Abstract
Eosinophils are a type of granulocyte key to immune system modulation seen in a number of disease processes. Nearly every major organ system can be connected to peripheral eosinophilia through a number of different disease processes, ranging from benign conditions to malignancy. In this paper, we review both common and rare causes of peripheral eosinophilia, their symptoms, and a framework for the workup of peripheral eosinophilia of unknown etiology.
1. Introduction
Eosinophils are a type of white blood cell that play a role in immune system modulation. They are granulocytic, as characterized by the presence of granules (small structures containing enzymes and proteins) in their cytoplasm, which stain readily with eosin, a red dye (Figure 1). The major proteins found include major basic protein, eosinophil-derived neurotoxin, cationic protein, and eosinophil peroxidase. Eosinophils are involved in the body’s defense against certain types of pathogens, especially parasites, and their role in allergic reactions. These cells are particularly effective against parasites such as helminths, releasing substances that can damage the parasite’s outer membrane. Eosinophil levels are often measured as part of a complete blood count (CBC) during routine blood tests. Abnormalities in eosinophil counts can be indicative of various medical conditions, including allergies, parasitic infections, autoimmune diseases, and certain types of cancers [1,2].
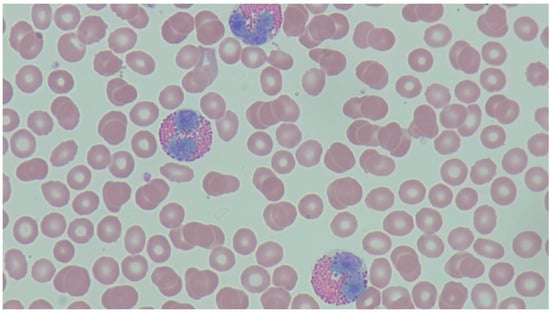
Figure 1.
Peripheral Eosinophilia—the peripheral blood smear demonstrates increased eosinophils characterized by a bilobed appearance with eosinophilic granules. There are adjacent red blood cells along with scattered platelets present. Courtesy of John Irlam, DO.
Eosinophils are produced in the bone marrow from the multipotent hematopoietic stem cell favoring the myeloid lineage. When specific transcription factors such as PU.1 are expressed at high levels, an increase in myeloid differentiation occurs, which is ultimately responsible for the commitment and differentiation of each subtype. Specifically, PU.1 is an antagonist to a protein zinc finger GATA-1, which is partially responsible for eosinophil specification. While there are multiple transcription factors and interleukins involved in the differentiation and specification of eosinophils, the most notable appear to be IL-3, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), and IL-5, which work synergistically in the development of these specialized granulocytes. Of these three, IL-5 is responsible for the induction and prolonged life of eosinophils and their terminal differentiation [1,2,3].
Eosinophils are found throughout the body and specifically where epithelial cells are more likely to be exposed to environmental stimuli, with a higher concentration being found in the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts. When released into the bloodstream, eosinophils have an estimated half-life ranging from 8 to 18 h [3]. Eosinophils migrate into tissues via cell adhesion molecules and cytokines prompting via expression of CCL11 (Figure 2) [3,4]. Once there, tissue eosinophils may survive from 2 to 5 days, surviving in vitro 14 days or longer with appropriate cytokine signaling [3].
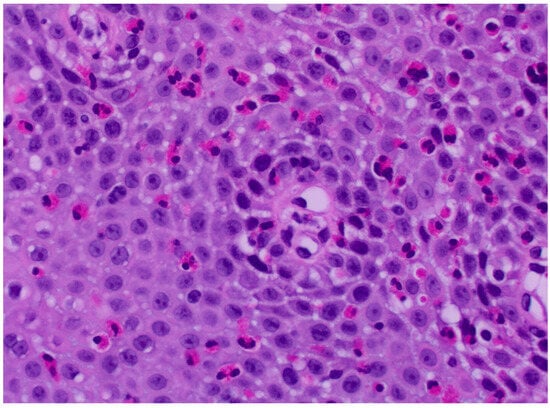
Figure 2.
Tissue Eosinophilia—this slide shows migration of eosinophils into the tissue of the esophagus in a case of eosinophilic esophagitis. Courtesy of Michael Anreder, MD.
An eosinophil count is routinely seen on a complete blood count (CBC) in the range of 0–5% and an absolute count of less than 500 cells per microliter. Eosinophilia is defined as an absolute eosinophil count (AEC) greater than 500 eosinophils per microliter and not solely an elevated percentage of eosinophils found on CBC. Hypereosinophilia is described as an AEC greater than 1500 cells per microliter with or without end organ damage, and a hypereosinophilic syndrome has additional end organ damage in relation to the eosinophilia [4]. The eosinophilia has to occur on at least two occasions over a minimum of 4 weeks in order to be diagnostic.
Eosinophilia is divided into primary eosinophilia, which includes clonal and idiopathic, and secondary (reactive) eosinophilia, which is incited by parasitic infections, allergic reactions, vasculitides, drug reactions, and oncologic origin. Distinguishing clonal from idiopathic eosinophilia involves a review of histology, with cytogenetic or molecular evidence suggestive of a myeloid malignancy. While there is no number that specifically equates to cancer, significant eosinophilia should prompt a myeloid neoplastic workup [3,4].
This paper will serve as an overview of the causes of peripheral eosinophilia and its workup. Discussion will be systems based and will be followed by workup algorithms. A brief overview of the diseases covered can be seen in Table 1.

Table 1.
Conditions Causing Eosinophilia by Organ System.
2. Cutaneous Processes
Though several cutaneous conditions are known to cause tissue eosinophilia, not all of them will induce peripheral eosinophilia [5]. Additional cutaneous processes with blood eosinophilia not mentioned below, but further expanded upon in other sections, include infectious causes, drug induced hypersensitivity syndrome (DiHS), and eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA). Figure 3 presents a flowsheet to aid the differential diagnosis of peripheral eosinophilia presenting with cutaneous manifestations.
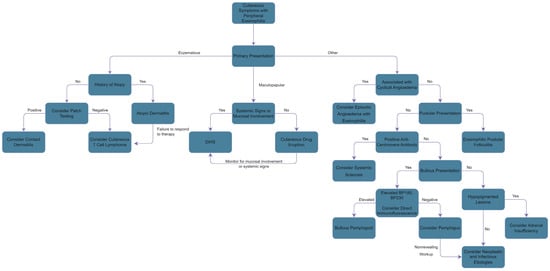
Figure 3.
Differential Diagnosis of Peripheral Eosinophilia with Cutaneous Manifestations.
2.1. Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a complex and multifactorial atopic disease with multiple phenotypes [6]. Clinically, AD is seen primarily in the flexural folds in adults and the face, neck, and extensor sites of the extremities of infants [5]. While it is primarily a pediatric disease with a young onset, 77–91% of individuals have persistent or relapsing dermatitis throughout adulthood. In addition, it also occurs together with respiratory allergies, such as asthma, approximately 50% of the time [7].
This disease is primarily a defect in epidermal barrier function that allows allergen or toxin penetration, eliciting an immune response. Keratinocytes release thymic stromal lymphopoietin, IL-33, and IL-25, leading to the activation of Th2 cells. These cells then release IL-4 and IL-13, and separately IL-31, which promotes itching in AD [6]. Peripheral eosinophilia is present in most patients with AD and roughly correlates with disease severity [8]. Tissue eosinophilia is present in both chronic and acute AD [5]. Participants with severe AD concomitantly with sensitization to common allergens exhibited eosinophilia more frequently than those with mild-to-moderate disease. It is for this reason that peripheral eosinophilia is being further studied as a diagnostic tool in differentiating atopic AD vs. non-atopic causes and its correlation with other allergic processes [9]. The exact extent of the contribution of eosinophils in AD is unclear, though it is noted that mepolizumab, an anti-IL-5 therapy, only had slight effects on disease severity even though it significantly decreased blood eosinophil levels [5].
2.2. Contact Dermatitis
Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) is an eczematous reaction that can be acute or chronic and is triggered by contact allergens. ACD is characterized by the emergence of itchy, red, and flakey rashes, sometimes accompanied by blisters. These rashes have a delayed onset and take weeks to heal. They are particularly prominent at sites of direct contact but can spread to other parts of the body. However, if the allergen is airborne, the reaction can have a widespread presentation. Moreover, both new and old products can be the cause of ACD. Manufacturers may alter ingredients over time, and a product causing the reaction, even with minimal weekly contact, can result in a persistent rash. The specific cause of ACD is difficult to ascertain, and patch testing may be required to make a final diagnosis [10]. It is mediated by both the innate and adaptive immune system, mostly through type 1 mechanisms [5]. There is some evidence that allergic contact dermatitis can lead to peripheral eosinophilia, notably in the cases of epoxy resin used in blunt hemodialysis needles and a surgeon’s exposure to volatile anesthetics [11,12].
2.3. Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphomas
Cutaneous T-cell lymphomas (CTCL) are characterized by clonal accumulations to T-cells in the skin [13]. This disorder is associated with erythroderma, severe pruritis, and lymphadenopathy, though symptoms can be elusive and a strong index of suspicion must be maintained to identify this condition [5]. CTCL is thought to induce eosinophilia due to T-helper 2 clones increasing production of cytokines specific to eosinophil proliferation [13]. CTCL tumor lines are noted to spontaneously produce IL-5 (and other cytokines), which may cause the peripheral eosinophilia in the disease [14]. Both Sézary Syndrome and mycosis fungoides have been associated with eosinophilia [14,15].
2.4. Eosinophilic Cellulitis/Dermatitis (Wells’ Syndrome)
Eosinophilic cellulitis/dermatitis (EC), also known as Wells’ syndrome, is a rare inflammatory disorder with uncertain incidence [16]. The exact etiology and pathophysiology of Wells’ syndrome is unknown, but it is considered to be part of hypereosinophilic syndromes. Studies have found an increased expression of IL-5 in both the tissue and blood [5]. Patients present with a warm erythematous skin lesion that waxes and wanes and resembles cellulitis but lacks a clear source of infection and response to antibiotics. The lesions can be diffuse or localized erythematous plaques, initially presenting with burning or pruritis. Subsequently, patients develop involution of the lesion over 2–8 weeks, resulting in skin atrophy and hyperpigmentation [16]. A typical finding to aid in diagnosis is the histopathologic presence of “flame figures”, which are eosinophil granule proteins covering amorphous collagen fibers [5]. In a review of 32 cases of idiopathic eosinophilic cellulitis, 96% of cases had “flame figures” and 67% presented with peripheral eosinophilia [16]. Therefore, while peripheral eosinophilia is commonly seen, it is not used as a primary diagnostic factor.
2.5. Episodic Angioedema with Eosinophilia (Gleich’s Syndrome)
Another urticarial cutaneous disorder with peripheral eosinophilia is Gleich’s syndrome, or Episodic Angioedema with Eosinophilia (EAE). Like Wells’ syndrome, it is a rare cutaneous variant of hypereosinophilic syndromes, with uncertain incidence. Patients present with angioedema, urticaria, transient weight gain, fever, and eosinophilia at 3–4 week intervals. The exact pathophysiology is unknown, but early studies have found T-cell clonality with notably abnormal CD3-CD4+ cells. Symptoms are preceded by a cyclic rise in IL-5 and other type 2 cytokines, with subsequent activation of blood and tissue eosinophils by T lymphocytes [17,18]. Recent studies have also started to find cycling of other cell lines, such as neutrophils and lymphocytes, which suggests a multilineage cell cycling disorder [5].
2.6. Bullous Pemphigoid
Bullous pemphigoid (BP), a bullous skin disorder, is caused by an autoimmune response against hemidesmosomal antigens. It most commonly affects elderly patients aged 60–80. Classically, it presents with a period of pruritis followed by urticarial or eczematous lesions, followed by tense fluid-filled bullae, though the presentation is heterogenous [19]. A 2018 case-control study with 225 BP patients and 1125 control subjects showed that 50.2% of patients with bullous pemphigoid had pathologic peripheral eosinophilia, compared to 4.3% of control subjects [20]. Of the patients with bullous pemphigoid, 17.8% had moderate eosinophilia and 1.3% had severe eosinophilia, compared to none of the control patients. Patients with eosinophilia were significantly older at presentation (80.9 vs. 73.5, p = 0.003), had increased palmoplantar involvement, and tended to present more frequently with the urticarial stage of the disease. Detection of anti-basement membrane antibodies was significantly higher in patients with eosinophilia. Survival was significantly worse for those with eosinophilia at 5 years (p = 0.008) [20]. Workup should include BP autoantibodies BP180 and BP230 [19].
2.7. Pemphigus
Pemphigus vegetans is a rare subtype representing 1–2% of cases of pemphigus vulgaris [21]. Vegetating plaques of the flexural areas are considered characteristic of this variant [21]. In a retrospective review, 13 of 14 cases showed eosinophilia [21]. There may be a link in the involvement of IgG4IgG2 auto-antibodies and cytokines, leading to chemotaxis of eosinophils [21]. Pemphigus herpetiformis has also been associated with eosinophilia—in a case series, three of eight patients were found to have peripheral eosinophilia [22]. Characteristic of pemphigus vegetans is positive IgG and C3 on direct immunofluorescence [21]. Pemphigus-like lesions have also been seen in hypereosinophilic syndromes associated with FIP1L1-PDGFRA fusion gene (4q12) [23].
