Light Chain Stabilization: A Therapeutic Approach to Ameliorate AL Amyloidosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
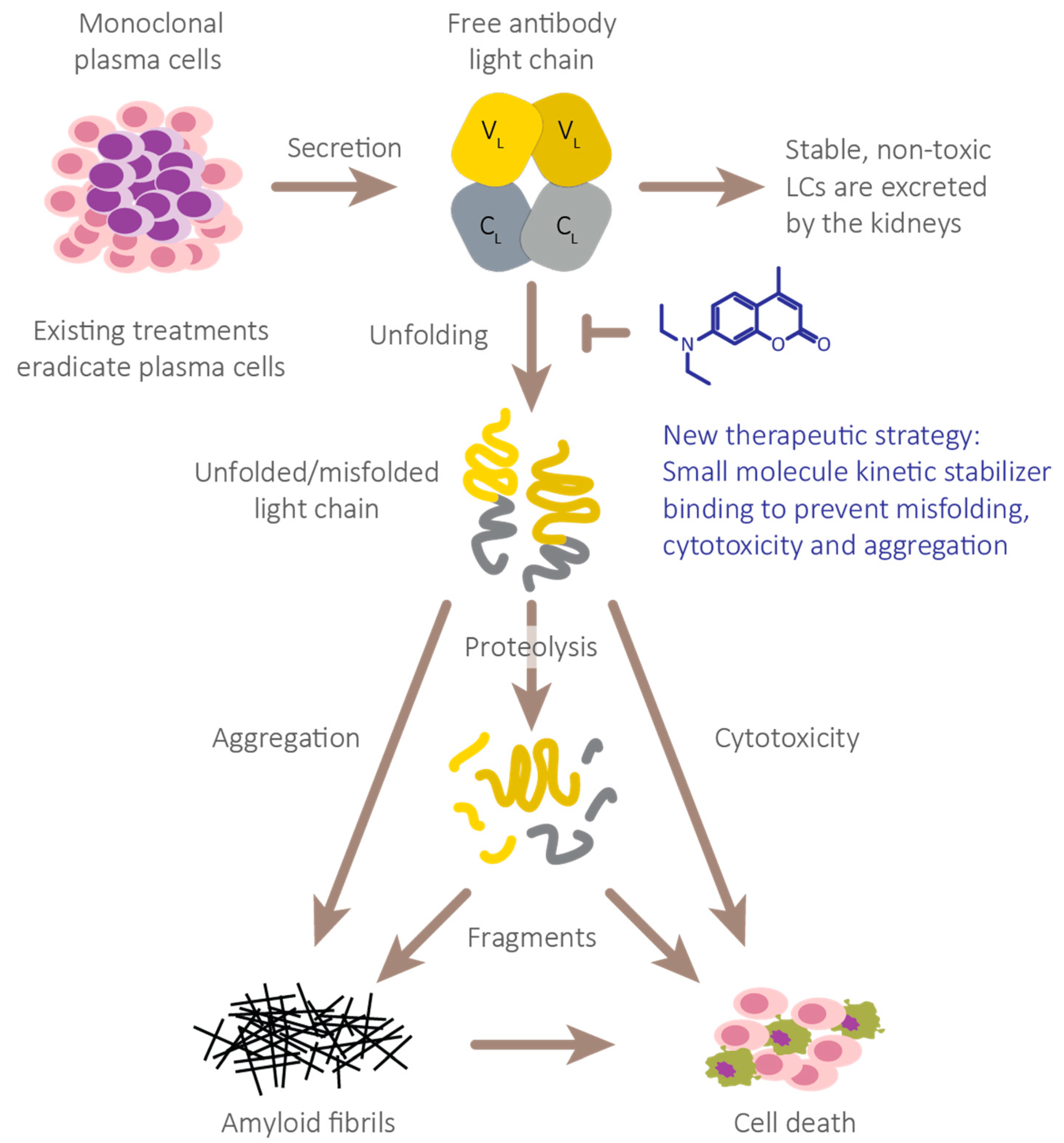
2. AL Amyloid Is Assembled from Non-Natively Folded LC Peptides
3. (Kinetic) Stability as a Measurable, Unifying Parameter to Define LC Toxicity
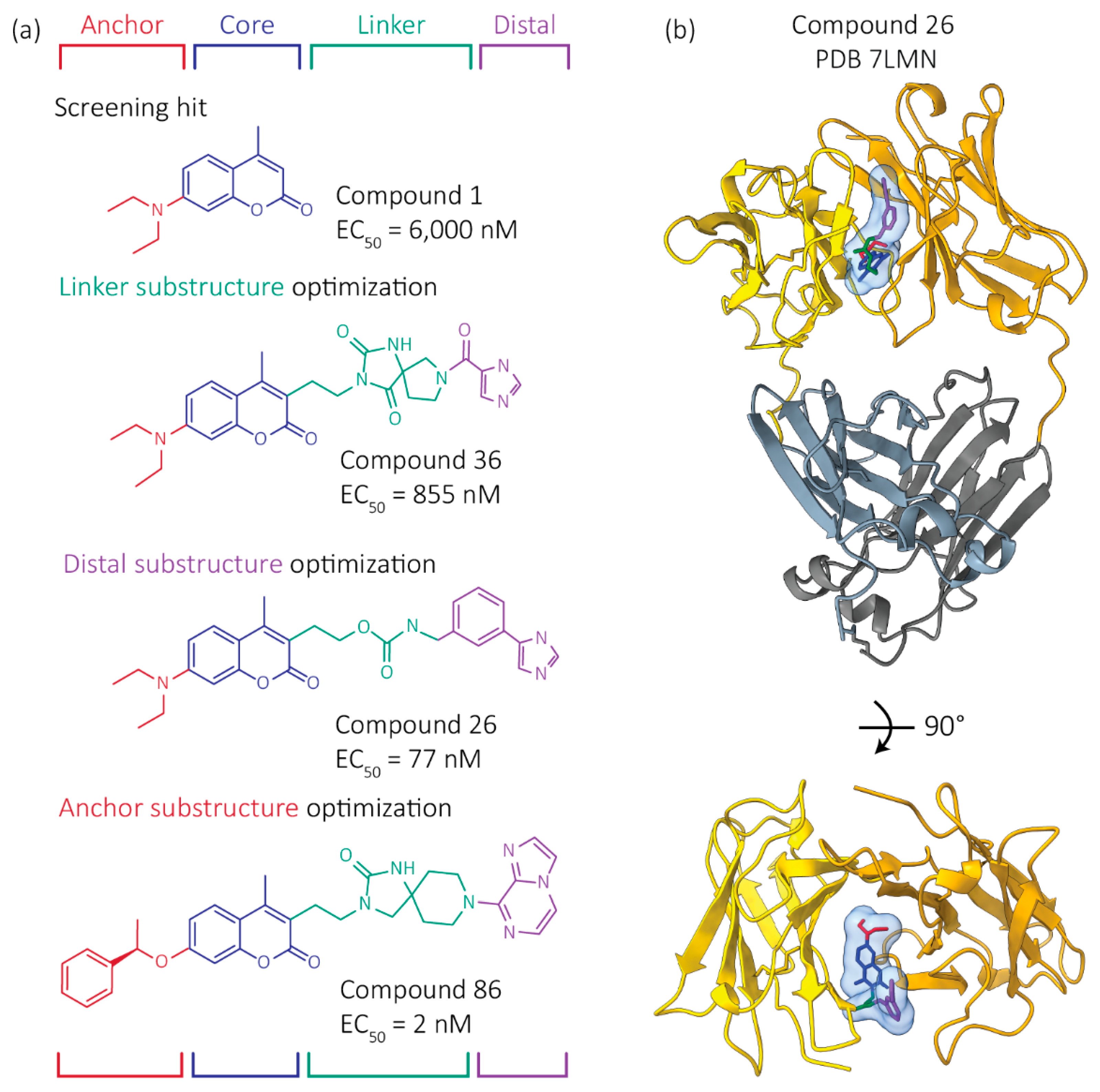
4. Progress to Date: Structure-Based Small Molecule FL LC Stabilizer Discovery
5. Potential Clinical Utility in AL
6. Considerations for Using FL LC Kinetic Stabilizers
7. Conclusions and Perspective
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Merlini, G.; Dispenzieri, A.; Sanchorawala, V.; Schönland, S.O.; Palladini, G.; Hawkins, P.N.; Gertz, M.A. Systemic Immunoglobulin Light Chain Amyloidosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2018, 4, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenner, G.; Harbaugh, J.; Ohms, J.; Harada, M.; Cuatrecasas, P. An amyloid protein: The amino-terminal variable fragment of an immunoglobulin light chain. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1970, 41, 1287–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terry, W.D.; Page, D.L.; Kimura, S.; Isobe, T.; Osserman, E.F.; Glenner, G.G. Structural Identity of Bence Jones and Amyloid Fibril Proteins in a Patient with Plasma Cell Dyscrasia and Amyloidosis. J. Clin. Investig. 1973, 52, 1276–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glenner, G.G.; Terry, W.; Harada, M.; Isersky, C.; Page, D. Amyloid Fibril Proteins: Proof of Homology with Immunoglobulin Light Chains by Sequence Analyses. Science 1971, 172, 1150–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glenner, G.G.; Ein, D.; Eanes, E.D.; Bladen, H.A.; Terry, W.; Page, D.L. Creation of "Amyloid" Fibrils from Bence Jones Proteins in vitro. Science 1971, 174, 712–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buxbaum, J. Mechanisms of disease: Monoclonal immunoglobulin deposition. Amyloidosis, light chain deposition disease, and light and heavy chain deposition disease. Hematol. Clin. N. Am. 1992, 6, 323–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, K.E.; Sletten, K.; Westermark, P. Fragments of the constant region of immunoglobulin light chains are constituents of AL-amyloid proteins. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 251, 642–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenner, G.G. Amyloid deposits and amyloidosis. The beta-fibrilloses (first of two parts). N. Engl. J. Med. 1980, 302, 1283–1292. [Google Scholar]
- Gallo, G.; Goñi, F.; Boctor, F.; Vidal, R.; Kumar, A.; Stevens, F.J.; Frangione, B.; Ghiso, J. Light chain cardiomyopathy. Structural analysis of the light chain tissue deposits. Am. J. Pathol. 1996, 148, 1397–1406. [Google Scholar]
- Linke, R.P.; Tischendorf, F.W.; Zucker-Franklin, D.; Franklin, E.C. The formation of amyloid-like fibrils in vitro from Bence Jones Proteins of the VlambdaI subclass. J. Immunol. 1973, 111, 24–26. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, N.; Hilton, P.; Tighe, J.; Hobbs, J. Treatment of “Primary” Renal Amyloidosis with Melphalan. Lancet 1972, 300, 616–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubrey, S.; Mendes, L.; Skinner, M.; Falk, R.H. Resolution of Heart Failure in Patients with AL Amyloidosis. Ann. Intern. Med. 1996, 125, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, M.S.; Schwartz, J.H.; Gundapaneni, B.; Elliott, P.M.; Merlini, G.; Waddington-Cruz, M.; Kristen, A.V.; Grogan, M.; Witteles, R.; Damy, T.; et al. Tafamidis Treatment for Patients with Transthyretin Amyloid Cardiomyopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, R.; Jain, M.; Teller, P.; Connors, L.; Ngoy, S.; Skinner, M.; Falk, R.H.; Apstein, C.S. Infusion of Light Chains From Patients With Cardiac Amyloidosis Causes Diastolic Dysfunction in Isolated Mouse Hearts. Circulation 2001, 104, 1594–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, J.; Mishra, S.; Shi, J.; Plovie, E.; Qiu, Y.; Cao, X.; Gianni, D.; Jiang, B.; Del Monte, F.; Connors, L.H.; et al. Stanniocalcin1 is a key mediator of amyloidogenic light chain induced cardiotoxicity. