B- and T-/NK-Cell Lymphomas in the 2022 International Consensus Classification of Mature Lymphoid Neoplasms and Comparison with the WHO Fifth Edition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. ICC 2022: What Is New in B-Cell Neoplasms
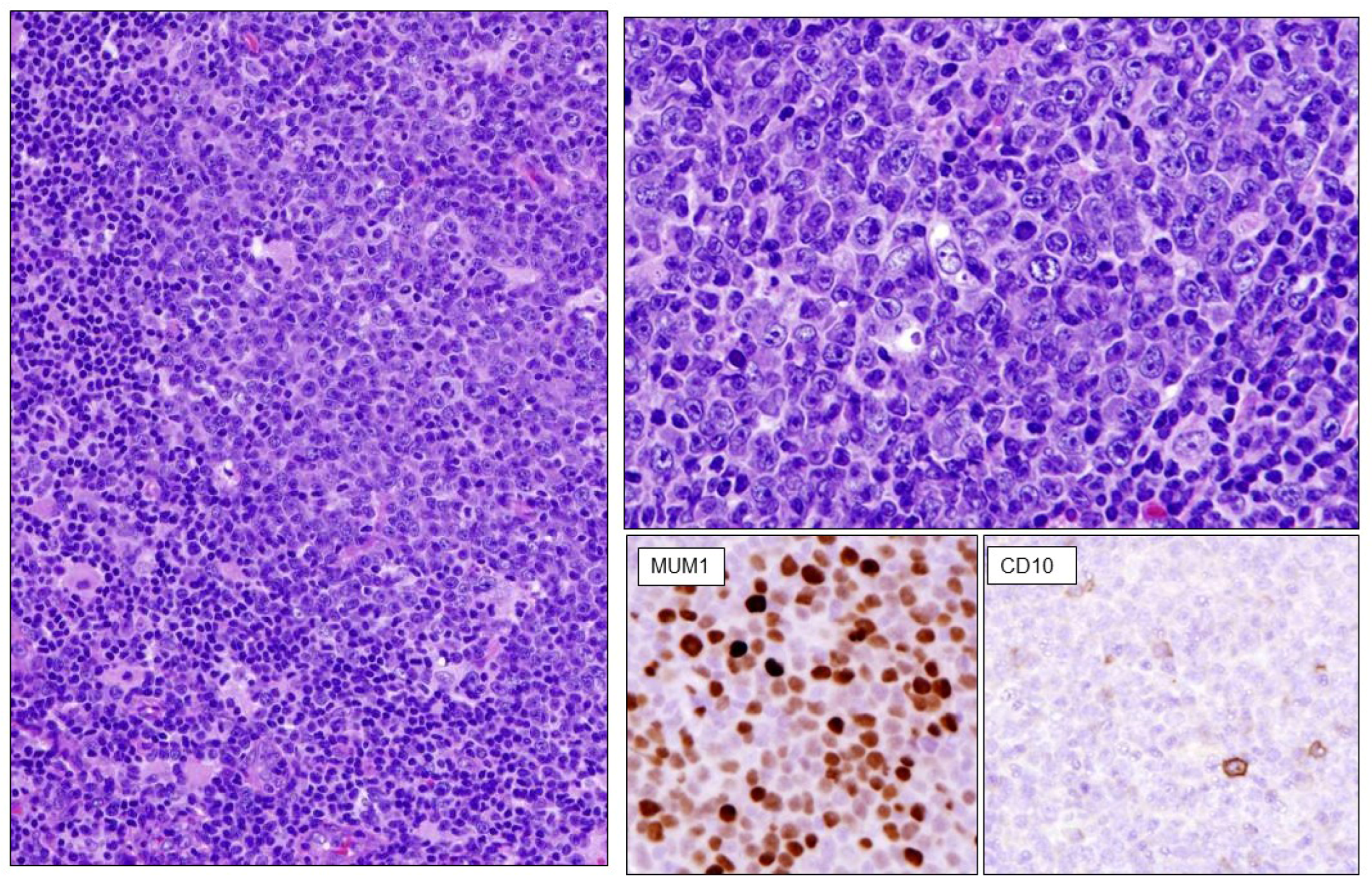
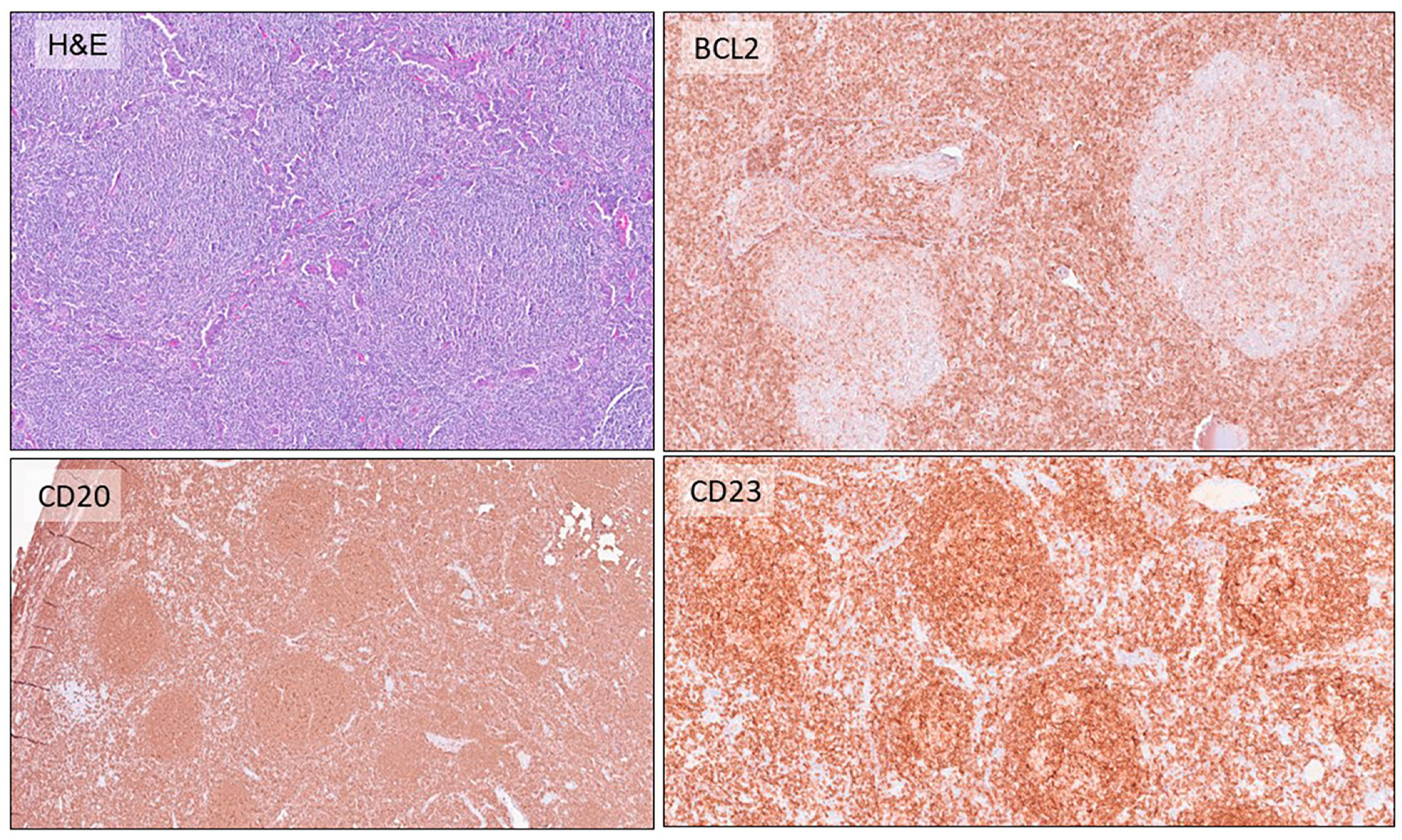
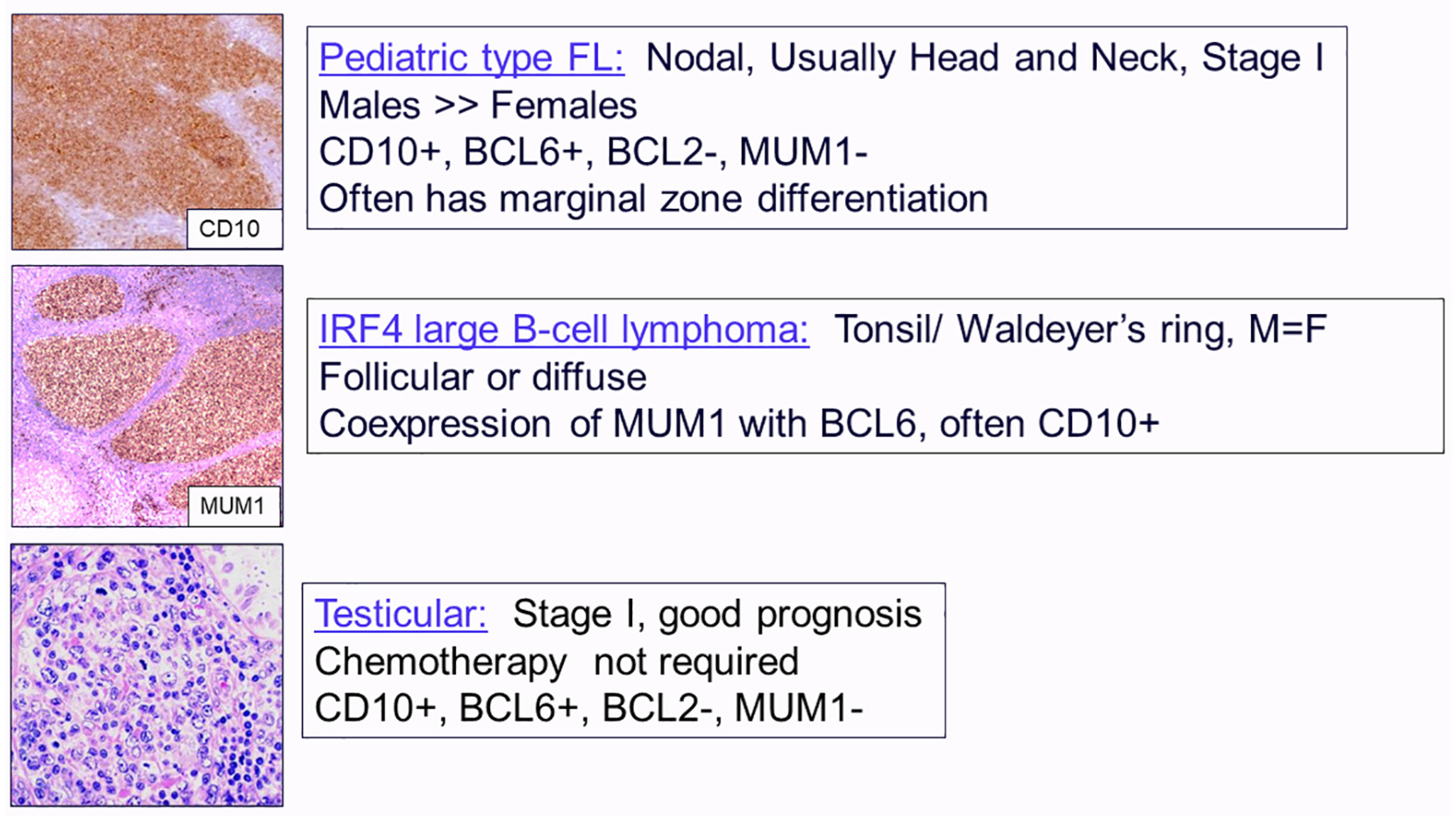
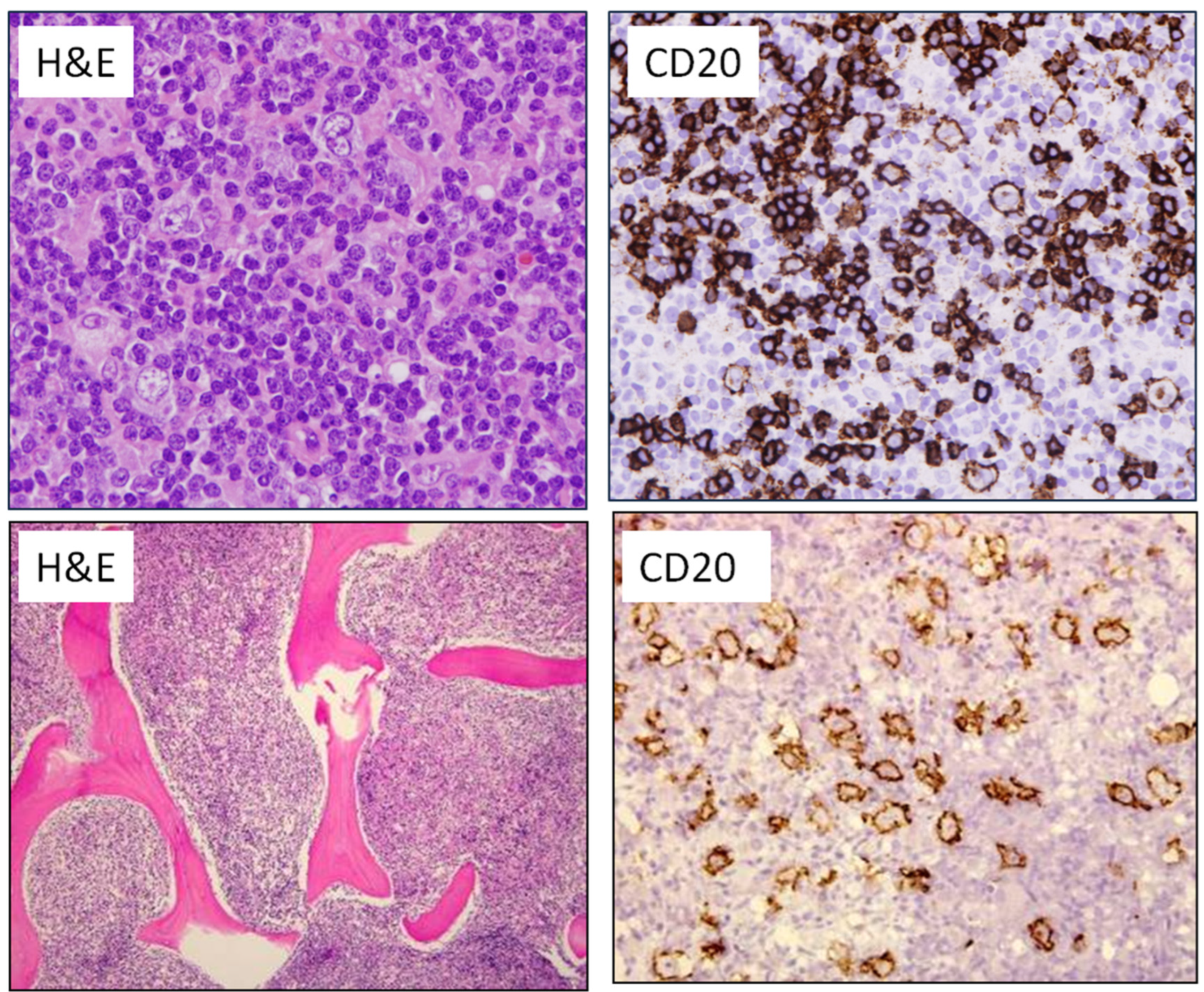
2.1. Follicular Lymphomas
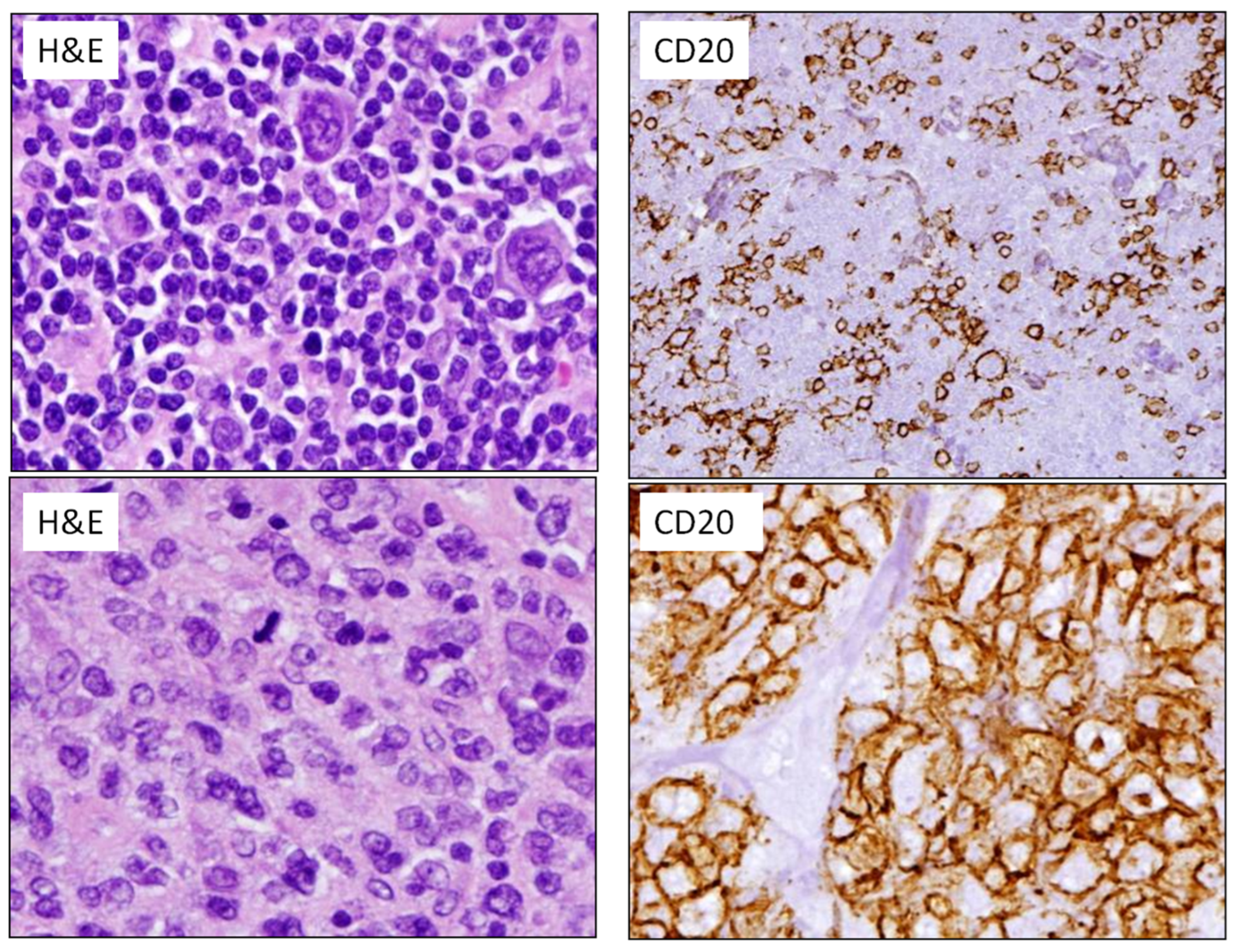
2.2. Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphomas
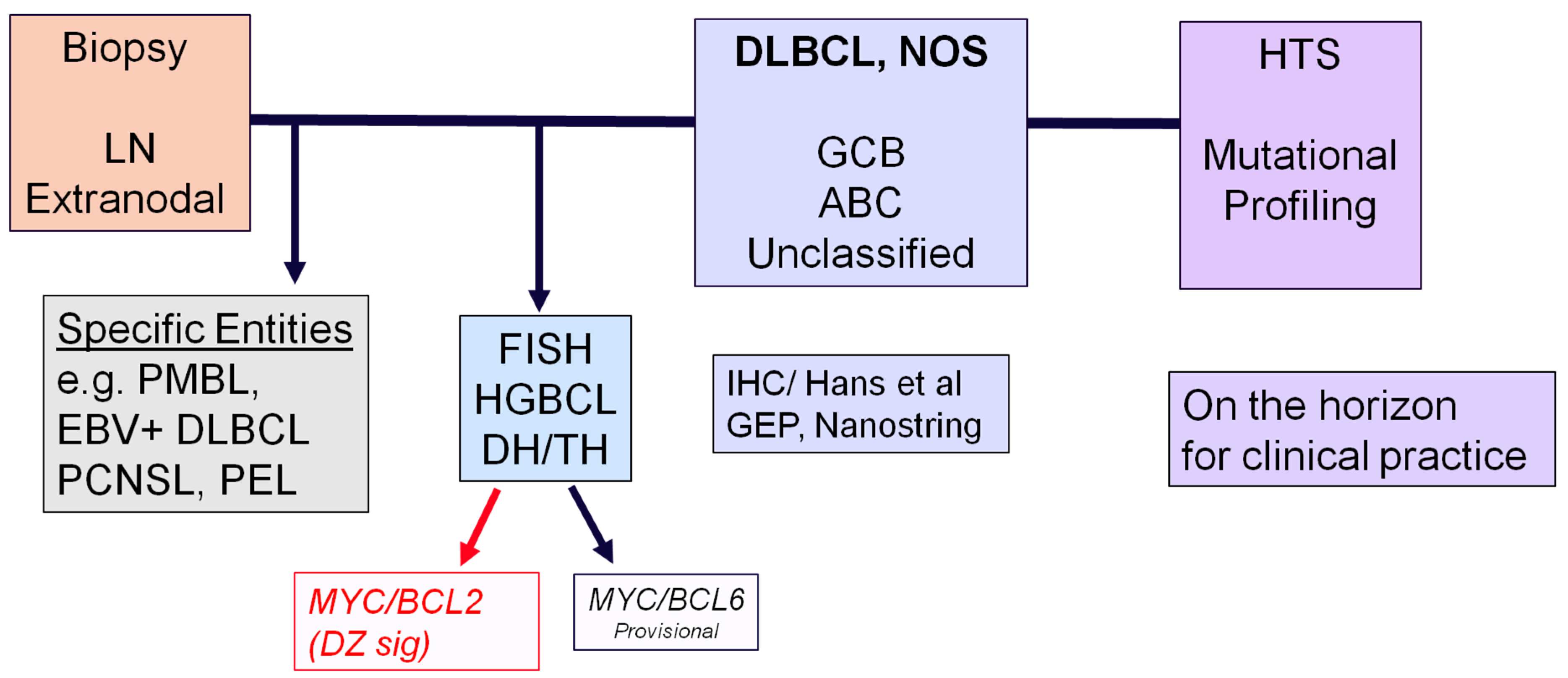
2.3. High-Grade B-Cell Neoplasms
3. Flow Chart for the Diagnosis of Aggressive B-Cell Lymphomas
4. ICC 2022 Proposal: Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
5. Gray-Zone Lymphoma
6. EBV-Positive Large B-Cell Lymphoma
7. HHV8- and EBV-Negative Primary Effusion-Based Lymphoma
8. Changes in the Classification in the T-/NK-Cell Neoplasms
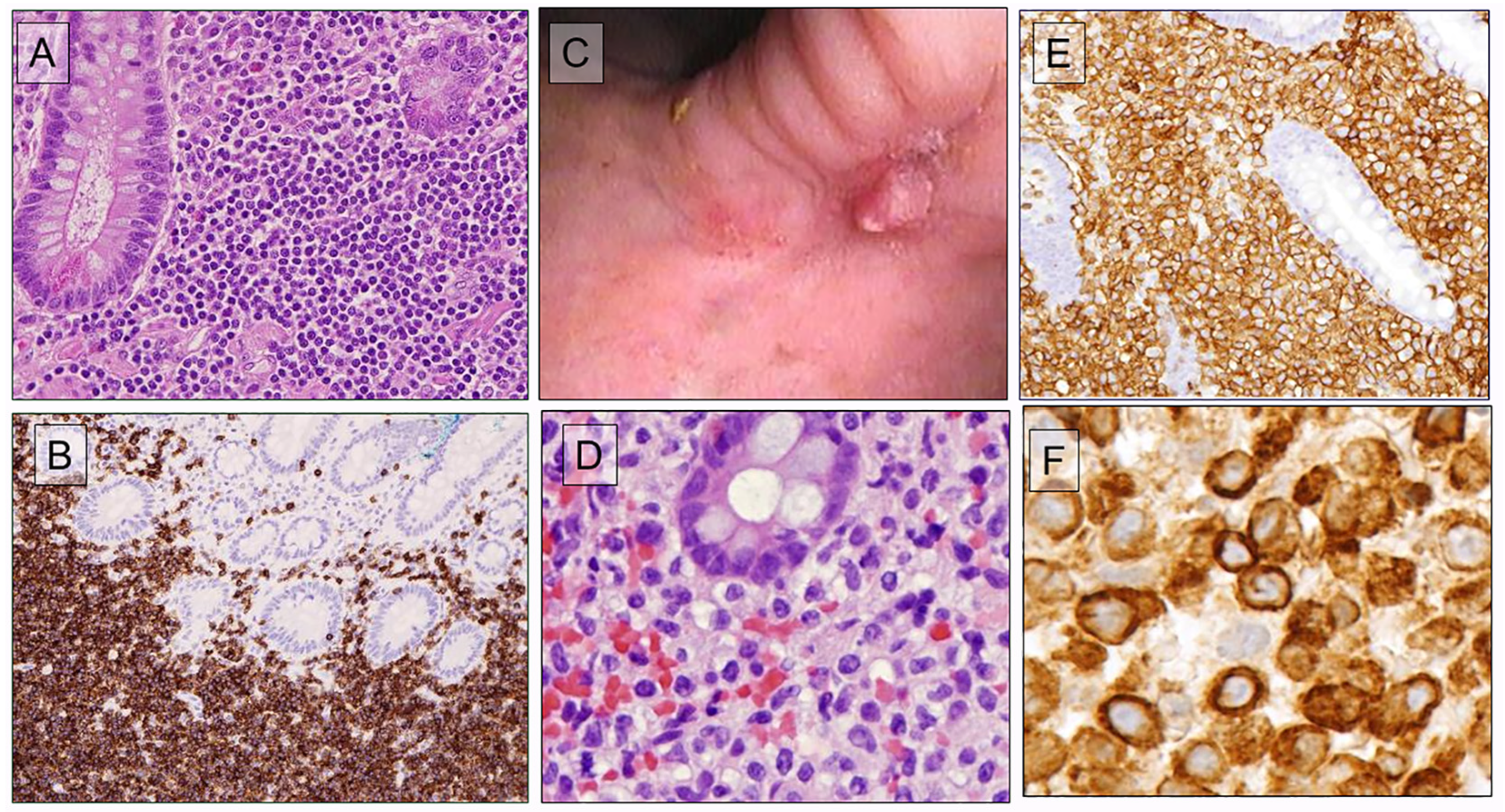
8.1. Indolent Gastrointestinal T-/NK-Cell Neoplasms
8.2. Type 2 Refractory Celiac Disease
8.3. Anaplastic Large-Cell Lymphoma ALK-Negative
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jaffe, E.S.; Harris, N.; Stein, H.; Vardiman, J.W. (Eds.) World Health Organization Classification of Tumours. In Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, 3rd ed.; IARC: Lyon, France, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Harris, N.L.; Jaffe, E.S.; Pileri, S.A.; Stein, H.; Thiele, J.; Vardiman, J.W. (Eds.) World Health Organization Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, 4th ed.; IARC: Lyon, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Harris, N.L.; Jaffe, E.S.; Pileri, S.A.; Stein, H.; Thiele, J.; Vardiman, J.W. (Eds.) WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues; Revised 4th ed.; IARC: Lyon, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Campo, E.; Jaffe, E.S.; Cook, J.R.; Quintanilla-Martinez, L.; Swerdlow, S.H.; Anderson, K.C.; Brousset, P.; Cerroni, L.; de Leval, L.; Dirnhofer, S.; et al. The International Consensus Classification of Mature Lymphoid Neoplasms: A Report from the Clinical Advisory Committee. Blood 2022, 140, 1229–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alaggio, R.; Amador, C.