2.8. Eosinophilic Pustular Folliculitis
Eosinophilic pustular folliculitis (EPF) is a chronic, relapsing dermatosis primarily of patients of East Asian descent [24]. It is characterized by pruritic, follicular papulopustules with a predilection for seborrheic areas which are relapsing and remitting, sometimes leaving residual hyperpigmentation [24]. The disease is more often found in males by a ratio of 5:1 [24]. EPF is associated with HIV, suggesting a role for immune dysfunction in the disease [24]. The presence of eosinophilia is suggested to follow the same course seen in HIV, with hypersensitivity reactions leading to an activation of Th2 cells, causing an increase in IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13, promoting growth and recruitment of eosinophils [24].
2.9. Systemic Sclerosis
The primary clinical finding in systemic sclerosis is skin thickness. It can be divided into diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis, a severe form of the disease, and limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis [25]. Systemic sclerosis causes widespread microvascular endothelial injury, autoimmunity-mediated inflammation, and pathological fibroproliferative lesions [26]. An estimated 18–22% of patients with systemic sclerosis had associated eosinophilia without a known cause [25,26]. It was most commonly associated with diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis (70.6%) and was associated with male sex and longer duration of disease [25]. Persistently high eosinophilia was found to be less common than periodic eosinophilia (11% vs. 18%, respectively) [26]. Persistent eosinophilia was associated with higher anti-centromere antibody positivity, better baseline percent predicted total lung capacity, and lower baseline C-reactive protein [26]. Peripheral eosinophilia is also independently associated with skin ulceration [27]. The role and mechanism of eosinophilia in systemic sclerosis are unknown [25]; one theory suggests damage to endothelial cells causes the release of IL-33, leading to TH2 polarization and IL-13 dependent fibrosis, leading to the induction of IL-5 [26].
3. Respiratory Processes
Numerous respiratory diseases are known to cause peripheral eosinophilia. We have broken down the respiratory system into the upper and lower regions for ease of discussion. Figure 4 presents a flowsheet to aid the differential diagnosis of peripheral eosinophilia presenting with cutaneous manifestations.
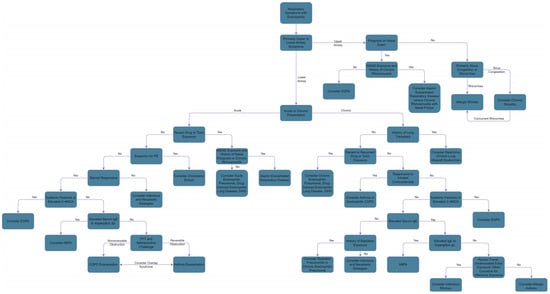
Figure 4.
Differential Diagnosis of Peripheral Eosinophilia with Respiratory Manifestations.
4. Upper Respiratory Processes
4.1. Allergic Rhinitis
Allergic Rhinitis (AR) is characterized by inflammation of the nasal mucosa in response to allergen exposure and can manifest itself in conjunction with peripheral eosinophilia. Eosinophils, found locally and systemically, serve as an indication of the body’s response to an allergen. Evidence indicates that during seasonal AR, there is bone marrow stimulation, leading to an increase in circulating eosinophils. Some studies suggest that in patients with AR, there is a higher AEC than in the general population. However, there does not appear to be a clear relationship between AEC and clinical severity. Further, depending on the degree of sensitivity and the type of allergen, there is variability in the AEC [28].
4.2. Chronic Sinusitis
Chronic sinusitis occurs due to persistent inflammation of the nasal sinuses and has been commonly associated with peripheral eosinophilia. Similarly to allergic rhinitis, eosinophilia in chronic sinusitis reflects a relationship between allergens and the body’s immunologic response. A previous study highlighted the correlation between CT findings for chronic sinusitis and peripheral eosinophilia. One study reported 87% of the patients had extensive disease and proposed that peripheral eosinophilia in conjunction with CT findings indicating chronic sinusitis was indicative of severity [29]. However, peripheral eosinophilia displays low specificity and sensitivity for chronic sinusitis (49.4% and 84.7%, respectively) [30].
4.3. Nasal Polyps
Chronic rhinosinusitis can be associated with nasal polyps. The condition is characterized by type 2 immune response and often has recurrent and severe disease [31]. The development of nasal polyps is an interaction of the innate and adaptive immune system with remodeling of the nasal mucosa [31]. Chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps has a pathophysiology linked to asthma, including upregulation of type 2 cytokines IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 and increased IgE mediated release of immune mediators [31]. The control of nasal polyps is directly linked to the control of asthma and treatment of one often affects the severity of the other [31]. Peripheral eosinophilia is likely linked to the upregulation of IL-5 in this process [32]. The diagnosis of nasal polyps is based on nasal endoscopy and tissue biopsy, which often shows tissue eosinophilia [31].
5. Lower Respiratory Processes
Due to the distinct vascular supply of the lungs, the migration of eosinophils into the lower respiratory tract is not fully understood [33]. The alveolar spaces are supplied by the lower pressure pulmonary arterial circulation, while the systemic bronchial arteries supply the remainder of the airways. Airway eosinophil migration is speculated to be caused by post-capillary capture and endothelial transmigration, while alveolar migration is presumed to be largely due to chemoattractants [33]. A 2018 study postulated that IL-33 plays a central role in alveolar migration due to its elevation in acute eosinophilic pneumonia [34]. Endothelial injury induces IL-33 production, leading to recruitment and activation of type-2 innate lymphoid cells which produce IL-5 and IL-13, attracting and activating eosinophils in the lung [34]. The evaluation of suspected lower airway eosinophilia is complex. Sputum cytology requires a “lengthy and detailed” technique that renders it one of the most expensive components of evaluation, after bronchoscopy [33]. Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) and biopsy can be used to identify eosinophilia, though it is important to remember that samples from one lung region do not necessarily correlate with samples from other regions [33].
5.1. Aspirin-Exacerbated Respiratory Disease
Aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease (AERD), also known as NSAID-exacerbated respiratory disease (NERD), is a complex process that is associated with eosinophilia. AERD can be recognized clinically by a classic triad: chronic rhinosinusitis, nasal polyposis, and asthma exacerbations after the ingestion of aspirin or other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) [35]. Aspirin results in an increase of IFN-γ produced by peripheral blood lymphocytes [36]. Increased IFN-γ initiates a cascade of events that leads to eosinophilia. These events include: increased gene transcription of eosinophils, activation of eosinophils (via IL-4), and stimulation of the eosinophil maturation process [37]. Consequently, there is an overall increase in the absolute eosinophil count (AEC).
In addition, aspirin’s mechanism of action (irreversible inhibition of cyclooxygenase 1 (COX-1)) results in the decreased production of prostaglandins, specifically prostaglandin E2 (PGE2). Normally, PGE2 suppresses eosinophil activation. However, aspirin removes this inhibitory effect, leading to an increased AEC. Additionally, since the COX-1 pathway is inhibited, metabolites preceding the COX-1 reaction accumulate and are eventually diverted into an alternative cascade via the leukotriene pathway. The overall effect of this shunting is an increase in leukotrienes and the inflammatory, asthma-like symptoms of AERD.
5.2. Asthma
Eosinophilic asthma may be associated with increased severity, atopy, late presentation of disease, or being refractory to steroids. While 50% or more of asthma that is well controlled on inhaled corticosteroids may be eosinophilic asthma, only 20–25% of those with asthma will have peripheral eosinophilia [33]. Diagnosis of eosinophilic asthma requires at least one of the following: sputum eosinophils ≥ 1%, blood eosinophil count ≥ 150, or fractional exhaled nitrogen ≥ 20 parts per billion [38]. While discussing treatment is outside the scope of this review, it is important to note that the efficacy of anti-cytokine therapy for eosinophilic asthma is correlated with the degree of peripheral eosinophilia [33]. In the setting of asthma, tissue eosinophilia is a common occurrence.
Hypereosinophilia is rare in asthma, constituting 0.3% of all cases [39]. In the context of hypereosinophilia, patients should be evaluated for allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, vasculitis, parasitic infection, and even lympho- or myeloproliferative disorders. Evaluation with tryptase, complete blood count, and vitamin B12 levels is recommended [39]. A study of childhood asthma revealed that among patients with uncontrolled disease, a superimposed JAK2 mutation may contribute to their severe asthma and eosinophilia [39].
5.3. Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis
Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA) is an allergic lung disease in response to Aspergillus sp., with increased susceptibility in individuals who have pre-existing asthma, cystic fibrosis, or other lung disorders. ABPA can be seen in 2–9% of patients with cystic fibrosis [33]. Peripheral eosinophilia has been found in ABPA, and monitoring the eosinophil levels is an important aspect of diagnosis and management. Because ABPA presents similarly to asthma and other chronic lung diseases, in addition to CBC, PFTs, serum IgE, sputum samples, and chest imaging, it is recommended patients be tested by skin prick for Aspergillus sp. [40].
5.4. Eosinophilic Pneumonia
Idiopathic eosinophilic pneumonias are uncommon and can present either as an acute or chronic process [33]. Chronic eosinophilic pneumonia may represent as much as 1–3% of interstitial lung diseases and is associated with marked tissue and peripheral eosinophilia, with blood eosinophil counts in the thousands and BAL eosinophils greater than 40% of total cells [33]. Chest imaging can be helpful; however, characteristic findings of dense peripheral infiltrates occur in less than 50% of cases [33]. Biopsy may show other processes, such as idiopathic organizing pneumonia, which are not commonly associated with eosinophilia [33].
Acute eosinophilic pneumonia (AEP) is an uncommon cause of acute respiratory illness that exhibits a spectrum of severity from relatively benign to acute respiratory distress syndrome and fatality [34]. The pathogenesis is poorly understood and likely varies with underlying cause [34]. The most current diagnostic tool for AEP is the modified Philit criteria, defined as: (1) acute onset of febrile respiratory manifestations < 1 month in duration; (2) bilateral diffuse infiltrates on chest radiograph; (3) >25% eosinophils on BAL or eosinophilic pneumonia on lung biopsy; and (4) absence of known causes of pulmonary eosinophilia including drugs, toxins, and infections [41]. AEP has been associated with a number of inciting events, the most common of which is smoking, including cigarettes, cigars, electronic cigarettes, and marijuana [34]. Other causes include antimicrobials, antidepressants, NSAIDs, vaccinations, dust inhalations, parasites, and fungi, and multiple others as discussed by De Giacomi et al. [34]. Narrowing the cause to drug or toxin induced eosinophilic pneumonia can be difficult. Five criteria developed by Solomon and Schwarz may help to differentiate this from other causes: (1) the presence of modified Philit–criteria eosinophilic pneumonia; (2) exposure to the offending agent within an appropriate time frame; (3) exclusion of other causes of eosinophilic pneumonia; (4) clinical improvement after removal of the offending agent; and (5) recurrence upon rechallenge [34]. The most common clinical symptoms in AEP are nonproductive cough, dyspnea, and fever, with occasional malaise, myalgia, night sweats, chills, and pleuritic chest pain [34]. AEP will initially show neutrophilic leukocytosis, with eosinophil counts increasing over the following days [34]. Chest radiography will often include patchy ground-glass opacities, often in tandem with consolidation opacities and interlobular septal thickening. Thickened bronchovascular bundles and lymph node enlargement are also common.
5.5. Drug-Induced Eosinophilic Lung Disease
Outside of the context of drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome (discussed later), drug-induced eosinophilic lung disease can occur based on exposure to several drugs. These drugs significantly overlap with DiHS and include NSAIDs, antidepressants, amiodarone, anticonvulsants, and antibiotics [33].
5.6. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Approximately one-third of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) have evidence of eosinophilic inflammation. In particular, evidence has suggested the existence of various COPD exacerbation phenotypes that display certain inflammatory characteristics with individualized biomarkers [42]. An eosinophilic predominant phenotype displays a considerable Type 2 T helper cell (Th2) response along with the associated cytokine response (IL-4, IL-5, IL-9, IL-13) and an increased basement membrane thickness. Blood and sputum eosinophilia in COPD may predict the response to inhaled steroids, which could reflect the sensitivity of Th2 cells to corticosteroids [43]. Clinical trials comparing the level of eosinophilia in patients with eosinophilic-COPD and asthma-COPD (history of asthma) have revealed a significant increase in eosinophilic airway inflammation in the former [44]. Furthermore, Siddiqui et al. demonstrated a particularly favorable response to corticosteroids in patients with COPD and peripheral eosinophilia [45]. A higher eosinophil count was associated with a better corticosteroid treatment response and a subsequent fall in the AEC when treatment concluded [46].
5.7. Lung Transplantation
Chronic lung rejection of lung allografts can be characterized as either obstructive processes or restrictive chronic lung allograft dysfunction (rCLAD), with approximately 30% of cases associated with the latter [33]. BAL of rCLAD patients displaying eosinophilia had worse overall survival and rejection-free survival. BAL eosinophil count was also significantly correlated with peripheral eosinophilia [47]. The mean peripheral eosinophil count was 330 cells/μL at the time of diagnosis, and a blood eosinophil count of > 240 was associated with a 71% sensitivity and 86% specificity in predicting 1 year survival [48].