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2013, 108, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavatelli, F.; Imperiini, E.; Orrù, S.; Rognoni, P.; Sarnataro, D.; Palladini, G.; Malpasso, G.; Soriano, M.E.; Di Fonzo, A.; Valentini, V.; et al. Novel mitochondrial protein interactors of immunoglobulin light chains causing heart amyloidosis. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 4614–4628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imperlini, E.; Gnecchi, M.; Rognoni, P.; Sabidó, E.; Ciuffreda, M.C.; Palladini, G.; Espadas, G.; Mancuso, F.; Bozzola, M.; Malpasso, G.; et al. Proteotoxicity in cardiac amyloidosis: Amyloidogenic light chains affect the levels of intracellular proteins in human heart cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Joshi, S.; Ward, J.E.; Buys, E.P.; Mishra, D.; Morgado, I.; Fisch, S.; Lavatelli, F.; Merlini, G.; Dorbala, S.; et al. Zebrafish model of amyloid light chain cardiotoxicity: Regeneration versus degeneration. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2019, 316, H1158–H1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Guan, J.; Jiang, B.; Brenner, D.A.; del Monte, F.; Ward, J.; Connors, L.; Sawyer, D.B.; Semigran, M.J.; Macgillivray, T.E.; et al. Amyloidogenic light chains induce cardiomyocyte contractile dysfunction and apoptosis via a non-canonical p38 MAPK pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4188–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepys, M.B.; Booth, D.R.; Hutchinson, W.L.; Gallimore, J.R.; Collins, I.M.; Hohenester, E. Amyloid P component. A critical review. Amyloid 1997, 4, 274–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavatelli, F.; Perlman, D.H.; Spencer, B.; Prokaeva, T.; McComb, M.E.; Théberge, R.; Connors, L.; Bellotti, V.; Seldin, D.C.; Merlini, G.; et al. Amyloidogenic and Associated Proteins in Systemic Amyloidosis Proteome of Adipose Tissue. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2008, 7, 1570–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ami, D.; Lavatelli, F.; Rognoni, P.; Palladini, G.; Raimondi, S.; Giorgetti, S.; Monti, L.; Doglia, S.M.; Natalello, A.; Merlini, G. In situ characterization of protein aggregates in human tissues affected by light chain amyloidosis: A FTIR microspectroscopy study. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, R.; Hong, Z.; Gong, H.; Laporte, K.; Skinner, M.; Seldin, D.C.; Costello, C.; Connors, L.; Trinkaus-Randall, V. Role of Glycosaminoglycan Sulfation in the Formation of Immunoglobulin Light Chain Amyloid Oligomers and Fibrils. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 37672–37682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, G.R.; Lazowski, P.; Kumar, A.; Vidal, R.; Baldwin, D.S.; Buxbaum, J.N. Renal and cardiac manifestations of B-cell dyscrasias with nonamyloidotic monoclonal light chain and light and heavy chain deposition diseases. Adv. Nephrol. Necker Hosp. 1998, 28, 355–382. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Palladini, G.; Dispenzieri, A.; Gertz, M.A.; Kumar, S.; Wechalekar, A.; Hawkins, P.N.; Schönland, S.; Hegenbart, U.; Comenzo, R.; Kastritis, E.; et al. New Criteria for Response to Treatment in Immunoglobulin Light Chain Amyloidosis Based on Free Light Chain Measurement and Cardiac Biomarkers: Impact on Survival Outcomes. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 4541–4549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snozek, C.L.H.; A Katzmann, J.; A Kyle, R.; Dispenzieri, A.; Larson, D.R.; Therneau, T.M.; Melton, L.J.; Kumar, S.; Greipp, P.R.; Clark, R.J.; et al. Prognostic value of the serum free light chain ratio in newly diagnosed myeloma: Proposed incorporation into the international staging system. Leukemia 2008, 22, 1933–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendelson, L.; Shelton, A.; Brauneis, D.; Sanchorawala, V. AL Amyloidosis in Myeloma: Red Flag Symptoms. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020, 20, 777–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathick, I.J.; Drosou, M.E.; Leung, N. Myeloma light chain cast nephropathy, a review. J. Nephrol. 2019, 32, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, A.; Weiss, D.T.; Kattine, A.A. Nephrotoxic Potential of Bence Jones Proteins. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991, 324, 1845–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diomede, L.; Rognoni, P.; Lavatelli, F.; Romeo, M.; DEL Favero, E.; Cantù, L.; Ghibaudi, E.; Di Fonzo, A.; Corbelli, A.; Fiordaliso, F.; et al. A Caenorhabditis elegans–based assay recognizes immunoglobulin light chains causing heart amyloidosis. Blood 2014, 123, 3543–3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Marqusee, S. Probing the High Energy States in Proteins by Proteolysis. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 343, 1467–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reixach, N.; Deechongkit, S.; Jiang, X.; Kelly, J.W.; Buxbaum, J.N. Tissue damage in the amyloidoses: Transthyretin monomers and nonnative oligomers are the major cytotoxic species in tissue culture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 2817–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayed, R.; Head, E.; Thompson, J.L.; McIntire, T.M.; Milton, S.C.; Cotman, C.W.; Glabe, C.G. Common Structure of Soluble Amyloid Oligomers Implies Common Mechanism of Pathogenesis. Science 2003, 300, 486–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selkoe, D.J.; Hardy, J. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer′s disease at 25 years. EMBO Mol. Med. 2016, 8, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastritis, E.; Palladini, G.; Minnema, M.C.; Wechalekar, A.D.; Jaccard, A.; Lee, H.C.; Sanchorawala, V.; Gibbs, S.; Mollee, P.; Venner, C.P.; et al. Daratumumab-Based Treatment for Immunoglobulin Light-Chain Amyloidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szalat, R.; Sarosiek, S.; Havasi, A.; Brauneis, D.; Sloan, J.M.; Sanchorawala, V. Organ responses after highdose melphalan and stemcell transplantation in AL amyloidosis. Leukemia 2021, 35, 916–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, B.M.; Wong, S.W.; Comenzo, R.L. Beyond the plasma cell: Emerging therapies for immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis. Blood 2016, 127, 2275–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manwani, R.; Cohen, O.; Sharpley, F.; Mahmood, S.; Sachchithanantham, S.; Foard, D.; Lachmann, H.J.; Quarta, C.; Fontana, M.; Gillmore, J.D.; et al. A prospective observational study of 915 patients with systemic AL amyloidosis treated with upfront bortezomib. Blood 2019, 134, 2271–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palladini, G.; Milani, P.; Merlini, G. Management of AL amyloidosis in 2020. Blood 2020, 136, 2620–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milani, P.; Sharpley, F.; Schönland, S.O.; Basset, M.; Mahmood, S.; Nuvolone, M.; Kimmich, C.; Foli, A.; Sachchithanantham, S.; Merlini, G.; et