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; Attygalle, A.D.; Araujo, I.B.O.; Berti, E.; Bhagat, G.; Borges, A.M.; Boyer, D.; Calaminici, M.; et al. The 5th edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Lymphoid Neoplasms. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1720–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaffe, E.S.; Carbone, A. Evolution in the Definition of Follicular Lymphoma and Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: A Model for the Future of Personalized Medicine. Hemato 2022, 3, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhavsar, S.; Liu, Y.C.; Gibson, S.E.; Moore, E.M.; Swerdlow, S.H. Mutational Landscape of TdT+ Large B-cell Lymphomas Supports Their Distinction From B-lymphoblastic Neoplasms: A Multiparameter Study of a Rare and Aggressive Entity. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2022, 46, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nann, D.; Ramis-Zaldivar, J.E.; Müller, I.; Gonzalez-Farre, B.; Schmidt, J.; Egan, C.; Salmeron-Villalobos, J.; Clot, G.; Mattern, S.; Otto, F.; et al. Follicular lymphoma t(14;18)-negative is genetically a heterogeneous disease. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 5652–5665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Salaverria, I.; Pittaluga, S.; Jegalian, A.G.; Xi, L.; Siebert, R.; Raffeld, M.; Hewitt, S.M.; Jaffe, E.S. Follicular lymphomas in children and young adults: A comparison of the pediatric variant with usual follicular lymphoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2013, 37, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramis-Zaldivar, J.E.; Gonzalez-Farre, B.; Balague, O.; Celis, V.; Nadeu, F.; Salmeron-Villalobos, J.; Andres, M.; Martin-Guerrero, I.; Garrido-Pontnou, M.; Gaafar, A.; et al. Distinct molecular profile of IRF4-rearranged large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2020, 135, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmeron-Villalobos, J.; Egan, C.; Borgmann, V.; Müller, I.; Gonzalez-Farre, B.; Ramis-Zaldivar, J.E.; Nann, D.; Balagué, O.; Lopez-Guerra, M.; Colomer, D.; et al. PNMZL and PTFL: Morphological variants with a common molecular profile—A unifying hypothesis. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 4661–4674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saksena, A.; Jain, A.; Pack, S.D.; Kim, J.; Lee, I.; Tyagi, M.; Xi, L.; Pittaluga, S.; Raffeld, M.; Jaffe, E.S. Follicle Center Lymphoma (FCL) of the Lower Female Genital Tract (LFGT): A Novel Variant of Primary Cutaneous Follicle Center Lymphoma (PCFCL). Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2023, 47, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, A.A.; Eisen, M.B.; Davis, R.E.; Ma, C.; Lossos, I.S.; Rosenwald, A.; Boldrick, J.C.; Sabet, H.; Tran, T.; Yu, X.; et al. Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature 2000, 403, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapuy, B.; Stewart, C.; Dunford, A.J.; Kim, J.; Kamburov, A.; Redd, R.A.; Lawrence, M.S.; Roemer, M.G.M.; Li, A.J.; Ziepert, M.; et al. Molecular subtypes of diffuse large B cell lymphoma are associated with distinct pathogenic mechanisms and outcomes. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, R.; Wright, G.W.; Huang, D.W.; Johnson, C.A.; Phelan, J.D.; Wang, J.Q.; Roulland, S.; Kasbekar, M.; Young, R.M.; Shaffer, A.L.; et al. Genetics and Pathogenesis of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1396–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, G.W.; Huang, D.W.; Phelan, J.D.; Coulibaly, Z.A.; Roulland, S.; Young, R.M.; Wang, J.Q.; Schmitz, R.; Morin, R.D.; Tang, J.; et al. A Probabilistic Classification Tool for Genetic Subtypes of Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma with Therapeutic Implications. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 551–568.e514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ennishi, D.; Hsi, E.D.; Steidl, C.; Scott, D.W. Toward a New Molecular Taxonomy of Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 1267–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilton, L.K.; Tang, J.; Ben-Neriah, S.; Alcaide, M.; Jiang, A.; Grande, B.M.; Rushton, C.K.; Boyle, M.; Meissner, B.; Scott, D.W.; et al. The double-hit signature identifies double-hit diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with genetic events cryptic to FISH. Blood 2019, 134, 1528–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alduaij, W.; Collinge, B.; Ben-Neriah, S.; Jiang, A.; Hilton, L.K.; Boyle, M.; Meissner, B.; Chong, L.; Miyata-Takata, T.; Slack, G.W.; et al. Molecular determinants of clinical outcomes in a real-world diffuse large B-cell lymphoma population. Blood 2023, 141, 2493–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, H.; Kalmbach, S.; Wagener, R.; Staiger, A.M.; Huttl, K.; Mottok, A.; Bens, S.; Traverse-Glehen, A.; Fontaine, J.; Siebert, R.; et al. A Diagnostic Approach to the Identification of Burkitt-like Lymphoma with 11q Aberration in Aggressive B-Cell Lymphomas. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2021, 45, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, N.L.; Jaffe, E.S.; Stein, H.; Banks, P.M.; Chan, J.K.; Cleary, M.L.; Delsol, G.; De Wolf-Peeters, C.; Falini, B.; Gatter, K.C.; et al. A revised European-American classification of lymphoid neoplasms: A proposal from the International Lymphoma Study Group. Blood 1994, 84, 1361–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichenauer, D.A.; Hartmann, S. Nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma: Current management strategies and evolving approaches to individualize treatment. Expert. Rev. Hematol. 2023, 16, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, K.H.; Connors, J.M.; Lai, A.; Al-Mansour, M.; Sehn, L.H.; Villa, D.; Klasa, R.; Shenkier, T.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Skinnider, B.; et al. Advanced-stage nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma compared with classical Hodgkin lymphoma: A matched pair outcome analysis. Blood 2014, 123, 3567–3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Natkunam, Y.; Bair, E.; Tibshirani, R.; Warnke, R.A. Characterization of variant patterns of nodular lymphocyte predominant hodgkin lymphoma with immunohistologic and clinical correlation. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2003, 27, 1346–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, E.; Jaffe, E.S. Taking gray zone lymphomas out of the shadows. Blood 2021, 137, 1703–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkozy, C.; Hung, S.S.; Chavez, E.A.; Duns, G.; Takata, K.; Chong, L.C.; Aoki, T.; Jiang, A.; Miyata-Takata, T.; Telenius, A.; et al. Mutational landscape of gray zone lymphoma. Blood 2021, 137, 1765–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frontzek, F.; Staiger, A.M.; Wullenkord, R.; Grau, M.; Zapukhlyak, M.; Kurz, K.S.; Horn, H.; Erdmann, T.; Fend, F.; Richter, J.; et al. Molecular profiling of EBV associated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leukemia 2023, 37, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolae, A.; Pittaluga, S.; Abdullah, S.; Steinberg, S.M.; Pham, T.A.; Davies-Hill, T.; Xi, L.; Raffeld, M.; Jaffe, E.S. EBV-positive large B-cell lymphomas in young patients: A nodal lymphoma with evidence for a tolerogenic immune environment. Blood 2015, 126, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gisriel, S.D.; Yuan, J.; Braunberger, R.C.; Maracaja, D.L.V.; Chen, X.; Wu, X.; McCracken, J.; Chen, M.; Xie, Y.; Brown, L.E.; et al. Human herpesvirus 8-negative effusion-based large B-cell lymphoma: A distinct entity with unique clinicopathologic characteristics. Mod. Pathol. 2022, 35, 1411–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, J.; Wright, G.; Wang, C.; Rosenwald, A.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Weisenburger, D.D.; Greiner, T.C.; Smith, L.; Guo, S.; Wilcox, R.A.; et al. Gene expression signatures delineate biological and prognostic subgroups in peripheral T-cell lymphoma. Blood 2014, 123, 2915–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amador, C.; Bouska, A.; Wright, G.; Weisenburger, D.D.; Feldman, A.L.; Greiner, T.C.; Lone, W.; Heavican, T.; Smith, L.; Pileri, S.; et al. Gene Expression Signatures for the Accurate Diagnosis of Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma Entities in the Routine Clinical Practice. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 4261–4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, A.; Gloghini, A. Subclassifying peripheral T-cell lymphoma NOS. Blood 2019, 134, 2120–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, K.; Yokoyama, M.; Ishizawa, S.; Terui, Y.; Nomura, K.; Marutsuka, K.; Nunomura, M.; Fukushima, N.; Yagyuu, T.; Nakamine, H.; et al. Lymphomatoid gastropathy: A distinct clinicopathologic entity of self-limited pseudomalignant NK-cell proliferation. Blood 2010, 116, 5631–5637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoor, A.; Pittaluga, S.; Beck, P.L.; Wilson, W.H.; Ferry, J.A.; Jaffe, E.S. NK-cell enteropathy: A benign NK-cell lymphoproliferative disease mimicking intestinal lymphoma: Clinicopathologic features and follow-up in a unique case series. Blood 2011, 117, 1447–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montes-Moreno, S.; King, R.L.; Oschlies, I.; Ponzoni, M.; Goodlad, J.R.; Dotlic, S.; Traverse-Glehen, A.; Ott, G.; Ferry, J.A.; Calaminici, M. Update