6. Cardiovascular Processes
6.1. Eosinophilic Myocarditis
Eosinophilic myocarditis (EM) is a form of myocardial inflammation with eosinophilic infiltration and concomitant eosinophilia. The clinical presentation of EM varies from asymptomatic to acute fulminant myocarditis (also known as necrotizing EM) to chronic cardiomyopathies (Loeffler cardiomyopathy) [49]. Acute EM generally has a worse prognosis compared to chronic [50]. EM generally presents as dyspnea, chest pain, fever, and nonspecific symptoms such as nausea, fatigue, or myalgia [49,51]. Patients also had abnormal electrocardiograms, increased troponin, and peripheral eosinophilia. Furthermore, they had decreased left ventricular ejection fractions (LVEF) with pericardial effusion that sometimes progressed to tamponade [49]. Definitive diagnosis relies on endomyocardial biopsies (EMB), although troponins, eosinophilia, and imaging, particularly cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR), are often used [51]. The sensitivity for EMB is only 54% [52]. EM is often fatal, especially in fulminant cases, but the exact mortality rate is unclear.
The severity of eosinophilic infiltration is believed to be influenced significantly by the underlying condition, the extent of eosinophilic exposure, and the duration of exposure [49]. The most common etiologies of EM are hypersensitivity reactions, eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis, hypereosinophilic syndromes, infectious, neoplastic, and idiopathic [49,51]. Unfortunately, the etiology is often discovered post-mortem [49].
Eosinophilic myocarditis occurs in individuals aged between 24 and 65, with an average age of 41, and occurs more frequently in males [49,50]. Hypersensitivity-associated EM was observed in a younger demographic, with an average age of 35, while EM associated with EGPA was more prevalent in older individuals, with an average age of 50 [49]. Eosinophilic myocarditis in the pediatric population was mainly seen due to idiopathic causes or hypersensitivity reaction [49]. Eosinophilic myocarditis associated with hypersensitivity is often caused by drug exposure. Heart transplant patients also have an increased incidence [50].
Although it is seen that a large percentage of patients with EM detected post-mortem have peripheral eosinophilia on admission, it is absent in up to 25% of patients [49]. However, it has been demonstrated that eosinophil counts can increase to greater than 500/mm3 7–12 days after admission [49]. Moreover, hypersensitivity EM, which had the highest occurrence of cardiac arrest, lacked peripheral eosinophilia (in up to 40% of cases) [49]. Thus, the absence of peripheral eosinophilia upon admission doesn’t necessarily exclude the diagnosis of EM. This is further demonstrated in that some studies state that even in EM associated with hypereosinophilic syndrome, a lack of peripheral eosinophilia cannot exclude the diagnosis [52]. Since the presence of peripheral eosinophilia varies across EM cases, it is important to consider other diagnostic criteria and clinical features.
6.2. Cholesterol Crystal Embolism
Cholesterol crystal embolism (CCE) has also been associated with peripheral eosinophilia. It has been found in some studies that around 20–70% of patients with CCE have peripheral eosinophilia [53,54,55].
7. Gastrointestinal Processes
7.1. Eosinophilic Esophagitis, Gastritis, and Colitis
Eosinophilia in the alimentary canal can result when there is abnormal accumulation of eosinophils throughout the digestive tract, notably in the esophagus, in the stomach, or within the intestines. Eosinophilic gastritis is an uncommon condition that occurs when eosinophils infiltrate the stomach lining, resulting in inflammation. It is generally not isolated and presents as gastroenteritis. The clinical manifestations are variable and can include nausea and vomiting due to protein-losing enteropathy. In a limited study, a recommended diagnosis for eosinophilic gastritis included greater than 30 eosinophils per high power field (HPF) in at least five HPFs in the absence of a known cause of eosinophilia [56]. Patients with peripheral eosinophilia and hypoalbuminemia were found to have a higher likelihood of positive biopsy [57].
The underlying mechanism of eosinophilic gastroenteritis is unknown, but the hypersensitivity aspect of the disease is the main focus. There are no standard diagnostic criteria, only recommended criteria, such as the aforementioned value from a small study. The recommendation is dietary elimination, as this disease process, similarly to eosinophilic esophagitis, is presumed to be related to an allergic response [58]. Similarly to many eosinophilic processes, the cause of eosinophilia is suspected to be allergic or infectious. Recruitment of eosinophils to the area causes localized damage via mediators such as eosinophilic cationic protein, eosinophil derived-neurotoxin, eosinophilic peroxidase, and major basic protein. The release of protein-specific agents causes cytokinetic, chemokinetic, and lipid mediators to further impart damage locally. One potential differentiator between eosinophilic esophagitis and eosinophilic gastroenteritis is the means of defense on a molecular level. It is the transcriptome of the type of mediators released that provides some rationale as to why some therapeutic strategies work and others fail. It has been reported that eosinophilic gastroenteritis can occur at any age but has a slightly male predilection and is more often to occur within the third and fourth decade of life. It was previously found to have a higher incidence in Japan in small studies conducted [59,60].
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is becoming an increasing cause of food dysphagia and impaction. While it presents in all age groups, it tends to affect children more vaguely. It has now been deemed the most common cause of dysphagia in young adulthood [61]. This condition is believed to be immune- or antigen-driven and is histopathologically defined as greater than or equal to 15 eosinophils per HPF with the addition of esophageal dysfunction in some capacity. In the pediatric population, EoE has been reported as refusing food; having food intolerance, reflux, and abdominal pain; and failure to thrive [62]. It has been suggested that a positive feedback loop from inflammation-induced epigenetic changes may explain refractory EoE [63]. Baseline peripheral eosinophil counts may be useful as an independent predictor of treatment nonresponse and food impaction, which could be used to help therapy selection [64]. While peripheral eosinophilia is not always present in this disease, it should still be considered when working up patients with peripheral eosinophilia and vague gastrointestinal symptoms [65].
Eosinophilic colitis (EC) is another rare eosinophilic gastrointestinal condition with bimodal distribution amongst neonates and young adults. Due to its location, the differential for EC is highly variable due to potential effects from parasitic causes, inflammatory causes via inflammatory bowel or celiac disease, viral causes, connective tissues disease, drug induced allergic reactions, and/or dietary causes. Like the other eosinophilic conditions of the alimentary canal, the presentation can include bloody diarrhea, abdominal pain, and weight loss. A history of atopy, food allergies, and peripheral eosinophilia can be found. In addition to colonoscopy and esophagogastroduodenoscopy, a skin prick test and radioallergosorbent test can be performed [66,67]. An investigation of peripheral eosinophilia in patients with ulcerative colitis found it was not a reliable indicator for disease activity or patient outcomes [68]. Given its variability, further study into the association of peripheral eosinophilia and inflammatory gastrointestinal conditions should be undertaken.
7.2. Eosinophilic Pancreatitis
Eosinophilia in pancreatitis is an infrequent finding. Due to its rarity, the criteria for its classification are not well-established, distinguishing it from other pancreatic conditions. Pancreatitis is characterized by pancreatic inflammation and may occasionally present with increased eosinophils, a condition referred to as eosinophilic pancreatitis (EP) [69]. Some researchers define EP as having peripheral eosinophil counts exceeding 1.5 × 109 for over six months, a history of allergic diseases, increased IgE levels, eosinophilic infiltration of organs, and a diagnosis of hypereosinophilic syndrome [70]. Interestingly, EP was initially termed acute eosinophilic insulitis when discovered in the pancreas of a newborn born to a diabetic mother [71]. EP often goes underdiagnosed, as its identification relies on endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography and endoscopic ultrasound, modalities primarily utilized for malignancy detection [69]. Additionally, it is noteworthy that other forms of pancreatitis (acute pancreatitis (AP), chronic pancreatitis (CP), autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP), and pancreatic cancer) may share similar symptoms and signs.
Normally, the pancreas is devoid of eosinophils, and the mechanism driving their infiltration during inflammation remains unclear. Recent research challenges established notions about the pathogenesis pathways of CP. While cerulein, an oligopeptide, was traditionally believed to trigger CP in mice, emerging findings now suggest that the accumulation of eosinophils in the pancreas plays a pivotal role in disease pathogenesis and fibrosis. Proposed mechanisms include the induction of pancreatic IL-18 during CP and related conditions, such as eosinophilic gastroenteritis. It is suggested that IL-18 functions by synthesizing and converting naive eosinophils into their pathogenic form [69]. In studies focused on understanding the pathogenesis of pancreatic cancer arising from CP (considered one of the leading risk factors for pancreatic cancer), it was discovered that NLRP3 (an inflammasome)-regulated IL-18 in activated macrophages promotes eosinophilic inflammation, triggering the TGF-β signaling pathway. TGF-β, in conjunction with SMAD4 (a transcription factor and a tumor suppressor), activates oncogenic proteins implicated in pancreatic neoplasm development [72]. Furthermore, research has revealed that mice deficient in IL-5 were protected from the induction of CP [73].
In AP, it has been suggested that obstruction of the pancreatic duct can result in duodenal swelling due to eosinophil infiltration. The pathogenesis of AP may explain its strong associations with eosinophilic gastroenteritis. A case report on a patient with eosinophilic gastroenteritis, diagnosed by eosinophilic infiltration in duodenal lamina propria biopsies, presented with acute pancreatitis and ascites. Recent studies propose that increased trypsin levels activate PAR2 in the duodenal mucosa or on the surface of eosinophils, leading to eosinophil degranulation and the release of cytokine factors that perpetuate the inflammatory response [74]. Another case report demonstrated a connection between cow milk consumption and eosinophilic gastroenteritis-associated AP [69]. Patients with CP often exhibit marked peripheral eosinophilia, with CP affecting males at a higher rate than females. Additionally, individuals with CP show impaired pancreatic exocrine function while maintaining normal endocrine function. The eosinophilic response in CP frequently results in correlated damage to the pleura, leading to effusion, pericarditis, and ascites [69,75,76]. As mentioned earlier, CP is a significant risk factor for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, one of the most malignant cancers [71]. Notably, alcoholism is a common cause of CP; however, numerous studies have demonstrated no difference in the incidence of eosinophilia between alcoholic and nonalcoholic pancreatitis [76].
Pancreatic cancer and eosinophilic pancreatitis (EP) exhibit numerous similarities, making accurate diagnosis challenging. EP typically presents with abdominal or mid-back pain and obstructive jaundice (associated symptoms are often pruritus acholic stools and icterus) [71]. While surgery is crucial in reducing perioperative morbidity and mortality for pancreatic cancer, it is unnecessary for EP patients. In previous cases, eosinophilic infiltration of the pancreas was frequently observed postmortem or after resection in patients [71]. A review article attempted to differentiate EP from cancer by categorizing presentations as either pancreatic or extrapancreatic. Pancreatic presentations involve features of AP because it mimics the obstructive presentation of pancreatic cancer. Common symptoms include abdominal pain that resolves spontaneously in a few hours and radiates to the back, jaundice, recurrent AP without a cause, fever, nausea, vomiting, and weight loss. Extrapancreatic presentations often demonstrate peripheral eosinophilia, eosinophil infiltration into other organs, and an obstructive pancreatic mass. Additionally, these patients may experience gastroenteritis [71]. Another method of differentiating EP from cancer is the use of a glucocorticoid diagnostic treatment, as EP is responsive to this, while cancer would not be [70].
Autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP), classified as a subtype of chronic pancreatitis (CP), is distinguished into two types. Type I, recognized as IgG4-related pancreatitis, often impacts multiple organs such as the pancreas, liver bile ducts, salivary glands, kidneys, and lymph nodes. On the other hand, Type II, known as idiopathic duct-centric pancreatitis, predominantly affects the pancreas. The differentiation between AIP and eosinophilic pancreatitis (EP) poses challenges due to symptom overlap. Both EP and AIP exhibit eosinophilia in pancreatic ducts, acini, and interstitium. In EP, the inflammatory cell composition includes neutrophils and eosinophils, while AIP lesions are characterized by a predominant presence of lymphocytes. Elevated IgE levels are associated with EP, contrasting with the increased IgG4 levels seen in AIP. AIP patients typically exhibit positive results for autoantibodies. Furthermore, they present with an enlarged “sausage-like” pancreas, differing from the “rock-hard” growth pattern observed in the pancreatic head or tail of non-AIP CP patients. Notably, AIP patients report a higher incidence of eosinophilia compared to those with non-AIP CP [69,71].
Eosinophilia in pancreatitis, notably EP, poses diagnostic challenges due to its infrequency and lack of well-established criteria. The evolving understanding of CP implicates eosinophils in disease pathogenesis and fibrosis. In AP, eosinophil infiltration, coupled with pancreatic duct obstruction, may contribute to duodenal swelling, further allowing for its misdiagnosis for conditions such as eosinophilic gastroenteritis. Distinguishing EP from pancreatic cancer requires careful consideration of symptoms, categorization of presentations, and responsiveness to glucocorticoid treatment, emphasizing the importance of accurate diagnosis for appropriate management. Unraveling the complexities of eosinophil involvement in pancreatitis is crucial for accurate diagnosis and tailored management strategies in these diverse pancreatic disorders.
