom industry in China. J. Manag. Anal. 2021, 8, 36–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hleewa, A.; Omar, S.; Mubarak, M.A. Success factors of using artificial intelligence. In Technological Sustainability and Business Competitive Advantage; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 169–184. [Google Scholar]
- Duman, I.; Eliiyi, U. Performance metrics and monitoring tools for sustainable network management. Bilişim Teknol. Derg. 2021, 14, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mithas, S.; Chen, Z.L.; Saldanha, T.J.V.; Silveira, A.D.O. How will artificial intelligence and Industry 4.0 emerging technologies transform operations management? Prod. Oper. Manag. 2022, 31, 4475–4487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spring, M.; Faulconbridge, J.; Sarwar, A. How information technology automates and augments processes: Insights from artificial intelligence based systems in professional service operations. J. Oper. Manag. 2022, 68, 592–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, J.; Chattopadhyay, M. Determinants and barriers of artificial intelligence adoption: A literature review. In Proceedings of the IFIP WG 8.6 International Conference on Transfer and Diffusion of IT, TDIT 2020, Tiruchirappalli, India, 11 December 2020; pp. 18–19. [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg, L.; Nilsson, S. Factors Influencing Readiness of Adopting AI: A Qualitative Study of How the TOE Framework Applies to AI Adoption in Governmental Authorities. Master’s Thesis, School of Industrial Engineering and Management (ITM), Stockholm, Sweden, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Dhamija, P.; Bag, S. Role of artificial intelligence in operations environment: A review and bibliometric analysis. TQM J. 2020, 32, 869–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laut, L.T.; Sugiharti, R.R.; Panjawa, J.L. Does tourism sector matter in regional economic development. Geo J. Tour. Geosites 2021, 37, 832–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.S.; Chen, C.L. An integrated perspective of TOE framework and innovation diffusion in broadband mobile applications adoption by enterprises. Int. J. Manag. Econ. Soc. Sci. 2017, 6, 14–39. [Google Scholar]
- Desouza, K.C.; Dawson, G.S.; Chenok, D. Designing, developing, and deploying artificial intelligence systems: Lessons from and for the public sector. Bus. Horiz. 2020, 63, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teggi, P.; Malakreddy, B.; Teggi, P.P.; Harivinod, N. AIOPS prediction for server stability based on ARIMA Model. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2021, 10, 128–134. [Google Scholar]
- Grover, P.; Kar, A.K.; Dwivedi, Y.K. Understanding artificial intelligence adoption in operations management: Insights from the review of academic literature and social media discussions. Ann. Oper. Res. 2022, 308, 177–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamath, R.R.; Liker, J.K. A second look at Japanese product development. Harv. Bus. Rev. 1994, 72, 154–165. [Google Scholar]
- Lippert, S.K.; Govindarajulu, C. Technological, organizational, and environmental antecedents to web services adoption. Commun. IIMA 2006, 6, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prashanth, S. Cisco Digital Network Readiness Model, Cisco. 2016. Available online: https://www.cisco.com/c/dam/en/us/solutions/collateral/enterprise-networks/digital-network-architecture/dna-readiness-model-overview.pdf (accessed on 28 May 2024).
- Davenport, T.H.; Ronanki, R. Artificial intelligence for the real world. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2018, 96, 108–116. [Google Scholar]

| Factors | Measurement Items | References | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technology | Relative Advantage (REA) |
| [54,67,68,69,70,71] |
| Compatibility (COM) |
| [56,69,70,71,72,73] | |
| Organization | Top Management Support (TMS) |
| [25,69,74,75,76] |
| Organizational Readiness (ORR) |
| [27,71,72,73,75,77] | |
| Environment | Competitive Pressure (COP) |
| [45,69,70,71,78] |
| Collaborative Environment (COE) |
| [65,67,69,75,79] | |
| Network Operation Productivity (NOP) |
| [39,41,43,44,45] | |
| Network Service Stability (NSS) |
| [53,54,55,56,80] | |
| AI Adoption in Network Operations (ANO) |