on lymphoproliferative disorders of the gastrointestinal tract: Disease spectrum from indolent lymphoproliferations to aggressive lymphomas. Virchows Arch. 2020, 476, 667–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, H.; Li, A.; Ouyang, B.; Da, Q.; Dong, L.; Liu, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Jin, X.; et al. Clinicopathological and molecular features of indolent natural killer-cell lymphoproliferative disorder of the gastrointestinal tract. Histopathology 2023, 82, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soderquist, C.R.; Lewis, S.K.; Gru, A.A.; Vlad, G.; Williams, E.S.; Hsiao, S.; Mansukhani, M.M.; Park, D.C.; Bacchi, C.E.; Alobeid, B.; et al. Immunophenotypic Spectrum and Genomic Landscape of Refractory Celiac Disease Type II. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2021, 45, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaffe, E.S. T-cell and NK-cell neoplasms of the gastrointestinal tract—Recurrent themes, but clinical and biological distinctions exist. Haematologica 2020, 105, 1760–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurent, C.; Nicolae, A.; Le Bras, F.; Haioun, C.; Fataccioli, V.; Amara, N.; Adélaïde, J.; Guille, A.; Schiano, J.M.; Tesson, B.; et al. Gene alterations in epigenetic modifiers and JAK-STAT signaling are frequent in breast implant-associated ALCL. Blood 2020, 135, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blombery, P.; Thompson, E.R.; Jones, K.; Arnau, G.M.; Lade, S.; Markham, J.F.; Li, J.; Deva, A.; Johnstone, R.W.; Khot, A.; et al. Whole exome sequencing reveals activating JAK1 and STAT3 mutations in breast implant-associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Haematologica 2016, 101, e387–e390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Follicular Lymphomas |
|---|
|
| Diffuse large B-cell lymphomas |
|
| High-Grade B-cell neoplasms |
|
| ICC Follicular lymphoma (Grade 1–2; 3A, 3B) In situ follicular neoplasia Duodenal type FL BCL2-R-negative, CD23-positive follicle center lymphoma (provisional) Primary cutaneous follicle center lymphoma Pediatric-type follicular lymphoma Testicular follicular lymphoma Large B-cell lymphoma with IRF4 rearrangement | WHO Classic follicular lymphoma (no grading) In situ follicular B-cell neoplasm Duodenal-type follicular lymphoma FL with unusual cytological features FL with predominantly diffuse growth pattern (dFL) Follicular large B-cell lymphoma Primary cutaneous follicle center lymphoma Pediatric-type follicular lymphoma |