8. Endocrine Processes
8.1. Adrenal Insufficiency
Peripheral eosinophilia can be seen in adrenal insufficiency and has been attributed to primary (adrenal glands), secondary (anterior pituitary), and tertiary (hypothalamus) causes.
Primary adrenal insufficiency (Addison’s disease) occurs due to direct damage to the adrenal glands. Commonly seen causes include: autoimmune, infectious (tuberculosis, CMV, HIV, and histoplasmosis), hemorrhage, infiltration (amyloidosis, tumors, and hemochromatosis), and medications that can inhibit cortisol production (fluconazole, ketoconazole, and rifampin) [77]. Secondary adrenal insufficiency occurs when the anterior pituitary fails to produce sufficient adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). Frequent etiologies seen here include: individuals that suddenly stop long-term glucocorticoid therapy, hypopituitarism, or sustained inhibition of the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis (HPA) [77]. Tertiary adrenal insufficiency occurs when corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) from the hypothalamus does not stimulate the release of ACTH. Tertiary cases are associated with glucocorticoid therapy, head trauma, and certain types of brain surgeries [77].
Irrespective of the etiology, adrenal insufficiency results in adrenal gland dysfunction and, subsequently, an inadequate production of adrenocortical hormones (mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, and androgens). Glucocorticoids have been shown to suppress the release of eosinophils into circulation from the bone marrow [78]. Additionally, glucocorticoids reduce the eosinophil production rate by mitigating lymphocyte activity [79]. Therefore, in adrenal insufficiency, the regulation of eosinophils is removed, leading to subsequent peripheral eosinophilia.
8.2. Hypopituitarism
Peripheral eosinophilia has been associated with a wide variety of presentations of hypopituitarism. While this could be considered a subtype of adrenal insufficiency, we believe it merits separate mention. The presumed mechanism is likely related to glucocorticoid deficiency, as described above. A case series involving three patients noted immune-related hypopituitarism after treatment with atezolizumab-bevacizumab therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma with decreased ACTH and cortisol levels [80]. These cases were associated with hyponatremia and, often, eosinophilia [80]. A separate case of a patient with pituitary macroadenoma exhibited eosinophilia [81]. Eosinophilia has also been associated with postpartum hypopituitarism (Sheehan’s syndrome) [82].
9. Rheumatologic and Musculoskeletal Processes
Peripheral eosinophilia is associated with a number of rare rheumatologic disorders. Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA) is a primary systemic small-to-medium vessel vasculitis associated with eosinophil-rich and necrotizing granulomatous inflammation, especially in the lungs, and with asthma. Eosinophils are thought to play a key role in EGPA’s clinical presentation. IL-5 production, key in eosinophil maturation, is increased in these patients [83]. While EGPA is considered a small vessel vasculitis, many patients will lack clinical evidence of vasculitis [33]. Only 41% of patients had proven or suspected vasculitis, only 53% of which displayed ANCA-positivity [84]. Radiographically, EGPA displays nonspecific consolidations and, rarely, distinct nodules. EGPA is commonly unmasked in patients by withdrawal of systemic corticosteroids [33]. It is suspected that the use of dupilumab, an anti-IL5 monoclonal antibody used in the therapy of asthma and other allergic conditions, leads to de-escalation of systemic corticosteroid therapy, which can also unmask EGPA [85].
Immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4RD) is a more recently defined disease associated with systemic fibrotic inflammation, which can have multisystem involvement [83]. The first sign of IgG4RD is often unexplained tissue swelling or mass involving one or more organs [86]. Associated findings include relegated IgG4 levels and biopsies with dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltration with a high percentage of IgG4+ plasma cells, storiform fibrosis, obliterative phlebitis, and tissue eosinophilia [86]. Although eosinophils are found in tissue biopsies, they do not appear to have a pathogenic role [83]. Peripheral blood eosinophilia was noted in 38% of IgG4RD patients compared to 9% of healthy controls, and eosinophil count was positively correlated with serum IgE and IgG4 [87]. A history of atopy was noted in 63% of patients with IgG4RD compared to 17% of healthy controls. Peripheral eosinophilia was classified as a “red flag” for IgG4RD [87]. It is suggested (but not confirmed) that eosinophils in IgG4RD may serve as a source of plasma cell survival factors, and recruitment of M2 macrophages and fibroblasts, leading to inflammatory fibrosis [86].
Diffuse fasciitis with eosinophilia is an uncommon disorder characterized by thickened skin, hypergammaglobulinemia, and peripheral eosinophilia. Tissue eosinophilia is not a required part of diagnosis. The role of eosinophils appears to be related to Th2 cytokine overproduction compared to healthy controls. Minor criteria for diagnosis include eosinophilia greater than 0.5 × 109/L [83].
Eosinophilic fasciitis (EF) is seen with erythema and non-pitting edema in the limb or trunk. The hands and face are spared, while the forearms, flanks, and upper legs are usually affected. Later, it proceeds to collagenous thickening of the subcutaneous fascia. In one article, 33 of 52 cases of EF presented with peripheral eosinophilia [88]. The etiology of EF varies, and reported cases have included medication exposure, autoimmune diseases, infection, initiation of hemodialysis, and even hematologic malignancies [13,88]. Definitive diagnosis requires full thickness biopsy and histopathological examination [89].
EF is also very difficult to distinguish from eosinophilia myalgia syndrome (EMS). Under pathological examination, the conditions cannot be differentiated. However, unlike EF, patients with EMS often present with a subacute onset of myalgias, peripheral neuropathy, and additional visceral involvement [90]. Cases have been reported with pneumonitis and neuropathy. EMS is primarily caused by exposure to a contaminant of tryptophan [83] found in dietary supplements, causing an epidemic in 1989. After being banned by the FDA, the incidence of EMS has also declined, but the ban has since been lifted. It is far less common now than previously, though a single case has been associated with L-tryptophan [83]. The exact pathogenesis of EMS has not been defined. It is possible that certain individuals lack protective immunogenetic markers, such that when they are exposed to L-tryptophan, or other similar agents, they are subject to more acute inflammation [90]. This includes eosinophil activation and degranulation with tissue fibrosis, driven by TGFB and IL-4 signaling.
Eosinophilic myositis is a rare group of disorders that have been described in case reports or small case series. The condition is characterized by severe muscle pain and peripheral eosinophilia. It appears to be triggered by trauma and heavy alcohol use, though the connection is uncertain due to the rarity of the condition. Eosinophils are thought to be part of the pathophysiology of muscle damage based on elevated IL-5 in biopsies [83].
10. Infectious Processes
Among individuals with eosinophilia, infectious etiologies must be considered. Consideration of travel history, possible exposure to contaminated food or water, insect bites, sexual contacts, patient demographics, accompanying symptoms, and the relative degree of the eosinophilia are extremely important [91,92].
The initial evaluation for a suspected infectious etiology of eosinophilia begins with a detailed history and physical exam. Physical symptoms such as hemodynamic instability, shortness of breath, altered mental status, neck stiffness, or focal neurological deficits may necessitate immediate intervention. Physical exam findings are nonspecific and can include lymphadenopathy, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, mucocutaneous lesions, skin necrosis, and gastrointestinal complaints. This information allows for further evaluation with diagnostic testing that is tailored to the individual [91,92].
Standardized diagnostic testing may include, but is not limited to, a review of prior blood work, a repeated complete blood count with differential (CBCD), and a comprehensive metabolic panel (CMP). Stool microscopy is used to further investigate some intestinal and hepatobiliary parasites. Relevant findings can include parasitic organisms, including protozoa and helminths [92].
A general overview of the infectious organisms that can result in eosinophilia include helminths, protozoa, fungi, a small subset of bacteria, mycobacteria, certain viral infections, and arthropods. Parasitic infections, particularly helminth (worm) infections, such as roundworms, hookworms, and tapeworms, are among the most common causes of infectious eosinophilia. Flukes, such as Schistosoma sp., are common outside North America and Europe and merit attention for those native to such areas or with recent travel [91]. Therefore, when developing a differential diagnosis for infectious eosinophilia, a consideration of these parasitic organisms should take precedence.
Mycobacterium infections are another infectious cause of eosinophilia, yet these cases are rare and present in a peculiar way. In particular, eosinophilia has been reported with Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium leprae [93], although the literature speculates that one of the agents to treat Mycobacterium leprae, Dapsone, can induce eosinophilia [94]. This speculation is not the same regarding tuberculosis (TB). TB has been associated with eosinophilia; however, the pathogenesis is still not completely known.
Noteworthy viral infections include human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and human T cell lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1). However, for these two viral infections, eosinophilia seems to emerge as a secondary cause. In the case of HIV, eosinophilia may occur as a result of a concomitant opportunistic infection or due to an associated condition such as eosinophilic folliculitis or adrenal insufficiency. Likewise, the eosinophilia that stems from the HTLV-1 virus is due to the association that that HTLV-1 virus is a proven cause of adult T-cell lymphoma, which can demonstrate significant eosinophilia [95].
11. Neoplastic Processes
Several neoplastic syndromes are associated with hypereosinophilia, including myeloid tumors, lymphoid tumors, and solid tumors. Primary hypereosinophilic syndrome is a notable condition characterized by an interstitial deletion, leading to a fusion product between the FIP1L1 gene and platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF). This fusion results in a gain-of-function mutation that continually promotes the proliferation and differentiation of eosinophils, leading to constitutive activation. The persistent nature of this fusion product yields stable, unregulated differentiation of eosinophils. The FIP1L1-PDGFRA fusion product has three potential outcomes: hypereosinophilia (as explored in this review), a myeloproliferative neoplastic leukemia not distinguished by eosinophilia, and T-cell leukemia. A common complaint associated with these conditions is malaise and weakness, particularly in the presence of eosinophilia. Additional symptoms may arise due to eosinophils infiltrating various organ systems [96].
JAK2 mutation is commonly seen in polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia, in the context of which hypereosinophilia may be observed. In patients with hypereosinophilia of unknown significance, 1.5–4% are found to have a JAK2 mutation, which is associated with a poor prognosis [39]. In a 10 year prospective study of 1200 patients, 3% of patients evaluated for severe asthma were found to be hypereosinophilic. Of these patients, three were found to have a JAK2 mutation, representing 9% of those with hypereosinophilia [39]. For these patients, loss of asthma control was seen 1 year prior to diagnosis of JAK2 mutation [39]. In the context of asthma, blood eosinophilia > 2000/mm3, pulmonary infiltrates, persistence of eosinophilia with oral steroid use, history of venous or arterial thrombosis, or thrombocytosis should trigger a thorough evaluation [39].
Lymphoid neoplasms with associated eosinophilia are rare but may include acute lymphocytic leukemia, Hodgkin’s lymphoma, and T-cell lymphomas. For example, of patients with hypereosinophilia, 12% are suspected to have abnormal T-cell populations [97]. Outside of tyrosine kinase activation, there are multiple theories regarding eosinophilia in lymphoid neoplasms. One theory suggests that T-cells are stimulated to release eosinophilopoietic growth factors by exogenous factors/antigens expressed by tumor cells [98]. Others theorize that the eosinophilia is due to abnormal lymphoid populations, especially T-lymphocytes. Some examples of these abnormalities include absence of CD3, immature T-cell (CD3+CD4−CD8−−), and elevated CD5 expression on CD3-CD4+. These abnormalities in T-cells are thought to increase production of IL-3, IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13, which in turn increases the production of eosinophils [98,99,100].
Lymphoid neoplasms can be subdivided into B-cell and T cell lymphomas and leukemias. However, they have been consistently grouped together with myeloid disorders under the WHO classification of “myeloid/lymphoid neoplasms with eosinophilia”, with four different gene rearrangements: PDGFRA-FIP1L1, PDGFB-ETV6, FGFR1-fusion genes, and PCM1-JAK2. PDGFRA-FIP1L1 is an 800 kilobase deletion of chromosome 4, which in turn leads to an activated tyrosine kinase, leading to clonal hypereosinophilia [100]. PDGFB-ETV6 translocation is associated with multiple neoplasms and there are many theories regarding its role in production of eosinophilia. This translocation occurs on the chromosome 5q31 region, the same region as several genes coding for multiple eosinophilopoietic cytokines (5q31-33), leading to some of the eosinophilia seen in these myeloproliferative disorders [101,102]. This mechanism is incompletely understood, and further research is still needed. Myeloid and lymphoid neoplasms from FGFR1 fusion genes are commonly seen with eosinophilia [103]. The most common variants are myeloproliferative neoplasm with eosinophilia or T lymphoblastic lymphoma with eosinophilia. Less often, they may present as acute myeloid leukemia [103]. There are several variants of this fusion gene, but the most common is a fusion with ZMYM2 that classically presents as T-lymphoblastic lymphoma or acute myeloid leukemia with eosinophilia and lymphadenopathy [104,105,106,107]. The gene rearrangement PCM1-JAK2 is a more recent addition to the WHO classification system and is associated with more with myeloid neoplasms than lymphoid. Clinically, these rearrangements have similar presentations, with a variety of symptoms including pruritus, fever, weight loss, fatigue, cardiac, and pulmonary symptoms. These patients also have a variety of abnormalities in blood work and organ involvement, which are largely dependent on which myeloid or lymphoid neoplasms the patient has [108]. However, it is important to distinguish between these different gene arrangements for disease prognosis and treatment [101,102,107].