al. Pomalidomide and dexamethasone grant rapid haematologic responses in patients with relapsed and refractory AL amyloidosis: A European retrospective series of 153 patients. Amyloid 2020, 27, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastritis, E.; Leleu, X.; Arnulf, B.; Zamagni, E.; Cibeira, M.T.; Kwok, F.; Mollee, P.; Hájek, R.; Moreau, P.; Jaccard, A.; et al. Bortezomib, Melphalan, and Dexamethasone for Light-Chain Amyloidosis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3252–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchorawala, V.; Sarosiek, S.; Schulman, A.; Mistark, M.; Migre, M.E.; Cruz, R.; Sloan, J.M.; Brauneis, D.; Shelton, A.C. Safety, tolerability, and response rates of daratumumab in relapsed AL amyloidosis: Results of a phase 2 study. Blood 2020, 135, 1541–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roussel, M.; Merlini, G.; Chevret, S.; Arnulf, B.; Stoppa, A.M.; Perrot, A.; Palladini, G.; Karlin, L.; Royer, B.; Huart, A.; et al. A prospective phase 2 trial of daratumumab in patients with previously treated systemic light-chain amyloidosis. Blood 2020, 135, 1531–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dispenzieri, A.; Kastritis, E.; Wechalekar, A.D.; Schönland, S.O.; Kim, K.; Sanchorawala, V.; Landau, H.J.; Kwok, F.; Suzuki, K.; Comenzo, R.L.; et al. A randomized phase 3 study of ixazomib–Dexamethasone versus physician’s choice in relapsed or refractory AL amyloidosis. Leukemia 2021, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staron, A.; Zheng, L.; Doros, G.; Connors, L.H.; Mendelson, L.M.; Joshi, T.; Sanchorawala, V. Marked progress in AL amyloidosis survival: A 40-year longitudinal natural history study. Blood Cancer J. 2021, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muchtar, E.; Gertz, M.A.; Lacy, M.Q.; Go, R.S.; Buadi, F.K.; Dingli, D.; Grogan, M.; AbouEzzeddine, O.F.; Hayman, S.R.; Kapoor, P.; et al. Ten-year survivors in AL amyloidosis: Characteristics and treatment pattern. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 187, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradwell, A.R.; Carr-Smith, H.D.; Mead, G.P.; Harvey, T.C.; Drayson, M. Serum test for assessment of patients with Bence Jones myeloma. Lancet 2003, 361, 489–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palladini, G.; Schönland, S.O.; Sanchorawala, V.; Kumar, S.; Wechalekar, A.; Hegenbart, U.; Milani, P.; Ando, Y.; Westermark, P.; Dispenzieri, A.; et al. Clarification on the definition of complete haematologic response in light-chain (AL) amyloidosis. Amyloid 2021, 28, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidana, S.; Dispenzieri, A.; Murray, D.L.; Go, R.S.; Buadi, F.K.; Lacy, M.Q.; Gonsalves, W.I.; Dingli, D.; Warsame, R.; Kourelis, T.; et al. Revisiting complete response in light chain amyloidosis. Leukemia 2020, 34, 1472–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, J.R.; Kohlhagen, M.C.; Dasari, S.; Vanderboom, P.M.; Kyle, R.A.; Katzmann, J.A.; Willrich, M.A.; Barnidge, D.R.; Dispenzieri, A.; Murray, D.L. Comprehensive Assessment of M-Proteins Using Nanobody Enrichment Coupled to MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry. Clin. Chem. 2016, 62, 1334–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dispenzieri, A.; Arendt, B.; Dasari, S.; Kohlhagen, M.; Kourelis, T.; Kumar, S.K.; Leung, N.; Muchtar, E.; Buadi, F.K.; Warsame, R.; et al. Blood mass spectrometry detects residual disease better than standard techniques in light-chain amyloidosis. Blood Cancer J. 2020, 10, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Paiva, B.; Anderson, K.C.; Durie, B.; Landgren, O.; Moreau, P.; Munshi, N.; Lonial, S.; Bladé, J.; Mateos, M.