|
|
| Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), not otherwise specified (NOS) Germinal center B-cell subtype Activated B-cell subtype Large B-cell lymphoma with 11q aberration Large B-cell lymphoma with IRF4 R (Nodular lymphocyte predominant B-cell lymphoma) T-cell/histiocyte-rich large B-cell lymphoma Primary DLBCL of the central nervous system Primary DLBCL of the testis Primary cutaneous DLBCL, leg type Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma Burkitt’s lymphoma High-grade B-cell lymphoma with MYC and BCL2 R High-grade B-cell lymphoma with MYC and BCL6 R High-grade B-cell lymphoma, NOS Primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma Mediastinal gray-zone lymphoma EBV-positive mucocutaneous ulcer EBV-positive DLBCL, NOS DLBCL associated with chronic inflammation Fibrin-associated DLBCL Lymphomatoid granulomatosis EBV-positive polymorphic B-cell lymphoproliferative disorder, NOS ALK-positive large B-cell lymphoma Plasmablastic lymphoma HHV8-associated lymphoproliferative disorder Multicentric Castleman’s disease HHV8-positive germinotropic lymphoproliferative disorder HHV8-positive DLBCL, NOS Primary effusion lymphoma HHV-8- and EBV-negative primary effusion-based lymphoma |
|
| |
| Proposal |
|
| High-Grade B-Cell Lymphomas with MYC and BCL2 Rearrangements |
|
| High-grade B-cell lymphomas with MYC and BCL6 rearrangements (provisional) |
|
| Nodal | Peripheral T-cell lymphoma, NOS Follicular helper T-cell lymphomas Anaplastic large-cell lymphoma, ALK-positive Anaplastic large-cell lymphoma, ALK-negative Primary nodal EBV-positive T-/NK-cell lymphoma |
| Extranodal | Extranodal NK-/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type Enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma Type II refractory celiac disease Monomorphic epitheliotropic intestinal T-cell lymphoma Indolent clonal T-cell lymphoproliferative disorder of the GI tract Indolent NK-cell lymphoproliferative disorder of the GI tract Breast-implant-associated anaplastic large-cell lymphoma |