Acute eosinophilic leukemia, an acute myelomonocytic leukemia with eosinophilia or M4Eo, is a specific subcategory of acute myeloid leukemia and is not considered to be a part of the myeloid/lymphoid neoplasms with eosinophilia that was mentioned above. M4Eo shows a distinct translocation on chromosome 16 (inv(16) and t16;16), which leads to the fusion of the CBFB gene to the smooth muscle myosin heavy MYH111, resulting in the CBFB-MYH11 fusion gene [109,110]. This fusion disrupts normal hematopoiesis and bone development, leading to impaired hematopoietic maturation and leukemogenesis [109]. Clinically, patients with M4EO have symptoms, such as fever and weight loss, that are found with other categories of AML. However, this subcategory seems to present with organomegaly and is more common in younger patient populations [111,112,113]. There is a high index for suspicion for M4Eo when the peripheral smear exhibits 5–10% eosinophils with distinct large basophilic granules and the typical eosinophilic granules in bone marrow aspirations [109,110,112]. Further investigation via fluorescent in situ hybridization, PCR, and cytogenetic testing can clarify this diagnosis.
11.1. Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
Chronic myeloid leukemia is the result of a fusion gene product of the breakpoint cluster region gene with the Abelson murine leukemia viral oncogene homolog 1 gene (BCR-ABL1). The fusion of these two genes results from a chromosomal translocation known as the Philadelphia chromosome (Ph chromosome). The BCR-ABL1 fusion gene produces a protein with constitutive tyrosine kinase activity. This abnormal protein, known as BCR-ABL1 fusion protein, is a key driver in the development and progression of chronic myeloid leukemia [102]. The constitutive nature of the tyrosine kinase activity leads to uncontrolled cell growth and division, causing the overproduction of myeloid cells and, thus, eosinophilia in some cases [114]. The presentation for people with CML varies from asymptomatic to fatigue, weight loss, and abdominal fullness secondary to organomegaly [102].
11.2. Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis
Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH) is a poorly understood disorder characterized by focal or disseminated lesions containing excessive CD1a+ langerin+ cells with dendritic cell features [115]. It is thought to arise from hematopoietic precursor cells. However, the exact mechanism is, so far, unknown [115]. Pathology of these lesions often reveals prominent inflammatory infiltration of T cells and eosinophils [115]. There is a case report of eosinophilia with lymphadenopathy in a 5 year old male which was diagnosed as LCH after ruling out other causes of secondary eosinophilia [116]. No cause for the eosinophilia was determined in this case [116]. Two other cases of eosinophilia in LCH have previously been described [117,118].
11.3. Mastocytosis
Mastocytosis is a heterogenous group of disorders characterized by abnormal proliferation and accumulation of mast cells and mast cell progenitors in various organs [119,120]. The three primary variants are cutaneous mastocytosis, systemic mastocytosis, and mast cell sarcoma [119]. Systemic mastocytosis (SM) represents about 10% of all cases of mastocytosis [119]. There are four SM variants: indolent systemic mastocytosis, SM with associated clonal hematologic non-mast cell lineage disease, aggressive SM, and mast cell leukemia [120]. About 20–30% of SM have an associated clonal hematologic non-mast cell lineage disease [120]. SM can also be associated with a primary eosinophil disorder, such as hypereosinophilic syndrome or chronic eosinophilic leukemia [120]. Eosinophilia is seen in 14–21% of SM [121]. Systemic mastocytosis associated with sustained eosinophilia (SM-eo) is a poor prognostic indicator, with significantly reduced probability of overall and event-free survival compared to SM without eosinophilia [120,121]. There was no single type of SM that was associated with sustained eosinophilia, and none of the reported cases had associated disorders causing a reactive eosinophilia [120]. The relationship of eosinophilia and SM is uncertain. In some cases, a clonal relationship has been “convincingly proven” [121]. From a physiologic standpoint, mast cells are regulated by eosinophil cytokines and, in turn, some mast cell cytokines and mediators are known to prolong eosinophil viability [121]. SM-eo was more commonly associated with splenomegaly, hepatomegaly, absence of urticaria pigmentosa-like skin lesions, elevated serum tryptase level, and concurrent clonal hematologic non-mast cell lineage disease [120]. There is at least one case report of SM-eo associated with destructive bone lesions, including vertebral compression fractures [122]. SM-eo was separately associated with “smoldering” multiple myeloma [123].
11.4. Solid Tumor
In the setting of adenocarcinomas or benign growth, IL-5 stimulation and secretion can result in peripheral eosinophilia [124]. The stimulation of IL-5 and pro-eosinophilic cytokines results in eosinophilic infiltration into tumor tissues and promotes angiogenesis. Eosinophilia in these instances results in a pro-cancerogenic state through promotion of migrations through cytokines and chemokines, pervasive invasion, and immunosuppressive environment. Activated eosinophils have an autocrine positive feedback system and can produce interleukins that corroborate with inciting inflammatory effects, such as TNF, IL-1, IL-6, and IL-8. In the setting of known solid tumors, eosinophilia can be correlated with poorer outcomes in certain cancers, as has been found in relation to head and neck squamous cell carcinomas.
12. Allergic and Immunologic Processes
12.1. Idiopathic Hypereosinophilic Syndrome
Hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) is defined as a peripheral AEC of >1500 or tissue eosinophilia associated with tissue or organ injury directly attributable to eosinophil-related cytokines or enzymes [125]. A diagnosis of idiopathic HES (iHES) is made when an underlying cause cannot be identified for 6 months or more [125]. Due to improvements in genetic testing, many cases previously diagnosed as iHES have been identified as somatic mutations in a number of genes (ASXL1, TET2, TP53, etc.) [125]. While an underlying cause of iHUS has yet to be determined, it is noted that the disorder lacks convincing evidence of clonality or abnormal bone marrow morphology [125]. Bone marrow examination of these patients will often be unremarkable except for an increase in eosinophils. The presence of mast cell proliferations, which are clustered or spindly, should lead to a workup of systemic mastocytosis with eosinophilia [125]. Classically, iHES is diagnosed after AEC > 1500 for 6 months. However, it has been more recently diagnosed after 4 weeks or with a complete blood count showing persistent eosinophilia at two checks at least 2 weeks apart. This change acknowledges the long-term risk of tissue damage with untreated iHES [125]. Clinical symptoms may include nonspecific constitutional symptoms such as fever, fatigue, malaise, or myalgia. It can involve any organ system but less frequently affects the muscles, joints, nervous system, or endocrine organs. Long-term disease mortality ranges from 10 to 15% and is associated with age > 60 years, cardiac involvement, cytopenia, low absolute lymphocyte count, increased neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio, and hepatosplenomegaly [125].
12.2. Hyper IgE Syndrome (Job Syndrome)
Hyper IgE syndromes (HIES) are a diverse group of inborn errors of immunity that increase infection susceptibility and cause eczema-like dermatitis [126]. HIES are defined by the triad of elevated IgE, dermatitis, and recurrent skin and lung infections, and has been linked to several mutations, including STAT3, TYK2, PGM3, ZNF341, CARD11, and IL6ST [126]. The disease presents in 50% of patients within the first 2 weeks of life with a newborn papulopustular rash resembling neonatal acne [126]. Abscess formation is characteristically “cold”, lacking the calor of typical abscesses, and requires prolonged antibiotic courses [126]. These abscesses and the dermatitis are frequently colonized with Staphylococcus aureus [126]. Mucocutaneous candidal infections are also extremely common in this population [126]. Eosinophilia is seen in about 70% of patients with HIES [126]. The median age of diagnosis is 10.2 years [126].
12.3. Drug-Induced Eosinophilia
Drug-induced eosinophilia is poorly understood and varies by drug type. There are three main cytokines implicated in eosinophilopoeisis: granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), IL-3, and IL-5 [127]. Additionally, administration of IL-2, which stimulates IL-5 production, can cause eosinophilia. A study showed that plasma IL-5 levels rapidly increased after IL-2 administration but were undetectable prior, suggesting a temporal relationship with IL-2 infusions [128]. Other drugs may induce eosinophilia through type IVb hypersensitivity reactions due to Th2 mediated immune response with the release of IL-4, IL-13, and IL-5 [127]. Cutaneous reactions are the most common manifestation of drug hypersensitivity. However, only 18% of these reactions result in peripheral eosinophilia, and not all patients with eosinophilia develop cutaneous symptoms [129,130]. Drug-induced eosinophilia is a diagnosis of exclusion and other etiologies should be considered [127]. Careful history of drug administration should be taken when considering this diagnosis [127]. The most common medications associated with eosinophilia are antibiotics, antiepileptics, antidepressants, anti-inflammatories, sulfonamides/sulfones, antihypertensives, HIV medications, allopurinol, ranitidine, and cyclosporine [131].
12.4. Drug-Induced Hypersensitivity Syndrome
Drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome (DiHS), also known as drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), is a type of severe cutaneous adverse reaction (SCAR) which is a type IV hypersensitivity. While there is no clear demographic associated with DiHS, the average patient is 50 years old at diagnosis (range of 31–64 years old) [132]. In the pediatric population, the age range is normally between 9 and 10 years of age [132]. DiHS is characterized by exanthem, fever, abnormal blood counts (especially eosinophilia), and organ involvement due to inflammation.
The drug class most commonly associated with DiHS is anticonvulsants (namely, carbamazepine, phenytoin, phenobarbital, lamotrigine, and valproic acid), followed by antibiotics (minocycline, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, vancomycin, amoxicillin, and dapsone) [132]. According to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the top perpetrators were vancomycin, carbamazepine, lamotrigine, allopurinol, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. Outside the realm of pharmacotherapeutics, DiHS has also been caused by trichloroethylene, an industrial solvent, and iodinated contrast media [132].
There are three proposed mechanisms of action for activation of T-cells in DiHS. The first is a hapten/prohapten model in which the drug binds to an endogenous protein or peptide, forming a complex. This complex is presented as an antigen, triggering an immune response. The second model is the pharmacological interaction model in which the drug directly interacts with human leukocyte antigens (HLAs) and T-cell receptors (TCRs), which stimulate T-cell activation. The last model is the altered self-peptide repertoire model in which the drug binds to HLAs and TCRs, causing a change in their conformation which then allows the receptors to bind. This model suggests that the drug-induced changes lead to the activation of T-cells, contributing to the hypersensitivity reaction [132].
CD8+ cytotoxic T-cells predominate in early-stage DiHS while CD4 helper T-cells, Th1 and Th2, predominate in the late stage. Th2 then recruits and activates the eosinophils and releases granules that cause cytotoxic injury. In the resolution stage, T-reg cells become exhausted and shift toward Th17 cells. It is in the early stage that DiHS begins to differentiate itself from other SCAR syndromes, such as Stevens–Johnson syndrome. The CD8+ cytotoxic T-cells expand into T-regulatory cells in DiHS. T-regulatory cell expansion can cause immunosuppression and hypogammaglobulinemia, which will be followed by elevated IgE and eosinophil levels in 2–3 weeks. Due to the immunosuppressive nature of T-regulatory cells, patients are vulnerable to reactivation of viruses, in particular HHV-6 [132].
Cutaneous and systemic manifestations characterize DiHS. The syndrome typically initiates with pruritus and fever, followed by a diverse morbilliform eruption spreading from the upper trunk to the lower extremities. Facial edema and erythema, potentially related to elevated vascular endothelial growth factor levels, are distinctive of the disease. Systemically, DiHS can affect hematologic, renal, pulmonary, and cardiac organs. Hematologic involvement is marked by eosinophilia, fever, and lymphadenopathy. Hepatic involvement, the most common, is usually due to phenytoin, allopurinol, and antitubercular antibiotics. It is usually associated with an elevation of transaminases. Renal involvement is demonstrated by increased creatinine and is due to carbamazepine, dapsone, vancomycin, and allopurinol. Pulmonary involvement presents as interstitial pneumonitis and is associated with minocycline. Cardiac involvement is the most limited and often presents with elevated cardiac enzymes. Involvement may lead to acute necrotizing eosinophilic myocarditis and heart failure. Ampicillin and minocycline are the antibiotics with the greatest associated risk [132]. The onset typically occurs 2–6 weeks after drug exposure, with specific triggers associated with rapid onset. At present, there are only three proposed diagnostic criteria of DiHS: Bocquet et al., J-SCAR, and RegiSCAR. However, no criteria have demonstrated great accuracy in diagnosing DiHS [133].