-V.; et al. International Myeloma Working Group consensus criteria for response and minimal residual disease assessment in multiple myeloma. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, e328–e346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staron, A.; Burks, E.J.; Lee, J.C.; Sarosiek, S.; Sloan, J.M.; Sanchorawala, V. Assessment of minimal residual disease using multiparametric flow cytometry in patients with AL amyloidosis. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 880–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muchtar, E.; Dispenzieri, A.; Jevremovic, D.; Dingli, D.; Buadi, F.K.; Lacy, M.Q.; Gonsalves, W.; Warsame, R.; Kourelis, T.V.; Hayman, S.R.; et al. Survival impact of achieving minimal residual negativity by multi-parametric flow cytometry in AL amyloidosis. Amyloid 2020, 27, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paiva, B.D.L.; Vidriales, M.-B.; Pérez, J.J.; López-Berges, M.-C.; Garcia-Sanz, R.; Ocio, E.M.; Heras, N.D.L.; Cuello, R.; De Coca, A.G.; Pardal, E.; et al. The clinical utility and prognostic value of multiparameter flow cytometry immunophenotyping in light-chain amyloidosis. Blood 2011, 117, 3613–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarosiek, S.; Varga, C.; Jacob, A.; Fulciniti, M.T.; Munshi, N.; Sanchorawala, V. Detection of minimal residual disease by next generation sequencing in AL amyloidosis. Blood Cancer J. 2021, 11, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maritan, M.; Romeo, M.; Oberti, L.; Sormanni, P.; Tasaki, M.; Russo, R.; Ambrosetti, A.; Motta, P.; Rognoni, P.; Mazzini, G.; et al. Inherent Biophysical Properties Modulate the Toxicity of Soluble Amyloidogenic Light Chains. J. Mol. Biol. 2020, 432, 845–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, G.J.; Kelly, J.W. The Kinetic Stability of a Full-Length Antibody Light Chain Dimer Determines whether Endoproteolysis Can Release Amyloidogenic Variable Domains. J. Mol. Biol. 2016, 428, 4280–4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, G.J.; Usher, G.; Kelly, J.W. Incomplete Refolding of Antibody Light Chains to Non-Native, Protease-Sensitive Conformations Leads to Aggregation: A Mechanism of Amyloidogenesis in Patients? Biochemistry 2017, 56, 6597–6614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, G.J.; Yan, N.L.; Mortenson, D.E.; Rennella, E.; Blundon, J.M.; Gwin, R.M.; Lin, C.-Y.; Stanfield, R.L.; Brown, S.J.; Rosen, H.; et al. Stabilization of amyloidogenic immunoglobulin light chains by small molecules. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 8360–8369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brumshtein, B.; Esswein, S.R.; Salwinski, L.; Phillips, M.L.; Ly, A.T.; Cascio, D.; Sawaya, M.R.; Eisenberg, D.S. Inhibition by small-molecule ligands of formation of amyloid fibrils of an immunoglobulin light chain variable domain. eLife 2015, 4, e10935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellotti, V.; Mangione, P.; Merlini, G. Review: Immunoglobulin Light Chain Amyloidosis—The Archetype of Structural and Pathogenic Variability. J. Struct. Biol. 2000, 130, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perfetti, V.; Ubbiali, P.; Vignarelli, M.C.; Diegoli, M.; Fasani, R.; Stoppini, M.; Lisa, A.; Mangione, P.; Obici, L.; Arbustini, E.; et al. Evidence that amyloidogenic light chains undergo antigen-driven selection. Blood 1998, 91, 2948–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodi, K.; Prokaeva, T.; Spencer, B.; Eberhard, M.; Connors, L.; Seldin, D.C. AL-Base: A visual platform analysis tool