| Leukemic/Systemic | T-cell prolymphocytic leukemia T-cell large granular lymphocytic leukemia Chronic lymphoproliferative disorder of NK-cells Aggressive NK-cell leukemia EBV-positive T-/NK-LPDs of childhood Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma Hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma |
| Cutaneous | Mycosis fungoides Sézary syndrome Primary cutaneous CD30-positive T-cell LPDs Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma Primary cutaneous gamma-delta T-cell lymphoma Primary cutaneous CD8-positive aggressive epidermotropic cytotoxic T-cell lymphoma Primary cutaneous acral CD8+ T-LPD Primary cutaneous CD4-positive small/medium T-LPD Hydroa vacciniforme-like LPD |
| Indolent clonal T-cell lymphoproliferative disorder of the gastrointestinal tract | Name changed (clonal) to emphasize importance of clonality in diagnosis. Considered a definite entity but is heterogeneous in phenotype and genotype (CD4 or CD8) (all αβ) May progress to more aggressive disease. |
| Indolent NK-cell lymphoproliferative disorder of the gastrointestinal tract (newly added) | The term replaces both NK-cell enteropathy and lymphomatoid gastropathy. Mutational studies provide evidence for the neoplastic origin. Recurrent mutations in JAK3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jaffe, E.S.; Carbone, A. B- and T-/NK-Cell Lymphomas in the 2022 International Consensus Classification of Mature Lymphoid Neoplasms and Comparison with the WHO Fifth Edition. Hemato 2024, 5, 157-170. https://doi.org/10.3390/hemato5020013
Jaffe ES, Carbone A. B- and T-/NK-Cell Lymphomas in the 2022 International Consensus Classification of Mature Lymphoid Neoplasms and Comparison with the WHO Fifth Edition. Hemato. 2024; 5(2):157-170. https://doi.org/10.3390/hemato5020013
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaffe, Elaine S., and Antonino Carbone. 2024. "B- and T-/NK-Cell Lymphomas in the 2022 International Consensus Classification of Mature Lymphoid Neoplasms and Comparison with the WHO Fifth Edition" Hemato 5, no. 2: 157-170. https://doi.org/10.3390/hemato5020013
APA StyleJaffe, E. S., & Carbone, A. (2024). B- and T-/NK-Cell Lymphomas in the 2022 International Consensus Classification of Mature Lymphoid Neoplasms and Comparison with the WHO Fifth Edition. Hemato, 5(2), 157-170. https://doi.org/10.3390/hemato5020013