12.5. Omenn Syndrome
Omenn syndrome (OS) is a form of severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) generally presenting in the first 8 weeks of life [134]. It is an autosomal recessive disorder typically associated with RAG1 or RAG2 and is part of general newborn screening [134]. It is characterized by exfoliative dermatitis, erythroderma, alopecia, lymphadenopathy (unlike classical SCID, which typically shows paucity or absence of lymph nodes), splenomegaly, and recurrent infections [134,135]. In the first year of life, it is often seen with diarrhea, pneumonitis (from Pneumocystis jiroveci or viruses such as cytomegalovirus or parainfluenza), and failure to thrive [135]. It is associated with a very poor prognosis due to opportunistic infections [134]. The thymus is dysplastic with few remnant lymphoid cells. However, unlike classical SCID, OS may present with normal or high lymphocyte counts [135]. The remaining T cell clones are predominantly Th2 and secrete IL-4, IL-9, IL-13, and IL-5, leading to eosinophilia [135].
13. Other Processes
Radiation Exposure
As radiation continues to grow as a neoadjuvant for immunomodulation, there have also been studies exploring radiation-related eosinophilia. It has been suggested that eosinophils are activated by irradiation, secondary to increased activity of CD8+ T cells within the tumor microenvironment, leading to peripheral demargination of eosinophils [136]. This abundance of eosinophils is primarily observed in the tumor microenvironment and is an important process in the anti-tumor response. However, it was found that intratumoral eosinophil abundance correlated with peripheral eosinophilia, as measured by CBC [136]. This was first observed in pelvic radiation, but has since been seen in nasopharyngeal carcinoma and non-small cell lung cancer [137].
Peripheral eosinophilia in the setting of radiation can also be seen with radiation injury. First, radiation can result in radiation pneumonitis. Thoracic radiotherapy is often used in breast, lung, and thoracic cancer. As a result of direct cytotoxicity and secondary fibrosis, the risk of radiation pneumonitis is directly related to the volume of lung irradiation and is also affected by dose [138]. Patients with radiation pneumonitis usually present with non-specific symptoms, such as cough, dyspnea, and fever, in the setting of radiation therapy [139]. Evaluation is usually a combination of clinical presentation and chest imaging, but pulmonary function tests (PFT) and bronchoscopy can also be used.
Although rare, there have been reported cases of radiation pneumonitis with eosinophilic alveolitis, resulting in peripheral eosinophilia. This has been reported primarily in patients receiving radiation for breast cancer and even, rarely, with lung cancer patients [140]. In these patients, the injury is seen on imaging to extend past the irradiated field. While in radiation pneumonitis, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid usually demonstrates non-specific lymphocytosis, in such cases of eosinophilic alveolitis, a predominance of eosinophils was observed. The mechanism of what causes eosinophilic alveolitis and subsequent peripheral eosinophilia is unclear, but it is suggested that there is a relationship with bronchial asthma. Many of the patients with radiation pneumonitis who subsequently develop eosinophilic alveolitis were found to have allergies or history of bronchial asthma. Radiation upregulates cytokines and activates Th2 inflammation. Type 1 hypersensitivity diseases have Th2 inflammation more easily [141].
Similarly, there have also been case reports illustrating chronic eosinophilic pneumonia (CEP) in patients, post-radiation. CEP is a rare eosinophilic lung disease that presents similarly to radiation pneumonitis. Patients often present with cough, fever, shortness of breath, and general malaise. Diagnosis requires a combination of clinical presentation, chest imaging, and bronchoalveolar lavage showing eosinophilia [142]. While CEP secondary to radiation itself is rare, with very little case reports published, peripheral blood eosinophilia is seen in 88 to 95% of patients with CEP [143].
14. Framework for Evaluation of Peripheral Eosinophilia
The evaluation of peripheral eosinophilia is complex and may involve numerous organ systems. As an aid to the differential diagnosis, we presented organ system-based evaluation flowsheets based on the most complex systems, the respiratory and integumentary systems. While not comprehensive, they may aid in the diagnosis of this complex condition. To aid in basic workup, we have also created a flowsheet inspired by a similar work by Curtis and Ogbogu, with modifications based on our literature review (Figure 5) [131].
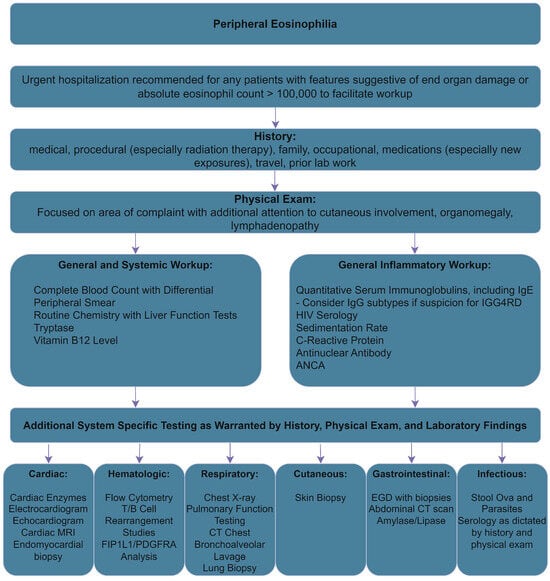
Figure 5.
Initial Workup of Peripheral Eosinophilia, adapted from [131].
The initial evaluation of unexplained eosinophilia should start with a thorough history and physical. Laboratory studies should involve a complete blood count and routine chemistry studies, including liver function tests, tryptase, B12 levels, and quantitative serum immunoglobulin levels, including IgE [127]. If IGG4RD is suspected, IgG subtypes can be considered as well. Serum troponin should also be measured and, if abnormal, cardiac MRI can be considered [127]. Imaging and functional studies that could be considered for the affected areas include computed tomography of affected areas, echocardiography, and pulmonary function testing [127]. For concerns of malignancy, bone marrow biopsy could be considered and further testing should be guided by the biopsy [127]. Additional testing of FIP1L1/PDGFRA by FISH or RT-PCR, flow cytometry, and T-/B-cell receptor rearrangement studies can be ordered [127].
15. Conclusions
Diseases presenting with peripheral eosinophilia are numerous. Evaluation requires careful balancing of clinicopathologic features as well as laboratory testing. Further research is needed to determine the role of eosinophilia in many of these diseases.
Author Contributions
M.D.W.—Vision and direction of the manuscript, with direct and significant contribution to all sections through literature review and editing. Creation of Figures and Tables. B.G.—Co-first author. Vision and direction of the manuscript, with direct and significant contribution to all sections through literature review and editing. Creation of Figures. C.A.—Direct contribution to multiple sections through editing and literature review. G.P.—Direct contribution to multiple sections through editing and literature review. J.M.—Contribution to literature review and review. I.W.—Contribution to literature review and review. S.D.—Vision and direction of manuscript, with direct contribution to all sections through editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
All authors report no relevant conflicts of interest.
References
- Chapman, J.; Zhang, Y. Histology, Hematopoiesis; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kanuru, S.; Sapra, A. Eosinophilia; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Park, Y.M.; Bochner, B.S. Eosinophil survival and apoptosis in health and disease. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2010, 2, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, G.; Gogia, A.; Kakar, A.; Miglani, P. Persistent Marked Peripheral Eosinophilia due to Tuberculosis: A Case Report. Iran. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 42, 102–105. [Google Scholar]
- Radonjic-Hoesli, S.; Brüggen, M.C.; Feldmeyer, L.; Simon, H.U.; Simon, D. Eosinophils in skin diseases. Semin. Immunopathol. 2021, 43, 393–409. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, D.K.; Schneider, L.; Asiniwasis, R.N.; Boguniewicz, M.; De Benedetto, A.; Ellison, K.; Frazier, W.T.; Greenhawt, M.; Huynh, J.; Kim, E.; et al. Atopic dermatitis (eczema) guidelines: 2023 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology/American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology Joint Task Force on Practice Parameters GRADE– and Institute of Medicine–based recommendations. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2023, 132, 274–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiferman, K.M. Eosinophils in atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1994, 94 Pt 2, 1310–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, D.; Braathen, L.R.; Simon, H.U. Eosinophils and atopic dermatitis. Allergy 2004, 59, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celakovska, J.; Bukac, J.; Ettler, K.; Vaneckova, J.; Krcmova, I.; Ettlerova, K.; Krejsek, J. Evaluation of Peripheral Blood Eosinophilia in Adolescent and Adult Patients Suffering from Atopic Dermatitis and the Relation to the Occurrence of Allergy to Aeroallergens. Indian. J. Dermatol. 2019, 64, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, B.L.; DeLeo, V.A. Allergic Contact Dermatitis. JAMA Dermatol. 2021, 157, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haussmann, J.; Pratt, M.; Linett, L.; Zimmerman, D. Allergic contact dermatitis and eosinophilia in association with a hemodialysis cannula. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2005, 45, e23–e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloréns Herrerias, J.; Delgado Navarro, C.; Ballester Luján, M.T.; Izquierdo Palomares, A. Long-term allergic dermatitis caused by sevoflurane: A clinical report. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2014, 58, 1151–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos-González, M.; Velasco Rodriguez, D.; Blanco Echevarría, A.; Postigo, C.; Ortiz Romero, P.; Díaz, R.A.; Rodriguez-Peralto, J.L. Eosinophilic fasciitis as a manifestation of a cutaneous T-cell lymphoma not otherwise specified. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 2013, 35, 666–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, M.; Nissen, M.H.; Gerwien, J.; Zocca, M.B.; Rasmussen, H.M.; Nakajima, K.; Röpke, C.; Geisler, C.; Kaltoft, K.; Ødum, N. Spontaneous interleukin-5 production in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma lines is mediated by constitutively activated Stat3. Blood 2002, 99, 973–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borish, L.; Dishuck, J.; Cox, L.; Mascali, J.J.; Williams, J.; Rosenwasser, L.J. Sézary syndrome with elevated serum IgE and hypereosinophilia: Role of dysregulated cytokine production. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1993, 92 Pt 1, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinno, H.; Lacroix, J.P.; Lee, J.; Izadpanah, A.; Borsuk, R.; Watters, K.; Gilardino, M. Diagnosis and management of eosinophilic cellulitis (Wells’ syndrome): A case series and literature review. Can. J. Plast. Surg. 2012, 20, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, P.; Herold, J.; Alpaugh, A.; Dinerman, E.; Holland-Thomas, N.; Stoddard, J.; Gurprasad, S.; Maric, I.; Simakova, O.; Schwartz, L.B.; et al. Episodic angioedema with eosinophilia (Gleich syndrome) is a multilineage cell cycling disorder. Haematologica. 2015, 100, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, J.A.; Bochner, B.S. Eosinophils and eosinophil-associated diseases: An update. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messingham, K.N.; Crowe, T.P.; Fairley, J.A. The Intersection of IgE Autoantibodies and Eosinophilia in the Pathogenesis of Bullous Pemphigoid. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2331. [Google Scholar]
- Kridin, K. Peripheral eosinophilia in bullous pemphigoid: Prevalence and influence on the clinical manifestation. Br. J. Dermatol. 2018, 179, 1141–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaraa, I.; Sellami, A.; Bouguerra, C.; Sellami, M.; Chelly, I.; Zitouna, M.; Makni, S.; Hmida, A.; Mokni, M.; Osman, A. Pemphigus vegetans: A clinical, histological, immunopathological and prognostic study. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2011, 25, 1160–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laws, P.M.; Heelan, K.; Al-Mohammedi, F.; Walsh, S.; Shear, N.H. Pemphigus herpetiformis: A case series and review of the literature. Int. J. Dermatol. 2015, 54, 1014–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curto-Barredo, L.; Segura, S.; Ishii, N.; Hashimoto, T.; Mascaró, J.M., Jr.; Espinet, B.; Besses, C.; Pujol, R.M. Pemphigus-like hypereosinophilic syndrome with FIP1L1-PDGFRA fusion gene: A challenging and uncommon clinical presentation. J. Dermatol. 2019, 46, 531–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sufyan, W.; Tan, K.B.; Wong, S.T.; Lee, Y.S. Eosinophilic pustular folliculitis. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2007, 131, 1598–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foocharoen, C.; Mahakkanukrauh, A.; Maleewong, P.; Maleewong, W.; Jumnainsong, A.; Pongkulkiat, P.; Teawtrakul, N.; Suwannaroj, S.; Nanagara, R. Prevalence of peripheral eosinophilia and clinical associations in systemic sclerosis patients. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 363, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punjasamanvong, S.; Muangchan, C. Persistent eosinophilia and associated organ involvement in Thai patients with systemic sclerosis: Data from the Siriraj scleroderma cohort. Arch. Rheumatol. 2021, 36, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, T.; Ikeda, T.; Inaba, Y.; Kunimoto, K.; Mikita, N.; Kaminaka, C.; Kanazawa, N.; Yamamoto, Y.; Tabata, K.; Fujii, T.; et al. Peripheral blood eosinophilia is associated with the presence of skin ulcers in patients with systemic sclerosis. J. Dermatol. 2019, 46, 334–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howarth, P.H. Eosinophils and rhinitis. Clin. Exp. Allergy Rev. 2005, 5, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, L.J.; Platts-Mills, T.A.E.; Douglas Phillips, C.; Hazen, K.C.; Gross, C.W. Chronic Sinusitis: Relationship of Computed Tomographic Findings to Allergy, Asthma, and Eosinophilia. JAMA 1994, 271, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, N.; Fried, M.P. Peripheral eosinophilia in the diagnosis of chronic rhinosinusitis. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2001, 22, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laidlaw, T.M.; Mullol, J.; Woessner, K.M.; Amin, N.; Mannent, L.P. Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps and Asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevaert, P.; Han, J.K.; Smith, S.G.; Sousa, A.R.; Howarth, P.H.; Yancey, S.W.; Chan, R.; Bachert, C. The roles of eosinophils and interleukin-5 in the pathophysiology of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2022, 12, 1413–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissler, J.C. Eosinophilic Lung Disease. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 354, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Giacomi, F.; Vassallo, R.; Yi, E.S.; Ryu, J.H. Acute Eosinophilic Pneumonia. Causes, Diagnosis, and Management. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 197, 728–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, R.; White, A.A.; Jackson, D.J.; Hopkins, C. Clinical evaluation and diagnosis of aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 148, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsia, J.; Sarin, N.; Oliver, J.H.; Goldstein, A.L. Aspirin and thymosin increase interleukin-2 and interferon-gamma production by human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Immunopharmacology 1989, 17, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinke, J.W.; Negri, J.; Liu, L.; Payne, S.C.; Borish, L. Aspirin activation of eosinophils and mast cells: Implications in the pathogenesis of aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walford, H.H.; Doherty, T.A. Diagnosis and management of eosinophilic asthma: A US perspective. J. Asthma Allergy 2014, 7, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tabèze, L.; Marchand-Adam, S.; Borie, R.; Justet, A.; Dupin, C.; Dombret, M.-C.; Crestani, B.; Taillé, C. Severe asthma with blood hypereosinophilia associated with JAK2 V617F mutation: A case series. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1802248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sisodia, J.; Bajaj, T. Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Rhee, C.K.; Min, K.H.; Yim, N.Y.; Lee, J.E.; Lee, N.R.; Chung, M.P.; Jeon, K. Clinical characteristics and corticosteroid treatment of acute eosinophilic pneumonia. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 41, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bafadhel, M.; McKenna, S.; Terry, S.; Mistry, V.; Reid, C.; Haldar, P.; McCormick, M.; Haldar, K.; Kebadze, T.; Duvoix, A.; et al. Acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Identification of biologic clusters and their biomarkers. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 184, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D. Blood Eosinophil Counts in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Biomarker of Inhaled Corticosteroid Effects. Tuberc. Respir. Dis. 2020, 83, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolsum, U.; Ravi, A.; Hitchen, P.; Maddi, S.; Southworth, T.; Singh, D. Clinical characteristics of eosinophilic COPD versus COPD patients with a history of asthma. Respir. Res. 2017, 18, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, S.H.; Guasconi, A.; Vestbo, J.; Jones, P.; Agusti, A.; Paggiaro, P.; Wedzicha, J.A.; Singh, D. Blood Eosinophils: A Biomarker of Response to Extrafine Beclomethasone/Formoterol in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 192, 523–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashkin, D.P.; Wechsler, M.E. Role of eosinophils in airway inflammation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2018, 13, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verleden, S.E.; Ruttens, D.; Vandermeulen, E.; van Raemdonck, D.E.; Vanaudenaerde, B.M.; Verleden, G.M.; Vos, R. Elevated bronchoalveolar lavage eosinophilia correlates with poor outcome after lung transplantation. Transplantation 2014, 97, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verleden, S.E.; Ruttens, D.; Vandermeulen, E.; Bellon, H.; Dubbeldam, A.; De Wever, W.; Dupont, L.J.; Van Raemdonck, D.E.; Vanaudenaerde, B.M.; Verleden, G.M.; et al. Predictors of survival in restrictive chronic lung allograft dysfunction after lung transplantation. J. Hear. Lung Transplant. 2016, 35, 1078–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brambatti, M.; Matassini, M.V.; Adler, E.D.; Klingel, K.; Camici, P.G.; Ammirati, E. Eosinophilic Myocarditis: Characteristics, Treatment, and Outcomes. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 2363–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, H.; Siddiqui, M.; Uddin, S.M.M.; Haq, A.; Yaqoob, U. The Clinicopathological Profile of Eosinophilic Myocarditis. Cureus 2018, 10, e3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Techasatian, W.; Gozun, M.; Vo, K.; Yokoyama, J.; Nagamine, T.; Shah, P.; Vu, K.; Zhang, J.; Nishimura, Y. Eosinophilic myocarditis: Systematic review. Heart 2023. [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, C.E.; Kakkar, E.; Dreskin, S.C.; Allen, L.A.; Groves, D.W.; Altman, N.L. Allergy and the Heart: Eosinophilic Myocarditis with Biventricular Thrombi. JACC Case Rep. 2020, 2, 1942–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochida, Y.; Ohtake, T.; Ishioka, K.; Oka, M.; Maesato, K.; Moriya, H.; Hidaka, S.; Kobayashi, S. Association between eosinophilia and renal prognosis in patients with pathologically proven cholesterol crystal embolism. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2020, 24, 680–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasinath, B.S.; Lewis, E.J. Eosinophilia as a clue to the diagnosis of atheroembolic renal disease. Arch. Intern. Med. 1987, 147, 1384–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecioni, I.; Fassio, F.; Gori, S.; Giudizi, M.G.; Romagnani, S.; Almerigogna, F. Eosinophilia in cholesterol atheroembolic disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 120, 1470–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lwin, T.; Melton, S.D.; Genta, R.M. Eosinophilic gastritis: Histopathological characterization and quantification of the normal gastric eosinophil content. Mod. Pathol. 2011, 24, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, E.J.; Greenberg, S.B.; Chang, N.C.; Corder, S.R.; Cowherd, E.L.; Dellon, E.S. Peripheral eosinophilia and hypoalbuminemia are associated with a higher biopsy diagnostic yield for eosinophilic gastroenteritis. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2021, 45, 101746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.H.; Anderson, L.; Zhang, K.; Weiss, G.A. Eosinophilic Gastritis/Gastroenteritis. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2021, 23, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, Y. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis: A state-of-the-art review. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 32, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, Y.; Furuta, K.; Ishimaura, N.; Ishihara, S.; Sato, S.; Maruyama, R.; Ohara, S.; Matsumoto, T.; Sakamoto, C.; Matsui, T.; et al. Clinical characteristics of Japanese patients with eosinophilic esophagitis and eosinophilic gastroenteritis. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 48, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuss, H.J.; Jungkunz, G. Nonlinear pharmacokinetics of chlorimipramine after infusion and oral administration in patients. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 1986, 10, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehman, H.K.; Lam, W. Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 66, 955–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffner, M.A.; Shoda, T.; Lal, M.; Mrozek, Z.; Muir, A.B.; Spergel, J.M.; Dellon, E.S.; Rothenberg, M.E. Persistent Esophageal Changes Following Histologic Remission in Eosinophilic Esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Muftah, M.; Barshop, K.; Redd, W.D.; Goldin, A.H.; Lo, W.K.; Chan, W.W. Baseline Peripheral Eosinophil Count Independently Predicts Proton Pump Inhibitor Response in Eosinophilic Esophagitis. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2023, 58, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaurrany, M.R.; Akil, M.A.; Punagi, A.Q.; Parewangi, A.M.L. Clinical profile and characteristics of eosinophilic esophagitis patients presenting with refractory gastroesophageal reflux disease in Makassar, Indonesia. Pan. Afr. Med. J. 2022, 41, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okpara, N.; Aswad, B.; Baffy, G. Eosinophilic colitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 2975–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfadda, A.A.; Storr, M.A.; Shaffer, E.A. Eosinophilic colitis: Epidemiology, clinical features, and current management. Therap Adv. Gastroenterol. 2011, 4, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haasnoot, M.L.; Mookhoek, A.; Duijvestein, M.; D’Haens, G.R.A.M.; Bredenoord, A.J. Prognostic Value of Colonic Tissue and Blood Eosinophils in Ulcerative Colitis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2023, 29, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manohar, M.; Kandikattu, H.K.; Upparahalli Venkateshaiah, S.; Yadavalli, C.S.; Mishra, A. Eosinophils in the pathogenesis of pancreatic disorders. Semin. Immunopathol. 2021, 43, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Fu, P.; Dong, X.; Qi, J.; Zhu, H. Eosinophilic pancreatitis: Three case reports and literature review. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 4, 559–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Pan, D.; Kang, K.; Sun, M.-J.; Li, Y.-L.; Sang, L.-X.; Chang, B. Eosinophilic pancreatitis: A review of the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2021, 9, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandikattu, H.K.; Manohar, M.; Verma, A.K.; Kumar, S.; Yadavalli, C.S.; Venkateshaiah, S.U.; Mishra, A. Macrophages-induced IL-18-mediated eosinophilia promotes characteristics of pancreatic malignancy. Life Sci. Alliance 2021, 4, e202000979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manohar, M.; Verma, A.K.; Venkateshaiah, S.U.; Mishra, A. Role of eosinophils in the initiation and progression of pancreatitis pathogenesis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2018, 314, G211–G222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agawa, S.; Futagami, S.; Yamawaki, H.; Tsushima, R.; Higuchi, K.; Habiro, M.; Kawawa, R.; Kodaka, Y.; Ueki, N.; Watanabe, Y.; et al. Trypsin may be associated with duodenal eosinophils through the expression of PAR2 in early chronic pancreatitis and functional dyspepsia with pancreatic enzyme abnormalities. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0275341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokoo, M.; Oguchi, H.; Kawa, S.; Homma, T.; Nagata, A. Eosinophilia associated with chronic pancreatitis: An analysis of 122 patients with definite chronic pancreatitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1992, 87, 455–460. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Lu, C.M.; Guo, T.; Qian, J.M. Eosinophilia associated with chronic pancreatitis. Pancreas 2009, 38, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huecker, M.R.; Bhutta, B.S.; Dominique, E. Adrenal Insufficiency; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Spry, C. Eosinophilia in Addison’s disease. Yale J. Biol. Med. 1976, 49, 411–413. [Google Scholar]
- Boyer, M.H.; Basten, A.; Beeson, P.B. Mechanism of Eosinophilia. III. Suppression of Eosinophilia by Agents Known to Modify Immune Responses. Blood 1970, 36, 458–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuichi, N.; Naganuma, A.; Kaburagi, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Hoshino, T.; Shibusawa, N.; Horiguchi, S.; Hatanaka, T.; Kakizaki, S.; Uraoka, T. Three cases of immune-related hypopituitarism after atezolizumab-bevacizumab treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 16, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.C.; Lin, H.D.; Huang, C.Y.; Chiang, Y.L. Unusual manifestations of adrenal insufficiency: A case report of hypopituitarism and Well’s syndrome after apoplexy of a silent pituitary gonadotropic adenoma. Medicine 2022, 101, e29274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratarasarn, C.; Rajatanavin, R.; Himathongkam, T. Salient clinical features of Sheehan’s syndrome. J. Med. Assoc. Thai. 1989, 72, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tamaki, H.; Chatterjee, S.; Langford, C.A. Eosinophilia in Rheumatologic/Vascular Disorders. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2015, 35, 453–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cottin, V.; Bel, E.; Bottero, P.; Dalhoff, K.; Humbert, M.; Lazor, R.; Sinico, R.A.; Sivasothy, P.; Wechsler, M.E.; Groh, M.; et al. Revisiting the systemic vasculitis in eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Churg-Strauss): A study of 157 patients by the Groupe d’Etudes et de Recherche sur les Maladies Orphelines Pulmonaires and the European Respiratory Society Taskforce on eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Churg-Strauss). Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Murag, S.; Melehani, J.; Filsoof, D.; Nadeau, K.; Sharon Chinthrajah, R. Dupilumab unmasks eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Chest 2021, 160, A8–A9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, B.; Zhong, J.; Dong, L. Role of eosinophilia in IgG4-related disease. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2022, 40, 1038–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culver, E.L.; Sadler, R.; Bateman, A.C.; Makuch, M.; Cargill, T.; Ferry, B.; Aalberse, R.; Barnes, E.; Rispens, T. Increases in IgE, Eosinophils, and Mast Cells Can be Used in Diagnosis and to Predict Relapse of IgG4-Related Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, 1444–1452.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakhanpal, S.; Ginsburg, W.W.; Michet, C.J.; Doyle, J.A.; Moore, S.B. Eosinophilic fasciitis: Clinical spectrum and therapeutic response in 52 cases. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 1988, 17, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danis, R.; Akbulut, S.; Altintas, A.; Ozmen, S.; Ozmen, C.A. Unusual presentation of eosinophilic fasciitis: Two case reports and a review of the literature. J. Med. Case Rep. 2010, 4, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, J.A.; Peterson, A.; Sufit, R.; Hinchcliff, M.E.; Mahoney, J.M.; Wood, T.A.; Miller, F.W.; Whitfield, M.L.; Varga, J. Post-epidemic eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome associated with L-tryptophan. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 3633–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, E.M.; Nutman, T.B. Eosinophilia in Infectious Diseases. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2015, 35, 493–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, N.M.; Lambert, J.; Ali, S.; Beer, P.A.; Cross, N.C.P.; Duncombe, A.; Ewing, J.; Harrison, C.N.; Knapper, S.; McLornan, D.; et al. Guideline for the investigation and management of eosinophilia. Br. J. Haematol. 2017, 176, 553–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrotra, S.; Dhiman, R.K.; Sircar, A.R. Hyper-eosinophilic syndrome with lepromatous leprosy. J. Assoc. Physicians India 1988, 36, 287–288. [Google Scholar]