for the study of amyloidogenic immunoglobulin light chain sequences. Amyloid 2009, 16, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rennella, E.; Morgan, G.J.; Kelly, J.W.; Kay, L.E. Role of domain interactions in the aggregation of full-length immunoglobulin light chains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 854–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Murray, D.; Dasari, S.; Milani, P.; Barnidge, D.; Madden, B.; Kourelis, T.; Arendt, B.; Merlini, G.; Ramirez-Alvarado, M.; et al. Assay to rapidly screen for immunoglobulin light chain glycosylation: A potential path to earlier AL diagnosis for a subset of patients. Leukemia 2018, 33, 254–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, F.J. Four structural risk factors identify most fibril-forming kappa light chains. Amyloid 2000, 7, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connors, L.H.; Jiang, Y.; Budnik, M.; Théberge, R.; Prokaeva, T.; Bodi, K.L.; Skinner, M. Heterogeneity in primary structure, post-translational modifications, and germline gene usage of nine full-length amyloidogenic kappa1 immunoglobulin light chains. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 14259–14271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radamaker, L.; Lin, Y.-H.; Annamalai, K.; Huhn, S.; Hegenbart, U.; Schönland, S.O.; Fritz, G.; Schmidt, M.; Fändrich, M. Cryo-EM structure of a light chain-derived amyloid fibril from a patient with systemic AL amyloidosis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swuec, P.; Lavatelli, F.; Tasaki, M.; Paissoni, C.; Rognoni, P.; Maritan, M.; Brambilla, F.; Milani, P.; Mauri, P.; Camilloni, C.; et al. Cryo-EM structure of cardiac amyloid fibrils from an immunoglobulin light chain AL amyloidosis patient. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radamaker, L.; Baur, J.; Huhn, S.; Haupt, C.; Hegenbart, U.; Schönland, S.; Bansal, A.; Schmidt, M.; Fändrich, M. Cryo-EM reveals structural breaks in a patient-derived amyloid fibril from systemic AL amyloidosis. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blancas-Mejía, L.M.; Horn, T.J.; Marin-Argany, M.; Auton, M.; Tischer, A.; Ramirez-Alvarado, M. Thermodynamic and fibril formation studies of full length immunoglobulin light chain AL-09 and its germline protein using scan rate dependent thermal unfolding. Biophys. Chem. 2015, 207, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lavatelli, F.; Mazzini, G.; Ricagno, S.; Iavarone, F.; Rognoni, P.; Milani, P.; Nuvolone, M.; Swuec, P.; Caminito, S.; Tasaki, M.; et al. Mass spectrometry characterization of light chain fragmentation sites in cardiac AL amyloidosis: Insights into the timing of proteolysis. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 16572–16584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzini, G.; Ricagno, S.; Caminito, S.; Rognoni, P.; Milani, P.; Nuvolone, M.; Basset, M.; Foli, A.; Russo, R.; Merlini, G.; et al. Protease-sensitive regions in amyloid light chains: What a common pattern of fragmentation across organs suggests about aggregation. FEBS J. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, M.; Wiese, S.; Adak, V.; Engler, J.; Agarwal, S.; Fritz, G.; Westermark, P.; Zacharias, M.; Fändrich, M. Cryo-EM structure of a transthyretin-derived amyloid fibril from a patient with hereditary ATTR amyloidosis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blancas-Mejía, L.M.; Ramirez-Alvarado, M. Recruitment of Light Chains by Homologous and Heterologous Fibrils Shows Distinctive Kinetic and Conformational Specificity. Biochemistry 2016, 55, 2967–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabat, E.A. Sequences of Proteins of Immunological Interest, 5th ed.; US Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, National Institutes of Health: Bethesda, MD, USA, 1991.
