RNF6 as an Oncogene and Potential Therapeutic Target—A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. RNF6 Functions
3. RNF6 as a Tumor Suppressor Gene
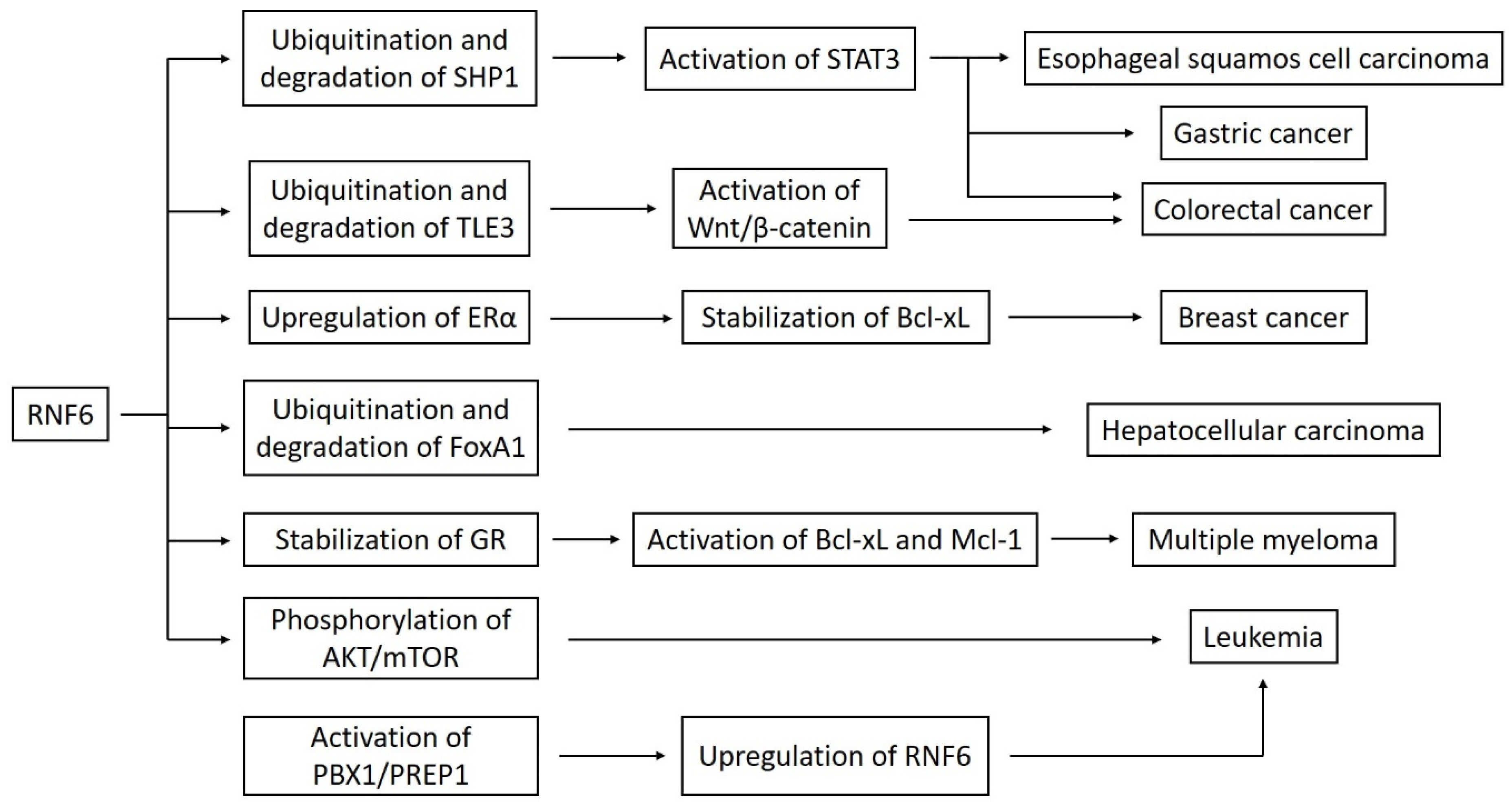
4. RNF6 as an Oncogene
5. RNF6 as a Prognostic Factor and Therapeutic Target
6. Challenges and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Macdonald, D.H.; Lahiri, D.; Sampath, A.; Chase, A.; Sohal, J.; Cross, N.C. Cloning and characterization of RNF6, a novel RING finger gene mapping to 13q12. Genomics 1999, 58, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Starza, R.; Wlodarska, I.; Aventin, A.; Falzetti, D.; Crescenzi, B.; Martelli, M.F.; Van den Berghe, H.; Mecucci, C. Molecular delineation of 13q deletion boundaries in 20 patients with myeloid malignancies. Blood 1998, 91, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, H.S.; Hu, N.; Gere, S.; Lu, N.; Su, H.; Goldstein, A.M.; Taylor, P.R.; Lee, M.P. Identification of somatic mutations of the RNF6 gene in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 4191–4193. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Shimelis, H.; Linn, D.E.; Jiang, R.; Yang, X.; Sun, F.; Guo, Z.; Chen, H.; Li, W.; Chen, H.; et al. Regulation of androgen receptor transcriptional activity and specificity by RNF6-induced ubiquitination. Cancer Cell 2009, 15, 270–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Cai, Y.; Yang, C.; Chen, Z.; Sun, H.; Xu, Y.; Chen, W.; Xu, D.; Tian, W.; Wang, H. Knockdown of RNF6 inhibits gastric cancer cell growth by suppressing STAT3 signaling. Oncotargets Ther. 2018, 11, 6579–6587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Wang, C. Potential Influences of RNF6 on Prognosis and Metastasis of Colorectal Cancer: A Clinical Analysis. Oncotargets Ther. 2020, 13, 2031–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Han, K.; Cao, B.; Mao, X. Ring finger protein 6 promotes breast cancer cell proliferation by stabilizing estrogen receptor alpha. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 20103–20112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Han, K.; Tang, X.; Zeng, Y.; Lin, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, B.; Wu, D.; Mao, X. The Ring Finger Protein RNF6 Induces Leukemia Cell Proliferation as a Direct Target of Pre-B-cell Leukemia Homeobox 1. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 9617–9628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Ma, D.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Z.; Sun, T.T.; Shen, C.; Yan, T.; Tian, X.; Yu, T.; Guo, F.; et al. RING-Finger Protein 6 Amplification Activates JAK/STAT3 Pathway by Modifying SHP-1 Ubiquitylation and Associates with Poor Outcome in Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 1473–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; He, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, L.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, B.; Wang, Q.; Mao, X.; Hu, S. Saponins From Paris forrestii (Takht.) H. Li Display Potent Activity against Acute Myeloid Leukemia by Suppressing the RNF6/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.Y.; Wang, W.W.; Huang, J.; Zhu, W. Ellagic acid induces esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell apoptosis by modulating SHP-1/STAT3 signaling. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2020, 36, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.M.; Ge, H.F.; Yang, C.C.; Cai, Y.; Chen, Z.; Tian, W.Z.; Tao, J.L. MicroRNA-26a-5p inhibits breast cancer cell growth by suppressing RNF6 expression. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2019, 35, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, J.; Hou, N.; Yang, W.; Jiang, Q.; Xue, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Xiong, X.; Wang, L.; Zhao, L.; et al. miR-203a suppresses cell proliferation by targeting RING-finger protein 6 in colorectal cancer. Anticancer Drugs 2020, 31, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joazeiro, C.A.; Weissman, A.M. RING finger proteins: Mediators of ubiquitin ligase activity. Cell 2000, 102, 549–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, F.; Deng, G.; Liu, Q.; Guo, W.; Haas, A.L.; Crosas, B.; Finley, D.; Taylor, A. Lys6-modified ubiquitin inhibits ubiquitin-dependent protein degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 20365–20374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, L.; Wang, C.; Spencer, E.; Yang, L.; Braun, A.; You, J.; Slaughter, C.; Pickart, C.; Chen, Z.J. Activation of the IkappaB kinase complex by TRAF6 requires a dimeric ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme complex and a unique polyubiquitin chain. Cell 2000, 103, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Xu, X.; Mao, C.Y.; Han, K.K.; Xu, Y.J.; Cao, B.Y.; Zhang, Z.B.; Sethi, G.; Tang, X.W.; Mao, X.L. RNF6 promotes myeloma cell proliferation and survival by inducing glucocorticoid receptor polyubiquitination. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2020, 41, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Amin, H.M.; Franko, B.; Frantz, C.; Shi, X.; Lai, R. Loss of SHP1 enhances JAK3/STAT3 signaling and decreases proteosome degradation of JAK3 and NPM-ALK in ALK+ anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. Blood 2006, 108, 2796–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wong, C.C.; Zhang, J.; Dong, Y.; Li, X.; Kang, W.; Chan, F.; Sung, J.; Yu, J. RNF6 Promotes Colorectal Cancer by Activating the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway via Ubiquitination of TLE3. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 1958–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Xiong, Q.; Jiang, X.; Zhou, S.; Liu, T. RNF6 facilitates metastasis and radioresistance in hepatocellular carcinoma through ubiquitination of FoxA1. Exp. Cell Res. 2019, 374, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tursun, B.; Schlüter, A.; Peters, M.A.; Viehweger, B.; Ostendorff, H.P.; Soosairajah, J.; Drung, A.; Bossenz, M.; Johnsen, S.A.; Schweizer, M.; et al. The ubiquitin ligase Rnf6 regulates local LIM kinase 1 levels in axonal growth cones. Genes Dev. 2005, 19, 2307–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, N.; Roth, M.J.; Polymeropolous, M.; Tang, Z.Z.; Emmert-Buck, M.R.; Wang, Q.H.; Goldstein, A.M.; Feng, S.S.; Dawsey, S.M.; Ding, T.; et al. Identification of novel regions of allelic loss from a genomewide scan of esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma in a high-risk Chinese population. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2000, 27, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Hu, N.; Goldstein, A.M.; Tang, Z.Z.; Roth, M.J.; Wang, Q.H.; Dawsey, S.M.; Han, X.Y.; Ding, T.; Huang, J.; et al. Allelic loss on chromosome bands 13q11-q13 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2001, 31, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Jiménez, F.; Muiños, F.; Sentís, I.; Deu-Pons, J.; Reyes-Salazar, I.; Arnedo-Pac, C.; Mularoni, L.; Pich, O.; Bonet, J.; Kranas, H.; et al. A compendium of mutational cancer driver genes. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 555–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network; Weinstein, J.N.; Collisson, E.A.; Mills, G.B.; Shaw, K.R.; Ozenberger, B.A.; Ellrott, K.; Shmulevich, I.; Sander, C.; Stuart, J.M. The Cancer Genome Atlas Pan-Cancer analysis project. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Chen, S.; Qiu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Qiu, F. Proteomic analysis of ubiquitination-associated proteins in a cisplatin-resistant human lung adenocarcinoma cell line. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 29, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Takahashi, H.; Uematsu, A.; Yamanaka, S.; Imamura, M.; Nakajima, T.; Doi, K.; Yasuoka, S.; Takahashi, C.; Takeda, H.; Sawasaki, T. Establishment of a Wheat Cell-Free Synthesized Protein Array Containing 250 Human and Mouse E3 Ubiquitin Ligases to Identify Novel Interaction between E3 Ligases and Substrate Proteins. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Shi, M.; Niu, H.M.; Yang, J.; Xia, M.Y.; Luo, J.F.; Chen, Y.J.; Zhou, Y.P.; Li, H. Substituting one Paris for another? In vitro cytotoxic and in vivo antitumor activities of Paris forrestii, a substitute of Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 218, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceci, C.; Lacal, P.M.; Tentori, L.; De Martino, M.G.; Miano, R.; Graziani, G. Experimental Evidence of the Antitumor, Antimetastatic and Antiangiogenic Activity of Ellagic Acid. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baradaran Rahimi, V.; Ghadiri, M.; Ramezani, M.; Askari, V.R. Antiinflammatory and anti-cancer activities of pomegranate and its constituent, ellagic acid: Evidence from cellular, animal, and clinical studies. Phytother. Res. 2020, 34, 685–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskra, J.N.; Schlicht, M.J.; Bosland, M.C. Effects of Black Raspberries and Their Ellagic Acid and Anthocyanin Constituents on Taxane Chemotherapy of Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, J.; Zhan, J.C.; Wang, G.Z.; Zhao, X.C.; Huang, W.D.; Zhou, G.B. The red wine component ellagic acid induces autophagy and exhibits anti-lung cancer activity in vitro and in vivo. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, T.; Huang, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, C.; Chu, X. MicroRNAs as Regulators, Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets in the Drug Resistance of Colorectal Cancer. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 40, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Lin, C.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, L.; Pan, X.; Quan, J.; Peng, X.; Li, W.; Li, H.; Xu, J.; et al. Oncogene miR-187-5p is associated with cellular proliferation, migration, invasion, apoptosis and an increased risk of recurrence in bladder cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 105, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Inhibitor/Potential Therapeutic Agent | Effect | Cancer Type | Inhibited Pathway | Study Model | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total saponins from Paris forrestii–TSPf | Downregulating RNF6 expression, inhibiting proliferation, promoting apoptosis, upregulating pro-apoptotic proteins, downregulating anti-apoptotic proteins | Acute myeloid leukemia | AKT/mTOR | Human myeloid leukemia cell lines K562 and HL-60; K562 cells xenograft in nude mice | Lu et al. [10] |
| Ellagic acid | Downregulating RNF6 expression, inhibiting proliferation, promoting apoptosis, downregulating anti-apoptotic proteins | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) | SHP1/STAT3 | ESCC cell lines Eca-109 and TE-1 | Xu et al. [11] |
| MicroRNA-26a-5p | Downregulating RNF6 expression, inhibiting cell growth, upregulating cell cycle regulatory proteins | Breast cancer | ERα/Bcl-xL | Breast cancer cell lines MCF-7 and T47D | Huang et al. [12] |
| MicroRNA-203a | Downregulating RNF6 expression, inhibiting cell growth, arresting cell cycle in the G1 phase | Colorectal cancer | - | Human colon cancer cell lines HCT116 and SW480 | Miao et al. [13] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zapolnik, P.; Pyrkosz, A. RNF6 as an Oncogene and Potential Therapeutic Target—A Review. BioTech 2020, 9, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech9040022
Zapolnik P, Pyrkosz A. RNF6 as an Oncogene and Potential Therapeutic Target—A Review. BioTech. 2020; 9(4):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech9040022
Chicago/Turabian StyleZapolnik, Paweł, and Antoni Pyrkosz. 2020. "RNF6 as an Oncogene and Potential Therapeutic Target—A Review" BioTech 9, no. 4: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech9040022
APA StyleZapolnik, P., & Pyrkosz, A. (2020). RNF6 as an Oncogene and Potential Therapeutic Target—A Review. BioTech, 9(4), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech9040022