| [64,65,67,68,81] | |
| Classification | Frequency (n) | Percentage (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Male | 142 | 88.8 |
| Female | 18 | 11.3 | |
| Age | Less than 30 | 3 | 1.9 |
| 30–less than 40 | 34 | 21.3 | |
| 40–less than 50 | 70 | 43.8 | |
| 50 or older | 53 | 33.1 | |
| Academic background | College Degree | 4 | 2.5 |
| Bachelor’s Degree | 92 | 57.5 | |
| Master’s degree (and above) | 64 | 40.0 | |
| Industrial Area | High Technology, Media, and Communications | 106 | 66.3 |
| Manufacturing and Distribution | 18 | 11.3 | |
| Finance and Healthcare | 23 | 14.4 | |
| Government and Public Sector | 8 | 5.0 | |
| Other | 5 | 3.1 | |
| Job Area | Management and Strategy | 24 | 15.0 |
| Finance, Procurement, and Human Resources | 3 | 1.9 | |
| Information Technology (IT) | 108 | 67.5 | |
| Sales and Marketing | 23 | 14.4 | |
| Other | 2 | 1.3 | |
| Work Experience | Less than 5 years | 8 | 5.0 |
| 5–less than 10 years | 20 | 12.5 | |
| 10–less than 15 years | 23 | 14.4 | |
| 15–less than 20 years | 35 | 21.9 | |
| More than 20 years | 74 | 46.3 | |
| Professional Area | Demander | 86 | 53.8 |
| Provider | 74 | 46.3 | |
| Variables | Measurement Item | Standard Loading | SE | t-Value | p-Value | CR | AVE | Cronbach α |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technology | REA | 0.783 | 0.844 | 0.734 | 0.626 | |||
| COM | 0.587 | 0.100 | 6.445 | *** | ||||
| Organization | TMS | 0.635 | 0.896 | 0.814 | 0.693 | |||
| ORR | 0.837 | 0.209 | 6.874 | *** | ||||
| Environment | COP | 0.786 | 0.800 | 0.671 | 0.637 | |||
| COE | 0.598 | 0.088 | 7.759 | *** | ||||
| Productivity | NOP1 | 0.852 | 0.912 | 0.777 | 0.859 | |||
| NOP3 | 0.838 | 0.086 | 12.050 | *** | ||||
| NOP4 | 0.768 | 0.081 | 10.804 | *** | ||||
| Stability | NSS2 | 0.863 | 0.858 | 0.671 | 0.843 | |||
| NSS3 | 0.832 | 0.098 | 9.837 | *** | ||||
| NSS4 | 0.654 | 0.117 | 7.576 | *** | ||||
| AI Adoption | ANO1 | 0.877 | 0.920 | 0.743 | 0.919 | |||
| ANO2 | 0.948 | 0.065 | 17.083 | *** | ||||
| ANO3 | 0.775 | 0.082 | 12.255 | *** | ||||
| ANO4 | 0.788 | 0.072 | 12.611 | *** |
| Factors | AVE | Technology | Organization | Environment | Productivity | Stability | AI Adoption |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technology | 0.734 | 0.857 | |||||
| Organization | 0.814 | 0.742 | 0.902 | ||||
| Environment | 0.671 | 0.654 | 0.784 | 0.819 | |||
| Productivity | 0.777 | 0.766 | 0.639 | 0.738 | 0.881 | ||
| Stability | 0.671 | 0.541 | 0.477 | 0.783 | 0.577 | 0.819 | |
| AI Adoption | 0.743 | 0.542 | 0.486 | 0.791 | 0.442 | 0.429 | 0.862 |
| Hypothesis (Path) | Standardized Regression Weights | t-Value | Hypothesis Adoption | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | Technology → Productivity | 0.578 | 2.761 ** | Adopted |
| H2 | Organization → Productivity | −0.120 | −0.604 | Rejected |
| H3 | Environment → Productivity | 0.445 | 2.744 ** | Adopted |
| H4 | Technology → Stability | 0.175 | 0.862 | Rejected |
| H5 | Organization → Stability | −0.403 | −1.515 | Rejected |
| H6 | Environment → Stability | 0.983 | 3.397 *** | Adopted |
| H7 | Productivity → AI Adoption | 0.313 | 2.992 ** | Adopted |
| H8 | Stability → AI Adoption | 0.297 | 2.718 ** | Adopted |
| Dependent Variable | Explanatory Variable | Direct Effect | Indirect Effect | Total Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AI Adoption | Productivity | 0.313 ** | 0.313 | |
| Stability | 0.297 ** | 0.297 | ||
| Technology | 0.233 | 0.233 | ||
| Organization | −0.157 | −0.157 | ||
| Environment | 0.432 * | 0.432 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Min, S.; Kim, B. AI Technology Adoption in Corporate IT Network Operations Based on the TOE Model. Digital 2024, 4, 947-970. https://doi.org/10.3390/digital4040047
Min S, Kim B. AI Technology Adoption in Corporate IT Network Operations Based on the TOE Model. Digital. 2024; 4(4):947-970. https://doi.org/10.3390/digital4040047
Chicago/Turabian StyleMin, Seoungkwon, and Boyoung Kim. 2024. "AI Technology Adoption in Corporate IT Network Operations Based on the TOE Model" Digital 4, no. 4: 947-970. https://doi.org/10.3390/digital4040047
APA StyleMin, S., & Kim, B. (2024). AI Technology Adoption in Corporate IT Network Operations Based on the TOE Model. Digital, 4(4), 947-970. https://doi.org/10.3390/digital4040047






_김_(김).png)