- Hrncic, R.; Wall, J.; Wolfenbarger, D.A.; Murphy, C.L.; Schell, M.; Weiss, D.T.; Solomon, A. Antibody-Mediated Resolution of Light Chain-Associated Amyloid Deposits. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 157, 1239–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, G. Barriers to Small Molecule Drug Discovery for Systemic Amyloidosis. Molecules 2021, 26, 3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, I.; Merlini, G.; Saraiva, M.J. 4′-iodo-4′-deoxydoxorubicin and tetracyclines disrupt transthyretin amyloid fibrils in vitro producing noncytotoxic species: Screening for TTR fibril disrupters. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.E.; Ren, R.; Toraldo, G.; SooHoo, P.; Guan, J.; O′Hara, C.; Seldin, D.C. Doxycycline reduces fibril formation in a transgenic mouse model of AL amyloidosis. Blood 2011, 118, 6610–6617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Souza, A.; Szabo, A.; Flynn, K.E.; Dhakal, B.; Chhabra, S.; Pasquini, M.C.; Weihrauch, D.; Hari, P.N. Adjuvant doxycycline to enhance anti-amyloid effects: Results from the dual phase 2 trial. EClinicalMedicine 2020, 23, 100361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, N.L.; Santos-Martins, D.; Nair, R.; Chu, A.; Wilson, I.A.; Johnson, K.A.; Forli, S.; Morgan, G.J.; Petrassi, H.M.; Kelly, J.W. Discovery of Potent Coumarin-Based Kinetic Stabilizers of Amyloidogenic Immunoglobulin Light Chains Using Structure-Based Design. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 6273–6299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, N.L.; Santos-Martins, D.; Rennella, E.; Sanchez, B.B.; Chen, J.S.; Kay, L.E.; Wilson, I.A.; Morgan, G.J.; Forli, S.; Kelly, J.W. Structural basis for the stabilization of amyloidogenic immunoglobulin light chains by hydantoins. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 30, 127356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulawa, C.E.; Connelly, S.; DeVit, M.; Wang, L.; Weigel, C.; Fleming, J.A.; Packman, J.; Powers, E.; Wiseman, L.; Foss, T.R.; et al. Tafamidis, a potent and selective transthyretin kinetic stabilizer that inhibits the amyloid cascade. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 9629–9634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arendt, B.K.; Ramirez-Alvarado, M.; Sikkink, L.A.; Keats, J.J.; Ahmann, G.J.; Dispenzieri, A.; Fonseca, R.; Ketterling, R.P.; Knudson, R.A.; Mulvihill, E.M.; et al. Biologic and genetic characterization of the novel amyloidogenic lambda light chain–secreting human cell lines, ALMC-1 and ALMC-2. Blood 2008, 112, 1931–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palladini, G.; Merlini, G. When should treatment of AL amyloidosis start at relapse? Early, to prevent organ progression. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 212–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchorawala, V. Delay treatment of AL amyloidosis at relapse until symptomatic: Devil is in the details. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 216–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldmann, T.A.; Strober, W.; Mogielnicki, R.P. The renal handling of low molecular weight proteins. II. Disorders of serum protein catabolism in patients with tubular proteinuria, the nephrotic syndrome, or uremia. J. Clin. Investig. 1972, 51, 2162–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basnayake, K.; Stringer, S.J.; Hutchison, C.A.; Cockwell, P. The biology of immunoglobulin free light chains and kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2011, 79, 1289–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feige, M.; Hendershot, L.M.; Buchner, J. How antibodies fold. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2010, 35, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zolla, S.; Buxbaum, J.; Franklin, E.C.; Scharff, M.D. Synthesis and assembly of immunoglobulins by malignant human plasmacytes. I. Myelomas producing gamma-chains and light chains. J. Exp. Med. 1970, 132, 148–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, L.; Orfanelli, U.; Resnati, M.; Raimondi, A.; Orsi, A.; Milan, E.; Palladini, G.; Milani, P.; Cerruti, F.; Cascio, P.; et al. The amyloidogenic light chain is a stressor that sensitizes plasma cells to proteasome inhibitor toxicity. Blood 2017, 129, 2132–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, T.; Maia, L.; da Silva, A.M.; Cruz, M.W.; Planté-Bordeneuve, V.; Lozeron, P.; Suhr, O.; Campistol, J.M.; Conceicao, I.; Schmidt, H.H.-J.; et al. Tafamidis for transthyretin familial amyloid polyneuropathy: A randomized, controlled trial. Neurology 2012, 79, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, M.D.; Waddington-Cruz, M.; Berk, J.L.; Polydefkis, M.; Dyck, P.J.; Wang, A.K.; Planté-Bordeneuve, V.; Barroso, F.A.; Merlini, G.; Obici, L.; et al. Inotersen Treatment for Patients with Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, D.; Gonzalez-Duarte, A.; O’Riordan, W.D.; Yang, C.-C.; Ueda, M.; Kristen, A.V.; Tournev, I.; Schmidt, H.H.; Coelho, T.; Berk, J.L.; et al. Patisiran, an RNAi Therapeutic, for Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Study Reference | Treatment | Dates | Number of Patients | Patient Status | HR (CR) | Renal Response | Cardiac Response | Median Survival |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Szalat et al. [36] | Autologous stem cell transplant | 2002–15 | 206 | ND | 69% (28%) | 54% | 62% | 3.7–14.5 years |
| Kastritis et al. [41] | Melphalan + dexamethasone + bortezomib | 2011–16 | 53 | ND | 79% (23%) | 44% | 38% | >50 months |
| Kastritis et al. (control) [41] | Melphalan + dexamethasone | 2011–16 | 56 | ND | 52% (20%) | 43% | 28% | 34 months |
| ANDROMEDA [35] | CyBorD + Daratumumab | 2018–19 | 195 | ND | 91.8% (53.3%) | 53.0% | 41.5% | >20 months |
| ANDROMEDA (control) [35] | CyBorD | 2018–19 | 193 | ND | 76.7% (18.1%) | 23.9% | 22.2% | >20 months |
| Sanchorawala et al. [42] | Daratumumab + dexamethasone | 2017–19 | 22 | RR | 90% (41%) | 67% | 50% | >28 months |
| Roussel et al. [43] | Daratumumab + dexamethasone | 2018–19 | 40 | RR | 70% (15%) | 31% | 29% | >36 months |
| Milani et al. [40] | Pomalidomide + dexamethasone | 2009–18 | 153 | RR | 44% (3%) | 20% | 11% * | 29 months |
| TOURMALINE-AL1 [44] | Ixazomib + dexamethasone | 2012–18 | 85 | RR | 53% (26%) | 28% | 18% | 34.8 months |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morgan, G.J.; Buxbaum, J.N.; Kelly, J.W. Light Chain Stabilization: A Therapeutic Approach to Ameliorate AL Amyloidosis. Hemato 2021, 2, 645-659. https://doi.org/10.3390/hemato2040042
Morgan GJ, Buxbaum JN, Kelly JW. Light Chain Stabilization: A Therapeutic Approach to Ameliorate AL Amyloidosis. Hemato. 2021; 2(4):645-659. https://doi.org/10.3390/hemato2040042
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorgan, Gareth J., Joel N. Buxbaum, and Jeffery W. Kelly. 2021. "Light Chain Stabilization: A Therapeutic Approach to Ameliorate AL Amyloidosis" Hemato 2, no. 4: 645-659. https://doi.org/10.3390/hemato2040042
APA StyleMorgan, G. J., Buxbaum, J. N., & Kelly, J. W. (2021). Light Chain Stabilization: A Therapeutic Approach to Ameliorate AL Amyloidosis. Hemato, 2(4), 645-659. https://doi.org/10.3390/hemato2040042