- Vinod, K.V.; Arun, K.; Dutta, T.K. Dapsone hypersensitivity syndrome: A rare life threatening complication of dapsone therapy. J. Pharmacol. Pharmacother. 2013, 4, 158–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, A.; Serpa, J.A. Eosinophilia in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus. Curr. HIV/AIDS Rep. 2015, 12, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, F.; Medeiros, L.J.; Bueso-Ramos, C.E.; Arboleda, P.; Miranda, R.N. Hematolymphoid neoplasms associated with rearrangements of PDGFRA, PDGFRB, and FGFR1. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2015, 144, 377–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Rech, K.L.; Otteson, G.E.; Horna, P.; Olteanu, H.; Pardanani, A.; Chen, D.; Jevremovic, D. Prevalence and spectrum of T-cell lymphoproliferative disorders in patients with Hypereosinophilia: A reference laboratory experience. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2020, 44, 151412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferruzzi, V.; Santi, E.; Gurdo, G.; Arcioni, F.; Caniglia, M.; Esposito, S. Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia with Hypereosinophilia in a Child: Case Report and Literature Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalejaiye, O.O.; Amaeshi, L.C.; Banjoko, O.O. Unusual Case of Hypereosinophilia in Hodgkin Lymphoma in a Nigerian Woman. AIM Clin. Cases 2024, 3, e230012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, P.; Khan, W.A. Myeloid/Lymphoid Neoplasms with Eosinophilia and Platelet Derived Growth Factor Receptor Alpha (PDGFRA) Rearrangement. In Leukemia; Li, W., Ed.; Exon Publications: Brisbane, Australia, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Pozdnyakova, O.; Orazi, A.; Kelemen, K.; King, R.; Reichard, K.K.; Craig, F.E.; Quintanilla-Martinez, L.; Rimsza, L.; George, T.I.; Horny, H.P.; et al. Myeloid/Lymphoid Neoplasms Associated with Eosinophilia and Rearrangements of PDGFRA, PDGFRB, or FGFR1 or with PCM1-JAK2. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2021, 155, 160–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, A.; Gotlib, J. Myeloid neoplasms with eosinophilia. Blood 2017, 129, 704–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bain, B.J. Myeloid and lymphoid neoplasms with eosinophilia and abnormalities of PDGFRA, PDGFRB or FGFR1. Haematologica 2010, 95, 696–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shomali, W.; Colucci, P.; George, T.I.; Kiladjian, J.-J.; Langford, C.; Patel, J.L.; Reiter, A.; Vannucchi, A.M.; Gotlib, J. Comprehensive response criteria for myeloid/lymphoid neoplasms with eosinophilia and tyrosine kinase gene fusions: A proposal from the MLN International Working Group. Leukemia 2023, 37, 981–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, Z.; Wen, L.; Zhang, L.; Chen, S. Case Report: A novel FGFR1 fusion in acute B-lymphoblastic leukemia identified by RNA sequencing. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1276695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urrea Pineda, L.Y.; Perilla, O.; Santiago-Pacheco, V.; Trujillo Montoya, S. Myeloproliferative Syndrome With Eosinophilia Associated With Translocation t(8; 13) and T-cell Lymphoblastic Lymphoma: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Cureus 2022, 14, e22734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, X.; Deng, J.; Yu, H.; Xu, R.; Zhu, Z.; Tu, S.; Hu, Y. Diagnostic application of next-generation sequencing in ZMYM2-FGFR1 8p11 myeloproliferative syndrome: A case report. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2016, 17, 785–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gerds, A.T.; Gotlib, J.; Bose, P.; Deininger, M.W.; Dunbar, A.; Elshoury, A.; George, T.I.; Gojo, I.; Gundabolu, K.; Hexner, E.; et al. Myeloid/Lymphoid Neoplasms with Eosinophilia and TK Fusion Genes, Version 3.2021, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Canc Netw. 2020, 18, 1248–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangaru, Z.; Shetty, S.; Visconte, V.; Liu, H.D.; Rogers, H.J. Acute myeloid leukemia with inv(16)(p13.1q22), abnormal eosinophils, and absence of peripheral blood and bone marrow blasts. Am. J. Hematol. 2016, 91, E273–E274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiffer, C.A.; Stone, R.M. Morphologic Classification and Clinical and Laboratory Correlates; BC Deckerl: Hamilton, ON, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Bahoush, G.; Vafapour, M.; Kariminejad, R. New translocation in acute myeloid leukemia M4 eos. Leuk. Res. Rep. 2020, 14, 100209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.T.; Hsieh, Y.C.; Lee, L.P.; Tzeng, C.C.; Chuang, S.S. Acute myelomonocytic leukemia with abnormal eosinophils: A case report with multi-modality diagnostic work-up. Chang. Gung Med. J. 2006, 29, 532–537. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Adriaansen, H.J.; te Boekhorst, P.A.; Hagemeijer, A.M.; van der Schoot, C.E.; Delwel, H.R.; van Dongen, J.J. Acute myeloid leukemia M4 with bone marrow eosinophilia (M4Eo) and inv(16)(p13q22) exhibits a specific immunophenotype with CD2 expression. Blood 1993, 81, 3043–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haseyama, Y.; Takeda, Y.; Kumano, K. Chronic myeloid leukemia presenting with marked eosinophilia. Rinsho Ketsueki. 2018, 59, 2594–2599. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Egeler, R.M.; Katewa, S.; Leenen, P.J.M.; Beverley, P.; Collin, M.; Ginhoux, F.; Arceci, R.J.; Rollins, B.J. Langerhans cell histiocytosis is a neoplasm and consequently its recurrence is a relapse: In memory of Bob Arceci. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2016, 63, 1704–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastogi, N.; Yadav, S.P. Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis Masquerading as Hypereosinophilia in a Child. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 41, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parambil, A.S.P.; Prem, S.; Jacob, P.M.; Nair, R.A. Mediastinal Mass with Hyper-eosinophilia in a Young Boy -A Diagnostic Dilemma. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, XD03–XD04. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohnishi, H.; Kandabashi, K.; Maeda, Y.; Kawamura, M.; Watanabe, T. Chronic eosinophilic leukaemia with FIP1L1-PDGFRA fusion and T6741 mutation that evolved from Langerhans cell histiocytosis with eosinophilia after chemotherapy. Br. J. Haematol. 2006, 134, 547–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozturk, K.; Cayci, Z.; Gotlib, J.; Akin, C.; George, T.I.; Ustun, C. Non-hematologic diagnosis of systemic mastocytosis: Collaboration of radiology and pathology. Blood Rev. 2021, 45, 100693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böhm, A.; Födinger, M.; Wimazal, F.; Haas, O.A.; Mayerhofer, M.; Sperr, W.R.; Esterbauer, H.; Valent, P. Eosinophilia in systemic mastocytosis: Clinical and molecular correlates and prognostic significance. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 120, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kluin-Nelemans, H.C.; Reiter, A.; Illerhaus, A.; van Anrooij, B.; Hartmann, K.; Span, L.F.R.; Gorska, A.; Niedoszytko, M.; Lange, M.; Scaffidi, L.; et al. Prognostic impact of eosinophils in mastocytosis: Analysis of 2350 patients collected in the ECNM Registry. Leukemia 2020, 34, 1090–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakane-Ishikawa, E.; Kodaka, T.; Tsunemine, H.; Itoh, K.; Akasaka, H.; Kusama, T.; Imaizumi, K.; Taketomi, M.; Sada, A.; Katayama, Y.; et al. Eosinophilia and bone lesion as clinical manifestations of aggressive systemic mastocytosis. J. Clin. Exp. Hematop. 2013, 53, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zanelli, M.; Ricci, S.; Zizzo, M.; Sanguedolce, F.; De Giorgi, F.; Palicelli, A.; Martino, G.; Ascani, S. Systemic Mastocytosis Associated with “Smoldering” Multiple Myeloma. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.L.; Chen, T.H.; Kuo, Y.J.; Lan, H.Y.; Yang, M.H.; Chu, P.Y. Tumor-associated tissue eosinophilia promotes angiogenesis and metastasis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Neoplasia 2023, 35, 100855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.A.; Orazi, A.; Gotlib, J.; Reiter, A.; Tzankov, A.; Hasserjian, R.P.; Arber, D.A.; Tefferi, A. The international consensus classification of eosinophilic disorders and systemic mastocytosis. Am. J. Hematol. 2023, 98, 1286–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsilifis, C.; Freeman, A.F.; Gennery, A.R. STAT3 Hyper-IgE Syndrome-an Update and Unanswered Questions. J. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 41, 864–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauscher, C.; Freeman, A. Drug-induced eosinophilia. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2018, 39, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Haelst Pisani, C.; Kovach, J.S.; Kita, H.; Leiferman, K.M.; Gleich, G.J.; Silver, J.E.; Dennin, R.; Abrams, J.S. Administration of interleukin-2 (IL-2) results in increased plasma concentrations of IL-5 and eosinophilia in patients with cancer. Blood 1991, 78, 1538–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichler, W.J. Delayed drug hypersensitivity reactions. Ann. Intern. Med. 2003, 139, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romagosa, R.; Kapoor, S.; Sanders, J.; Berman, B. Inpatient adverse cutaneous drug eruptions and eosinophilia. Arch. Dermatol. 2001, 137, 511–512. [Google Scholar]
- Curtis, C.; Ogbogu, P.U. Evaluation and Differential Diagnosis of Persistent Marked Eosinophilia. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2015, 35, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, B.M.; Fox, L.P.; Kaffenberger, B.H.; Korman, A.M.; Micheletti, R.G.; Mostaghimi, A.; Noe, M.H.; Rosenbach, M.; Shinkai, K.; Kwah, J.H.; et al. Drug-induced Hypersensitivity Syndrome/Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms. Part, I. Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Clinicopathological Features, and Prognosis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, B.M.; Fox, L.P.; Kaffenberger, B.H.; Korman, A.M.; Micheletti, R.G.; Mostaghimi, A.; Noe, M.H.; Rosenbach, M.; Shinkai, K.; Kwah, J.H.; et al. Drug-induced Hypersensitivity Syndrome/Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms. Part II. Diagnosis and Management. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutts, L.; Bakshi, A.; Walsh, M.; Parslew, R.; Eustace, K. Diagnosing Omenn syndrome. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2021, 38, 541–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, A.; Notarangelo, L.D.; Roifman, C.M. Omenn syndrome: Inflammation in leaky severe combined immunodeficiency. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 122, 1082–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.-N.; Luo, W.; Sun, C.; Jin, Z.; Zeng, X.; Alexander, P.B.; Gong, Z.; Xia, X.; Ding, X.; Xu, S.; et al. Radiation-induced eosinophils improve cytotoxic T lymphocyte recruitment and response to immunotherapy. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabc7609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghossein, N.A.; Bosworth, J.L.; Stacey, P.; Muggia, F.M.; Krishnaswamy, V. Radiation-related eosinophilia. Correlation with delayed hypersensitivity, lymphocyte count, and survival in patients treated by curative radiotherapy. Radiology 1975, 117, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marks, L.B.; Bentzen, S.M.; Deasy, J.O.; Kong, F.-M.; Bradley, J.D.; Vogelius, I.S.; El Naqa, I.; Hubbs, J.L.; Lebesque, J.V.; Timmerman, R.D.; et al. Radiation dose-volume effects in the lung. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2010, 76 (Suppl. S3), S70–S76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahi, M.S.; Parekh, J.; Pednekar, P.; Parmar, G.; Abraham, S.; Nasir, S.; Subramaniyam, R.; Jeyashanmugaraja, G.P.; Gunasekaran, K. Radiation-Induced Lung Injury-Current Perspectives and Management. Clin. Pract. 2021, 11, 410–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosono, Y.; Sawa, N.; Nakatsubo, S.; Ishijima, M.; Uenami, T.; Kanazu, M.; Akazawa, Y.; Yano, Y.; Mori, M.; Yamaguchi, T.; et al. Radiation Pneumonitis with Eosinophilic Alveolitis in a Lung Cancer Patient. Intern. Med. 2018, 57, 1281–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akuthota, P.; Weller, P.F. Eosinophilic pneumonias. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayasu, H.; Shirai, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Saigusa, M. Chronic eosinophilic pneumonia after radiation therapy for squamous cell lung cancer. Respir. Med. Case Rep. 2017, 22, 147–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchand, E.; Reynaud-Gaubert, M.; Lauque, D.; Durieu, J.; Tonnel, A.B.; Cordier, J.F. Idiopathic chronic eosinophilic pneumonia. A clinical and follow-up study of 62 cases. The Groupe d’Etudes et de Recherche sur les Maladies “Orphelines” Pulmonaires (GERM“O”P). Medicine 1998, 77, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).